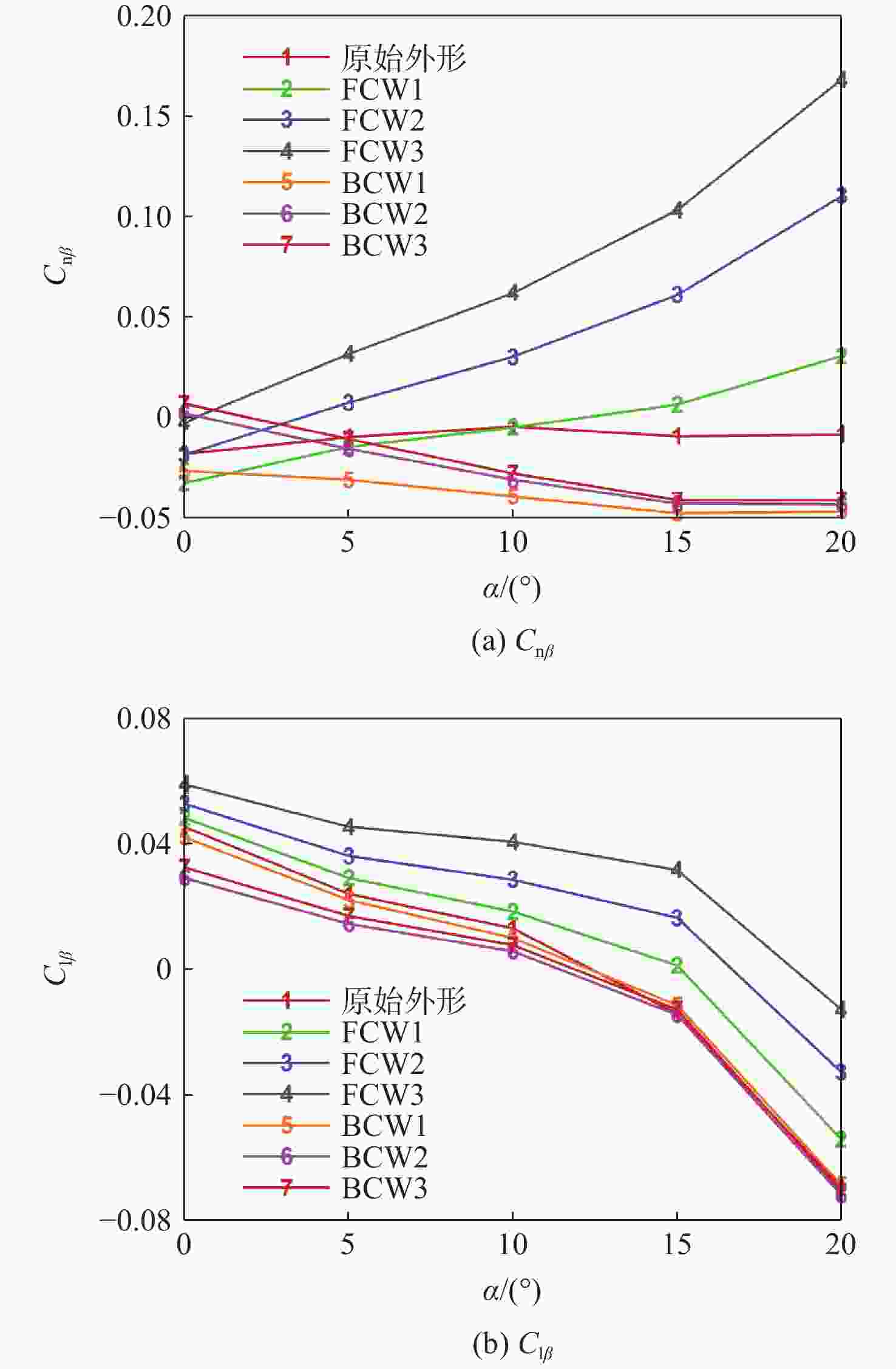
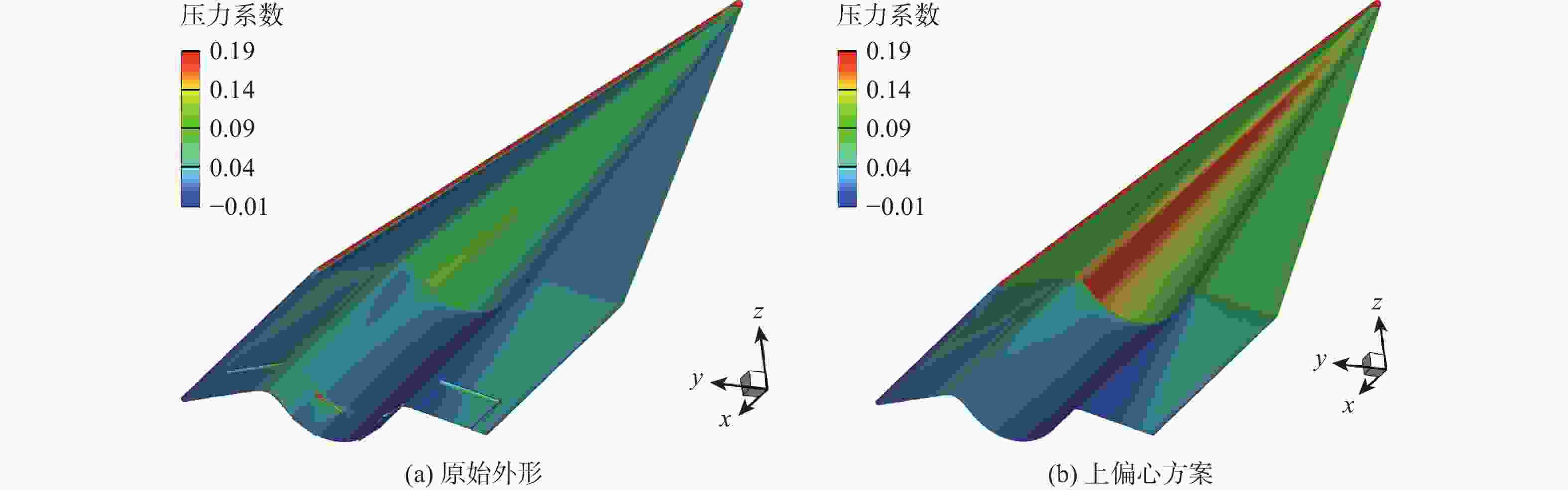
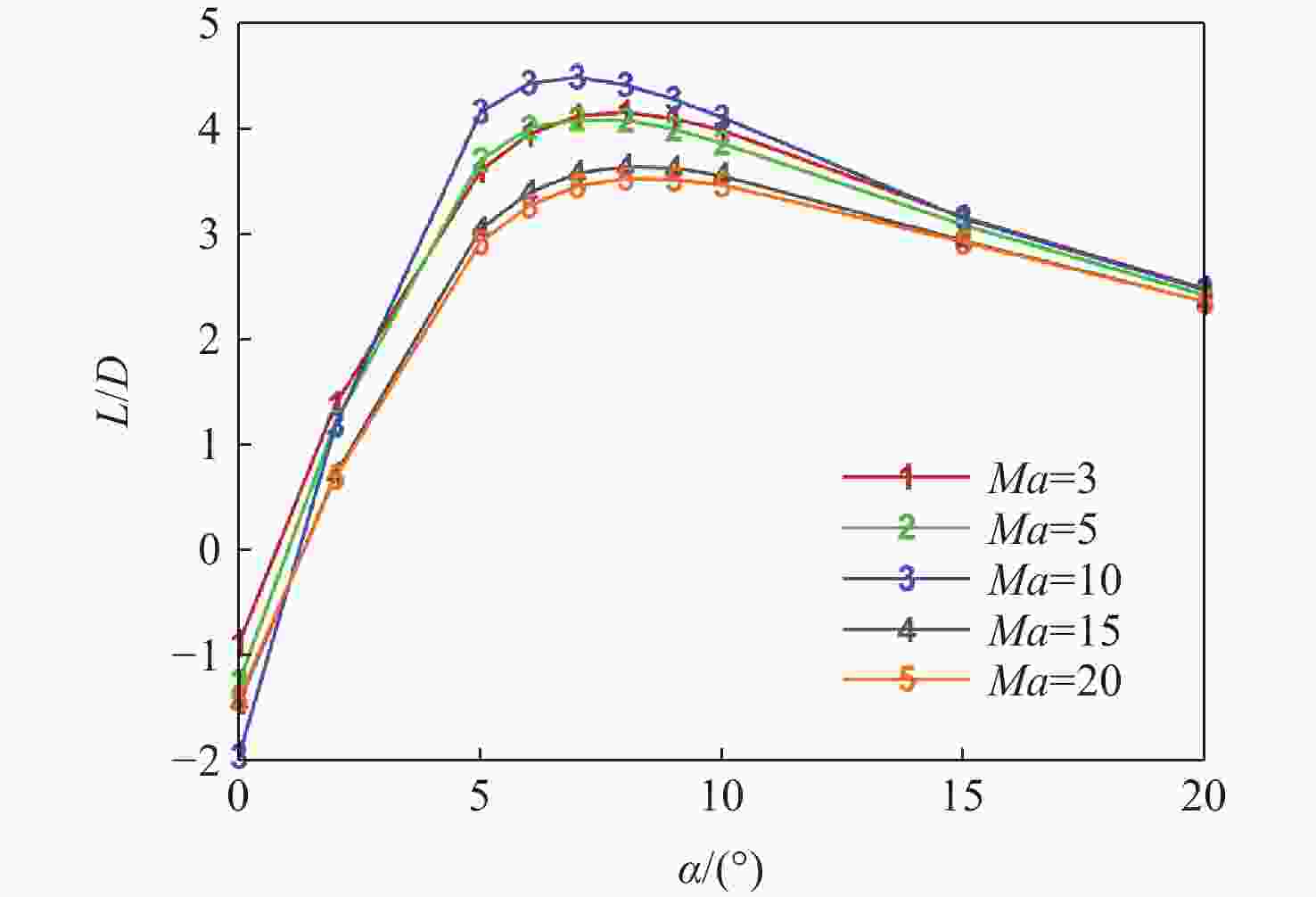
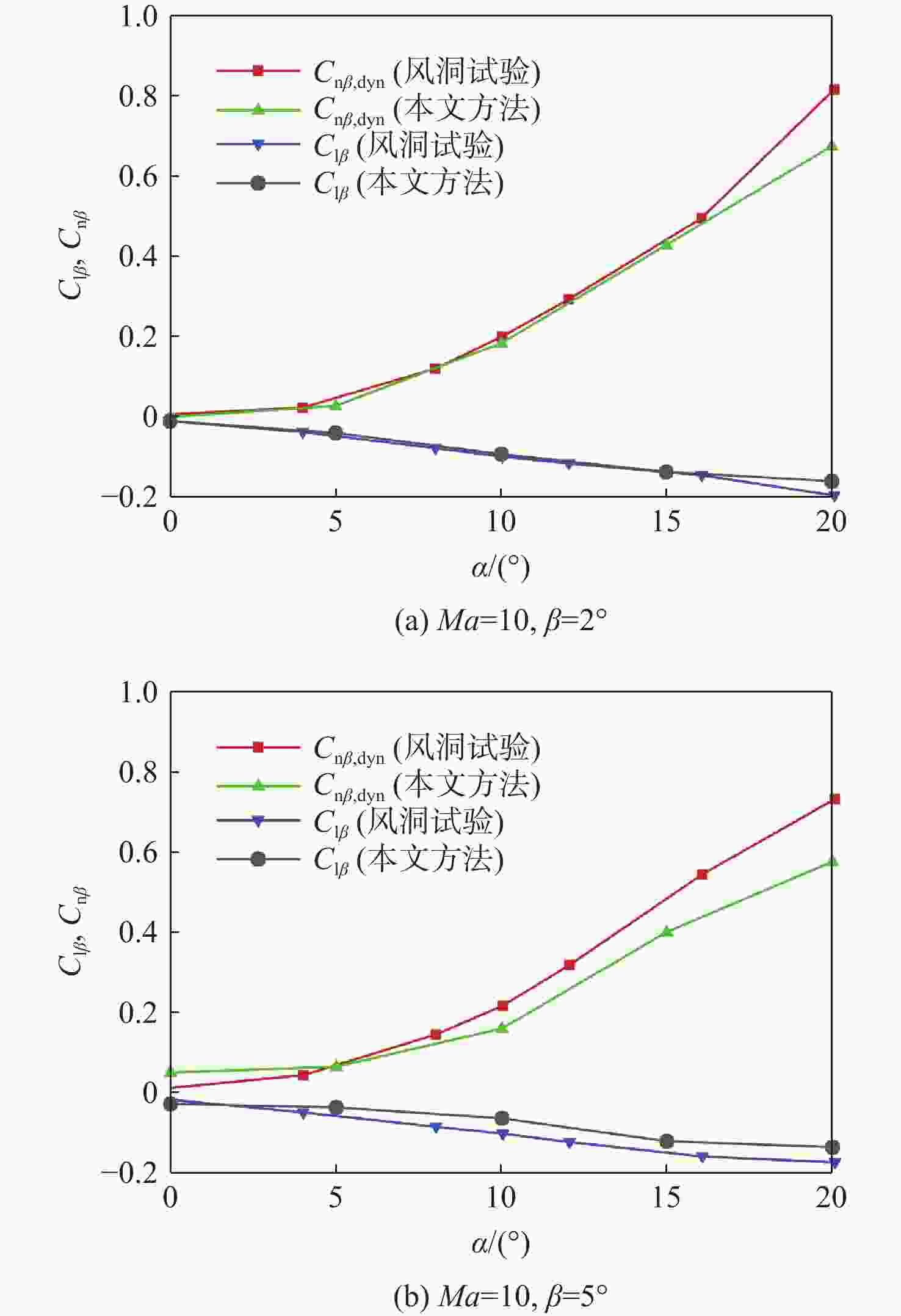
Study on lateral-directional stability of a practical high lift-to-drag ratio hypersonic vehicle with momentum lift augmentation
-
摘要:
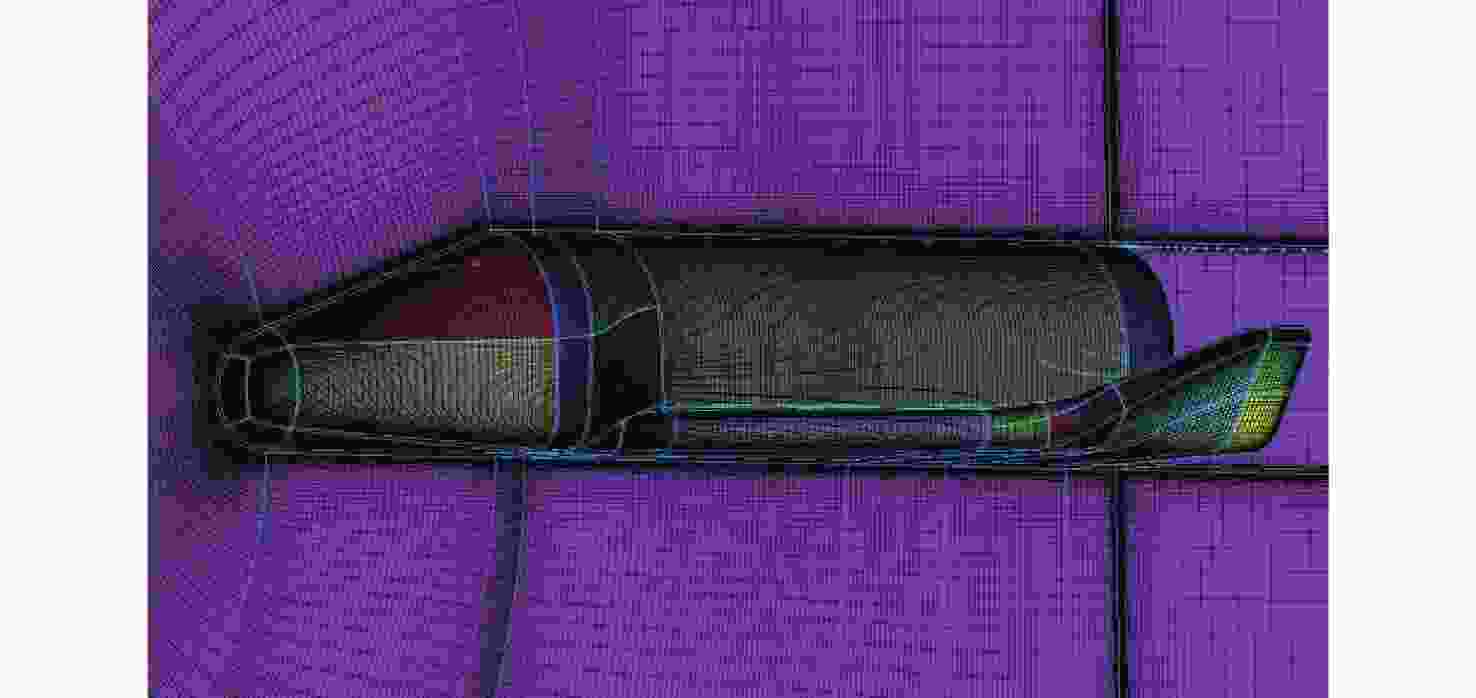
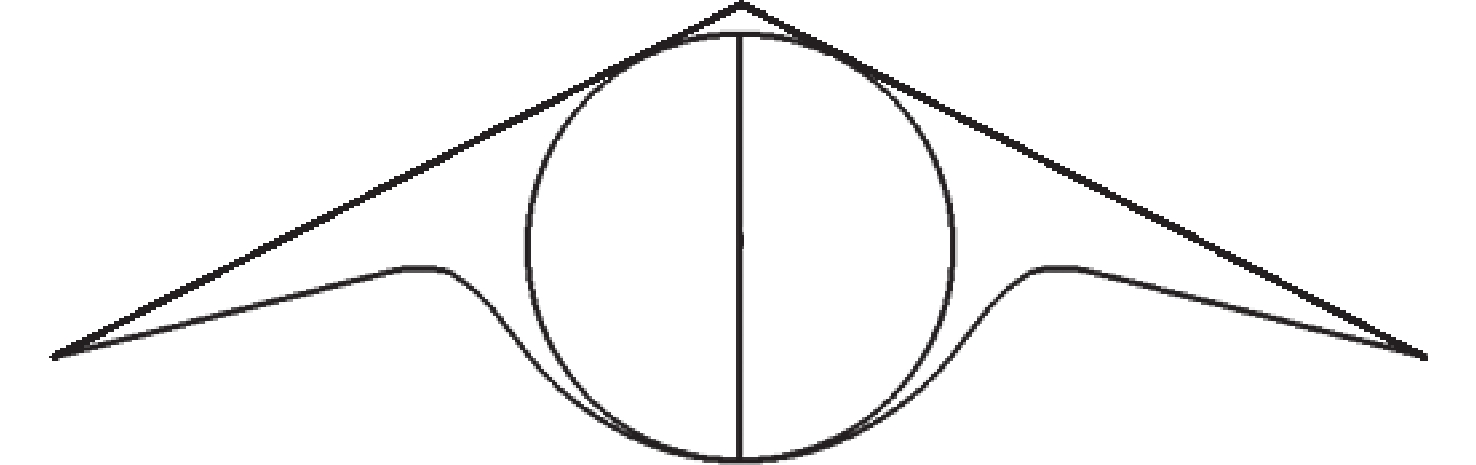
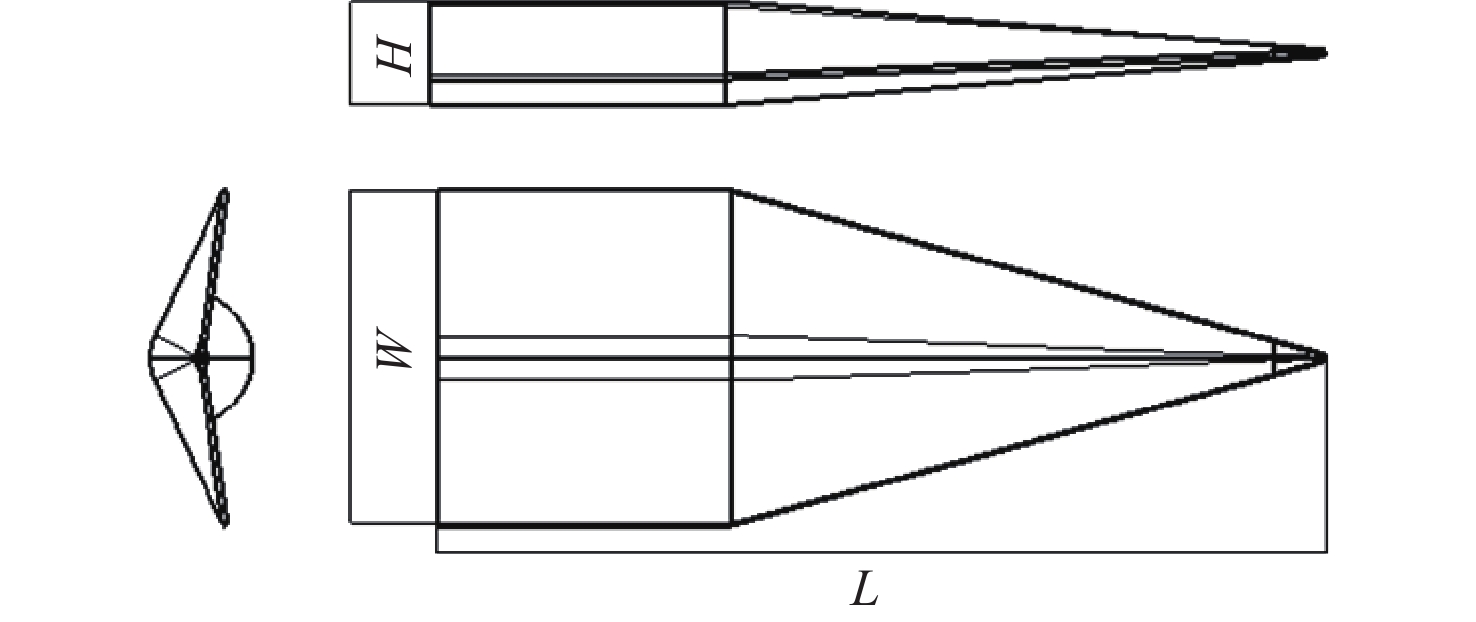
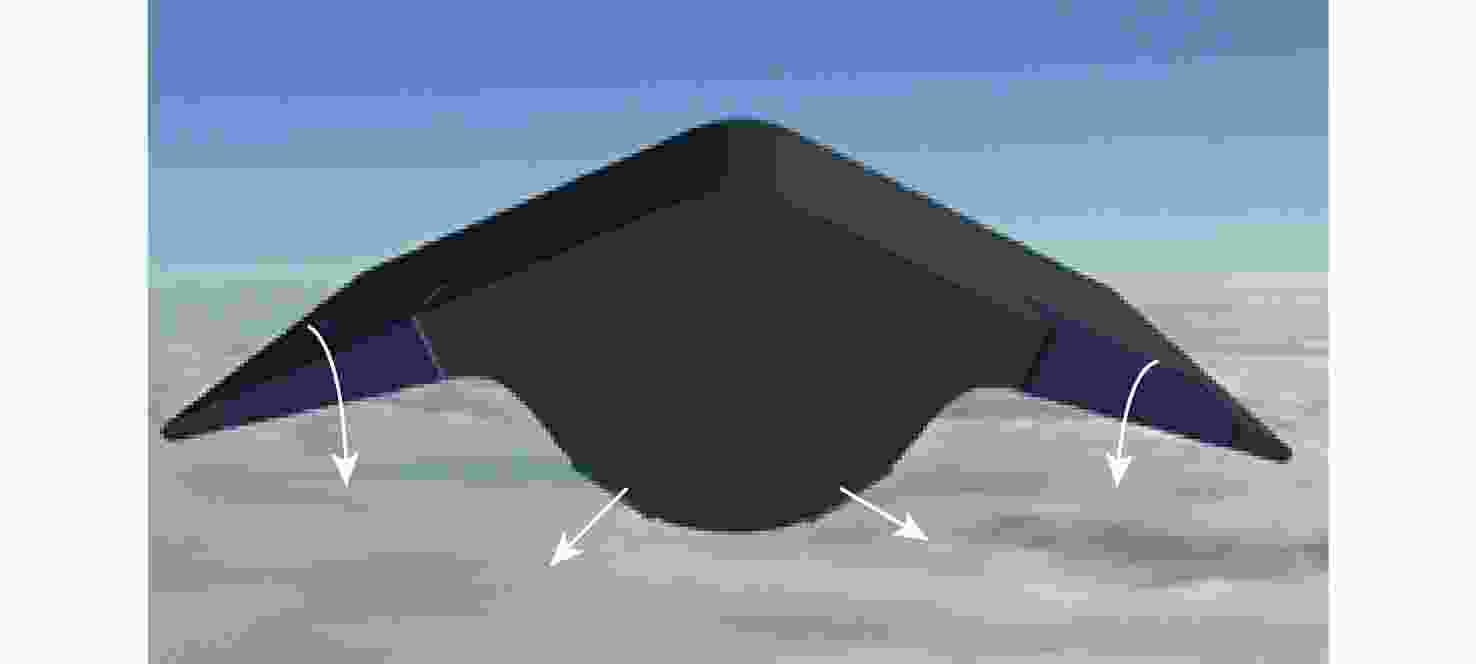
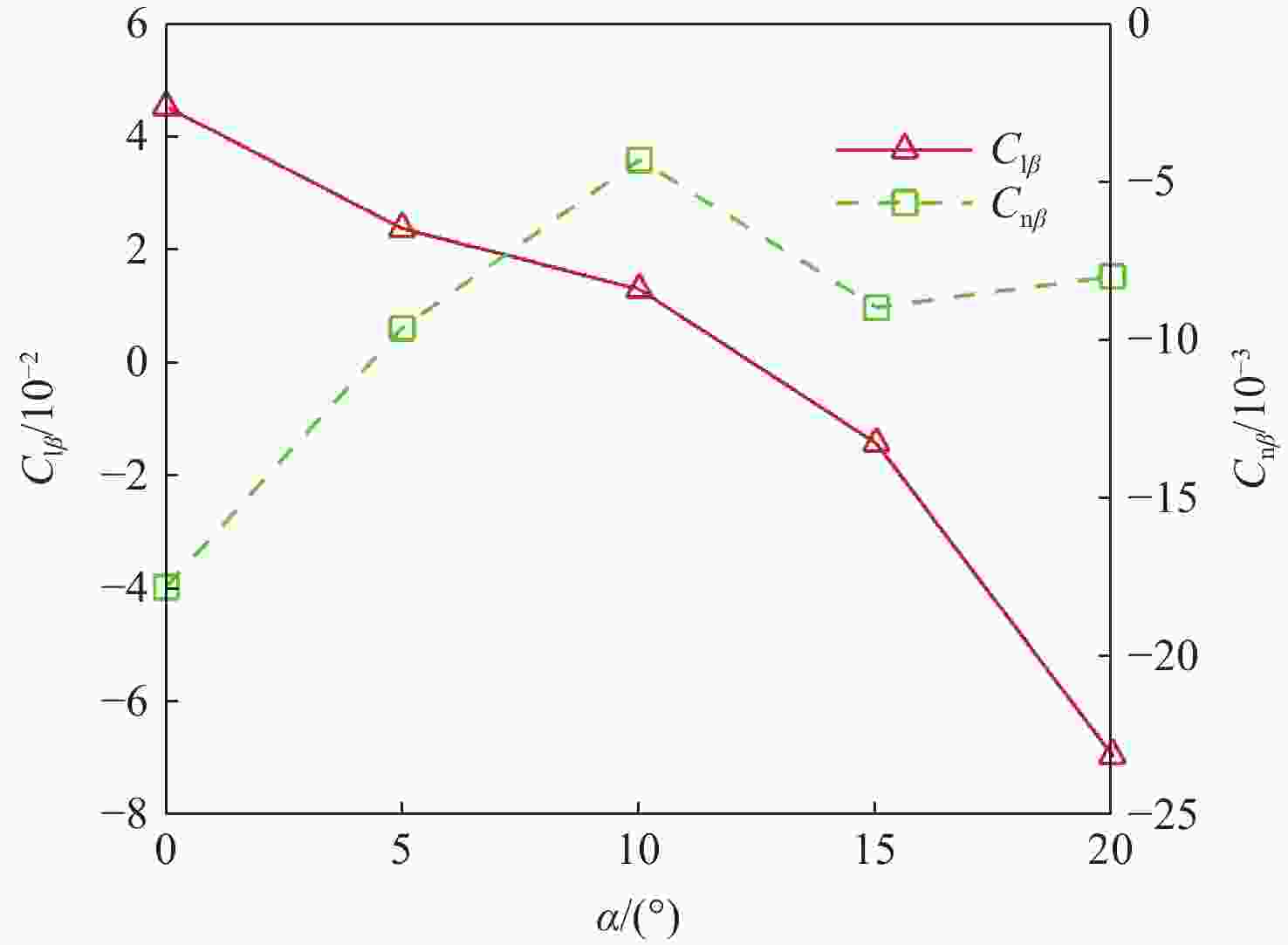
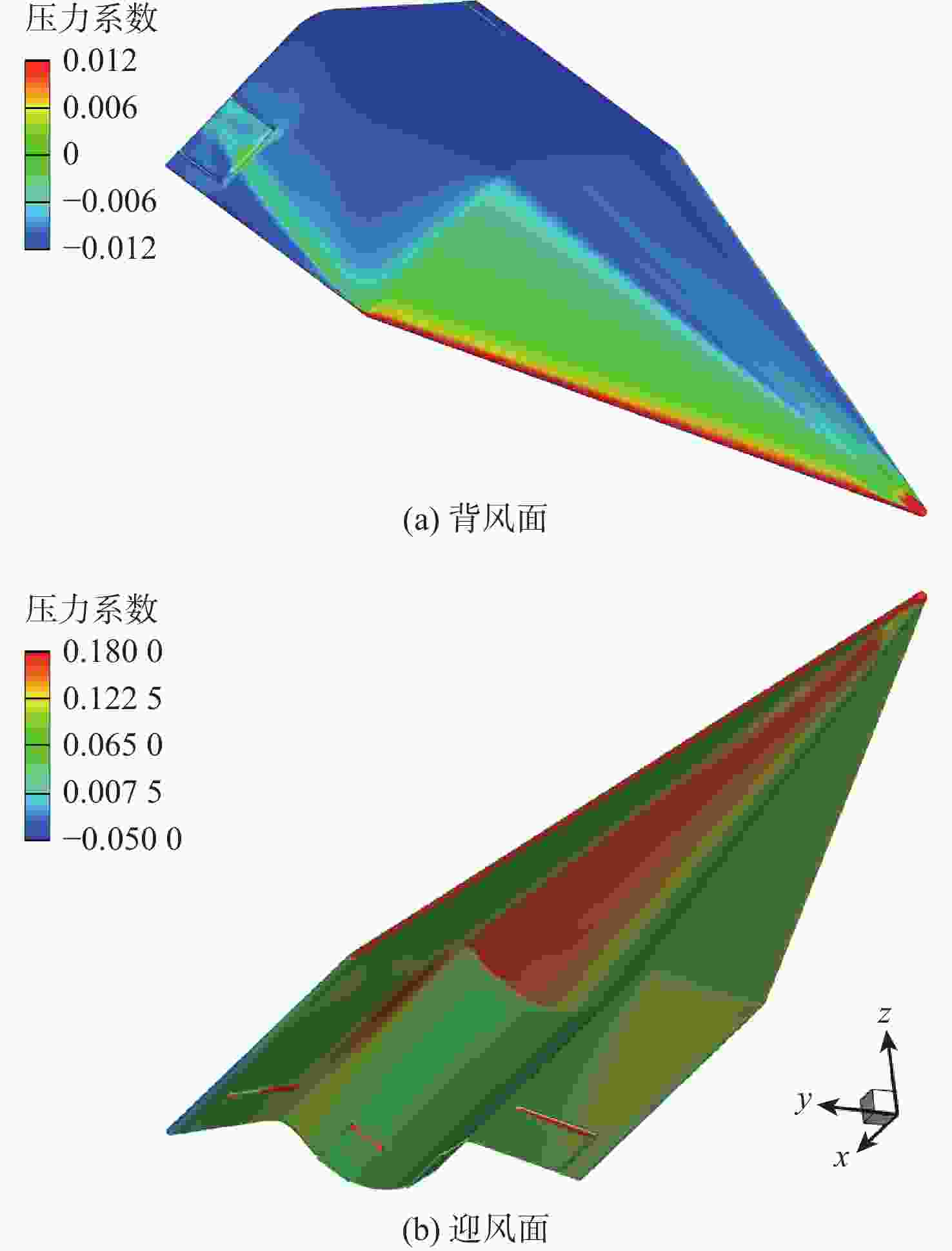
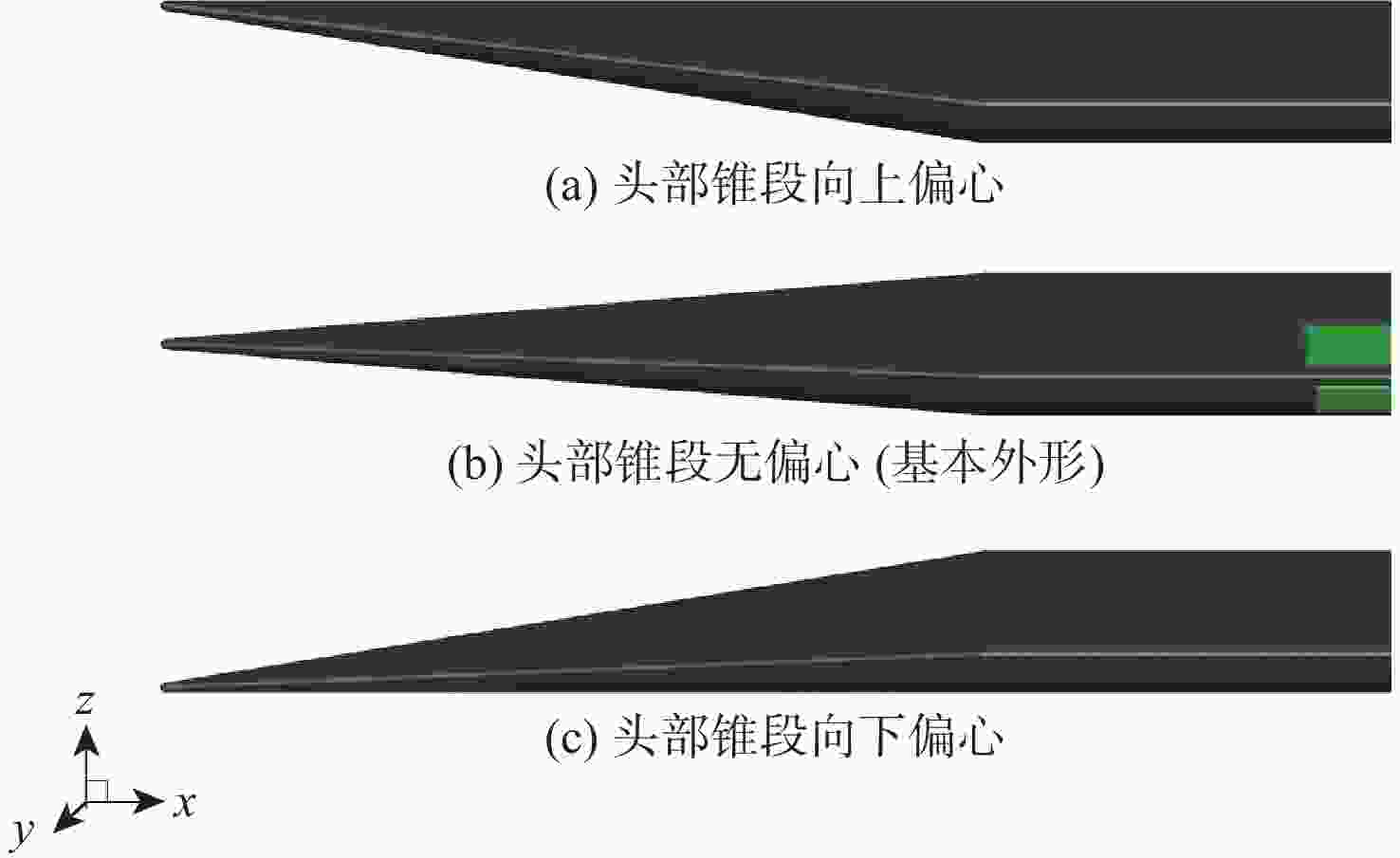
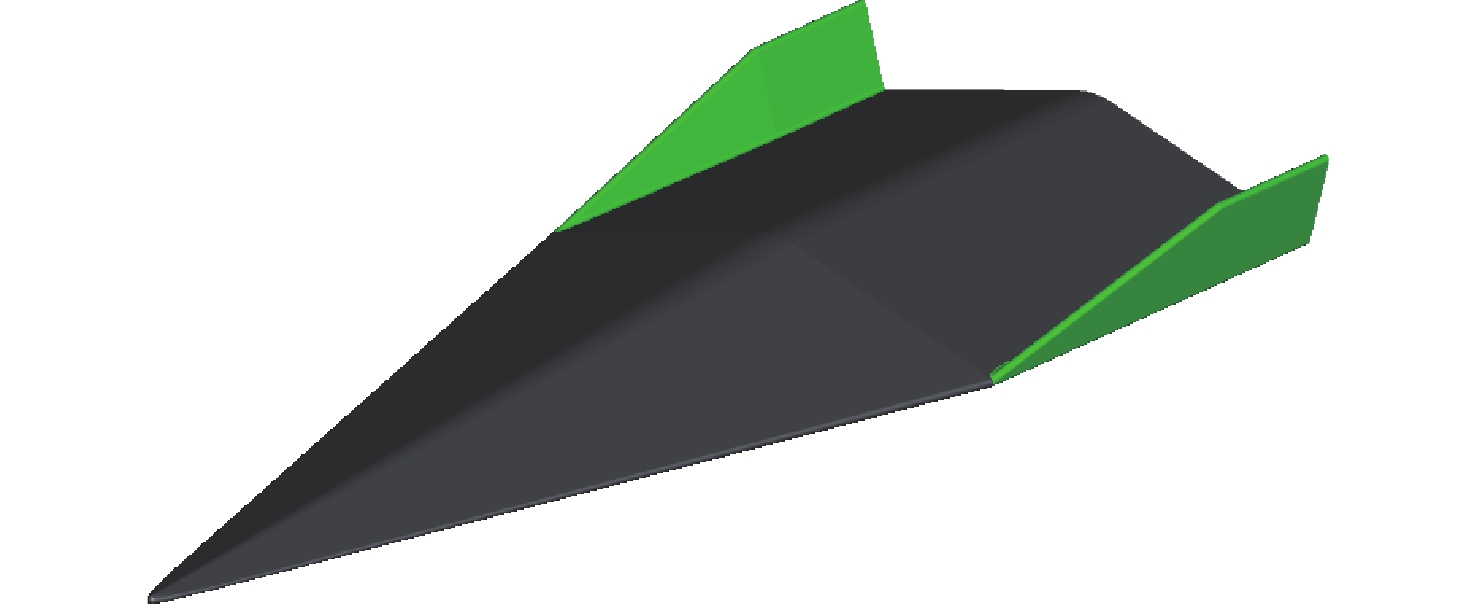
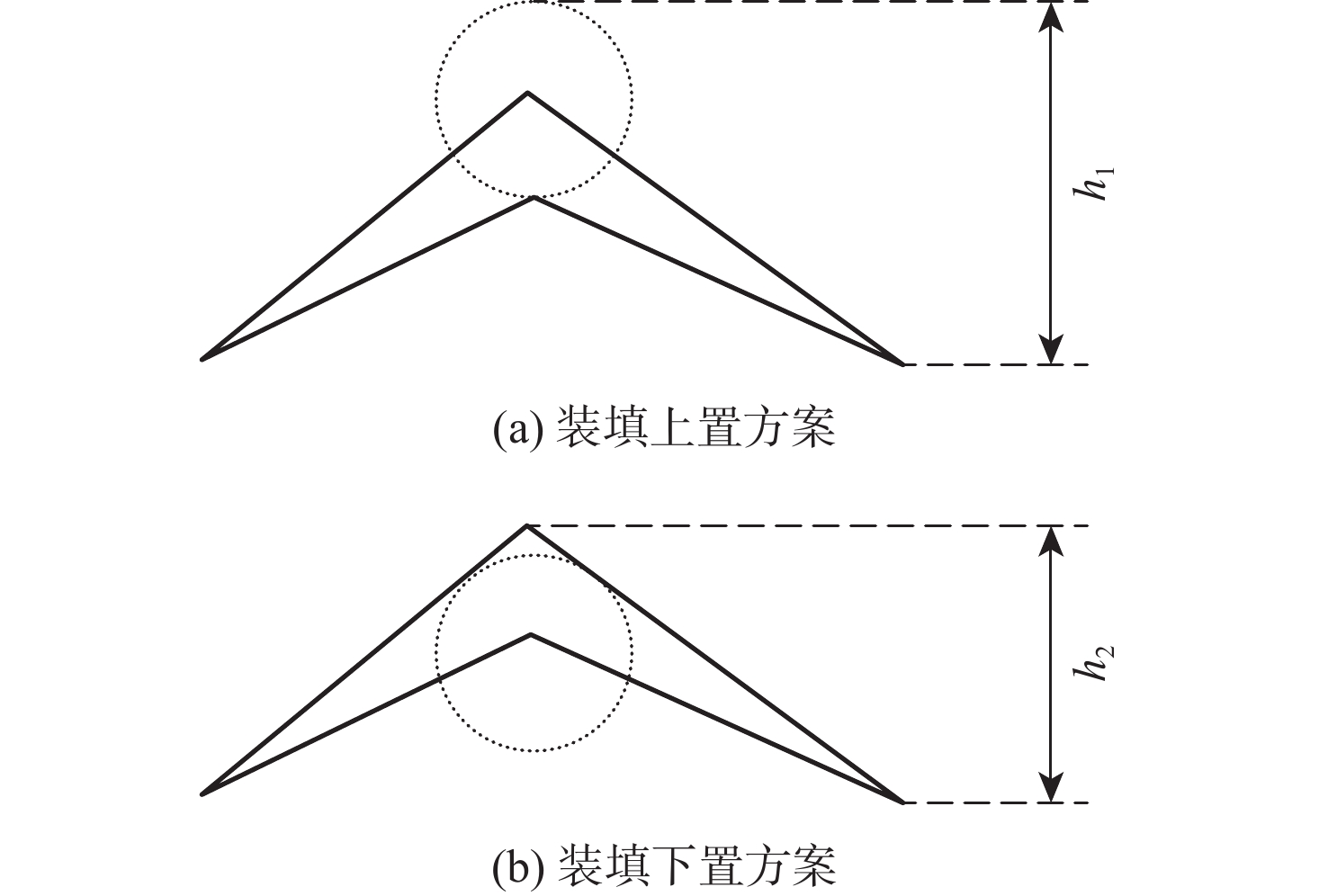
考虑高超声速飞行器装填、防热及操稳等多约束条件下的实用化设计需求,提出一种新型下反式高升阻比滑翔飞行器气动布局。借鉴乘波体飞行器的高升力设计方法及动量增升原理,该新型飞行器采用下反式后掠翼构型,上表面为光滑倒圆“Λ”形设计,下表面为内凹的装填空间,为尽可能避免长时间超远距离高超声速飞行带来的防热负担,采用后缘体襟翼及体侧扩张方向舵面设计。采用数值计算方法对所提布局思路进行验证分析,计算结果表明:在飞行高度为40 km,
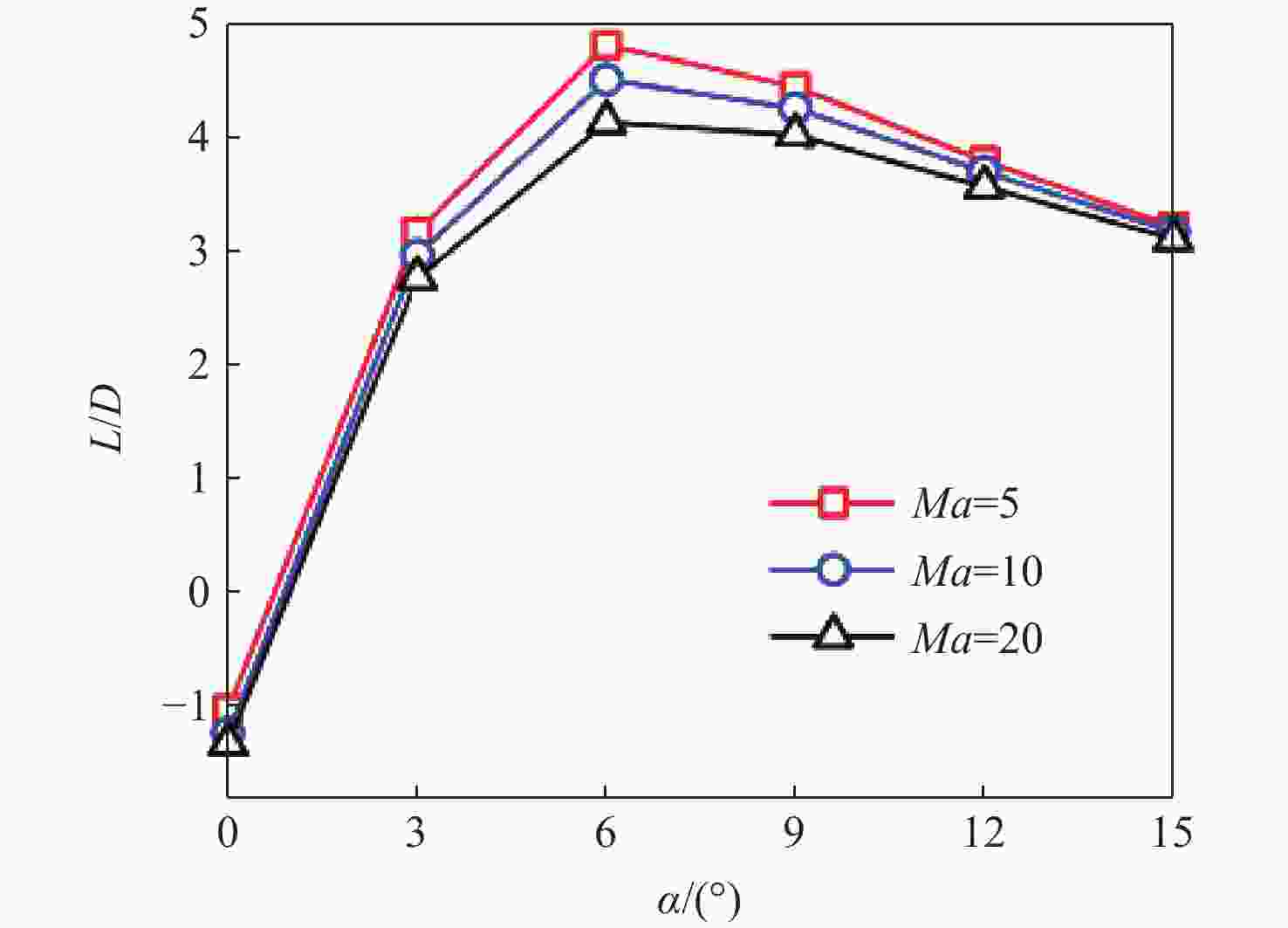
Ma =10的条件下升阻比可以达到4.48左右,在一定迎角范围内均具备很高的气动效率,验证了所提布局的有效性。同时重点针对所提布局共性的横航向稳定性问题基于数值模拟方法探讨了3种不同优化改进方案的效果及可行性,并采用风洞试验对两侧翼梢V尾的控制方案进行横航向稳定性控制效果的试验验证,结果表明:采用两侧翼梢V尾的控制方案是实现横航向稳定性控制的较优方案。Abstract:A new aerodynamic configuration concept for a hypersonic vehicle with a high lift-to-drag ratio is proposed to satisfy the constantly increasing practicability multi-constraints of high volumetric efficiency, control and stability, and acceptable thermal protection. The design principles of this practical configuration is inspired by the wave-rider design idea and momentum principle which incorporates inverted dihedral with an aft-sweeping wing, caret upper surface, and con-cavity lower surface are elaborated. A trailing edge flap and a body-fitted expansion rudder were used in place of the standard control surface's leading edge to prevent excessive heat flow during the prolonged hypersonic flight. The aerodynamic characteristics of this new configuration were obtained and discussed by applying numerical simulation with Navier-Stokes equations and wind tunnel test. The results show that the delta wing with a caret upper surface and concavity bottom surface can generate highly compressed air beneath the vehicle and reduce the loss of lifting pressure. The maximum lift-to-drag ratio achieves nearly 4.48 at
Ma =10 and 40Km altitude and maintains well at a wide range of angles of attack. At the same time, the effects and feasibility of three different optimization schemes are discussed based on the numerical simulation method, aiming at the common lateral and directional stability problem of the proposed configuration, and the wind tunnel test is used to verify the lateral and directional stability control effect of the scheme with two V winglets.The results show that the control scheme with two V winglets is the better scheme to realize the lateral and directional stability. -
-
[1] MOSES P L, RAUSCH V L, NGUYEN L T, et al. NASA hypersonic flight demonstrators—overview, status, and future plans[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2004, 55(3): 619-630. [2] MANSOUR N, PITTMAN J, OLSON L. Fundamental aeronautics hypersonics project: Overview[C]//Proceedings of the 39th AIAA Thermophysics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2007. [3] WHITMORE S, DUNBAR B. Orbital space plane: Past, present, and future[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA International Air and Space Symposium and Exposition: The Next 100 Years. Reston: AIAA, 2003. [4] WEILAND C. Aerodynamic data of space vehicles[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2014. [5] 唐伟, 冯毅, 杨肖峰, 等. 非惯性弹道飞行器气动布局设计实践[J]. 气体物理, 2017, 2(1): 1-12.TANG W, FENG Y, YANG X F, et al. Practices of aerodynamic configuration design for non-ballistic trajectory vehicles[J]. Physics of Gases, 2017, 2(1): 1-12(in Chinese). [6] ANDERSON J, LEWIS M. Hypersonic waveriders—where do we stand? [C]//Proceedings of the 31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 1993. [7] 高清, 赵俊波, 李潜. 类HTV-2横侧向稳定性研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(6): 657-662.GAO Q, ZHAO J B, LI Q. Study on lateral-directional stability of HTV-2 like configuration[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(6): 657-662(in Chinese). [8] 高清, 李潜. 美国高超声速飞行器横侧向稳定性研究[J]. 飞航导弹, 2012(12): 14-18.GAO Q, LI Q. Study on lateral stability of American hypersonic vehicle[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2012(12): 14-18(in Chinese). [9] 鲍文, 姚照辉. 综合离心力/气动力的升力体高超声速飞行器纵向运动建模研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2009, 30(1): 128-133.BAO W, YAO Z H. Study on longitudinal modeling for integrated centrifugal/aero force lifting-body hypersonic vehicles[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2009, 30(1): 128-133(in Chinese). [10] 马辉, 袁建平, 方群. 吸气式高超声速飞行器动力学特性分析[J]. 宇航学报, 2007, 28(5): 1100-1104.MA H, YUAN J P, FANG Q. Dynamics analysis of air-breathing hypersonic vehicle[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2007, 28(5): 1100-1104(in Chinese). [11] 闵昌万. 高超声速飞行器横侧向气动布局准则研究[J]. 宇航总体技术, 2018, 2(3): 1-10.MIN C W. The aerodynamic configuration criteria for the lateral-directional stability of hypersonic vehicle[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology, 2018, 2(3): 1-10(in Chinese). [12] LUNAN D A. Waverider, a revised chronology[C]//Proceedings of the 20th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2015. [13] NONWEILER T R F. Aerodynamic problems of manned space vehicles[J]. The Journal of the Royal Aeronautical Society, 1959, 63(585): 521-528. doi: 10.1017/S0368393100071662 [14] JONES J G, MOORE K C, PIKE J, et al. A method for designing lifting configurations for high supersonic speeds, using axisymmetric flow fields[J]. Ingenieur-Archiv, 1968, 37(1): 56-72. doi: 10.1007/BF00532683 [15] CORDA S, ANDERSON J. Viscous optimized hypersonic waveriders designed from axisymmetric flow fields[C]//Proceedings of the 26th Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 1988. [16] LYU Y C, JIANG C W, GAO Z X, et al. Passive waverider method and its validation[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2014 Conference and Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2014. [17] 刘荣健, 白鹏. 基于超声速有益干扰原理的气动构型概念综述[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(9): 023784.LIU R J, BAI P. Concept of aerodynamic configuration based on supersonic favorable interference principle: review[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(9): 023784(in Chinese). [18] EGGERS A J, SYVERTSON C A. Aircraft configurations developing high lift-drag ratios at high supersonic speeds: NACA-RM-A55L05 [R]. Washing, D. C. : NASA, 1956. [19] WILLIAM H, ALBAN III, KARL H, et al. Aerodynamic re-entry vehicle control with active and passive yaw flaps: USA, 7611095[P]. 2009-11-03. [20] 唐伟, 李为吉, 高晓成, 等. 削面/配平翼飞行器的气动计算及分析[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2004, 22(5): 541-544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2004.05.001TANG W, LI W J, GAO X C, et al. Aerodynamic prediction and analysis for a reentry vehicle with slice-ailerons[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2004, 22(5): 541-544(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2004.05.001 [21] 桂业伟, 刘磊, 代光月, 等. 高超声速飞行器流-热-固耦合研究现状与软件开发[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(7): 020844.GUI Y W, LIU L, DAI G Y, et al. Research status of hypersonic vehicle fluid-thermal-solid coupling and software development[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(7): 020844(in Chinese). [22] 刘磊, 代光月, 曾磊, 等. 气动力/热与结构多场耦合试验模型方案初步设计[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(11): 221165.LIU L, DAI G Y, ZENG L, et al. Preliminary test model design of fluid-thermal-structural interaction problems[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(11): 221165(in Chinese). [23] 邱波, 张昊元, 国义军, 等. 高超声速飞行器表面横缝旋涡结构及气动热环境数值模拟[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(11): 3515-3521.QIU B, ZHANG H Y, GUO Y J, et al. Numerical investigation for vortexes and aerodynamic heating environment on transverse gap on hypersonic vehicle surface[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(11): 3515-3521(in Chinese). [24] 张昊元, 宗文刚, 桂业伟. 高超声速飞行器前缘缝隙流动数值模拟研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(8): 893-900. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2014.08.005ZHANG H Y, ZONG W G, GUI Y W. Numerical investigation of flow in leading-edge gap of hypersonic vehicle[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(8): 893-900(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2014.08.005 [25] 李素循. 典型外形高超声速流动特性[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007.LI S X. Hypersonic flow characteristics of typical shape[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2007 (in Chinese). [26] 李海燕. 高超声速高温气体流场的数值模拟[D]. 绵阳: 中国空气动力研究与发展中心, 2007.LI H Y. Numerical simulation of hypersonic and high temperature gas flowfields[D]. Mianyang : China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center, 2007. [27] 丁峰. 吸气式高超声速飞行器内外流一体化“全乘波”气动设计理论和方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016.DING F. Research of a novel airframe/inlet integrated full-waverider aerodynamic design methodology for air-breathing hypersonic vehicles[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016 (in Chinese). [28] 陈冰雁, 徐国武. 临近空间高升阻比布局高速气动性能对比[J]. 力学季刊, 2014, 35(3): 464-472.CHEN B Y, XU G W. Comparison of aerodynamic characteristic of near space high lift-drag ratio configuration[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 464-472(in Chinese). [29] 唐伟. 新一代航天机动飞行器气动设计研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2005.TANG W. Aerodynamic design study for new generation aeronautical maneuverable vehicle[D]. Xi’an : Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2005. [30] 马强, 唐伟, 张鲁民. 带控制舵双锥体气动力工程计算方法研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2003, 24(6): 552-554. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2003.06.002MA Q, TANG W, ZHANG L M. Engineering prediction method for aerodynamics of biconic vehicle with flaps[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2003, 24(6): 552-554(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2003.06.002 [31] 唐伟, 张勇, 李为吉, 等. 二次曲线截面弹身的气动设计及优化[J]. 宇航学报, 2004, 25(4): 429-433.TANG W, ZHANG Y, LI W J, et al. Aerodynamic design and optimization for vehicles with conic cross section[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2004, 25(4): 429-433(in Chinese). [32] FENG Y, TANG W, GUI Y W. Aerodynamic configuration optimization by the integration of aerodynamics, aerothermodynamics and trajectory for hypersonic vehicles[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(33): 4608-4615. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0534-9 -







 下载:
下载: