Remaining useful life prediction of aeroengine based on SSAE and similarity matching
-
摘要:
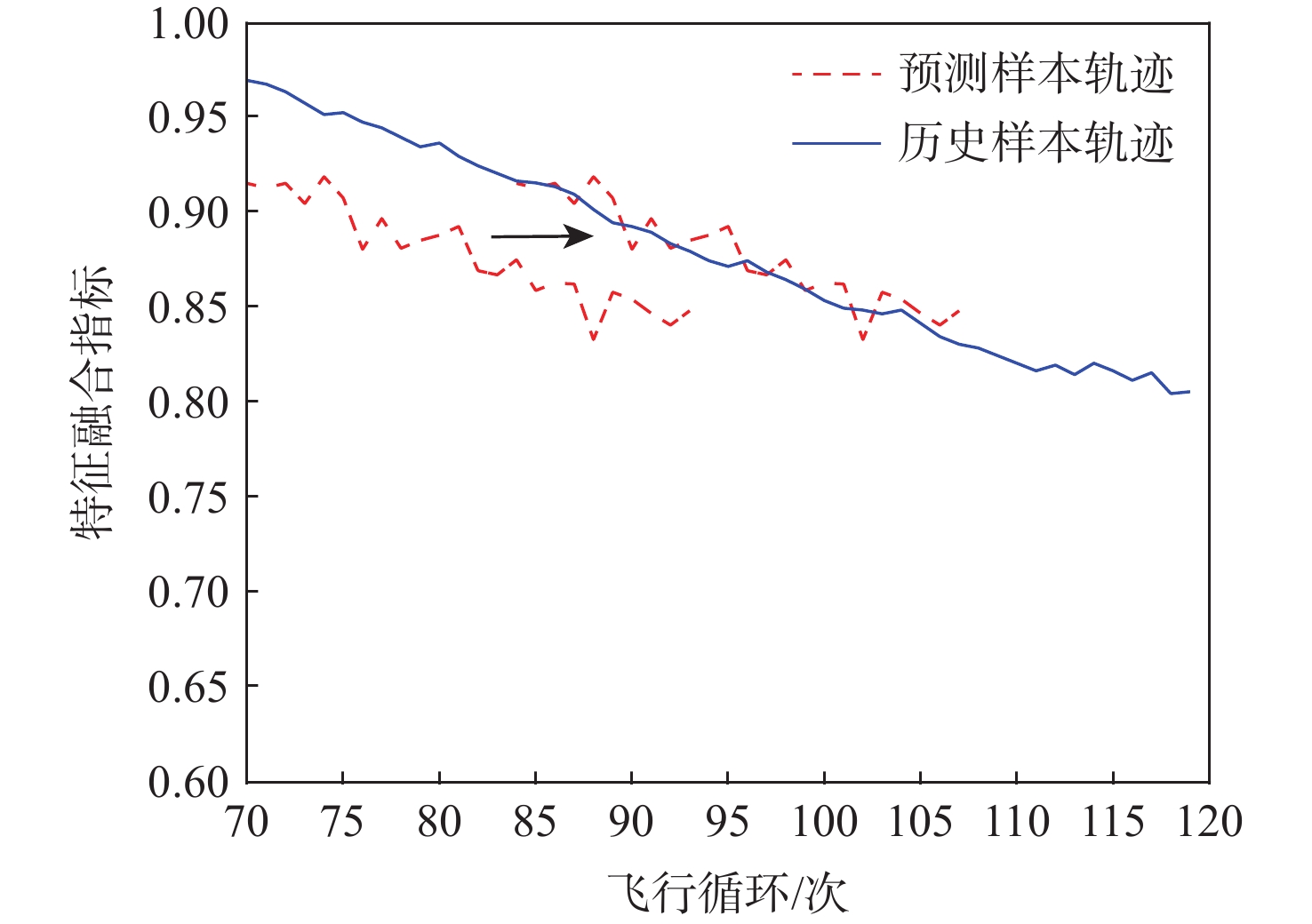
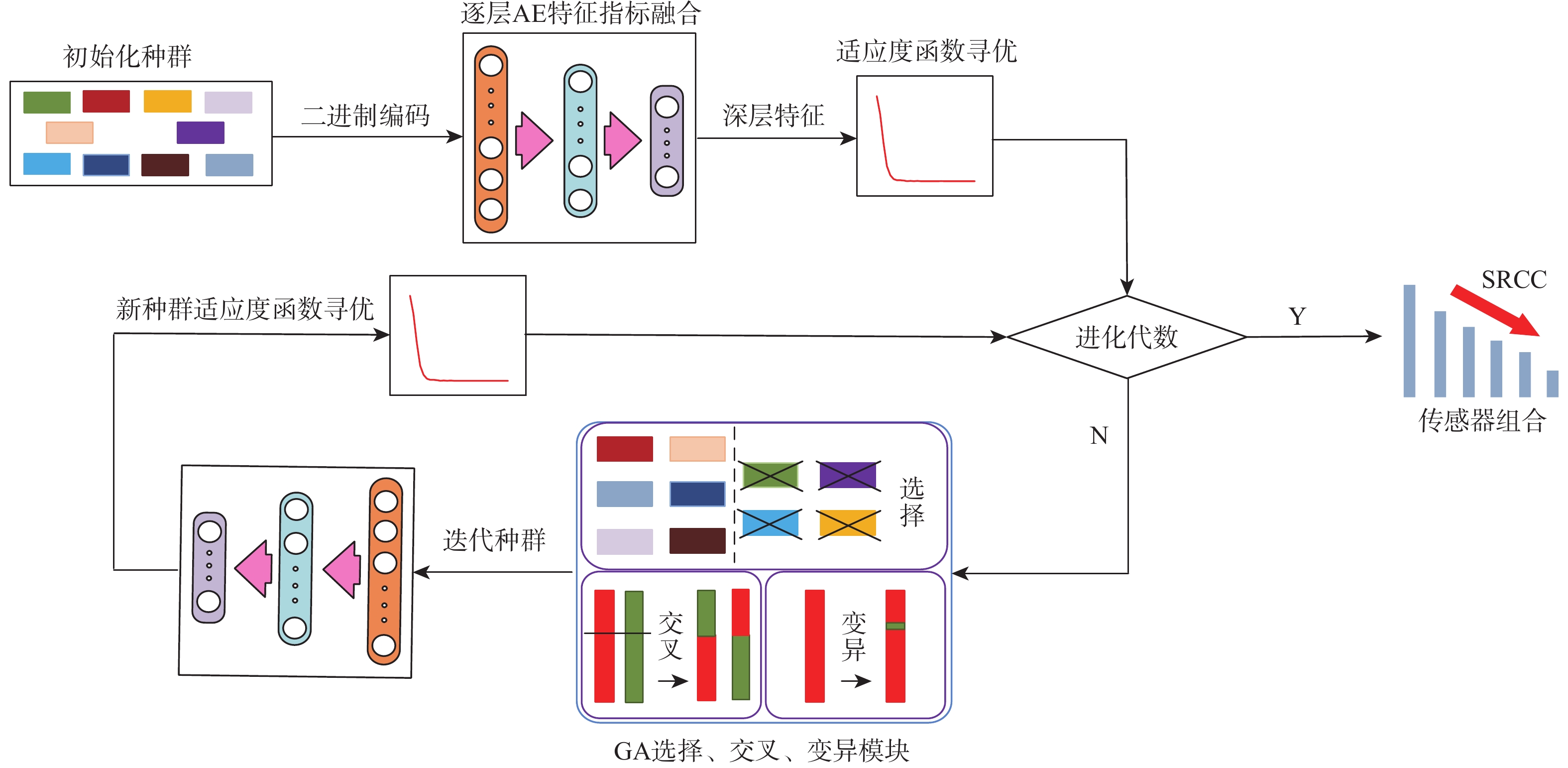
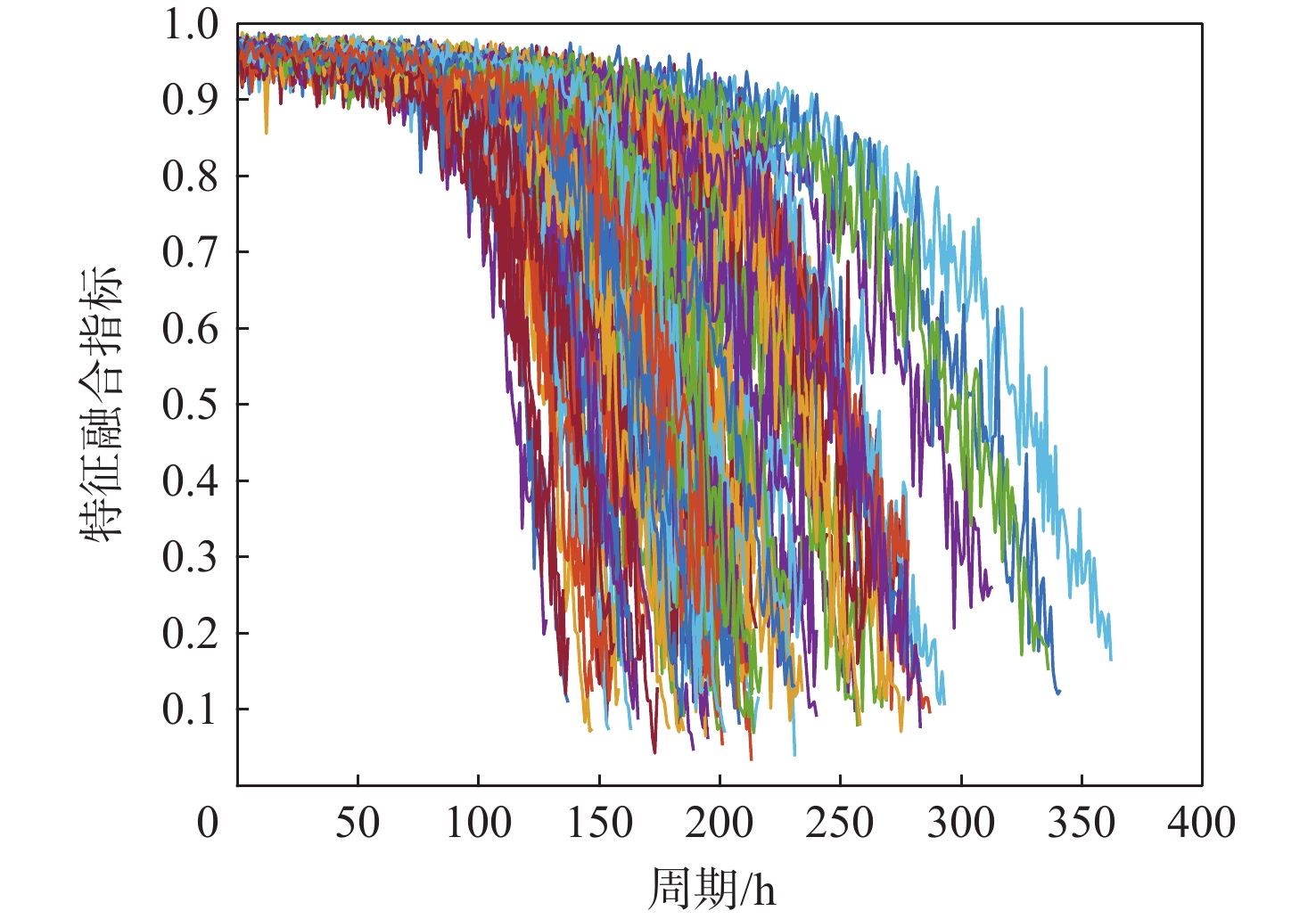
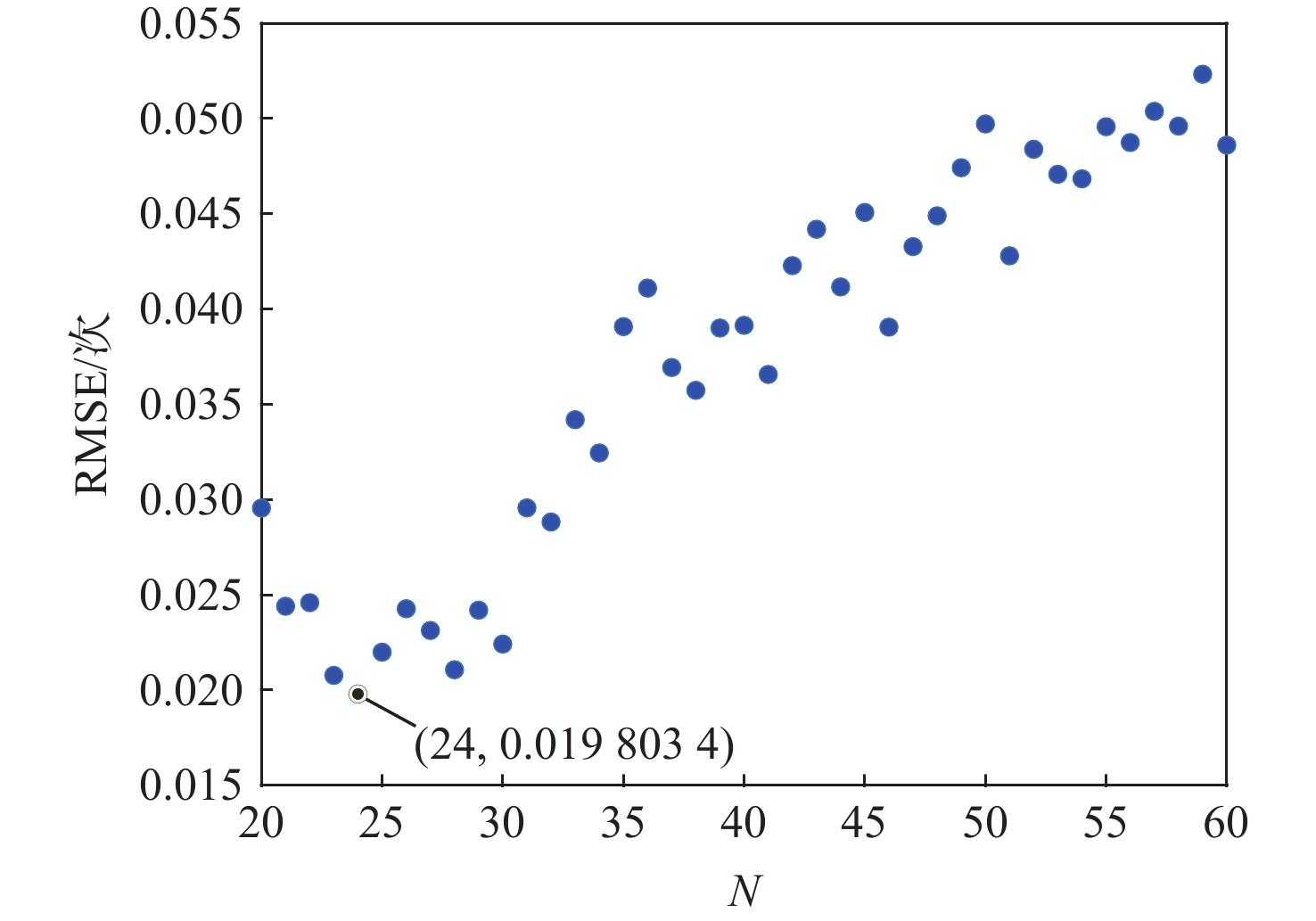
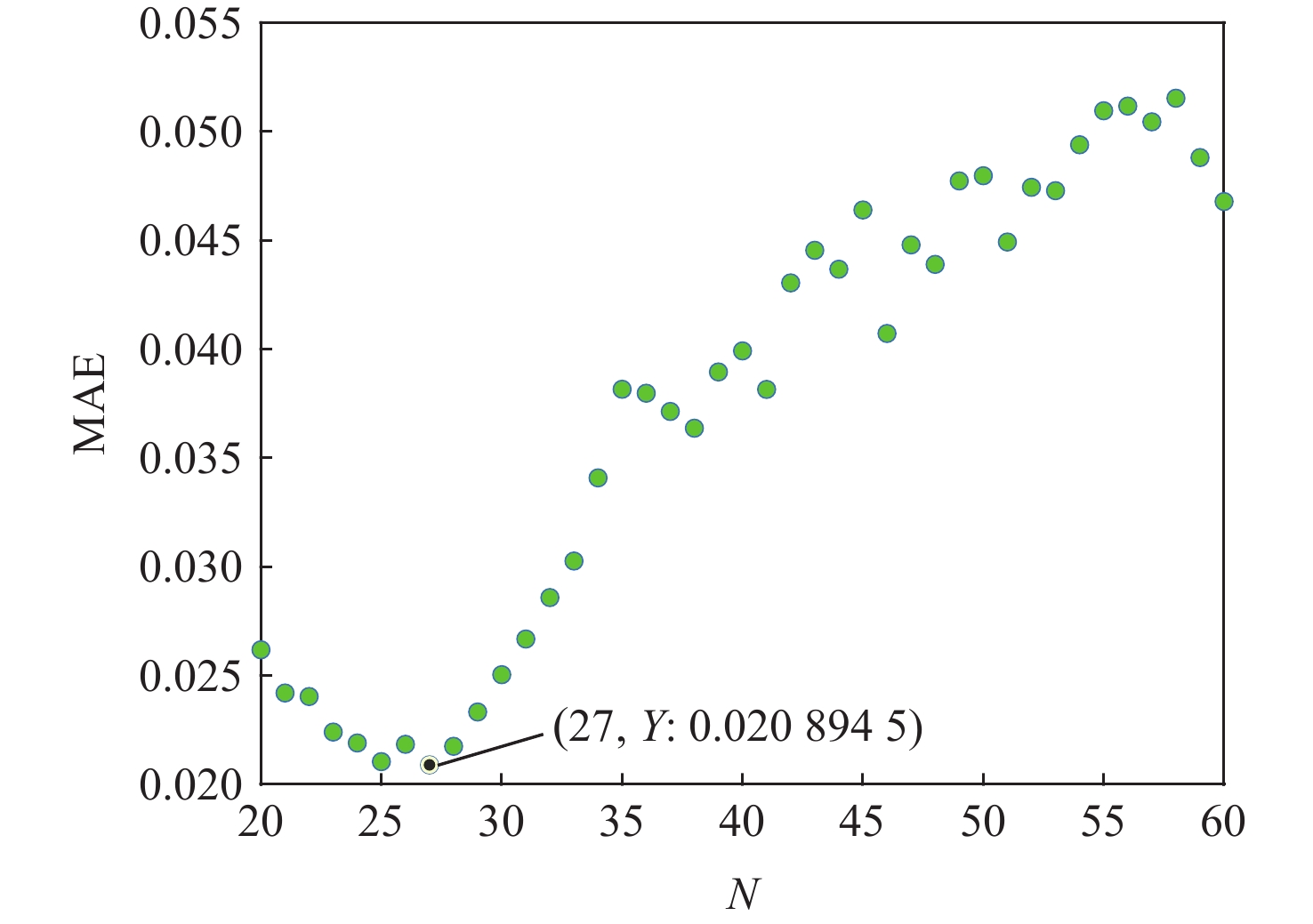
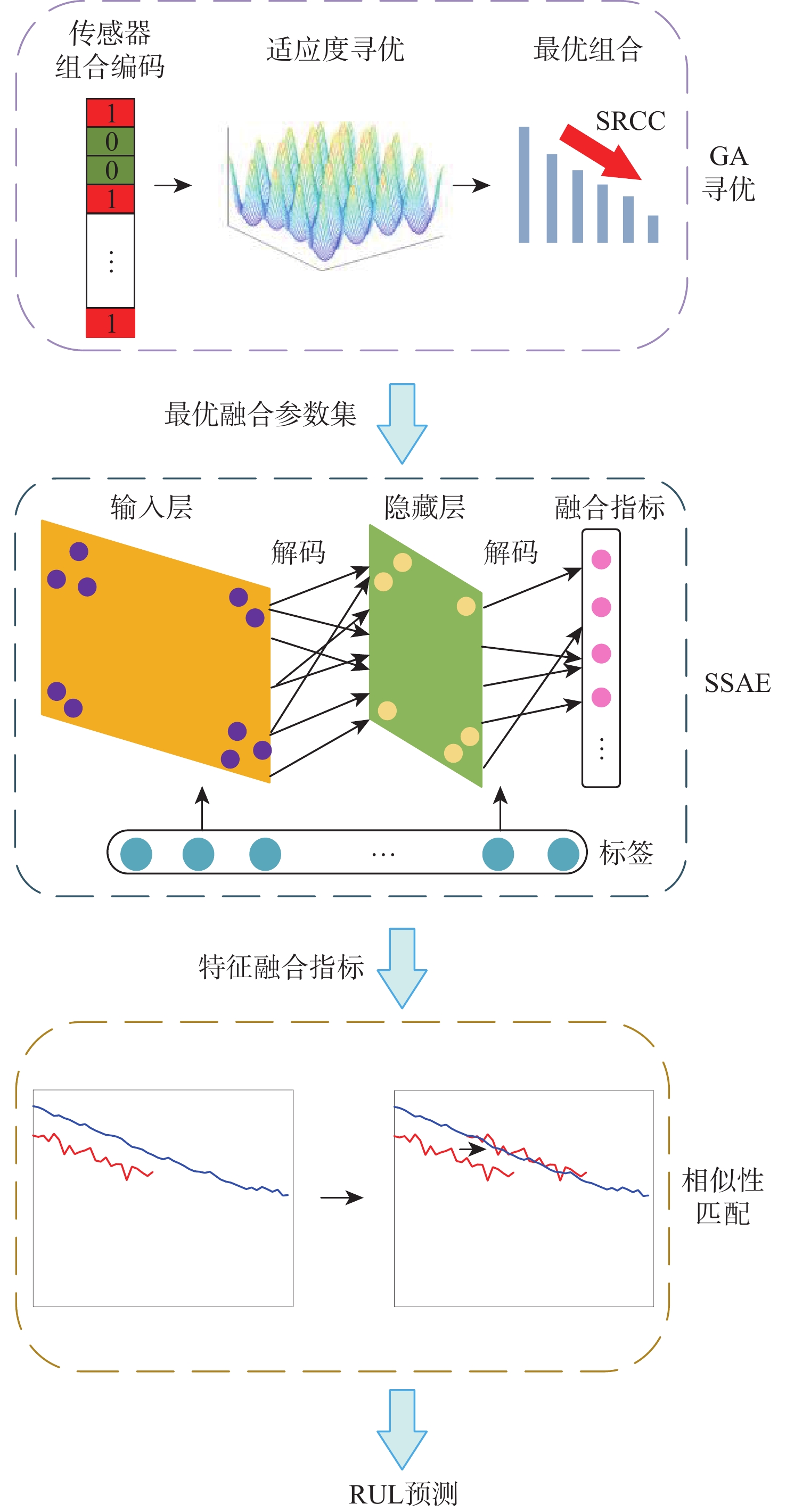
航空发动机作为高度复杂的热力机械,其剩余寿命(RUL)预测往往作为提高安全性和经济性的重要保障。为了提高航空发动机剩余寿命预测精度,提出一种基于堆栈稀疏自编码器(SSAE)及相似性匹配的剩余寿命预测方法。以Spearman秩相关系数(SRCC)作为适应度函数,利用遗传算法(GA)对融合参数候选集进行寻优;采用SSAE的结构融合最优参数集,生成特征融合指标;采用相似性匹配的方法在历史数据库内全局搜索最优匹配的历史轨迹,得到寿命预测结果;采用美国国家航空航天局(NASA)公布的C-MAPSS数据集验证该融合指标和方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 航空发动机 /
- 剩余寿命 /
- 堆栈稀疏自编码器 /
- Spearman秩相关系数 /
- 相似性匹配
Abstract:As a highly complex thermal machinery, the prognosis of the remaining useful life (RUL) of an aero-engine is often used as an important guarantee to improve safety and economy. In order to increase the engine’s remaining usable life prediction accuracy, a strategy based on stacked sparse autoencoders (SSAE) and similarity matching is proposed in this study. Firstly, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (SRCC) is utilized as a fitness function and optimizes the candidate set of fusion parameters through a genetic algorithm (GA). The SSAE fuses the optimal parameter set in order to generate the feature comprehensive index. The results of the life prediction are then obtained by using the similarity matching approach to search the history database worldwide for the best matching trajectory. Finally, the C-MAPSS dataset published by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is obtained to verify the validity of the fusion index and method.
-
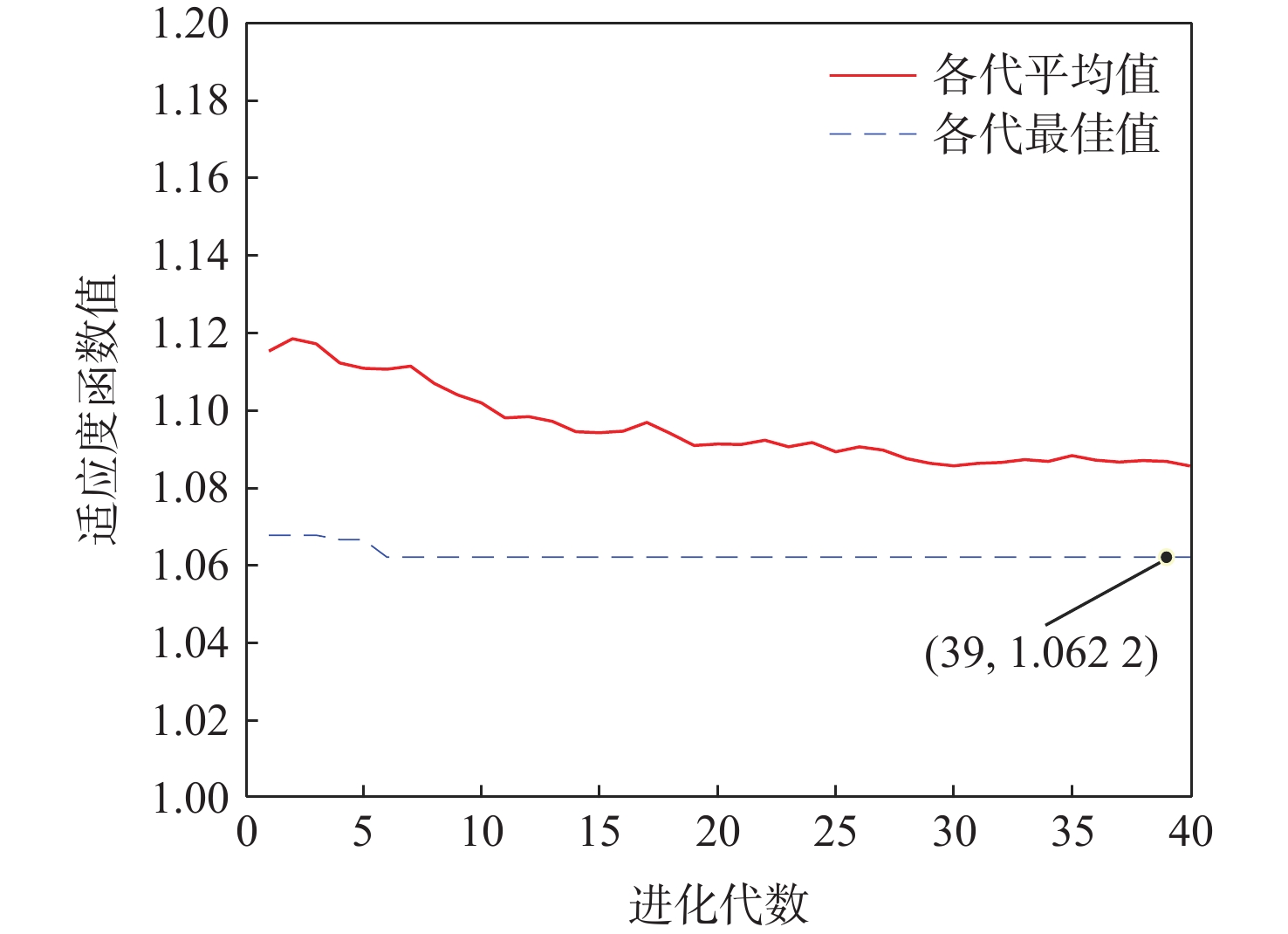
表 1 GA参数设定
Table 1. Parameter setting of GA
种群规模 交叉概率 变异概率 进化代数 编码长度 13 0.88 0.01 40 13 表 2 SSAE模型参数设定
Table 2. Parameter setting of SSAE model
参数 数值 输入层神经元个数 9 第1隐藏层神经元个数 4 第2隐藏层神经元个数 1 第3隐藏层神经元个数 4 输出层神经元个数 9 迭代轮次 100 编码器激活函数 sigmoid 解码器激活函数 purelin 稀疏参数 0.1 表 3 SRCC计算结果
Table 3. SRCC calculation results
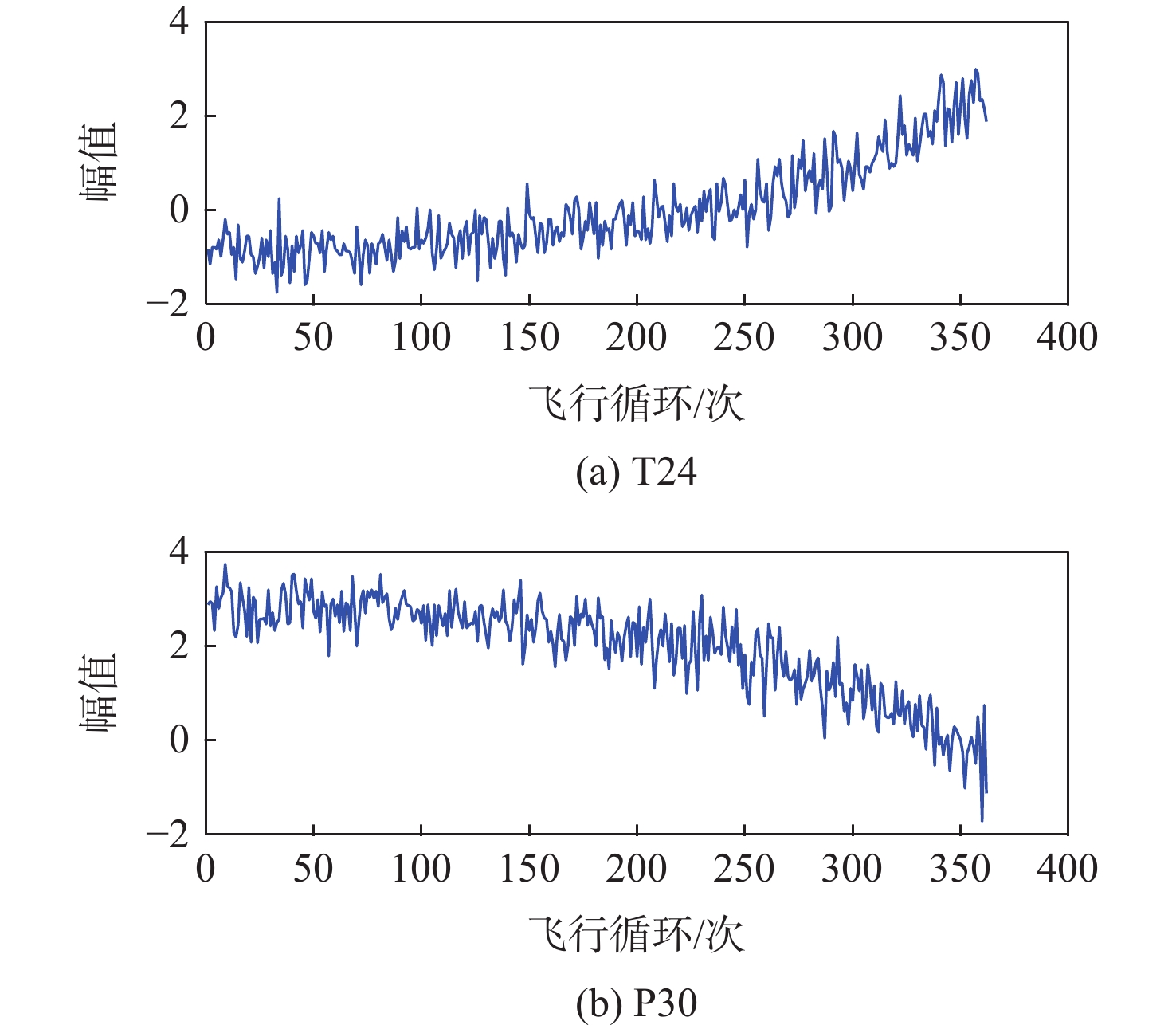
传感器参数 SRCC结果 LPC出口总温T24/℃ −273.525 HPC出口总温T30/℃ −273.482 LPT出口总温T50/℃ −273.601 HPC出口总压P30/kPa 0.112 风扇物理转速Nf/(r·min−1) −0.856 核心物理转速Nc/(r·min−1) 0.113 HPC出口静压Ps30 −0.125 燃油量与HPC出口静压比率CPhi 0.833 修正风扇转速NRf/(r·min−1) −0.855 修正核心转速NRc/(r·min−1) 0.551 涵道比rBPR −0.744 HPT冷却引气流量W31/(kg·s−1) 1.62 LPT冷却引气流量W32/(kg·s−1) 1.62 表 4 不同数据库大小的测试集结果
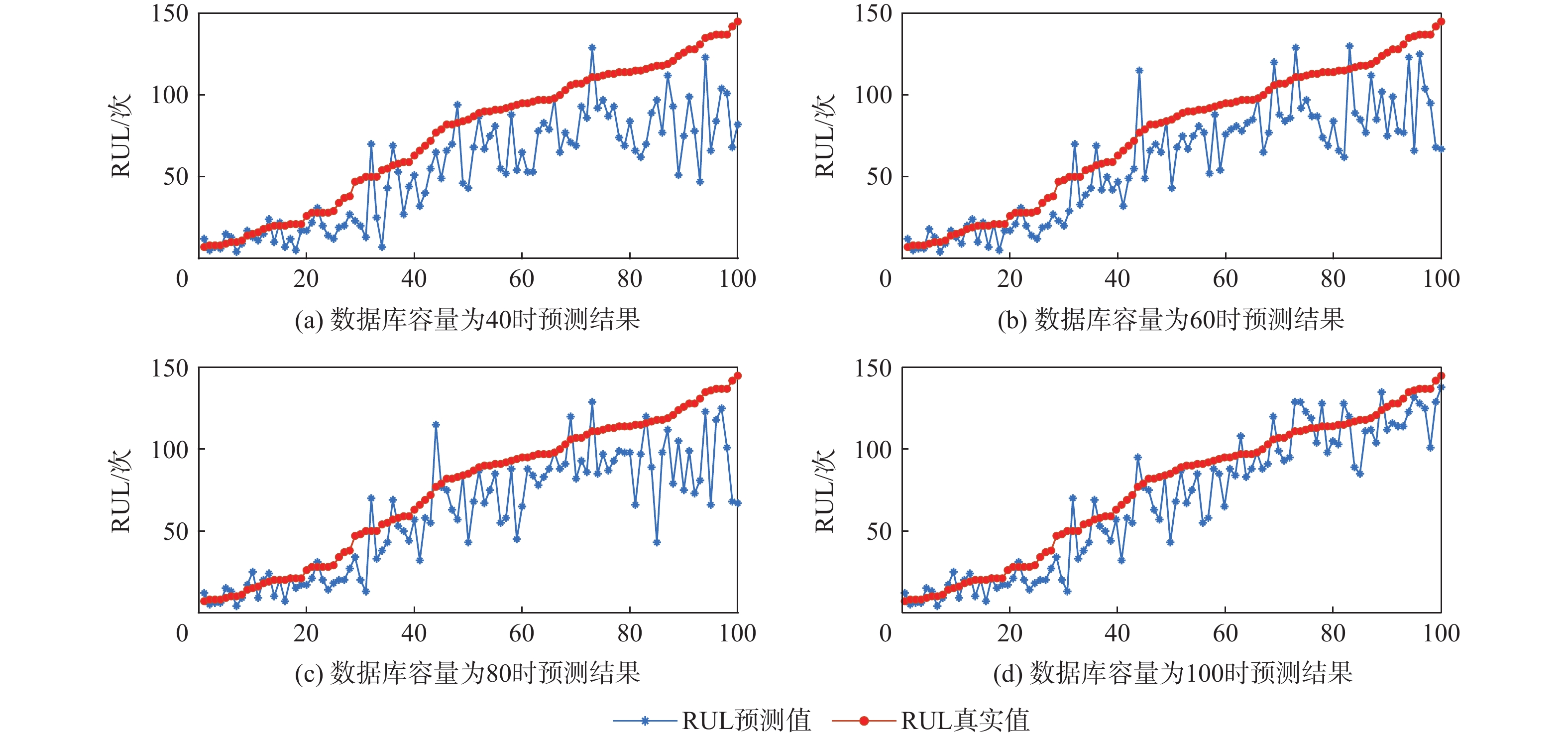
Table 4. Experimental results of different database size
数据库容量 RMSE/次 MAE/次 40 23.40 25.30 60 20.85 20.32 80 18.64 19.25 100 17.08 17.36 -
[1] KORDESTANI M, SAIF M, ORCHARD M E, et al. Failure prognosis and applications—A survey of recent literature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2021, 70(2): 728-748. doi: 10.1109/TR.2019.2930195 [2] PENG Y Z, WANG Y, ZI Y Y. Switching state-space degradation model with recursive filter/smoother for prognostics of remaining useful life[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(2): 822-832. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2810284 [3] ELLEFSEN A L, BJØRLYKHAUG E, ÆSØY V, et al. Remaining useful life predictions for turbofan engine degradation using semi-supervised deep architecture[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 183: 240-251. [4] ZIO E. Prognostics and health management (PHM): Where are we and where do we (need to) go in theory and practice[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 218: 108119. [5] HU Y, MIAO X W, SI Y, et al. Prognostics and health management: A review from the perspectives of design, development and decision[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 217: 108063. [6] LI H, ZHAO W, ZHANG Y X, et al. Remaining useful life prediction using multi-scale deep convolutional neural network[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 89: 106113. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106113 [7] SUN W J, ZHAO R, YAN R Q, et al. Convolutional discriminative feature learning for induction motor fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(3): 1350-1359. doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2672988 [8] EL-THALJI I, JANTUNEN E. A summary of fault modelling and predictive health monitoring of rolling element bearings[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 60-61: 252-272. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.02.008 [9] 谭治学, 钟诗胜, 林琳. 多源数据融合的民航发动机修后性能预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(6): 1106-1113. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0557TAN Z X, ZHONG S S, LIN L. Commercial aircraft engine post-repairing performance prediction based on fusion of multisource data[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(6): 1106-1113(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0557 [10] MUNEER A, TAIB S M, NASEER S, et al. Data-driven deep learning-based attention mechanism for remaining useful life prediction: Case study application to turbofan engine analysis[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(20): 2453. doi: 10.3390/electronics10202453 [11] 赵洪利, 张猛. 基于随机维纳过程的航空发动机性能衰退研究[J]. 推进技术, 2021, 42(3): 488-494. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190632ZHAO H L, ZHANG M. Performance degradation of aeroengines based on stochastic Wiener process[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2021, 42(3): 488-494(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190632 [12] 杜方舟, 孙有朝, 郭媛媛, 等. 基于数据的航空发动机排气温度裕度及剩余寿命计算方法[J]. 航空动力学报, 2020, 35(11): 2456-2464. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2020.11.023DU F Z, SUN Y C, GUO Y Y, et al. Calculation method of aero-engine exhaust gas temperature margin and remaining life based on data[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2020, 35(11): 2456-2464(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2020.11.023 [13] 赵洪利, 陈天铭, 郑涅. 基于特征融合多阶段相似的发动机寿命预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(5): 1430-1436. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.05.33ZHAO H L, CHEN T M, ZHENG N. Engine life prediction based on multi-stage similarity of comprehensive index[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(5): 1430-1436(in Chinese). doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.05.33 [14] 李京峰, 陈云翔, 项华春, 等. 基于LSTM-DBN的航空发动机剩余寿命预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(7): 1637-1644. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.28LI J F, CHEN Y X, XIANG H C, et al. Remaining useful life prediction for aircraft engine based on LSTM-DBN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(7): 1637-1644(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.28 [15] 李杰, 贾渊杰, 张志新, 等. 基于融合神经网络的航空发动机剩余寿命预测[J]. 推进技术, 2021, 42(8): 1725-1734. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200792LI J, JIA Y J, ZHANG Z X, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of aeroengine based on fusion neural network[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2021, 42(8): 1725-1734(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200792 [16] 洪骥宇, 王华伟, 倪晓梅. 基于降噪自编码器的航空发动机性能退化评估[J]. 航空动力学报, 2018, 33(8): 2041-2048. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2018.08.028HONG J Y, WANG H W, NI X M. Assessment of performance degradation for aero-engine based on denoising autoencoder[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2018, 33(8): 2041-2048(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2018.08.028 [17] 房友龙, 贺星, 刘东风, 等. 燃气轮机健康状态组合法综合评价[J]. 推进技术, 2020, 41(8): 1903-1913. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190336FANG Y L, HE X, LIU D F, et al. Combinatorial comprehensive assessment of gas turbine health condition[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2020, 41(8): 1903-1913(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190336 [18] 刘渊, 余映红, 田彦云, 等. 航空发动机排气温度基线建模新方法研究[J]. 推进技术, 2022, 43(4): 16-25. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200511LIU Y, YU Y H, TIAN Y Y, et al. Investigation on new method for baseline modelling of aeroengine exhaust gas temperature[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2022, 43(4): 16-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200511 [19] ZHANG Q, TSE P W T, WAN X, et al. Remaining useful life estimation for mechanical systems based on similarity of phase space trajectory[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(5): 2353-2360. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.10.041 [20] SAXENA A, GOEBEL K, SIMON D, et al. Damage propagation modeling for aircraft engine run-to-failure simulation[C]//Proceeding of the 2008 International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-9. [21] 彭开香, 皮彦婷, 焦瑞华, 等. 航空发动机的健康指标构建与剩余寿命预测[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2020, 37(4): 713-720.PENG K X, PI Y T, JIAO R H, et al. Health indicator construction and remaining useful life prediction for aircraft engine[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2020, 37(4): 713-720(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: