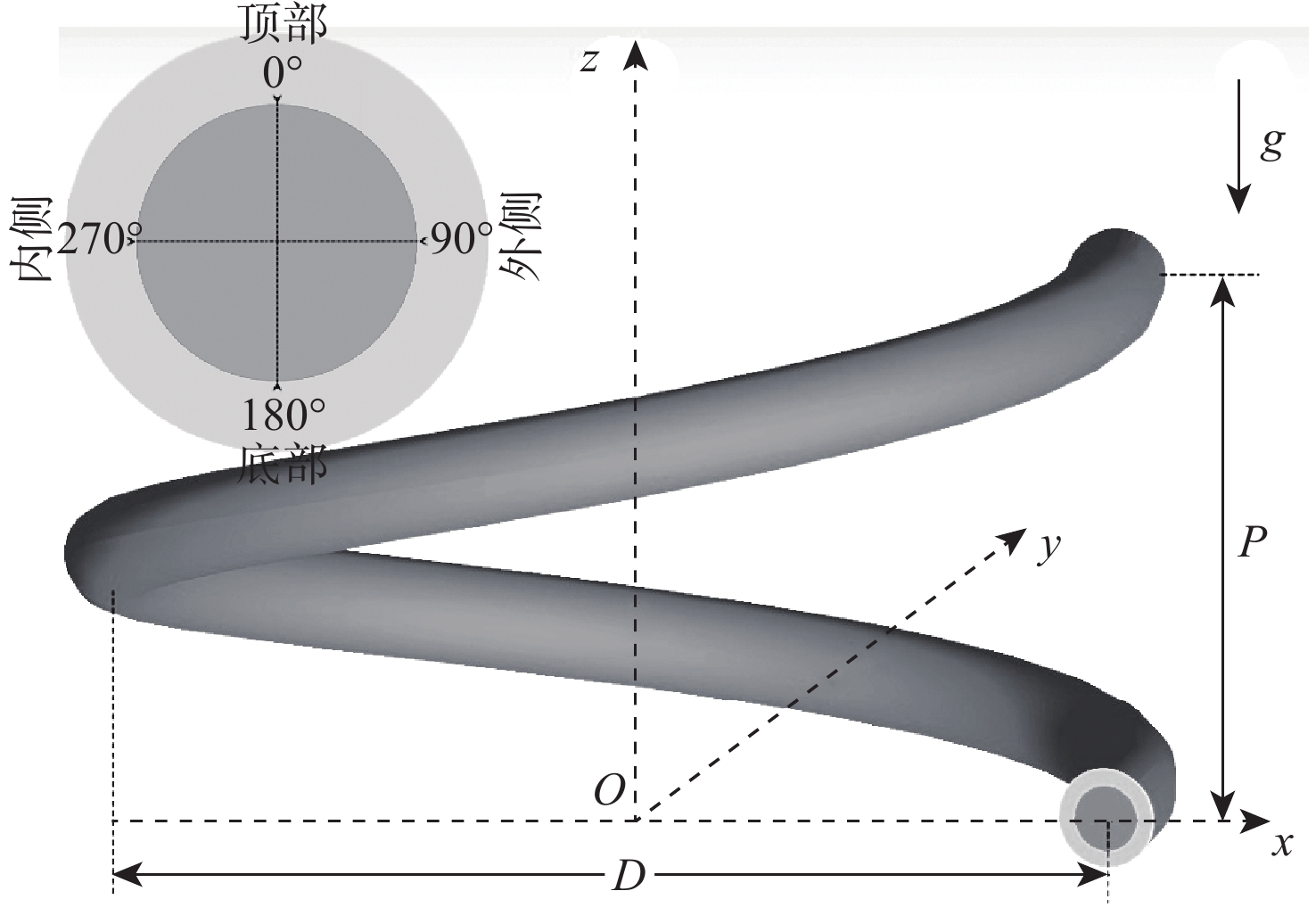
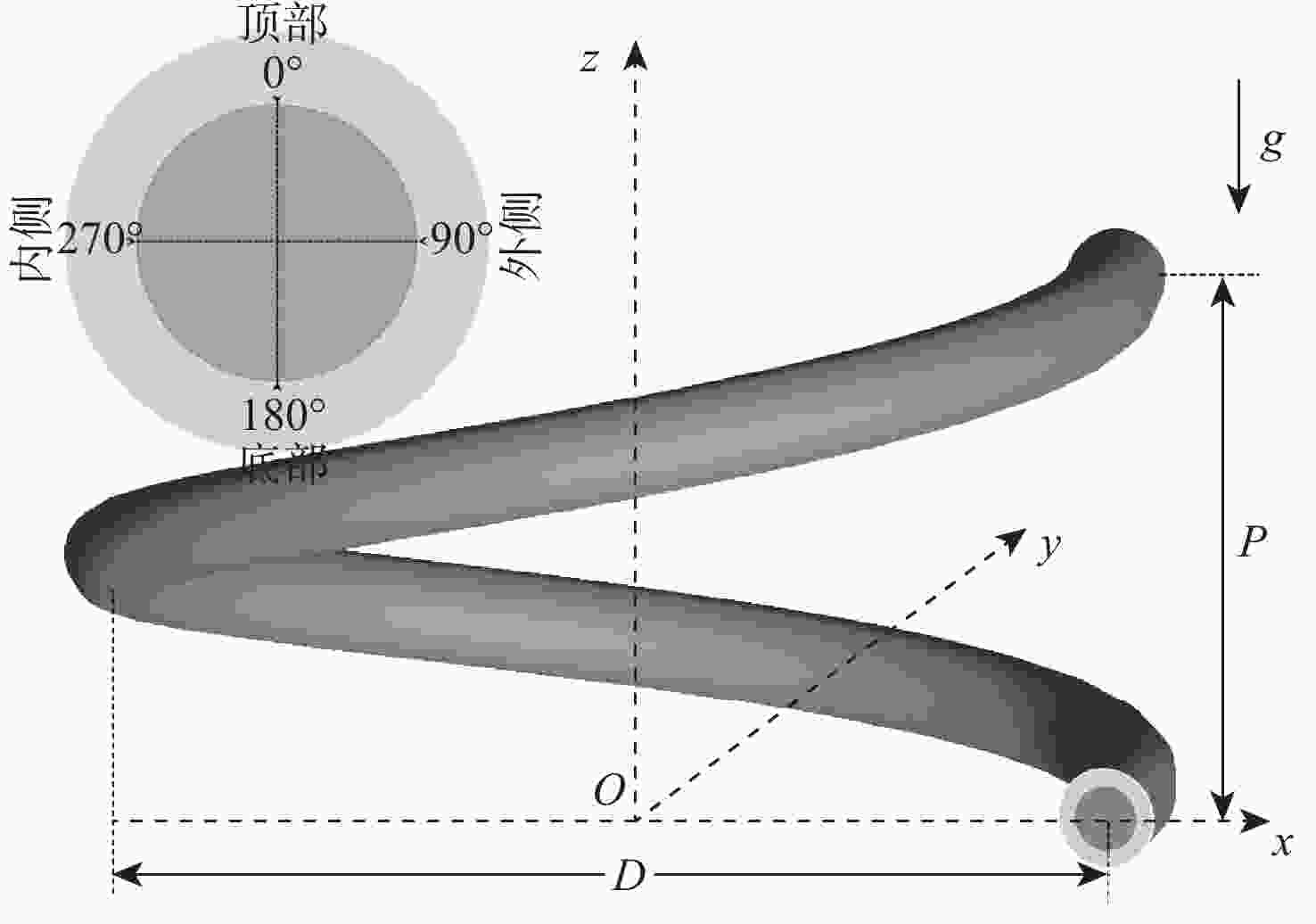
Influence and criterion of buoyancy force on heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in a vertical helical tube
-
摘要:
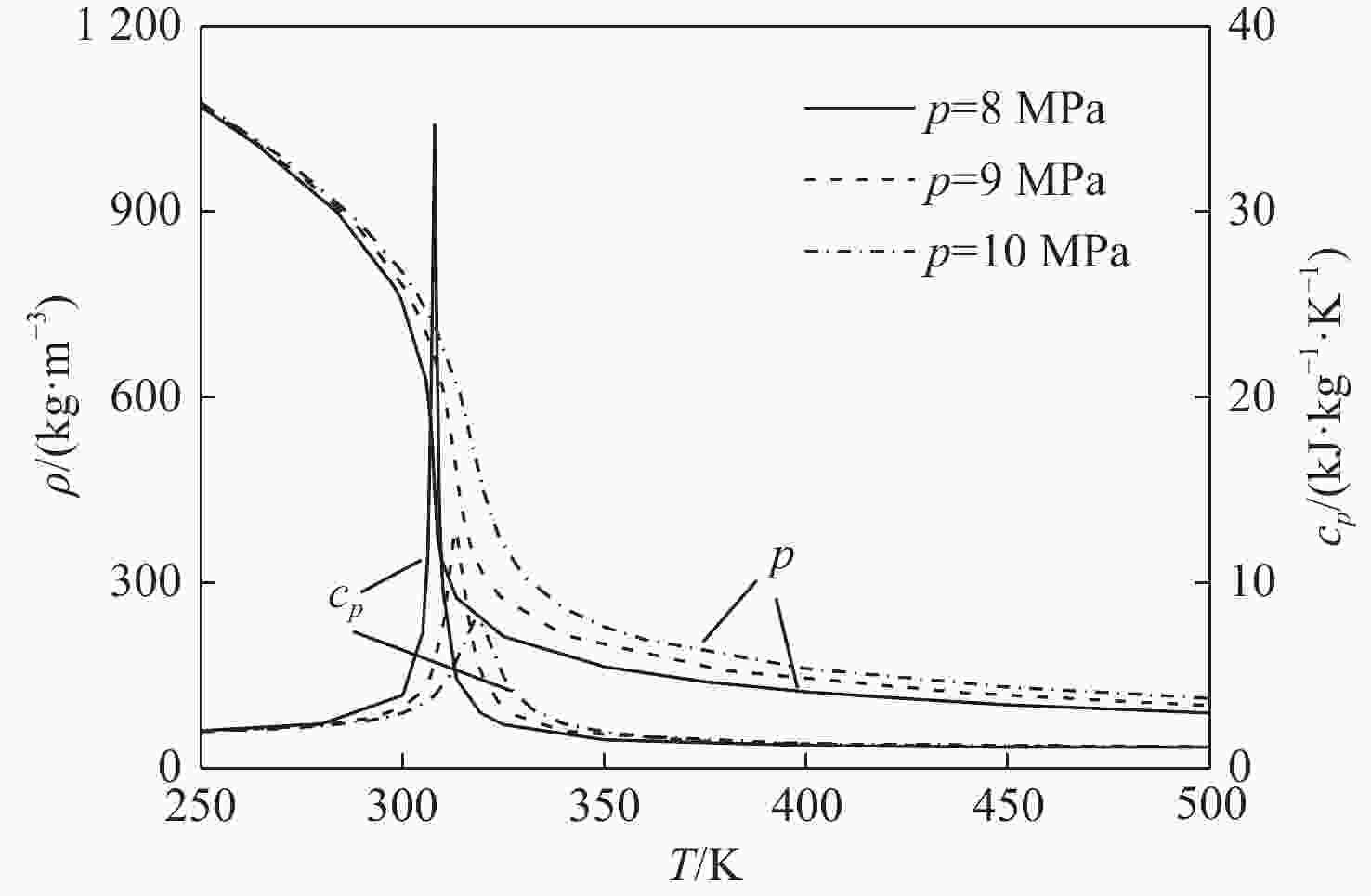
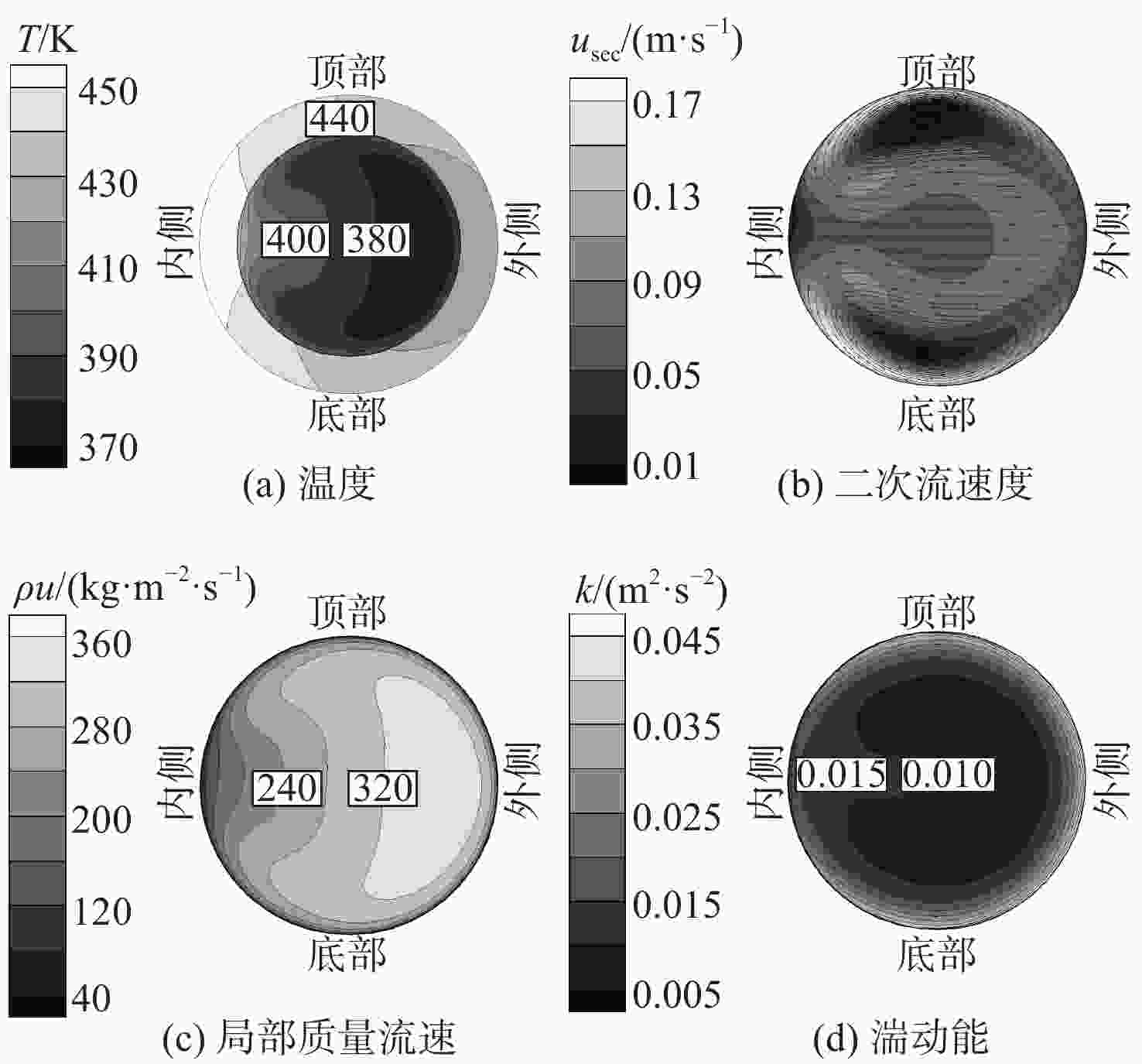
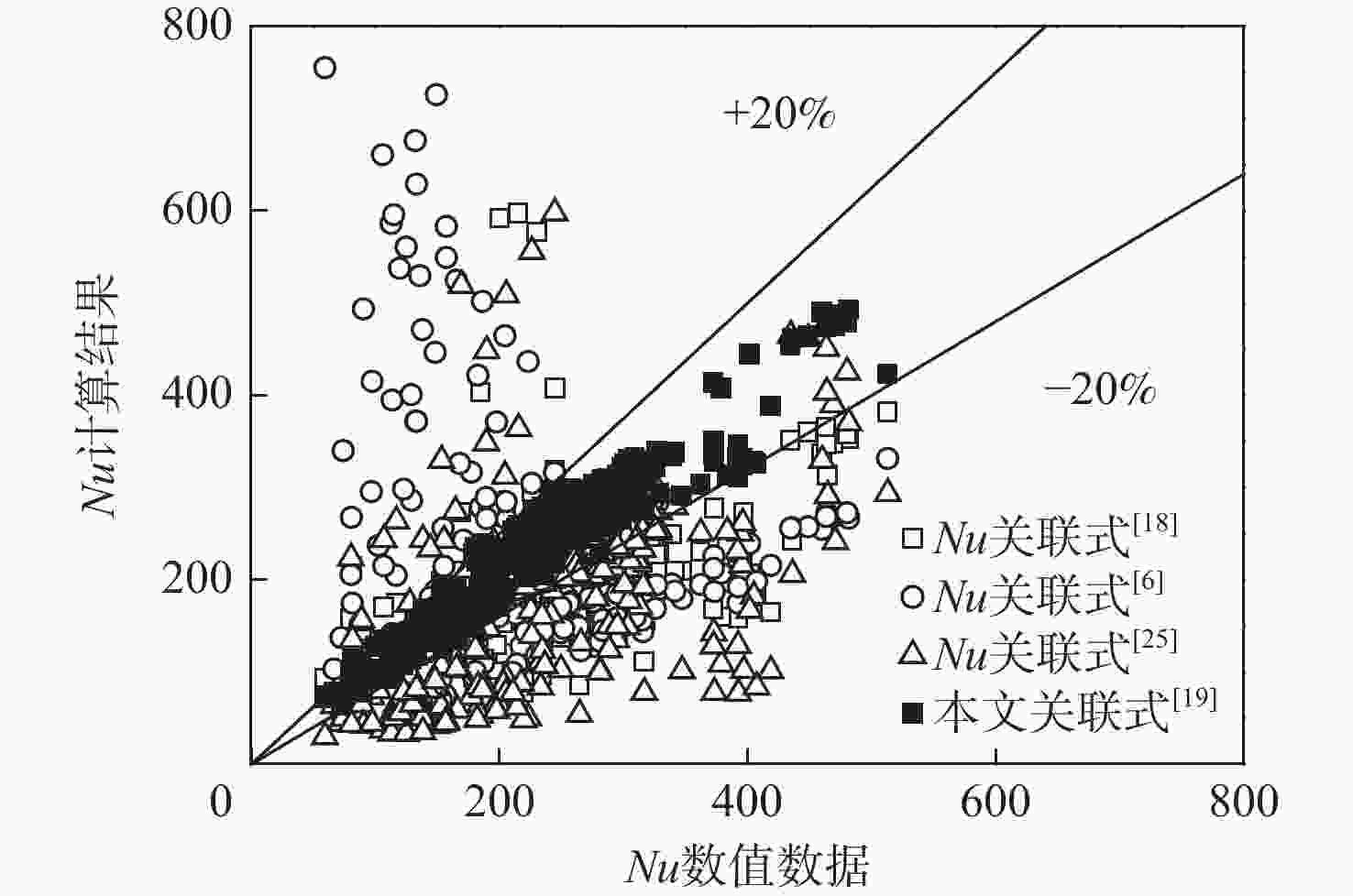
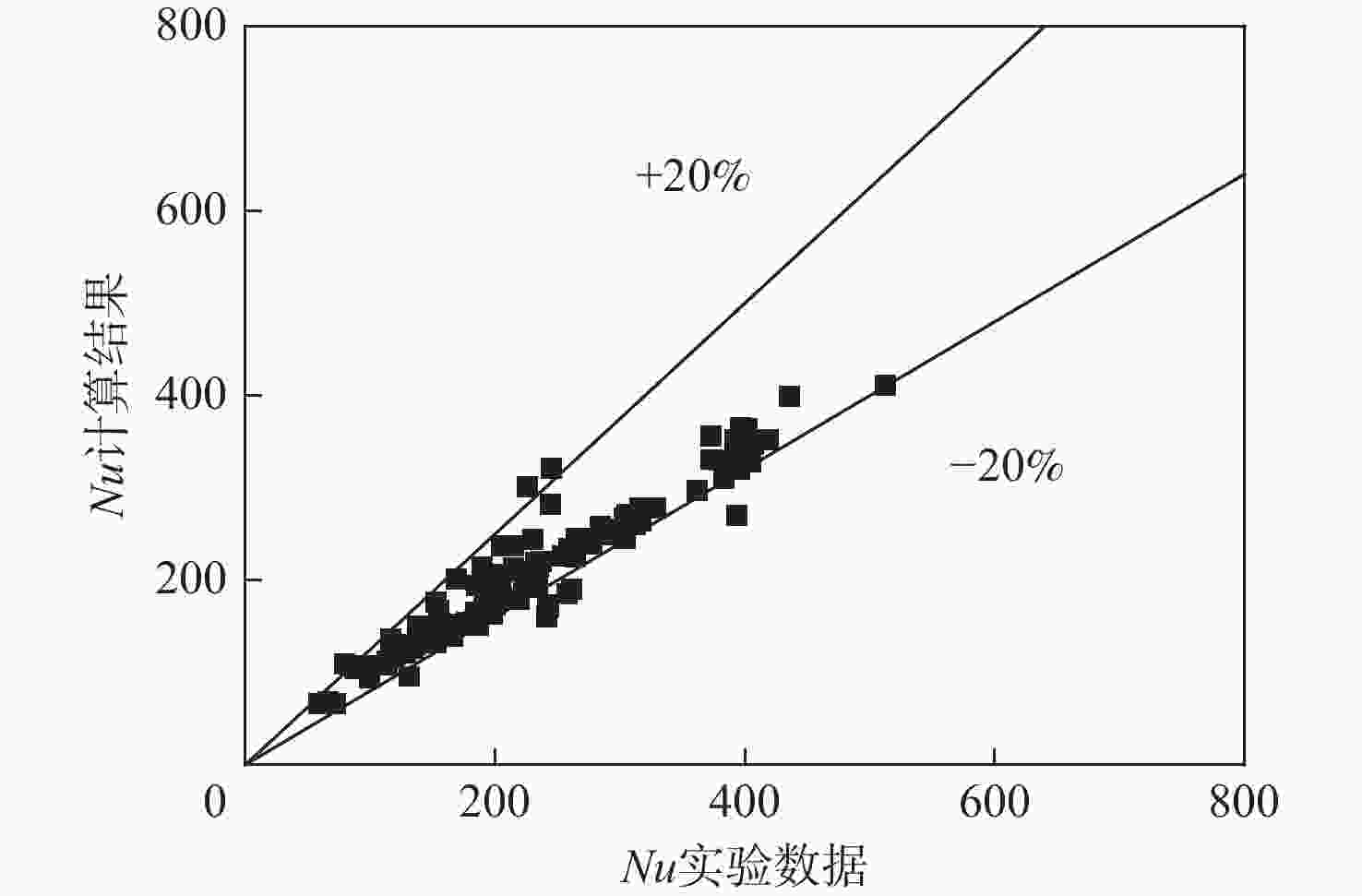
基于航空发动机间冷器的冷却换热问题,进行竖直螺旋管内超临界压力CO2换热数值研究。探究运行参数对沿流向和周向换热的影响机制。通过管截面温度场和流场分布阐述了浮升力和离心力引起的周向非均匀换热机制,评估二次流速度和强度。根据管道结构特性提出新的浮升力参数和浮升力影响判别准则,建立新的换热关联式。结果表明:管上游非均匀换热源于浮升力与离心力综合作用,管下游非均匀换热由离心力主导。当满足浮升力因子
Bu ≥1.6×10−5时,浮升力在换热中起主导作用。新换热关联式可以较好地适用于螺旋管内换热预测。Abstract:Numerical research was done on the heat transmission of supercritical CO2 in a vertical helical tube based on the cooling heat transfer in the aeroengine intercooler. The influence mechanisms of the operating parameters on heat transfer along the flow and circumferential directions were investigated. The distributions of the temperature field and flow field in tube cross-sections were used to describe the circumferential non-uniform heat transmission mechanism generated by the buoyancy force and centrifugal force. The secondary flow velocity and intensity were analyzed. According to the tube structure characteristics, the reasonable buoyancy parameter and buoyancy criteria were proposed, and the new heat transfer correlation was obtained. The results show that the centrifugal force predominates in the tube downstream while the buoyancy force and centrifugal force combine to provide non-uniform heat transfer in the tube upstream. When the buoyancy factor
Bu ≥1.6×10−5 is satisfied, the buoyancy force plays a leading role in heat transfer. The new heat transfer correlation can better predict the heat transfer in the helical tube.-
Key words:
- helical tube /
- supercritical /
- heat transfer /
- centrifugal force /
- buoyancy force /
- criterion
-
-
[1] 龚昊, 王占学, 刘增文. 间冷回热循环航空发动机参数匹配研究[J]. 航空动力学报, 2012, 27(8): 1809-1814. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2012.08.019GONG H, WANG Z X, LIU Z W. Study on thermodynamic cycle parameter matching for intercooled recuperated aero-engine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2012, 27(8): 1809-1814(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2012.08.019 [2] 龚昊, 王占学, 康涌, 等. 间冷回热航空发动机性能计算与分析[J]. 航空动力学报, 2014, 29(6): 1453-1461. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2014.06.027GONG H, WANG Z X, KANG Y, et al. Performance calculation and analysis of intercooled recuperated aero-engine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2014, 29(6): 1453-1461(in Chinese). doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2014.06.027 [3] 王占学, 龚昊, 刘增文, 等. 间冷回热航空发动机技术发展趋势分析[J]. 航空发动机, 2013, 39(6): 13-18.WANG Z X, GONG H, LIU Z W, et al. Analysis of technical development trend of intercooled recuperated aeroengine[J]. Aeroengine, 2013, 39(6): 13-18(in Chinese). [4] 赵璧, 宣益民. 航空发动机间冷器及回热器发展研究综述[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(9): 520934.ZHAO B, XUAN Y M. A review of research on intercoolers and recuperators in aero-engines[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(9): 520934(in Chinese). [5] JACOB F, ROLT A, SEBASTIAMPILLAI J, et al. Performance of a supercritical CO2 bottoming cycle for aero applications[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(3): 255. doi: 10.3390/app7030255 [6] BAI W J, ZHANG S J, LI H R, et al. Effects of abnormal gravity on heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in heated helically coiled tube[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 159: 113833. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.113833 [7] HUANG X R, ZHANG Z, YANG X T, et al. Numerical investigation on turbulent heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in a helically coiled tube[C]//Proceedings of 2018 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering. Beijing: Chinese Nuclear Society, 2018. [8] LIU X X, XU X X, LIU C, et al. Numerical study of the effect of buoyancy force and centrifugal force on heat transfer characteristics of supercritical CO2 in helically coiled tube at various inclination angles[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 116: 500-515. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.103 [9] LIU X X, XU X X, LIU C, et al. Heat transfer deterioration in helically coiled heat exchangers in trans-critical CO2 Rankine cycles[J]. Energy, 2018, 147: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.163 [10] LI Z H, ZHAI Y L, BI D P, et al. Orientation effect in helical coils with smooth and rib-roughened wall: Toward improved gas heaters for supercritical carbon dioxide Rankine cycles[J]. Energy, 2017, 140: 530-545. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.010 [11] YANG M, LI G R, LIAO F, et al. Numerical study of characteristic influence on heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in helically coiled tube with non-circular cross section[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 176: 121511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.121511 [12] LIU X X, XU X X, JIAO Y Z, et al. Flow structure with mixed turbulent flow of supercritical CO2 heated in helically coiled tube[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 189: 116684. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.116684 [13] LIU X X, XU X X, LIU C, et al. The effect of geometry parameters on the heat transfer performance of supercritical CO2 in horizontal helically coiled tube under the cooling condition[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2019, 106: 650-661. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2019.02.008 [14] ZHANG S J, XU X X, LIU C, et al. The buoyancy force and flow acceleration effects of supercritical CO2 on the turbulent heat transfer characteristics in heated vertical helically coiled tube[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 125: 274-289. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.04.033 [15] ZHANG S J, XU X X, LIU C, et al. The heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in helically coiled tube: Trade-off between curvature and buoyancy effect[J]. Energy, 2019, 176: 765-777. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.150 [16] XU X X, LIU C, DANG C B, et al. Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics of supercritical CO2 cooled in horizontal helically coiled tube[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2016, 67: 190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2016.03.010 [17] YANG M. Numerical study of the heat transfer to carbon dioxide in horizontal helically coiled tubes under supercritical pressure[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 109: 685-696. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.08.121 [18] ZHANG W, WANG S X, LI C D, et al. Mixed convective heat transfer of CO2 at supercritical pressures flowing upward through a vertical helically coiled tube[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 88: 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.10.031 [19] LI Z H, ZHAI Y L, LI K Z, et al. A quantitative study on the interaction between curvature and buoyancy effects in helically coiled heat exchangers of supercritical CO2 Rankine cycles[J]. Energy, 2016, 116: 661-676. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.005 [20] WANG K Z, XU X X, WU Y Y, et al. Numerical investigation on heat transfer of supercritical CO2 in heated helically coiled tubes[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2015, 99: 112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2015.02.001 [21] XU J L, YANG C Y, ZHANG W, et al. Turbulent convective heat transfer of CO2 in a helical tube at near-critical pressure[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 80: 748-758. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.09.066 [22] TAO Z, LI L W, ZHU J Q, et al. Numerical investigation on flow and heat transfer characteristics of supercritical RP-3 in inclined pipe[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(8): 1885-1894. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.05.007 [23] KIM D E, KIM M H. Experimental study of the effects of flow acceleration and buoyancy on heat transfer in a supercritical fluid flow in a circular tube[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2010, 240(10): 3336-3349. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2010.07.002 [24] ZHANG S J, XU X X, LIU C, et al. Experimental investigation of the heat transfer behaviors of CO2, propane and their binary non-azeotropic mixtures above critical pressure in helically coiled tube[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 180: 115842. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115842 [25] LI Y, CHEN Y Q, ZHANG Y C, et al. An improved heat transfer correlation for supercritical aviation kerosene flowing upward and downward in vertical tubes[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2020, 29(1): 131-143. doi: 10.1007/s11630-019-1197-2 -






 下载:
下载: