Stack-bucket algorithm for convolutional codes based on dynamic optimization regulation
-
摘要:
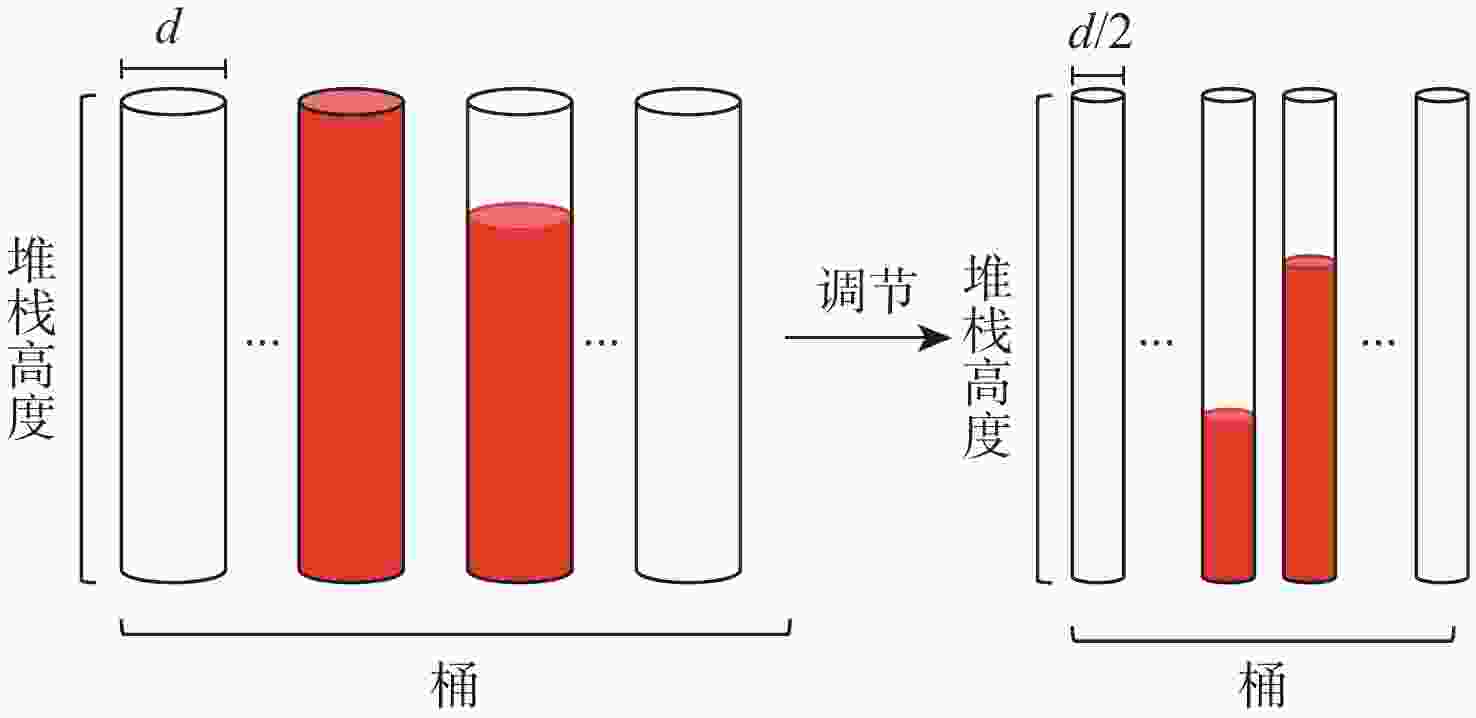
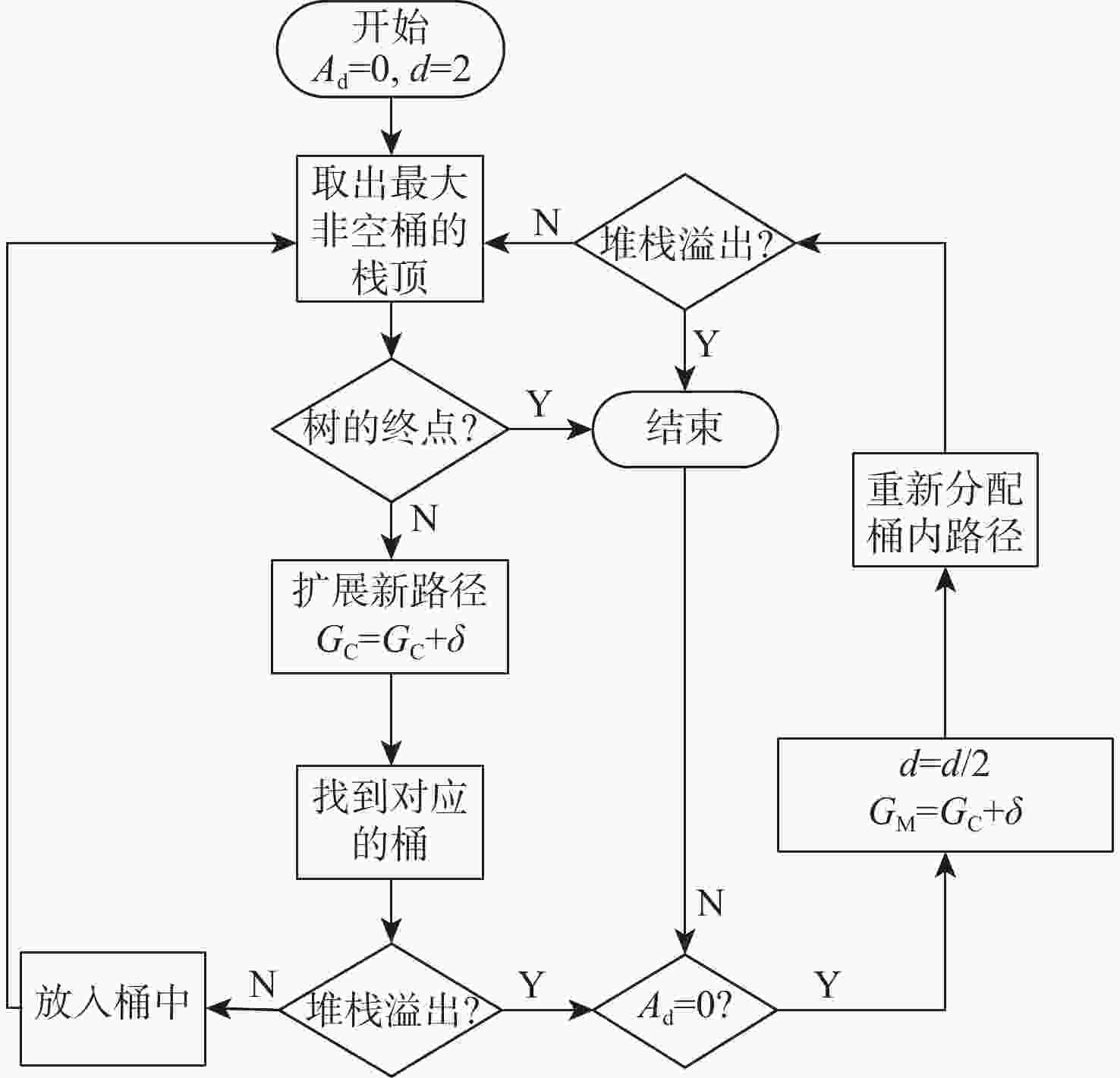
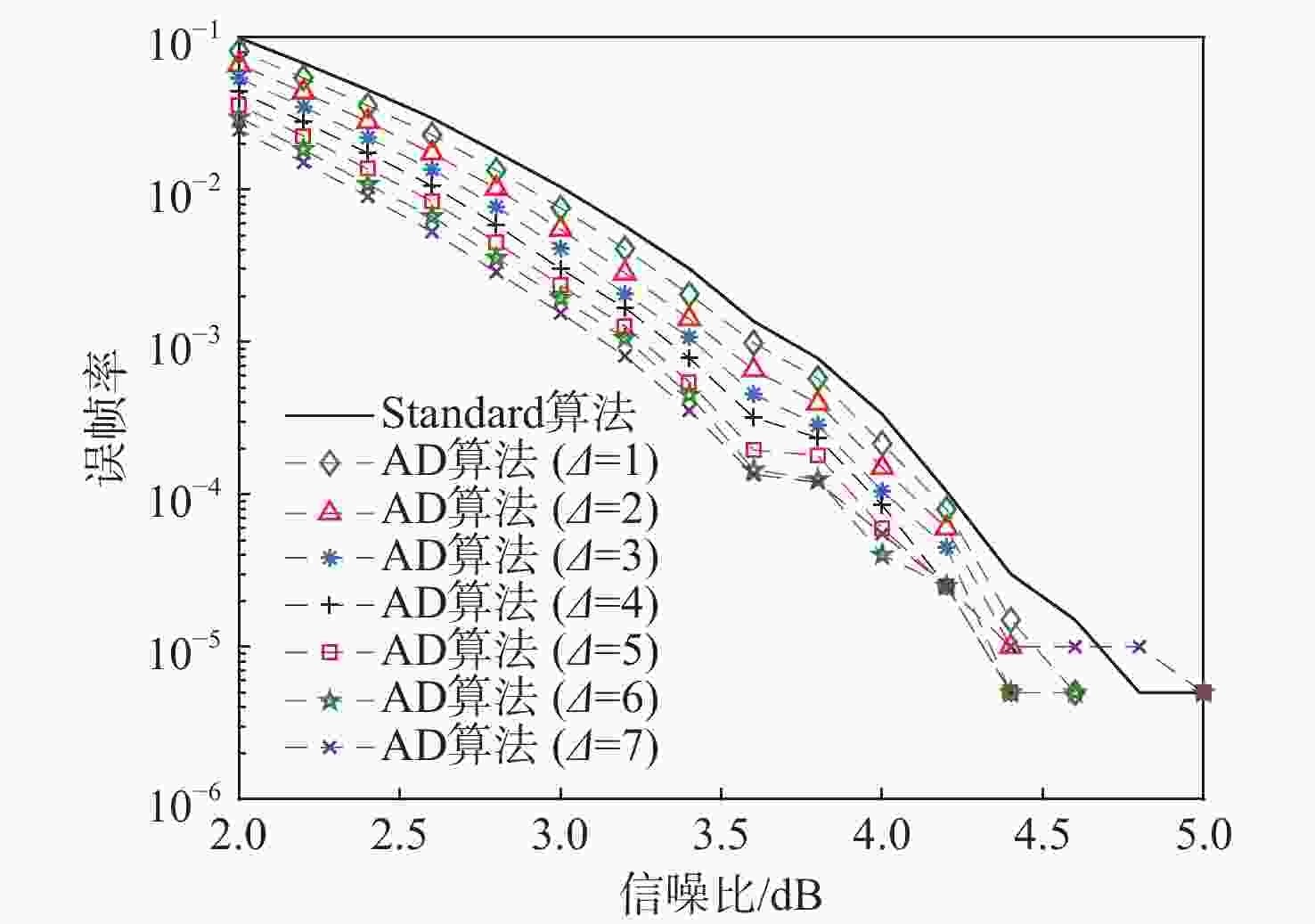
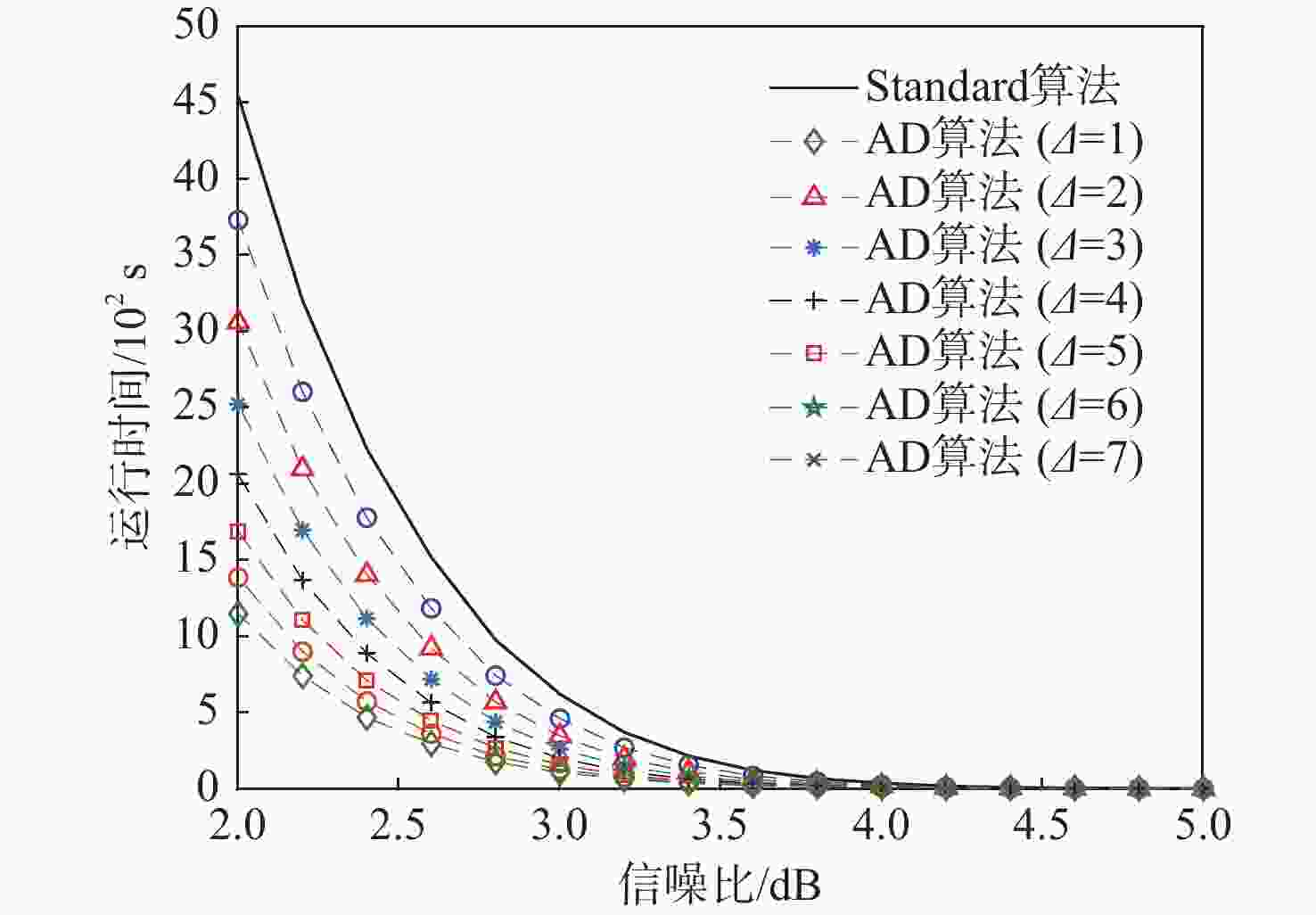
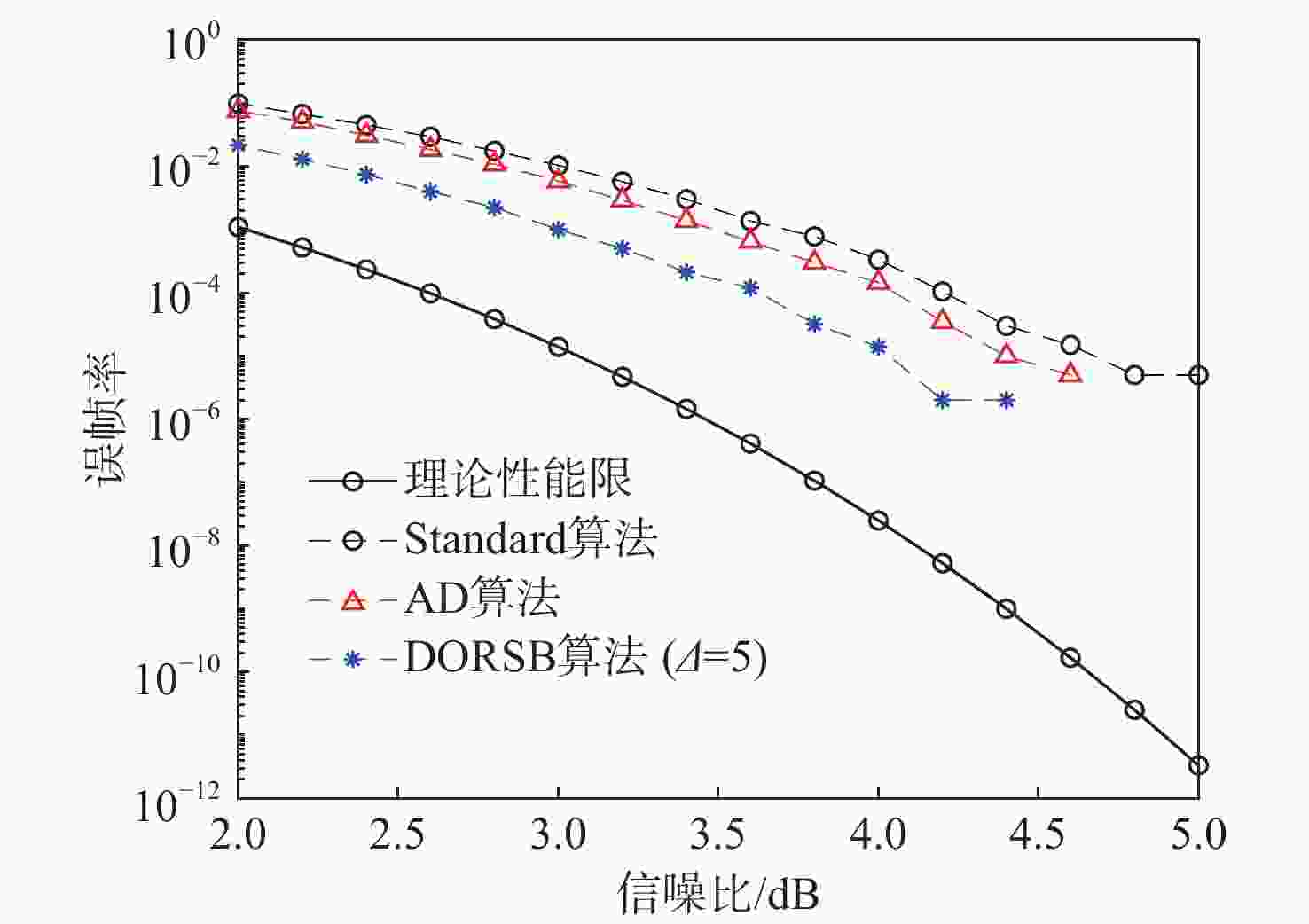
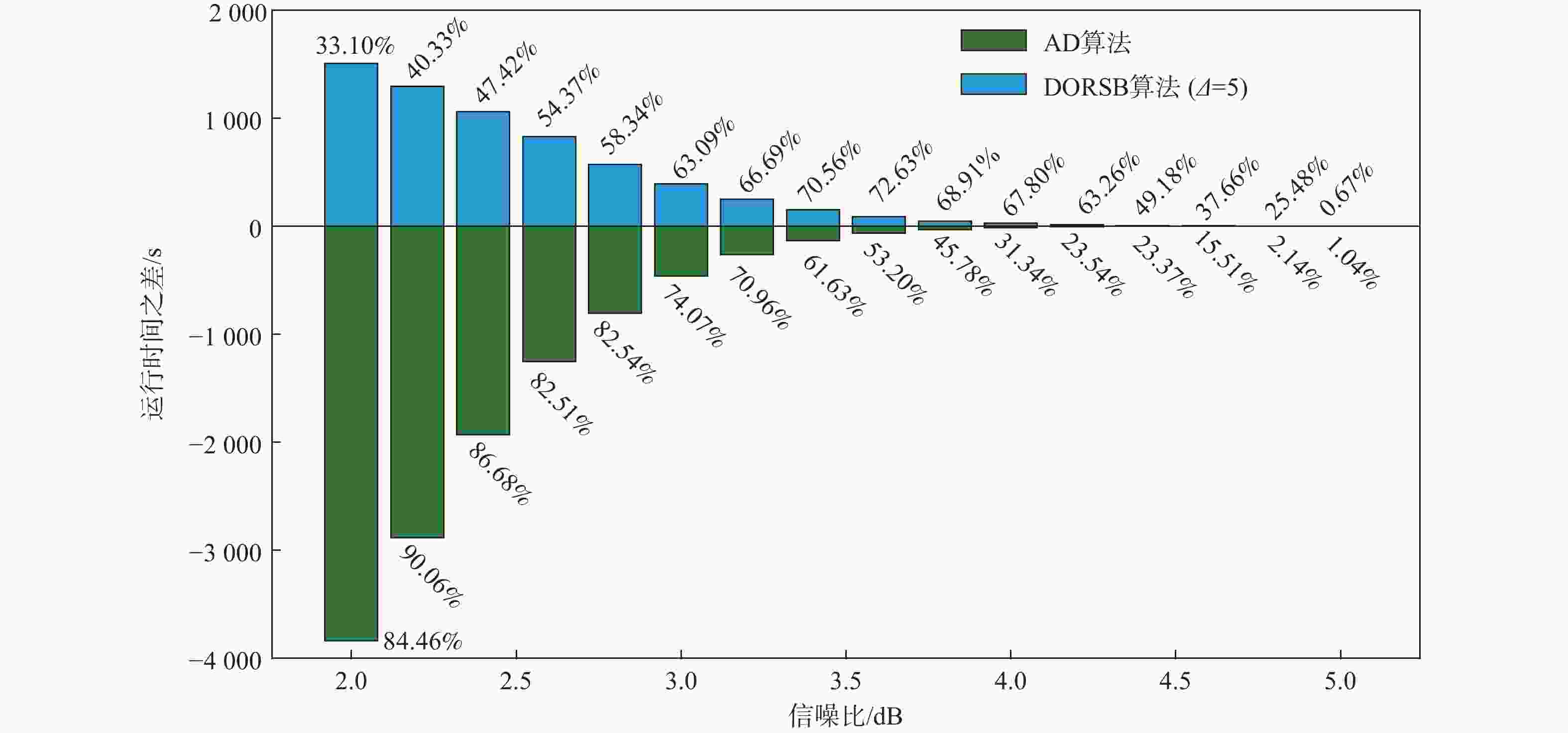
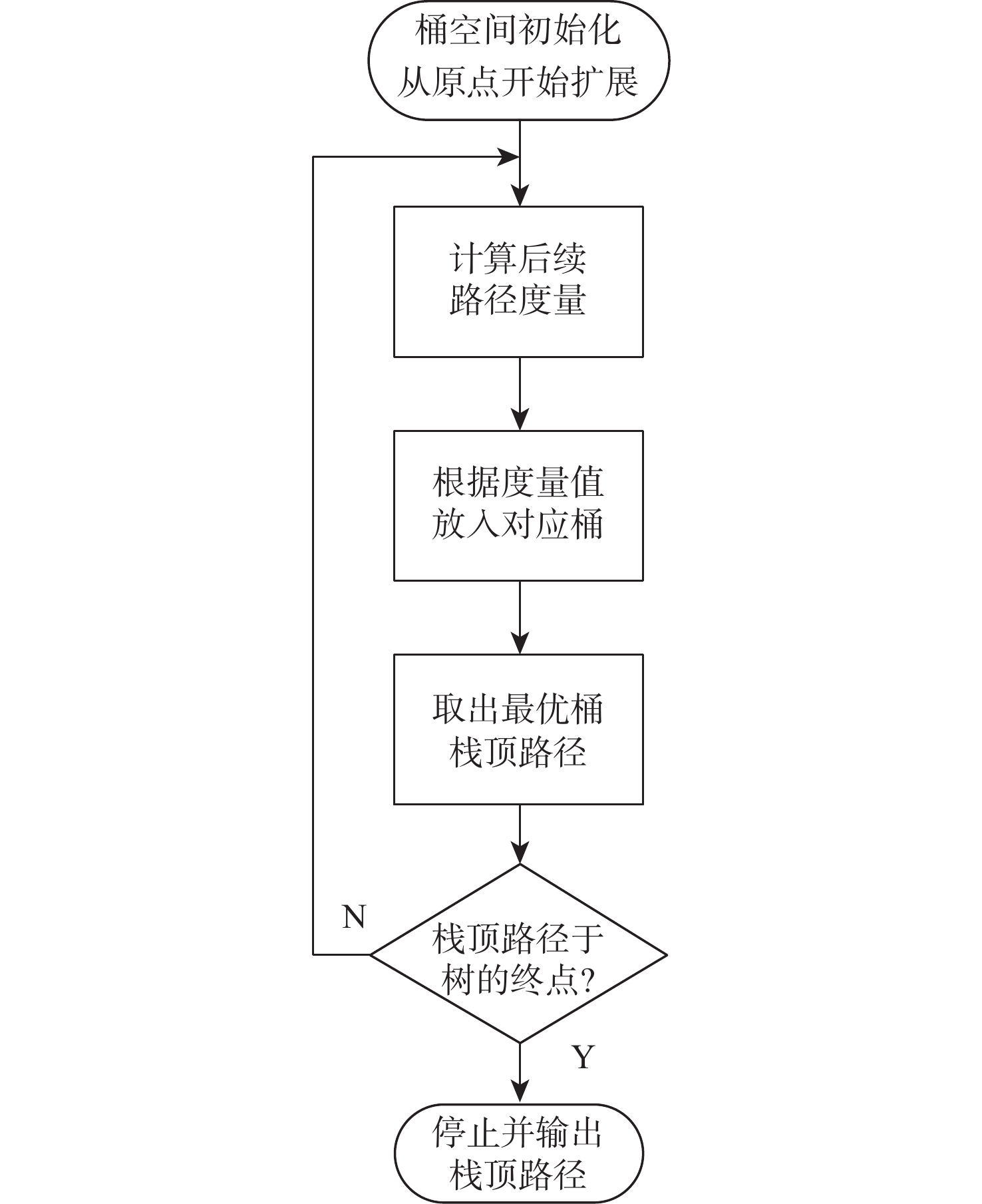
大约束长度卷积码具有抗干扰性强,难以破译等优点,被应用于卫星通信等领域。但低信噪比环境下,存在空间利用率低和译码复杂度高的缺点。针对此问题,提出一种基于动态寻优调节的卷积码堆栈-桶(DORSB)算法。所提算法采用新参数深度因子辅助路径存取,能够增大接近码树终点的路径优势,降低译码复杂度;并在堆栈溢出时,对桶的尺寸进行调节,对桶空间进行复用的同时降低误帧率,可有效提升空间利用率。仿真结果表明:在深度因子增量适当且误帧率为10−5的情况下,相比于标准堆栈-桶算法,所提算法误帧性能提高了约0.6 dB,并且时间复杂度最多能改善72.63%。
Abstract:Long constraint length convolutional codes are used in the fields of satellite communication due to their strong anti-interference and difficulty in decipherment. However, there are shortcomings of low space utilization and high decoding complexity in the low signal-to-noise ratio environment. To overcome the above problems, this paper proposed a stack-bucket algorithm (DORSB) based on dynamic optimization regulation. The proposed algorithm uses a new parameter depth factor to assist path access, which can increase the path advantage near the end of the code tree and reduce the decoding complexity. When the stack overflows, the size of the bucket is regulated to reuse the bucket space and reduce the frame error rate, which can effectively improve the space utilization. The simulation results show that when the depth factor increment is appropriate and the frame error rate is 10−5, compared with the standard stack bucket algorithm, the frame error performance of the proposed algorithm is improved by about 0.6 dB, and the time complexity can be improved by 72.63%.
-
表 1 Standard 算法和AD算法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of Standard algorithm and AD algorithm
信噪比/dB 译码算法 错帧数 运行时间/s 5.0 Standard 1 2.87 AD 0 2.90 4.0 Standard 67 38.54 AD 29 50.62 3.0 Standard 2 081 621.71 AD 1 171 1 082.29 2.0 Standard 19 782 4 544.14 AD 15 328 8 382.12 -
[1] LIAN B, KSCHISCHANG F R. Sequential decoding of short length binary codes: Performance versus complexity[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3195-3198. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3095895 [2] NEHA N. Implementation and performance analysis of convolution error correcting codes with code rate=1/2[C]//2016 International Conference on Micro-Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 482-486. [3] 周倜. 针对卷积码干扰优化及抗干扰方法[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020: 58-60.ZHOU T. Optimized jamming against convolutional code and its anti-jamming scheme[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020: 58-60(in Chinese). [4] GAUDIO L, MATUZ B, NINACS T, et al. Approximate ML decoding of short convolutional codes over phase noise channels[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(2): 325-329. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2955730 [5] 黄肖玲, 杨华龙. 大约束度卷积码快速译码方法的研究[J]. 通信学报, 2010, 31(3): 57-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2010.03.009HUANG X L, YANG H L. Research of fast decoding for longer constraint length convolutional codes[J]. Journal on Communications, 2010, 31(3): 57-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-436X.2010.03.009 [6] DHALIWAL S, SINGH N, KAUR G. Performance analysis of convolutional code over different code rates and constraint length in wireless communication[C]//2017 International Conference on I-SMAC. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 464-468. [7] JOHANNESSON R, ZIGANGIROV K S. Fundamentals of convolutional coding[M]. 2nd ed. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 283-330. [8] LI K P, KALLEL S. A bidirectional multiple stack algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1999, 47(1): 6-9. doi: 10.1109/26.747805 [9] IMTAWIL V, SURAKAMPONTORN W. Parallel decoding scheme for a multiple stack algorithm[J]. IEEE Proceedings Communications, 2005, 152(6): 959-964. doi: 10.1049/ip-com:20050036 [10] ÇAVDAR T, GANGAL A. A new sequential decoding algorithm based on branch metric[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2007, 43(4): 1093-1100. doi: 10.1007/s11277-007-9285-0 [11] HAN Y S, CHEN P N, WU H B. A maximum-likelihood soft-decision sequential decoding algorithm for binary convolutional codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2002, 50(2): 173-178. doi: 10.1109/26.983310 [12] SHIEH S L, CHEN P N, HAN Y S. Reduction of computational complexity and sufficient stack size of the MLSDA by early elimination[C]//2007 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1671-1675. [13] ZHENG H T, CHEN B, ABANTO-LEON L F, et al. Complexity-adjustable SC decoding of polar codes for energy consumption reduction[J]. IET Communications, 2019, 13(14): 2088-2096. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2018.5643 [14] ROWSHAN M, BURG A, VITERBO E. Polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes: Sequential decoding vs list decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 1434-1447. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3052550 [15] ZHANG T T, ZHANG J K, ZHOU Z W, et al. FPGA-based large constraint length convolution code encoder verification[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2019, 1237(4): 042060. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1237/4/042060 [16] JELINEK F. Fast sequential decoding algorithm using a stack[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 1969, 13(6): 675-685. doi: 10.1147/rd.136.0675 [17] LIN S, COSTELLO J. Error control coding[M]. New York: Prentice Hall, 2001: 313-465. [18] FANO R. A heuristic discussion of probabilistic decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1963, 9(2): 64-74. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1963.1057827 [19] DOLINAR S, DIVSALAR D, POLLARA F. Code performance as a function of block size: TMO Progress Report 42-133 [R]. Washton, D. C. : NASA, 1998. -







 下载:
下载: