Nonlinear flutter modes and flutter suppression of an all-movable fin with freeplay
-
摘要:
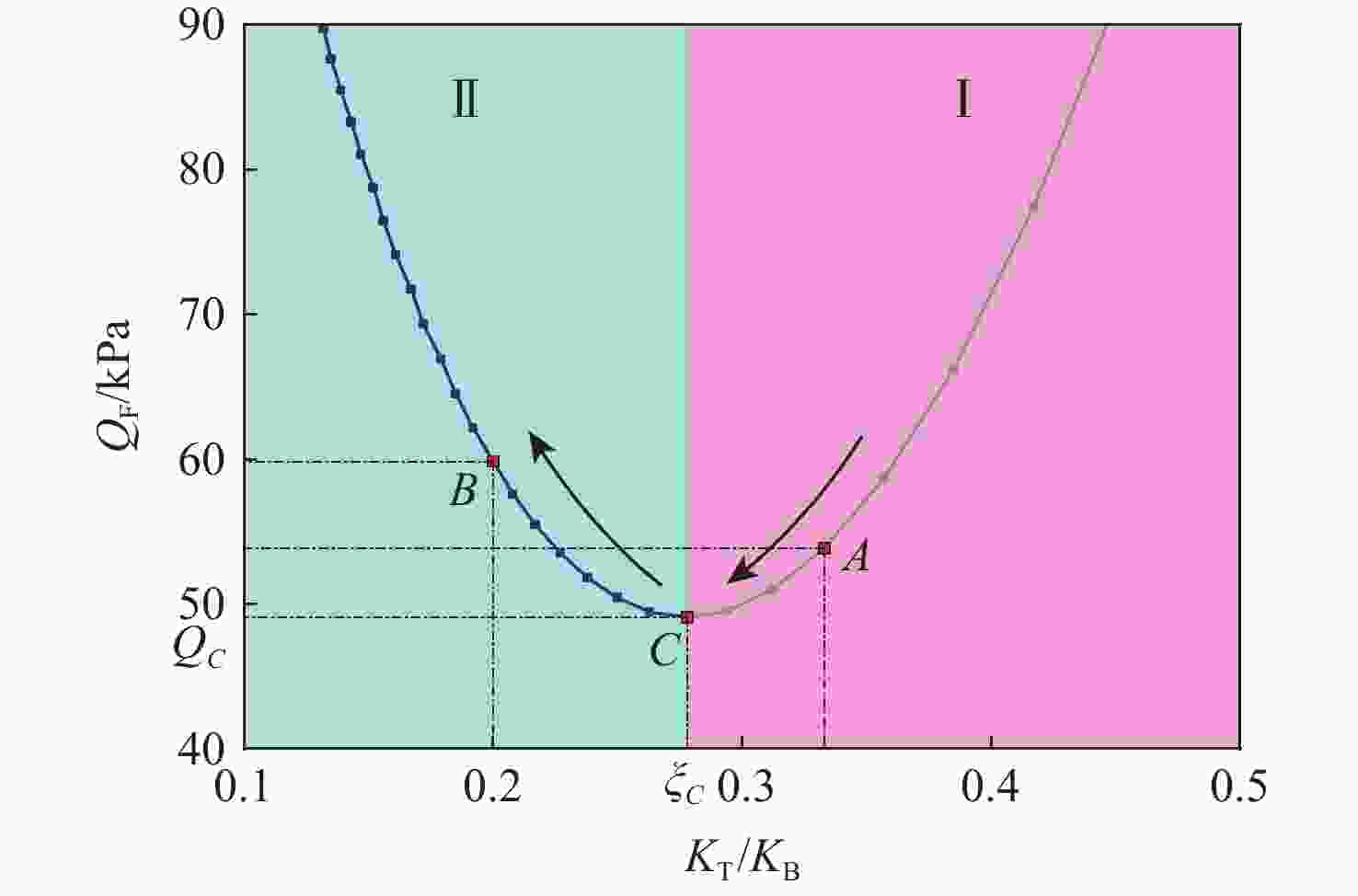
间隙非线性环节广泛存在于飞行器的结构当中,由其引发的极限环振荡(LCO)往往造成结构的疲劳破坏,但目前关于全动舵面非线性颤振机理和被动抑制方法的研究相对较少。针对典型含扭转间隙小展弦比全动舵面开展分析,提出了2种典型的非线性颤振模式,并探索相应的非线性颤振被动抑制方法。基于描述函数法和活塞理论建立舵面的动力学模型,考虑到间隙非线性环节导致刚度降低的效果,计算对比了2种不同扭转刚度下全动舵面的非线性颤振特性,进而提出了2种不同的非线性颤振模式,其中,模式Ⅱ不存在稳定的极限环振荡过程,可以有效抑制低于线性颤振边界的极限环振荡问题;研究了舵面根部弯曲扭转刚度和质量特性对非线性颤振模式和极限环初始动压的影响,提出相应的非线性颤振被动抑制策略。针对所提算例,数值计算结果表明:通过调整舵面根部弯曲扭转刚度或质量特性可以提高极限环初始动压,甚至改变非线性颤振模式,从而达到非线性颤振抑制的目的。
Abstract:Freeplay nonlinearity widely exists in the structure of aircraft, which can bring limit cycle oscillations (LCO), leading to the fatigue failure of the structure. There is relatively little research on the mechanism and passive suppression of the nonlinear flutter for all-movable fins. Therefore, this paper proposes two different nonlinear flutter modes and provides passive suppression methods. The dynamic model is developed using the describing function method and piston theory. Considering that the torsional stiffness is reduced due to the existence of the freeplay, nonlinear flutter characteristics under different torsional stiffnesses are compared and two different nonlinear flutter modes are defined, in which mode Ⅱ doesn’t contain stable LCO, effectively suppressing the LCO below the linear flutter boundary. Then the influence of bending and torsional stiffnesses and mass moments of inertia on nonlinear flutter modes and the dynamic pressure of LCO appearance is studied, and some nonlinear flutter passive suppression methods are proposed. The findings indicate that reasonable adjustment of the bending and torsional stiffnesses or mass moments of inertia can raise the dynamic pressure of LCO appearance and even change the nonlinear flutter mode, so as to suppress the nonlinear flutter.
-
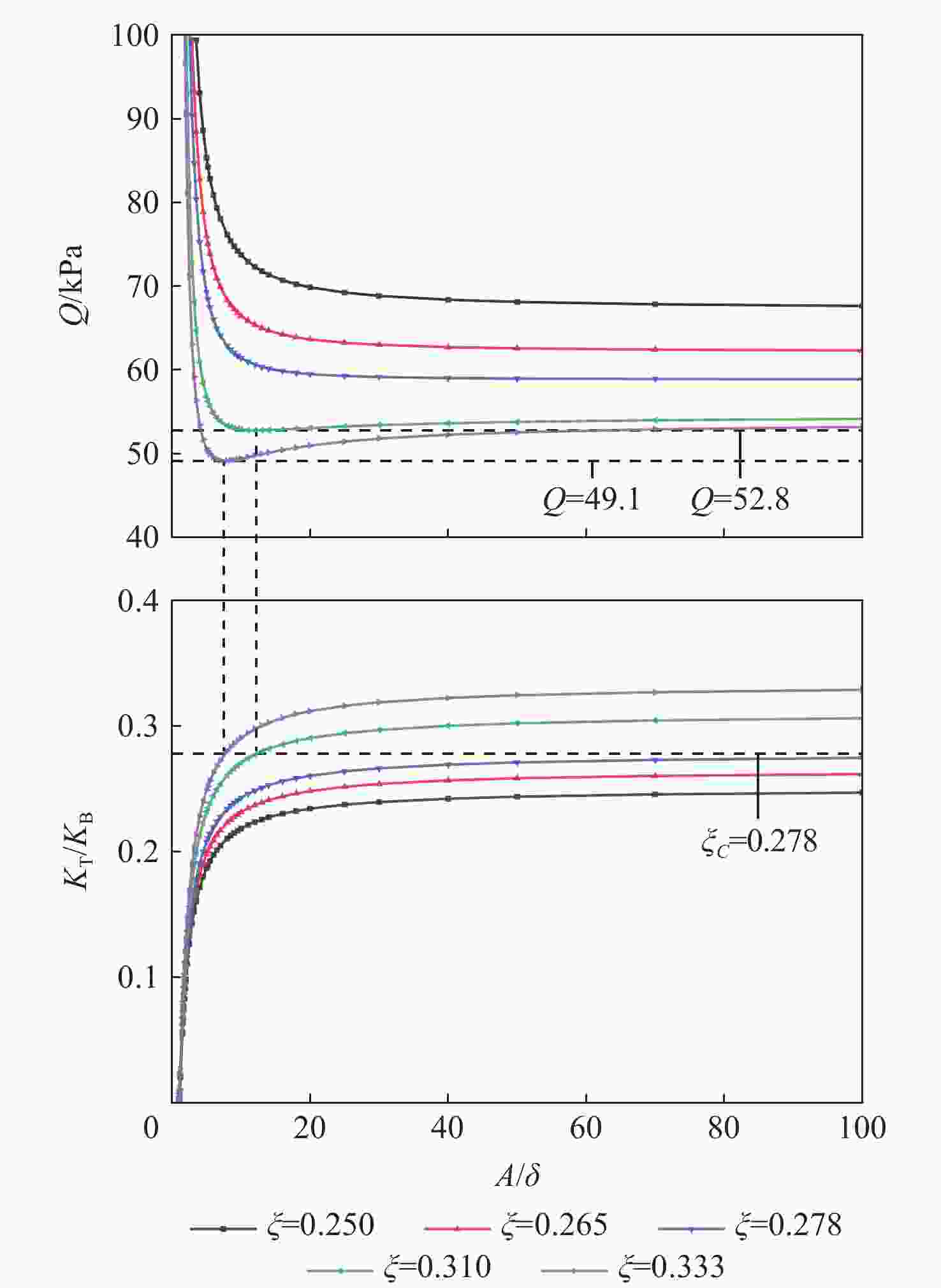
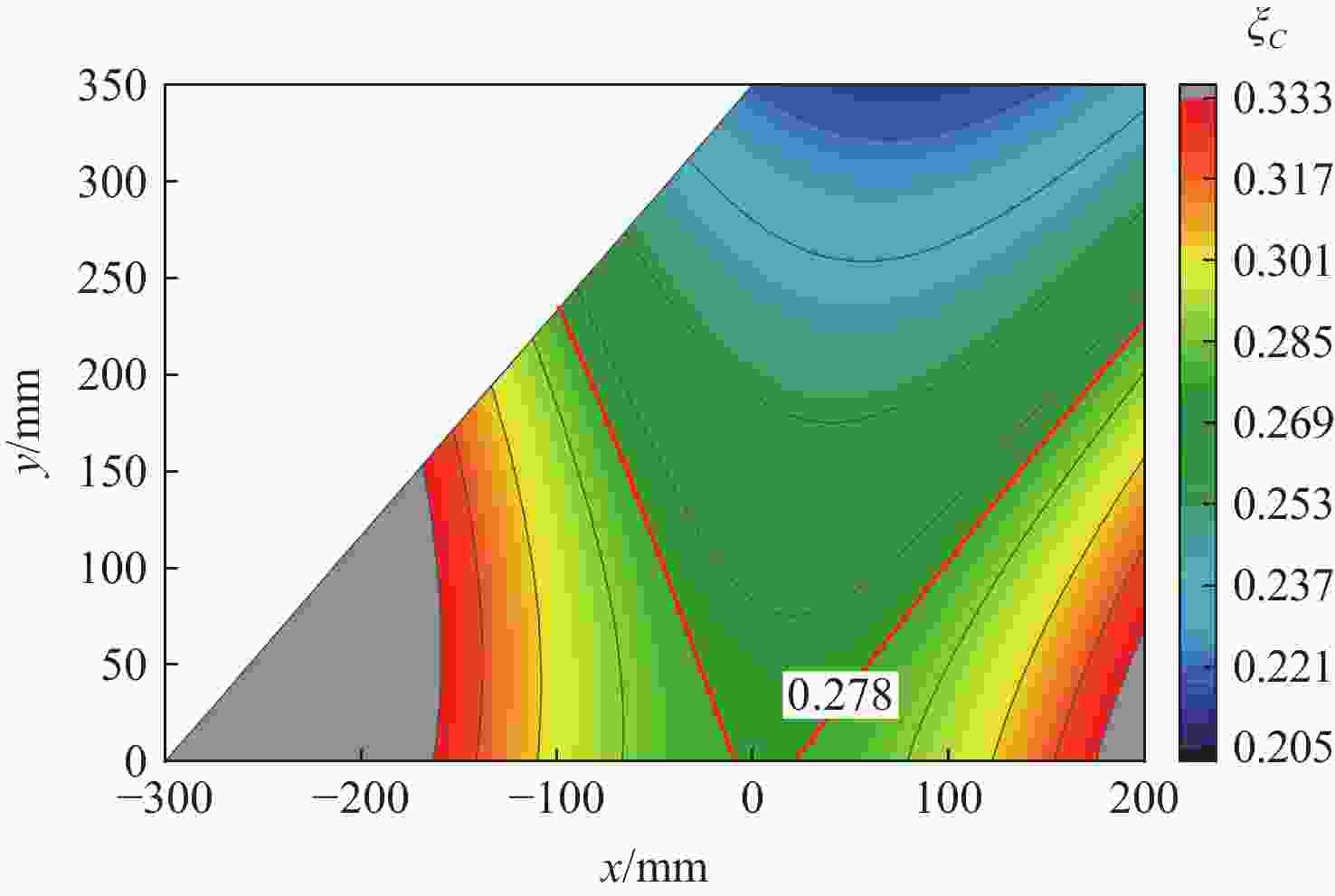
图 3 ${{{{\bar K}_{\text{T}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{{\bar K}_{\text{T}}}} {{K_{\text{T}}}}}} \right. } {{K_{\text{T}}}}}$随$ {A \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {A \delta }} \right. } \delta } $变化情况
Figure 3. ${{{{\bar K}_{\text{T}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{{\bar K}_{\text{T}}}} {{K_{\text{T}}}}}} \right. } {{K_{\text{T}}}}}$ with variation of $ {A \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {A \delta }} \right. } \delta } $
表 1 全动舵面结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of all-movable fin
参数 数值 质量$m/{\text{kg}}$ $ 3.794 $ 质心${ {\left[ { {x_{\text{c} } },{y_{\text{c} } } } \right]} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { {\left[ { {x_{\text{c} } },{y_{\text{c} } } } \right]} {\rm{m}}} } \right. } {\rm{m}}}$ $[0.012,{\text{ }}0.154]$ 转动惯量${ { {I_{xx} } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {I_{xx} } } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} } } \right. } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} }$ $1.275 \times {10^{ - 1}}$ 转动惯量${ { {I_{xy} } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {I_{xy} } } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} } } \right. } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} }$ $2.042 \times {10^{ - 2}}$ 转动惯量${ { {I_{yy} } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {I_{yy} } } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} } } \right. } {\left( { {\text{kg} } \cdot { {\text{m} }^2} } \right)} }$ $4.035 \times {10^{ - 2}}$ 弯曲弹簧刚度${ { {K_{\text{B} } } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {K_{\text{B} } } } {\left( { {\text{N} }\cdot{\text{m} } \cdot {\text{ra} }{ {\text{d} }^{ - 1} } } \right)} } } \right. } {\left( { {\text{N} }\cdot{\text{m} }\cdot {\text{ra} }{ {\text{d} }^{ - 1} } } \right)} }$ $ 9.0 \times {10^3} $ 扭转弹簧刚度${ { {K_{\text{T} } } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { { {K_{\text{T} } } } {\left( { {\text{N} }\cdot{\text{m} } \cdot {\text{ra} }{ {\text{d} }^{ - 1} } } \right)} } } \right. } {\left( { {\text{N} }\cdot{\text{m} }\cdot {\text{ra} }{ {\text{d} }^{ - 1} } } \right)} }$ $ 3.0 \times {10^3} $ 表 2 模态频率计算结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of modal frequency calculation results
Hz 模态阶数 简化模型 有限元模型 1 37.77 37.31 2 50.68 50.23 3 407.12 4 517.66 5 573.28 表 3 线性颤振结果
Table 3. Linear flutter results
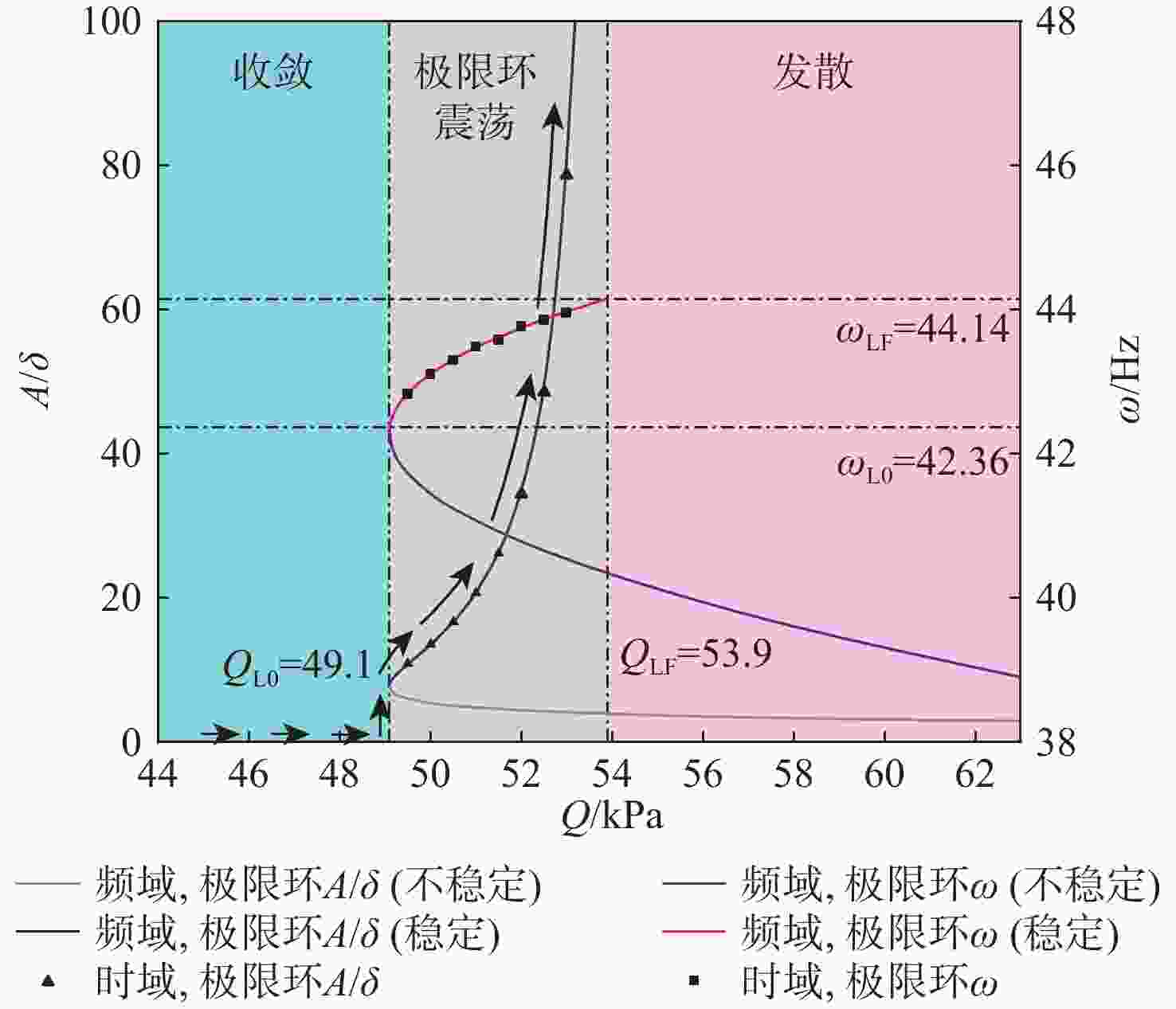
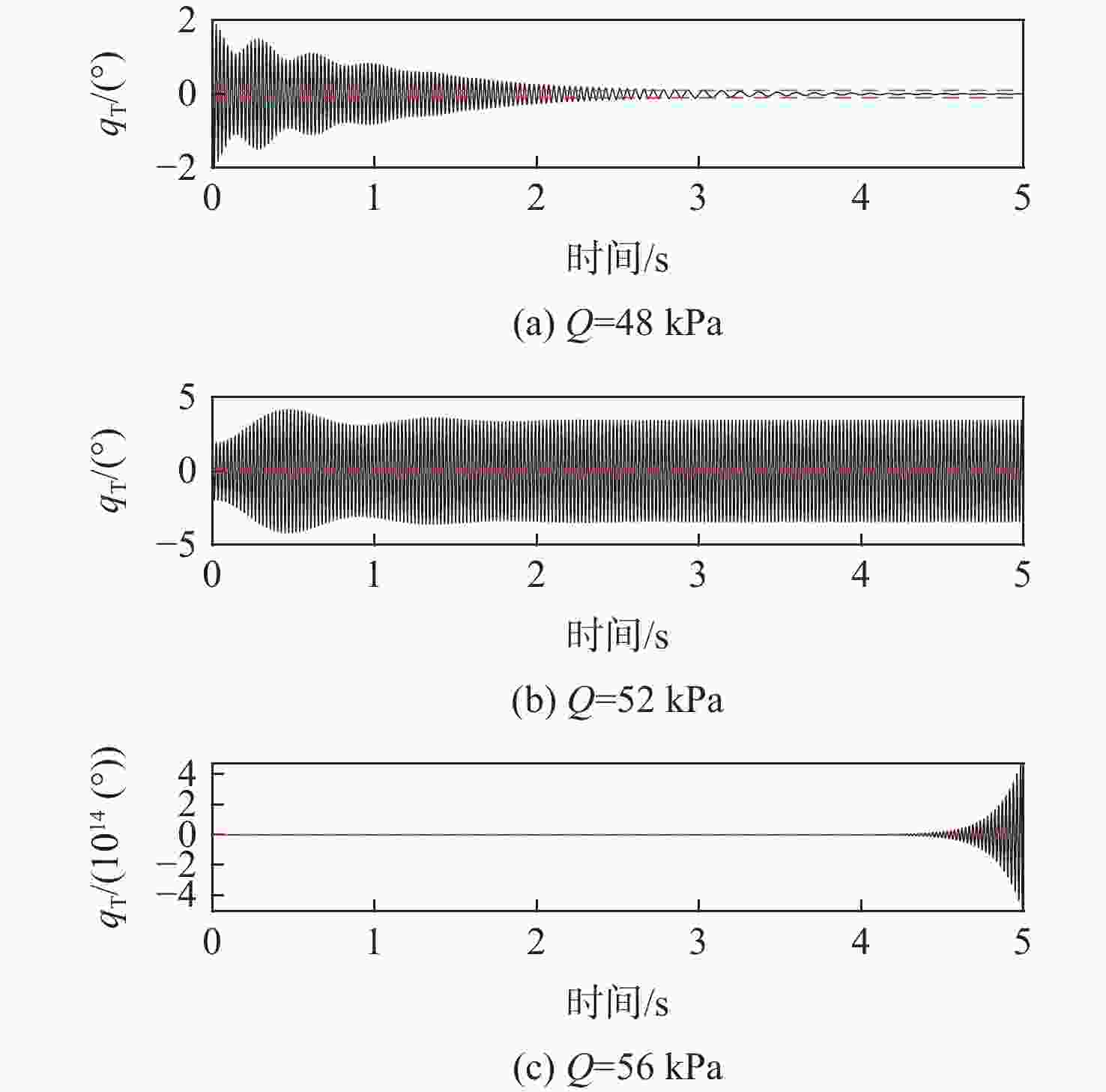
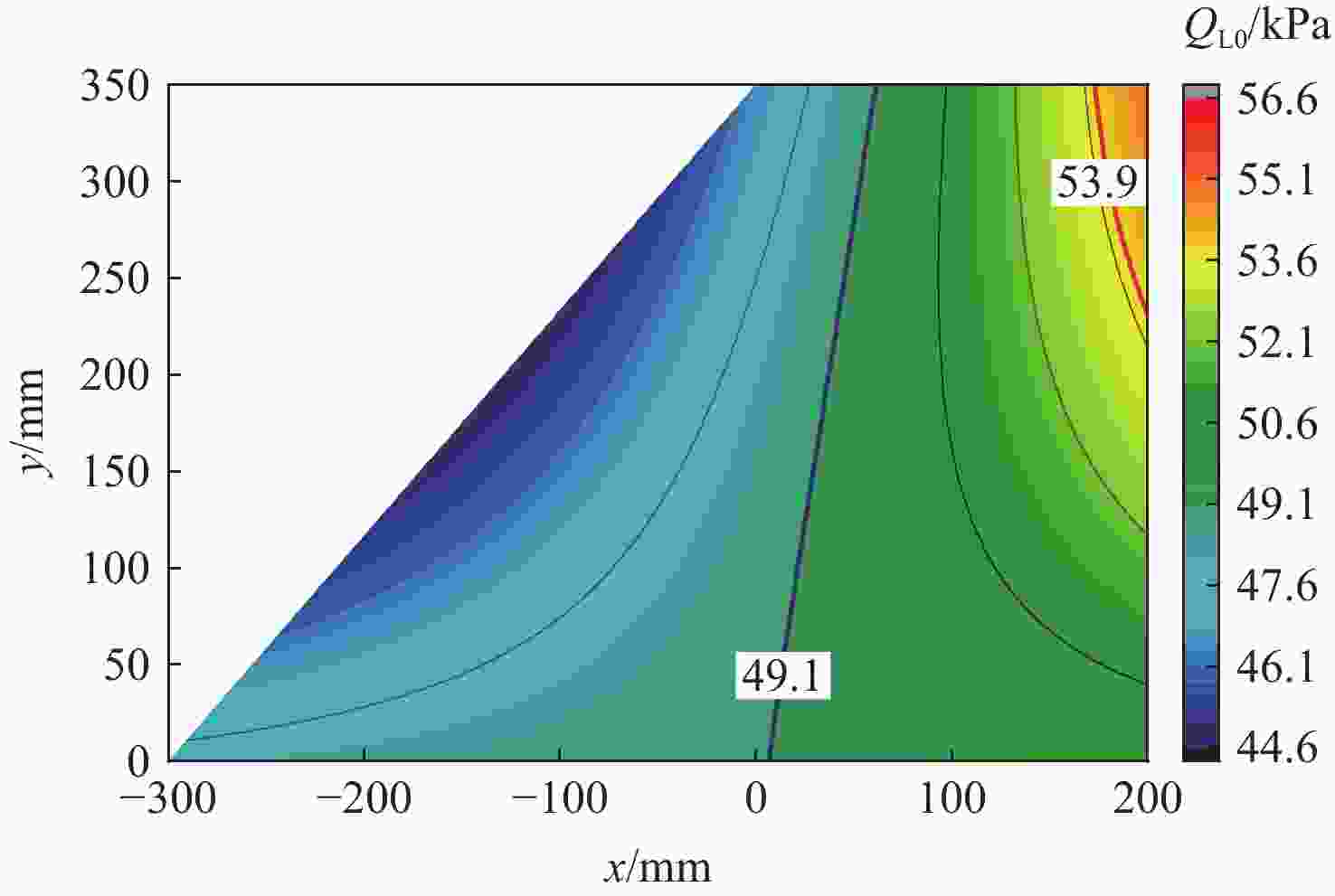
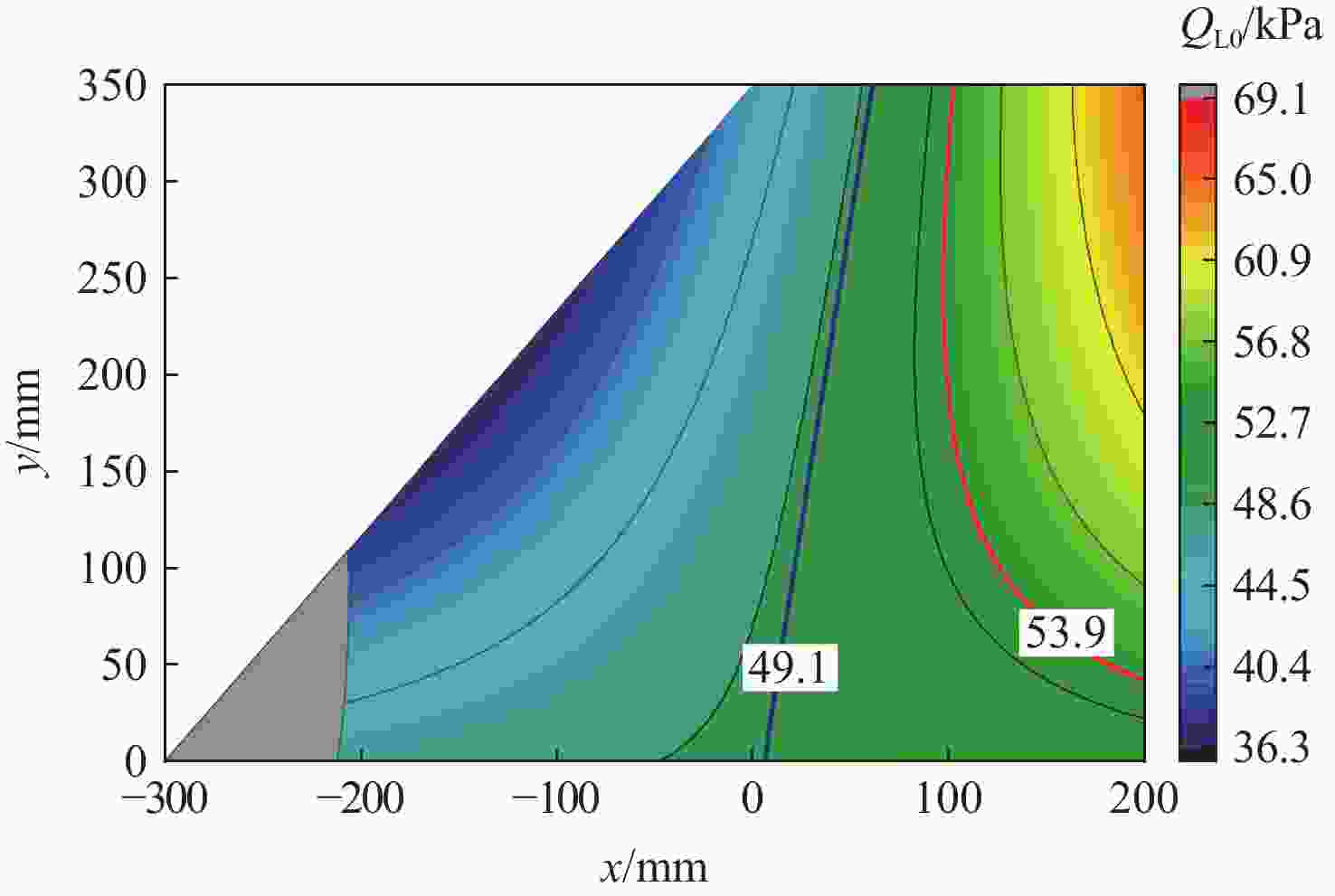
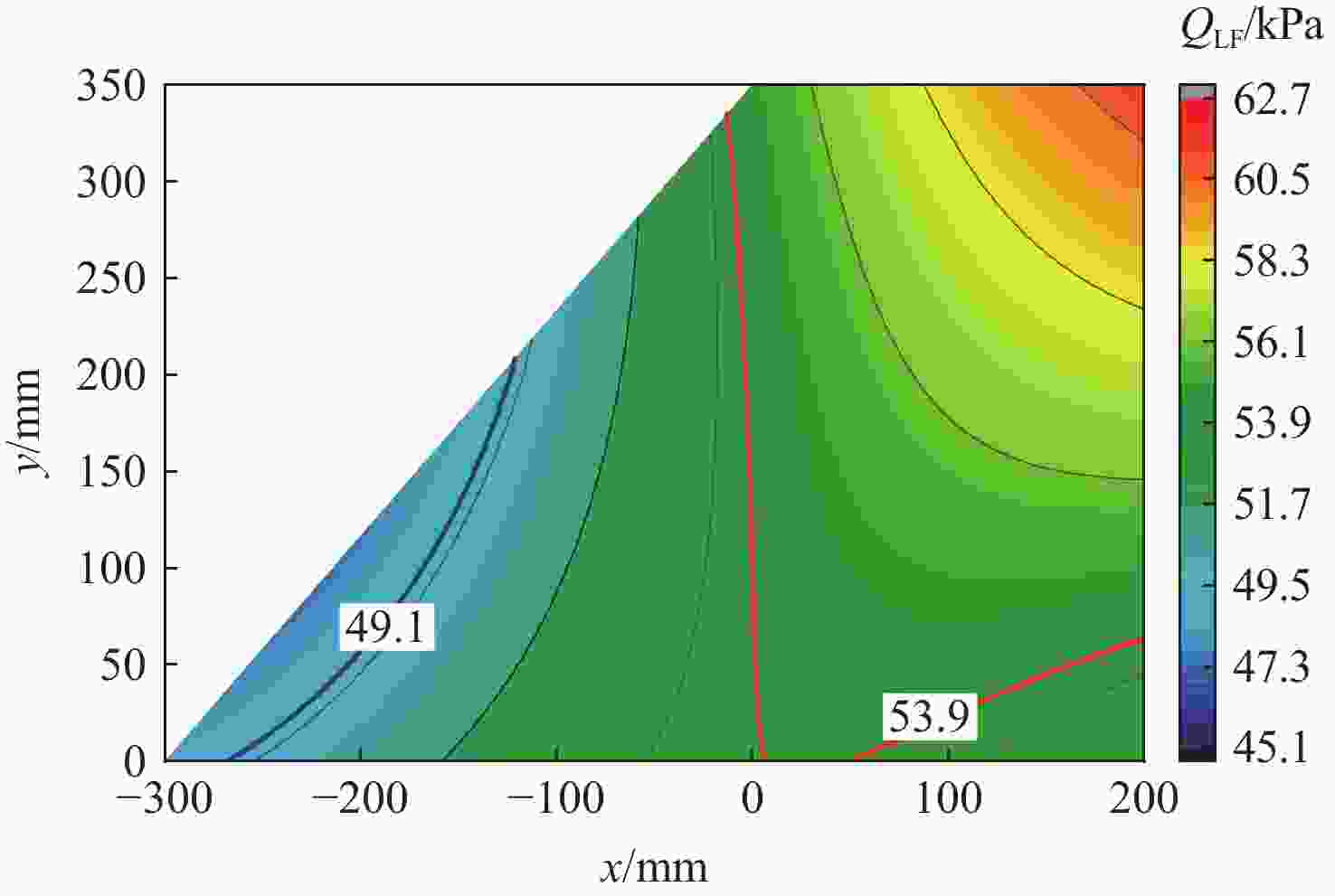
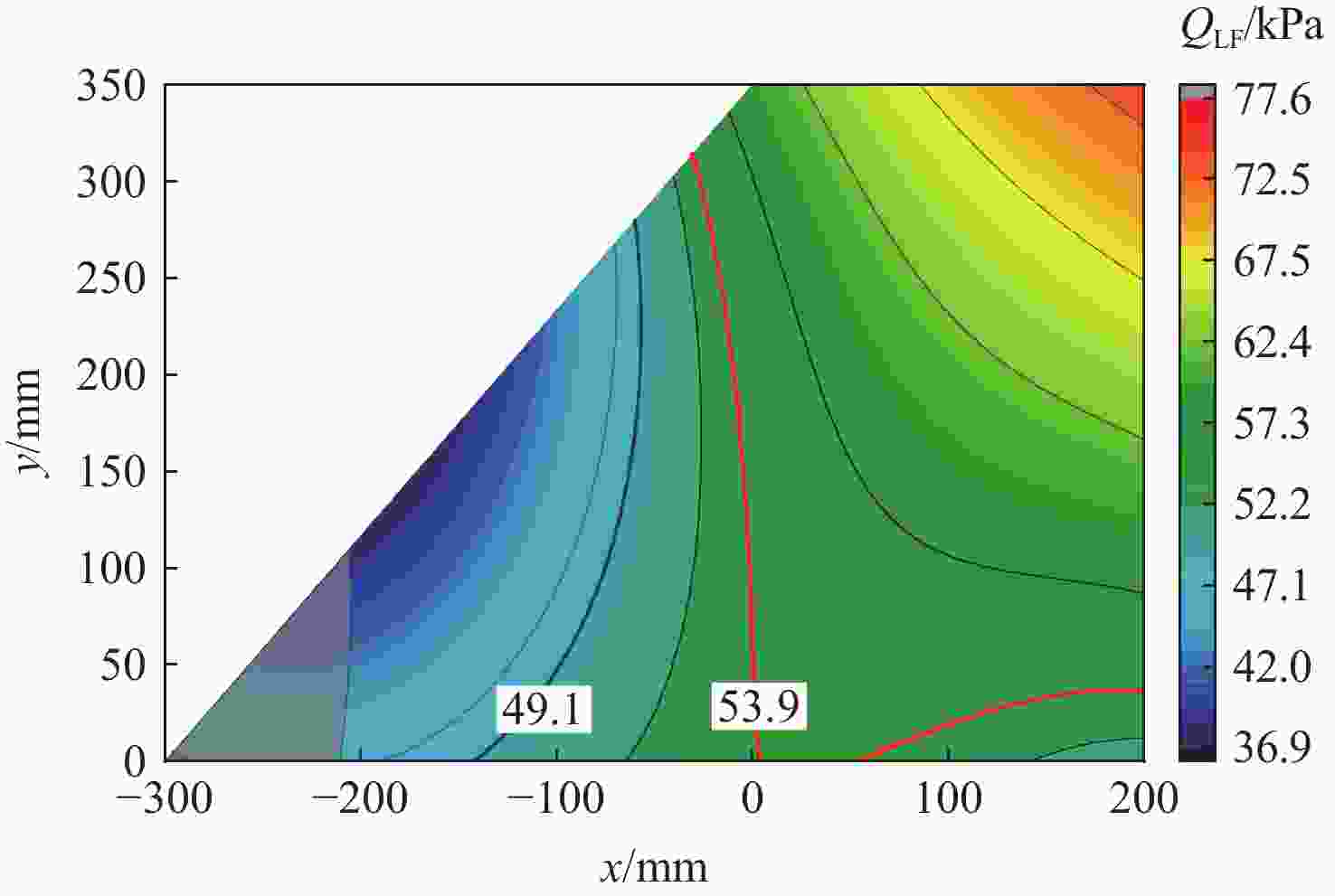
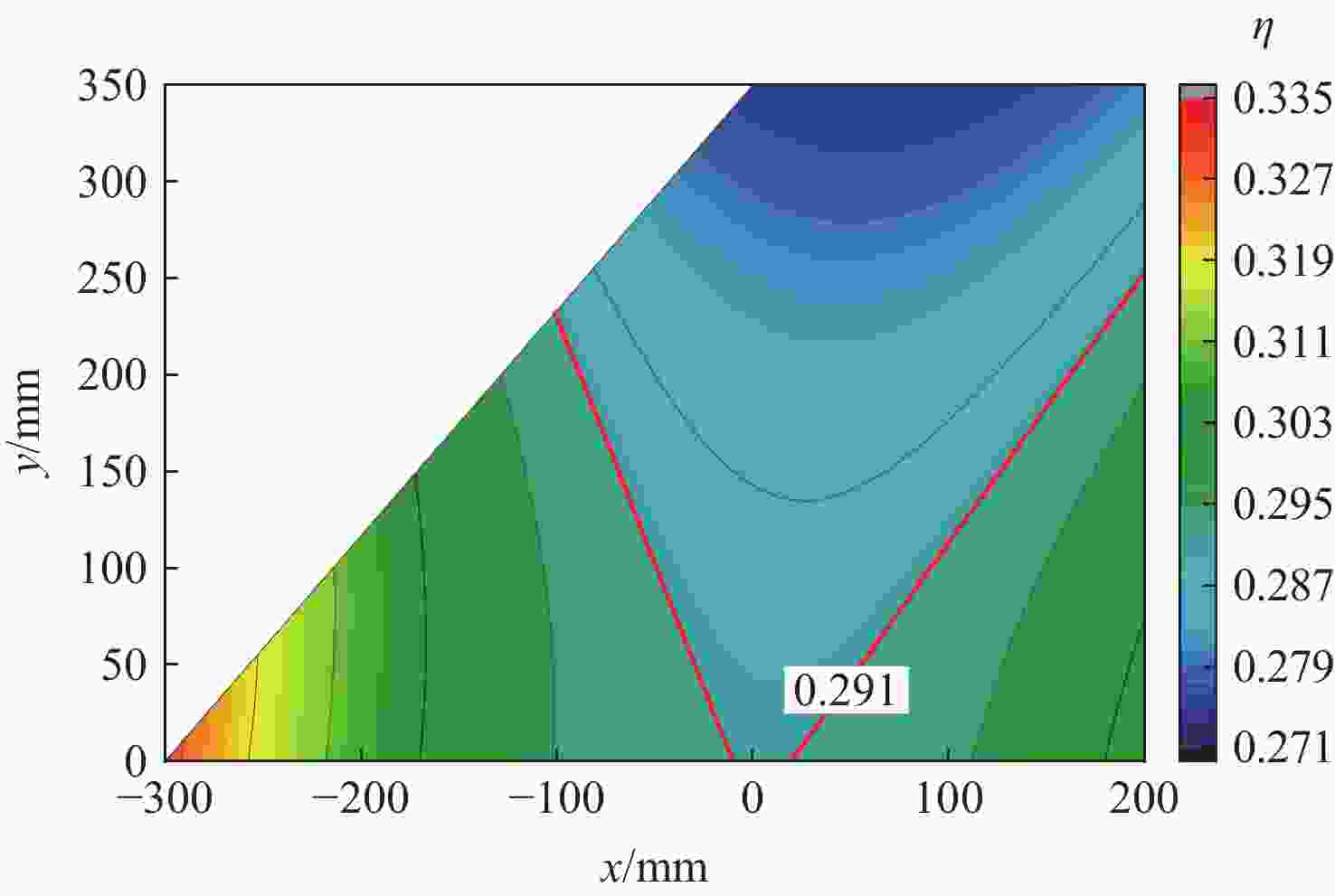
计算方法 ${\omega _{\rm{F}}/{\rm{Hz} } }$ ${V_{\text{F} } }/\left({\rm{m}\cdot {\rm{s} } }^{-1}\right)$ ${Q_{\text{F} } }/{\rm{kPa} }$ 本文方法 44.14 939.78 53.87 ZAERO(前2阶) 42.72 928.83 52.63 ZAERO(前5阶) 42.72 928.85 52.63 -
[1] 杨超, 吴志刚, 万志强, 等. 飞行器气动弹性原理[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2016: 165-171.YANG C, WU Z G, WAN Z Q, et al. Flight vehicle aeroelasticity Principle[M]. 2rd ed. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2016: 165-171(in Chinese). [2] ZHAO L C, YANG Z C. Chaotic motions of an airfoil with non-linear stiffness in incompressible flow[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1990, 138(2): 245-254. doi: 10.1016/0022-460X(90)90541-7 [3] 赵永辉. 气动弹性力学与控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 7-10.ZHAO Y H. Aeroelastic mechanics and control[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 7-10(in Chinese). [4] 张仁嘉, 吴志刚, 杨超. 电动伺服舵系统动力学建模及颤振分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(7): 1368-1376.ZHANG R J, WU Z G, YANG C. Dynamic modeling and flutter analysis of a fin-actuator system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(7): 1368-1376(in Chinese). [5] 卢晋, 吴志刚, 杨超. 电动舵机模块化建模及动刚度仿真[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(4): 765-778.LU J, WU Z G, YANG C. Modular modeling and dynamic stiffness simulation of electromechanical actuator[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(4): 765-778(in Chinese). [6] LAURENSON R M, TRN R M. Flutter analysis of missile control surfaces containing structural nonlinearities[J]. AIAA Journal, 1980, 18(10): 1245-1251. doi: 10.2514/3.50876 [7] LEE B H K, TRON A. Effects of structural nonlinearities on flutter characteristics of the CF-18 aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1989, 26(8): 781-786. doi: 10.2514/3.45839 [8] LEE I, KIM S H. Aeroelastic analysis of a flexible control surface with structural nonlinearity[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1995, 32(4): 868-874. doi: 10.2514/3.46803 [9] CONNER M D, TANG D M, DOWELL E H, et al. Nonlinear behavior of a typical airfoil section with control surface freeplay: A numerical and experimental study[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1997, 11(1): 89-109. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1996.0068 [10] TANG D, DOWELL E H, VIRGIN L N. Limit cycle behavior of an airfoil with a control surface[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1998, 12(7): 839-858. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1998.0174 [11] PADMANABHAN M A, DOWELL E H, PASILIAO C L. Computational study of aeroelastic limit cycles due to localized structural nonlinearities[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2018, 55(4): 1531-1541. doi: 10.2514/1.C034645 [12] LEE B H K, PRICE S J, WONG Y S. Nonlinear aeroelastic analysis of airfoils: Bifurcation and chaos[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1999, 35(3): 205-334. doi: 10.1016/S0376-0421(98)00015-3 [13] PANCHAL J, BENAROYA H. Review of control surface freeplay[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2021, 127: 100729. [14] BUENO D D, WAYHS-LOPES L D, DOWELL E H. Control-surface structural nonlinearities in aeroelasticity: A state of the art review[J]. AIAA Journal, 2022, 60(6): 3364-3376. doi: 10.2514/1.J060714 [15] 赵永辉, 胡海岩. 具有操纵面间隙非线性二维机翼段的气动弹性分析[J]. 航空学报, 2003, 24(6): 521-525. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2003.06.010ZHAO Y H, HU H Y. Aeroelastic analysis of a two-dimensional airfoil with control surface freeplay nonlinearity[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2003, 24(6): 521-525(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2003.06.010 [16] 李道春, 向锦武. 控制面间隙对非线性二元机翼气动弹性响应的影响[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(8): 1385-1391. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.08.005LI D C, XIANG J W. Effect of control surface freeplay on nonlinear aeroelastic responses of an airfoil[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(8): 1385-1391(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.08.005 [17] 杨智春, 田玮, 谷迎松, 等. 带集中非线性的机翼气动弹性问题研究进展[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(7): 2013-2044. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0140YANG Z C, TIAN W, GU Y S, et al. Advance in the study on wing aeroelasticity with concentrated nonlinearity[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(7): 2013-2044(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0140 [18] 隋鑫, 韩敬永, 刘博, 等. 含间隙舵面非线性动力学分析[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 2020(3): 107-110.SUI X, HAN J Y, LIU B, et al. Nonlinear dynamical analysis of the rudder with gaps[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2020(3): 107-110(in Chinese). [19] WANG X Y, WU Z G, SUN Y K, et al. A novel method for estimating three-domain limit cycles in a 3D wing-aileron model with freeplay in aileron deflection[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2021, 105: 103286. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2021.103286 [20] WU Z G, YANG N, YANG C. Identification of nonlinear structures by the conditioned reverse path method[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2015, 52(2): 373-386. doi: 10.2514/1.C032424 [21] YANG N, WANG N, ZHANG X, et al. Nonlinear flutter wind tunnel test and numerical analysis of folding fins with freeplay nonlinearities[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(1): 144-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.12.011 [22] 何昊南, 于开平, 唐宏, 等. 有间隙折叠舵面的振动实验与非线性建模研究[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(5): 1476-1488. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-119HE H N, YU K P, TANG H, et al. Vibration experiment and nonlinear modelling research on the folding fin with freeplay[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(5): 1476-1488(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-119 [23] HE H N, TANG H, YU K P, et al. Nonlinear aeroelastic analysis of the folding fin with freeplay under thermal environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2020, 33(9): 2357-2371. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.05.005 [24] 王强, 马志赛, 张欣, 等. 基于模态综合法的含间隙折叠舵面动态特性分析[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(5): 223507.WANG Q, MA Z S, ZHANG X, et al. Dynamic characteristic analysis for a folding fin with freeplay nonlinearities based on mode synthesis method[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(5): 223507(in Chinese). [25] SUN Y K, YANG C, WU Z G, et al. Nonlinear system identification of an all movable fin with rotational freeplay by subspace-based method[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1205. [26] XUAN C W, HAN J L, ZHANG B, et al. Hypersonic flutter and flutter suppression system of a wind tunnel model[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(9): 2121-2132. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.02.009 [27] FIROUZ-ABADI R D, ALAVI S M, SALARIEH H. Analysis of non-linear aeroelastic response of a supersonic thick fin with plunging, pinching and flapping free-plays[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 40: 163-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.03.019 [28] TIAN W, YANG Z C, ZHAO T. Nonlinear aeroelastic characteristics of an all-movable fin with freeplay and aerodynamic nonlinearities in hypersonic flow[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2019, 116: 123-139. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2019.06.004 [29] 李家旭, 田玮, 谷迎松. 考虑间隙非线性的控制舵非线性气动弹性分析[J]. 航空工程进展, 2020, 11(6): 827-835. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2020.06.010LI J X, TIAN W, GU Y S. Nonlinear aero-elastic analysis of control fin with free-play nonlinearity[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2020, 11(6): 827-835(in Chinese). doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2020.06.010 [30] 宋晨, 吴志刚, 杨超. 二元机翼滑模变结构控制颤振主动抑制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(12): 1400-1403.SONG C, WU Z G, YANG C. Sliding mode variable structure control of flutter suppression for two-dimensional wing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(12): 1400-1403(in Chinese). [31] 李道春, 向锦武. 间隙非线性气动弹性颤振控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2007, 33(6): 640-643. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.06.003LI D C, XIANG J W. Flutter control of aeroelasticity with freeplay nonlinearity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2007, 33(6): 640-643(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.06.003 [32] 贾尚帅, 丁千. 含间隙超音速二元弹翼非线性颤振与主动控制[J]. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学, 2013, 43(4): 390-400.JIA S S, DING Q. Nonlinear flutter and active control of the supersonic two-dimensional missile wings with a freeplay[J]. Scientia Sinica: Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2013, 43(4): 390-400(in Chinese). [33] 聂雪媛, 郑冠男, 杨国伟. 含间隙非线性机翼跨声速颤振时滞反馈控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(10): 1980-1988.NIE X Y, ZHENG G N, YANG G W. Time delay feedback control for transonic flutter of airfoil with free-play nonlinearity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(10): 1980-1988(in Chinese). [34] 史晓鸣, 梅睿, 张晓宏, 等. 配重位置对全动舵面颤振抑制效果研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2016, 33(2): 268-272.SHI X M, MEI R, ZHANG X H, et al. Effect of balance mass location on flutter of an all-moving rudder[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2016, 33(2): 268-272(in Chinese). [35] LEE Y S, VAKAKIS A F, BERGMAN L A, et al. Suppression aeroelastic instability using broadband passive targeted energy transfers. Part 1: Theory[J]. AIAA Journal, 2007, 45(3): 693-711. doi: 10.2514/1.24062 [36] LEE Y S, KERSCHEN G, MCFARLAND D M, et al. Suppressing aeroelastic instability using broadband passive targeted energy transfers. Part 2: Experiments[J]. AIAA Journal, 2007, 45(10): 2391-2400. doi: 10.2514/1.28300 [37] TIAN W, ZHAO T, GU Y S, et al. Nonlinear flutter suppression and performance evaluation of periodically embedded nonlinear vibration absorbers in a supersonic FGM plate[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022, 121: 107198. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.107198 [38] 王永岩. 动态子结构方法理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 33-43.WANG Y Y. Theory and application of dynamic substructure method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 33-43(in Chinese). [39] 杨宁. 间隙非线性结构的气动弹性建模与分析方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2015: 119-120.YANG N. Studies on aeroelastic modeling and analysis methods of structures with freeplay nonlinearity[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2015: 119-120(in Chinese). [40] ASHLEY H, ZARTARIAN G. Piston theory-A new aerodynamic tool for the aeroelastician[J]. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, 1956, 23(12): 1109-1118. doi: 10.2514/8.3740 [41] SHEN S F. An approximate analysis of nonlinear flutter problems[J]. Journal of the Aerospace Sciences, 1959, 26(1): 25-32. doi: 10.2514/8.7914 -







 下载:
下载: