-
摘要:
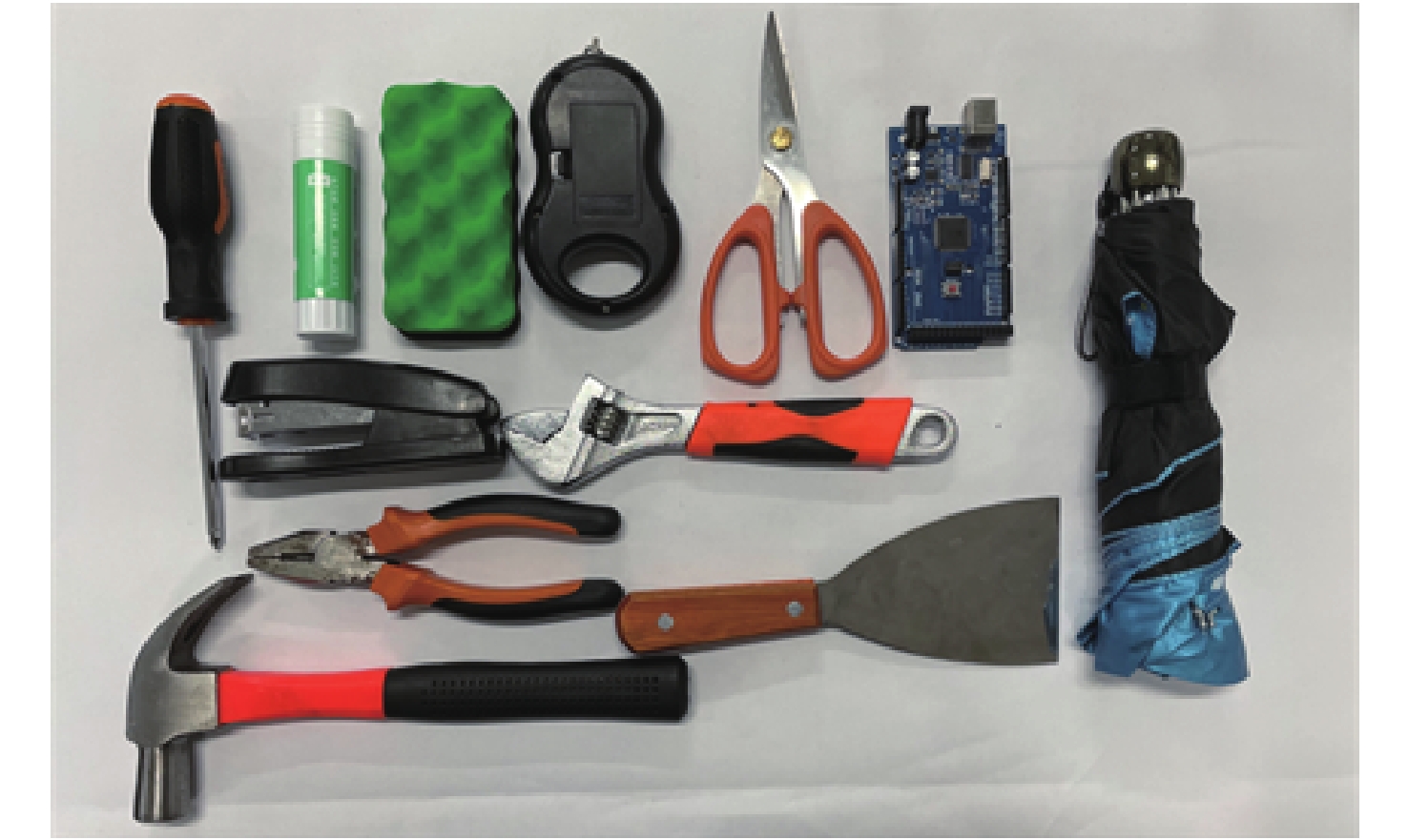
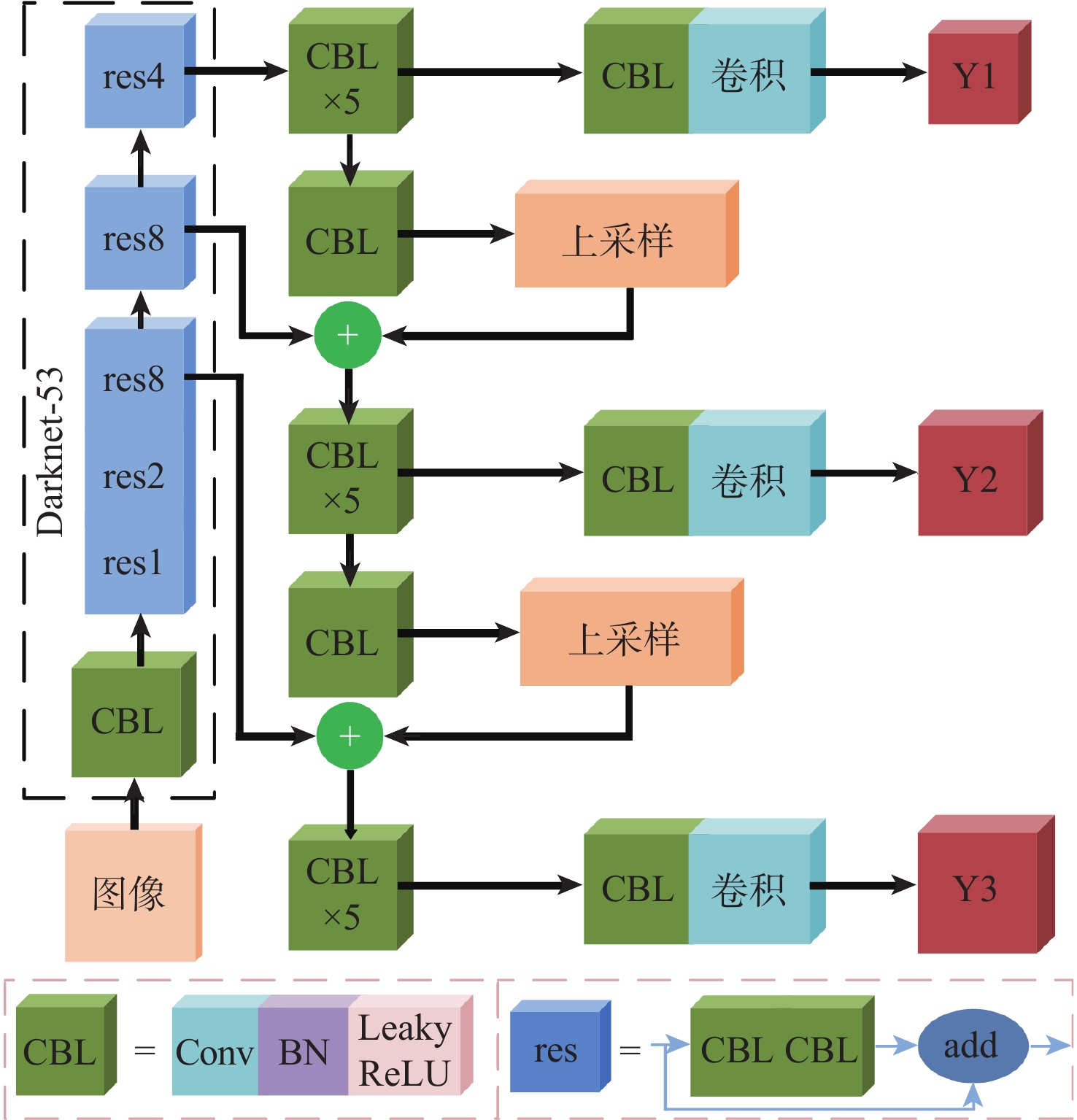
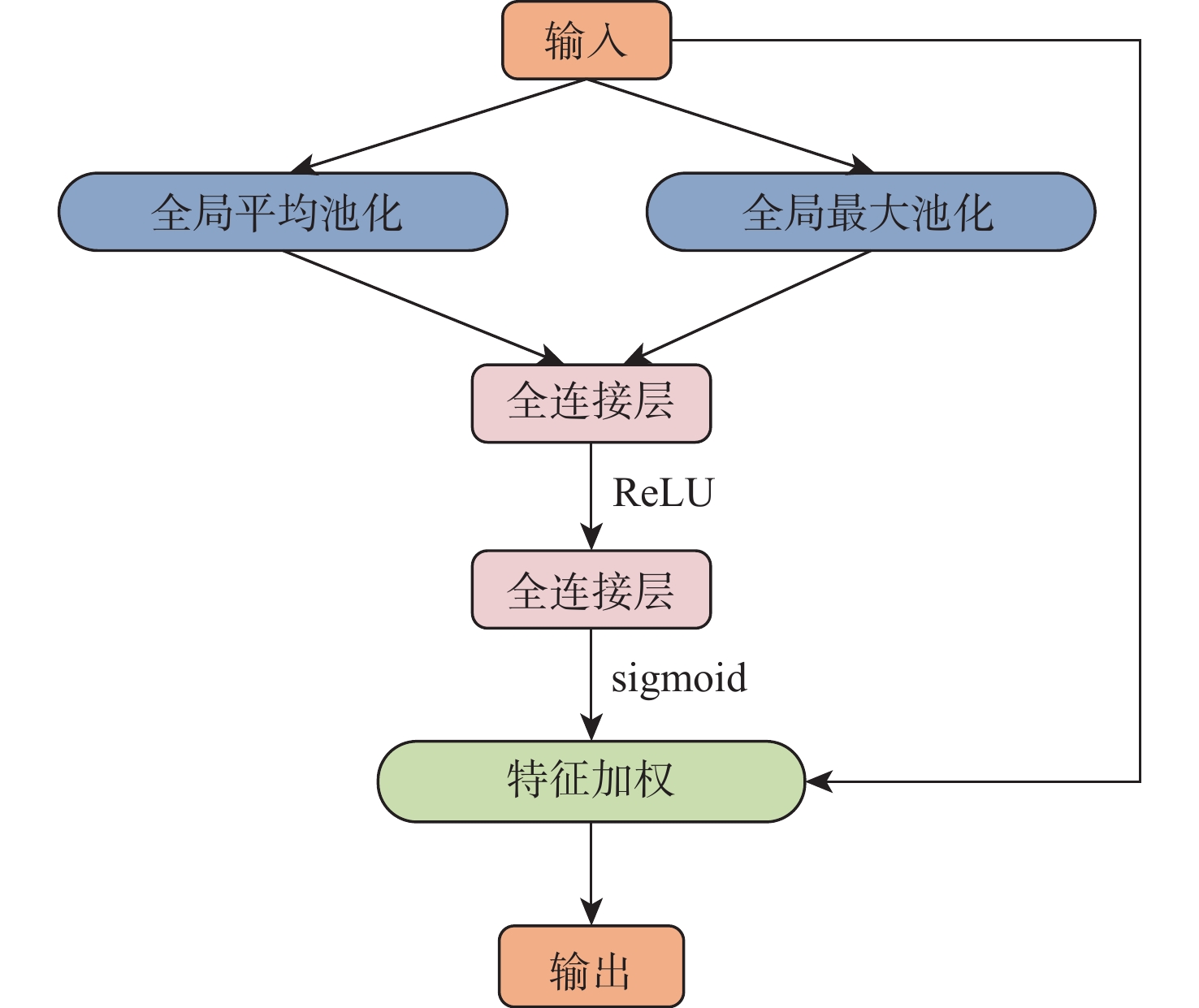
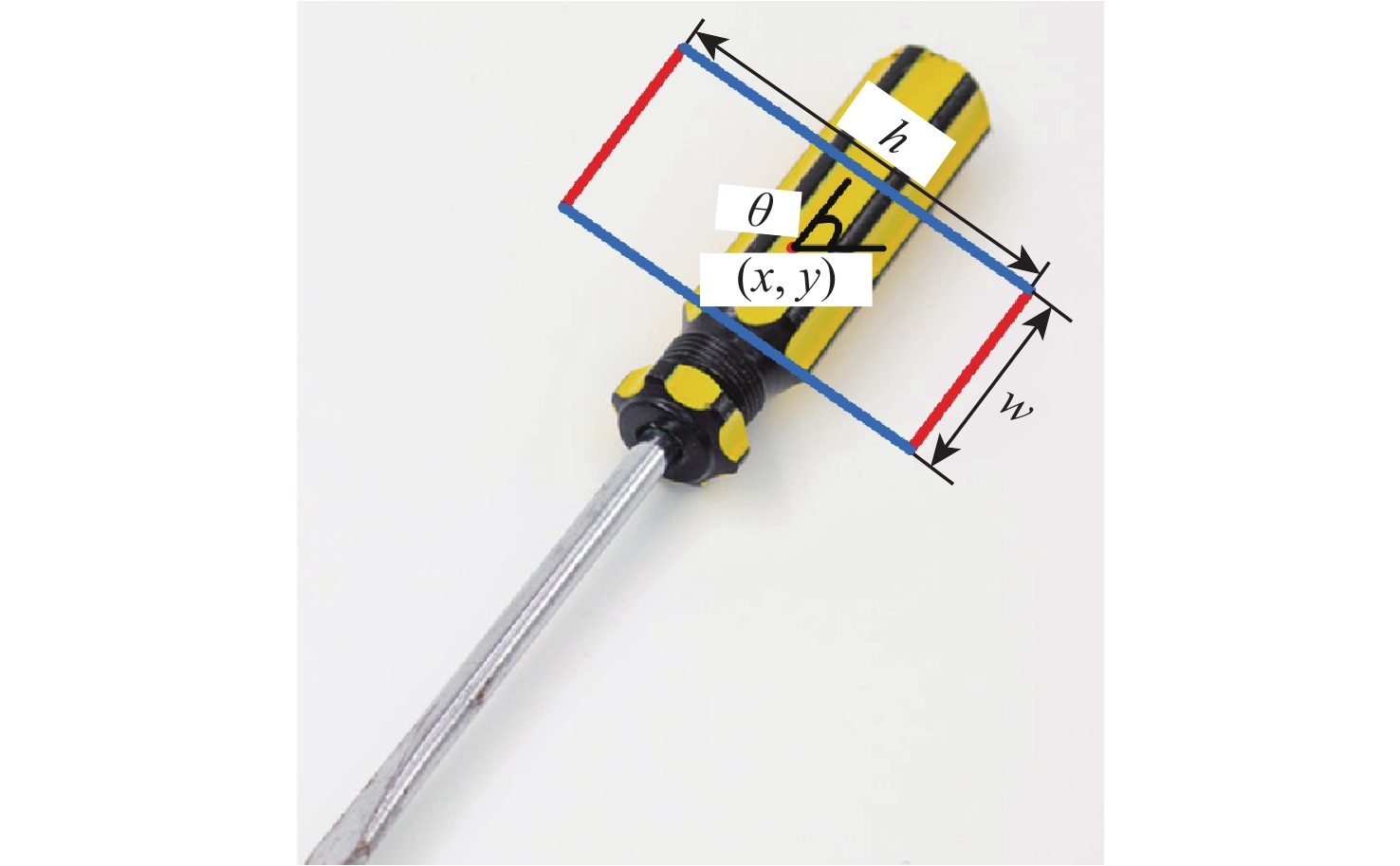
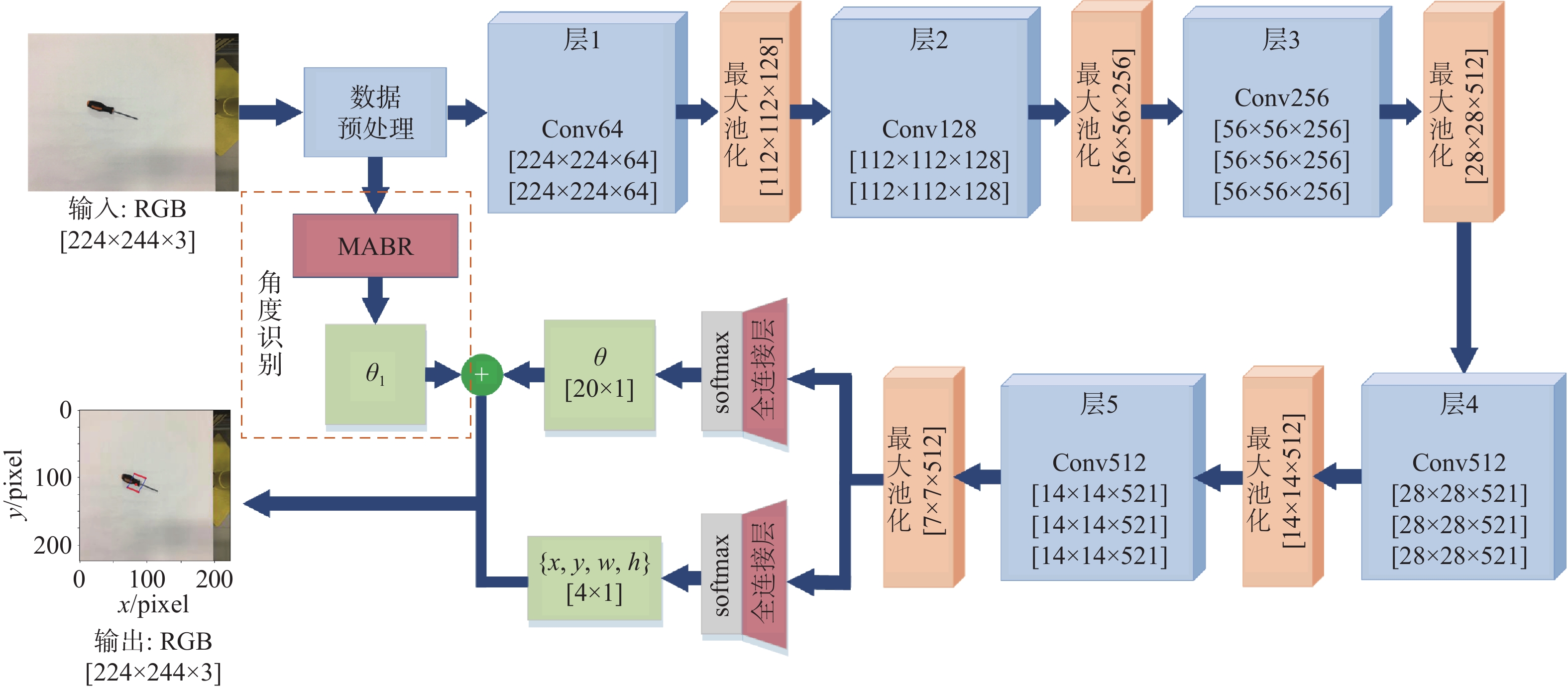
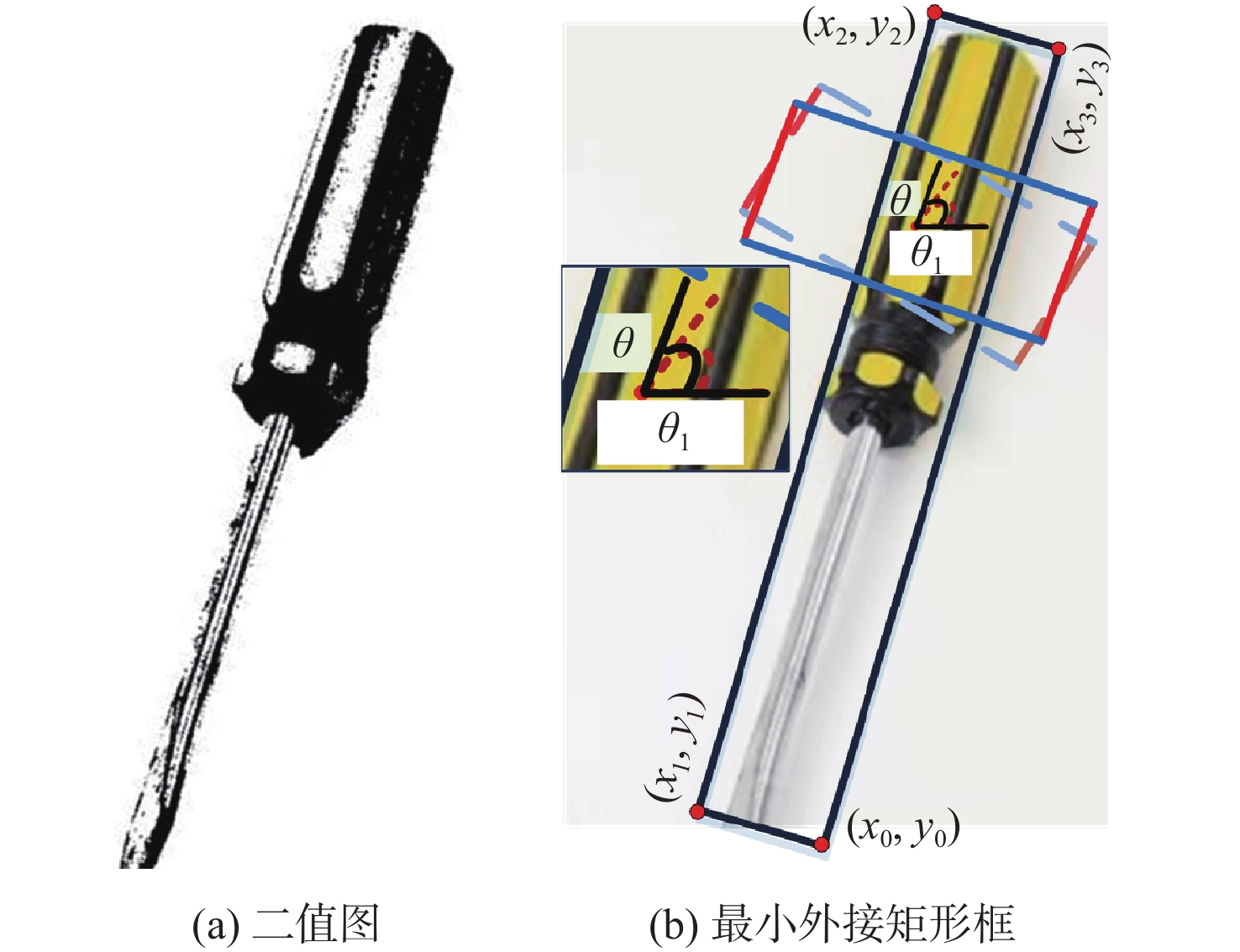
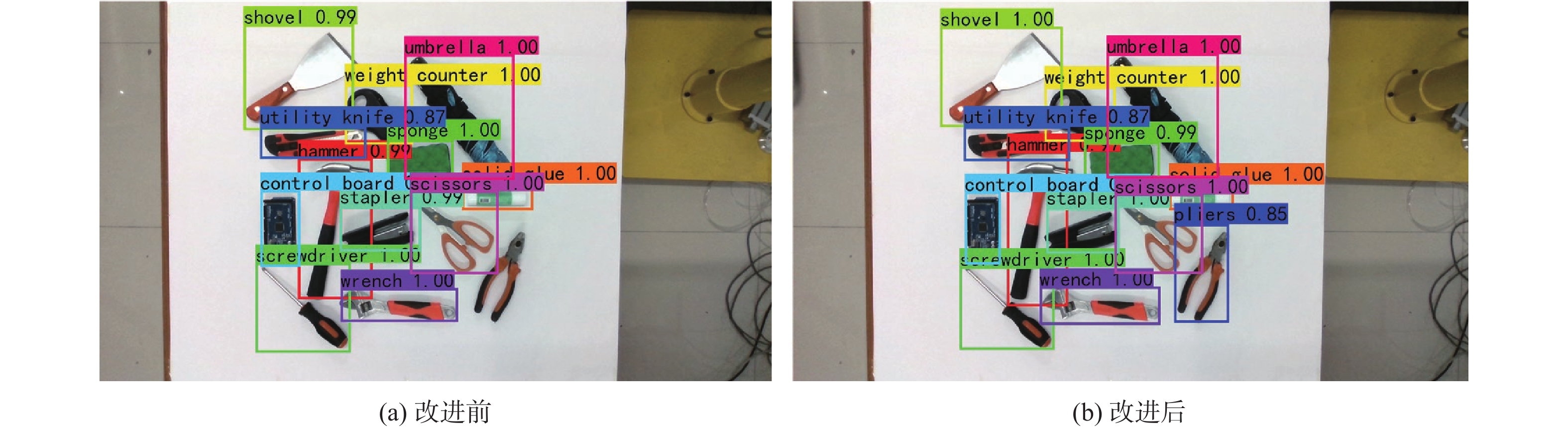
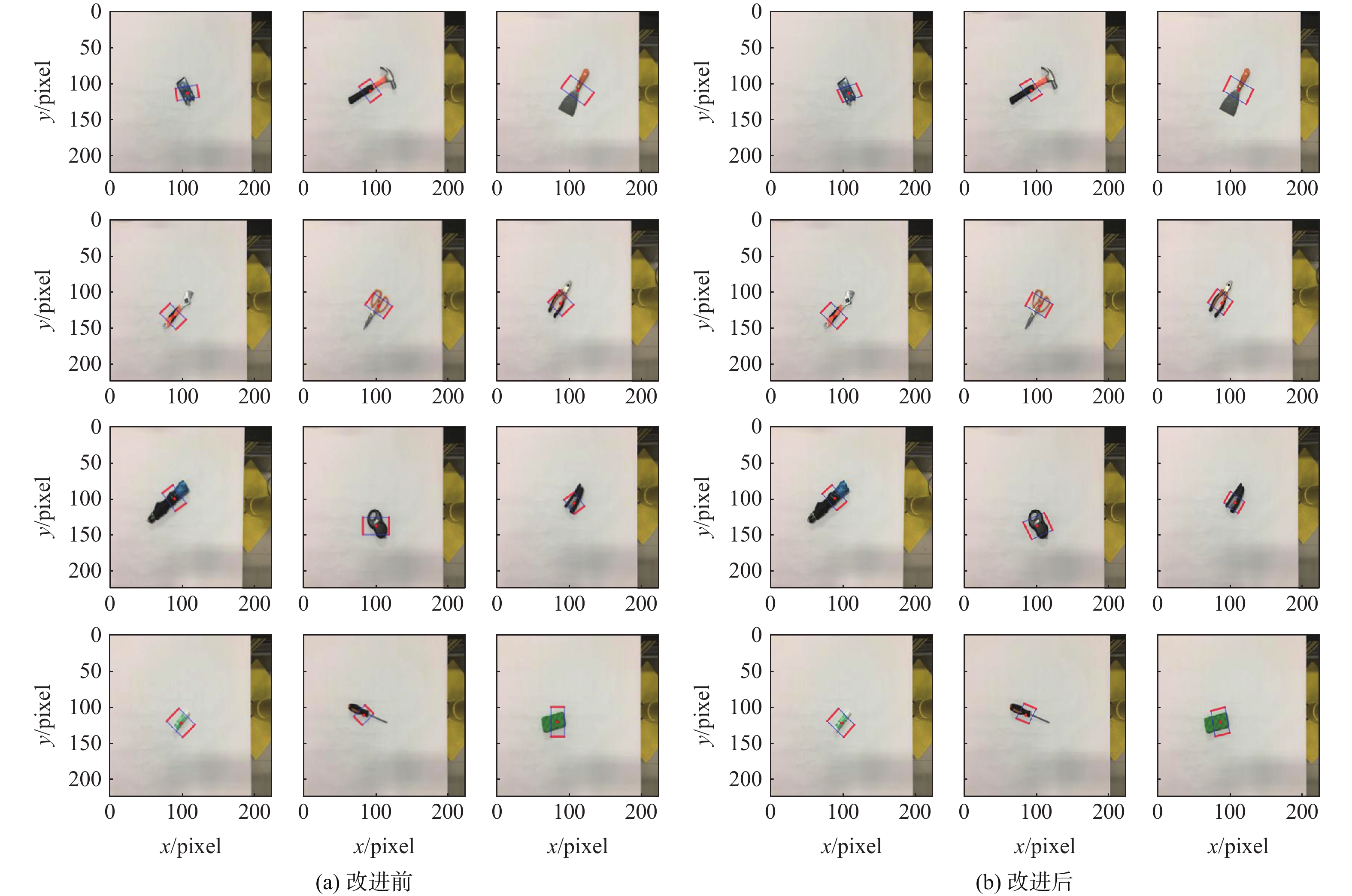
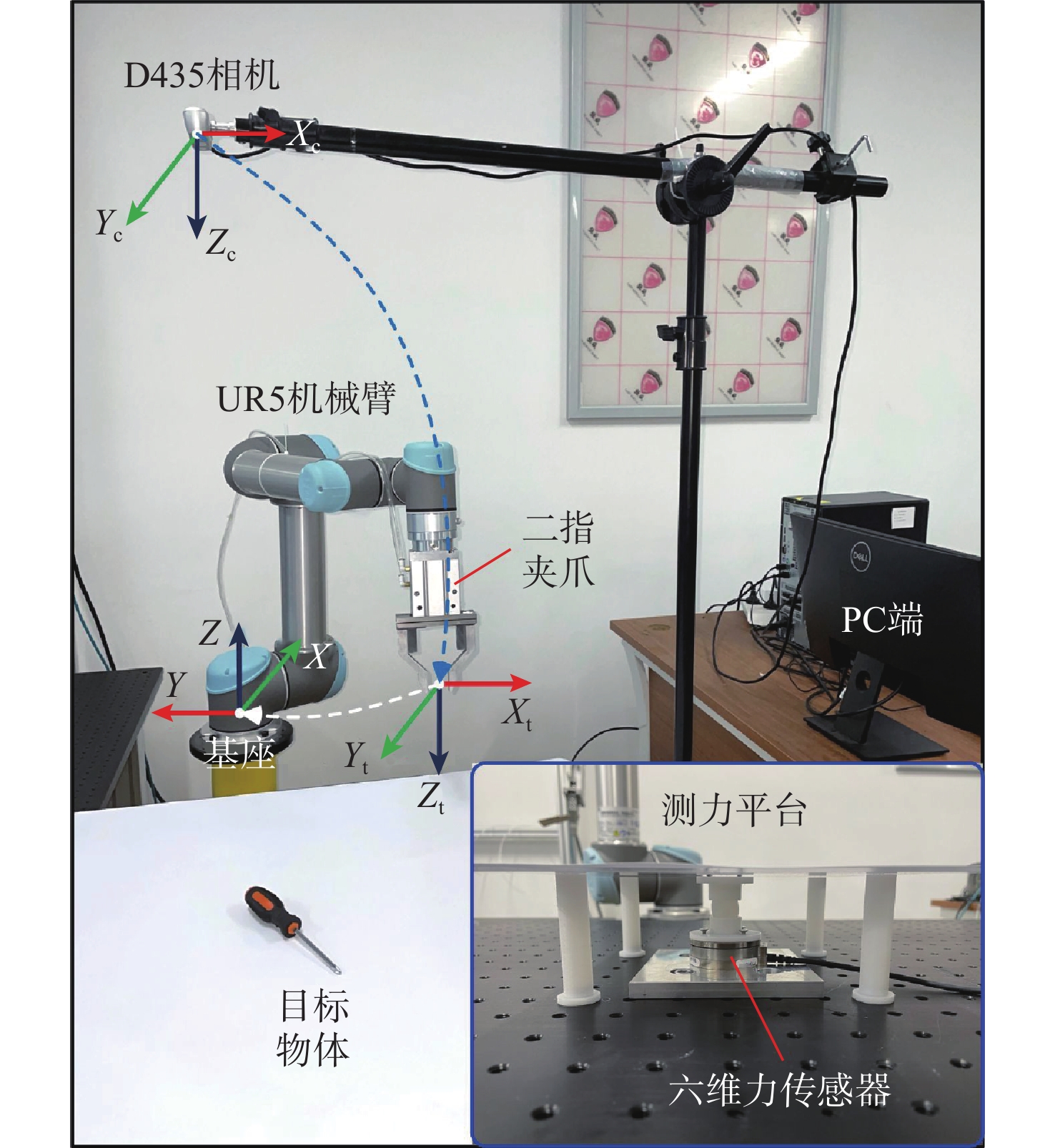
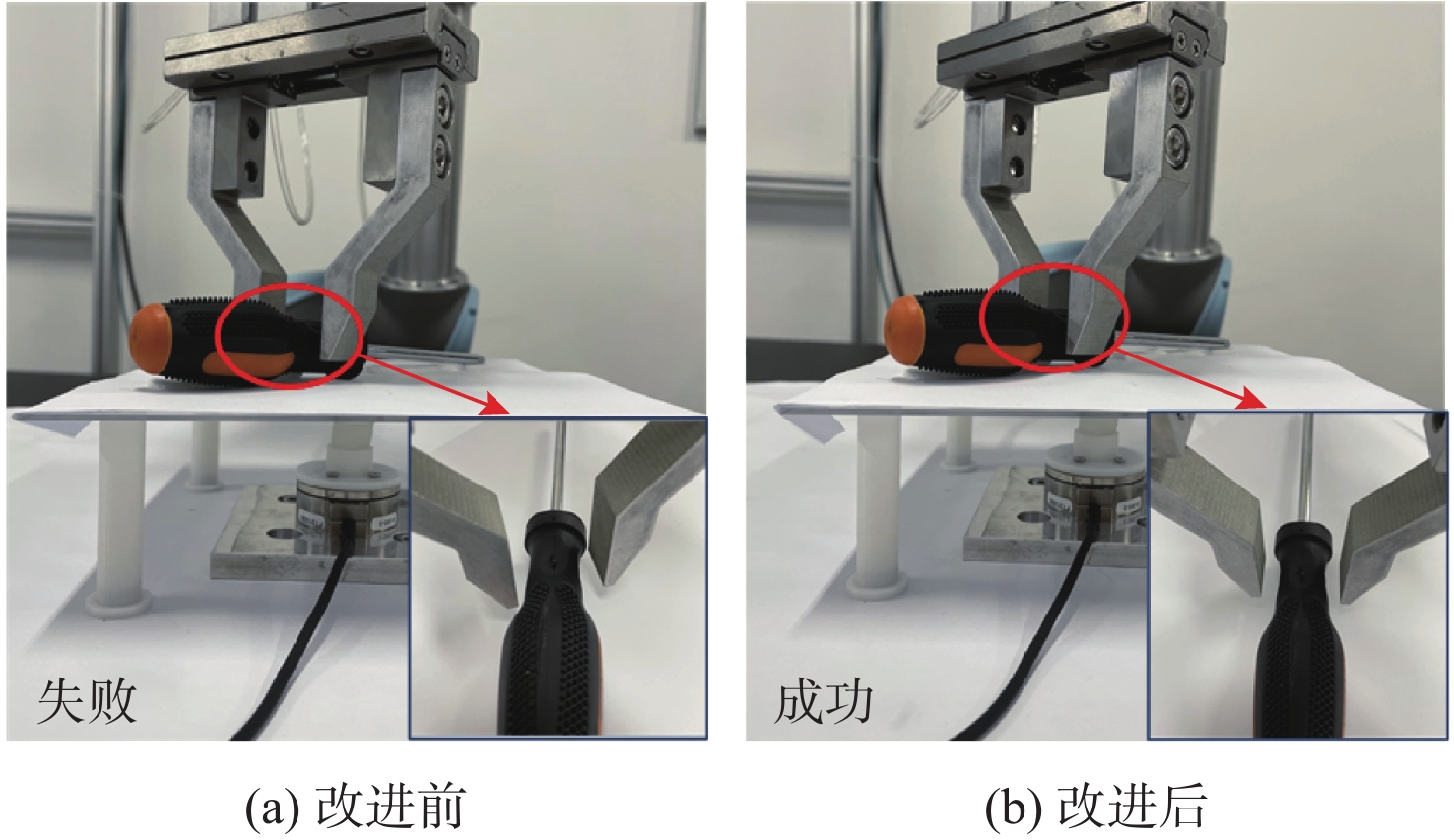
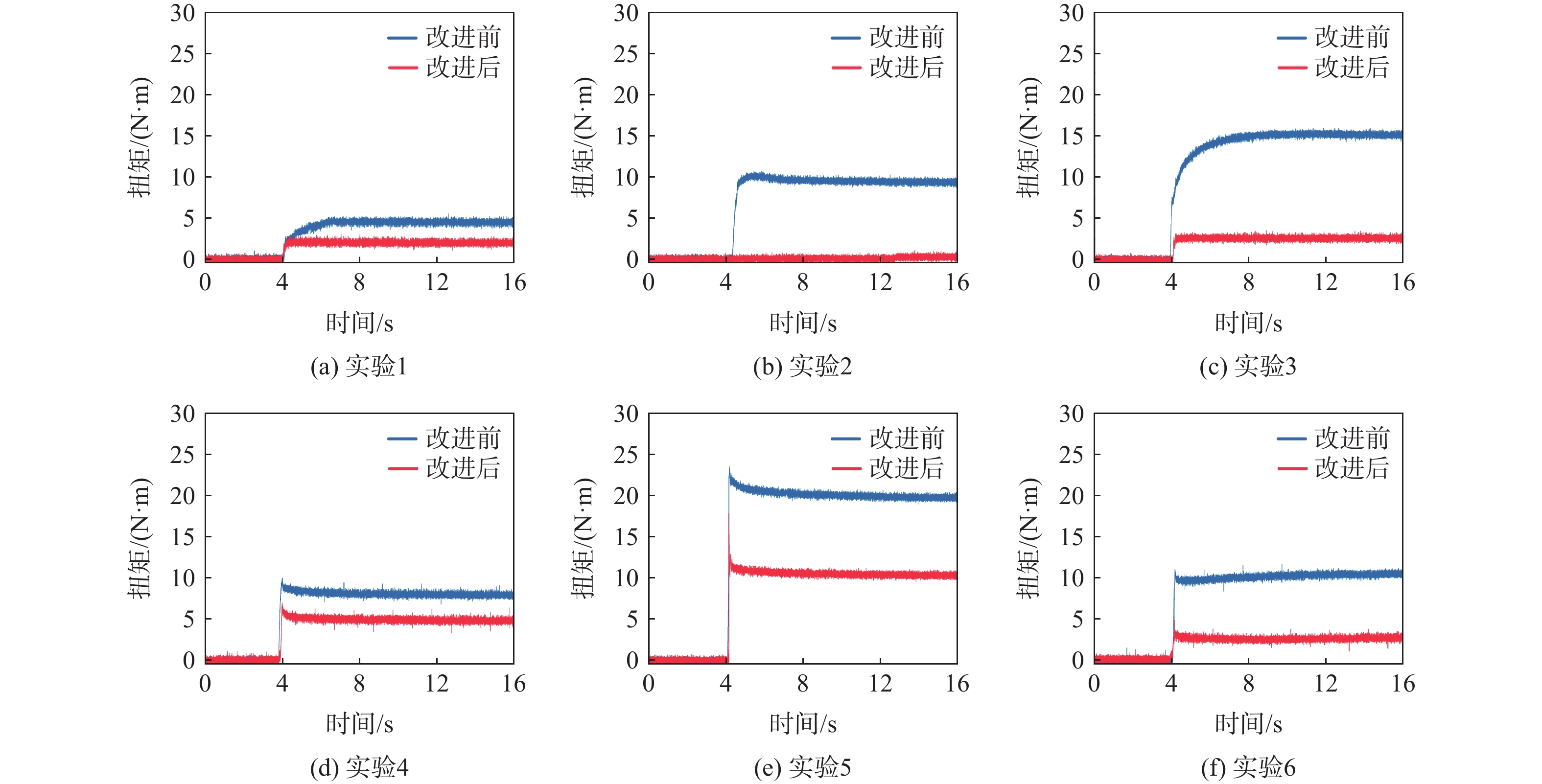
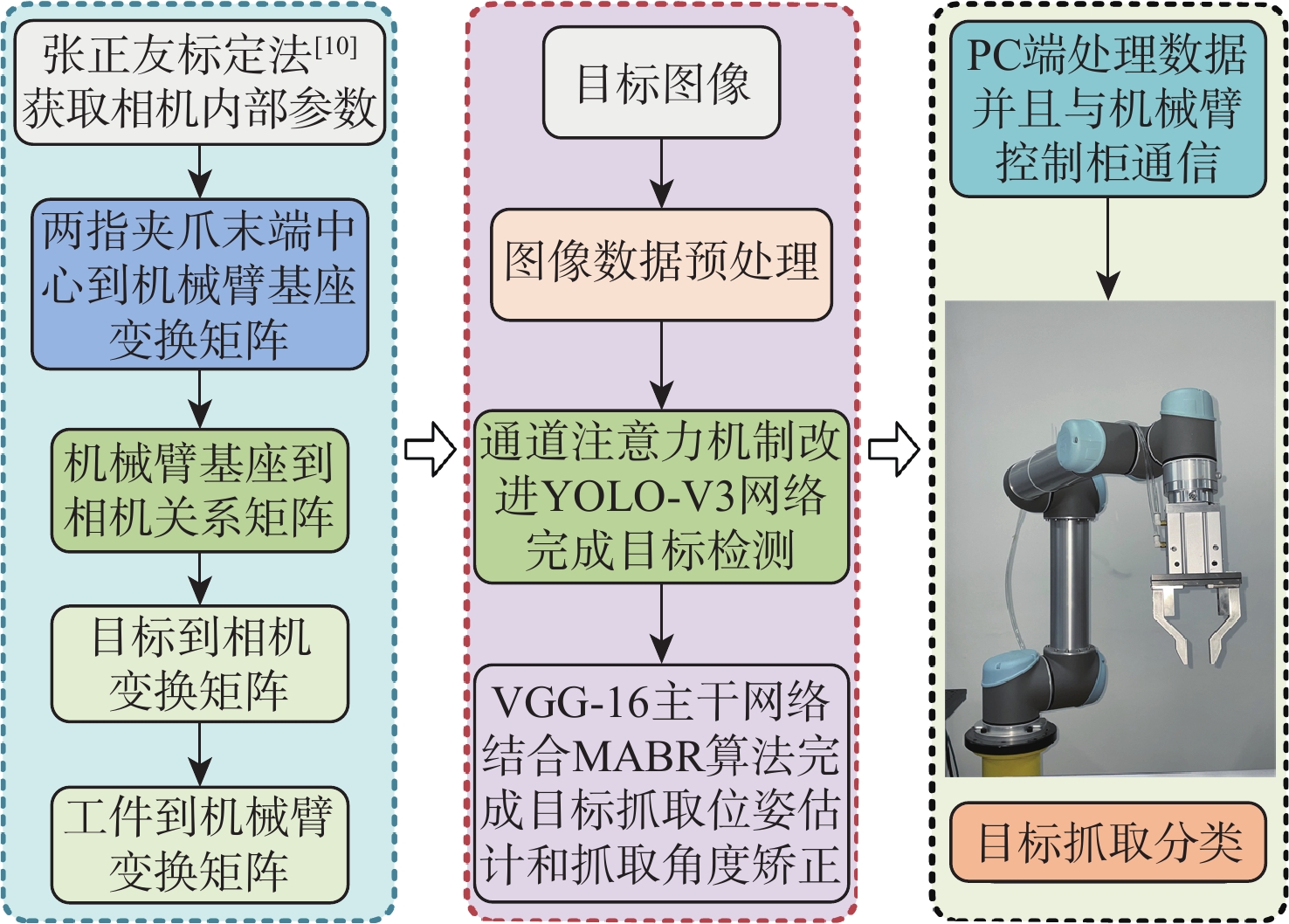
针对现有机器人抓取系统对硬件设备要求高、难以适应不同物体及抓取过程产生较大有害扭矩等问题,提出一种基于深度学习的视觉检测及抓取方法。采用通道注意力机制对YOLO-V3进行改进,增强网络对图像特征提取的能力,提升复杂环境中目标检测的效果,平均识别率较改进前增加0.32%。针对目前姿态估计角度存在离散性的问题,提出一种基于视觉几何组-16(VGG-16)主干网络嵌入最小面积外接矩形(MABR)算法,进行抓取位姿估计和角度优化。改进后的抓取角度与目标实际角度平均误差小于2.47°,大大降低两指机械手在抓取过程中对物体所额外施加的有害扭矩。利用UR5机械臂、气动两指机械手、Realsense D435相机及ATI-Mini45六维力传感器等设备搭建了一套视觉抓取系统,实验表明:所提方法可以有效地对不同物体进行抓取分类操作、对硬件的要求较低、并且将有害扭矩降低约75%,从而减小对物体的损害,具有很好的应用前景。
Abstract:This paper proposes a deep learning based visual detection and grasping method to solve the problems of the existing robotic grasping systems, including high hardware costs, difficulty in adapting to different objects, and large harmful torques. The channel attention mechanism is used to enhance the ability of the network to extract image features, improving the effect of target detection in complex environments using the improved YOLO-V3. It is found that the average recognition rate is increased by 0.32% compared with that before the improvement. In addition, to address the discreteness of estimated orientation angles, an embedded minimum area bounding rectangle (MABR) algorithm based on VGG-16 backbone network is proposed to estimate and optimize the grasping position and orientation. The average error between the improved predicted grasping angle and the actual angle of the target is less than 2.47°, significantly reducing the additional harmful torque applied by the two-finger gripper to the object in the grasping process. This study then builds a visual grasping system, using a UR5 robotic arm, a pneumatic two-finger robotic gripper, a Realsense D435 camera, and an ATI-Mini45 six-axis force/torque sensor. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively grasp and classify objects, with low requirements for hardware. It reduces the harmful torque by about 75%, thereby reducing damage to grasped objects, and showing a great application prospect.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- neural network /
- object detection /
- pose estimation /
- robotic grasping
-
表 1 不同网络结构对比
Table 1. Comparison of different network structure
网络结构 准确率/% 运行时间/s cornell数据集 实验目标 双层网络结构ResNet-50 91.30 87.11 0.932 单层网络结构ResNet-50 91.12 86.69 0.714 单层网络结构
VGG-1690.89 87.19 0.286 表 2 位姿估计结果
Table 2. Pose estimation results
目标 目标抓取点(u, v)/像素 目标抓取角度/(°) 目标实际角度/(°) 改进前 改进后 改进前 改进后 control board (107, 112.2) (107, 112.2) 100 124 123 hammer (92.3, 109.3) (92.3, 109.3) 30 18 23 shovel (111.3, 108.5) (111.3, 108.5) 50 62 59 wrench (87.5, 132.5) (87.5, 132.5) 40 46 44 scissors (104.5, 118.3) (104.5, 118.3) 50 53 54 pliers (88.1, 114.5) (88.1, 114.5) 40 48 52 umbrella (88.5, 98.4) (88.5, 98.4) 30 35 35 weight counter (100.5, 136.2) (100.5, 136.2) 90 135 127 stapler (106.9, 104.7) (106.9, 104.7) 30 46 48 solid glue (98.2, 120.9) (98.2, 120.9) 40 45 45 screwdriver (83.6, 110.2) (83.6, 110.2) 130 161 162 sponge (84.6, 118.7) (84.6, 118.7) 180 13 14 表 3 抓取实验数据
Table 3. Experimental data of grasping
编号 目标抓取点(x, y, z)/mm 目标抓取角度/(°) 目标实际角度/(°) 抓取扭矩/(N·mm) 改进前 改进后 改进前 改进后 改进前 改进后 实验1 (153.41, −675.29, 102.35) (153.41, −675.29, 102.35) 50 52 53 4.0 2.3 实验2 (13122, −603.70, 99.16) (13122, −603.70, 99.16) 50 58 58 9.5 0.3 实验3 (161.96, −558.44, 102.71) (161.96, −558.44, 102.71) 140 157 156 15.0 2.6 实验4 (111.15, −574.50, 98.79) (111.15, −574.50, 98.79) 10 21 19 8.0 5.0 实验5 (114.63, −732.19, 96.96) (114.63, −732.19, 96.96) 30 39 47 19.0 11.0 实验6 (102.68, −657.68, 100.41) (102.68, −657.68, 100.41) 40 51 50 10.6 2.5 实验7 (127.41, −675.63, 100.53) (127.41, −675.63, 100.53) 40 46 45 4.0 1.5 实验8 (155.39, −597.67, 105.50) (155.39, −597.67, 105.50) 50 53 55 8.0 3.8 实验9 (176.65, −690.90, 103.57) (176.65, −690.90, 103.57) 90 111 113 17.5 4.0 实验10 (131.77, −739.27, 100.34) (131.77, −739.27, 100.34) 100 112 112 12.5 0 实验11 (194.20, −687.68, 101.49) (194.20, −687.68, 101.49) 30 36 35 5.0 2.5 实验12 (127.47, −590.49, 100.38) (127.47, −590.49, 100.38) 30 63 63 25.0 0 -
[1] DU G G, WANG K, LIAN S G, et al. Vision-based robotic grasping from object localization, object pose estimation to grasp estimation for parallel grippers: A review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54(3): 1677-1734. doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09888-5 [2] 翟敬梅, 董鹏飞, 张铁. 基于视觉引导的工业机器人定位抓取系统设计[J]. 机械设计与研究, 2014, 30(5): 45-49.ZHAI J M, DONG P F, ZHANG T. Positioning and grasping system design of industrial robot based on visual guidance[J]. Machine Design & Research, 2014, 30(5): 45-49(in Chinese). [3] WEI H, PAN S C, MA G, et al. Vision-guided hand–eye coordination for robotic grasping and its application in tangram puzzles[J]. AI, 2021, 2(2): 209-228. doi: 10.3390/ai2020013 [4] MALLICK A, DEL POBIL A P, CERVERA E. Deep learning based object recognition for robot picking task[C]// Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-9. [5] 白成超, 晏卓, 宋俊霖. 结合深度学习的机械臂视觉抓取控制[J]. 载人航天, 2018, 24(3): 299-307.BAI C C, YAN Z, SONG J L. Visual grasp control of robotic arm based on deep learning[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2018, 24(3): 299-307(in Chinese). [6] 黄怡蒙, 易阳. 融合深度学习的机器人目标检测与定位[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2020, 56(24): 181-187.HUANG Y M, YI Y. Robot object detection and localization based on deep learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2020, 56(24): 181-187(in Chinese). [7] JIANG Y, MOSESON S, SAXENA A. Efficient grasping from RGBD images: Learning using a new rectangle representation[C]// 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 3304-3311. [8] CHU F J, XU R N, VELA P A. Real-world multiobject, multigrasp detection[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(4): 3355-3362. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2852777 [9] 夏浩宇, 索双富, 王洋, 等. 基于Keypoint RCNN改进模型的物体抓取检测算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42(4): 236-246.XIA H Y, SUO S F, WANG Y, et al. Object grasp detection algorithm based on improved Keypoint RCNN model[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(4): 236-246(in Chinese). [10] ZHANG Z Y. Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations[C]// Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 666-673. [11] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08) [2022-03-08]. [12] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10) [2022-03-08]. [13] SONG R, LI F M, FU T Y, et al. A robotic automatic assembly system based on vision[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(3): 1157. doi: 10.3390/app10031157 [14] 尹宏鹏, 陈波, 柴毅, 等. 基于视觉的目标检测与跟踪综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1466-1489.YIN H P, CHEN B, CHAI Y, et al. Vision-based object detection and tracking: a review[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1466-1489(in Chinese). [15] 王玺坤, 姜宏旭, 林珂玉. 基于改进型YOLO算法的遥感图像舰船检测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1184-1191.WANG X K, JIANG H X, LIN K Y. Remote sensing image ship detection based on modified YOLO algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1184-1191(in Chinese). [16] ZHANG N, DONAHUE J, GIRSHICK R, et al. Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 834-849. [17] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]// 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1440-1448. [18] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [19] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]/2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [20] 刘元宁, 吴迪, 朱晓冬, 等. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033.LIU Y N, WU D, ZHU X D, et al. User interface components detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv3[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033(in Chinese). [21] 熊军林, 赵铎. 基于RGB图像的二阶段机器人抓取位置检测方法[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报, 2020, 50(1): 1-10.XIONG J L, ZHAO D. Two-stage grasping detection for robots based on RGB images[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2020, 50(1): 1-10(in Chinese). [22] TEKIN B, SINHA S N, FUA P. Real-time seamless single shot 6D object pose prediction[C]/2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 292-301. [23] KUMRA S, KANAN C. Robotic grasp detection using deep convolutional neural networks[C]// 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 769-776. -







 下载:
下载: