-
摘要:
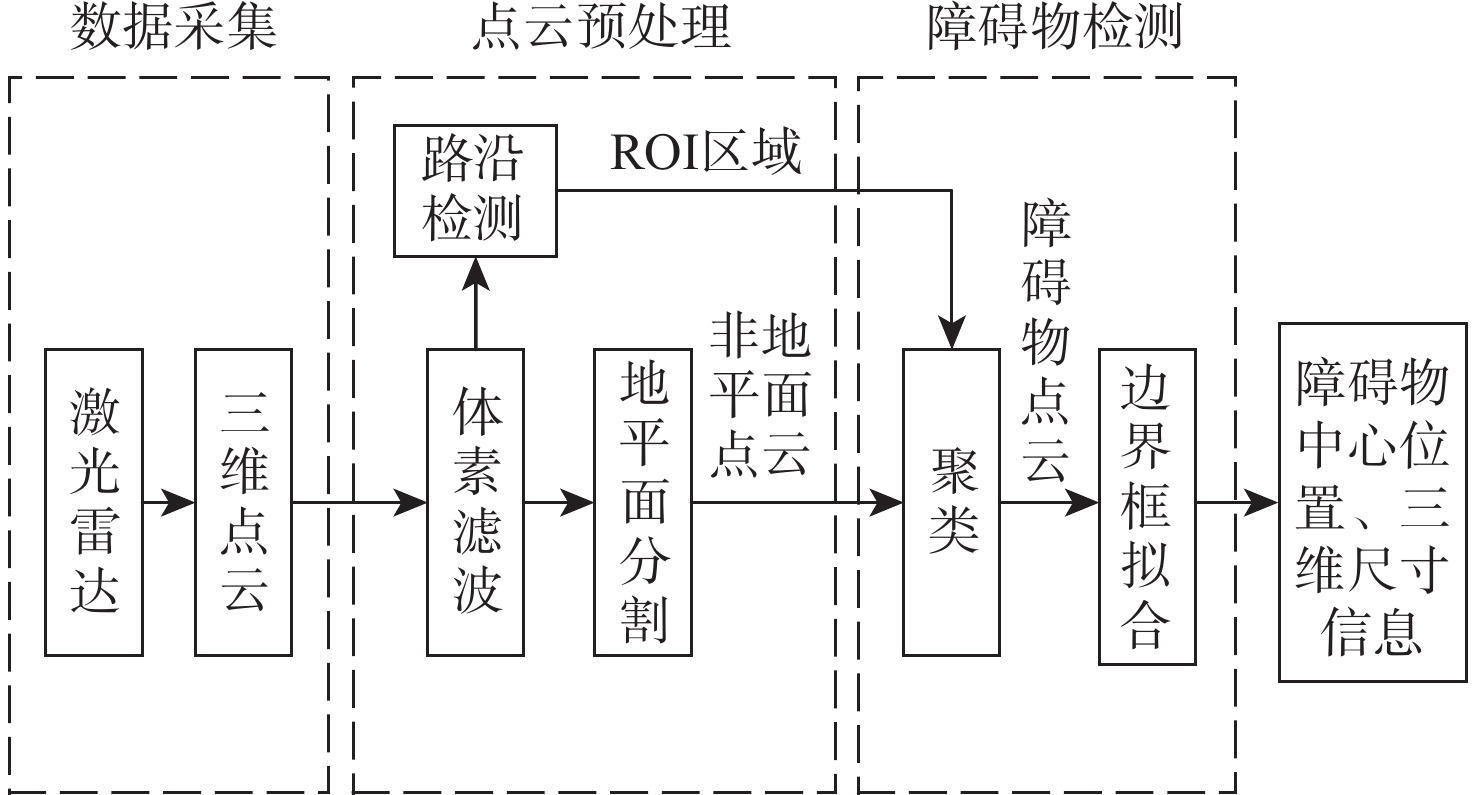
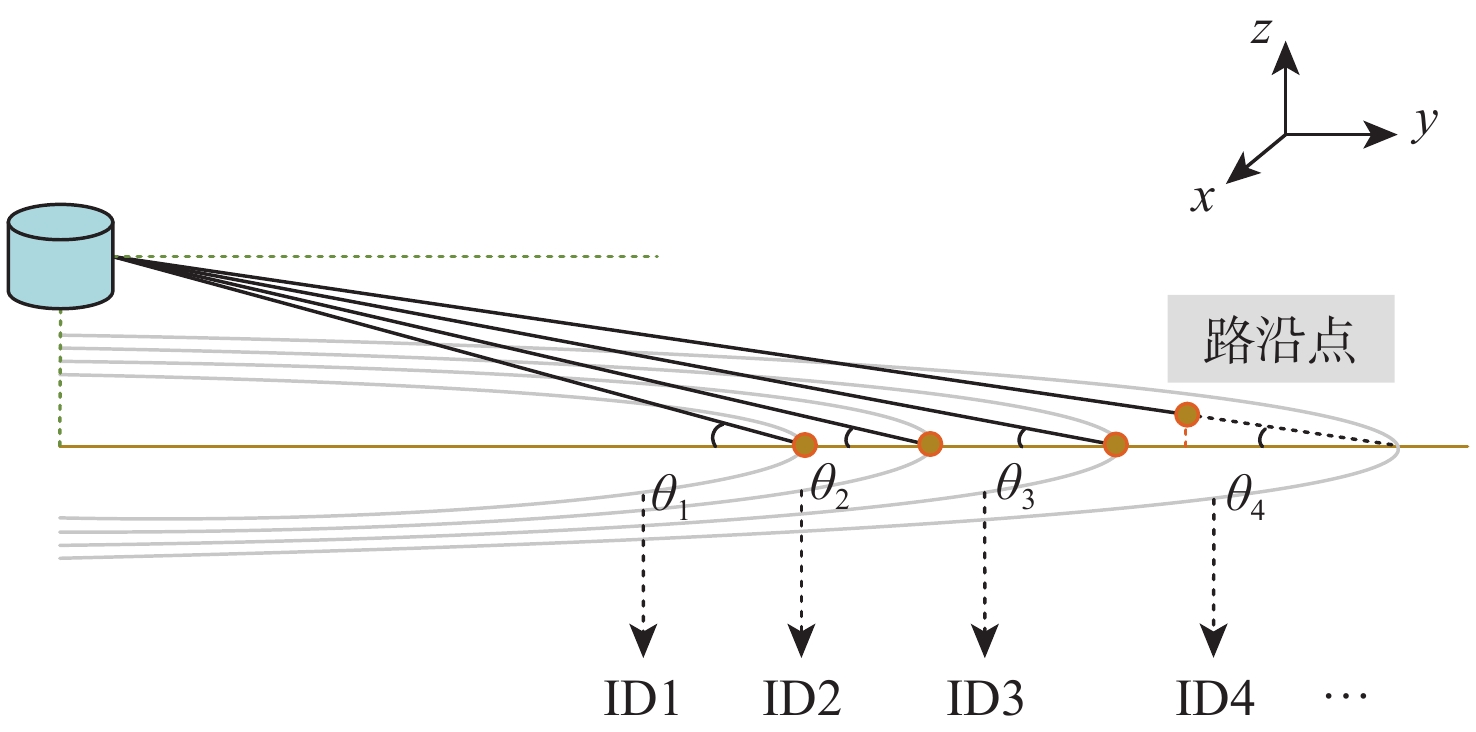
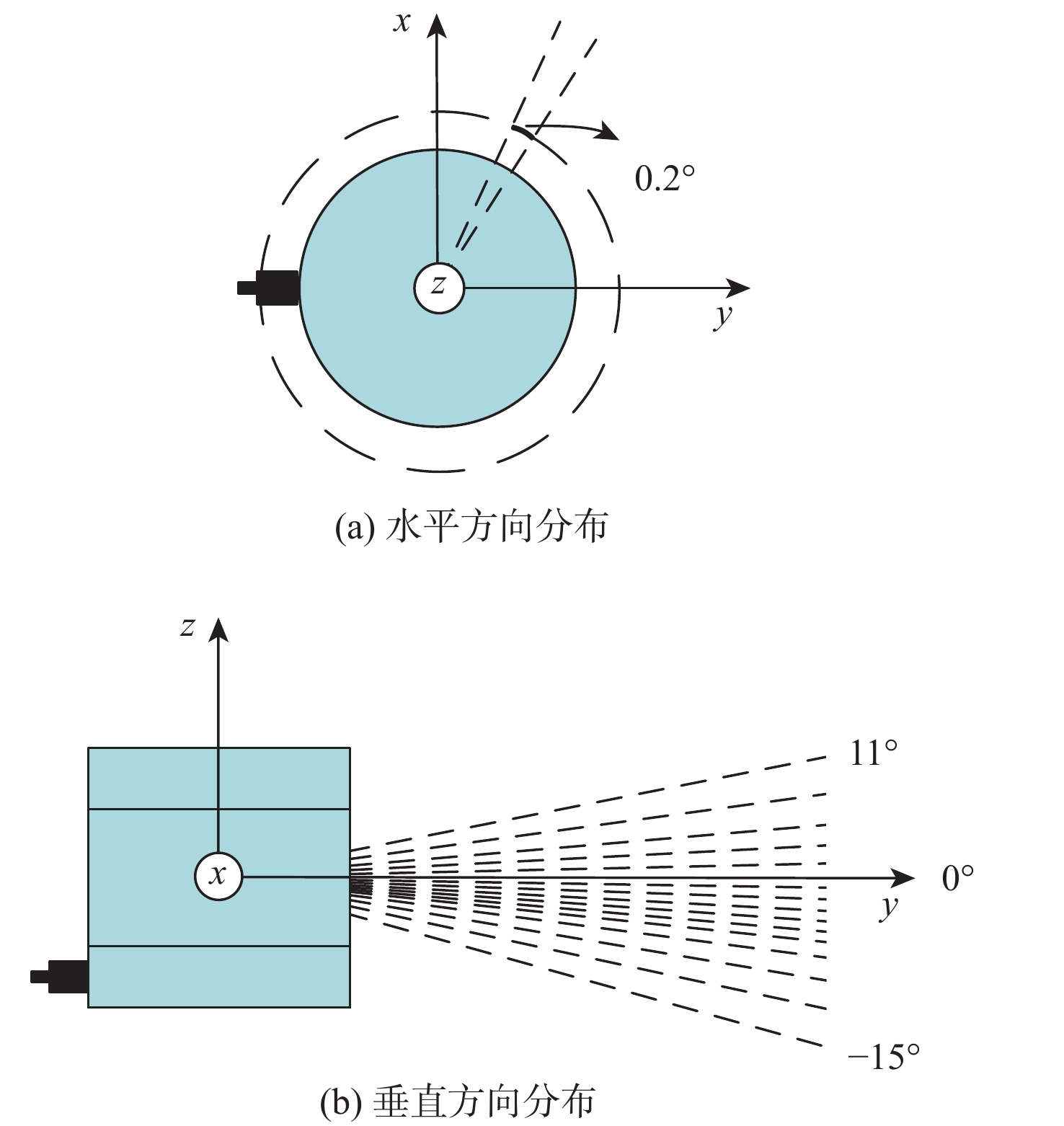
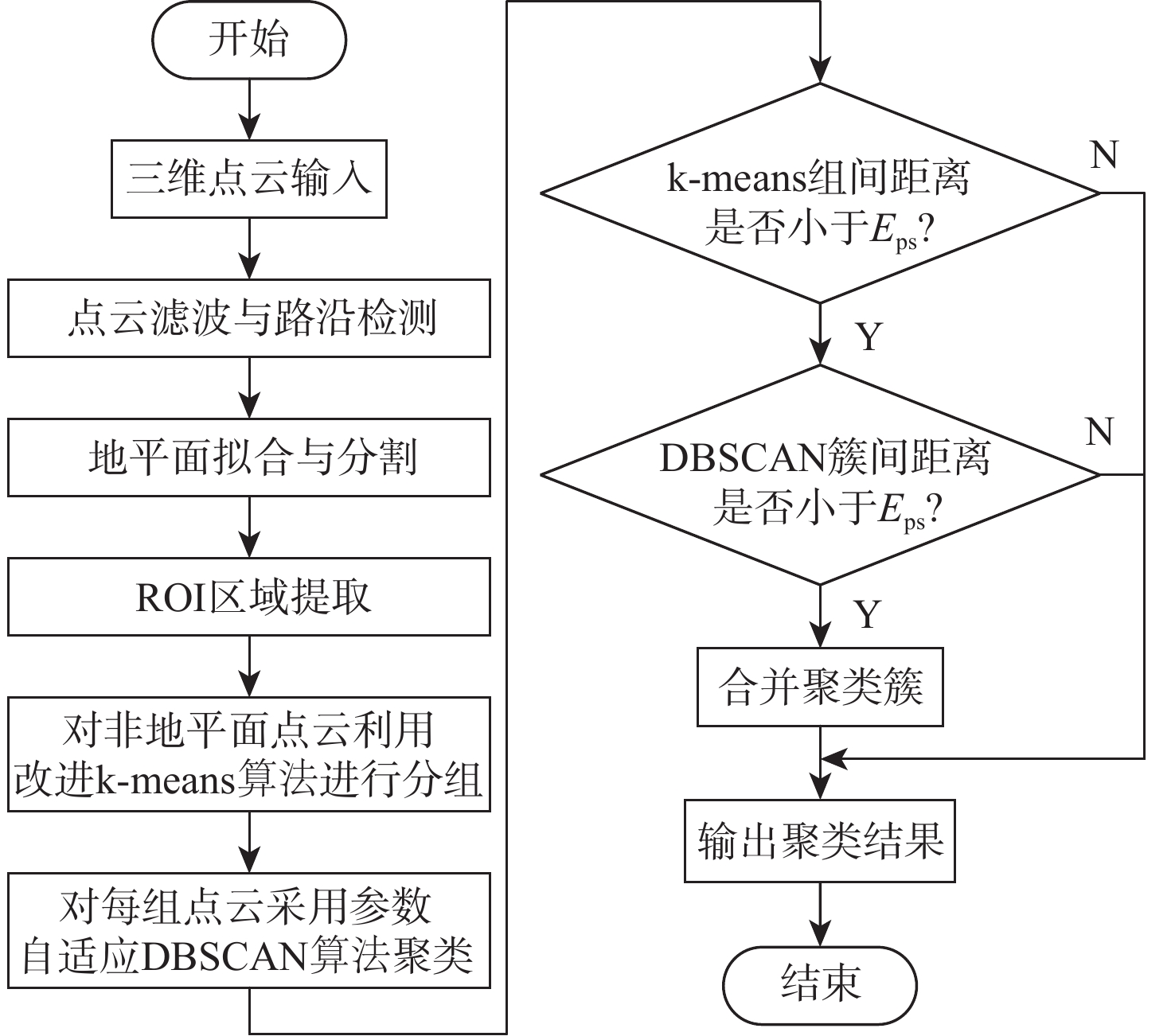
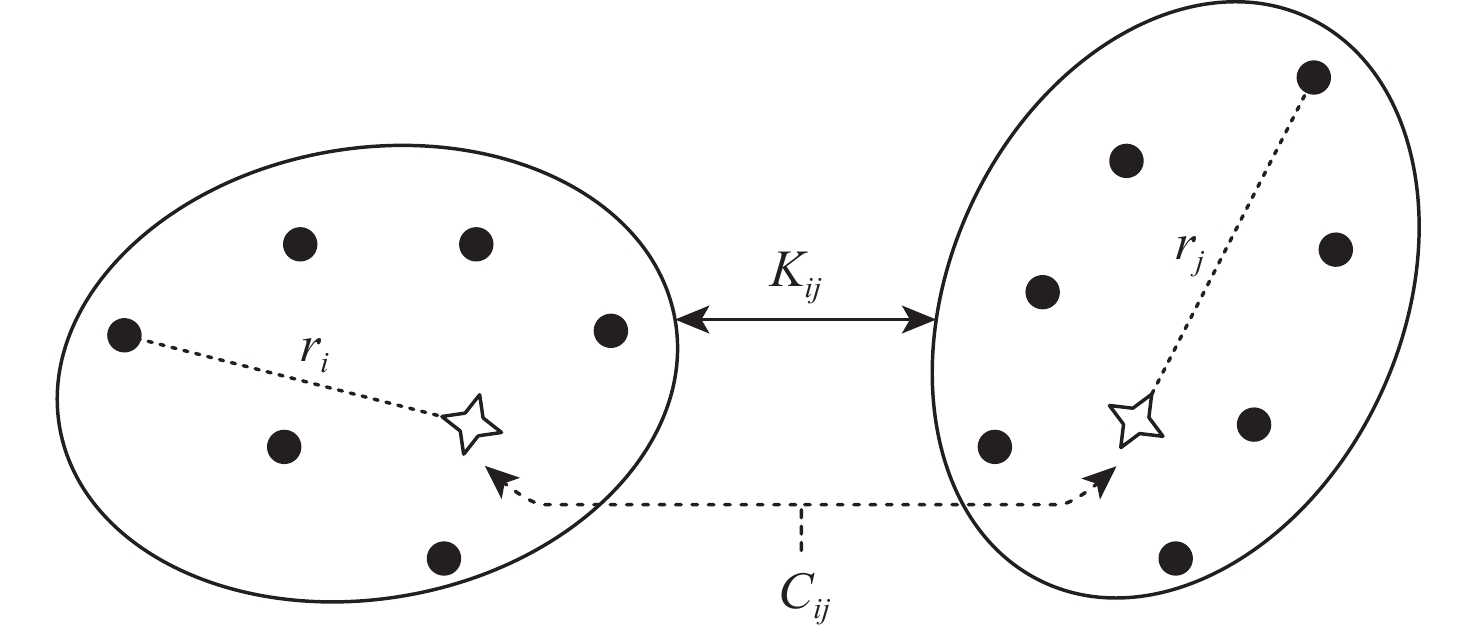
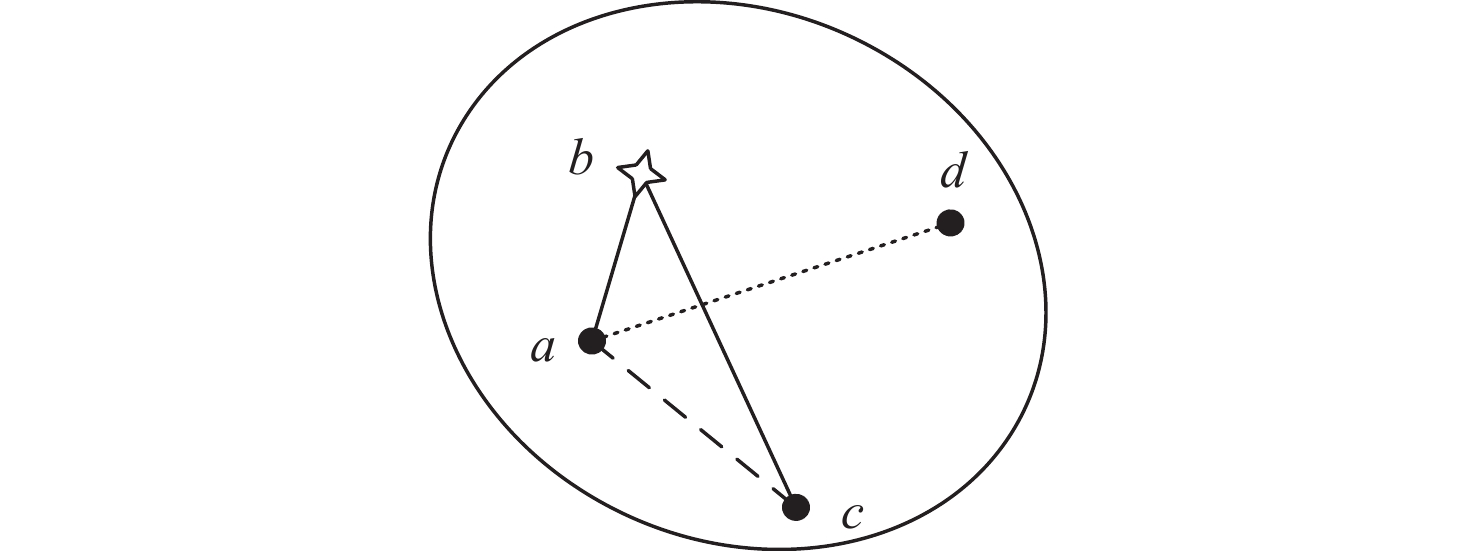
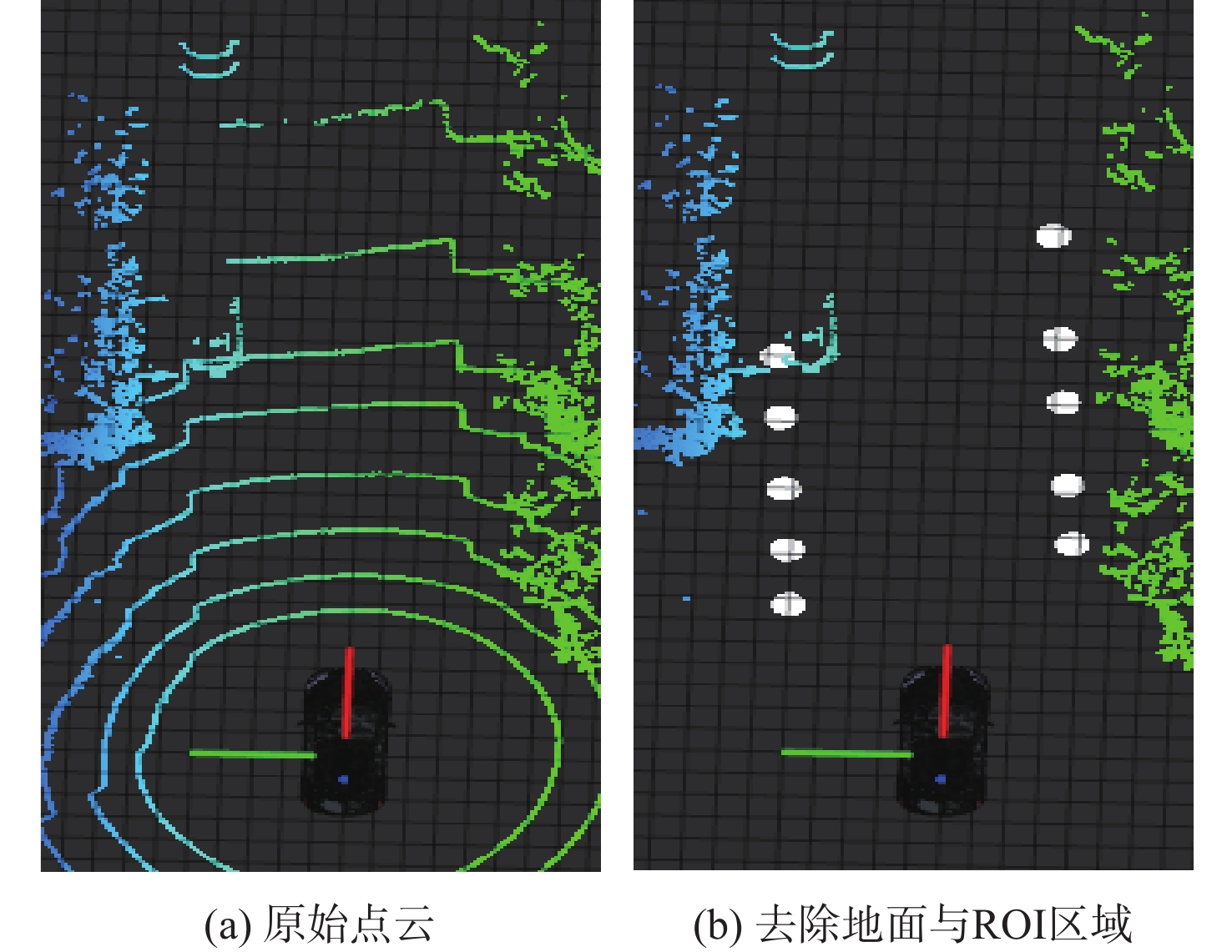
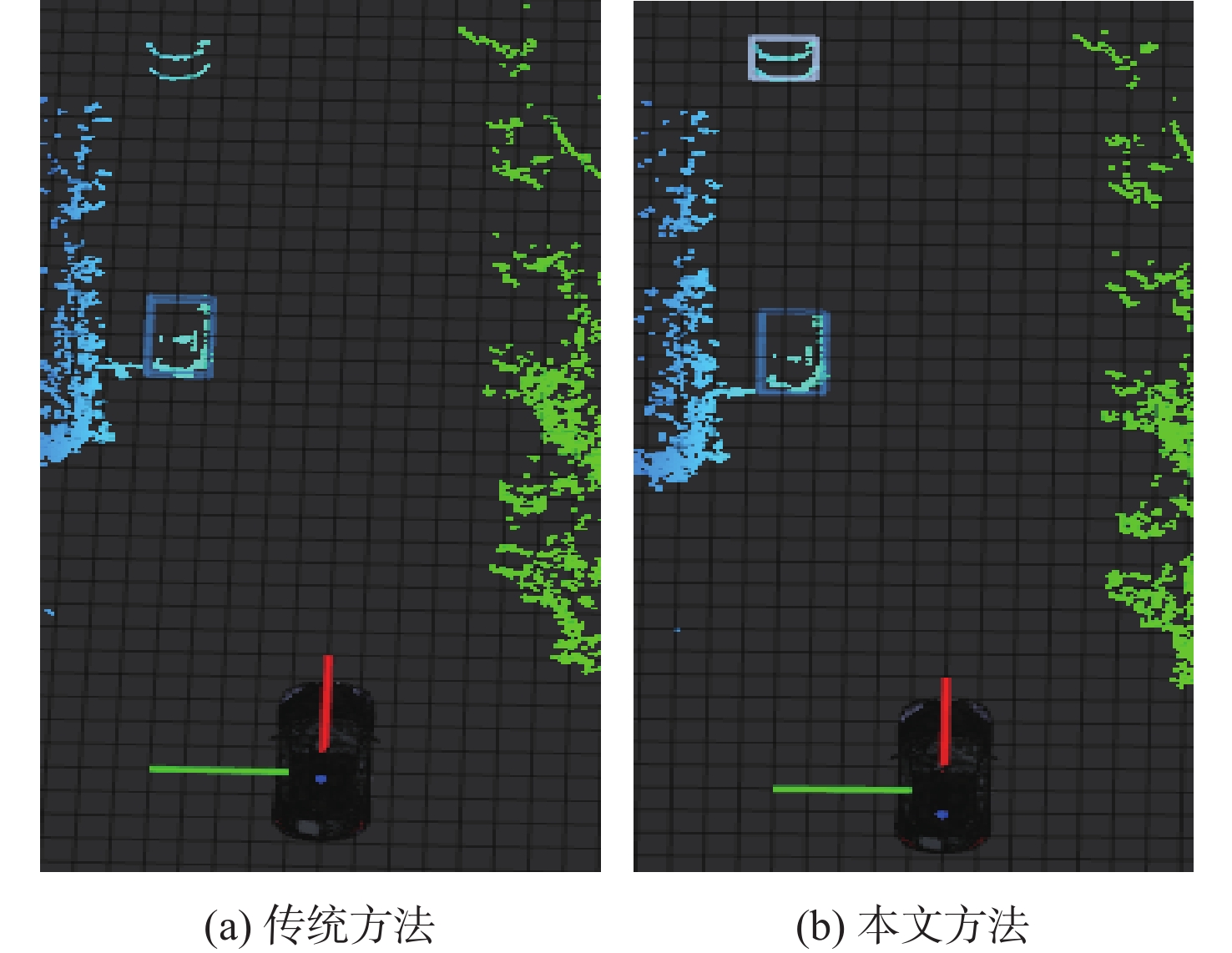
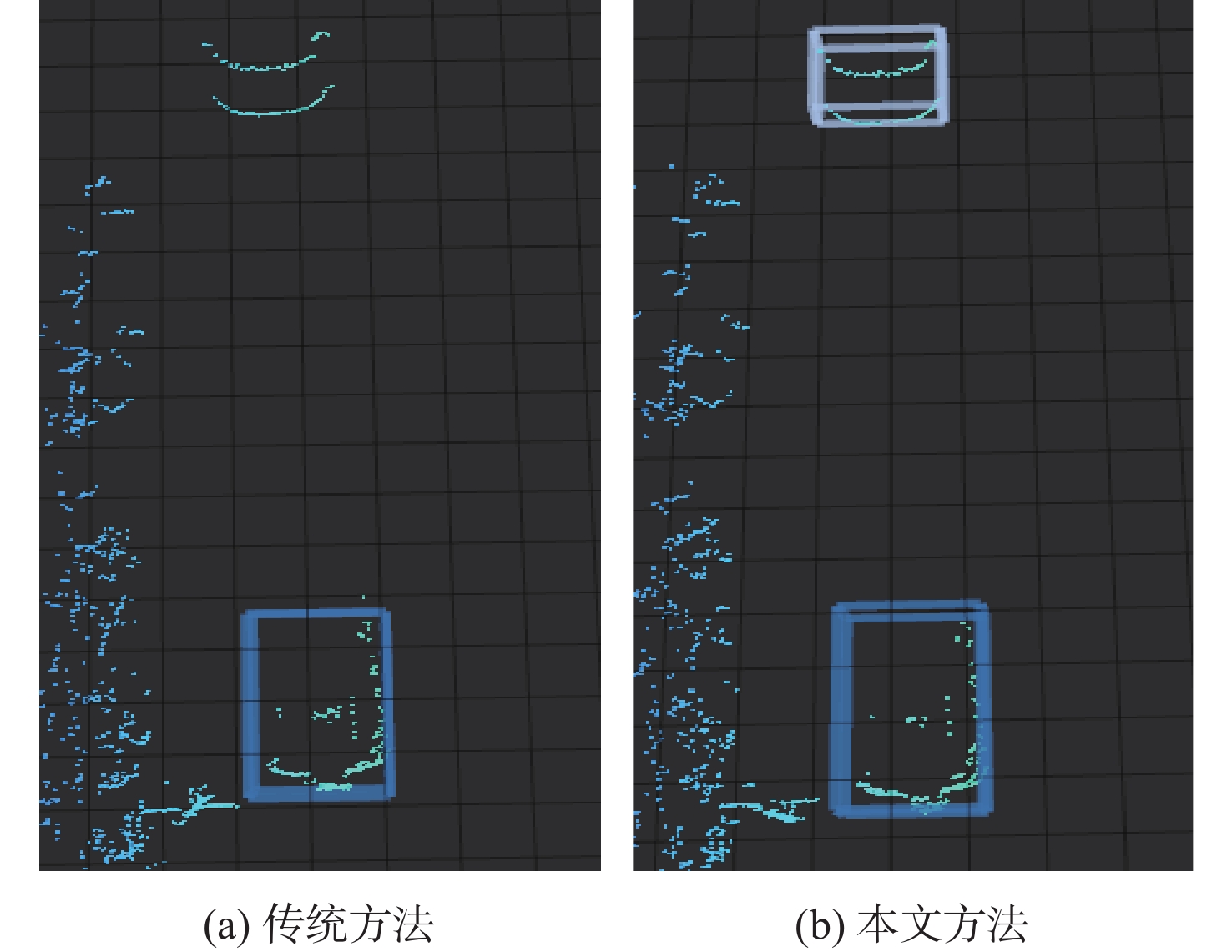
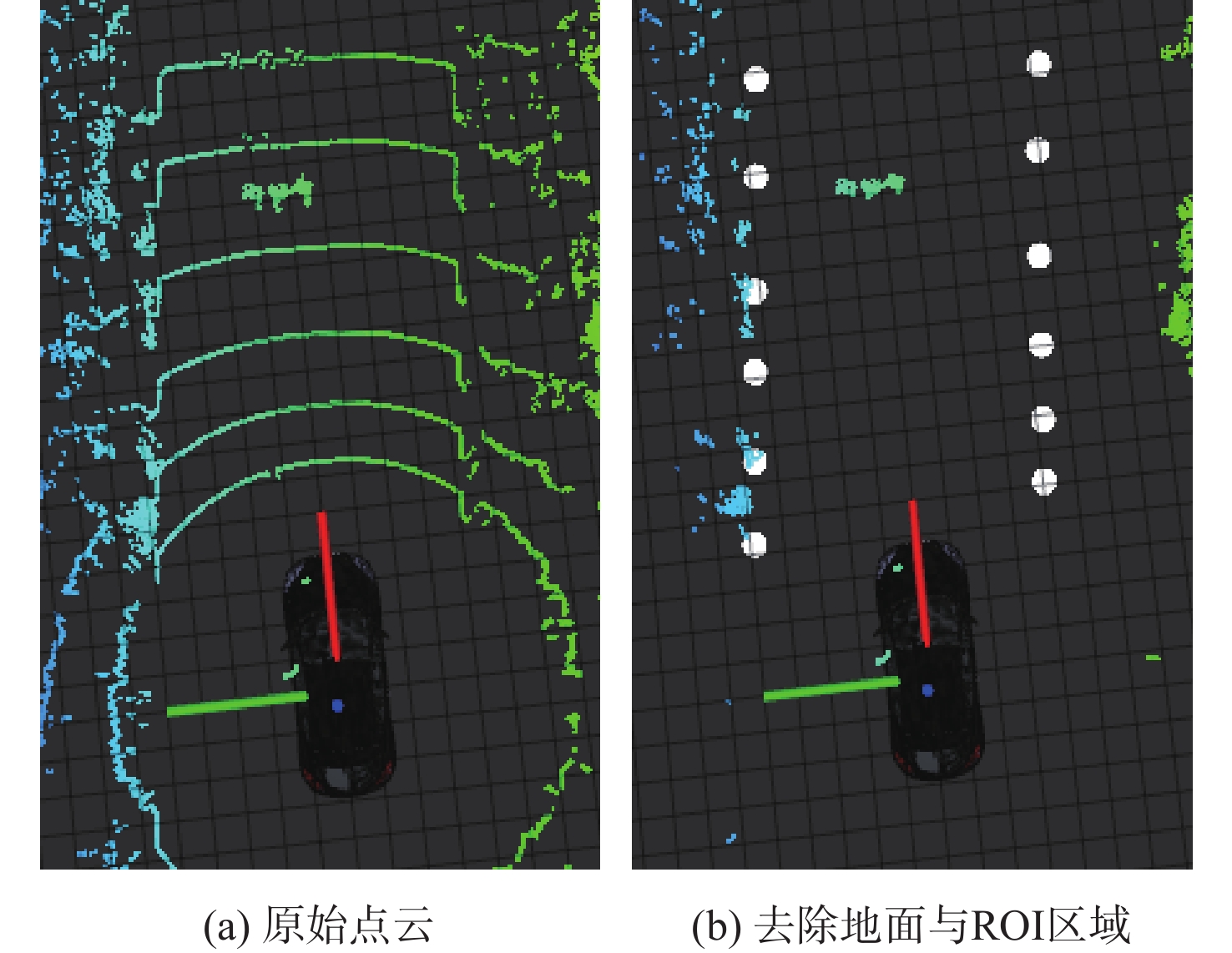
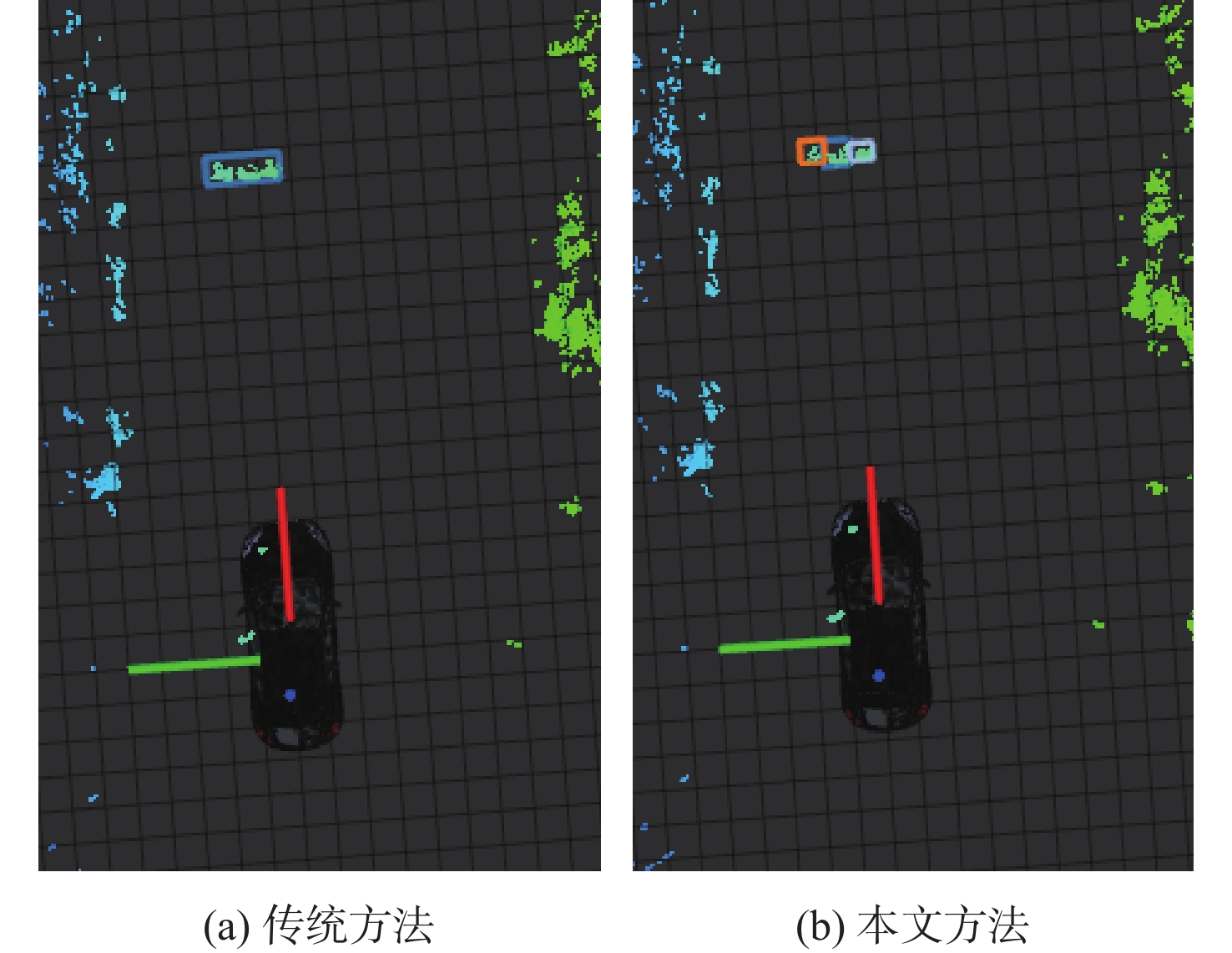
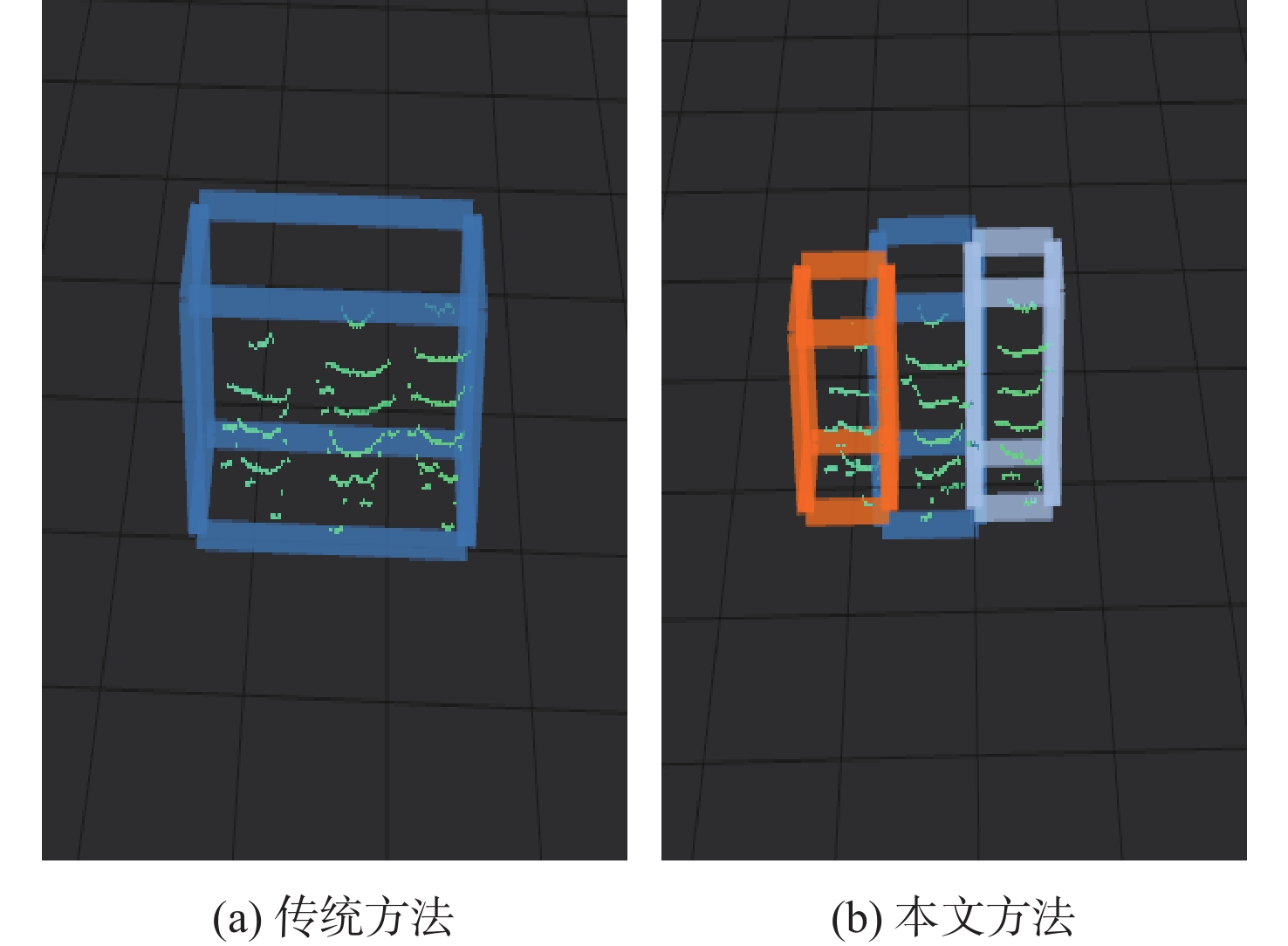
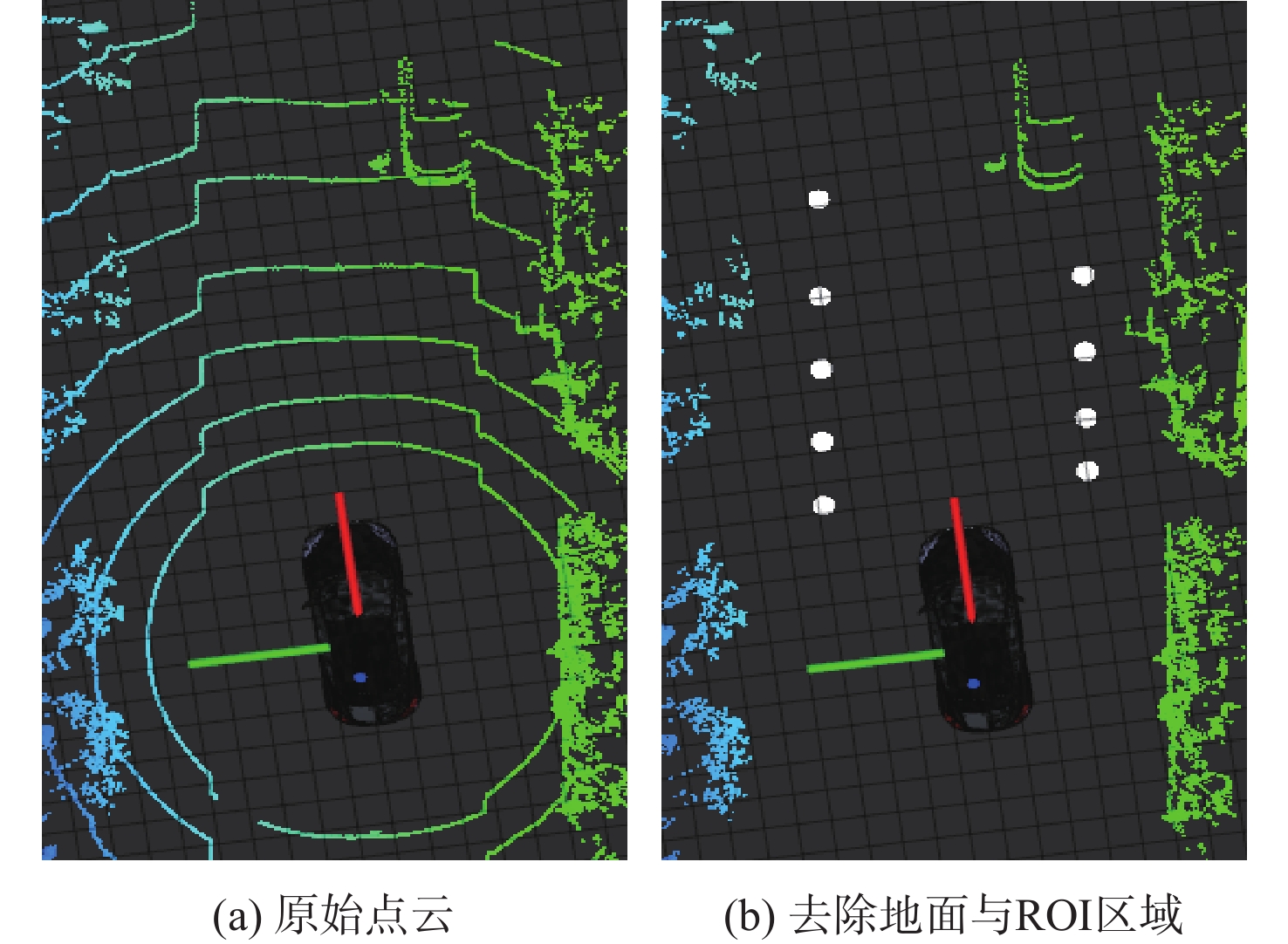
针对无人车在园区环境下采集的激光三维点云中远距离障碍物易漏检、相邻障碍物存在欠分割和过分割且算法耗时较大等问题,根据激光束在水平和垂直方向上的分布不同,通过自适应调整聚类半径,提出了改进的具有噪声基于密度的空间聚类 (DBSCAN)算法,并基于分组聚类思想结合改进的k-means算法提出了一种快速且准确的障碍物检测方法。根据感兴趣区域 (ROI)内三维点云的密度特征,利用改进的k-means算法对其初步分组;对每组内的点云使用参数自适应的DBSCAN算法进行并行聚类;对组边界上符合条件的聚类簇进行合并,完成障碍物检测。实车实验结果表明:与传统方法相比,所提方法障碍物检测正检率提高17.5%,平均耗时缩短23.6%。
Abstract:For the 3D point cloud collected by the LiDAR on the intelligent vehicle in the park environment, there exist some problems, for example, the obstacles far away from the LiDAR are easily missed, adjacent obstacles are prone to incompletely or excessively differentiate, and the algorithm is time-consuming. To solve these problems, the improved density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is proposed by adaptively changing the clustering radius based on laser beams that are distributed differently in the horizontal and vertical directions. It is also suggested to combine the upgraded k-means algorithm with the concept of group clustering to create a quick and accurate obstacle identification technique. Firstly, the 3D point clouds in the region of interest (ROI) are preliminarily grouped by using the improved k-means algorithm according to 3D point clouds density characteristics. Then, the point clouds in each group are clustered in parallel using the parameter adaptive DBSCAN algorithm. Finally, the clusters on the qualified group boundary are merged to complete the obstacle detection. The experimental findings indicate that when compared to the conventional approaches, the suggested method’s true positive rate of obstacle detection is enhanced by 17.5%, and the average time consumption is decreased by 23.6%.
-
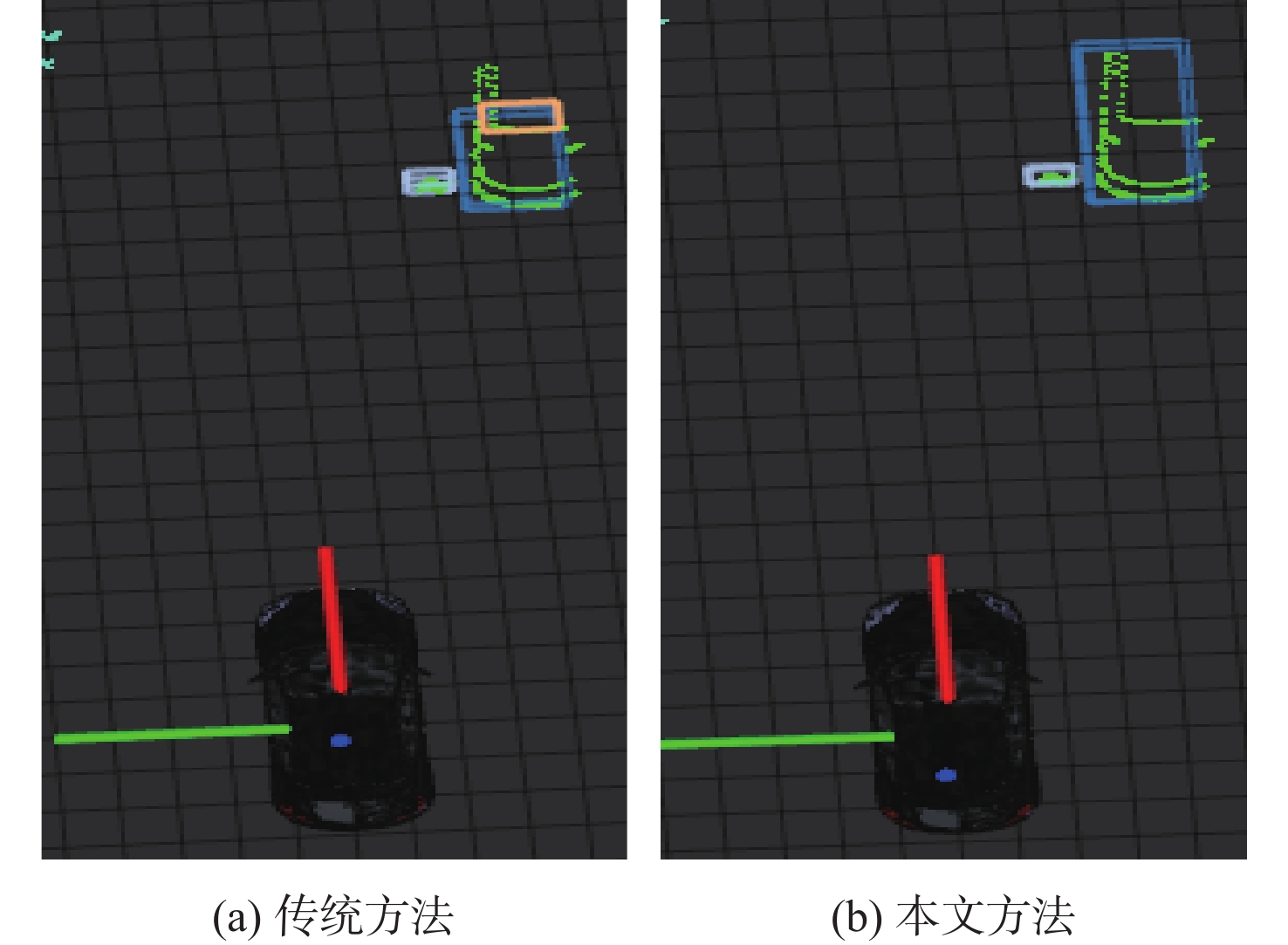
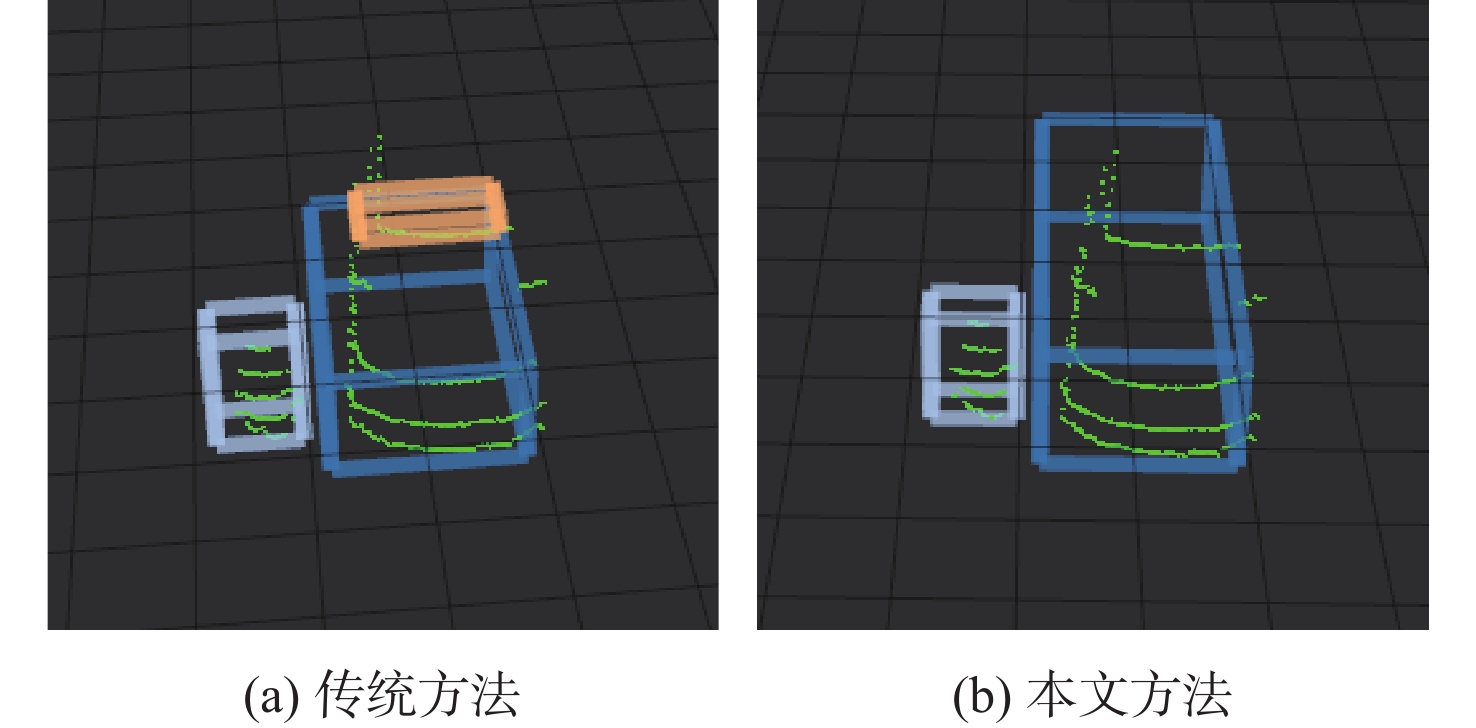
表 1 障碍物位置信息
Table 1. Obstacle location information
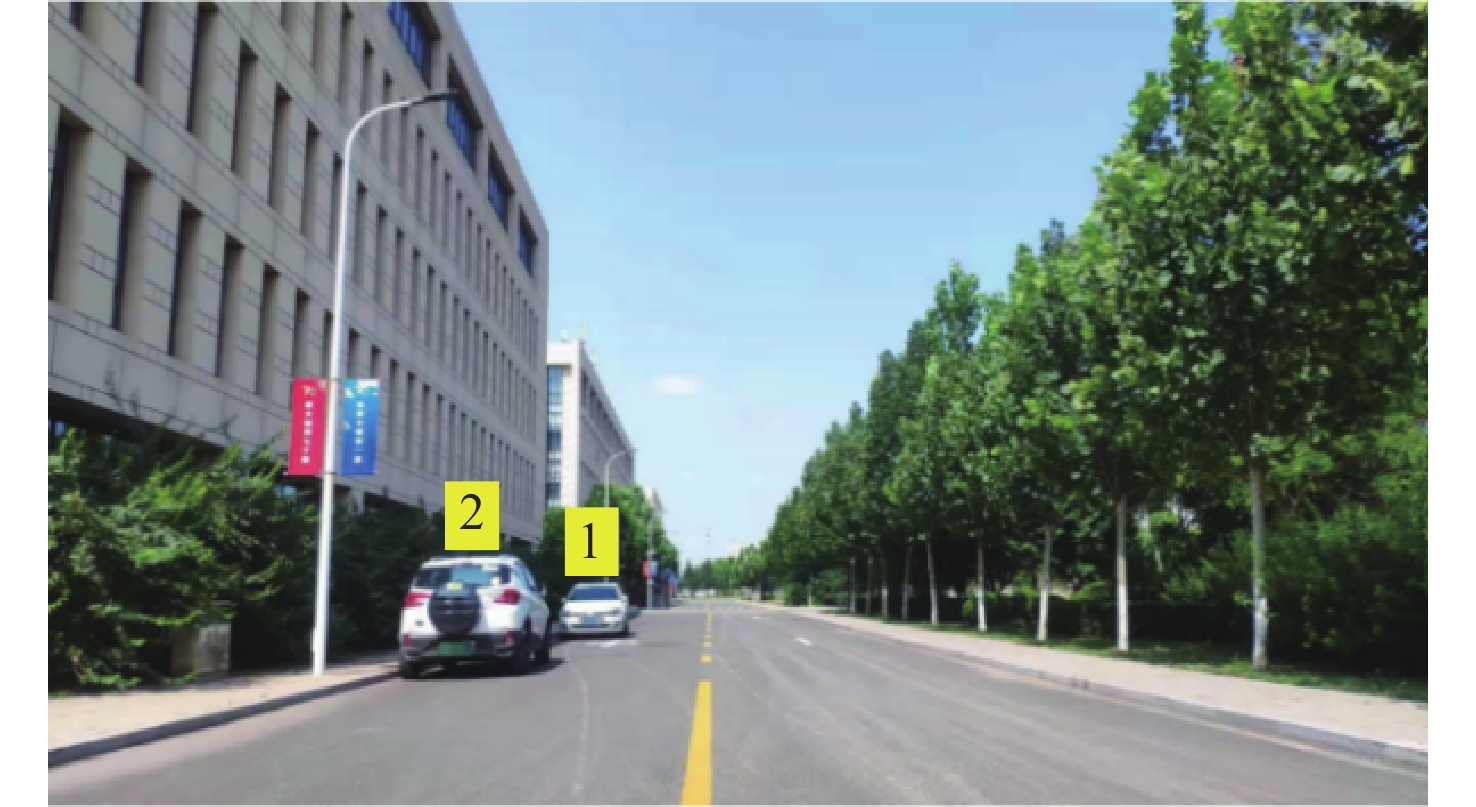
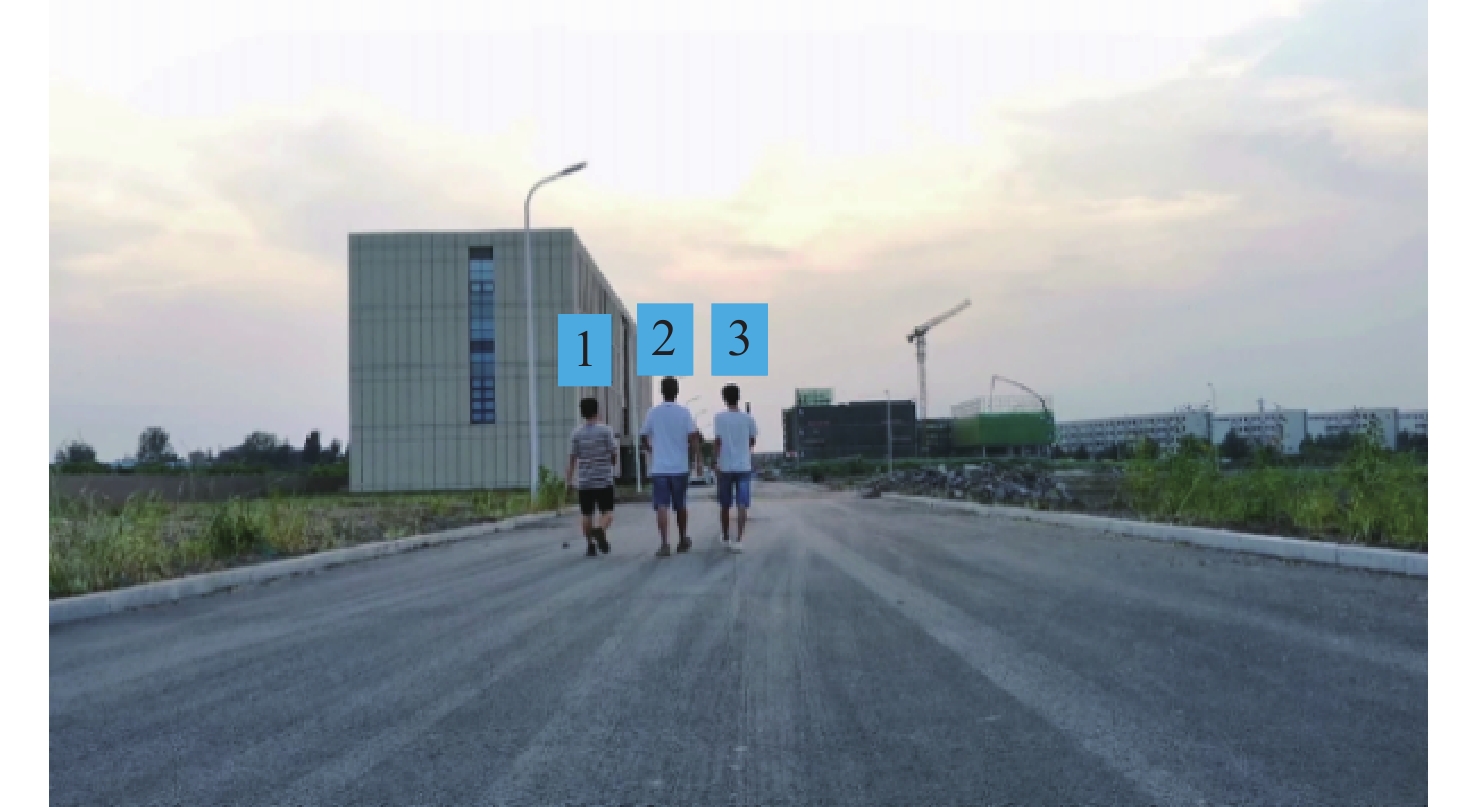
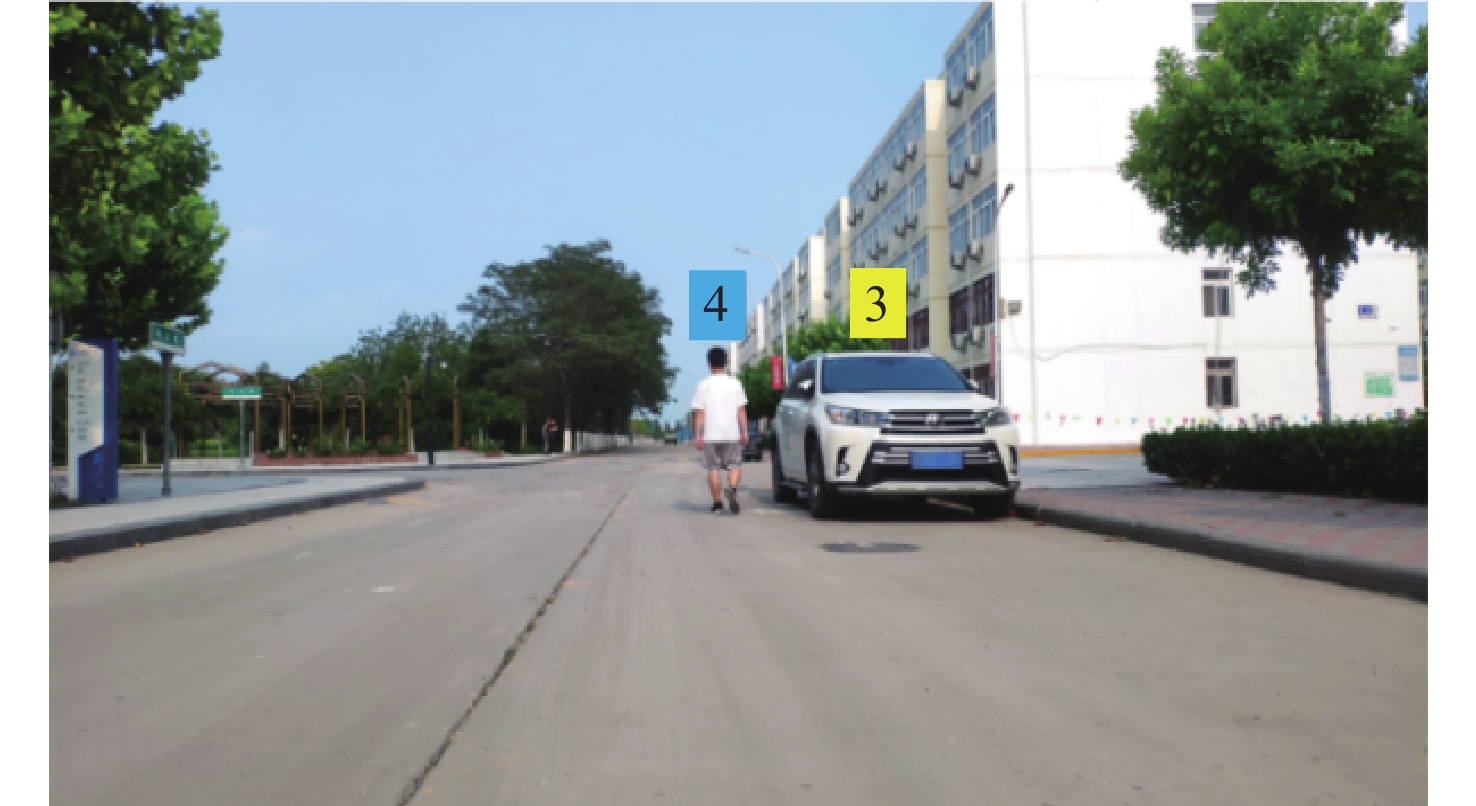
m 场景 障碍物位置 传统DBSCAN 本文方法 实际测量值 场景1 1号车 漏检 (30.01,4.25) (30.25,4.30) 2号车 (15.09,5.71) (15.11,5.81) (15.17,5.85) 场景2 1号行人 欠分割 (17.13,1.51) (17.05,1.45) 2号行人 欠分割 (17.12,0.31) (17.15,0.5) 3号行人 欠分割 (17.15,−0.45) (17.15,−0.55) 场景3 4号行人 (15.15,−3.32) (15.17,−3.29) (15.25,−3.20) 3号车 过分割 (16.18,−4.11) (16.25,−4.20) 表 2 障碍物检测结果
Table 2. Obstacle detection results
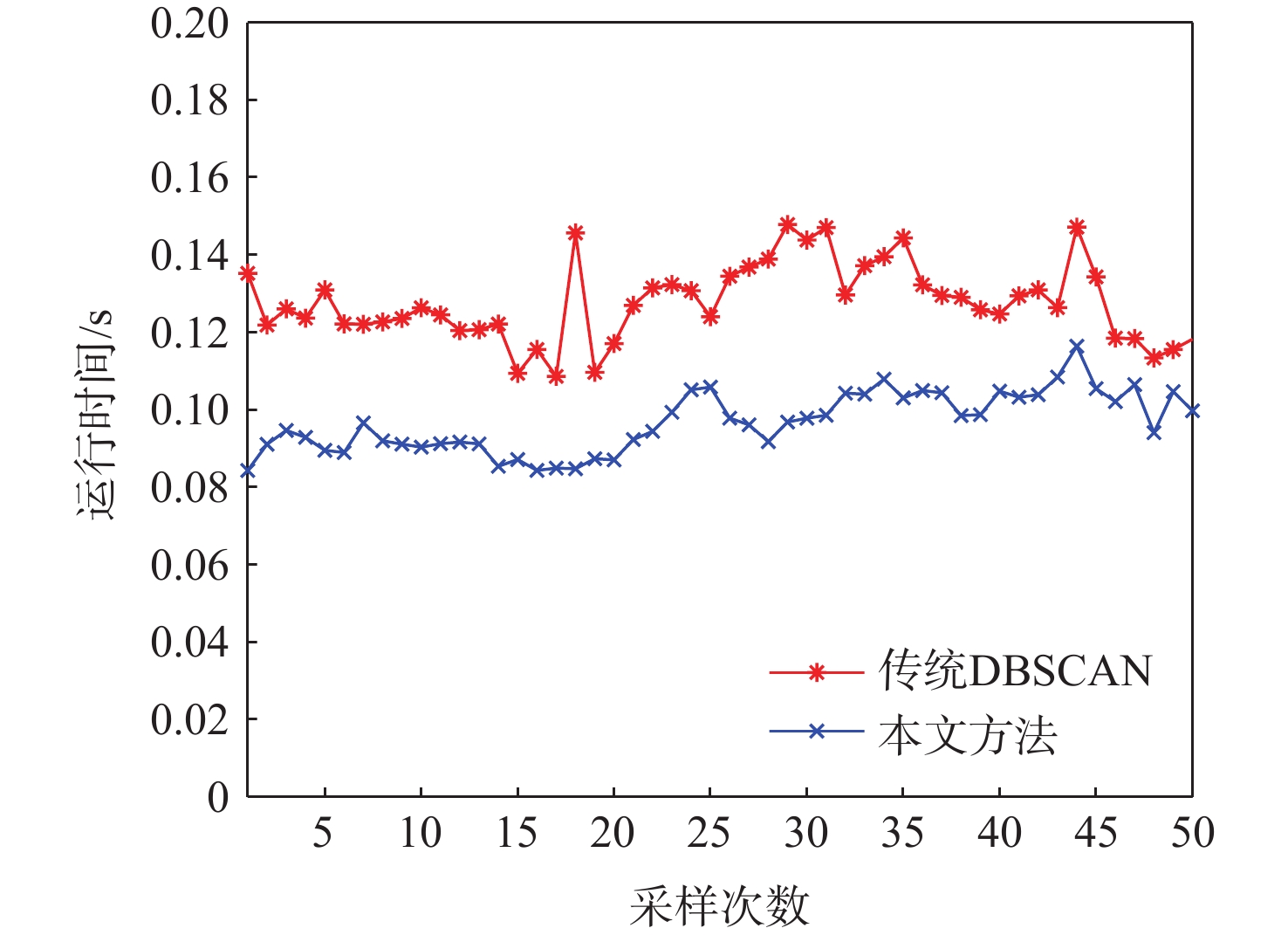
方法 障碍物数量 正检率/% 误检率/% 漏检率/% 平均耗时/s 传统DBSCAN 800 74.2 6.3 19.5 0.1271 本文方法 800 91.7 2.2 6.1 0.0971 -
[1] WEN L H, JO K H. Three-attention mechanisms for one-stage 3D object detection based on LiDAR and camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(10): 6655-6663. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3048719 [2] LEE H, MOTES J, MORALES M, et al. Parallel hierarchical composition conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(4): 7001-7008. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3096476 [3] WANG Z, ZHAO X M, CHEN Z W, et al. A dynamic cooperative lane-changing model for connected and autonomous vehicles with possible accelerations of a preceding vehicle[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 173(2): 114675. [4] BARZEGAR A, DOUKHI O, LEE D J. Design and implementation of an autonomous electric vehicle for self-driving control under GNSS-denied environments[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(8): 3688. doi: 10.3390/app11083688 [5] CHEN Y C, HUANG F Y, LIU B Q, et al. Significant obstacle location with ultra-wide FOV LWIR stereo vision system[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 129(2): 106076. [6] 夏显召, 朱世贤, 周意遥, 等. 基于阈值的激光雷达K均值聚类算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(1): 115-121.XIA X Z, ZHU S X, ZHOU Y Y, et al. LiDAR K-means clustering algorithm based on threshold[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(1): 115-121(in Chinese). [7] 徐国艳, 牛欢, 郭宸阳, 等. 基于三维激光点云的目标识别与跟踪研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(1): 38-46.XU G Y, NIU H, GUO C Y, et al. Research on target recognition and tracking based on 3D laser point cloud[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(1): 38-46(in Chinese). [8] HE C, ZENG H, HUANG J, et al. Structure aware single-stage 3D object detection from point cloud[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 13-19. [9] ZHOU Y, TUZEL O. VoxelNet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 18-23. [10] 汪文琪, 李宗春, 付永健, 等. 基于改进多规则区域生长的点云多要素分割[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(5): 198-212.WANG W Q, LI Z C, FU Y J, et al. Multi-factor segmentation of point cloud based on improved multi-rule region growing[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(5): 198-212(in Chinese). [11] 宗长富, 文龙, 何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113.ZONG C F, WEN L, HE L. Object detection based on Euclidean clustering algorithm with 3D laser scanner[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 107-113(in Chinese). [12] 郭烈, 马跃, 岳明, 等. 驾驶特性的识别评估及其在智能汽车上的应用综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(2): 7-20.GUO L, MA Y, YUE M, et al. Overview of recognition and evaluation of driving characteristics and their applications in intelligent vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(2): 7-20(in Chinese). [13] 戴阳阳, 李朝锋, 徐华. 初始点优化与参数自适应的密度聚类算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2016, 42(1): 203-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2016.01.036DAI Y Y, LI C F, XU H. Density clustering algorithm with initial point optimization and parameter self-adaption[J]. Computer Engineering, 2016, 42(1): 203-209(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2016.01.036 [14] FENG L, LIU K, TANG F, et al. GO-DBSCAN: Improvements of DBSCAN algorithm based on grid[J]. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 2017, 9(3): 151-155. doi: 10.7763/IJCTE.2017.V9.1129 [15] 谢德胜, 徐友春, 王任栋, 等. 基于三维激光雷达的无人车障碍物检测与跟踪[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(8): 952-959. doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2018.08.013XIE D S, XU Y C, WANG R D, et al. Obstacle detection and tracking for unmanned vehicles based on 3D laser radar[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(8): 952-959(in Chinese). doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2018.08.013 [16] BRYANT A, CIOS K. RNN-DBSCAN: A density-based clustering algorithm using reverse nearest neighbor density estimates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2018, 30(6): 1109-1121. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2787640 [17] 蔡怀宇, 陈延真, 卓励然, 等. 基于优化DBSCAN算法的激光雷达障碍物检测[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(7): 83-90.CAI H Y, CHEN Y Z, ZHUO L R, et al. LiDAR object detection based on optimized DBSCAN algorithm[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2019, 46(7): 83-90(in Chinese). [18] WANG C X, JI M, WANG J, et al. An improved DBSCAN method for LiDAR data segmentation with automatic EPS estimation[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2019, 19: 172. doi: 10.3390/s19010172 [19] 汪世财, 谈东奎, 谢有浩, 等. 基于激光雷达点云密度特征的智能车障碍物检测与跟踪[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 42(10): 1311-1317.WANG S C, TAN D K, XIE Y H, et al. Obstacle detection and tracking for intelligent vehicle based on density characteristics of point cloud using 3D lidar[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology: (Natural Science), 2019, 42(10): 1311-1317(in Chinese). [20] LI H, LIU X J, LI T, et al. A novel density-based clustering algorithm using nearest neighbor graph[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 102(6): 107206. [21] ZERMAS D, IZZAT I, PAPANIKOLOPOULOS N. Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds: A paradigm on LiDAR data for autonomous vehicle applications[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5067-5073. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 台少瑜,李云伍,赵颖,林先卬,黎远江,王义成. 基于激光雷达自适应聚类半径的树冠检测研究. 中国农机化学报. 2024(02): 221-226+266 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 褚昕悦,赵旭,李连鹏,刘文,代牮. 基于体素特征融合的FOD目标智能认知. 应用激光. 2023(08): 151-158 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(13)
-







 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术

