-
摘要:
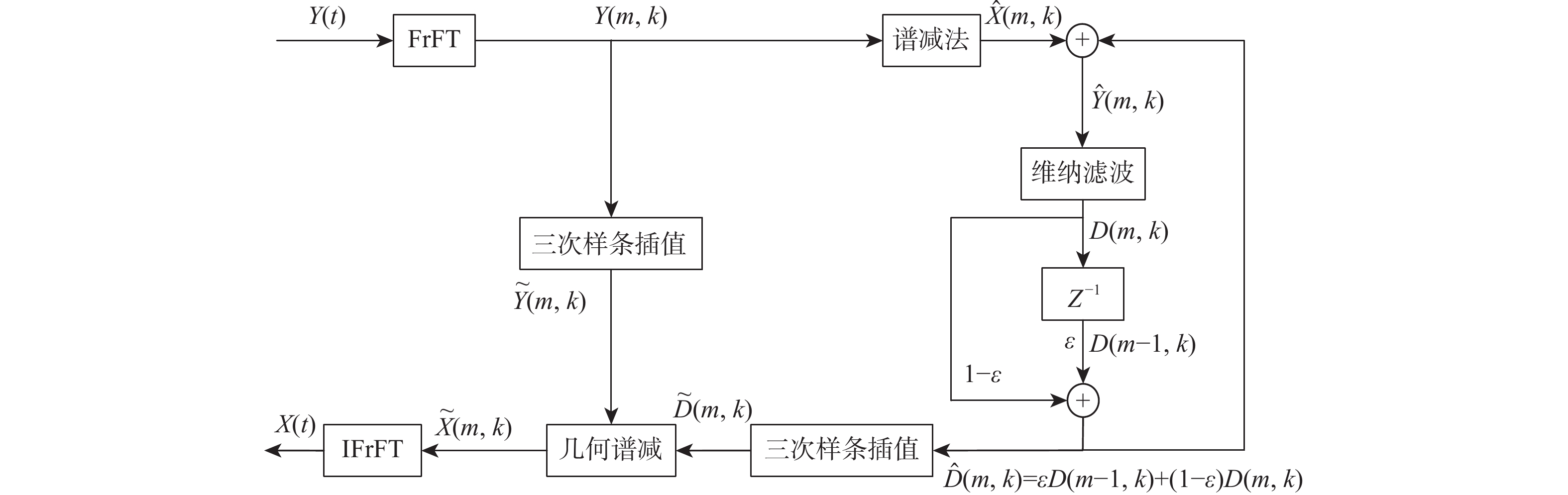
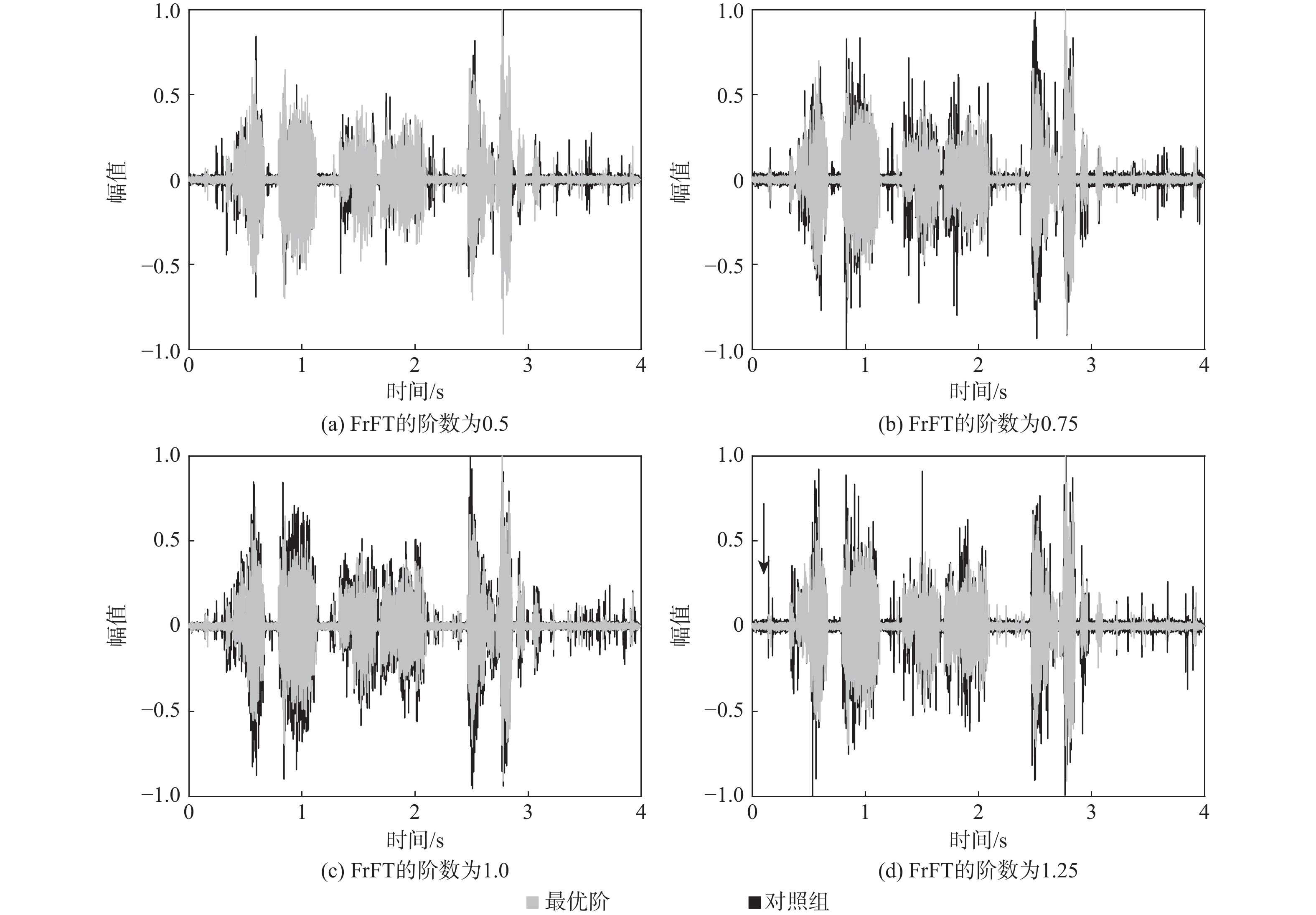
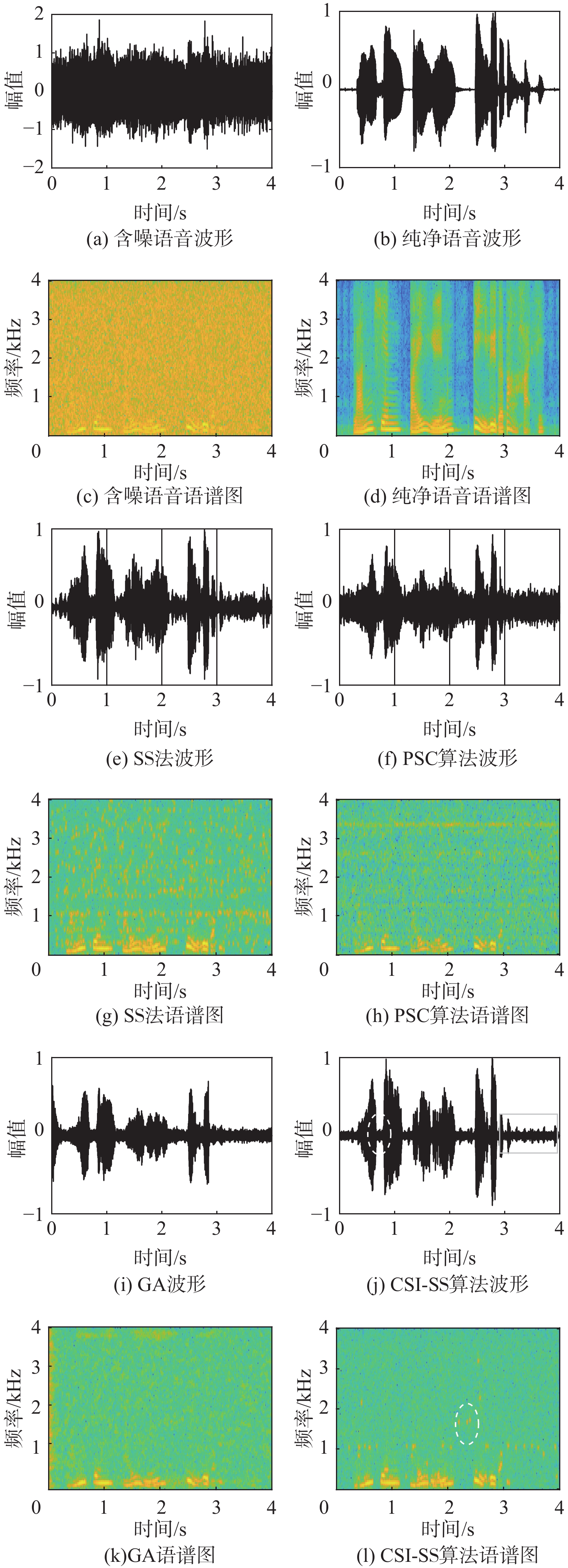
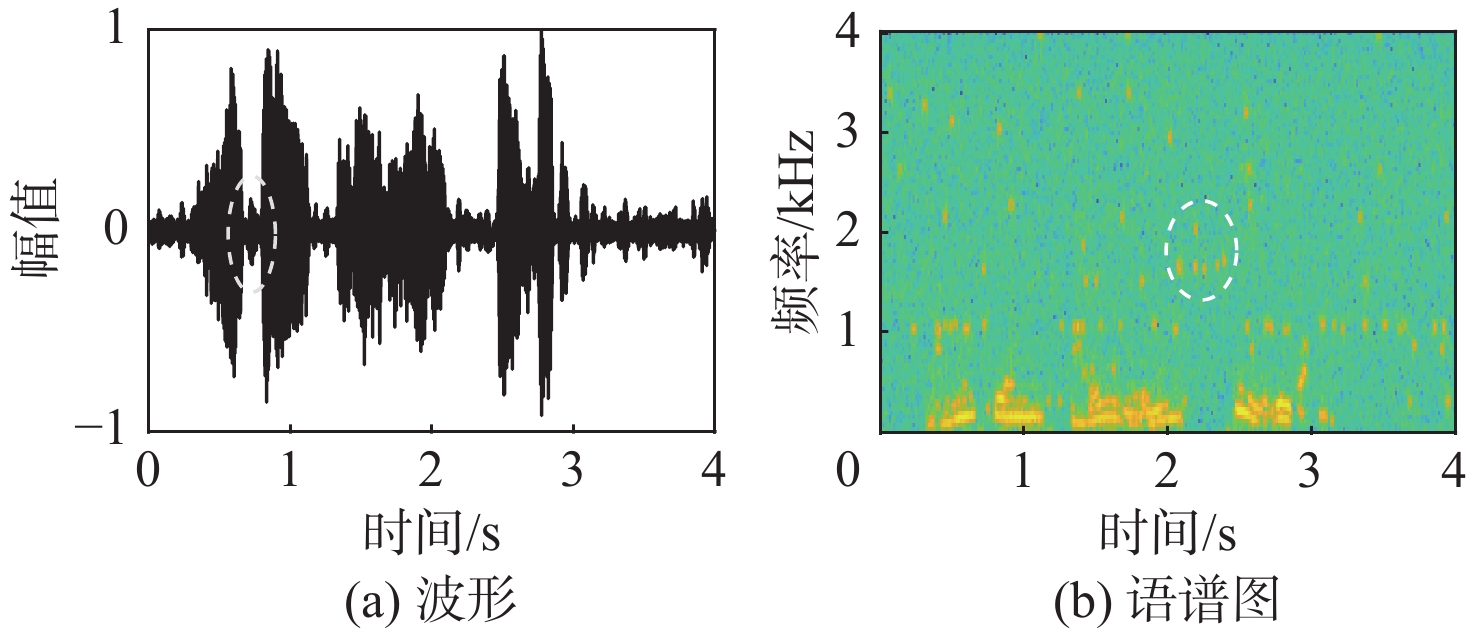
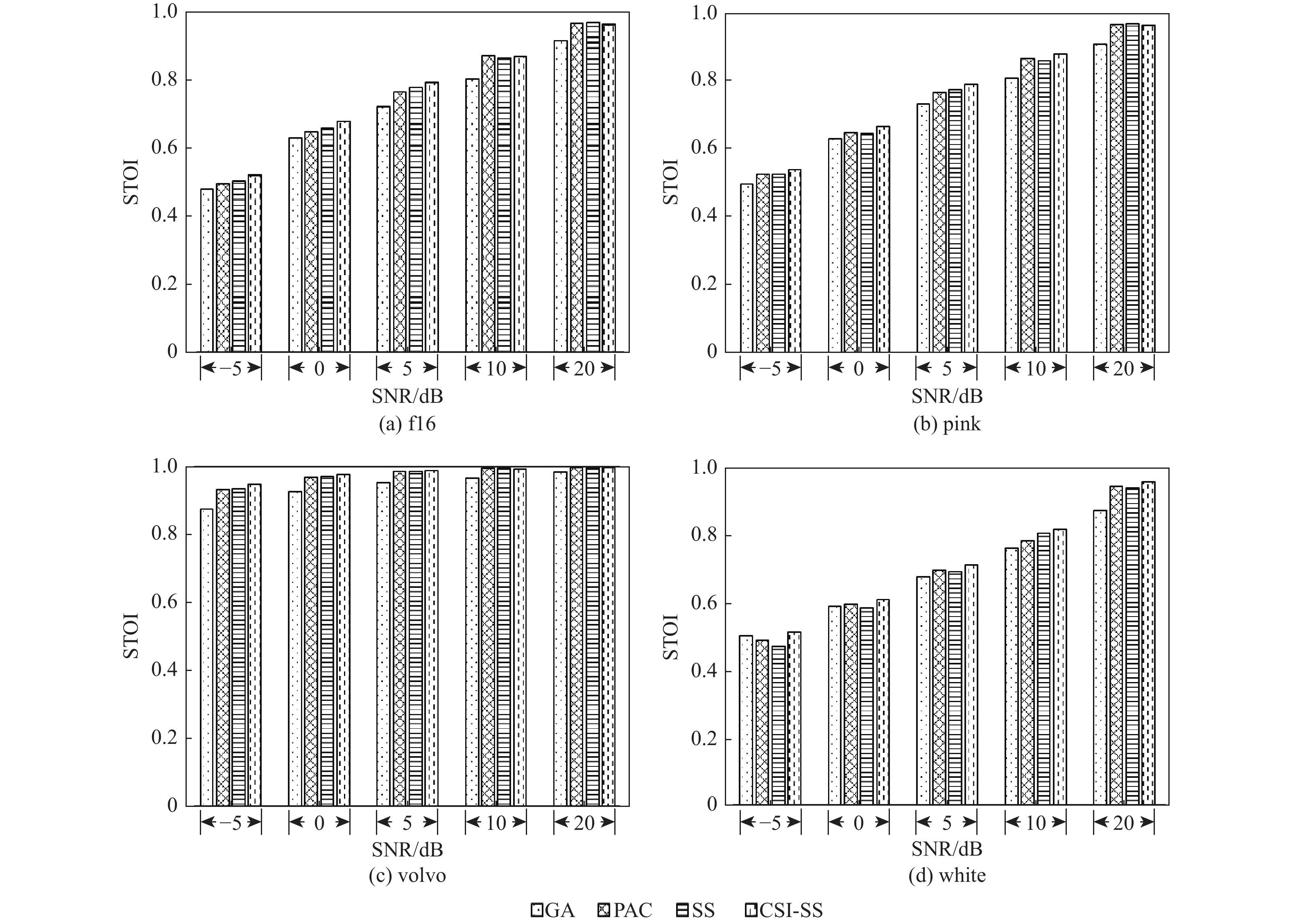
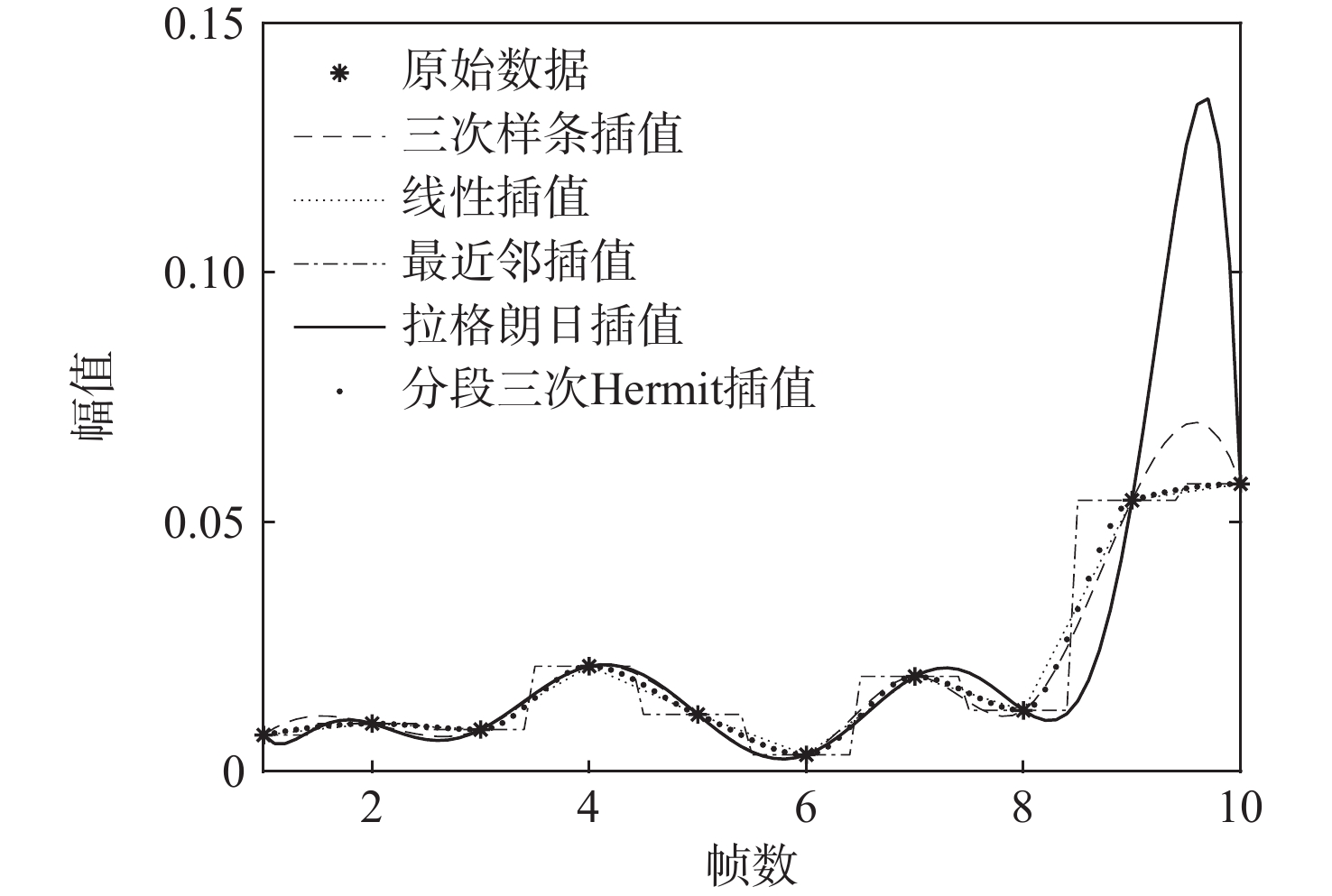
语音识别系统易受噪声影响,采用谱减法等传统语音增强算法滤除噪声,但存在“音乐噪声”的困扰。针对该类问题,提出一种基于分数阶傅里叶与三次样条插值的语音增强算法。对语音进行分数阶傅里叶变换,并采用谱减法对含噪语音进行预处理,通过基于维纳滤波的噪声估计器来估计噪声,实现噪声的迭代更新;采用三次样条插值将含噪语音与估计噪声进行函数化;将函数化后的含噪语音与估计噪声进行几何谱减法处理,获得纯净语音。仿真结果显示:与传统的语音增强算法相比,所提算法在改善“音乐噪声”的问题上效果明显,同时也改善了语音可懂性和语音质量。
Abstract:The speech recognition system is susceptible to noise. In order to filter noise, traditional speech enhancement methods such as spectral subtraction are often used by researchers, but these methods are troubled by “music noise”. To solve this problem, a speech enhancement algorithm based on cubic spline interpolation is proposed in this paper. Firstly, speech is subjected to the fractional Fourier transform, spectral subtraction is employed to preprocess noisy speech, and the Wiener filter noise estimator is utilized to realize the iterative update of noise. Secondly, the speech with noise and the estimated noise is functioned by cubic spline interpolation. A geometric spectrum subtraction algorithm is then used to process the functional speech with noise and the estimated noise to produce the pure speech. The simulation results show that compared with the traditional speech noise reduction algorithm, the proposed algorithm has an obvious effect on improving the “music noise” problem, and also greatly improves speech intelligibility and speech quality.
-
表 1 语音加权权值
Table 1. Speech weighted weight
噪声 σY μY σD μD white 0.99 0.18 0.75 0.22 pink 0.97 0.44 0.77 0.16 f16 0.98 0.59 0.73 0.32 volvo 1.00 0.20 0.86 0.40 表 2 不同噪声环境下的PESQ值
Table 2. PESQ values in different noise environments
算法 PESQ值(f16) PESQ值(pink) −5 dB 0 dB 5 dB 10 dB 20 dB −5 dB 0 dB 5 dB 10 dB 20 dB GA 1.0161 1.6396 1.8808 2.2017 2.8965 0.8978 1.4933 2.0319 2.4368 2.9058 PSC 1.3841 1.5920 2.0251 2.4186 3.1484 1.1554 1.4638 2.0066 2.4852 3.1574 SS 1.1567 1.5268 1.9874 2.4415 3.1496 1.1305 1.5966 2.0346 2.4793 3.1836 CSI-SS 1.4928 1.7302 2.2403 2.4125 3.0083 1.3764 1.7208 2.1142 2.324 3.0432 算法 PESQ值(volvo) PESQ值(white) −5 dB 0 dB 5 dB 10 dB 20 dB −5 dB 0 dB 5 dB 10 dB 20 dB GA 2.3785 2.7559 3.1169 3.3298 3.6643 0.369 0.9824 1.467 2.0601 2.6876 PSC 2.7069 3.1217 3.3643 3.5617 3.9995 1.1392 1.3286 1.7016 2.1485 2.8672 SS 2.6385 2.926 3.2008 3.6607 4.0343 1.1099 1.3514 1.7921 2.284 2.8803 CSI-SS 2.8624 3.2412 3.4102 3.5542 3.8011 1.2985 1.5902 1.9999 2.0527 2.8752 注:−5,0,5,10,20 dB表示信噪比。 -
[1] WANG L L, HU X, HU J, et al. Research on control system of an exoskeleton upper-limb rehabilitation robot[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(6): 1168-1175. [2] LAVANYA T, NAGARAJAN T, VIJAYALAKSHMI P. Multi-level single-channel speech enhancement using a unified framework for estimating magnitude and phase spectra[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2020, 28: 1315-1327. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2020.2986877 [3] DROPPO J. Single channel enhancement for speech recognition [C]//Proceedings of the 2008 Hands-Free Speech Communication and Microphone Arrays. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 93-97. [4] WANG D X, YIN F L, ZHANG H C. Experiment evaluation of microphone array placement for speech enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Test and Measurement. Dalian: ISTM, 2005: 1583-1586. [5] BOLL S F, FPROCESSING S. Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1979, 27(2): 113-120. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1979.1163209 [6] JAMIESON D G, BRENNAN R L, CORNELISSE L E. Evaluation of a speech enhancement strategy with normal-hearing and hearing-impaired listeners[J]. Ear and Hearing, 1995, 16(3): 274-286. doi: 10.1097/00003446-199506000-00004 [7] FLANAGAN J L, JOHNSTON J D, ZAHN R, et al. Computer-steered microphone arrays for sound transduction in large rooms[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1985, 78(5): 1508-1518. doi: 10.1121/1.392786 [8] ZELINSKI R. A microphone array with adaptive post-filtering for noise reduction in reverberant rooms[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 2578-2581. [9] GNANAMANICKAM J, NATARAJAN Y, SRI PREETHAA K R. A hybrid speech enhancement algorithm for voice assistance application[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(21): 7025. doi: 10.3390/s21217025 [10] 张晓艳, 张天骐, 葛宛营, 等. 联合深度神经网络和凸优化的单通道语音增强算法[J]. 声学学报, 2021, 46(3): 471-480.ZHANG X Y, ZHANG T Q, GE W Y, et al. Monaural speech enhancement combining deep neural network and convex optimation[J]. Acta Acustica, 2021, 46(3): 471-480(in Chinese). [11] BEROUTI M, SCHWARTZ R, MAKHOUL J. Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2003: 208-211. [12] LU Y, LOIZOU P C. A geometric approach to spectral subtraction[J]. Speech Communication, 2008, 50(6): 453-466. doi: 10.1016/j.specom.2008.01.003 [13] WEI Y, ZENG Y M, LI C. Single-channel speech enhancement based on subband spectral entropy[J]. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 2018, 66(3): 100-113. doi: 10.17743/jaes.2018.0003 [14] SIM B L, TONG Y C, CHANG J S, et al. A parametric formulation of the generalized spectral subtraction method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 1998, 6(4): 328-337. doi: 10.1109/89.701361 [15] MURAKAMI T, ISHIDA Y A. Adaptive filtering for attenuating musical noise caused by spectral subtraction[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing. Baixas: ISCA, 2006: 1443. [16] 宋智威, 熊成林, 黄路, 等. 基于牛顿插值的单相整流器功率前馈无差拍控制[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42(11): 3623-3629.SONG Z W, XIONG C L, HUANG L, et al. Power feedback-forward and deadbeat control of single-phase rectifier based on Newton interpolation[J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(11): 3623-3629(in Chinese). [17] 牛少彰, 钮心忻, 杨义先, 等. 基于拉格朗日插值公式的数字水印分存算法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2003, 26(3): 8-11.NIU S Z, NIU X X, YANG Y X, et al. Digital watermarking sharing algorithm based on Lagrange interpolation formula[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2003, 26(3): 8-11(in Chinese). [18] PHUNG V M, NGUYEN V M, PHAN T H. Hermite interpolation on algebraic curves in C2[J]. Indagationes Mathematicae, 2019, 30(5): 874-890. doi: 10.1016/j.indag.2019.07.001 [19] HUSSAIN M Z, IRSHAD M, SARFRAZ M, et al. Interpolation of discrete time signals using cubic spline function[C]//Processings of the 19th International Conference on Information Visualisation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 454-459. [20] HWANG S, BYUN J, PARK Y C. Performance comparison evaluation of speech enhancement using various loss functions[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of Korea, 2021, 40(2): 176-182. [21] KOLBAEK M, TAN Z H, JENSEN J. On the relationship between short-time objective intelligibility and short-time spectral-amplitude mean-square error for speech enhancement[J]. IEEE-ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2019, 27(2): 283-295. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2018.2877909 [22] SALEEM N, KHATTAK M I, NAWAZ A, et al. Perceptually weighted β-order spectral amplitude Bayesian estimator for phase compensated speech enhancement[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 178: 108007. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108007 -







 下载:
下载: