Effect of high altitude and low pressure on cycle performance of lithium-ion batteries
-
摘要:
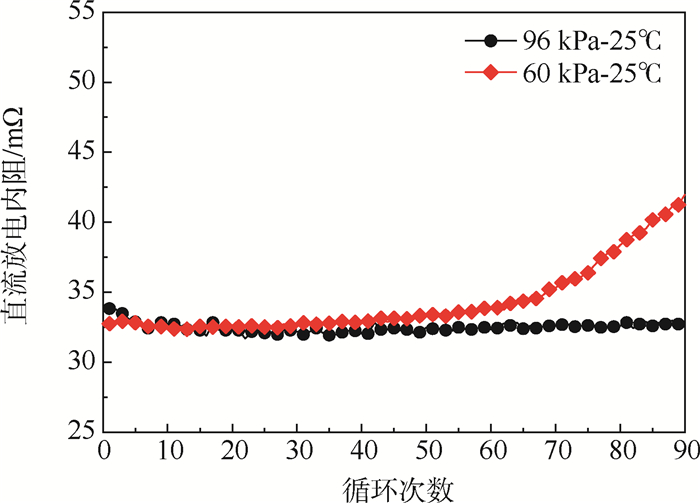
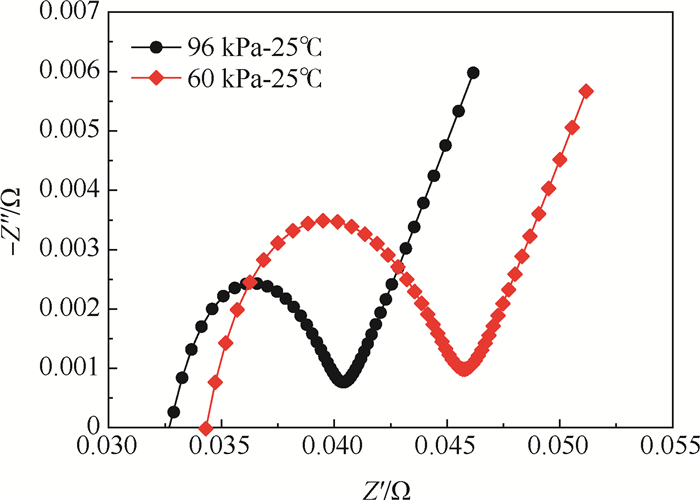
随着锂离子电池在中国高高原地区及机场的应用,其在高海拔低气压环境下的循环性能及老化机制成为一个亟须解决的问题。对此,在96 kPa-25℃(常温常压)及60 kPa-25℃(常温低压)环境下,通过电池健康状态、直流放电内阻、电化学阻抗、容量增量及微分电压曲线等电池电化学特征参数对NCM523软包锂离子电池的老化行为进行了分析。研究表明:60 kPa低气压环境加速了锂离子电池老化进程,电池内部结构受60 kPa低气压应力影响,致使电池欧姆阻抗和电荷转移阻抗较常压工况分别增加6.22%和45.76%,锂脱嵌反应受限,电池界面动力学衰退;因电池阻抗增大造成以正极活性锂离子损失主导的循环容量加速衰减,电池健康状态衰减率较常压工况高3.08%。
Abstract:Lithium-ion batteries have been used in high-altitude areas and airports in China, and therefore it is urgent to investigate their cycle performance and aging mechanism in high-altitude and low-pressure environments. The aging behavior of NCM523 pouch lithium-ion batteries is analyzed in terms of electrochemical characteristics such as battery health status, charging energy, direct current internal resistance, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, capacity increase and differential voltage curves under 96 kPa-25℃ (normal temperature and pressure) and 60 kPa-25℃ (normal temperature and low pressure). The results show that the low pressure of 60 kPa accelerates the aging process of lithium-ion batteries. The internal structure of the battery is affected by low pressure, which increases the ohmic resistance and charge transfer resistance of the battery by 6.22% and 45.76%, respectively, compared with those under normal pressure. In addition, the lithium deintercalation reaction is limited, and the kinetic properties of the battery interface are reduced. Due to the increase of the battery impedance, the cycle capacity decays rapidly, determined by the loss of active Li+ of the cathode. The attenuation rate of the battery health state is higher by 3.08% than that under atmospheric pressure.
-
Key words:
- lithium-ion battery /
- high altitude /
- low pressure /
- aging mechanism /
- characteristic parameter
-
表 1 实验用锂离子电池参数
Table 1. Lithium-ion battery parameters of experiment
参数 规格 电池类型 LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2/石墨,软包 电芯工艺 卷绕式 折数 20 额定容量/mAh 5 000 截止电压/V 2.75~4.2 标称电压/V 3.7 尺寸/(mm×mm×mm) 75×68×7 -
[1] 贺元骅, 郭绪乾, 伍毅. 高高原火行为研究进展[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2014, 33(5): 497-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2014.05.007HE Y H, GUO X Q, WU Y. Research progress of combustion characteristics at high plateau[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2014, 33(5): 497-500(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2014.05.007 [2] HOU J, YANG M, WANG D, et al. Fundamentals and challenges of lithium Ion batteries at temperatures between -40 and 60℃[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(18): 1904152. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201904152 [3] 周芳, 刘思, 侯敏. 锂电池技术在储能领域的应用与发展趋势[J]. 电源技术, 2019, 43(2): 348-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2019.02.050ZHOU F, LIU S, HOU M. Application and development tendency of lithium battery technology in energy storage field[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 43(2): 348-350 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2019.02.050 [4] REN D S, FENG X N, LU L, et al. Overcharge behaviors and failure mechanism of lithium-ion batteries under different test conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 250: 323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.015 [5] ANDO K, MATSUDA T, IMAMURA D. Degradation diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries with a LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2and LiMn2O4 blended cathode using dV/dQ curve analysis[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 390: 278-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.043 [6] NAUMANN M, SPINGLER F B, JOSSEN A. Analysis and modeling of cycle aging of a commercial LiFePO4/graphite cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 451: 227666. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227666 [7] ARIS A M, SHABANI B. An experimental study of a lithium ion cell operation at low temperature conditions[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 110: 128-135. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.117 [8] SITU W, YANG X, LI X, et al. Effect of high temperature environment on the performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 battery[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2017, 104: 743-748. [9] ZHANG L, MA Y, CHENG X, et al. Degradation mechanism of over-charged LiCoO2/mesocarbon microbeads battery during shallow depth of discharge cycling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 329: 255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.030 [10] JIANG L, LUO Z, WU T, et al. Overcharge behavior and early warning analysis of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2/C lithium-ion battery with high capacity[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166(6): A1055-A1062. doi: 10.1149/2.0661906jes [11] LIU S, WINTER M, LEWERENZ M, et al. Analysis of cyclic aging performance of commercial Li4Ti5O12-based batteries at room temperature[J]. Energy, 2019, 173(15): 1041-1053. [12] GANG N, HARAN B, POPOV B N. Capacity fade study of lithium-ion batteries cycled at high discharge rates[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 117(1-2): 160-169. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00029-6 [13] MAYSAM S, ABARDEH R H. Air pressure dependence of natural-convection heat transfer[J]. Lecture Notes in Engineering & Computer Science, 2010, 2184(1): 1183-1192. [14] 廖成龙, 王刘涛, 王健雁, 等. 动力锂电池系统运行环境条件对其性能影响的研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2020, 48(7): 167-170. doi: 10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2020.07.038LIAO C L, WANG L T, WANG J Y, et al. Study on the influence of operating environment condition on the performance of REESS[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2020, 48(7): 167-170(in Chinese). doi: 10.19817/j.cnki.issn1006-3536.2020.07.038 [15] COOK R W, SWAN L G, PLUCKNETT K P. Failure mode analysis of lithium ion batteries operated for low Earth orbit CubeSat applications[J]. The Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 31(4): 101561. [16] 刘磊, 王芳, 任山, 等. 海拔高度对动力电池性能的影响研究[J]. 电源技术, 2018, 42(11): 51-53.LIU L, WANG F, REN S, et al. Influence of altitude on perfor-mance of power battery for electric vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 42(11): 51-53(in Chinese). [17] XIE S, REN L, YANG X, et al. Influence of cycling aging and ambient pressure on the thermal safety features of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448: 227425. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227425 [18] LU T, LUO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Degradation analysis of commercial lithium-ion battery in long-term storage[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017, 164(4): A775-A784. doi: 10.1149/2.1321704jes [19] 闫建忠, 张海林, 薄茜, 等. 长期存储对锂离子电池性能的影响[J]. 电池工业, 2011, 16(4): 201-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2011.04.002YAN J Z, ZHANG H L, BO X, et al. Effects of long-time storage on the performance of Li-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2011, 16(4): 201-204(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7923.2011.04.002 [20] WILHELM J, SEIDLMAYER S, KEIL P, et al. Cycling capacity recovery effect: A coulombic efficiency and post-mortem study[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 365: 327-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.08.090 [21] 罗卓. 锂离子电池综合使用性能的评价、修复及相关机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009: 15-27.LUO Z. Evaluation, repair and related mechanisms of lithium-ion batteries[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009: 15-27(in Chinese). [22] LIU J, DUAN Q, MA M, et al. Aging mechanisms and thermal stability of aged commercial 18650 lithium ion battery induced by slight overcharging cycling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 445: 227263. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227263 [23] CHO H M, CHOI W S, GO J Y, et al. A study on time-dependent low temperature power performance of a lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 198: 273-280. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.09.111 [24] SCHMIDT J P, CHROBAK T, ENDER M, et al. Studies on LiFePO4 as cathode material using impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(12): 5342-5348. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.09.121 [25] BARAI A, CHOUCHELAMANE G H, GUO Y, et al. A study on the impact of lithium-ion cell relaxation on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 280: 74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.097 [26] CLARK C, SIMON E. Evaluation of lithium polymer technology for small satellite applications[C]//21st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, 2007: 1-11. [27] BARAI A, TANGIRALA R, UDDIN K, et al. The effect of external compressive loads on the cycle lifetime of lithium-ion pouch cells[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2017, 13: 211-219. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2017.07.021 [28] LIU S, XIONG L, HE C. Long cycle life lithium ion battery with lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM) cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 261: 285-291. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.083 [29] LIU S, SU J, ZHAO J, et al. Unraveling the capacity fading mechanisms of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 393: 92-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.029 [30] FLY A, CHEN R. Rate dependency of incremental capacity analysis (dQ/dV) as a diagnostic tool for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 29: 101329. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101329 [31] SMITH A J, DAHN J R. Delta differential capacity analysis[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(3): A290-A293. doi: 10.1149/2.076203jes [32] 苏来锁. 多应力作用下能量型锂离子电池的老化行为研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016: 7-9.SU L S. Study of energy type lithium-ion cell degradation behavior under multiple stresses[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016: 7-9(in Chinese). [33] KATO H, KOBAYASHI Y, MIYASHIRO H. Differential voltage curve analysis of a lithium-ion battery during discharge[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 398: 49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.07.043 [34] BLOOM I, JANSEN A N, ABRAHAM D P, et al. Differential voltage analyses of high-power, lithium-ion cells: 1. Technique and application[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 139(1-2): 295-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.07.021 -








 下载:
下载: