-
摘要:
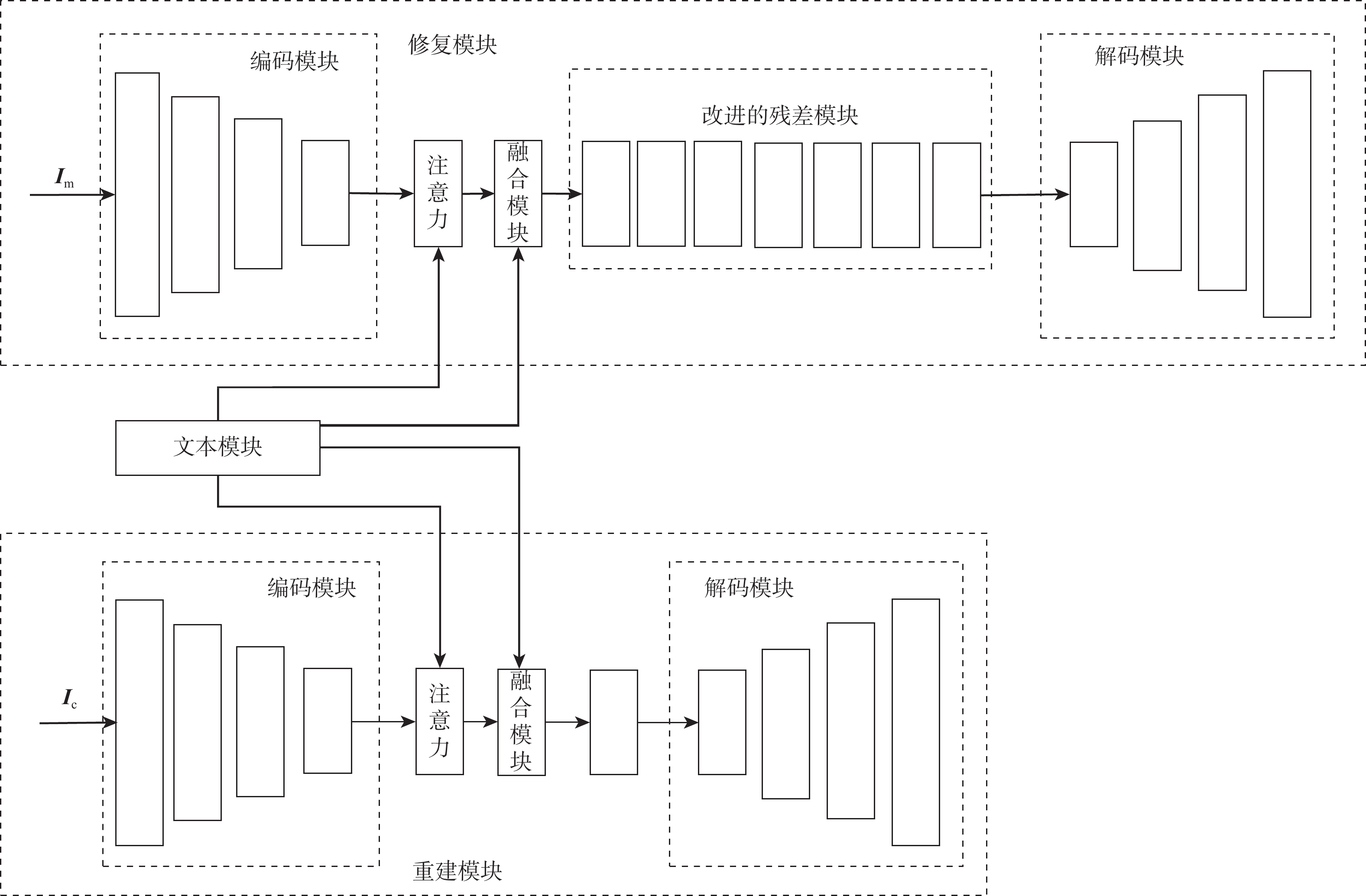
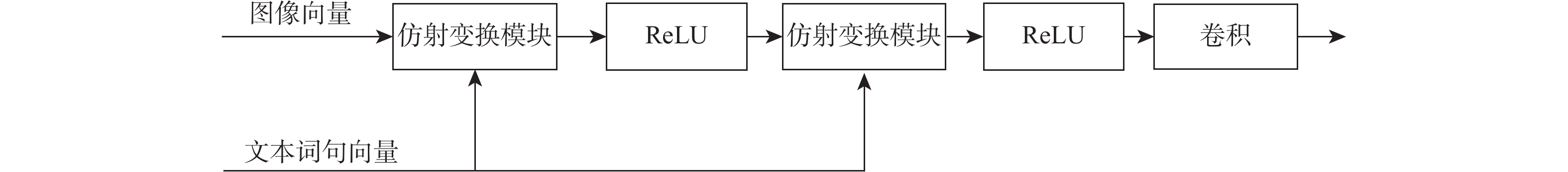
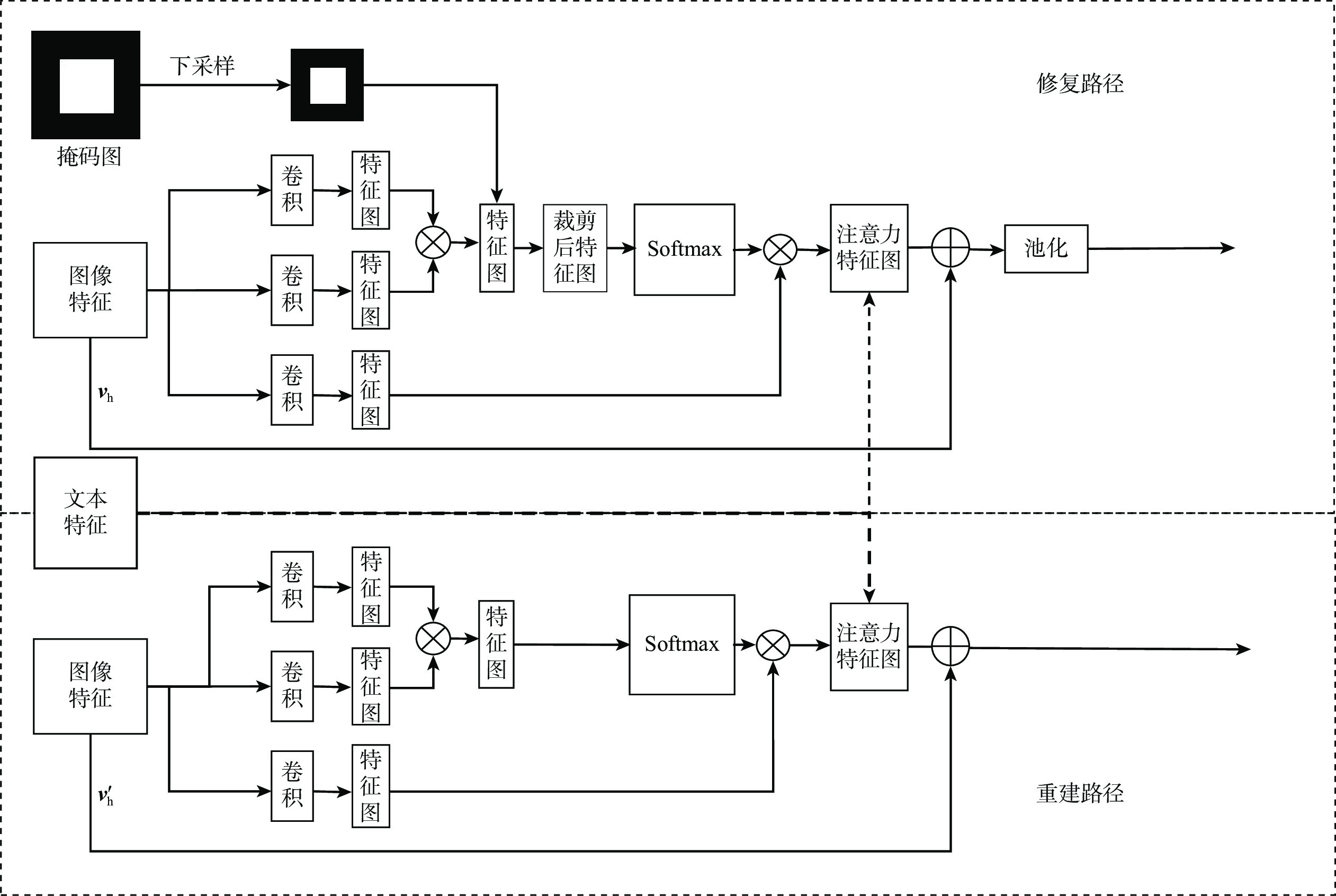
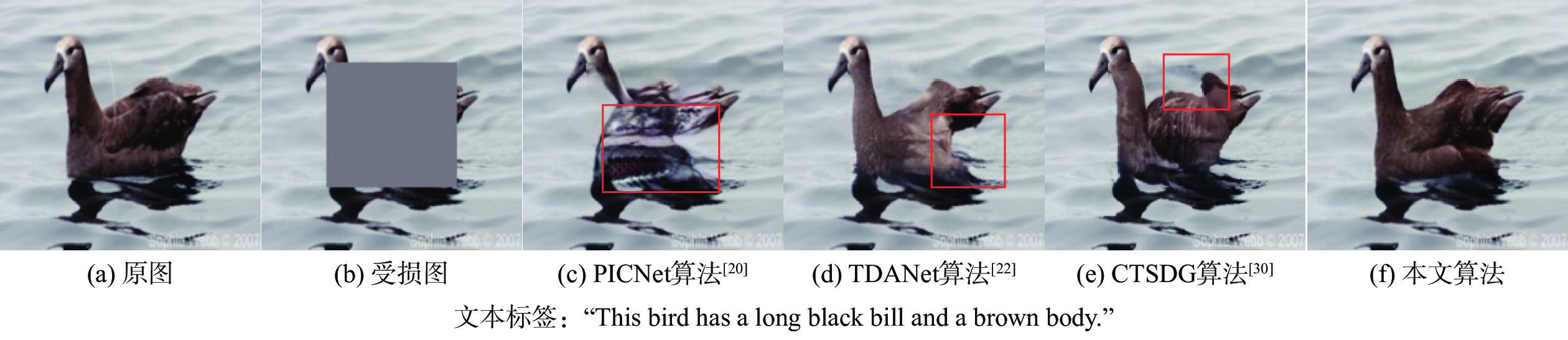
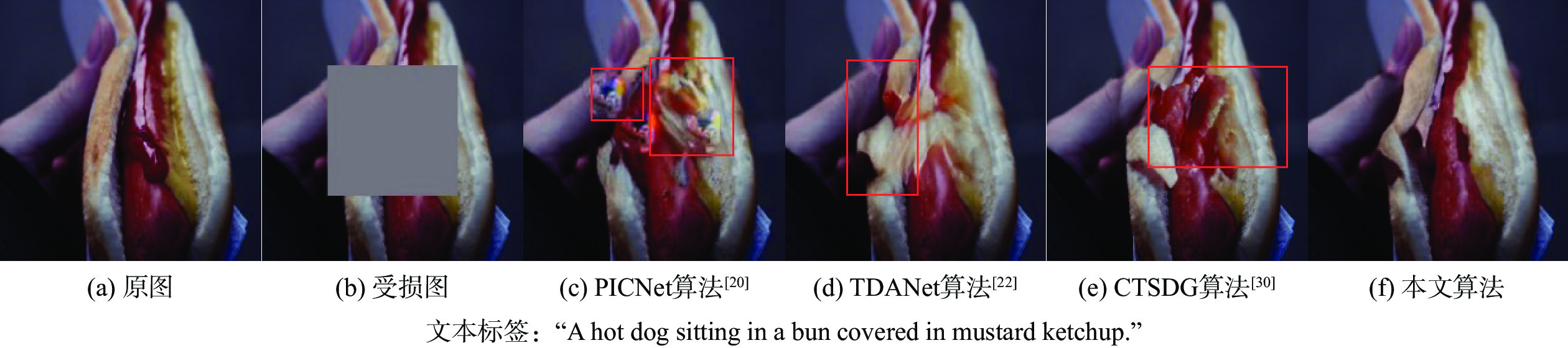
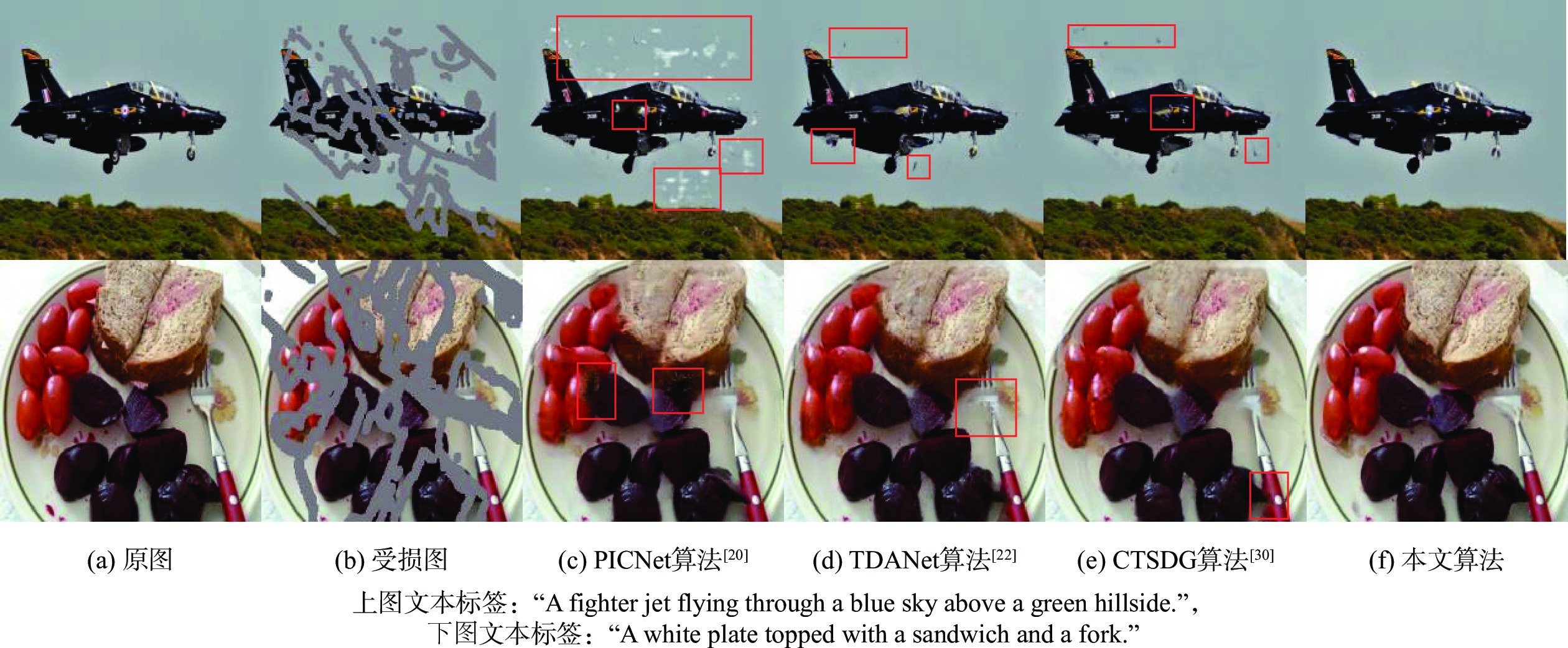
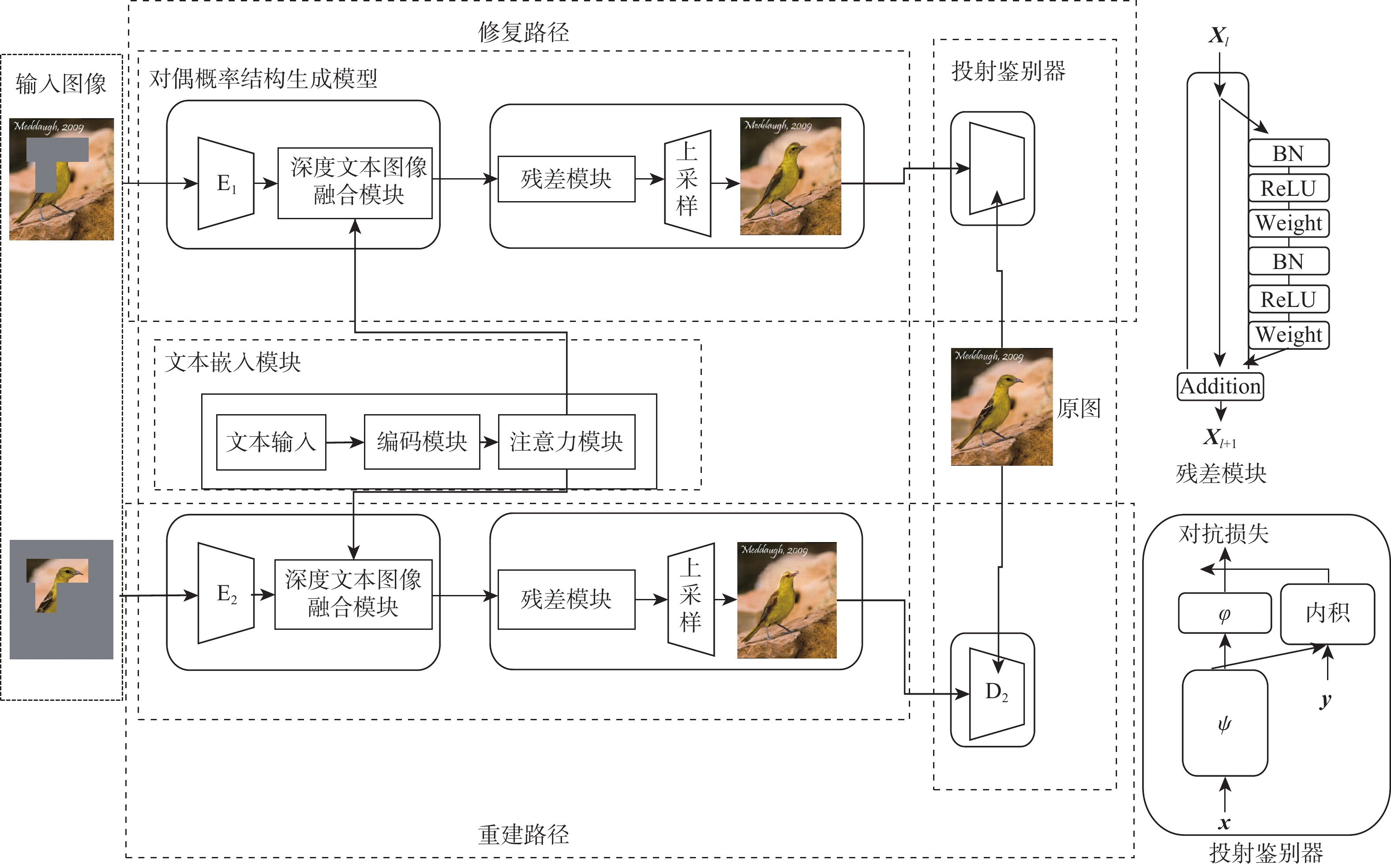
为解决现有图像修复算法因缺乏足够的上下文信息导致修复大面积破损时效果差且修复结果不可控的缺陷,提出了双重模态文本引导的图像修复算法。引入文本标签作为修复的控制引导,确保修复结果的整体与区域一致,并增加修复的可控多样性。设计双重模态掩码注意力机制提取破损区域的语义信息;通过深度文本图像融合模块加深生成器中的文本图像融合过程,并应用图像文本匹配损失最大化生成图像与文本之间的语义相似度;采用投射鉴别器训练生成图像与真实图像增强修复图像的真实性。在2个带有文本标签的数据集上进行定量和定性实验,结果表明:生成的修复图像与引导文本描述一致,可根据不同的文字描述生成多样的结果。
Abstract:A bimodal text-guided image inpainting model is proposed to address shortcomings of the existing image restoration algorithms, such as the restored results are poor and uncontrollable when repairing large areas of distortions due to lack of sufficient contextual information. The proposed algorithm introduces text labels as the control guide for restoration to ensure the overall and regional consistency of the inpainted results and to increase the controllable diversity of the results. Firstly, a dual bi-modal mask attention mechanism is designed to extract semantic information from the damaged region. Subsequently, the text image fusion process in the generator is deepened by a deep text-image fusion module, and the image-text matching loss is applied to maximize the semantic similarity between the generated images and the text. Finally, a projection discriminator is used to train the generated image with the original image to enhance the authenticity of the restored image. Quantitative and qualitative experiments are conducted on two datasets with textual labels. The experimental results demonstrate that the repaired images are consistent with the guidance text description, and various results can be generated according to various textual descriptions.
-
Key words:
- image inpainting /
- text guidance /
- attention mechanism /
- text-image fusion /
- image-text matching loss
-
表 1 对规则掩码在CUB/COCO数据集上定量对比
Table 1. Quantitative comparison of rule masks on CUB/COCO datasets
表 2 对不规则掩码在CUB/COCO数据集上定量对比
Table 2. Quantitative comparison of irregular masks on CUB/COCO datasets
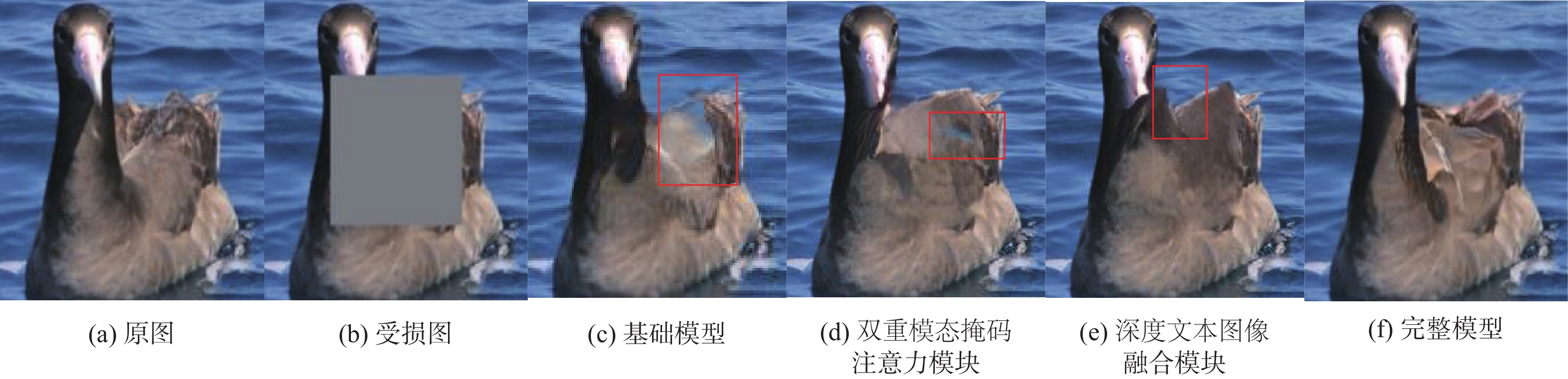
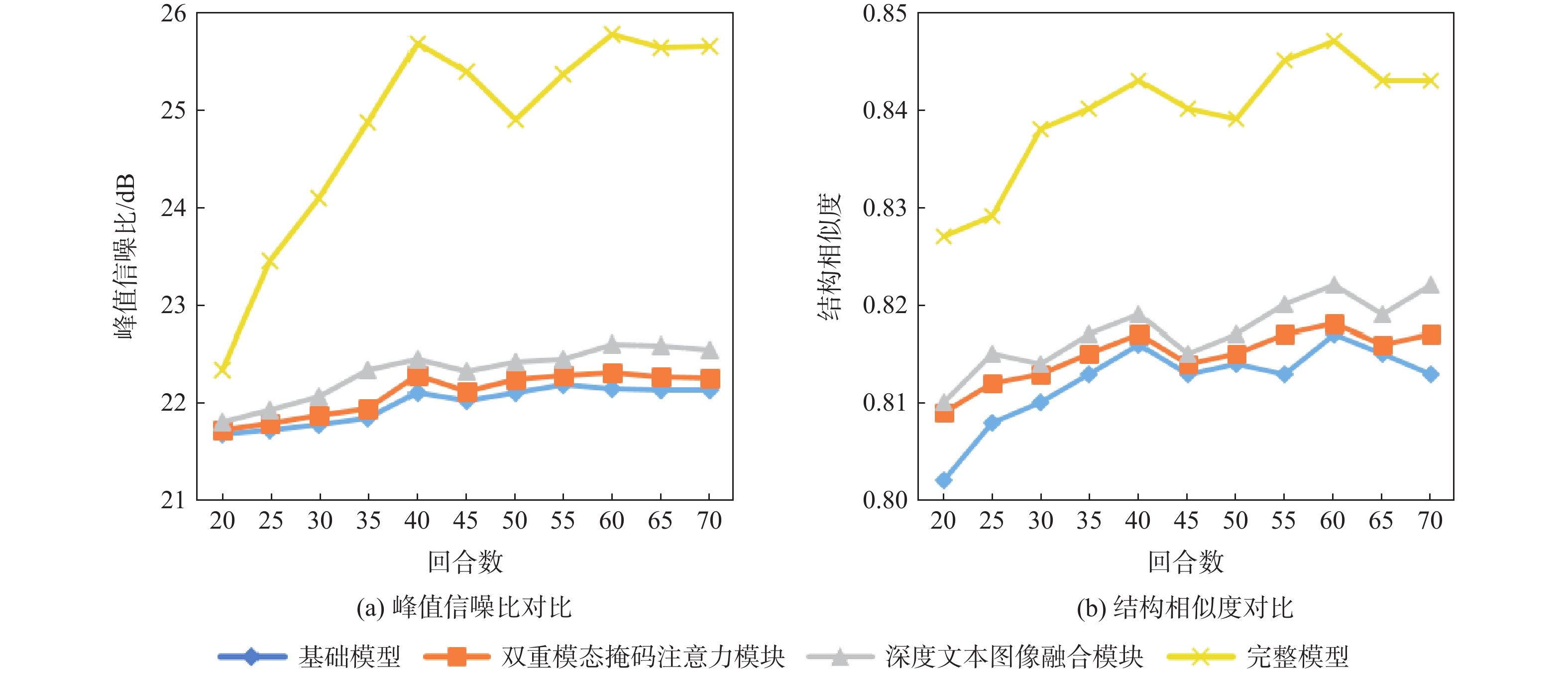
表 3 消融实验定量对比
Table 3. Quantitative comparison of ablation experiments
修复算法 峰值信噪比/dB 结构相似度 平均绝对误差 基础模型 22.15 0.817 33.82 双重模态掩码
注意力模块22.31 0.818 32.27 深度文本图像
融合模块22.60 0.822 31.52 完整模型 25.77 0.847 27.54 -
[1] BERTALMIO M, SAPIRO G, CASELLES V, et al. Image inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Computer Graphics. New York: ACM, 2000: 417-424. [2] 胡循勇, 杨晓梅, 李昊怡, 等. 融合低秩和稀疏先验的结构性缺失图像修复[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(5): 855-862.HUX Y, YANG X M, LI H Y, et al. Structural missing image inpainting based on low rank and sparse prior[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(5): 855-862(in Chinese). [3] WANG X, ZHANG D, XING G. A novel image recovery method based on discrete cosine transform and matched blocks[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 73(3): 1945-1954. doi: 10.1007/s11071-013-0915-7 [4] 王兴元, 张继明. 一种基于混沌和汉明码的数字图像篡改检测及修复算法[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(2): 73-83.WANG X Y, ZHANG J M. A novel image authentication and recovery algorithm based on chaos and Hamming code[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(2): 73-83(in Chinese). [5] XIA Z, WANG X, WANG C, et al. Subpixel-based accurate and fast dynamic tumor image recognition[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 2018, 8(5): 925-931. doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2018.2390 [6] LIN Z, ZHAO Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Weakly-supervised video moment retrieval via semantic completion network[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2020, 34(7): 11539-11546. [7] PATHAK D, KRAHENBUHL P, DONAHUE J, et al. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 2536-2544. [8] IIZUKA S, SIMO-SERRA E, ISHIKAWA H. Globally and locally consistent image completion[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-14. [9] MA Y, LIU X, BAI S, et al. Coarse-to-fine image inpainting via region-wise convolutions and non local correlation[C]//Proceedings of the IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 2019: 3123-3129. [10] SHIN Y G, SAGONG M C, YEO Y J, et al. PEPSI++: Fast and lightweight network for image inpainting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 32(1): 252-265. [11] LIU H , JIANG B, XIAO Y, et al. Coherent semantic attention for image inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4170-4179. [12] WANG N, WANG W, HU W, et al. Thank a mural inpainting based on multi-scale adaptive partial convolution and stroke-like mask[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3720-3733. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3064268 [13] YAN Z, LI X, LI M, et al. Shift-Net: Image inpainting via deep feature rearrangement[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on the Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018, 1: 1-17. [14] YU J, LIN Z, YANG J, et al. Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4471-4480. [15] 李海燕, 黄和富, 郭磊, 等. 基于残缺图像样本的生成对抗网络图像修复方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(10): 1949-1958.LI H Y, HUANG H F, GUO L, et al. Image inpainting method based on incomplete image samples in generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(10): 1949-1958(in Chinese). [16] 李海燕, 吴自莹, 郭磊, 等. 基于混合空洞卷积网络的多鉴别器图像修复[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(3): 40-45.LI H Y, WU Z Y, GUO L, et al. Multidiscriminator image inpainting algorithm based on hybrid dilated convolution network[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(3): 40-45(in Chinese). [17] 徐涛, 周纪勇, 张国梁, 等. 场内外特征融合的残缺图像精细修复[J]. 光学精密工程, 2021, 29(10): 2481-2494. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2481XU T, ZHOU J Y, ZHANG G L, et al. Fine restoration of incomplete image with external features and image features[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(10): 2481-2494(in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212910.2481 [18] 张雪菲, 程乐超, 白升利, 等. 基于变分自编码器的人脸图像修复[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2020, 32(3): 401-409.ZHANG X F, CHEN L C, BAI S L, et al. Face image restoration based on variational autoencoder[J]. Journal of Computer Aided Design and Graphics, 2020, 32(3): 401-409(in Chinese). [19] WALKER J, DOERSCH C, GUPTA A, et al. An uncertain future: Forecasting from static images using variational autoencoders[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on the Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 835-851. [20] ZHANG C, CHAM T J, CAI J. Pluralistic image completion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1438-1447. [21] NAZERI, NG E, JOSEPH T, et al. EdgeConnect: Generative image inpainting with adversarial edge learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3265-3274. [22] ZHANG L, CHEN Q, HU B, et al. Text-guided neural image inpainting[C]//Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2020: 1302-1310. [23] SOHN K, LEE H, YAN X. Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 3483-3491. [24] ZHANG H, XU T, LI H, et al. StackGAN: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5907-5915. [25] DOERSCH C. Tutorial on variational autoencoders[EB/OL]. (2021-01-03)[2021-11-01]. [26] BAO J, CHEN D, WEN F, et al. CVAE-GAN: Fine-grained image generation through asymm-etric training[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2745-2754. [27] XU T, ZHANG P, HUANG Q, et al. AttnGAN: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1316-1324. [28] DUAN K, PARIKH D, CRANDALL D, et al. Discovering localized attributes for fine-grained recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 3474-3481. [29] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on the Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [30] GUO X, YANG H, HUANG D. Image inpainting via conditional texture and structure dual generation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 14134-14143. -







 下载:
下载: