-
摘要:
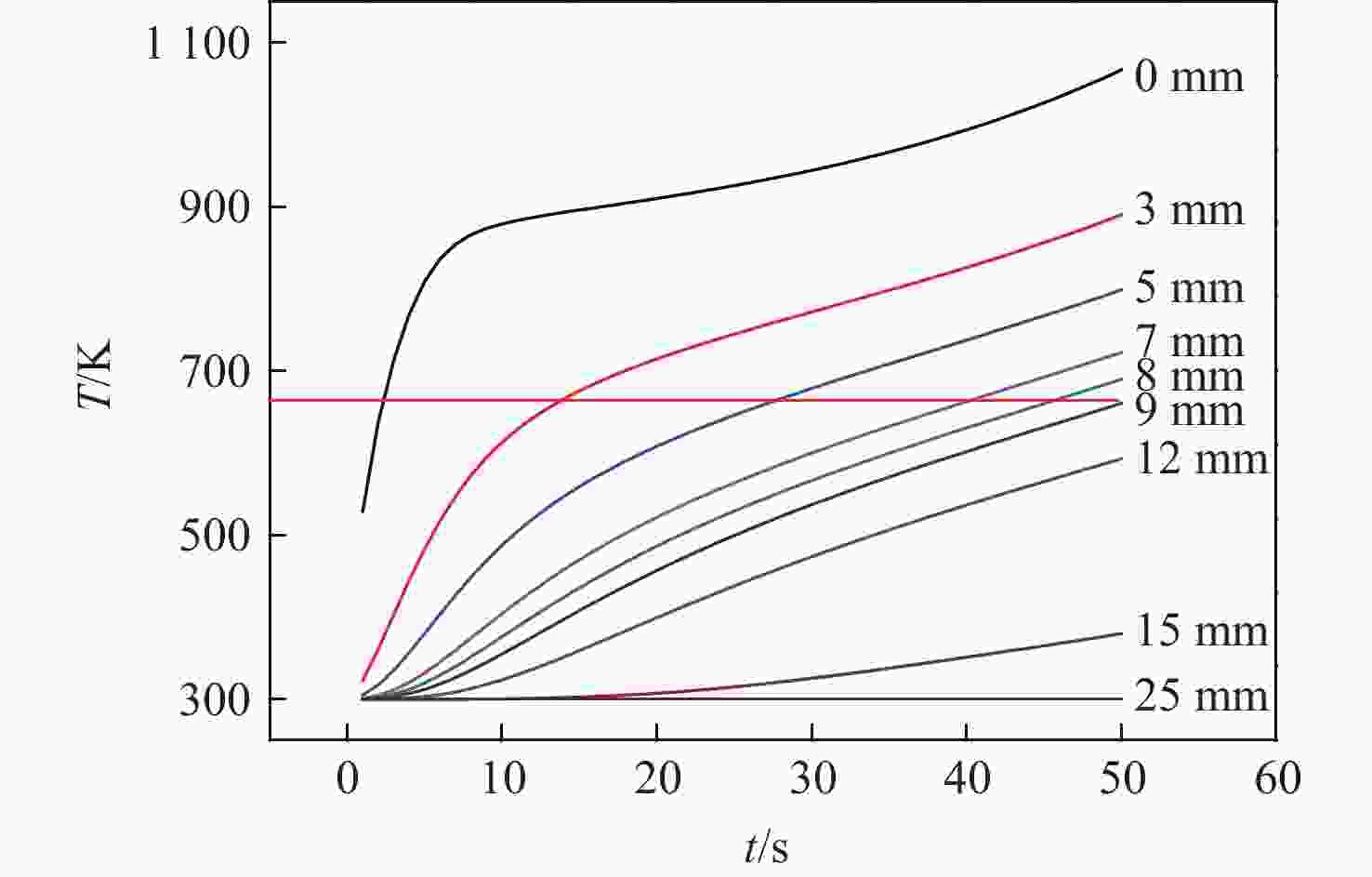
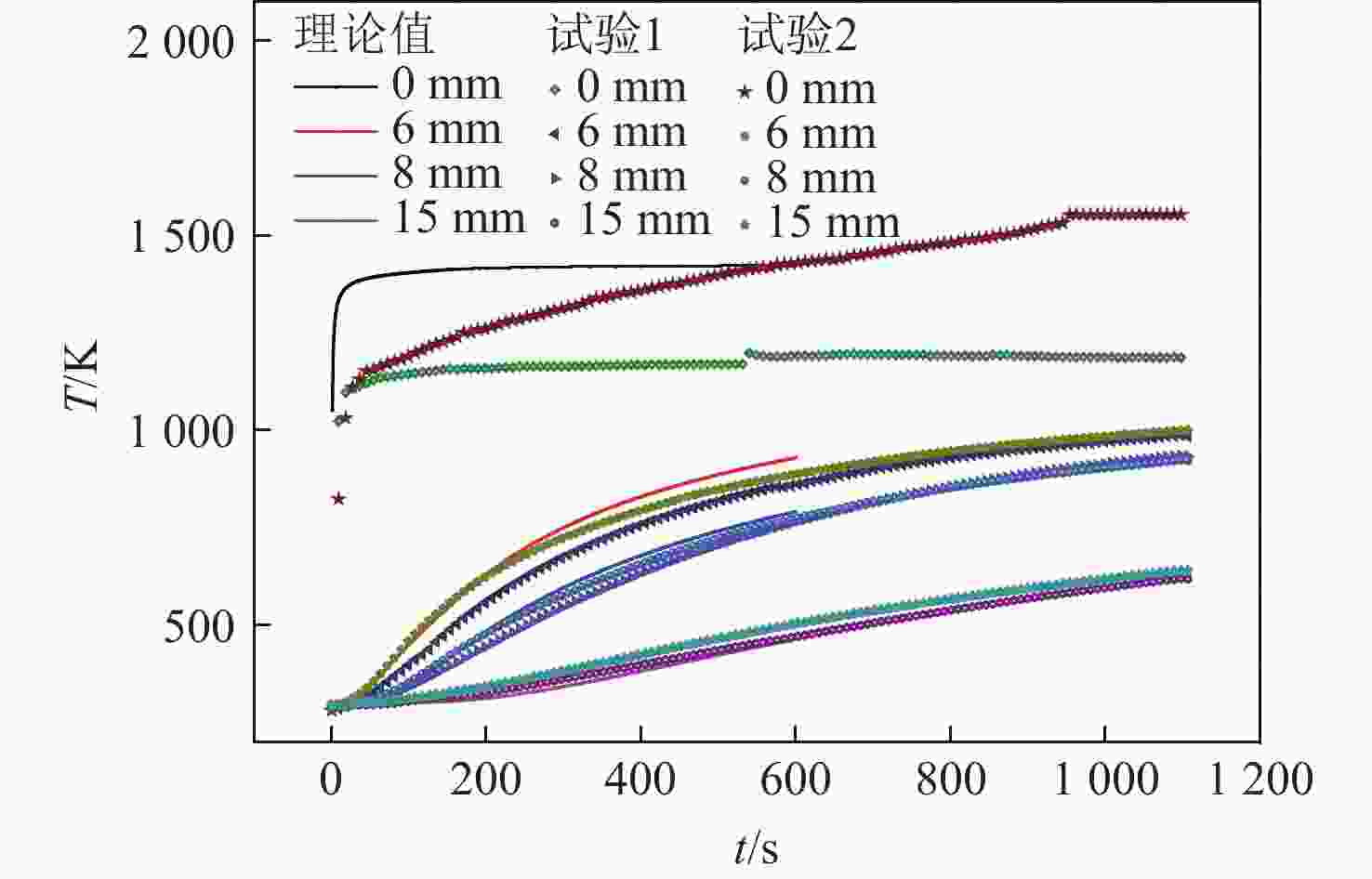
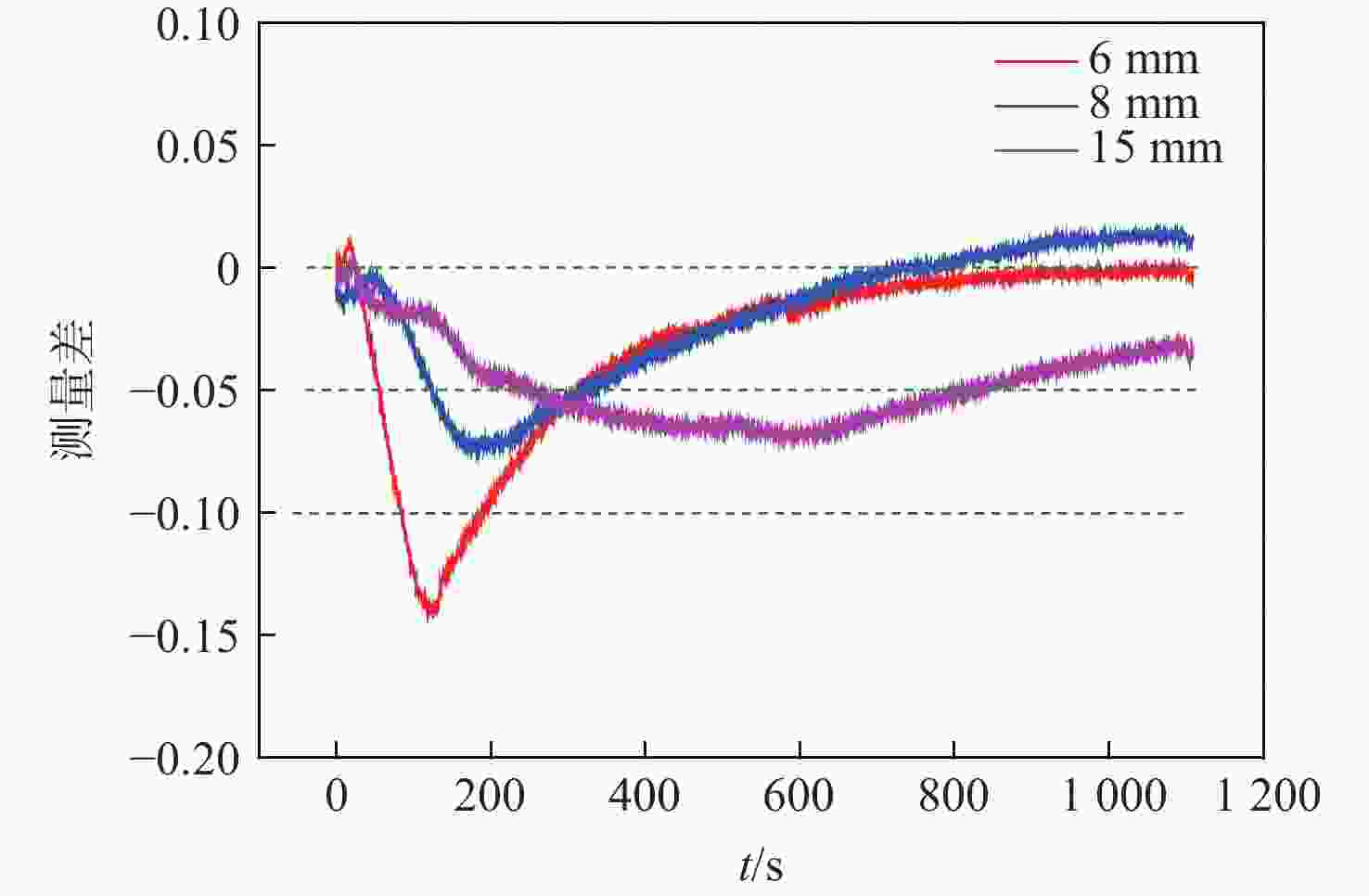
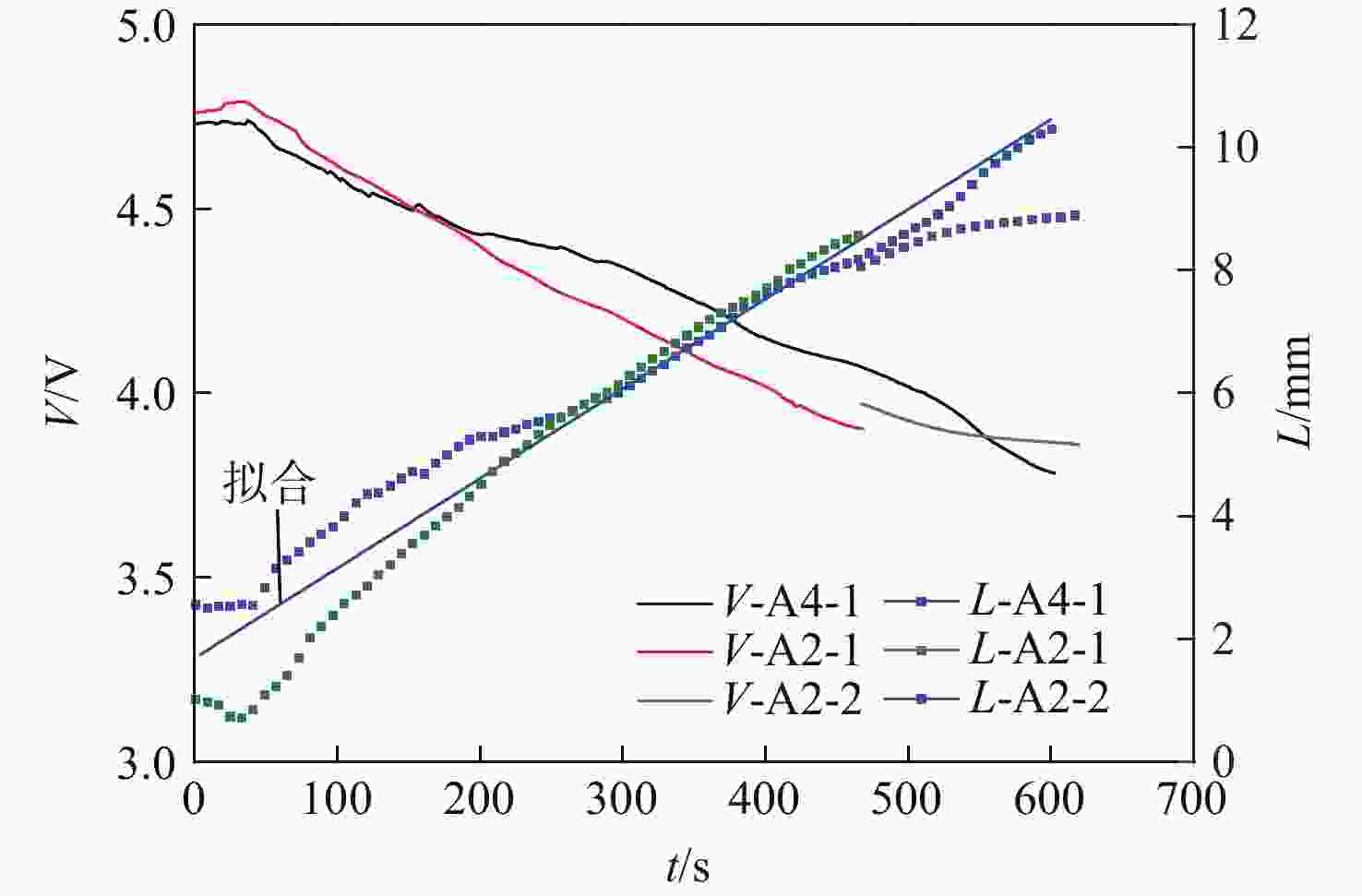
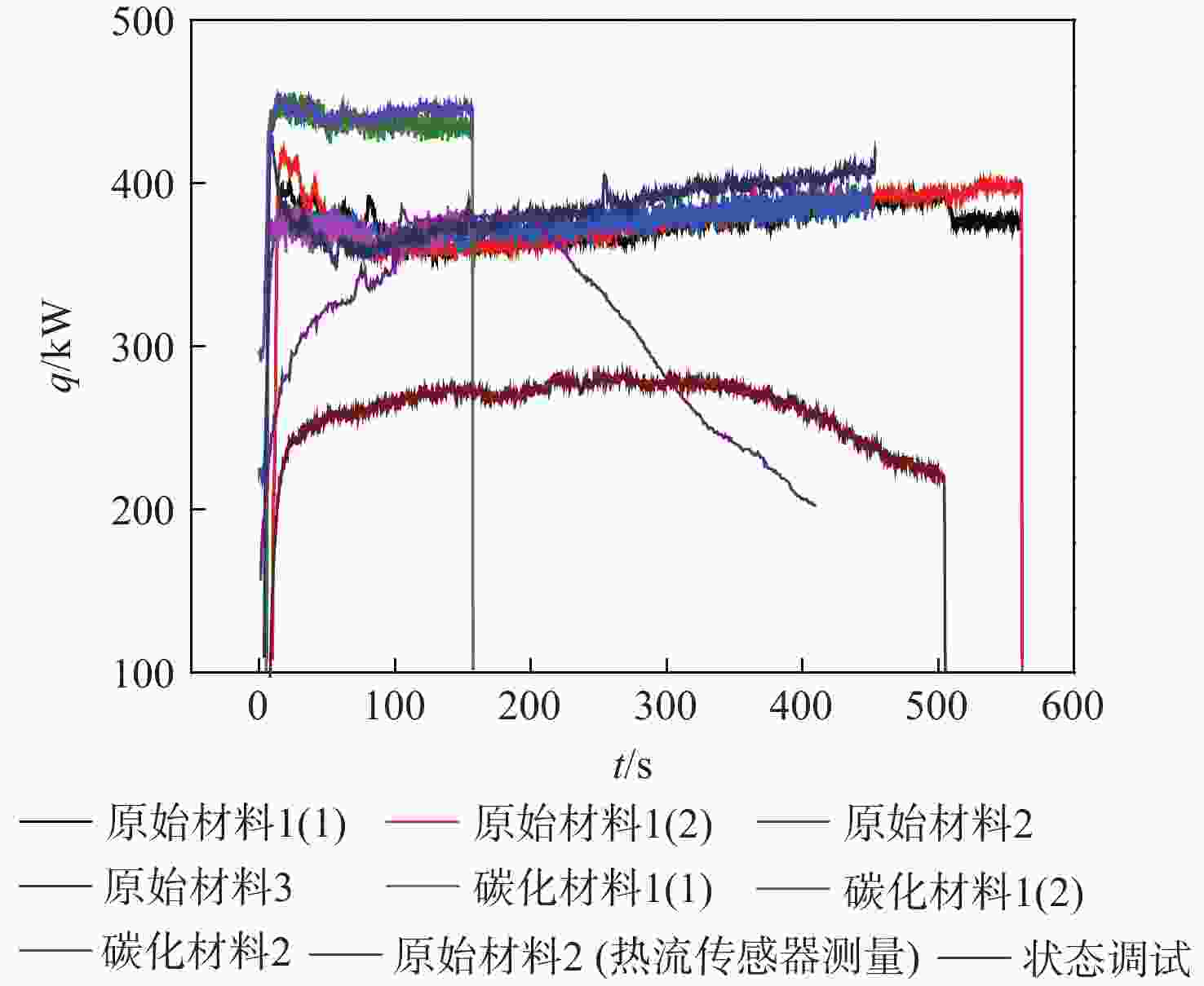
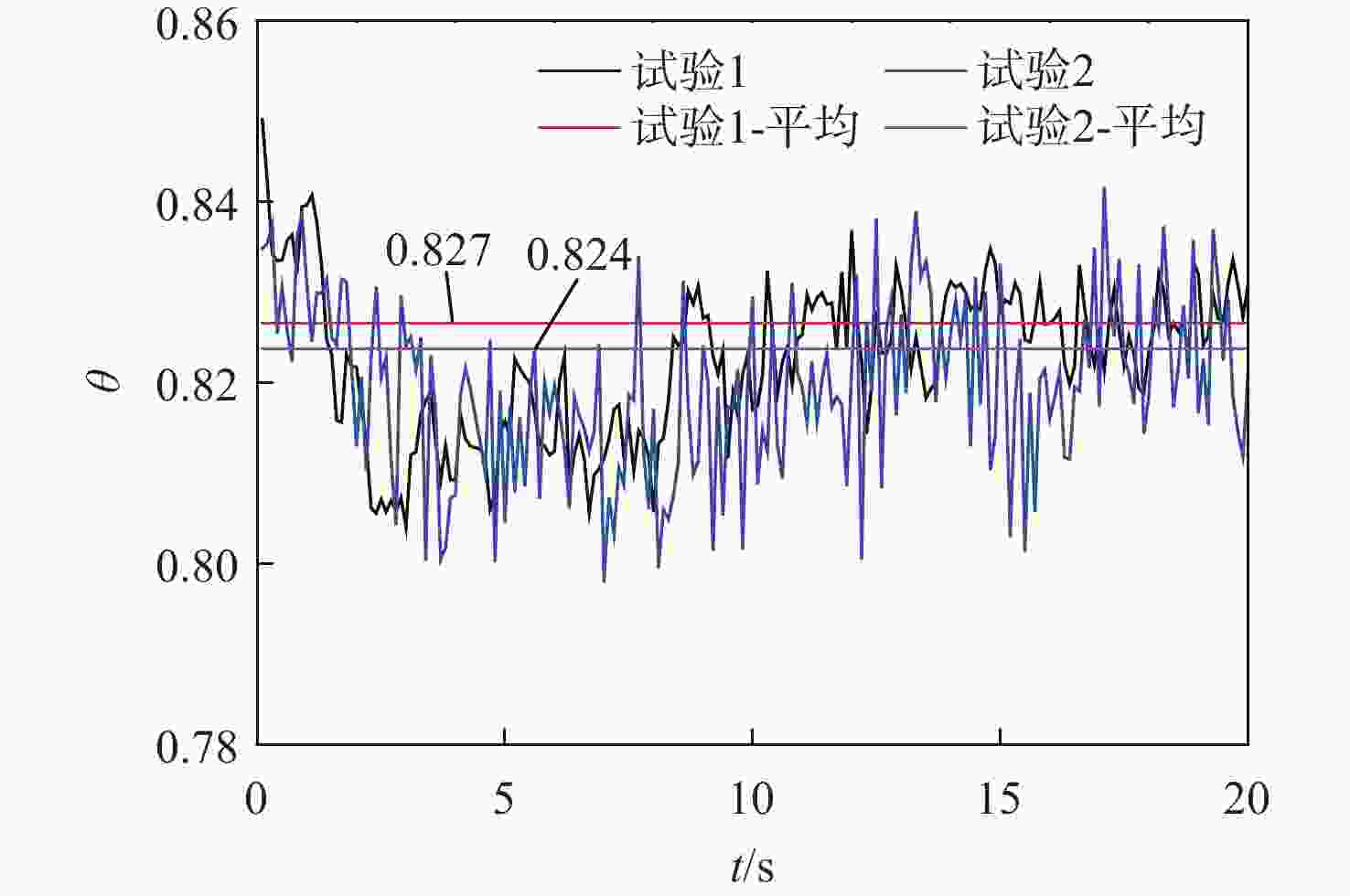
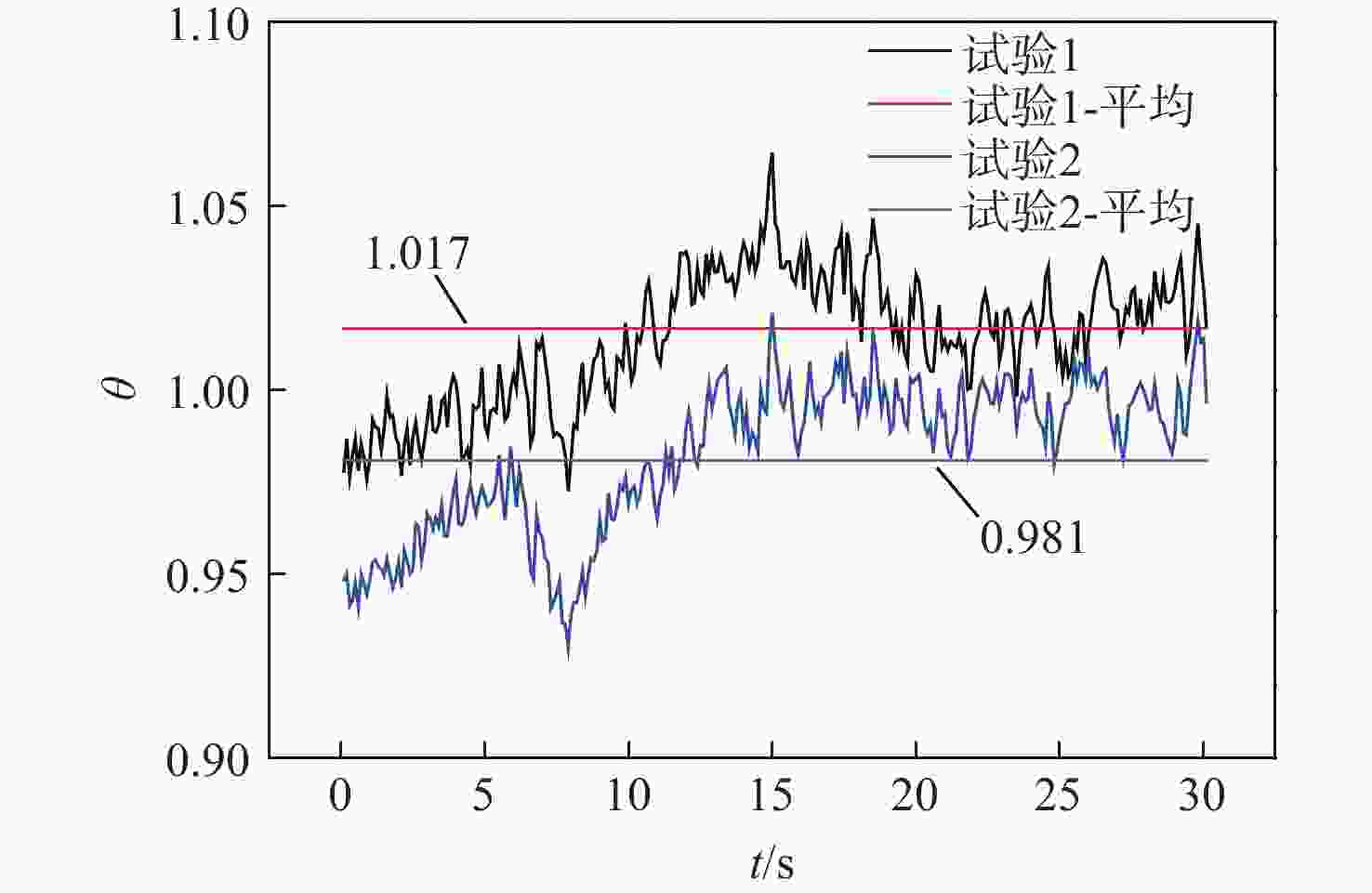
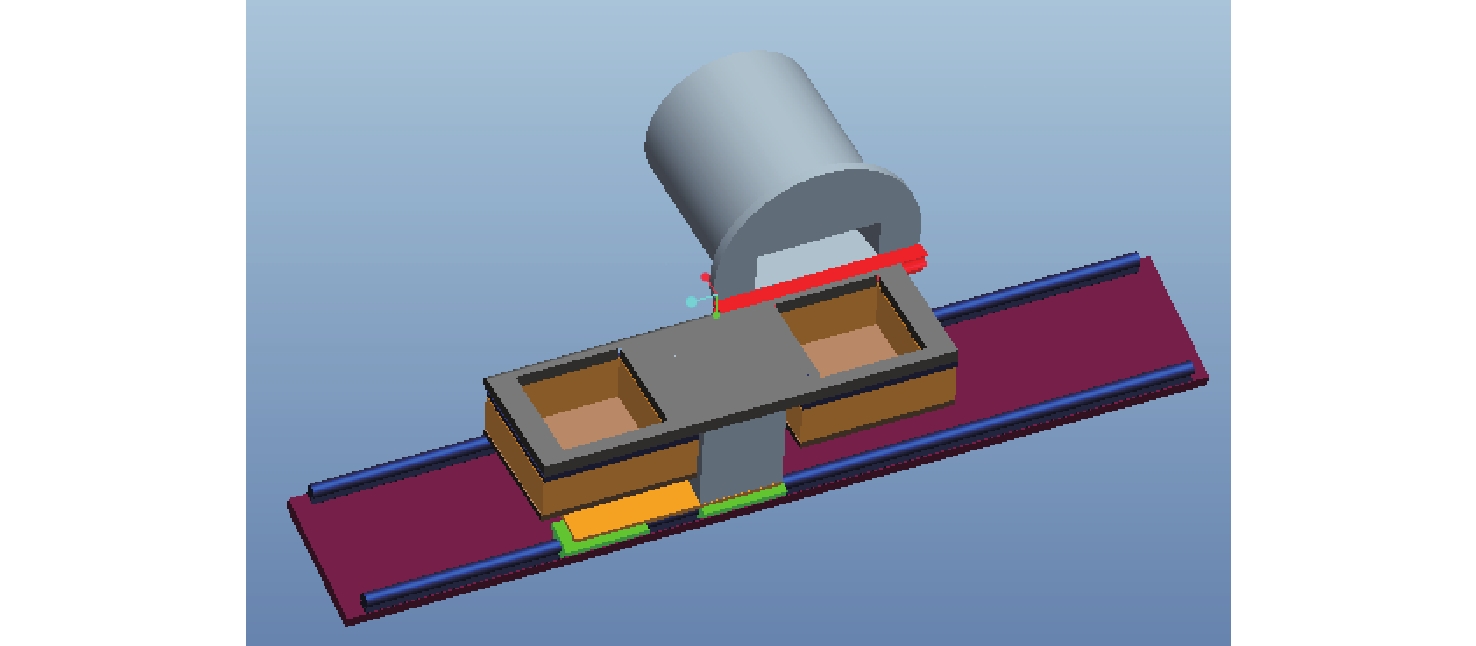
通过合理设计对比模型,提出一种新型树脂基复合材料引射因子测试方法,针对新型树脂基复合材料开展电弧风洞试验,获得树脂基材料有热解气体引射和无热解气体引射时壁面热流密度,研究树脂基材料在特定热环境条件下的引射效应,获取能够评价新型树脂基材料引射效应的引射因子。结果表明:试验状态下,石英酚醛复合材料炭化速度大于石英杂化酚醛复合材料;石英酚醛复合材料引射因子约为0.825,在实际设计中此类材料需要考虑引射效应对表面热流的影响;石英杂化酚醛复合材料引射因子约为1,热解气体引射产生的热阻塞效应基本可以忽略。
Abstract:By reasonably designing the comparison model, a new test method for the injection factor of resin matrix composites is proposed. The arc wind tunnel test is carried out for the new resin matrix composites to obtain the wall heat flux density of resin matrix materials with and without pyrolysis gas injection. The ejection factor, which may assess the ejection effect of new resin matrix materials, is generated by examining the ejection effect of resin matrix composites under particular thermal environment circumstances. The results show that: the carbonization rate of quartz phenolic materials is higher than that of quartz hybrid phenolic materials; The ejection factor of quartz phenolic materials is about 0.825. The impact of the ejection effect on the flux of surface heat should be taken into account in practical design. Quartz hybrid phenolic materials have an ejection factor of roughly 1, making it possible to largely overlook the thermal blocking effect brought on by gas pyrolysis.
-
Key words:
- New resin matrix composites /
- ejection effect /
- ejection factor /
- heat flux /
- experiment test
-
表 1 材料基础物性参数
Table 1. Fundamental physical parameters of materials
材料 密度/
(kg·m−3)热导率/
(W·m−1·K−1)比热容/
(J·kg−1·K−1)xy方向拉
伸强度/MPa压缩强
度/MPa石英酚醛 0.91 0.22 1.1 20.8 66.7 石英杂
化酚醛0.496 0.05 1.0 29.9 2.5 -
[1] 李玮洁. 变密度炭化复合材料的热防护模型及其数值模拟[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2017.LI W J. Thermal protection models and numerical simulation for variable density charring materials[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017 (in Chinese). [2] 刘骁, 国义军, 刘伟, 等. 碳化材料三维烧蚀热响应有限元计算研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(9): 1150-1156.LIU X, GUO Y J, LIU W, et al. Numerical simulation research on three-dimensional ablative thermal response of charring ablators[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(9): 1150-1156(in Chinese). [3] SHI S B, LI L J, LIANG J, et al. Surface and volumetric ablation behaviors of SiFRP composites at high heating rates for thermal protection applications[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 102: 1190-1198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.06.085 [4] 李仲平. 防热复合材料发展与展望[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(2): 1-9.LI Z P. Major advancement and development trends of TPS composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2011, 28(2): 1-9(in Chinese). [5] 时圣波. 高硅氧/酚醛复合材料的烧蚀机理及热—力学性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.SHI S B. Ablation mechanism and thermo-mechanical behavior of silica/phenolic composites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013 (in Chinese). [6] LI W J, HUANG H M, XU X L. A coupled thermal/fluid/chemical/ablation method on surface ablation of charring composites[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 725-736. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.02.052 [7] 杨琼梁, 史晓鸣, 许斌, 等. 烧蚀防热层与结构耦合热传导分析的交替计算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(8): 1854-1858.YANG Q L, SHI X M, XU B, et al. Alternative algorithm for heat transfer analysis of ablative protection layer coupled with structure[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(8): 1854-1858(in Chinese). [8] 郭瑾, 黄海明. 热解气体燃烧对炭化复合材料烧蚀热响应影响规律[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2020, 40(6): 41-47.GUO J, HUANG H M. Effect of pyrolysis gases combustion on surface ablation of charring material[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2020, 40(6): 41-47(in Chinese). [9] 杨凯威, 张杨, 梁欢, 等. 高超声速飞行器热流密度/分层温度/碳化层研究[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2018, 38(3): 33-39.YANG K W, ZHANG Y, LIANG H, et al. Study on heat flux density/stratified temperature/carbonization layer of hypersonic vehicle[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2018, 38(3): 33-39(in Chinese). [10] MATSUURA Y, HIRAI K, KAMITA T, et al. A challenge of modeling thermo-mechanical response of silica-phenolic composites under high heating rates[C]// Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2019. [11] SAKAI T, TOMITA M, SUZUKI T, et al. Post-test sample analysis of fiber reinforced plastic using arcjet[C]// Proceedings of the 10th AIAA/ASME Joint Thermophilic and Heat Transfer Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2010. [12] MILOS F, CHEN Y K, GOKCEN T. Non-equilibrium ablation of phenolic impregnated carbon ablator[C]// Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2010. [13] 姜贵庆, 刘连元. 高速气流传热与烧蚀热防护[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2003: 52-66.JIANG G Q, LIU L Y. Heat transfer of hypersonic gas and ablation thermal protection[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2003: 52-66 (in Chinese). [14] 黄志澄. 高超声速飞行器空气动力学[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1995.HUANG Z C. Aerodynamics of hypersonic vehicle[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1995 (in Chinese). [15] 郭梅梅, 匡松连, 华小玲, 等. 树脂基复合材料的分解防热效率[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2012, 42(2): 58-60.GUO M M, KUANG S L, HUA X L, et al. Heat-resistant effect of pyrolysis of resin composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2012, 42(2): 58-60(in Chinese). [16] 王国雄, 马鹏飞. 弹头技术(上)[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 1993.WANG G X, MA P F. Warhead technology[M]. Beijing: China Aerospace Publishing House, 1993 (in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: