-
摘要:
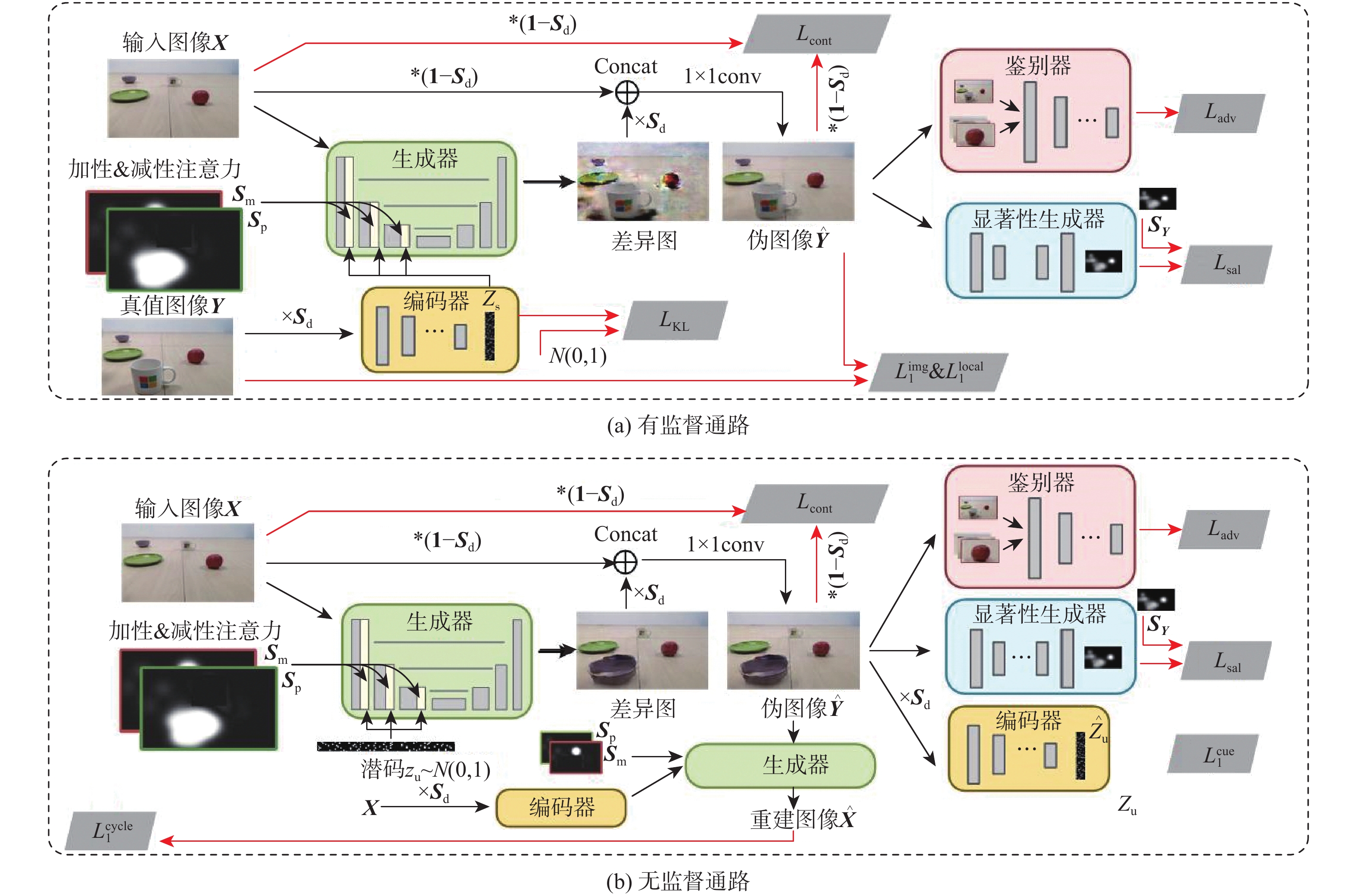
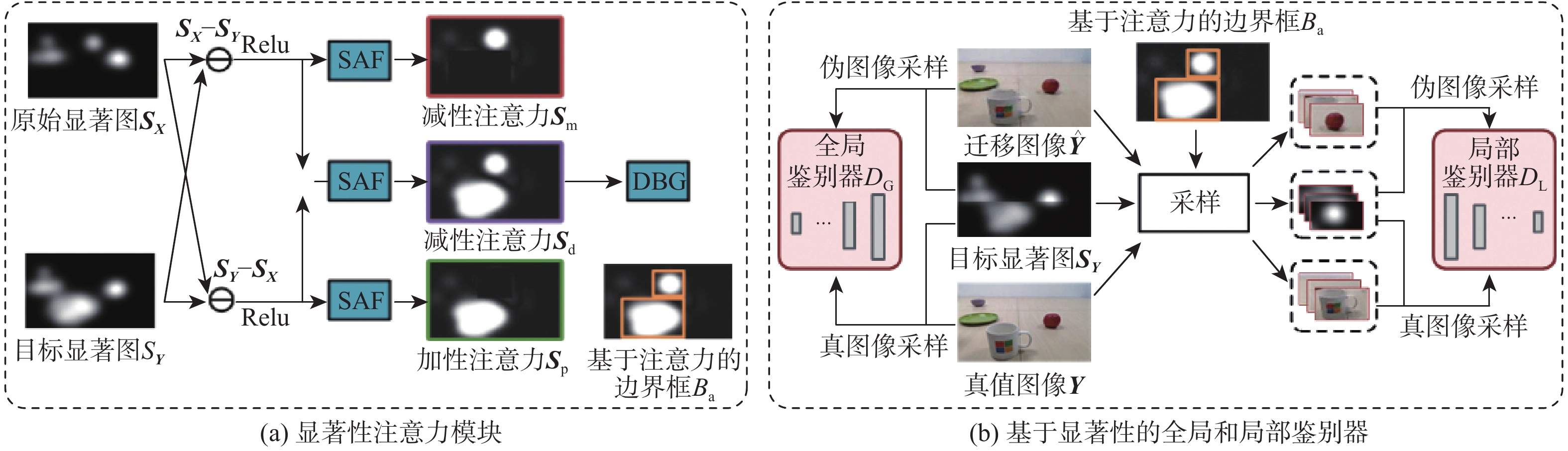
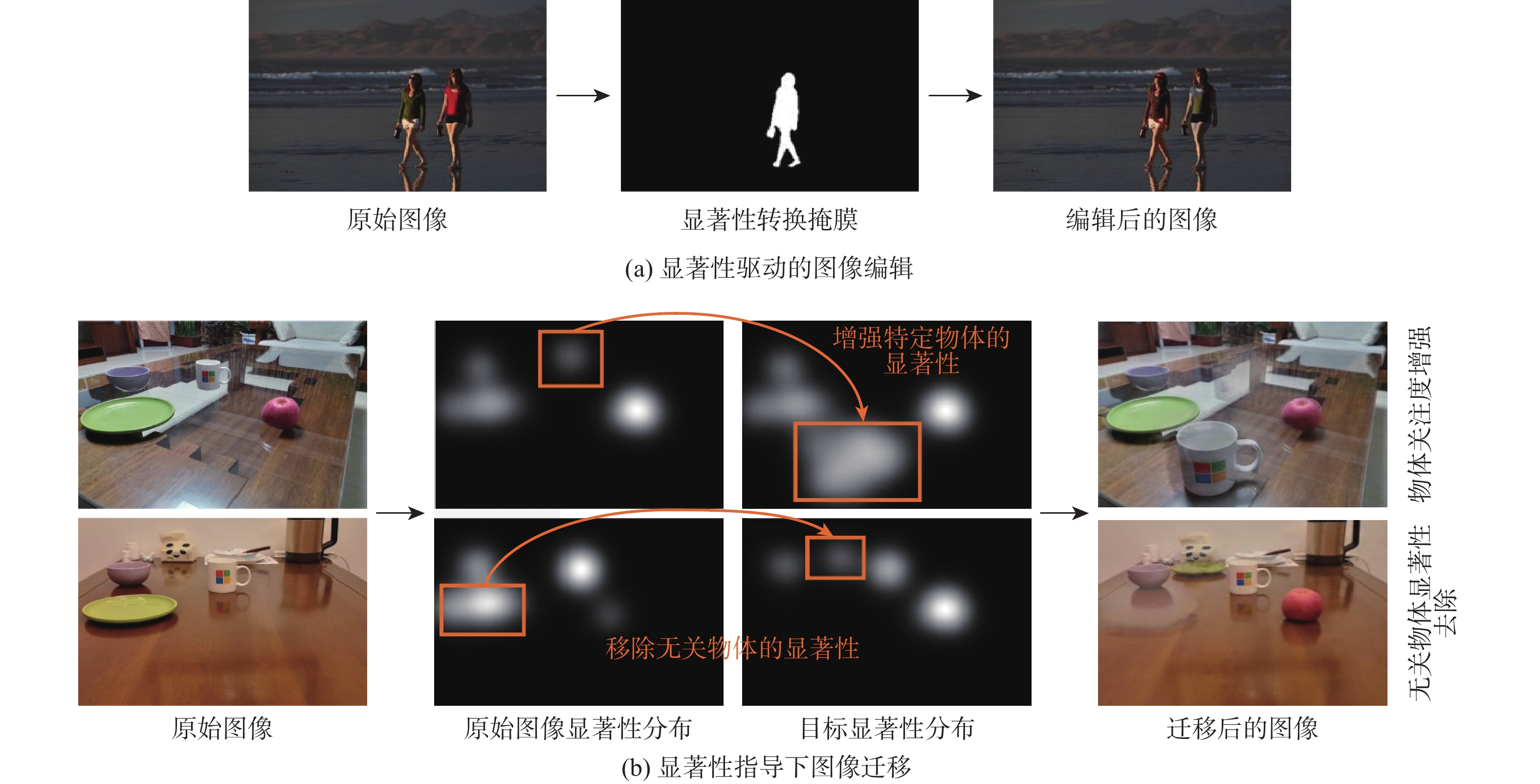
开拓了显著性指导下图像迁移新任务,在图像内容及保真度不变条件下,为使迁移后图像满足用户指定的显著图分布,提出一种全新的生成对抗网络 (SalG-GAN)方法。对于给定的原始图像和目标显著图,所提方法可高效生成符合目标显著图的迁移图像。在所提方法中,引入解耦表示框架用于激励模型,针对相同的显著图输入,生成内容不同的迁移图像;在该框架基础上,设计基于显著图的注意模块作为一种特殊的注意力机制,辅助网络在图像迁移过程中聚焦于关键区域;同时,在所提方法中构造基于显著性的生成器、编码器、全局和局部鉴别器等深度网络结构。此外,建立用于显著性指导下图像迁移任务的大规模数据集,用于训练和评估所提方法,具体包括一个大规模的合成数据集和一个包括人眼视觉注意点的真实数据集。在2个数据集上的实验结果表明:所提方法在显著性指导下图像迁移任务中具有优异性能,远优于基准生成对抗网络方法。
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel task for saliency-guided image translation, with the goal of image-to-image translation conditioned on the user specified saliency map. To address this problem, we develop a novel generative adversarial network (GAN) method -based model, called SalG-GAN method. Given the original image and target saliency map, proposed method can generate a translated image that satisfies the target saliency map. In proposed method, a disentangled representation framework is proposed to encourage the model to learn diverse translations for the same target saliency condition. A saliency-based attention module is introduced as a special attention mechanism to facilitate the developed structures of saliency-guided generator, saliency cue encoder, and saliency-guided global and local discriminators. Furthermore, we build a synthetic dataset and a real-world dataset with labeled visual attention for training and evaluating proposed method. The experimental results on both datasets verify the effectiveness of our model for saliency-guided image translation.
-
Key words:
- saliency /
- generative adversarial network /
- image translation /
- attention mechanism /
- dataset
-
表 1 本文方法和基准方法的性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparision between the propsoed and baseline methods
方法 FI DS SKL SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C HAG 60.31 69.63 45.21 0.26 ± 0.12 0.65 ± 0.22 0.73 ± 0.12 CycleGAN 34.81 106.45 114.58 0.03 ± 0.02 0.03 ± 0.03 0.43 ± 0.33 BicycleGAN 113.92 122.03 118.67 0.06 ± 0.05 0.08 ± 0.03 0.38 ± 0.28 本文方法 30.48 48.78 53.35 0.34 ± 0.17 0.02 ± 0.01 0.08 ± 0.02 0.02 ± 0.01 0.02 ± 0.01 0.11 ± 0.07 表 2 用户研究:使用本文方法和基准方法获得的结果偏好
Table 2. Userstudy: Preference between results obtained using proposed and baseline methods
方法 真实性/% 显著性/% 一致性/% SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C SGIT-S SGIT-R SGIT-C HAG 8.0 25.2 47.3 4.2 9.4 2.0 18.1 21.6 41.7 CycleGAN 21.0 12.3 2.0 21.3 16.3 12.1 10.1 16.4 2.1 BicycleGAN 15.5 8.4 2.0 17.8 10.3 12.0 10.0 14.1 2.1 本文方法 55.5 54.1 48.7 56.7 64.0 73.9 61.8 47.9 55.1 -
[1] EL-NOUBY A, SHARMA S, SCHULZ H, et al. Tell, draw, and repeat: Penerating and modifying images based on continual linguistic instruction[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10303-10311. [2] HONG S, YANG D D, CHOI J, et al. Inferring semantic layout for hierarchical text-to-image synthesis[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7986-7994. [3] ISOLA P, ZHU J Y, ZHOU T H, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5967-5976. [4] ZHAO B, MENG L L, YIN W D, et al. Image generation from layout[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 8576-8585. [5] CHOI Y, CHOI M, KIM M, et al. StarGAN: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8789-8797. [6] YIN W D, LIU Z W, CHANGE LOY C. Instance-level facial attributes transfer with geometry-aware flow[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 9111-9118. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33019111 [7] JOHNSON J, GUPTA A, LI F F. Image generation from scene graphs[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1219-1228. [8] KARRAS T, LAINE S, AILA T M. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4396-4405. [9] WANG T C, LIU M Y, ZHU J Y, et al. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional GANs[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8798-8807. [10] ZHU J Y, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2242-2251. [11] BAU D, ZHU J Y, STROBELT H, et al. GAN dissection: Visualizing and understanding generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-12-26)[2021-10-20]. [12] YU J H, LIN Z, YANG J M, et al. Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4470-4479. [13] MATEESCU V A, BAJIC I V. Visual attention retargeting[J]. IEEE MultiMedia, 2016, 23(1): 82-91. doi: 10.1109/MMUL.2015.59 [14] MECHREZ R, SHECHTMAN E, ZELNIK-MANOR L. Saliency driven image manipulation[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2019, 30(2): 189-202. doi: 10.1007/s00138-018-01000-w [15] FRIED O, SHECHTMAN E, GOLDMAN D B, et al. Finding distractors in images[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1703-1712. [16] NGUYEN T V, NI B B, LIU H R, et al. Image re-attentionizing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2013, 15(8): 1910-1919. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2013.2272919 [17] ITTI L, KOCH C, NIEBUR E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254-1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [18] JIANG L, XU M, WANG X F, et al. Saliency-guided image translation[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16504-16513. [19] CHEN Y C, CHANG K J, TSAI Y H, et al. Guide your eyes: Learning image manipulation under saliency guidance[C]//British Machine Vision Conference. Cardiff: BMVA Press, 2019. [20] WONG L K, LOW K L. Saliency retargeting: An approach to enhance image aesthetics[C]//2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 73-80. [21] GATYS L A, KÜMMERER M, WALLIS T S A, et al. Guiding human gaze with convolutional neural networks[EB/OL]. (2017-09-18)[2021-10-20]. [22] MEJJATI Y A, GOMEZ C F, KIM K I, et al. Look here! A parametric learning based approach to redirect visual attention[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 343-361. [23] HAGIWARA A, SUGIMOTO A, KAWAMOTO K. Saliency-based image editing for guiding visual attention[C]//Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Pervasive Eye Tracking & Mobile Eye-Based Interaction. New York: ACM, 2011: 43-48. [24] MENDEZ E, FEINER S, SCHMALSTIEG D. Focus and context in mixed reality by modulating first order salient features[C]//International Symposium on Smart Graphics. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 232-243. [25] BERNHARD M, ZHANG L, WIMMER M. Manipulating attention in computer games[C]//2011 IEEE 10th IVMSP Workshop: Perception and Visual Signal Analysis. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 153-158. [26] ZHU J Y, ZHANG R, PATHAK D, et al. Multimodal image-to-image translation by enforcing bi-cycle consistency[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: NIPS, 2017: 465-476. [27] LARSEN A B L, SØNDERBY S K, LAROCHELLE H, et al. Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2016: 1558-1566. [28] MAO X D, LI Q, XIE H R, et al. Least Squares generative adversarial networks[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2813-2821. [29] JIANG M, HUANG S S, DUAN J Y, et al. SALICON: Saliency in context[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1072-1080. [30] JOHNSON J, HARIHARAN B, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. CLEVR: A diagnostic dataset for compositional language and elementary visual reasoning[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1988-1997. [31] ZHOU B L, LAPEDRIZA A, KHOSLA A, et al. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1452-1464. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2723009 [32] MIYATO T, KATAOKA T, KOYAMA M, et al. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-02-16)[2021-10-18]. [33] ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, LEMPITSKY V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization[EB/OL]. (2016-07-27)[2021-10-24]. [34] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2014-12-22)[2021-10-25]. [35] HEUSEL M, RAMSAUER H, UNTERTHINER T, et al. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 6629-6640. [36] ZHANG R, ISOLA P, EFROS A A, et al. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric[C]//2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 586-595. [37] LEE H Y, TSENG H Y, HUANG J B, et al. Diverse image-to-image translation via disentangled representations[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 36-52. -







 下载:
下载: