-
摘要:
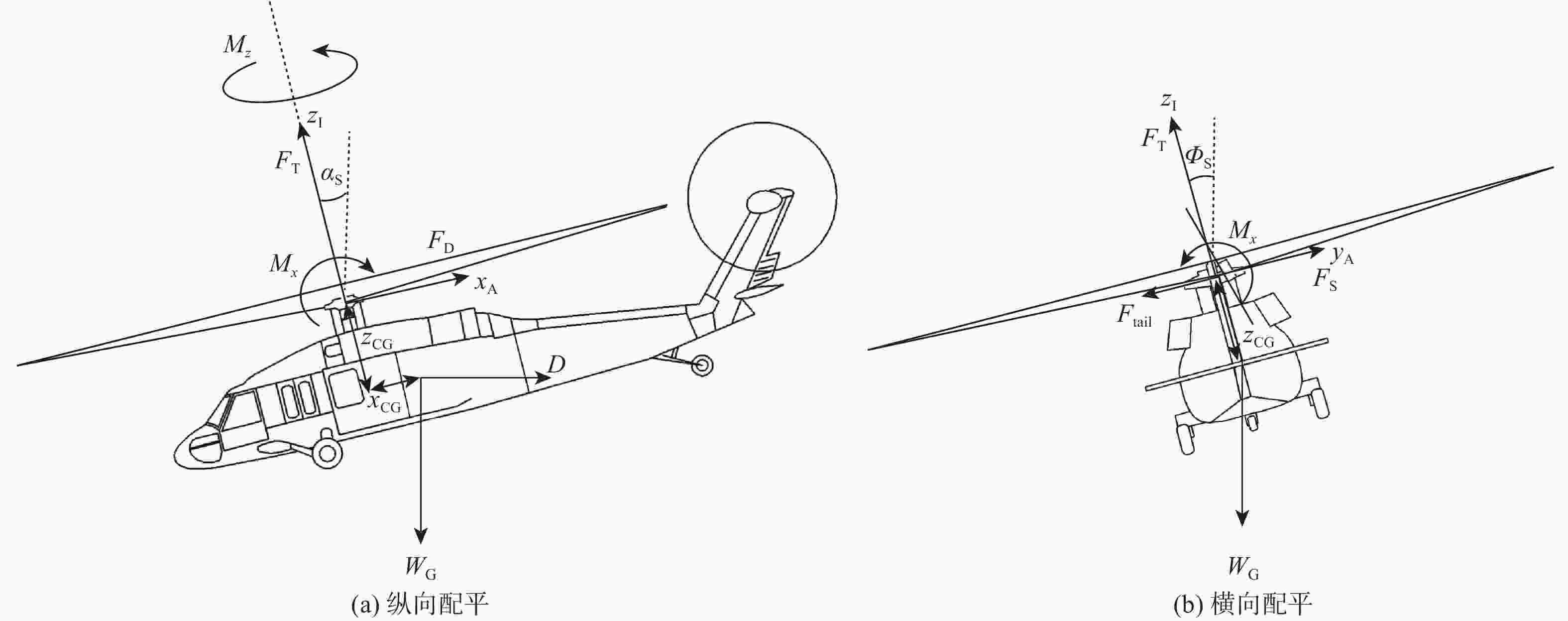
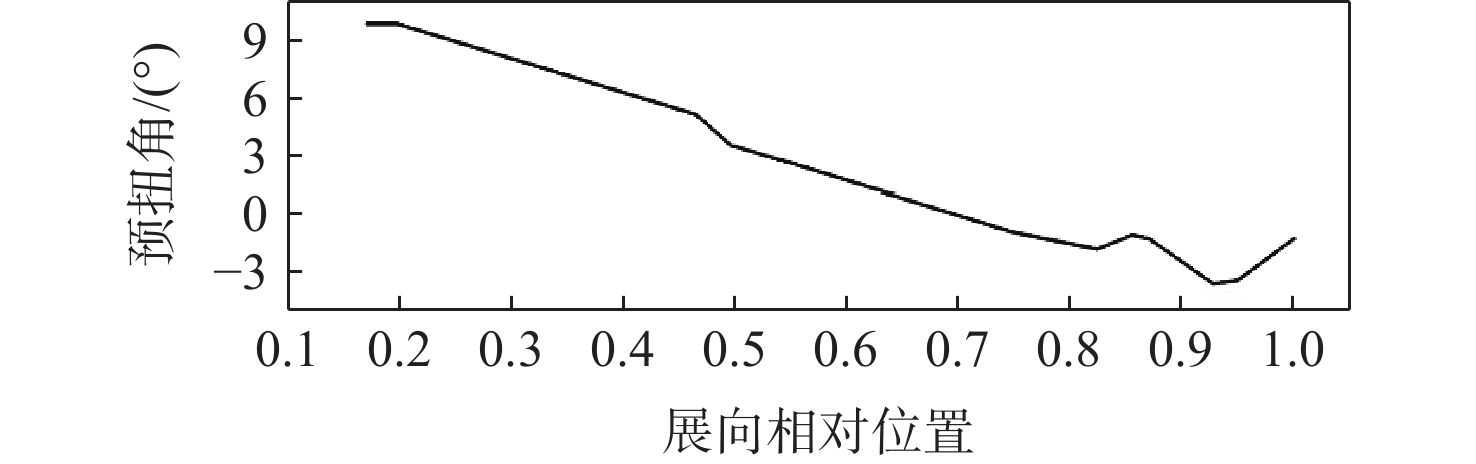
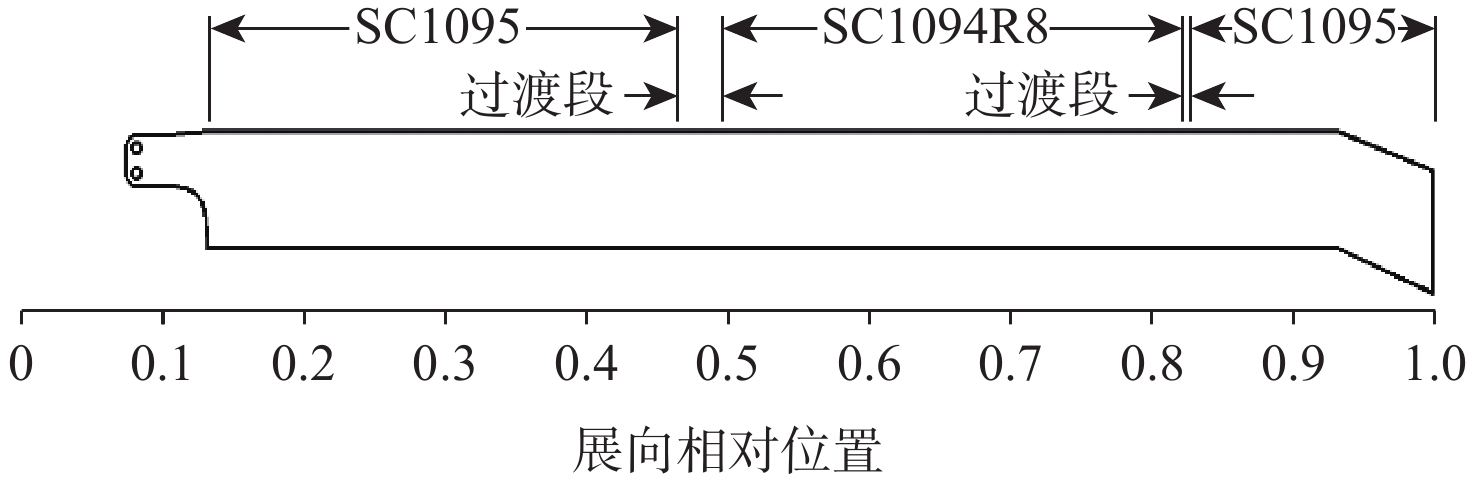
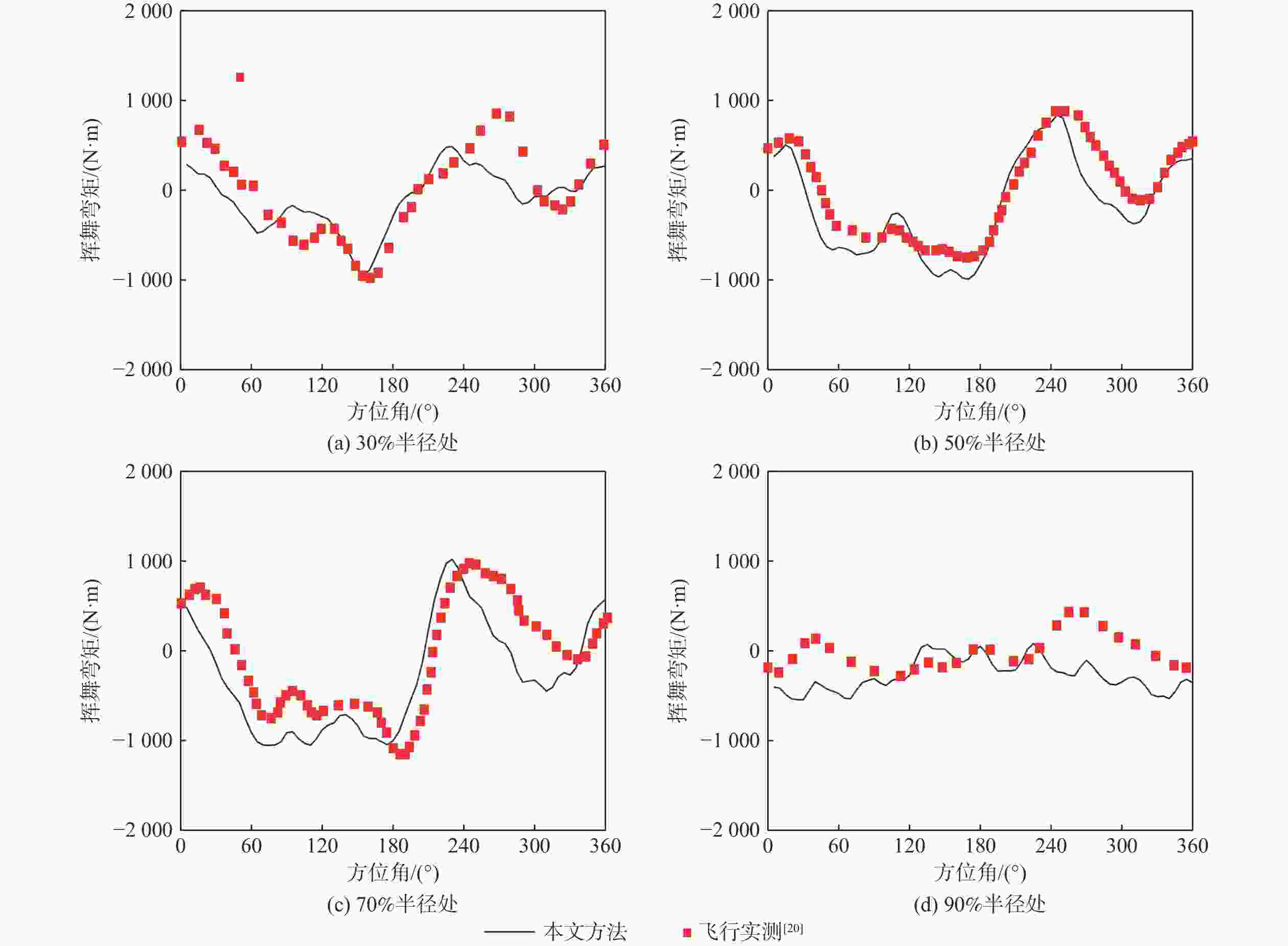
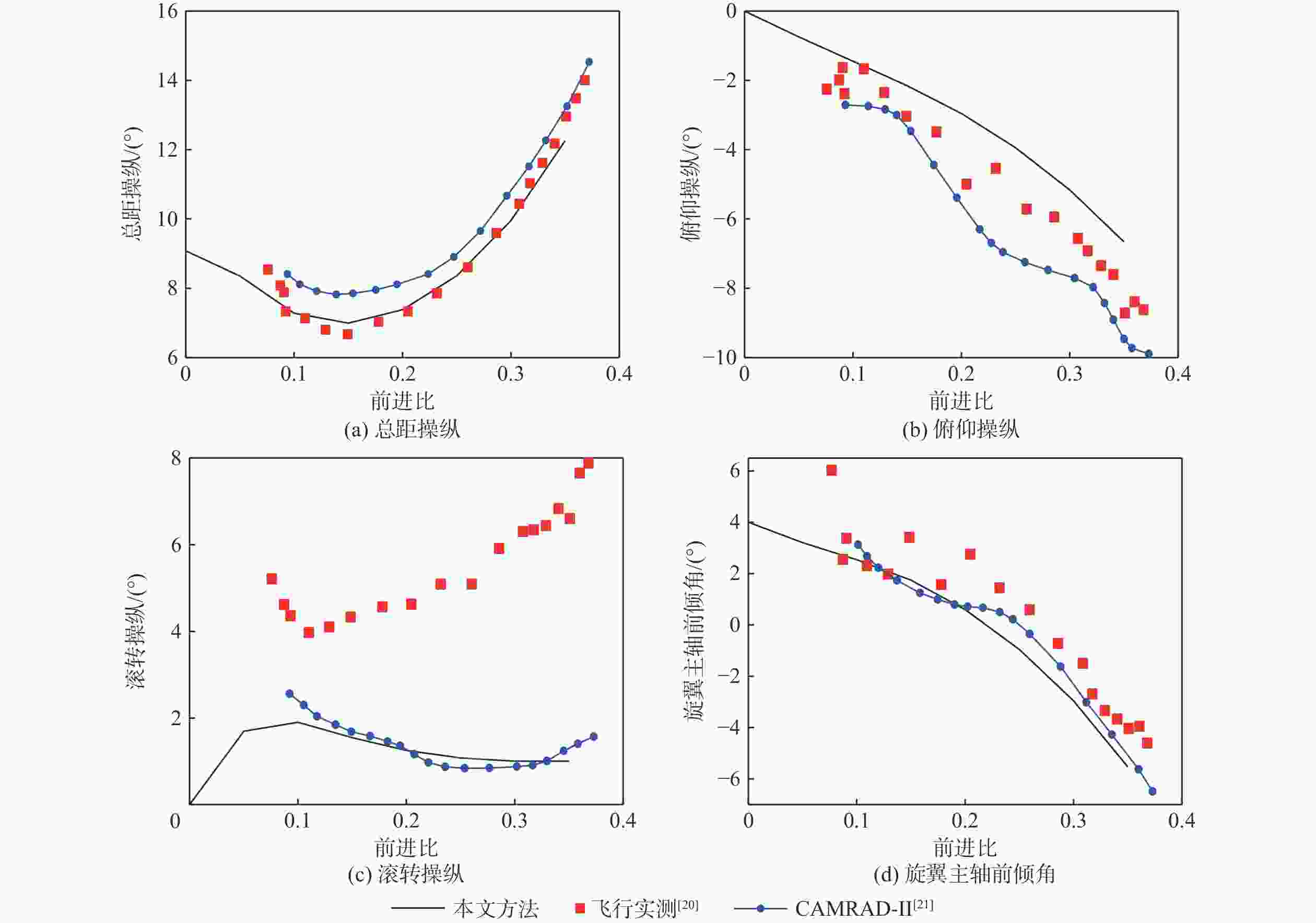
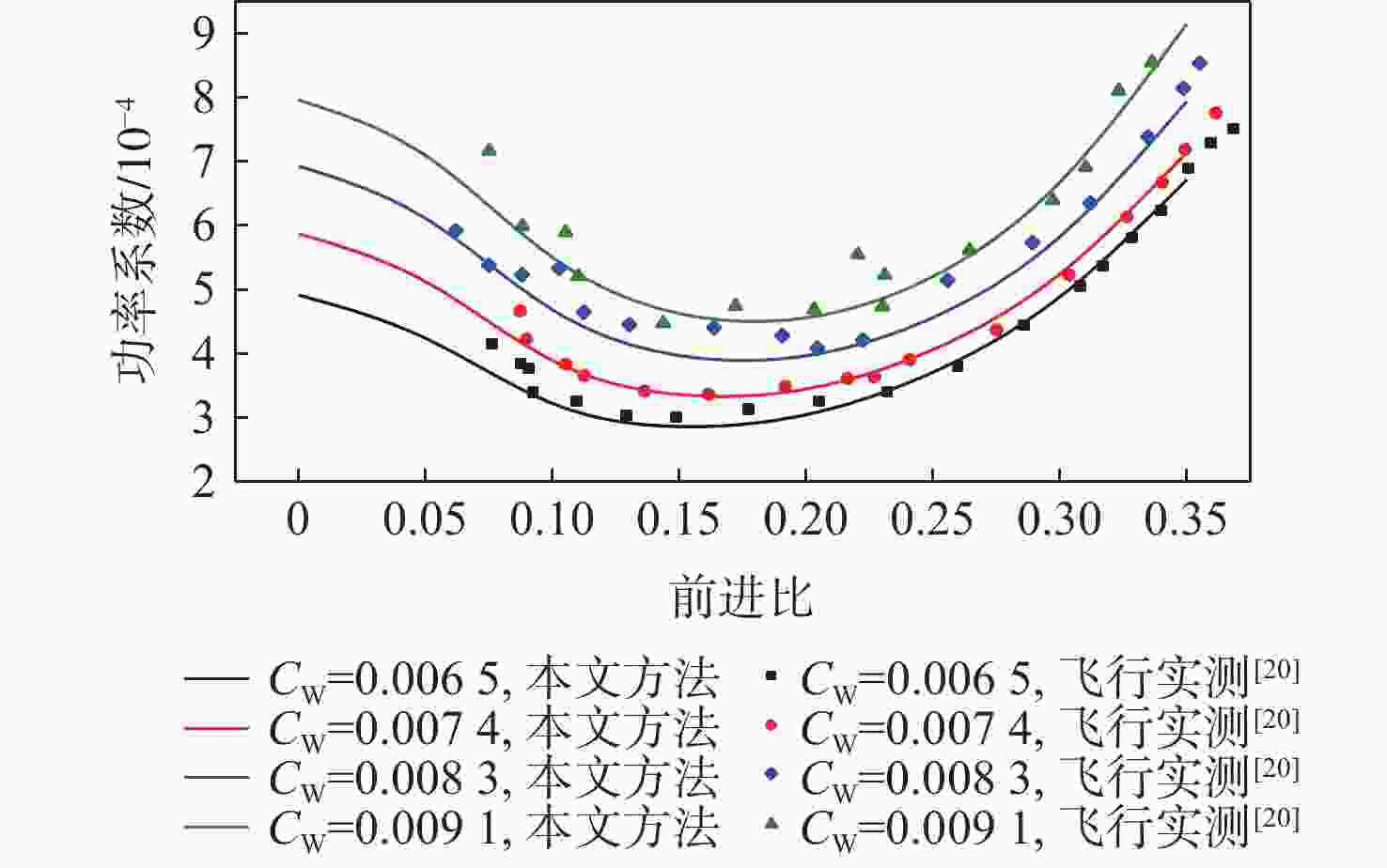
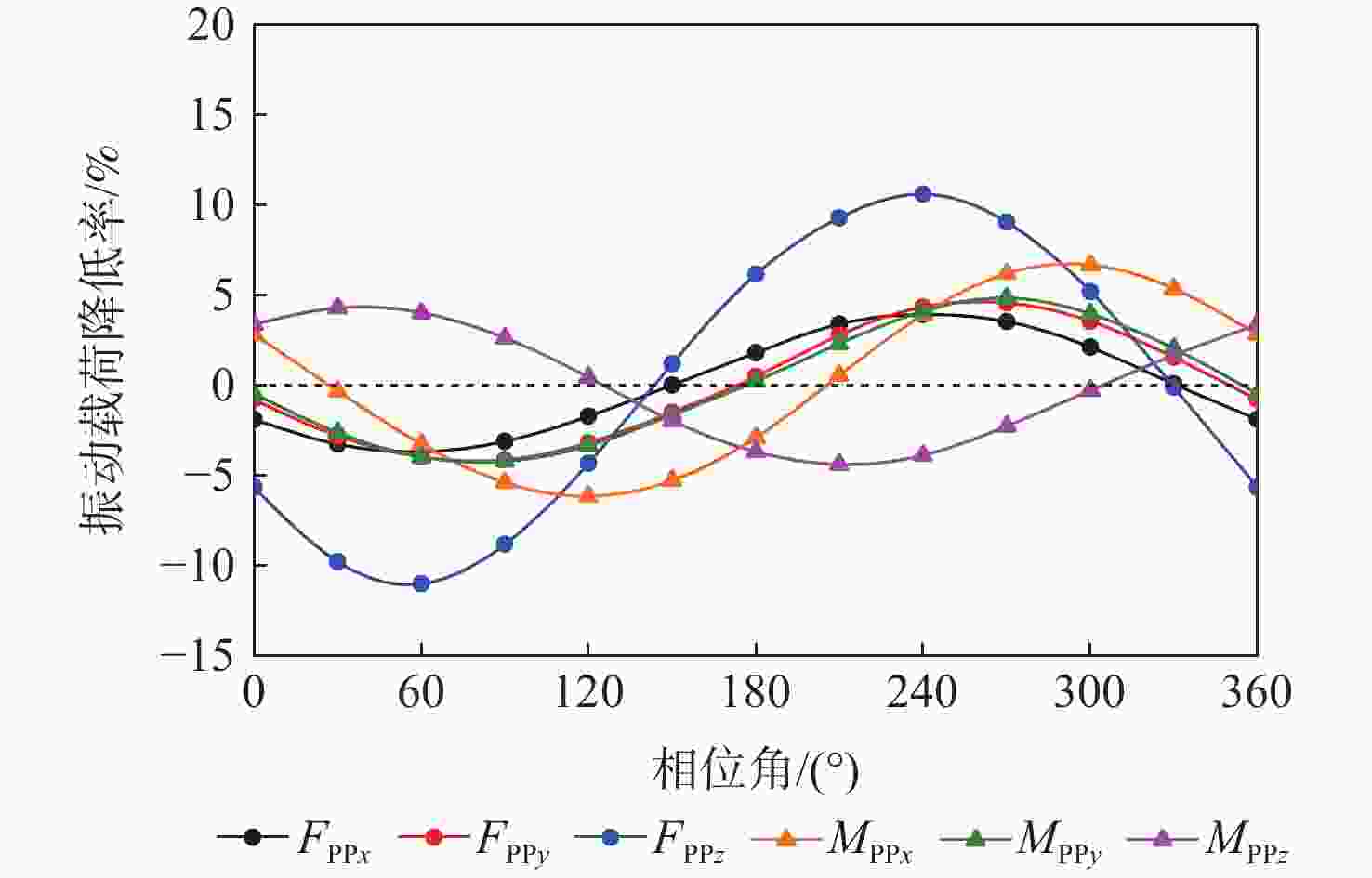
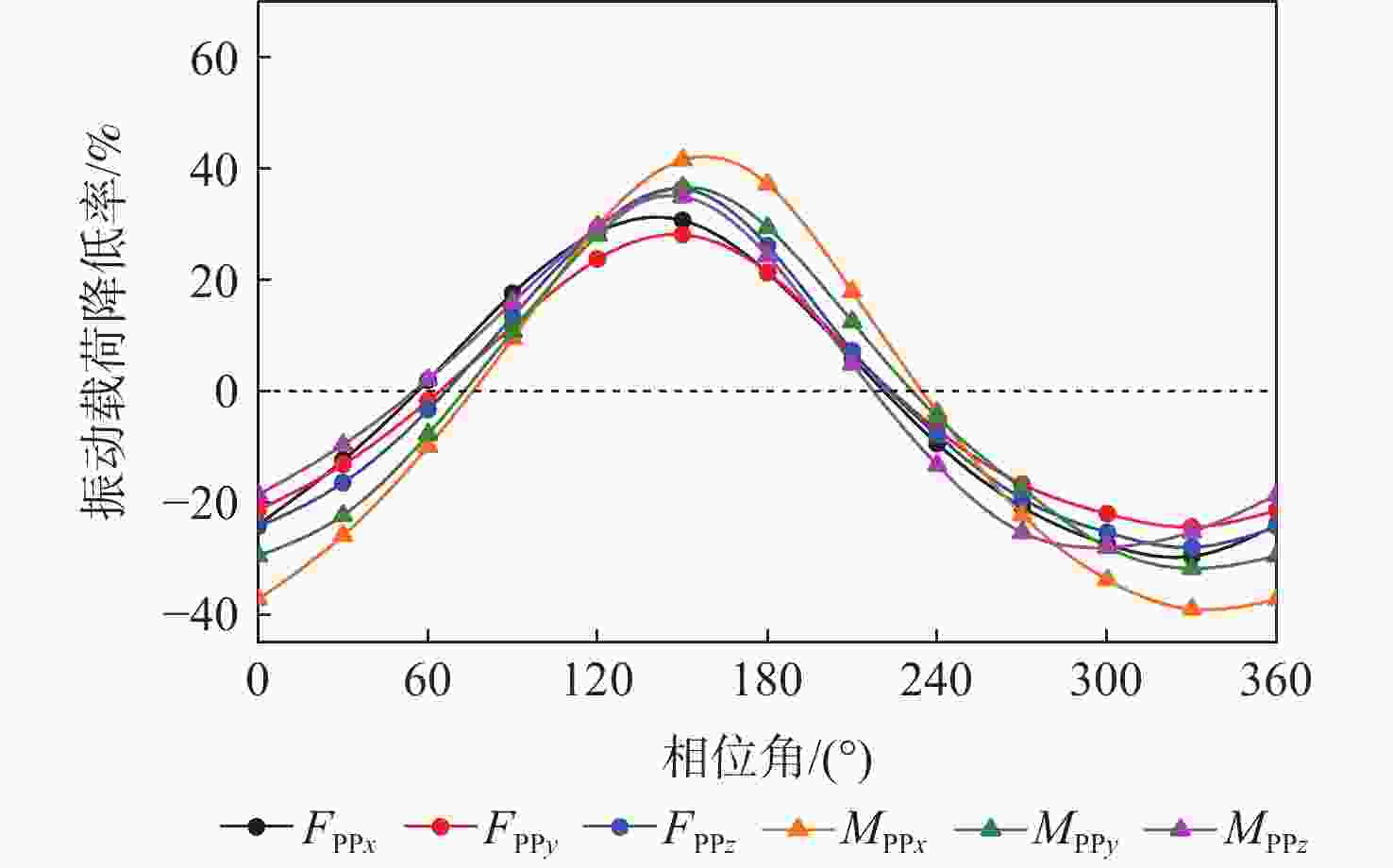
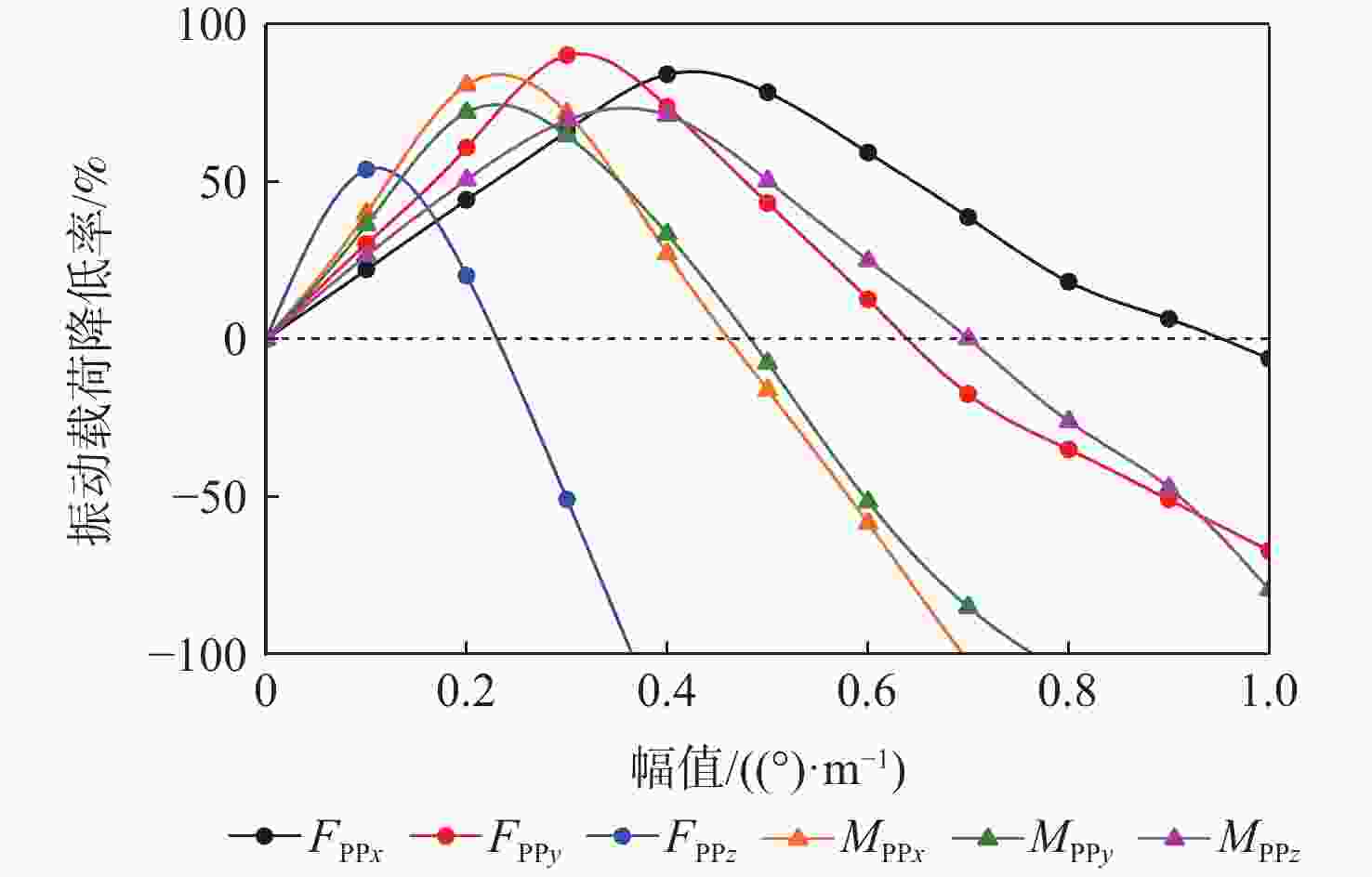
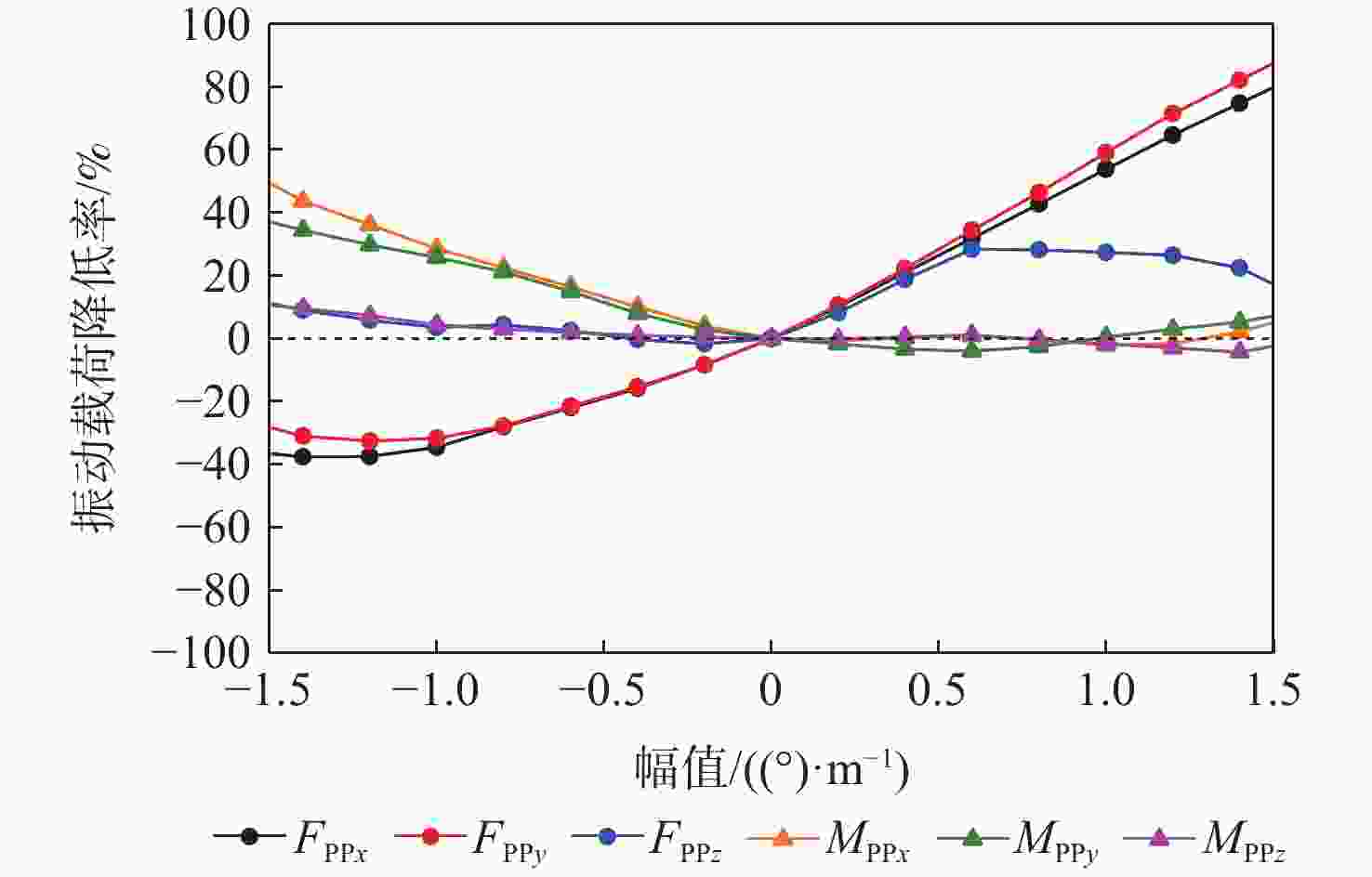
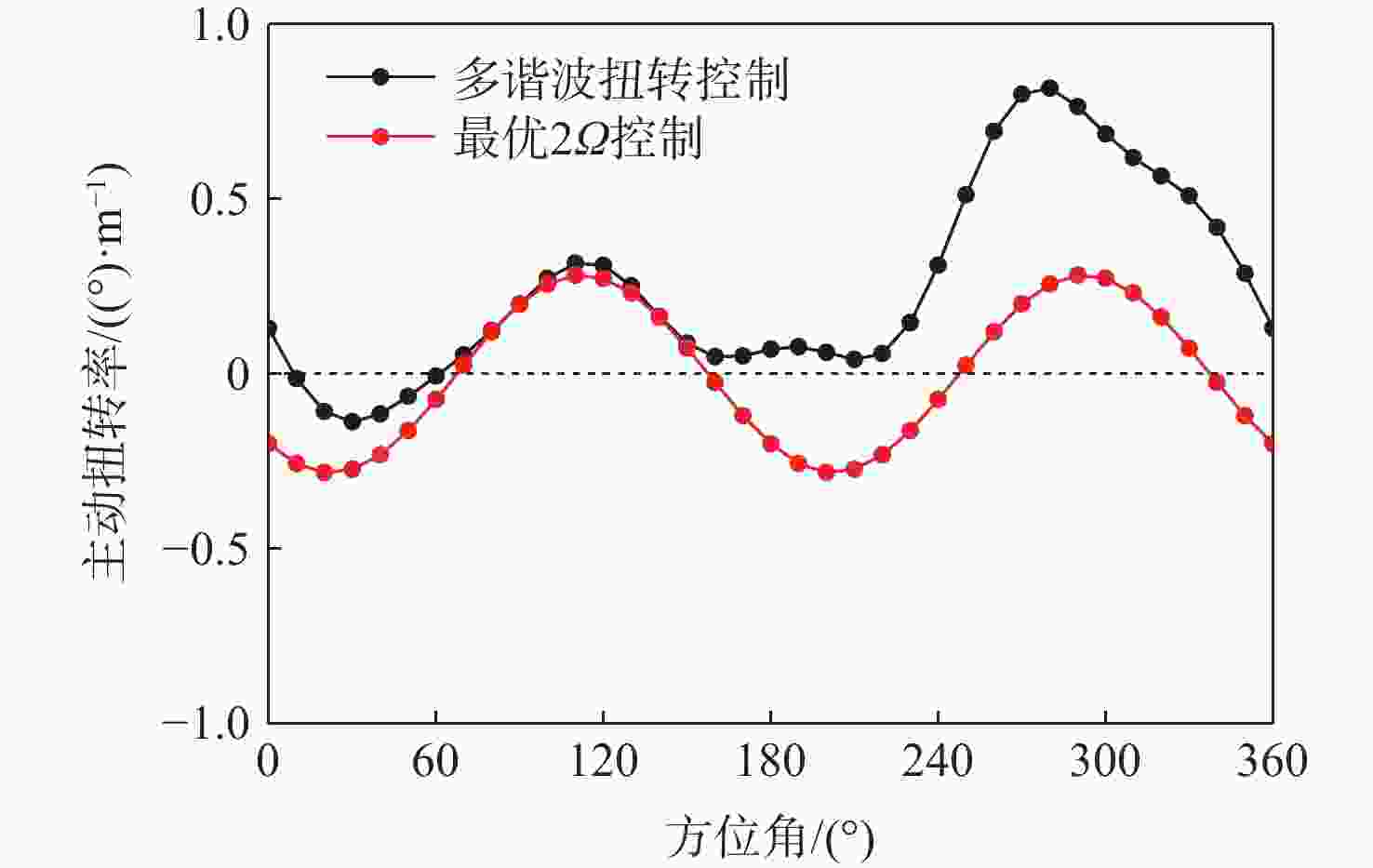
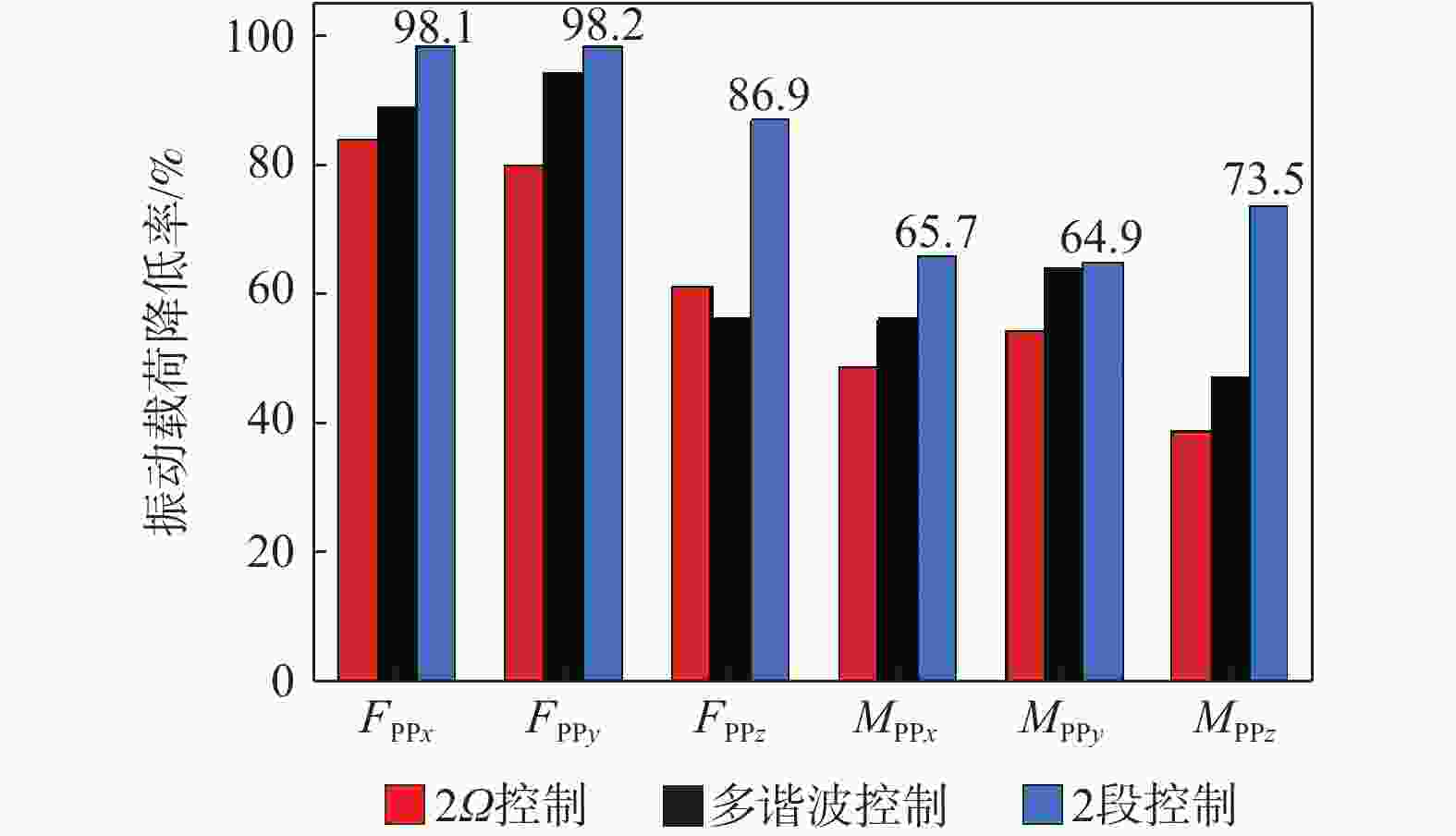
为降低旋翼前飞状态的桨毂振动载荷水平,应用主动扭转旋翼技术,开展最优控制方案研究。建立基于中等变形梁理论的旋翼气动弹性动力学模型,以预测稳态飞行的桨毂振动载荷。使用UH-60A直升机旋翼算例验证所建模型准确性并作为研究基准。通过谐波相位及幅值变参分析,研究单谐波扭转控制对振动载荷的影响。构建基于遗传算法的主动扭转旋翼控制参数优化框架,开展展向一致多谐波扭转控制参数优化与分段多谐波扭转控制方案优化。结果表明:优化的多谐波扭转控制相比单谐波主动扭转控制可起到更好的桨毂振动载荷减缓效果。而以桨叶中点为分段点的最优2段扭转控制方案,通过对内外段桨叶施加不同的扭转控制规律,进一步降低了六方向的振动载荷水平。
Abstract:The active twist control rotor is investigated to evaluate the effectiveness in rotor vibration reduction. A numerical model for predicting the isolated rotor vibration loads in steady level flight is deployed and validated by modeling a UH-60A rotor. A parametric sweep of the amplitude and phase angle for uniform single-harmonic active twist control is conducted to demonstrate the effects on rotor vibration loads. The optimal control schedule of the uniform multi-harmonic twist control for vibration reduction are obtained using an optimization framework based on genetic algorithm. The results indicate that the uniform multi harmonic twist control reduces the rotor vibration loads more than the uniform single-harmonic active twist control. An optimal 2 segment twist control layout with the segment point at the midpoint of the blade achieves further rotor vibration reduction by applying divergent control schedules to each segment.
-
Key words:
- helicopter /
- rotor /
- active control /
- vibration reduction /
- optimization
-
表 1 UH-60A直升机旋翼主要参数
Table 1. Rotor main parameters of UH-60A helicopter
参数 数值 旋翼半径/m 8.1788 桨叶弦长/m 0.5273 挥舞摆振铰外伸量/m 0.381 桨叶线密度/(kg·m−1) 13.92 旋翼转速/(rad·s−1) 27.0 桨叶片数 4 -
[1] FRIEDMANN P P, MILLOTT T A. Vibration reduction in rotorcraft using active control - A comparison of various approaches[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1995, 18(4): 664-673. doi: 10.2514/3.21445 [2] CH K. Active rotor control for helicopters: motivation and survey on higher harmonic control[J]. CEAS Aeronautical Journal, 2011, 1(1): 3-22. [3] MCHUGH F J, SHAW J. Helicopter vibration reduction with higher harmonic blade pitch[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 1978, 23(4): 26-35. doi: 10.4050/JAHS.23.26 [4] HAM N D. Individual-blade-control research in the MIT VTOL Technology Laboratory: NASA-CR-177121 [R]. Washington, D. C.: Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1986. [5] 徐海, 王华明, 杨仁国. 独立桨叶高阶谐波变距对旋翼垂向载荷的影响分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 48(2): 200-204. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2016.02.008XU H, WANG H M, YANG R G. Analysis on effect of individual high harmonic blade pitch on vertical hub load[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2016, 48(2): 200-204(in Chinese). doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2016.02.008 [6] FRIEDMANN P P. On-blade control of rotor vibration, noise, and performance: Just around the corner? The 33rd Alexander nikolsky honorary lecture[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2014, 59(4): 1-37. [7] CHEN P C, CHOPRA I. Wind tunnel test of a smart rotor model with individual blade twist control[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1997, 8(5): 414-425. doi: 10.1177/1045389X9700800504 [8] MILLOTT T, FRIEDMANN P. Vibration reduction in helicopter rotors using an active control surface located on the blade[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1992. [9] VISWAMURTHY S R, GANGULI R. An optimization approach to vibration reduction in helicopter rotors with multiple active trailing edge flaps[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2004, 8(3): 185-194. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2003.10.003 [10] YEO H, LIM J W. Application of a slotted airfoil for UH60A helicopter performance: AD-A480499[R]. Moffett Field: NASA Ames Research Center, 2002. [11] KOMP D, KUMAR S, HAJEK M, et al. Effect of active camber morphing on rotor performance and control loads[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 108: 106311. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106311 [12] CHEN P C, CHOPRA I. Induced strain actuation of composite beams and rotor blades with embedded piezoceramic elements[J]. Smart Materials & Structures, 1996, 5(1): 35. [13] WILBUR M L, MIRICK P H, YEAGER W T, et al. Vibratory loads reduction testing of the NASA/Army/MIT active twist rotor[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2002, 47(2): 123-133. doi: 10.4050/JAHS.47.123 [14] SHIN S J, CESNIK C E S, HALL S R. Closed-loop control test of the NASA/Army/MIT active twist rotor for vibration reduction[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2005, 50(2): 178-194. doi: 10.4050/1.3092854 [15] YOU Y H, JUNG S N, KIM C J. Optimal deployment schedule of an active twist rotor for performance enhancement and vibration reduction in high-speed flights[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2017, 30(4): 1427-1440. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2017.04.017 [16] 张宇杭, 韩东, 万浩云. 桨叶分段线性扭转对旋翼性能的提升[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(5): 225264.ZHANG Y H, HAN D, WAN H Y. Rotor performance improvement by blade piecewise linear twist[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 225264(in Chinese). [17] ZHANG X C, WAN Z Q, YAN D. Optimal segment control of active twist rotor for power reduction in forward flight[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(3): 1041. doi: 10.3390/app11031041 [18] HODGES D H, DOWELL E H. Nonlinear equations of motion for the elastic bending and torsion of twisted nonuniform rotor blades: NASA-TN-d-7818[R]. Moffett Field : NASA Ames Research Center, 1975. [19] PETERS D A, HAQUANG N. Technical note: Dynamic inflow for practical applications[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 1988, 33(4): 64-68. doi: 10.4050/JAHS.33.64 [20] YEO H, POTSDAM M. Rotor structural loads analysis using coupled computational fluid dynamics/computational structural dynamics[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2016, 53(1): 87-105. doi: 10.2514/1.C033194 [21] YEO H, BOUSMAN W G, JOHNSON W. Performance analysis of a utility helicopter with standard and advanced rotors[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2004, 49(3): 250-270. doi: 10.4050/JAHS.49.250 [22] KOVALOVS A, BARKANOV E, RUCHEVSKIS S, et al. Optimisation methodology of a full-scale active twist rotor blade[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 178: 85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.01.067 -







 下载:
下载: