-
摘要:
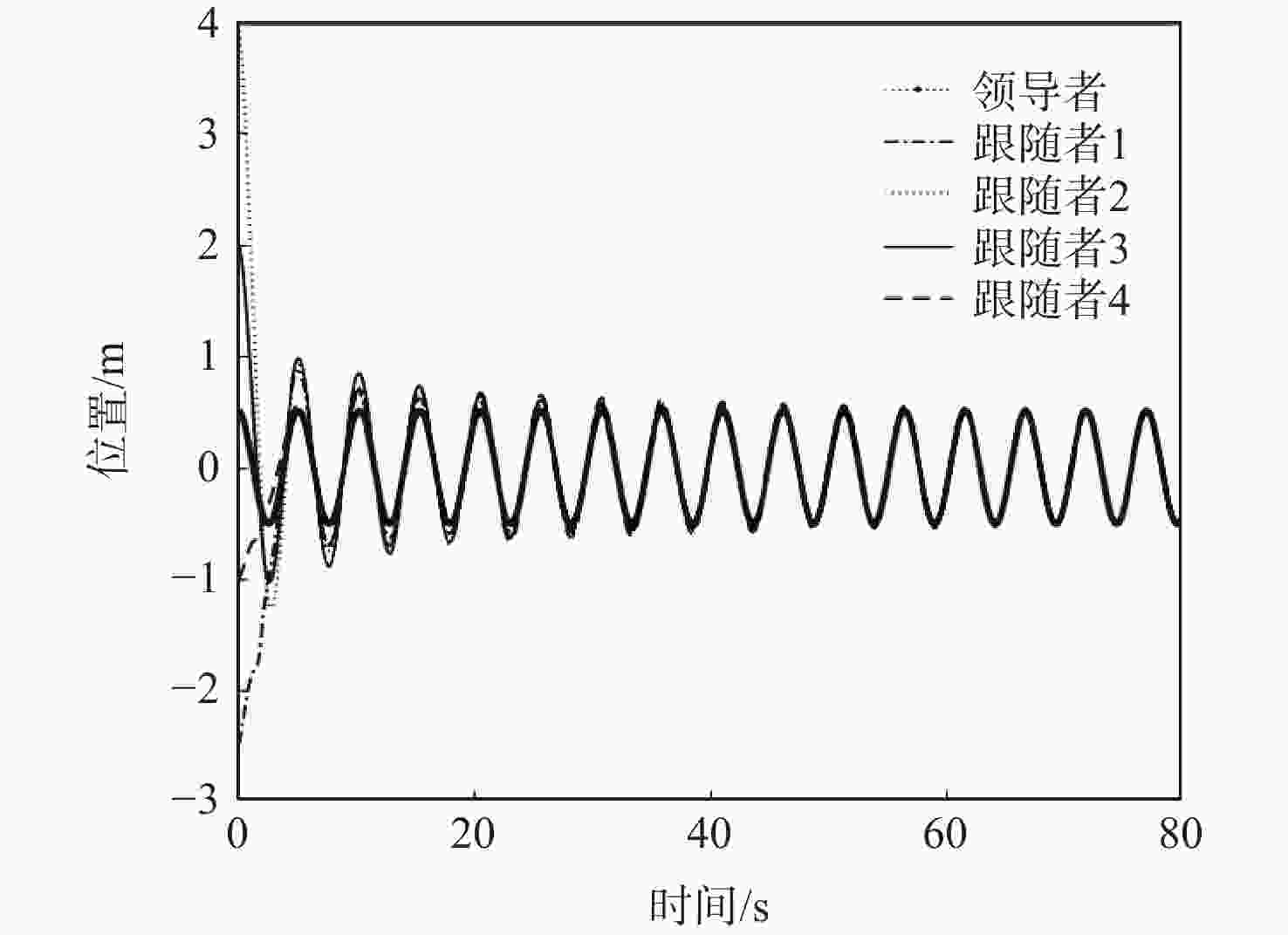
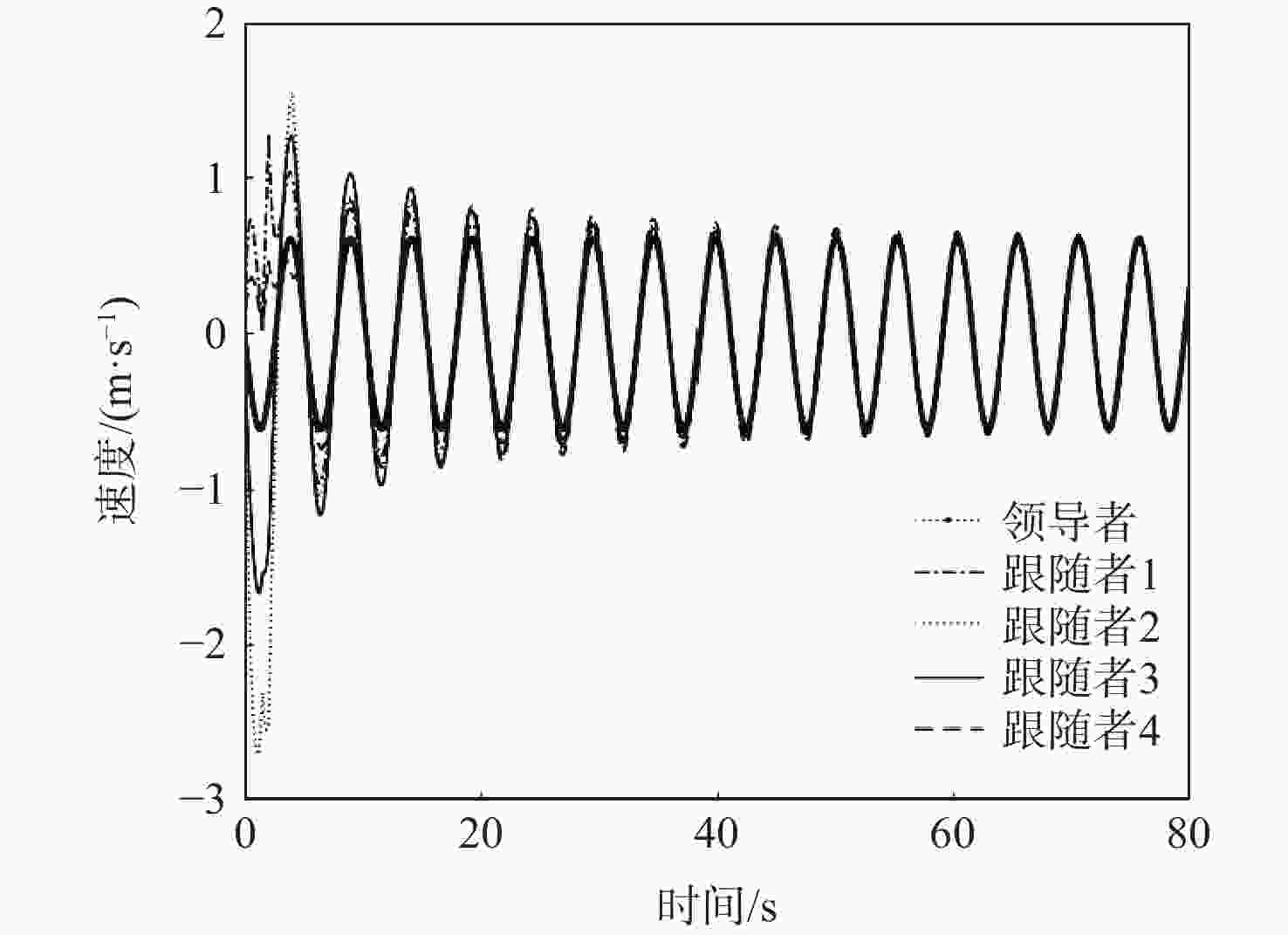
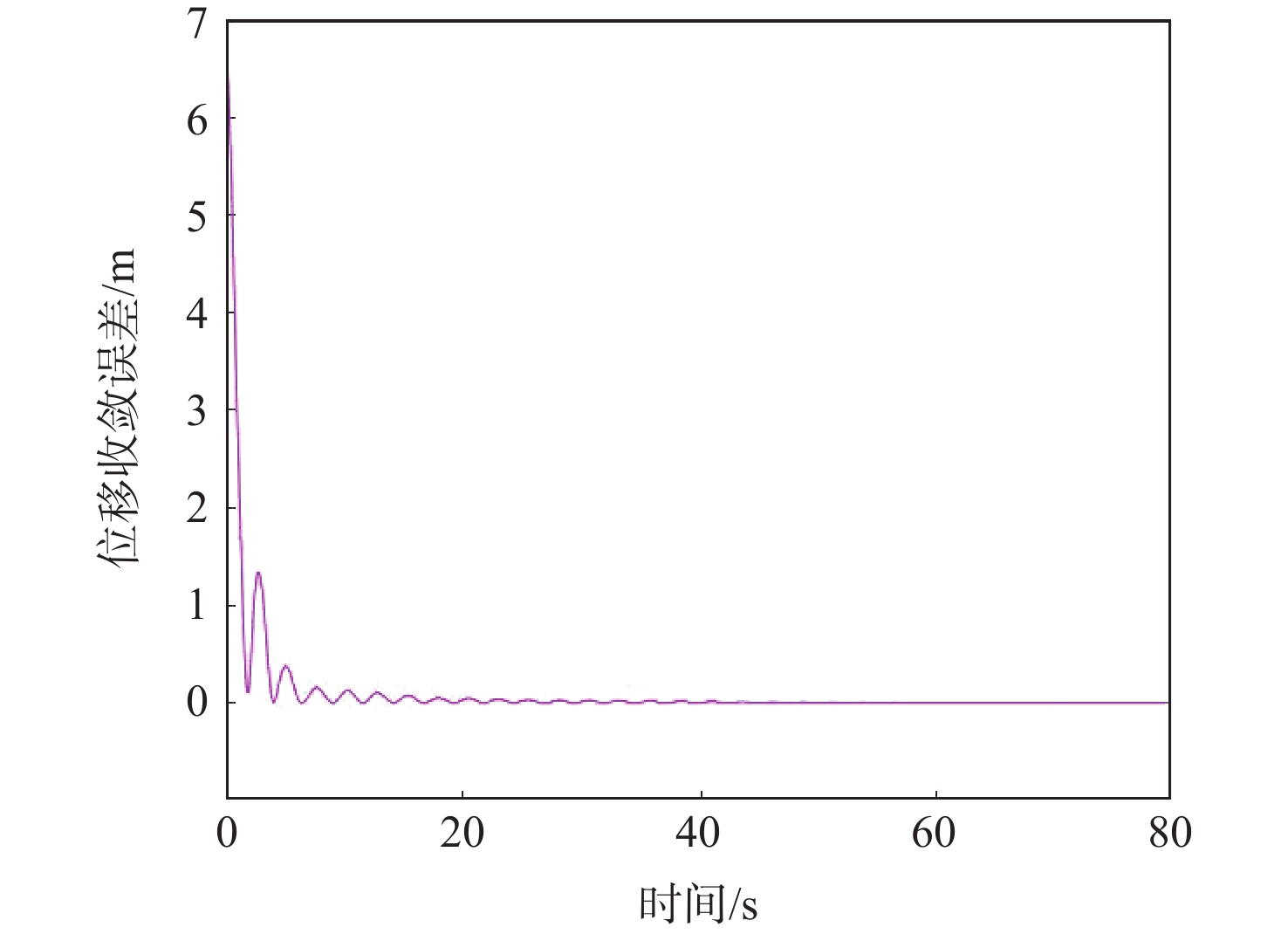
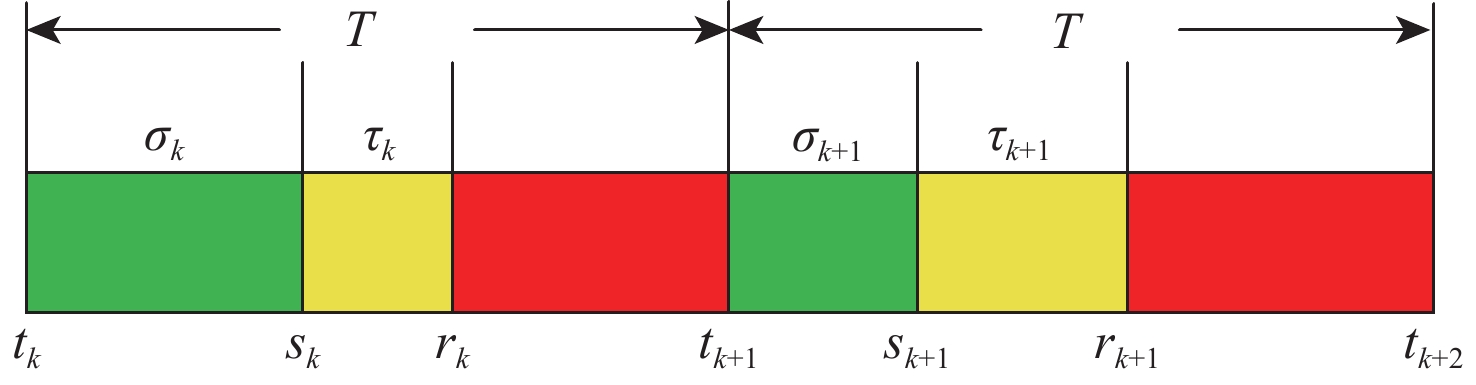
考虑到实际应用中,由于外部干扰或通信能力有限,连续通信有时无法保证,研究了间歇通信下二阶多智能体的跟踪控制问题。在持续性通信无法保证的场景下,为了提升间歇通信下系统的收敛性能,引入非周期性的持续-保持控制机制,设计了一种面向二阶多智能体系统的一致性跟踪控制协议。基于矩阵论和图论知识,并结合双线性变换证明了非周期性间歇通信结构下系统可以实现一致性跟踪,进而得到了针对无向拓扑网络的一致性跟踪条件。仿真实验验证了理论结果的正确性。
-
关键词:
- 二阶多智能体系统 /
- 跟踪控制 /
- 间歇通信 /
- 非周期性持续-保持控制 /
- 一致性
Abstract:In practical applications, continuous communication cannot be guaranteed due to external interference or limited communication ability. Therefore, this study investigates the tracking control problem of second-order multi-agent systems with intermittent communication. To improve the convergence performance of the system when continuous communication is not guaranteed, a second-order consensus tracking control protocol is designed by introducing an aperiodic persistent-hold control strategy. Based on the matrix and graph theory, and combined with bilinear transformation, it is proved that the multi-agent system achieves consensus tracking under the aperiodic intermittent communication. Then, the consensus tracking condition for second-order multi-agent systems with the undirected topology is obtained. Finally, the simulation examples verify the theoretical results.
-
-
[1] WANG W, HUANG J S, WEN C Y, et al. Distributed adaptive control for consensus tracking with application to formation control of nonholonomic mobile robots[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(4): 1254-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.028 [2] YANG A, NAEEM W, IRWIN G W, et al. Stability analysis and implementation of a decentralized formation control strategy for unmanned vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2014, 22(2): 706-720. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2013.2259168 [3] CAI H, HUANG J. Leader-following adaptive consensus of multiple uncertain rigid spacecraft systems[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(1): 1-13. [4] MA R F, CHEN H H, HUANG Y R, et al. Smart grid communication: Its challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2013, 4(1): 36-46. doi: 10.1109/TSG.2012.2225851 [5] WEI R, BEARD R W. Consensus algorithms for double-integrator dynamics[J]. Distributed Consensus in Multi-vehicle Cooperative Control: Theory and Applications, 2008: 77-104. [6] WEI Z, CHENG D Z. Leader-following consensus of second-order agents with multiple time-varying delays[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(12): 1994-1999. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.08.003 [7] WANG F Y, LIU Z X, CHEN Z Q. A novel leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems with smart leader[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2018, 16(4): 1483-1492. doi: 10.1007/s12555-017-0266-0 [8] HONG Y G, HU J P, GAO L X. Tracking control for multi-agent consensus with an active leader and variable topology[J]. Automatica, 2006, 42(7): 1177-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.02.013 [9] HE W L, CHEN G R, HAN Q L, et al. Network-based leader-following consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems via distributed impulsive control[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 380: 145-158. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.06.005 [10] SU H S, WANG M Z, WANG X, et al. Semiglobal observer-based leader-following consensus with input saturation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 61(6): 2842-2850. [11] MA C Q, XIE L H. Necessary and sufficient conditions for leader-following bipartite consensus with measurement noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2018, 50(5): 1976-1981. [12] 魏志强, 翁哲鸣, 化永朝, 等. 切换拓扑下异构无人集群编队-合围跟踪控制[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(2): 326504.WE Z Q, WENG Z M, HUA Y C, et al. Formation-containment tracking control for heterogeneous unmanned swarm systems with switching topologies[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(2): 326504(in Chinese). [13] WANG H J, XUE B, XUE A K. Leader-following consensus control for semi-Markov jump multi-agent systems: an adaptive event-triggered scheme[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(1): 428-447. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.10.031 [14] WEN G H, DUAN Z S, YU W W, et al. Consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with delayed nonlinear dynamics and intermittent communications[J]. International Journal of Control, 2013, 86(2): 322-331. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2012.727473 [15] FAN Z P, SU H S, CHEN S M, et al. Semi-global leader-following coordination of multi-agent systems with input saturation and aperiodic intermittent communications[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(2): 1051-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.05.005 [16] HUANG N, DUAN Z S, ZHAO Y. Leader-following consensus of second-order non-linear multi-agent systems with directed intermittent communication[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 8(10): 782-795. [17] HU A H, CAO J D, HU M F. Consensus of leader-following multi-agent systems in time-varying networks via intermittent control[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2014, 12(5): 969-976. doi: 10.1007/s12555-013-0223-5 [18] WANG F Y, LIU Z X, CHEN Z Q. Leader-following consensus of second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems with intermittent position measurements[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(10): 1-16. [19] GUO Y, QIAN Y, WANG P F. Leader-following consensus of delayed multi-agent systems with aperiodically intermittent communications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 466: 49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.014 [20] MU R, WEI A, LI H, et al. Leader-following consensus for multi-agent systems with actuator faults via adaptive event-triggered control[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(2): 1327-1349. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.11.027 [21] LIU C L, LIU S, ZHANG Y, et al. Consensus seeking of multi-agent systems with intermittent communication: A persistent-hold control strategy[J]. International Journal of Control, 2020, 93(9): 2161-2167. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2018.1548784 [22] HORN R A, JOHNSON C R. Matrix analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press , 1985. [23] LIU C L, ZHANG Y, CHEN Y Y. Persistent-hold consensus control of first-order multi-agent systems with intermittent communication[C]//23rd International Symposium on Mathematical Theory of Networks and Systems, 2018. -







 下载:
下载: