-
摘要:
扑翼机具备仿鸟类的外形,能够隐蔽执行侦查监视任务,合理设计翼面形状和运动过程能够提升扑翼飞行气动效应。当前针对扑翼翼面设计问题,缺乏考虑流固耦合效应的优化设计研究,还未在设计阶段考虑改变柔性翼面形状对扑翼气动特性的影响,且现有研究只涉及对翼面形状或扑翼运动的单因素分析讨论,缺乏综合2种设计因素的优化设计。针对定速前飞的柔性扑翼翼面进行气动特性优化设计,采用Newmark-
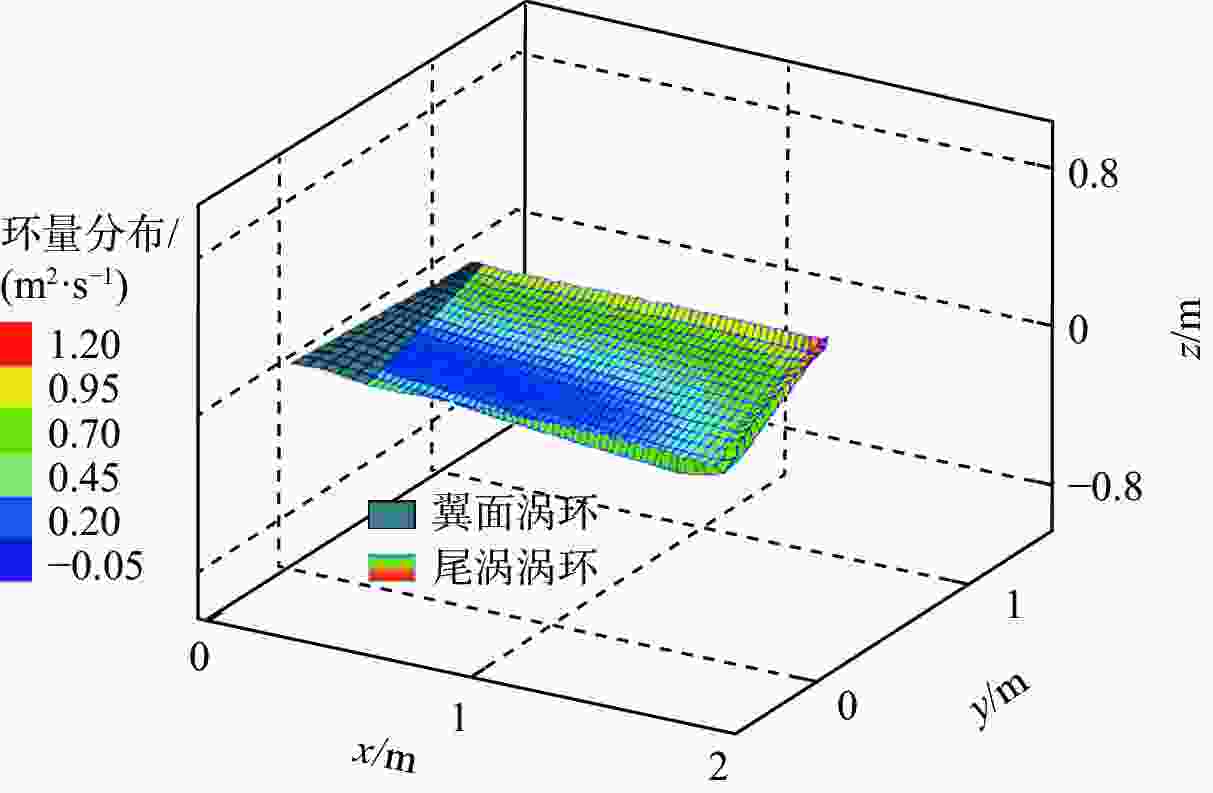
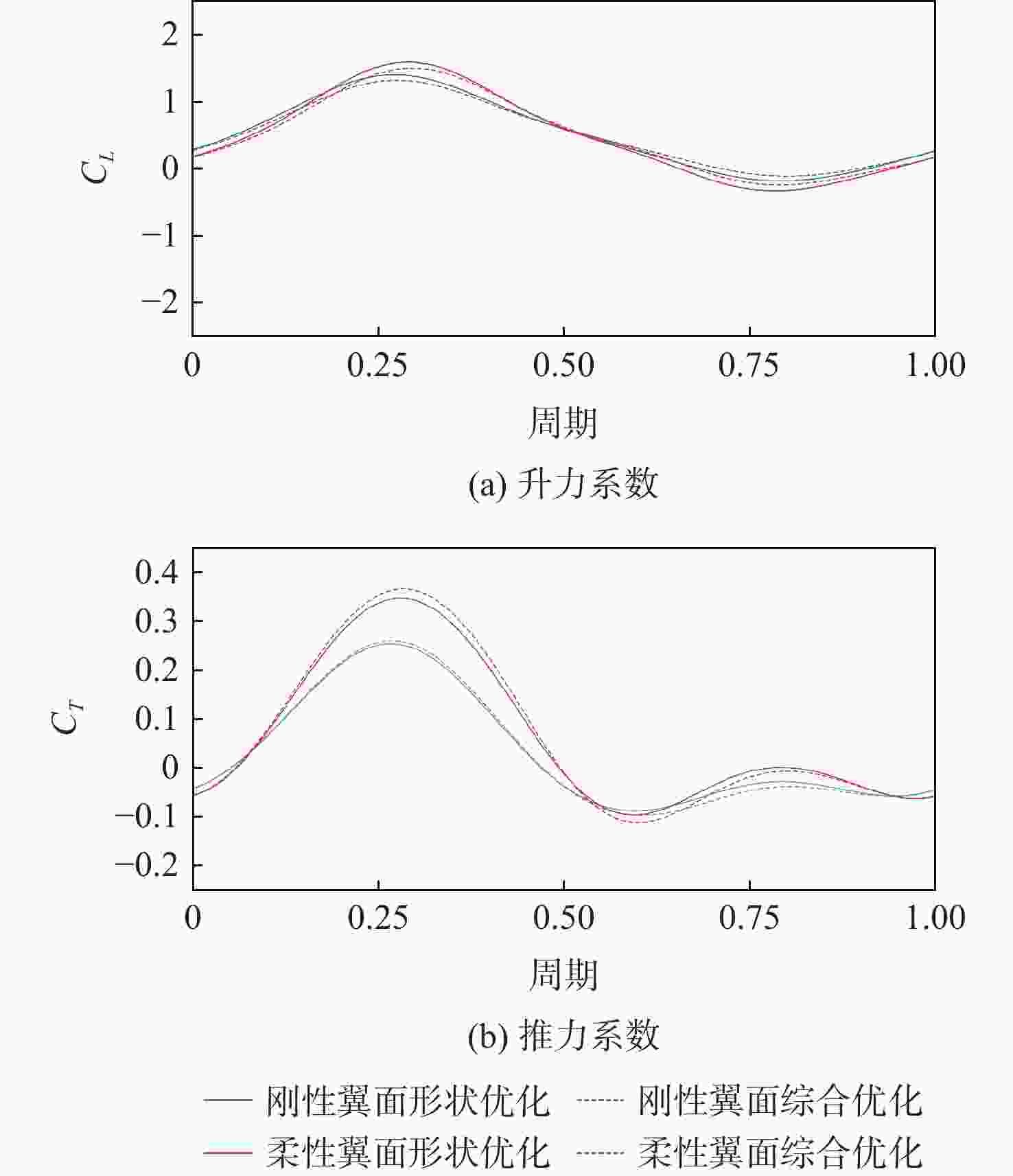
β 方法求解结构响应,并与现成软件求解器的计算结果进行对比,验证结构动力学计算方法的准确性,用非定常涡格法(UVLM)计算扑翼气动力,搭建了高效的流固耦合计算框架。由于扑翼复杂设计空间具有多个局部最优点,采用与并行计算结合的细分矩形(DIRECT)全局优化算法,提高计算效率,对柔性扑翼翼面的形状和运动参数进行迭代优化,确定最大化推进效率的设计参数,并与刚性模型优化结果进行对比。结果表明:柔性扑翼翼面形状和运动优化设计能够获得更高的推进效率,与只采用形状优化相比最优推进效率提高了5.6%,比刚性模型优化结果提高了27.0%。Abstract:With the development of advanced materials and microelectronic technology, the design and manufacture of flapping wing aircraft has become a research topic of great concern in recent years. The bird-like shape makes it suitable for conversion investigation and monitoring. The best shape and motion can enhance the aerodynamic impact of flapping flight, according to research conducted both domestically and internationally. However, research on flapping wing design less considering the effect of fluid-structure interaction, and the influence of changing the shape of a flexible flapping wing on the aerodynamic characteristics has not been considered in the design stage. Moreover, the existing researches only involve single-factor analysis and lack the optimal design combining both wing shape and flapping motion. In this paper, an effective fluid-structure coupling framework is used to optimize the aerodynamics of a flexible flapping wing in forward flight at constant speed. The structural response is solved by the Newmark-
β method, and its accuracy is verified compared with the calculation results of the ready-made software. The unsteady vortex lattice method (UVLM) is used to calculate the aerodynamic force. This research uses parallel computing to increase the effectiveness of the divide rectangle (DIRECT) global optimization technique since the complicated design space of the flapping wing includes several Local optimum states. The shape and motion parameters of a flexible flapping wing are iteratively optimized to determine a design scheme to maximize propulsion efficiency. The results of the rigid model are also compared. The results show that the optimal design of the shape and motion of a flexible flapping wing can obtain higher propulsion efficiency. It is improved by 5.6% compared to that of shape optimization and 27.0% compared to that of rigid model. -
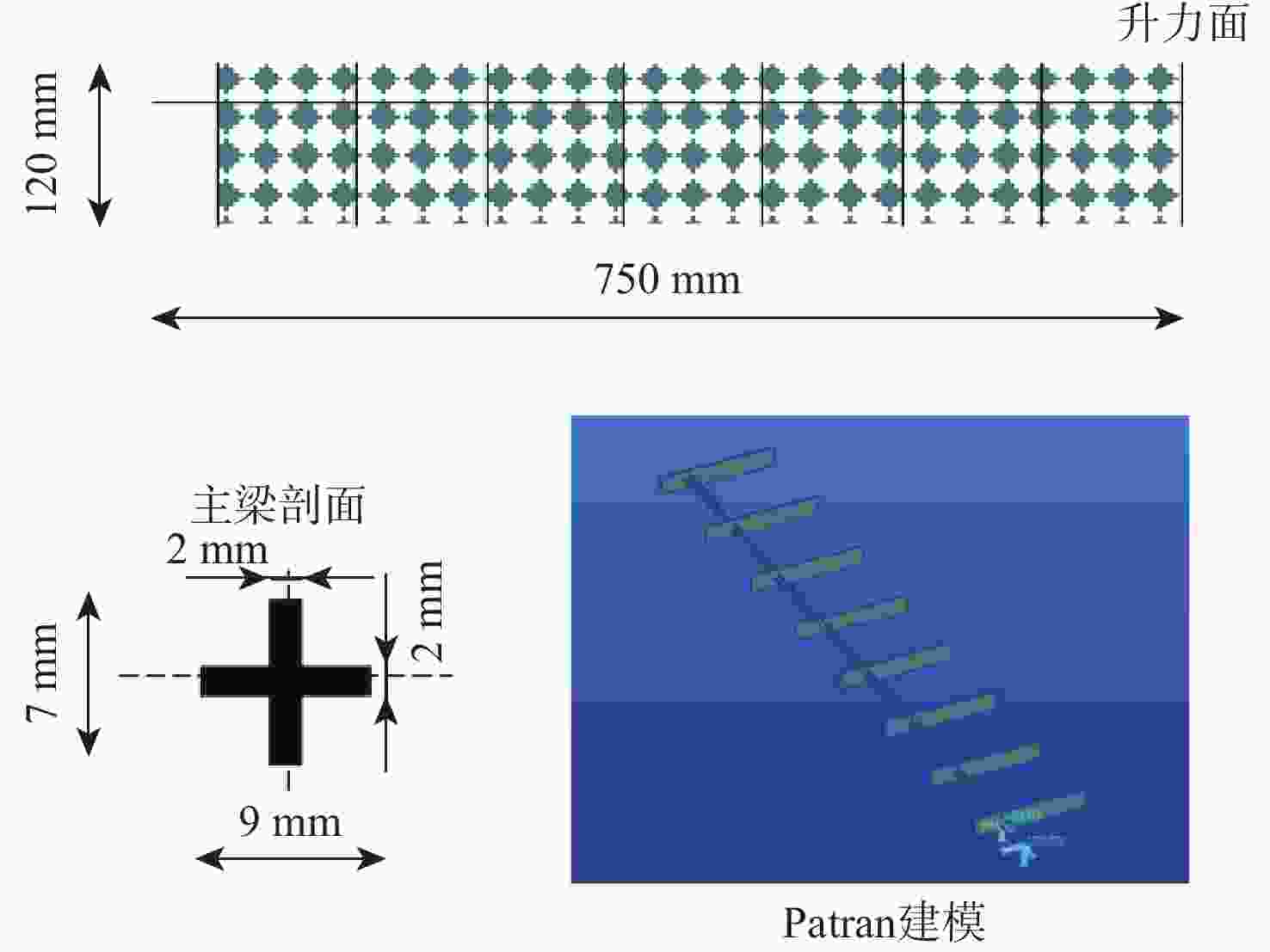
表 1 结构动力学验证材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters for structural dynamics validation
类型 密度/(kg·m−3) 泊松比 弹性模量/GPa 主梁材料 2700 0.34 70 翼肋材料 1800 0.3 210 表 2 优化翼面的初始参数
Table 2. Initial parameters of wing model optimization
半展长/
m平均弦长/
m根梢比 1/4弦线后
掠角/(°)密度/
(kg·m−3)弹性模量/
GPa1.08 0.1648 7.244 0 1200 5.2 表 3 2种优化问题的参数组合
Table 3. Set of parameters in two cases of optimization
项目 形状参数/mm 运动参数/(°) 形状优化 $0\; \leqslant {x_1} \leqslant 30\;$ $ {\theta _0}{\rm{ = }}{3.4} $ $0\; \leqslant {x_2} \leqslant 10\;$ ${\theta _{\rm{a}}}{\rm{ = } }{12}$ 综合优化 $- 30\; \leqslant {x_3} \leqslant 0\;$ $ {3} \leqslant {\theta _0} \leqslant {5} $ $- 10\; \leqslant {x_4} \leqslant 0\;$ ${10} \leqslant {\theta _{\rm{a}}} \leqslant {15}$ 表 4 以最大推进效率为目标的优化结果
Table 4. Optimal results for maximum propulsion efficiency
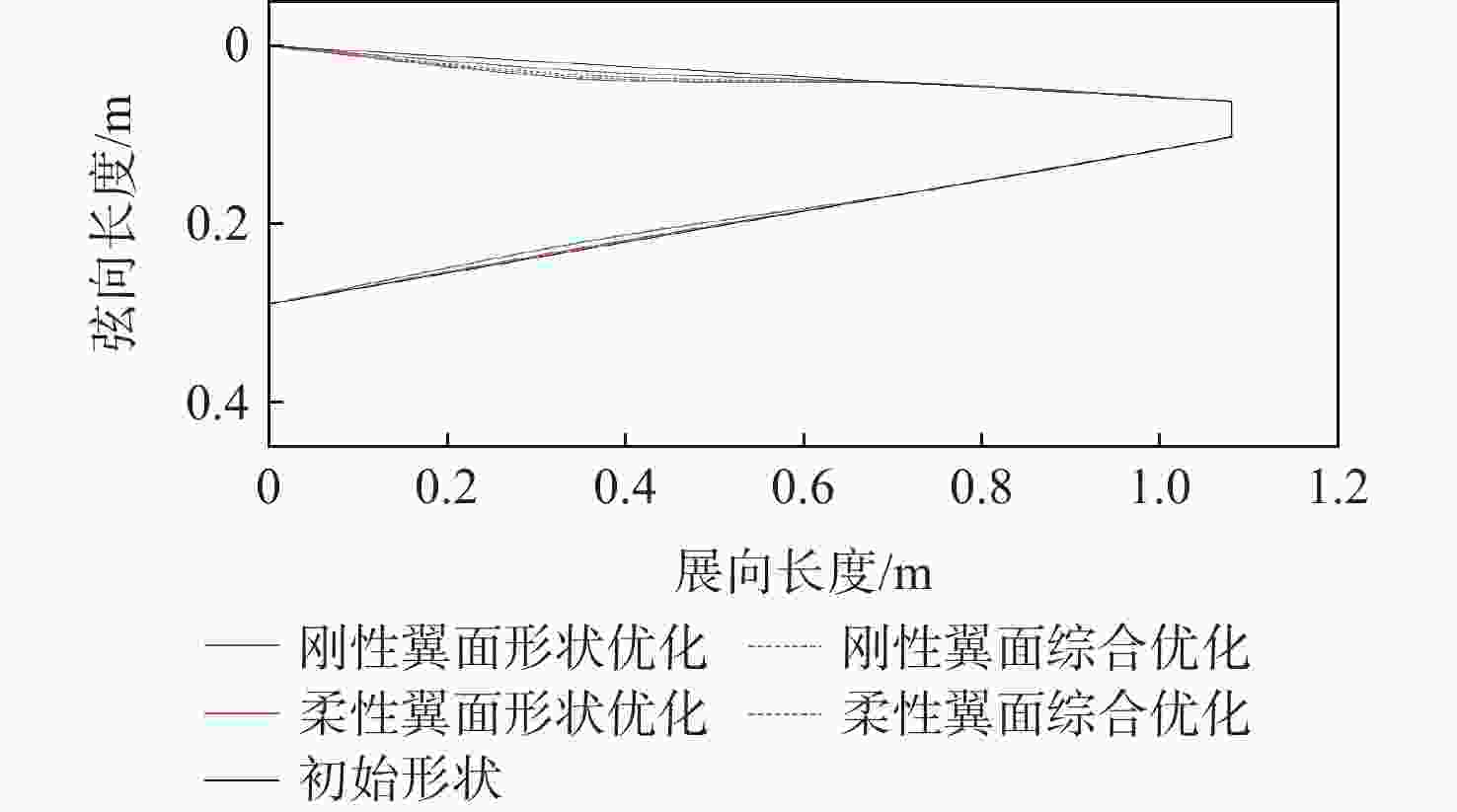
项目 推进效率$ \eta $ 形状参数/mm 角度/(°) $ {x_1} $ $ {x_2} $ $ {x_3} $ $ {x_4} $ $ {\theta _0} $ ${\theta _{\rm{a}}}$ 形状优化 刚性翼面 0.146 17.1 0.0 −8.8 −0.1 柔性翼面 0.178 7.9 0.0 −2.3 −0.1 综合优化 刚性翼面 0.148 15.0 0.1 −8.3 −0.2 3.35 12.13 柔性翼面 0.188 12.7 0.0 −1.0 0.0 3.39 15.00 -
[1] KEENNON M, KLINGEBIEL K, WON H. Development of the nano hummingbird: A tailless flapping wing micro air vehicle[C]// Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2012. [2] RAZAK N A, DIMITRIADIS G. Experimental study of wings undergoing active root flapping and pitching[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2014, 49: 687-704. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2014.06.009 [3] NICK T P S, TAI Y C, HO C M, et al. Microbat: A palm-sized electrically powered ornithopter[C]//Proceedings of the NASA/JPL Workshop on Biomorphic Robotics. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 2001. [4] SRIGRAROM S, CHAN W L. Flow field of flapping albatross-like wing and sound at low reynolds number[J]. Journal of Unmanned System Technology, 2013, 1(2): 1-2. [5] GHOMMEM M, HAJJ M R, MOOK D T, et al. Global optimization of actively morphing flapping wings[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2012, 33: 210-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2012.04.013 [6] GHOMMEM M, COLLIER N, NIEMI A H, et al. On the shape optimization of flapping wings and their performance analysis[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2014, 32(1): 274-292. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2013.10.010 [7] LARIJANI R. A non-linear aeroelastic model for the study of flapping-wing flight[D]. Toronto : University of Toronto, 2000. [8] REICHERT T. Kinematic optimization in birds, bats and ornithopters[D]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 2011. [9] ZHU Q A. Numerical simulation of a flapping foil with chordwise or spanwise flexibility[J]. AIAA Journal, 2007, 45(10): 2448-2457. doi: 10.2514/1.28565 [10] KAMAKOTI R, SHYY W. Fluid-structure interaction for aeroelastic applications[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2004, 40(8): 535-558. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2005.01.001 [11] GABLONSKY J M. Modifications of the DIRECT algorithm [D]. Raleigh: North Carolina State University, 2001. [12] WU Y E, XIE C C, MENG Y, et al. Kinematic optimization of a flexible wing undergoing flapping and pitching[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2021, 2021: 1-14. [13] KATZ J, PLOTKIN A. Low speed aerodynamics: From wing theory to panel methods [M]. Singapore: Mcgraw-Hill Press, 1991. [14] XIE C C, YANG C. Surface splines generalization and large deflection interpolation[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(3): 1024-1026. doi: 10.2514/1.24571 [15] GHOMMEM M, COLLIER N, NIEMI A H, et al. Shape optimisation and performance analysis of flapping wings[C]// Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Engineering Computational Technology. Stirlingshire: Civil-Comp Press, 2012. -







 下载:
下载: