Rapid prediction technology of missile aerodynamic characteristics based on PINN model
-
摘要:
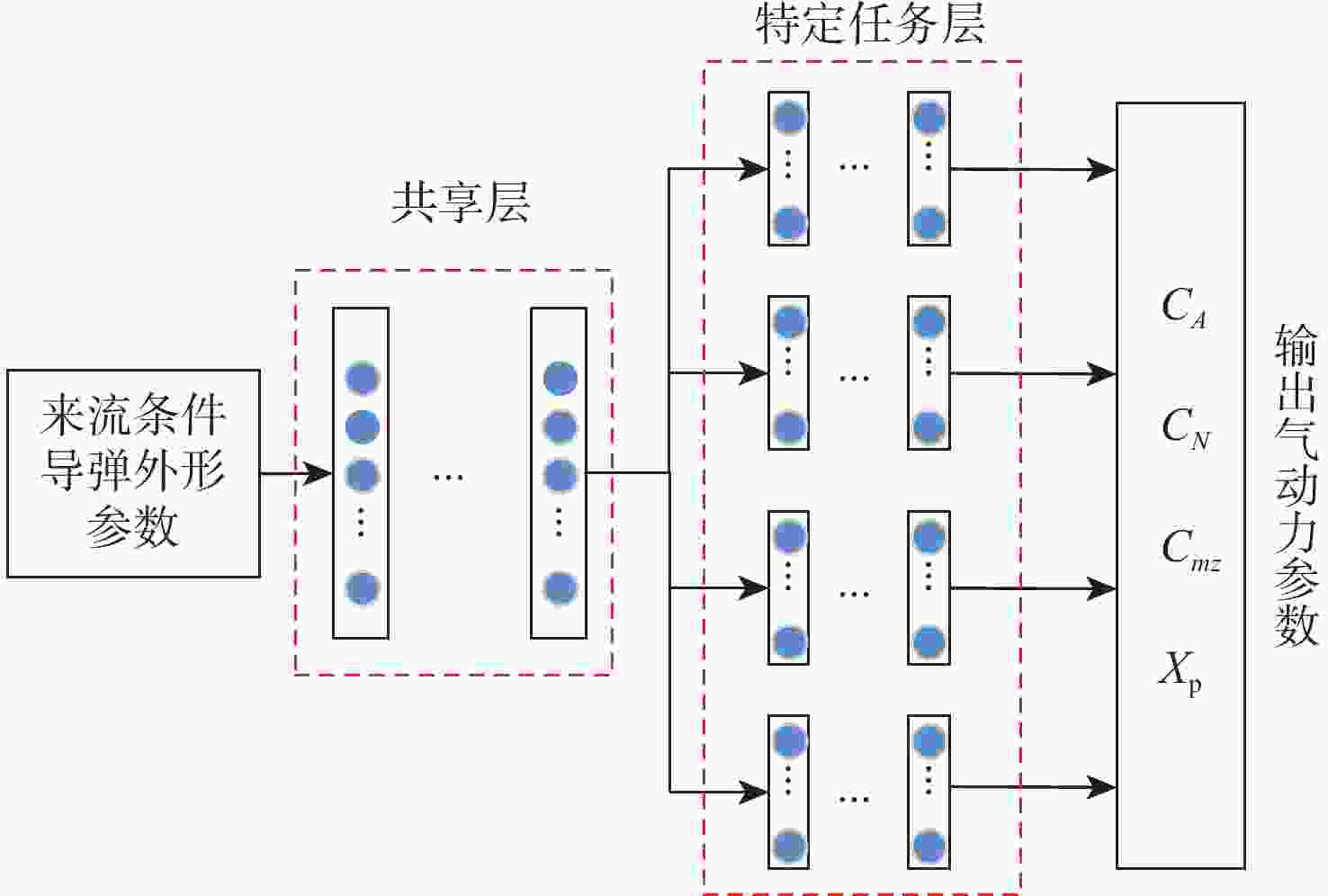
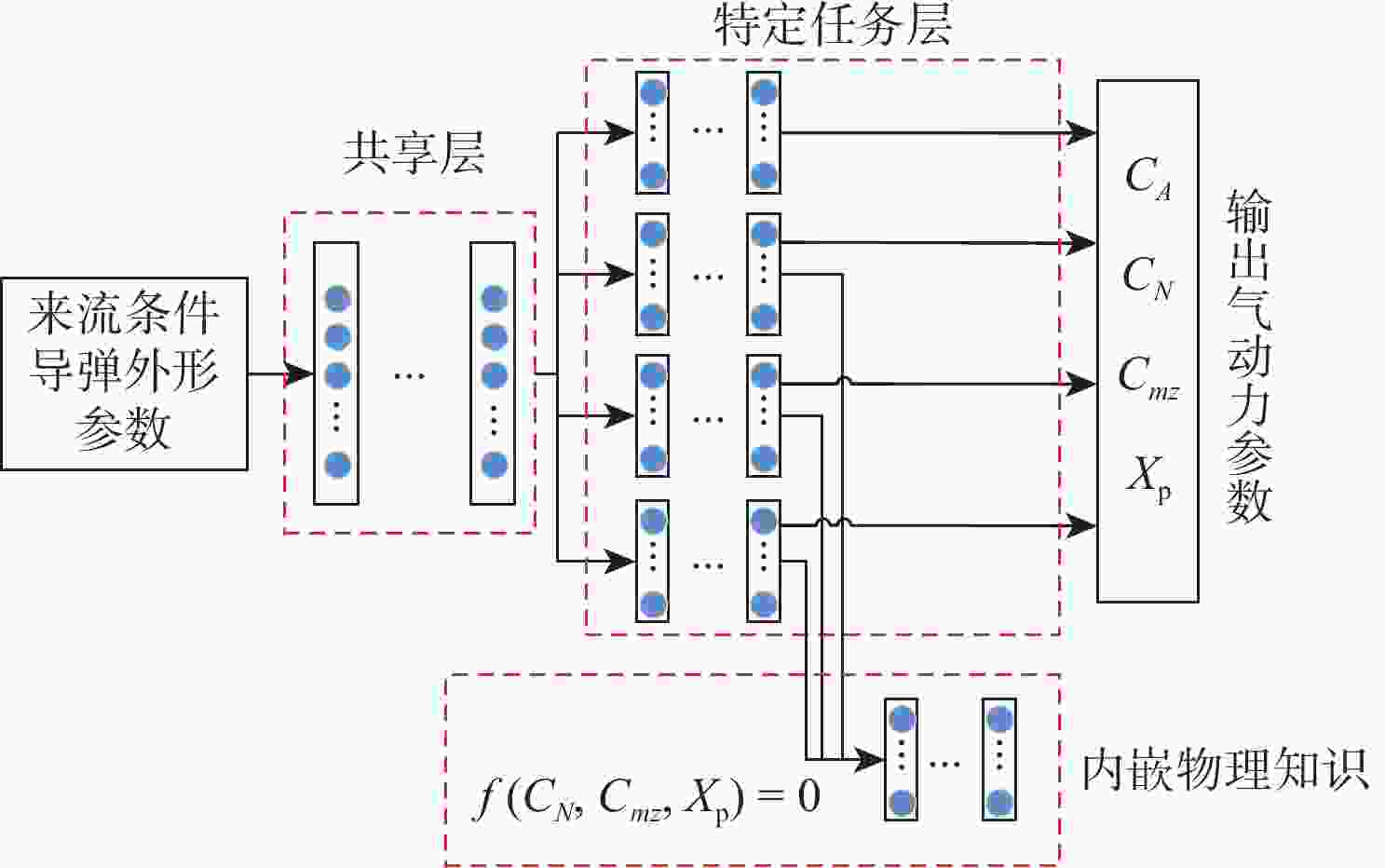
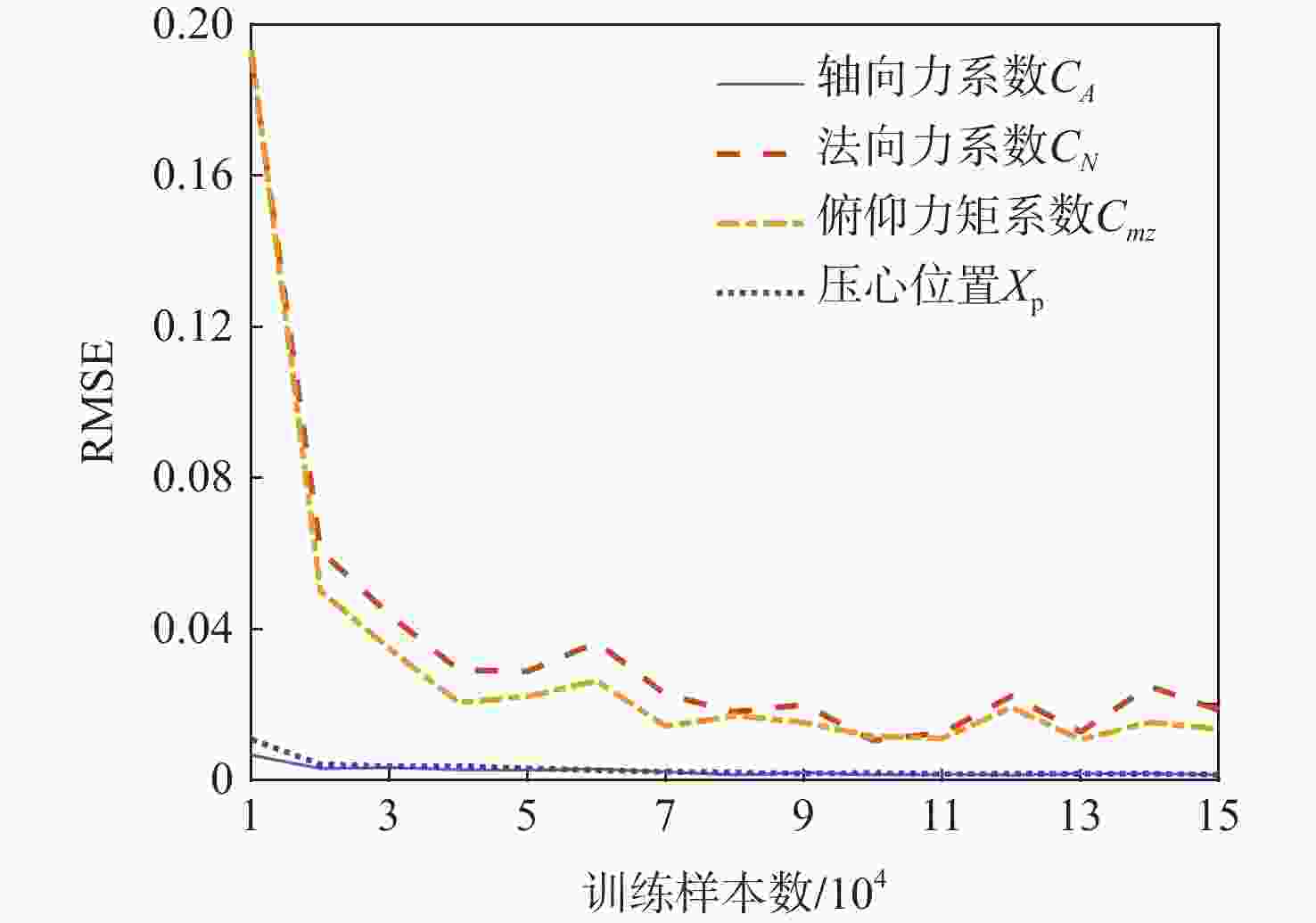
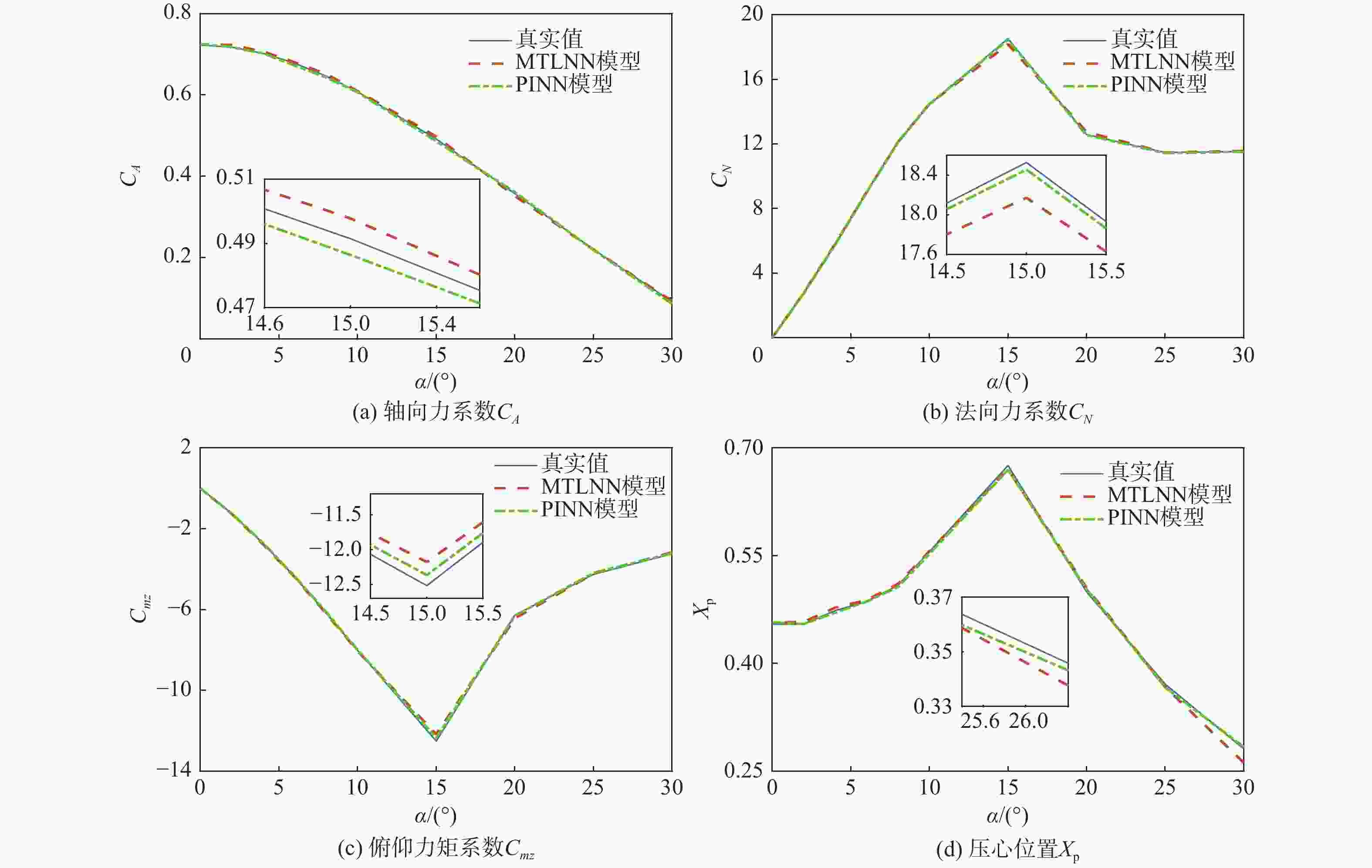
随着内嵌物理机理神经网络(PINN)模型的兴起,PINN模型开始应用于许多学科领域。为了实现导弹气动特性的快速预测,借助工程算法,构建了导弹气动数据集,以此训练导弹气动特性预测模型,包含基于多任务学习的神经网络(MTLNN)模型及在MTLNN模型基础上内嵌物理知识的PINN模型。数值模拟通过选取测试集,对比了MTLNN模型和PINN模型的预测效果,结果表明:PINN模型的预测精度较高,且基本控制在1%以内。探究PINN模型的泛化能力,测试集选取导弹气动数据集包络范围之外的数据,PINN模型预测精度仍然高于MTLNN模型。由于PINN模型引入了气动特性参数之间的物理机理,模型对训练样本数量的依赖程度降低,可以进一步节约数据获取成本,为导弹优化设计提供有力工具。
-
关键词:
- 内嵌物理机理神经网络 /
- 导弹 /
- 气动特性 /
- 快速预测 /
- 数据驱动
Abstract:With the rise of the physical-informed neural network (PINN) model, the PINN model has been applied to many subjects. With the aid of the missile engineering algorithm, the missile aerodynamic data set is created in order to train the multi-task learning neural network (MTLNN) model and the physical-informed -PINN model, two models that can quickly predict missile aerodynamic characteristics. By selecting test sets, the numerical simulation compares the prediction results of the MTLNN model with the PINN model, and the result shows that the prediction accuracy of the PINN model is higher, and the prediction relative error is less than 1%. Finally, the generalization ability of PINN model is explored. The test set selects data outside the envelope range of the missile aerodynamic data set. In this case, the prediction accuracy of the PINN model is higher than that of the MTLNN model. The PINN model has a physical mechanism connecting the parameters that control aerodynamic properties, which makes the model less reliant on the volume of training samples. This can further reduce data collection costs and give a strong tool for missile optimization design.
-
Key words:
- PIMTLNN /
- missile /
- aerodynamic characteristics /
- rapid prediction /
- data-driven
-
表 1 基于多任务学习的网络参数
Table 1. Network parameters based on multi-task learning
编号 结构类型 神经元节点数 层数 激活函数 1 共享层/隐藏层 1024 1 relu 2 共享层/隐藏层 512 1 relu 3 共享层/隐藏层 256 3 relu 4 共享层/隐藏层 128 1 relu 5 任务层/隐藏层 64 1 relu 6 任务层/隐藏层 32 3 relu 7 任务层/隐藏层 16 5 relu 8 任务层/隐藏层 8 4 relu 9 任务层/输出层 1 1 linear 表 2 不同状态的外插对比
Table 2. Extrapolation comparison of different states
测试集 气动特性参数 预测误差RMSE 误差减少/% 测试集 气动特性参数 预测误差RMSE 误差减少/% MTLNN模型 PINN模型 MTLNN模型 PINN模型 第1组 CA 0.003665 0.003758 第3组 CA 0.003337 0.003812 CN 0.102228 0.093603 8.44 CN 0.060644 0.027035 55.42 Cmz 0.119224 0.076152 36.13 Cmz 0.047269 0.043482 8.01 Xp 0.004239 0.002134 49.67 Xp 0.002280 0.003299 第2组 CA 0.004096 0.002591 36.73 第4组 CA 0.002605 0.002937 CN 0.045346 0.026937 40.60 CN 0.046499 0.038052 18.17 Cmz 0.047311 0.030314 35.93 Cmz 0.053012 0.043537 17.87 Xp 0.001888 0.001613 14.56 Xp 0.001615 0.001481 8.28 -
[1] 胡伟杰, 黄增辉, 刘学军, 等. 基于自动核构造高斯过程的导弹气动性能预测[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524093.HU W J, HUANG Z H, LIU X J, et al. Missile aerodynamic performance prediction of Gaussian process through automatic kernel construction[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524093(in Chinese). [2] 原智杰, 张公平, 崔茅, 等. 基于神经网络的导弹气动参数预测[J]. 航空兵器, 2020, 27(5): 28-32.YUAN Z J, ZHANG G P, CUI M, et al. Prediction of missile’s aerodynamic parameters based on neural network[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2020, 27(5): 28-32(in Chinese). [3] 王怡星, 韩仁坤, 刘子扬, 等. 流体力学深度学习建模技术研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524779.WANG Y X, HAN R K, LIU Z Y, et al. Progress of deep learning modeling technology for fluid mechanics[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524779(in Chinese). [4] 陈冰雁, 刘传振, 白鹏, 等. 使用深度残差网络的乘波体气动性能预测[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2019, 37(3): 505-509.CHEN B Y, LIU C Z, BAI P, et al. Aerodynamic prediction for waveriders using deep residual learning[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2019, 37(3): 505-509(in Chinese). [5] 柴聪聪, 王强, 易贤, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的结冰翼型气动参数预测[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(5): 13-18.CHAI C C, WANG Q, YI X, et al. Aerodynamic parameters prediction of airfoil ice accretion based on convolutional neural network[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(5): 13-18(in Chinese). [6] 陈海, 钱炜祺, 何磊. 基于深度学习的翼型气动系数预测[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2018, 36(2): 294-299.CHEN H, QIAN W Q, HE L. Aerodynamic coefficient prediction of airfoils based on deep learning[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2018, 36(2): 294-299(in Chinese). [7] 吕召阳, 聂雪媛, 赵奥博. 基于CNN机翼气动系数预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(3): 674-680.LYU Z Y, NIE X Y, ZHAO A B. Prediction of wing aerodynamic coefficient based on CNN[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(3): 674-680(in Chinese). [8] 聂春生, 黄建栋, 王迅, 等. 基于POD方法的复杂外形飞行器热环境快速预测方法[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2017, 35(6): 760-765.NIE C S, HUANG J D, WANG X, et al. Fast aeroheating prediction method for complex shape vehicles based on proper orthogonal decomposition[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 760-765(in Chinese). [9] 侯强, 苏纬仪, 孙斐, 等. 高超声速乘波体扩容设计及流场快速预测[J]. 航空动力学报, 2021, 36(3): 564-574.HOU Q, SU W Y, SUN F, et al. Design of improving volumetric efficiency of hypersonic waverider and rapid prediction of flow field[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2021, 36(3): 564-574(in Chinese). [10] 张智超, 高太元, 张磊, 等. 基于径向基神经网络的气动热预测代理模型[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524167.ZHANG Z C, GAO T Y, ZHANG L, et al. Aeroheating agent model based on radial basis function neural network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524167(in Chinese). [11] 张天姣, 钱炜祺, 周宇, 等. 人工智能与空气动力学结合的初步思考[J]. 航空工程进展, 2019, 10(1): 1-11.ZHANG T J, QIAN W Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Preliminary thoughts on the combination of artificial intelligence and aerodynamics[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2019, 10(1): 1-11(in Chinese). [12] 何磊, 张显才, 钱炜祺, 等. 基于长短时记忆神经网络的非定常气动力建模方法[J]. 飞行力学, 2021, 39(5): 8-12.HE L, ZHANG X C, QIAN W Q, et al. Unsteady aerodynamics modeling method based on long short-term memory neural network[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2021, 39(5): 8-12(in Chinese). [13] 杜涛, 许晨舟, 王国辉, 等. 人工智能气动特性预测技术在火箭子级落区控制项目的应用[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(1): 61-73.DU T, XU C Z, WANG G H, et al. The application of aerodynamic coefficients prediction technique via artificial intelligence method to rocket first stage landing area control project[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(1): 61-73(in Chinese). [14] 柴聪聪, 易贤, 郭磊, 等. 基于BP神经网络的冰形特征参数预测[J]. 实验流体力学, 2021, 35(3): 16-21.CHAI C C, YI X, GUO L, et al. Prediction of ice shape characteristic parameters based on BP nerual network[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 35(3): 16-21(in Chinese). [15] 金晓威, 赖马树金, 李惠. 物理增强的流场深度学习建模与模拟方法[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(10): 2616-2629.JIN X W, LAI M S J, LI H. Physics-enhanced deep learning methods for modelling and simulating flow fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(10): 2616-2629(in Chinese). [16] KARNIADAKIS G E, KEVREKIDIS I G, LU L, et al. Physics-informed machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(6): 422-440. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00314-5 [17] 赵暾, 周宇, 程艳青, 等. 基于内嵌物理机理神经网络的热传导方程的正问题及逆问题求解[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2021, 39(5): 19-26.ZHAO T, ZHOU Y, CHENG Y Q, et al. Solving forward and inverse problems of the heat conduction equation using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2021, 39(5): 19-26(in Chinese). [18] 张伟伟, 寇家庆, 刘溢浪. 智能赋能流体力学展望[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524689.ZHANG W W, KOU J Q, LIU Y L. Prospect of artificial intelligence empowered fluid mechanics[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524689(in Chinese). [19] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2018.10.045 [20] MAO Z P, JAGTAP A D, KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks for high-speed flows[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 360: 112789. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.112789 [21] RAO C P, SUN H, LIU Y. Physics-informed deep learning for incompressible laminar flows[J]. Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters, 2020, 10(3): 207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.taml.2020.01.039 [22] JIN X W, CAI S Z, LI H, et al. NSFnets (Navier-Stokes flow nets): Physics-informed neural networks for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 426: 109951. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109951 [23] BUHENDWA A B, ADAMI S, ADAMS N A. Inferring incompressible two-phase flow fields from the interface motion using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Machine Learning With Applications, 2021, 4: 100029. doi: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100029 [24] CHEN W Q, WANG Q, HESTHAVEN J S, et al. Physics-informed machine learning for reduced-order modeling of nonlinear problems[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 446: 110666. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110666 [25] WANG K, CHEN Y, MEHANA M, et al. A physics-informed and hierarchically regularized data-driven model for predicting fluid flow through porous media[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 443: 110526. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110526 [26] 张钰, 刘建伟, 左信. 多任务学习[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(7): 1340-1378.ZHANG Y, LIU J W, ZUO X. Survey of multi-task learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(7): 1340-1378(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: