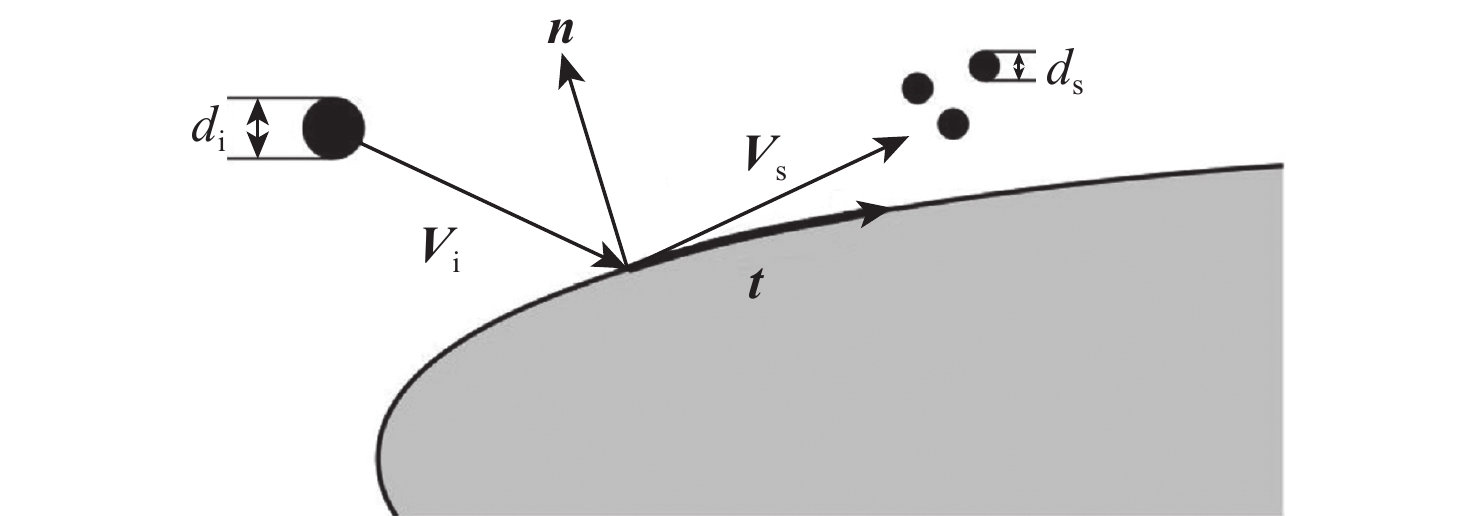
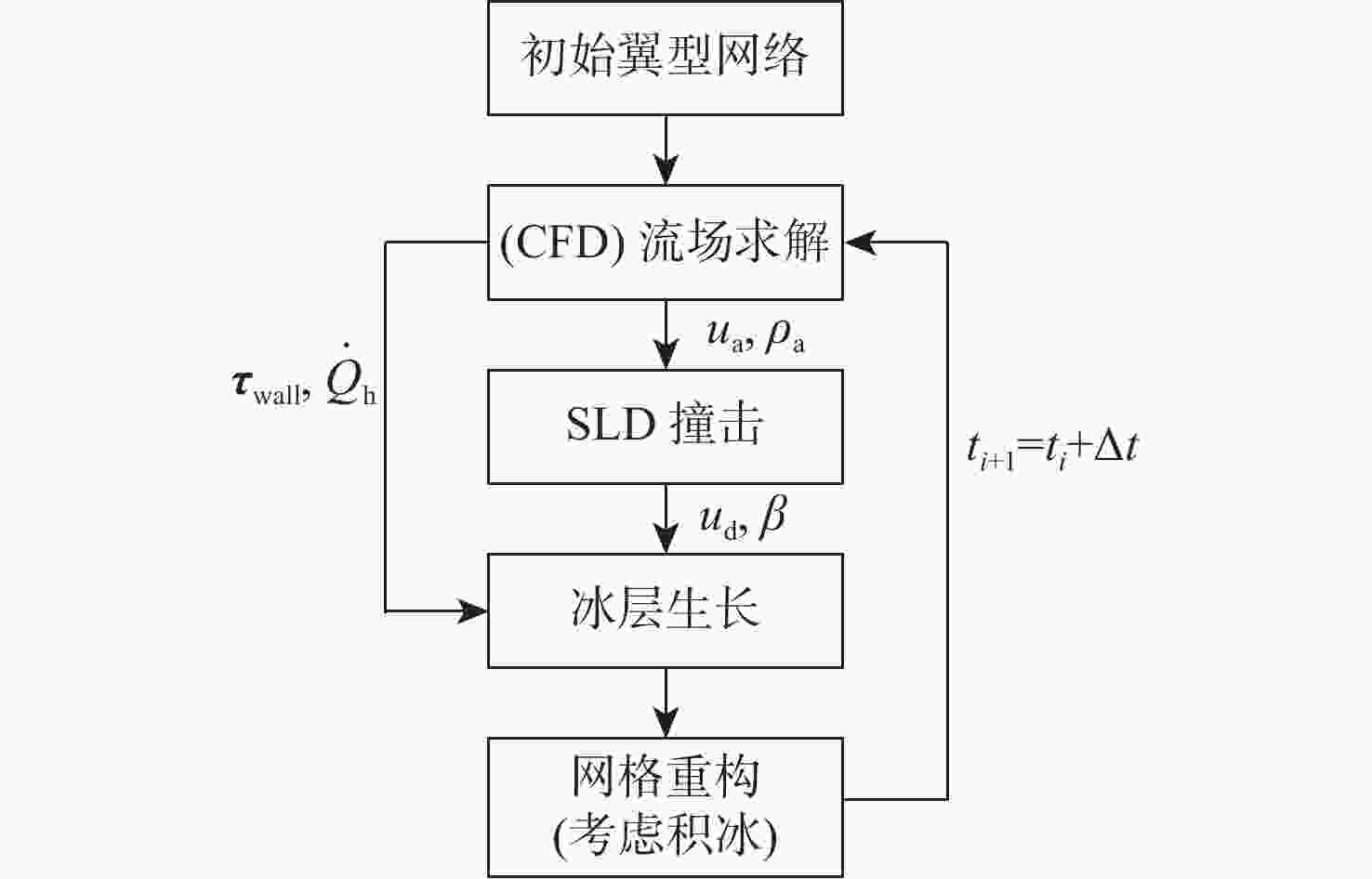
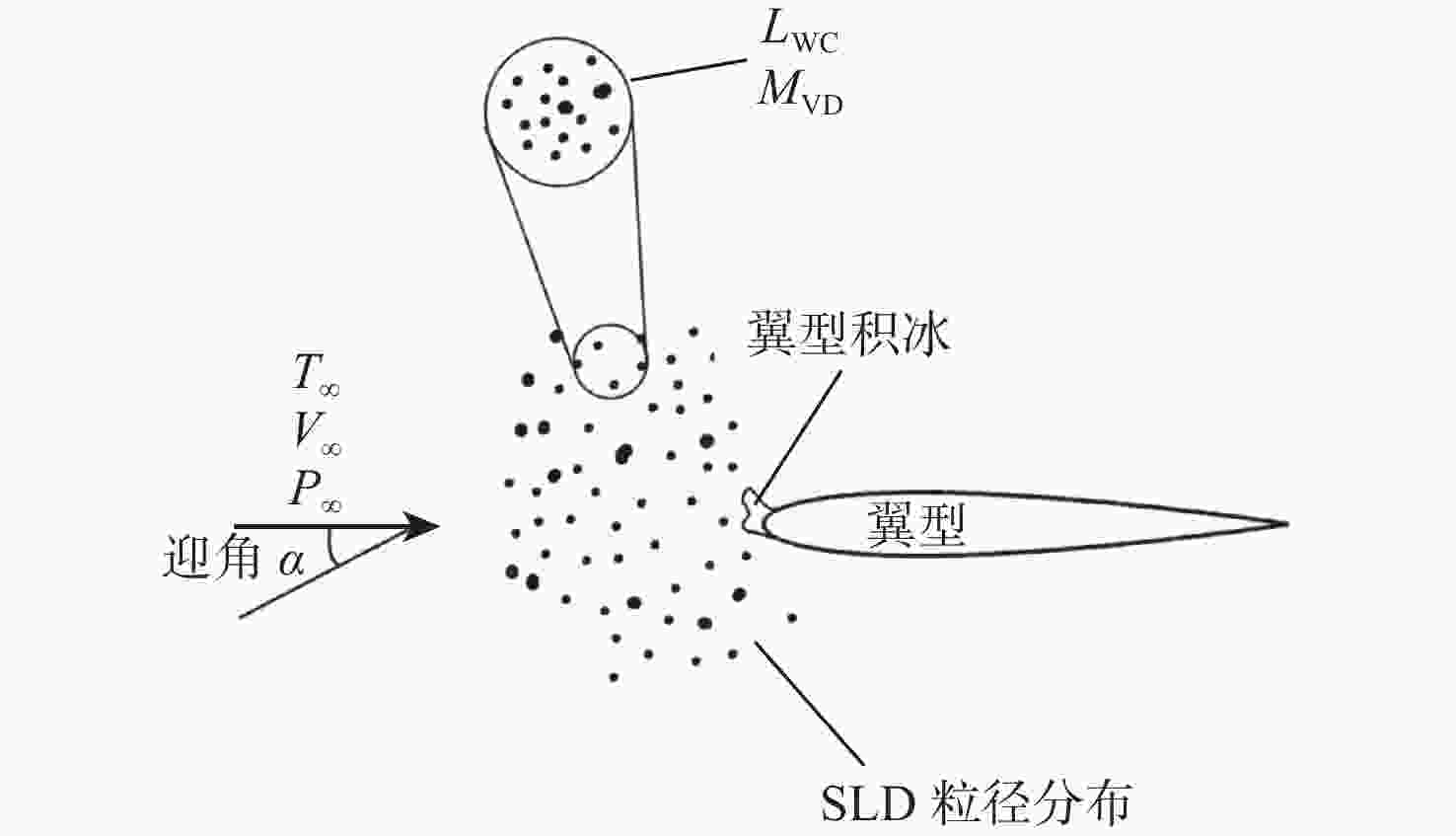
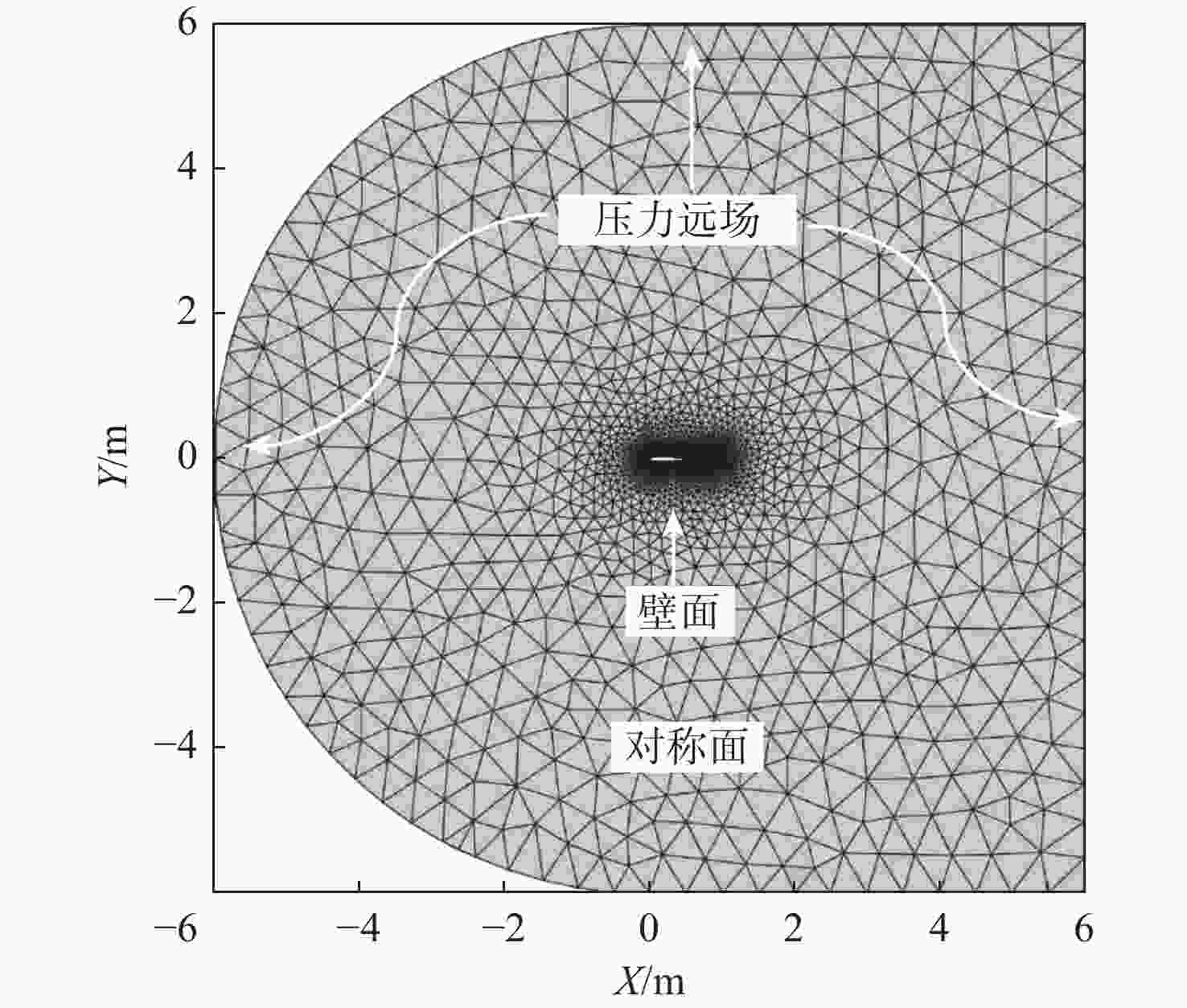
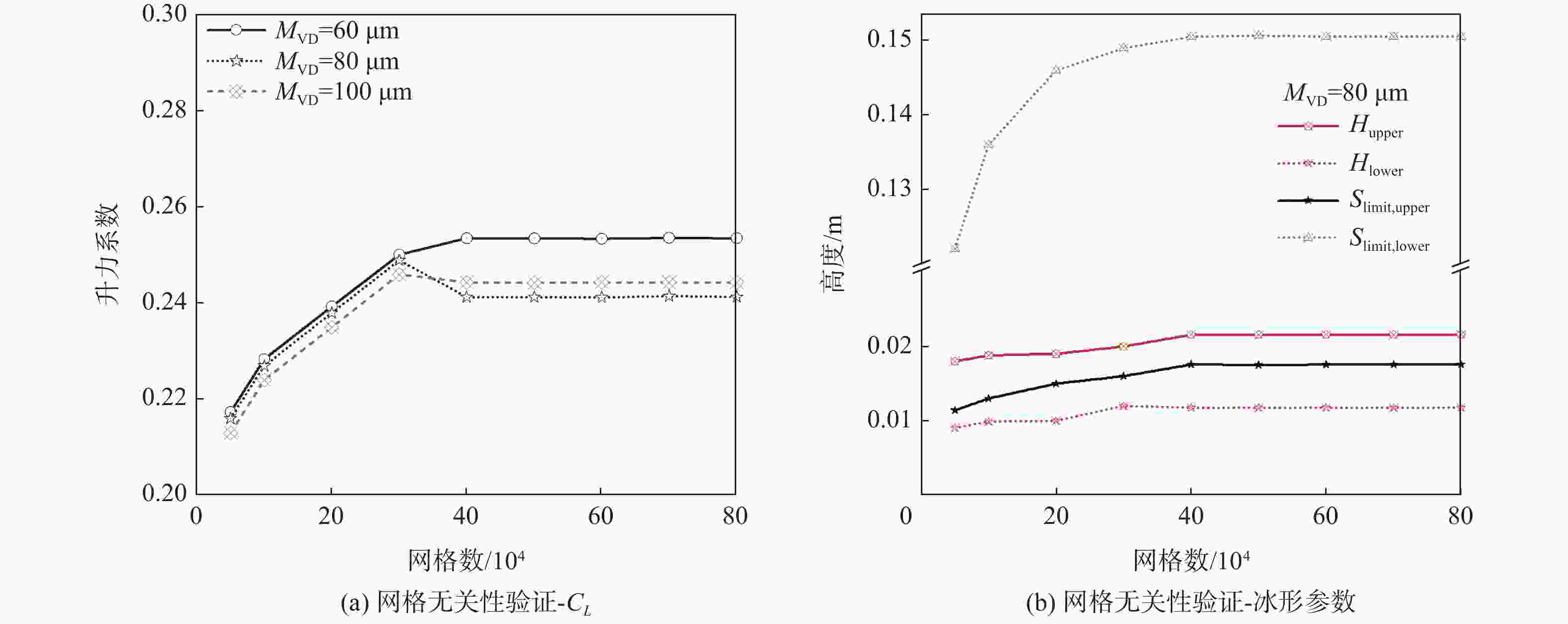
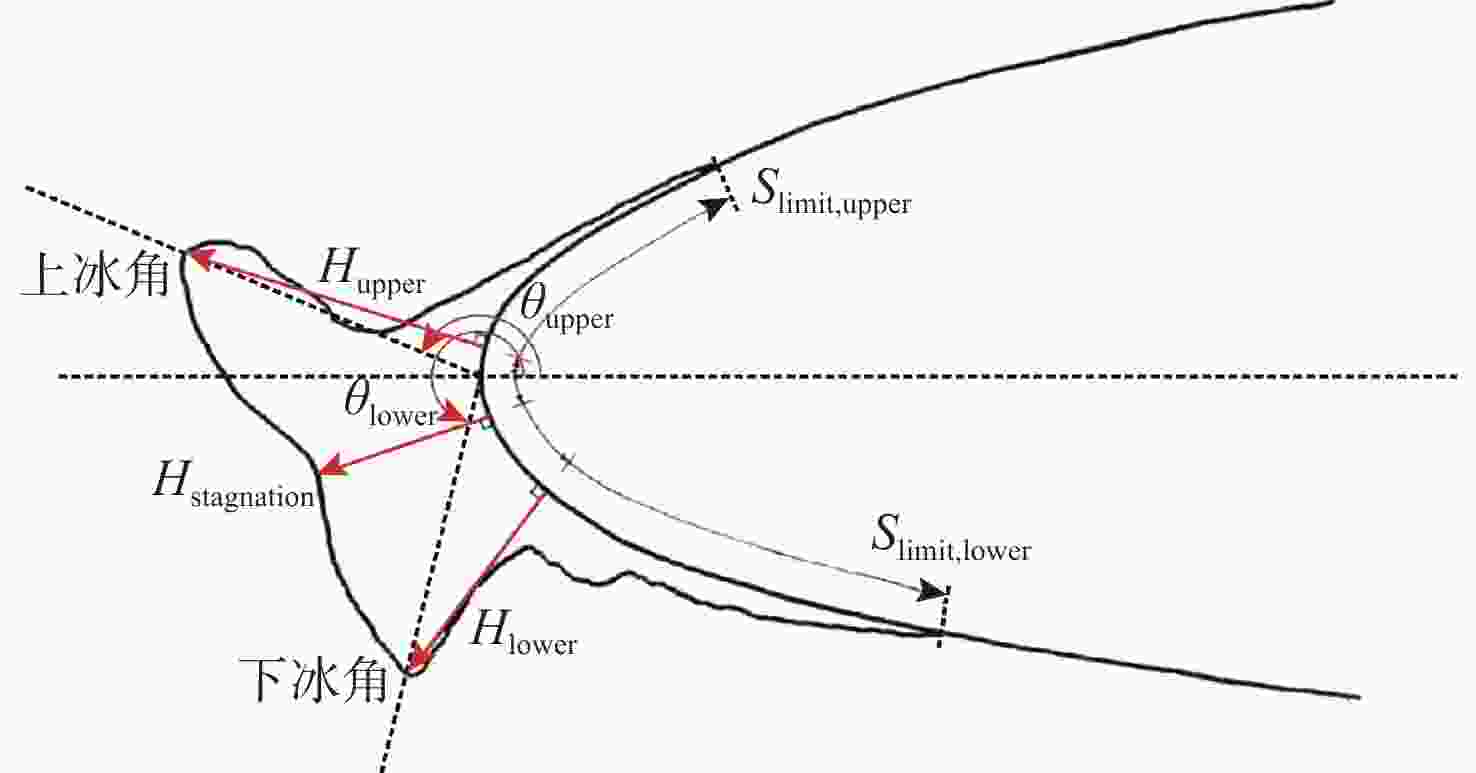
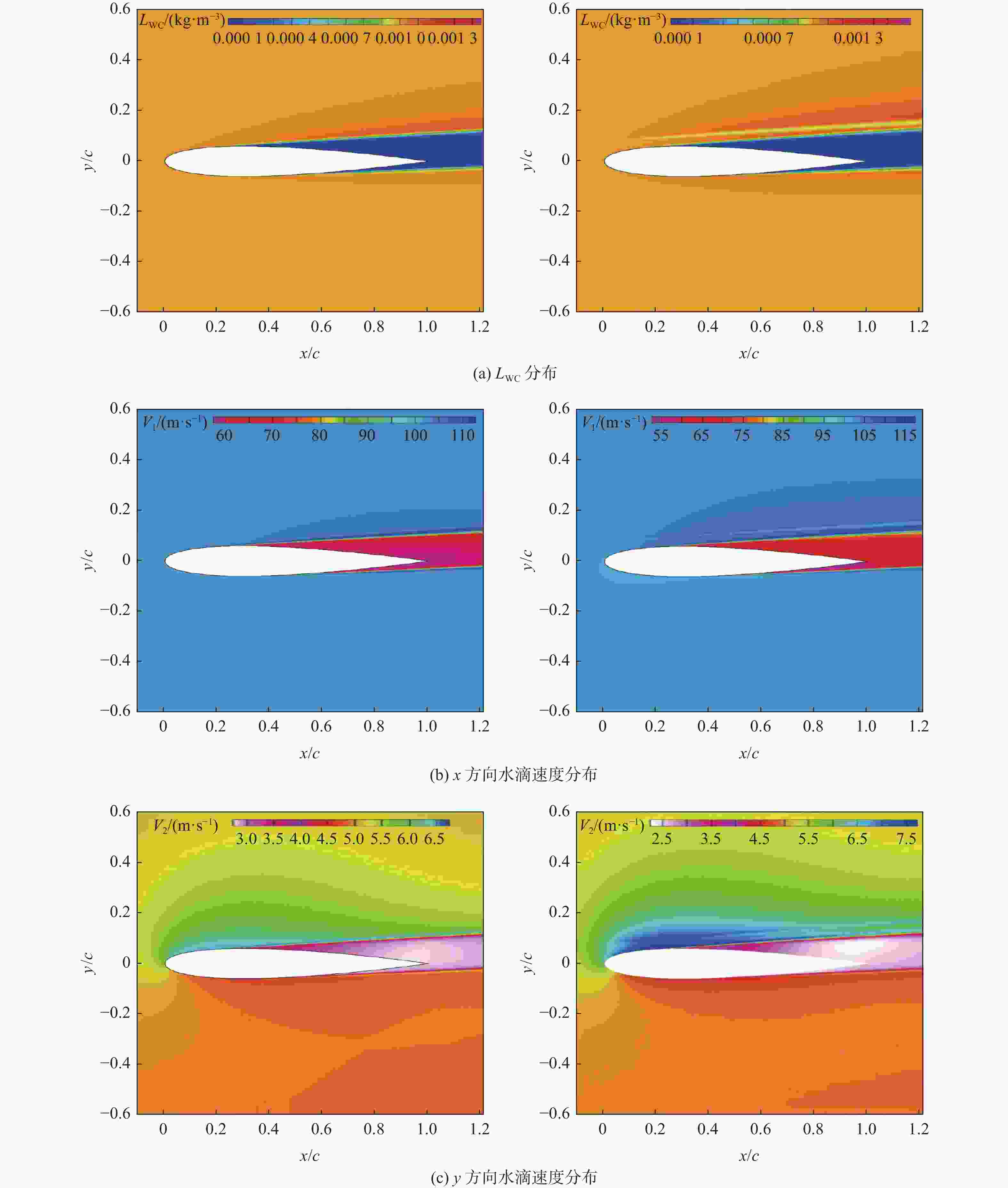
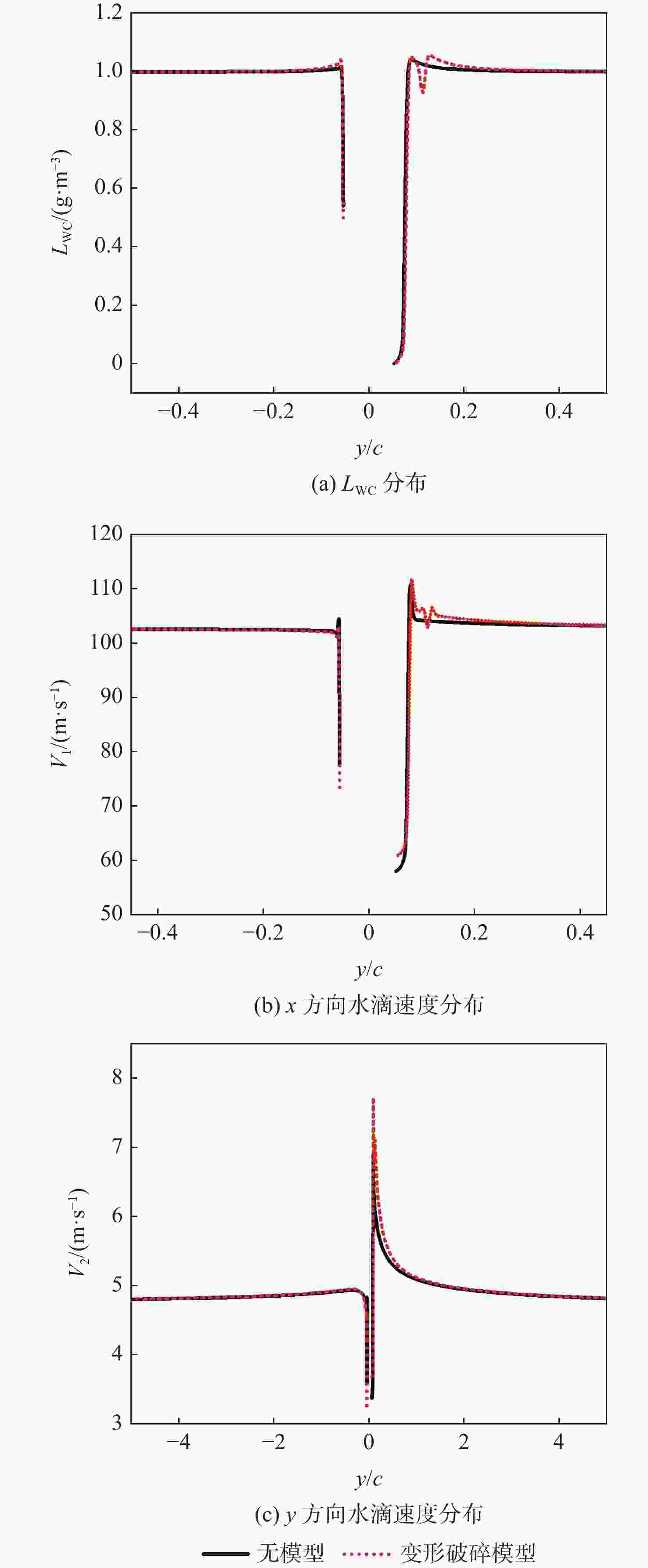
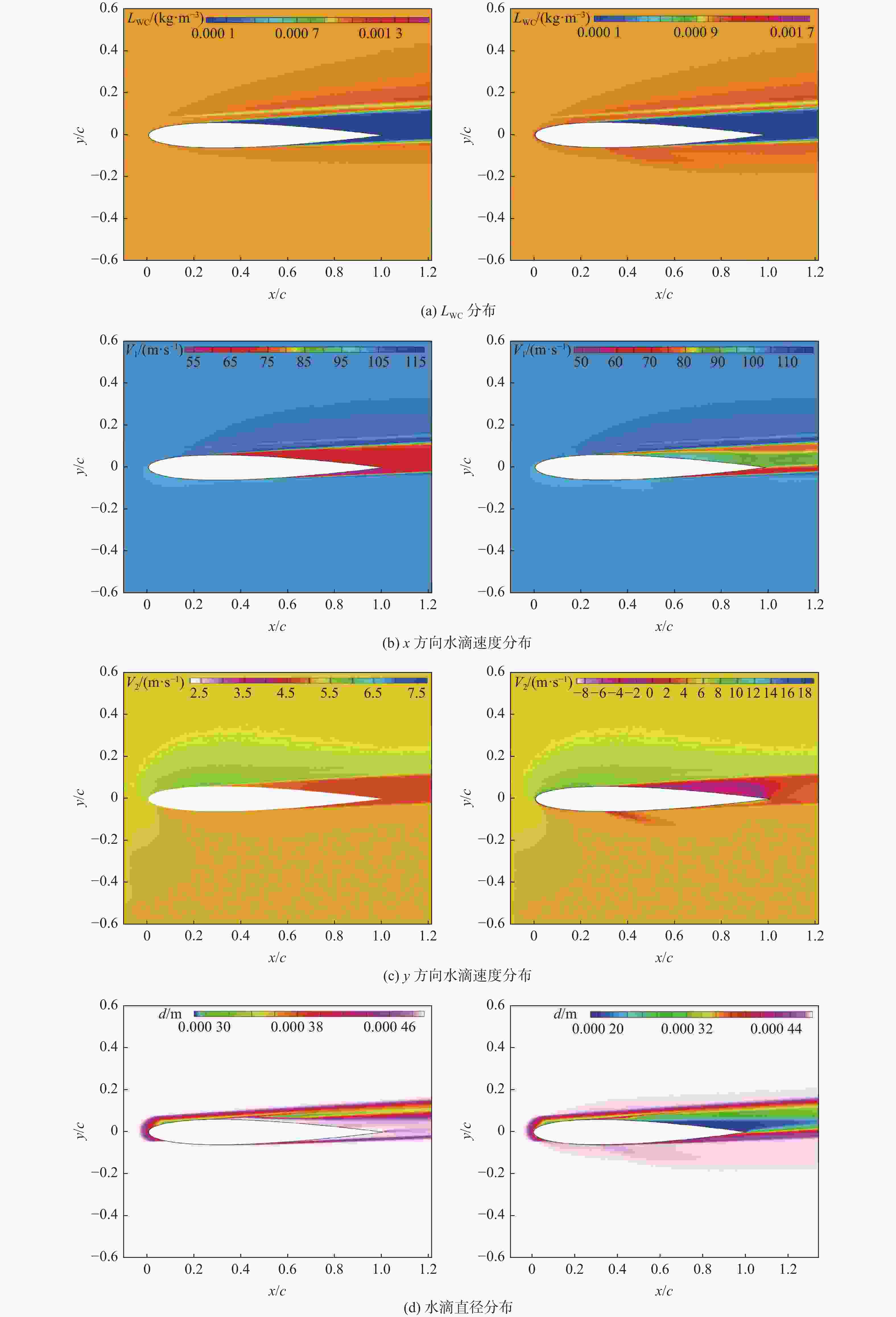
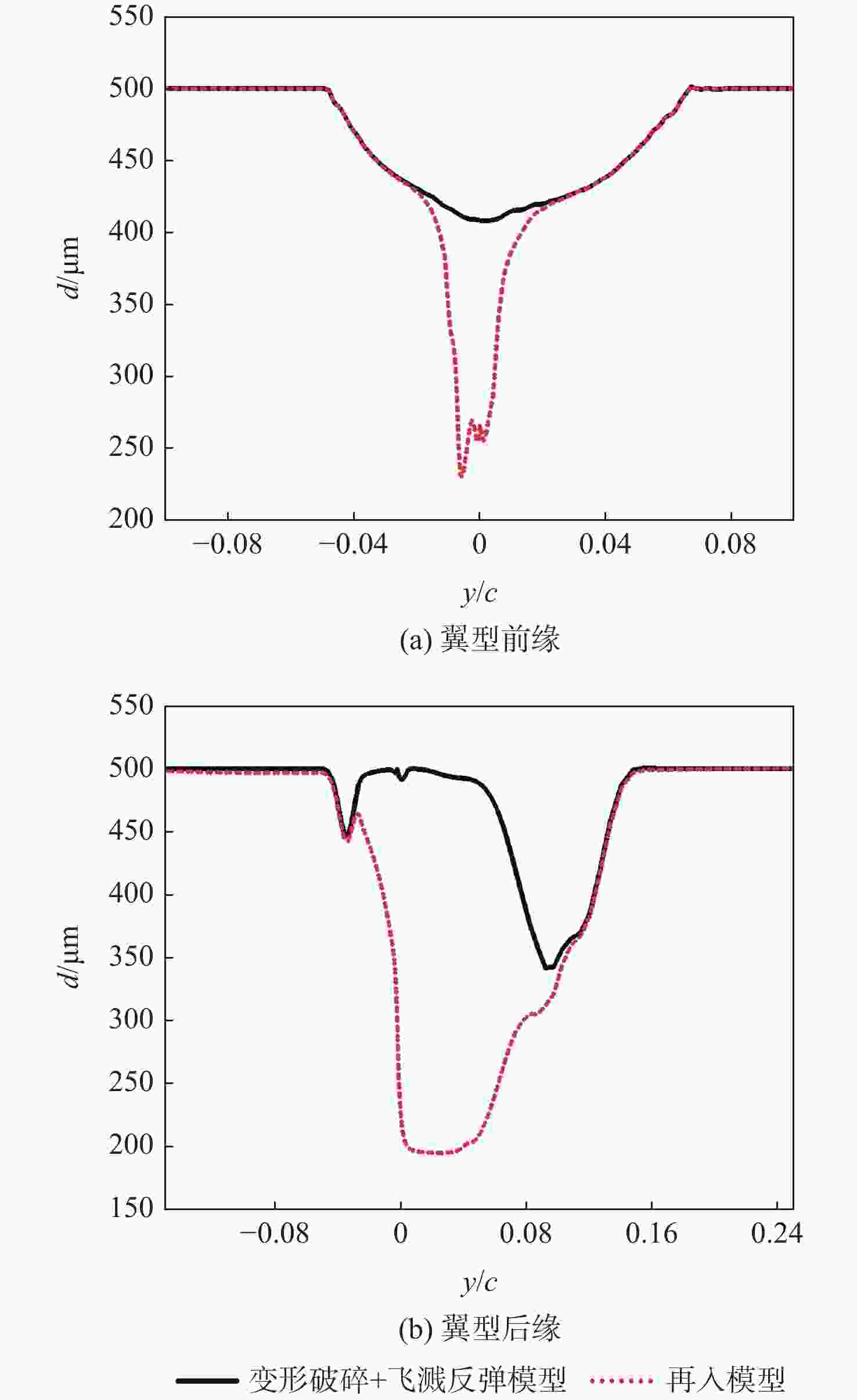
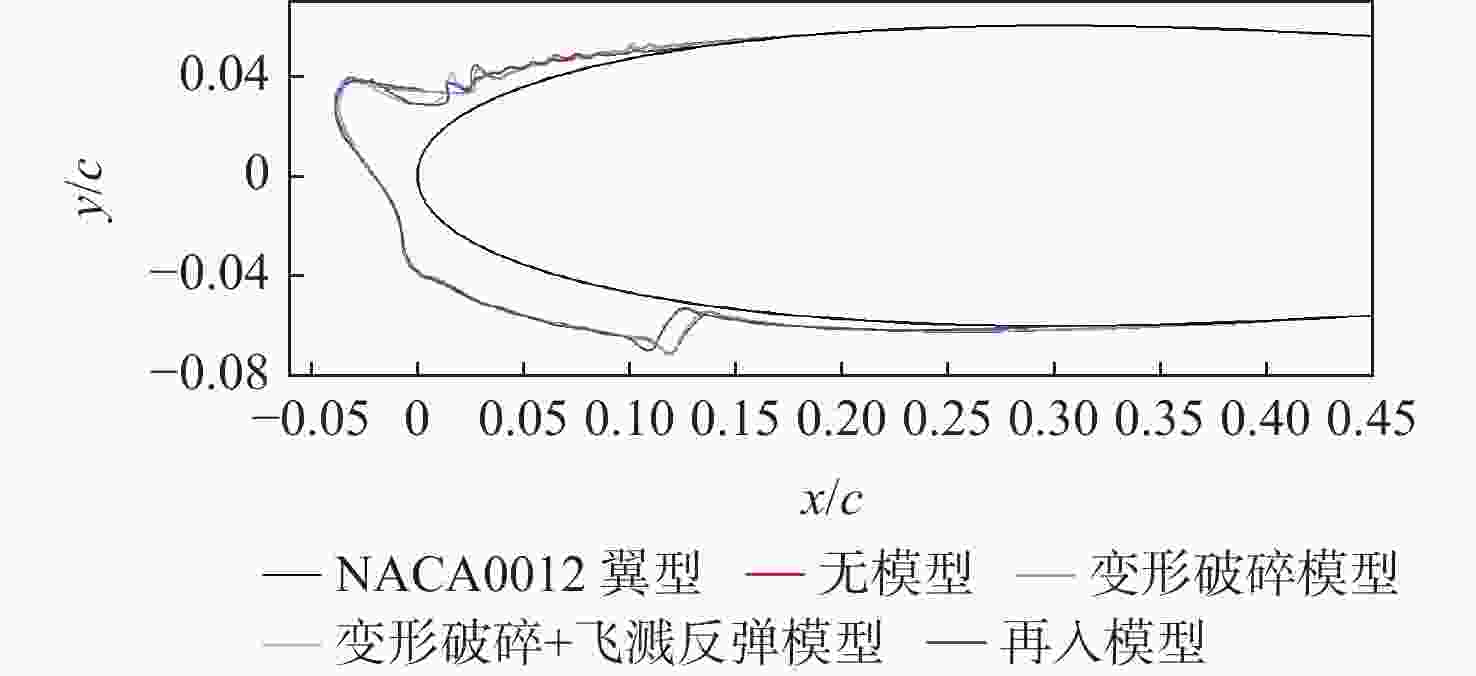
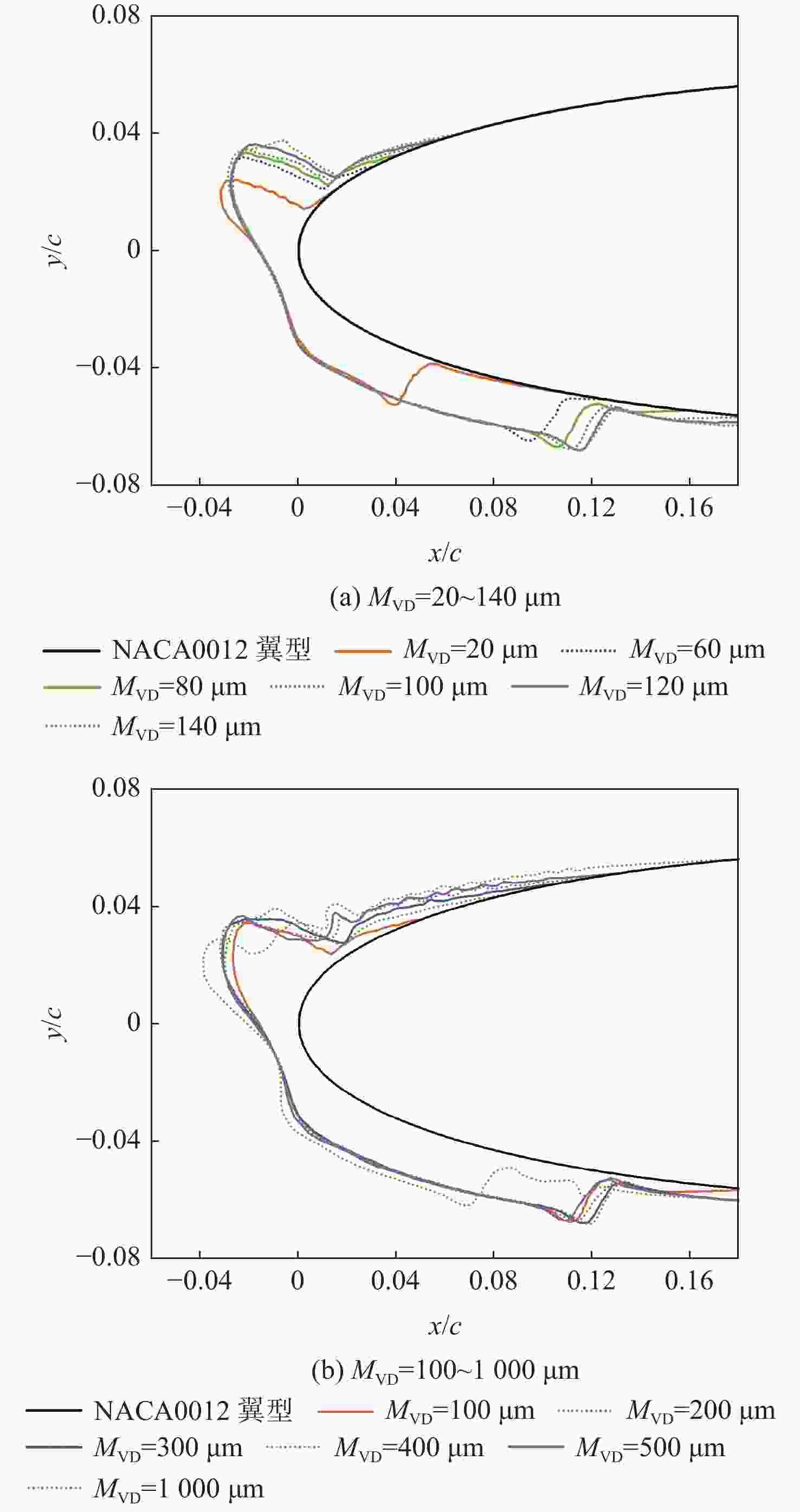
-
摘要:
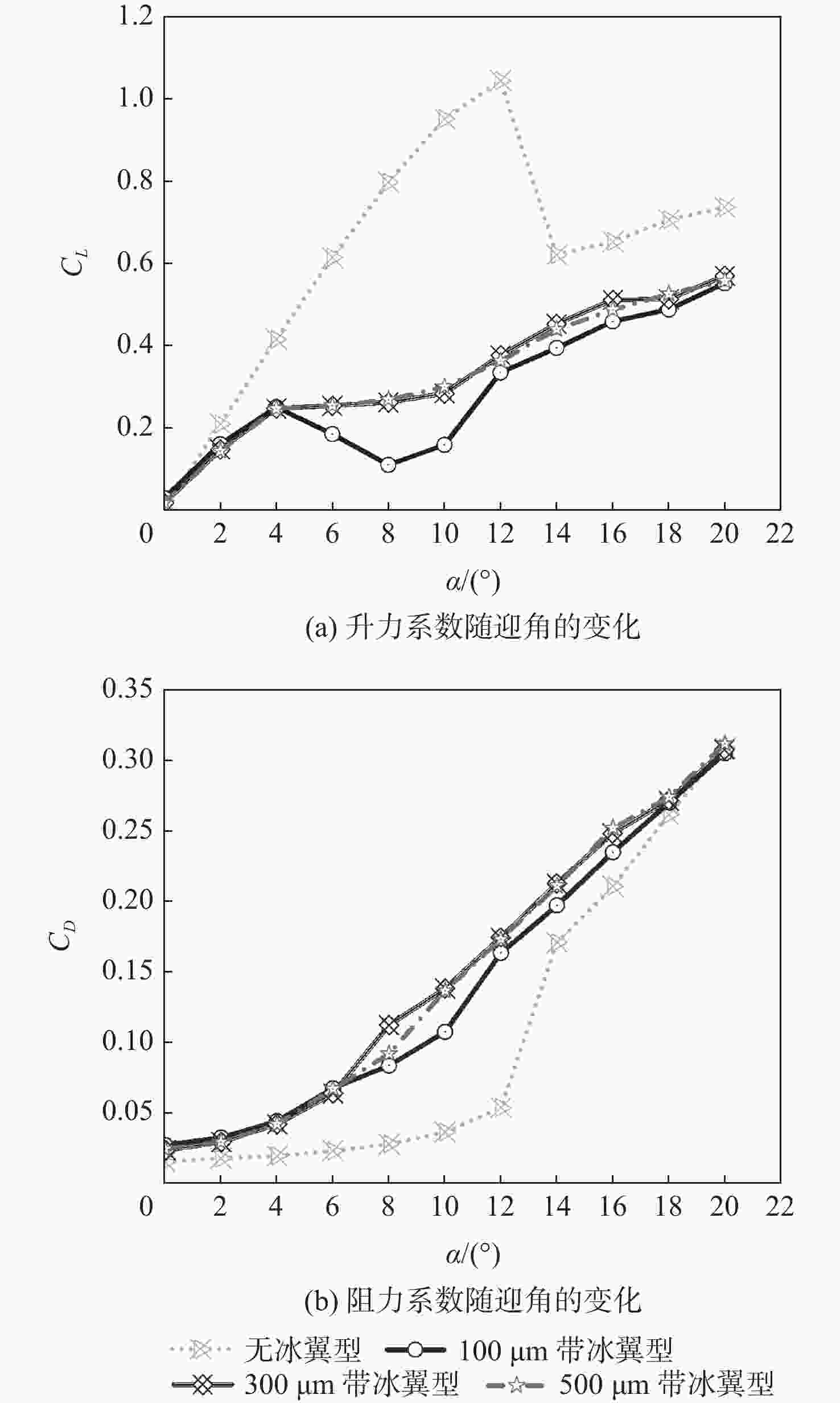
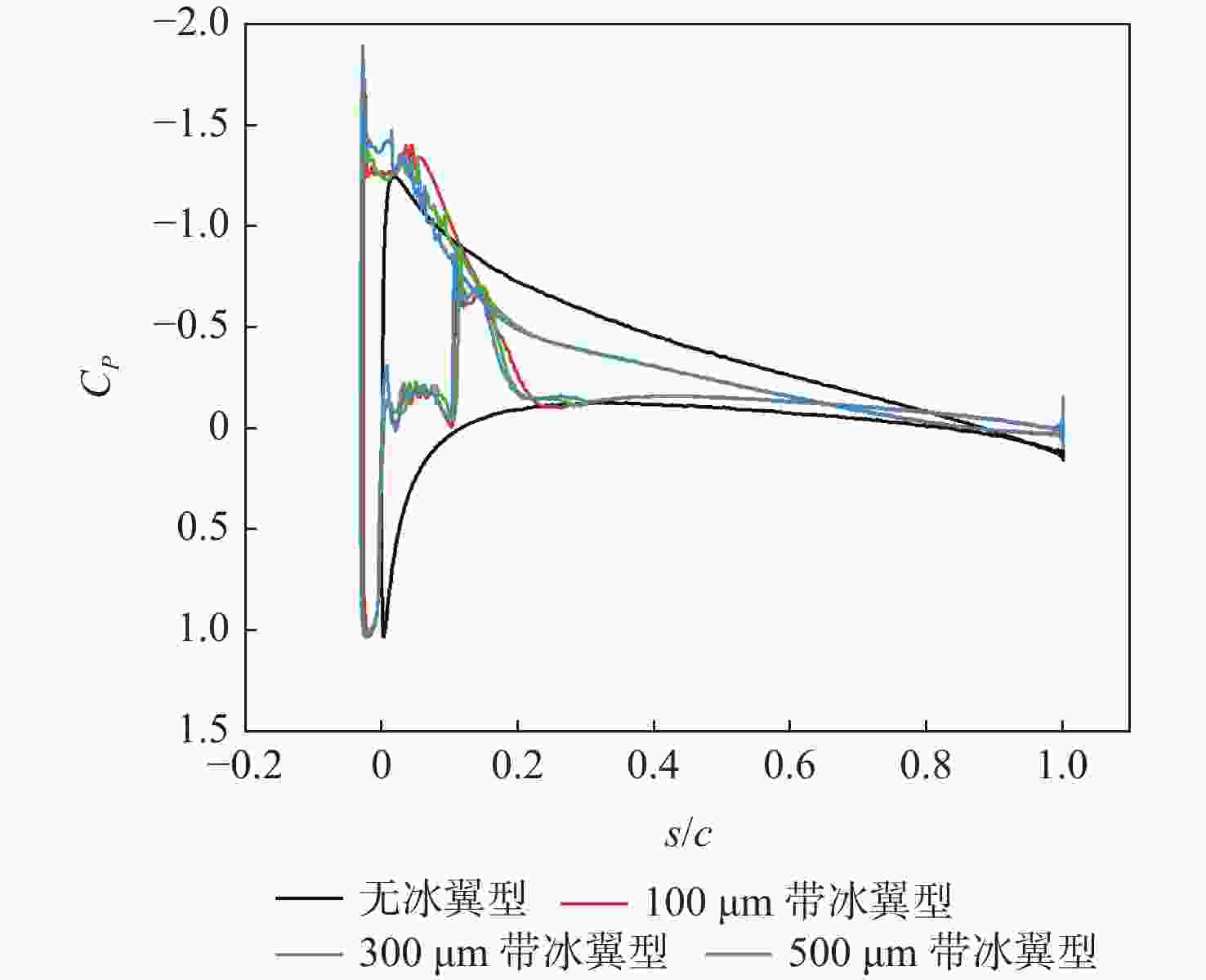
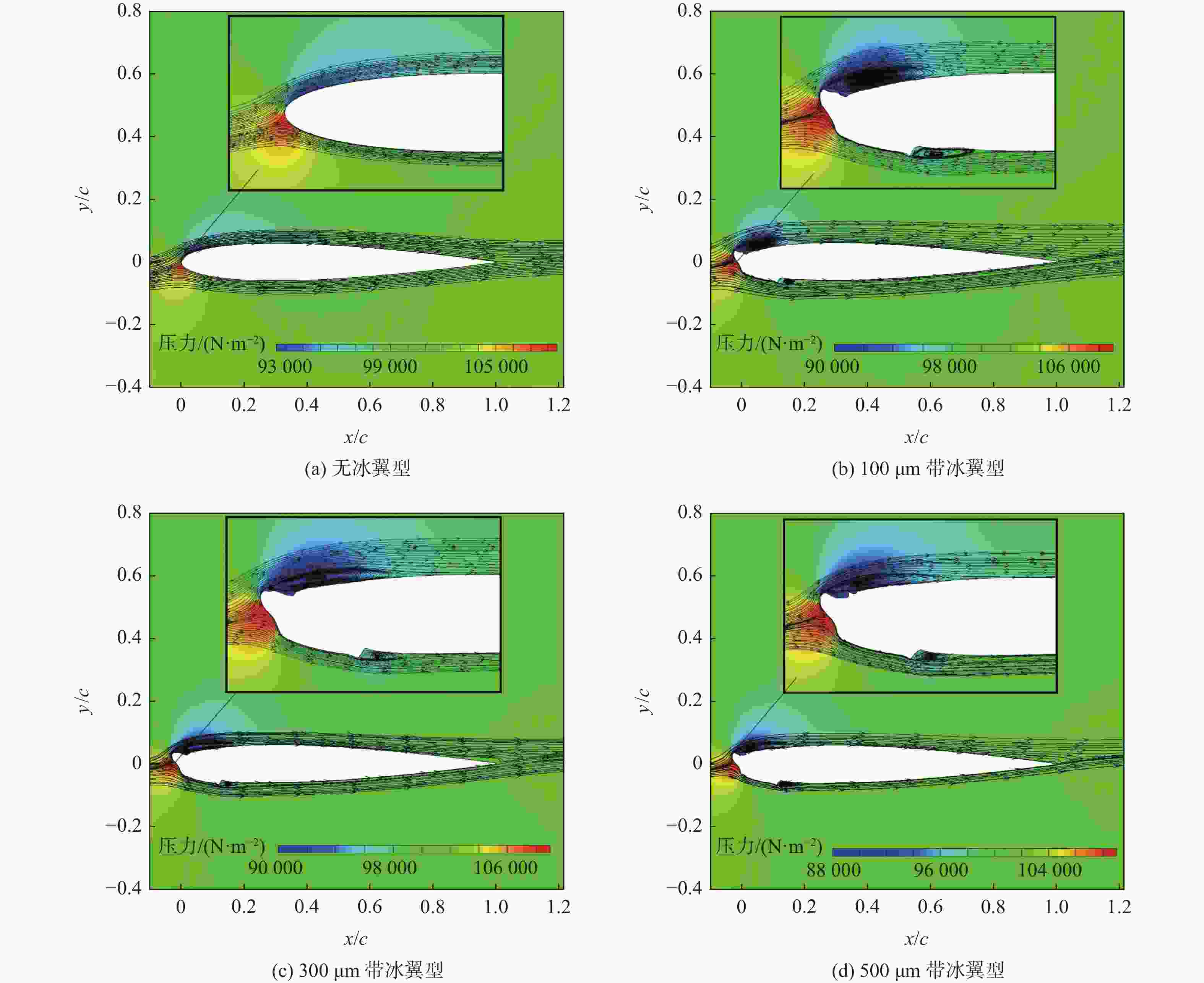
过冷大水滴(SLD)是极端危险的飞行环境之一。因大粒径水滴独特的动力学行为变形破碎、飞溅反弹,传统结冰计算方法难以准确地反映SLD结冰情况。采用Navier-Stokes方法求解流场、Euler方法计算水滴撞击、Shallow Water模型模拟结冰,并与NASA实验结果进行了对比验证方法可信。结果表明:SLD动力学行为对结冰和冰形影响较大。其中,变形破碎改变了水滴运动轨迹和撞击范围,降低了水滴撞击极限,导致上下结冰极限减小2.83 %、2.13 %;飞溅降低了驻点附近水滴收集率,导致前缘积冰量减少8.09 %;反弹显著降低了水滴撞击极限,导致上下结冰极限减小30.69 %、20.01 %;撞击后飞溅反弹二次水滴再入流场使得上下结冰极限增加6.14 %、3.71 %。同时,与干净翼型相比带冰翼型空气动力学性能严重退化,在相同迎角下,升力更小、阻力更大、气动效率更低。
Abstract:Supercooled large droplets (SLD) represent one of the most hazardous flight conditions. The unique dynamic behavior of large droplets, including deformation, fragmentation, splash, and rebound, poses challenges for accurately assessing SLD icing using traditional icing calculation methods. In this study, the Navier-Stokes method was employed to solve the flow field, the Euler method was used to calculate droplet impact, and the Shallow Water model was utilized to simulate ice accretion. The credibility of the proposed methodology was verified by comparing the results with NASA experimental data. The findings demonstrate that the dynamic behavior of SLD significantly influences icing and ice formation. Specifically, deformation and fragmentation alter the trajectory and impact range of droplets, reducing the droplet impact limit, resulting in a 2.83% and 2.13% decrease in upper and lower icing limits, respectively. Splashing reduces the collection efficiency of droplets near the stagnation point, resulting in an 8.09% reduction in leading-edge ice accretion. Rebound considerably lowers the droplet impact limit, leading to a 30.69% and 20.01% decrease in upper and lower icing limits, respectively. Moreover, the re-entry of secondary droplets into the flow field following rebound increases the upper and lower icing limits by 6.14% and 3.71%, respectively. Furthermore, the aerodynamic performance of the ice-contaminated airfoil significantly deteriorates compared to a clean airfoil. At the same angle of attack, the lift decreases, the drag increases, and the aerodynamic efficiency decreases.
-
表 1 验证算例工况
Table 1. Working conditions of examples to be verified
算例 来流速度/(n mile·h−1) 静温/℃ 迎角/(°) LWC/(g·m−3) MVD/μm 结冰时间/s 1 200 −10.79 3.8 1.00 20 231 2 100 −9 0 1.17 140 14×60 3 100 −18 0 1.46 170 11×60 表 2 翼型前缘冰形特征参数模拟误差
Table 2. Simulation error of ice shape characteristic parameters of airfoil leading edge
% 算例 特征参数模拟误差 Hupper Hlower Hstagnation θupper θlower 1 8.7 2.7 4.2 0.7 3.0 2 −2.3 −9.7 −8.7 2.5 −1.9 3 −3.2 1.9 −2.7 −2.1 7.6 表 3 不同动力学行为对翼型前缘冰形特征参数的影响
Table 3. Effects of different dynamic behaviors on ice shape characteristic parameters at airfoil leading edge
% 模型 特征参数变化 Hupper Hlower θupper θlower Slimit,upper Slimit,lower 变形破碎 −0.73 0.09 −0.31 0.01 −2.83 −2.13 飞溅反弹 −4.33 3.52 1.41 −0.57 −30.69 −21.01 再入 2.97 −2.14 −0.18 0.03 6.14 3.71 表 4 数值模拟工况
Table 4. Working conditions of numerical simulation
来流速度/
(n mile·h−1)静温/℃ 静压/Pa 迎角/(°) LWC/
(g·m−3)结冰
时间/s200 −10.79 101325 3.8 1.00 210 表 5 翼型前缘冰形特征参数的变化
Table 5. Variation of ice shape characteristic parameters at the airfoil leading edge
MVD/μm ΔHupper% ΔHlower% Δθupper% Δθlower% ΔSlimit,upper% ΔSlimit,lower% 60 −1.52 −5.82 −10.35 5.99 287.84 6.36 80 1.22 0.63 −1.51 0.64 54.31 13.82 100 0.16 −0.59 −1.21 0.29 32.44 11.83 120 −0.76 −0.33 −2.35 0.16 14.56 5.41 140 4.33 −0.52 4.07 0.03 16.41 5.43 200 1.84 −0.33 −0.76 0.19 32.99 10.73 300 4.05 −0.12 1.01 −0.13 26.13 9.08 400 3.19 −1.53 2.53 −0.06 12.57 3.85 500 −1.60 0.93 0.98 −0.18 27.23 5.25 1000 12.53 17.04 13.25 −3.81 67.04 12.13 -
[1] FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION. Airplane and engine certification requirements in supercooled large drop, mixed phase, and ice crystal icing conditions: RIN 2120–AJ34[S]. Washington, D. C. : Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), DOT, 2010. [2] VILLEDIEU P, TRONTIN P, GUFFOND D, et al. SLD Lagrangian modeling and capability assessment in the frame of ONERA 3D icing suite[C]//4th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference. Reston: AIAA 2012: 3132. [3] HONSEK R, HABASHI W G, AUBE M S. Eulerian modeling of in-flight icing due to supercooled large droplets[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2008, 45(4): 1290-1296. doi: 10.2514/1.34541 [4] BOURGAULT Y, HABASHI W G, DOMPIERRE J, et al. A finite element method study of Eulerian droplets impingement models[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2015, 29(4): 429-449. [5] IULIANO E, MINGIONE G, PETROSINO F, et al. Eulerian modeling of SLD physics towards more realistic aircraft icing simulation[C]// AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2010: 7676. [6] LEAL L G. Bubbles, drops and particles[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1979, 5(3): 229-230. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(79)90021-1 [7] PILCH M, ERDMAN C A. Use of breakup time data and velocity history data to predict the maximum size of stable fragments for acceleration-induced breakup of a liquid drop[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1987, 13(6): 741-757. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(87)90063-2 [8] HSIANG L P, FAETH G M. Near-limit drop deformation and secondary breakup[J]. Int Multiphase Flow, 1992, 18(5): 635-652. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(92)90036-G [9] O'ROURKE P J, AMSDEN A A. The TAB method for numerical calculation of spray droplet breakup: No. 872089[R]. Toronto: SAE Technical Paper, 1987: 148-161. [10] CLARK M M. Drop breakup in a turbulent flow-I. Conceptual and modeling considerations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1988, 43(3): 671-679. doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(88)87025-8 [11] IBRAHIM E A, YANG H Q, PRZEKWAS A J. Modeling of spray droplets deformation and breakup[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 1993, 9(4): 651-654. doi: 10.2514/3.23672 [12] BAI C, GOSMAN A D. Development of methodology for spray impingement simulation: No. 950283[R]. Detroit: SAE Transactions, 1995: 550-568. [13] MUNDO C, SOMMERFELD M, TROPEA C. Droplet-wall collisions: Experimental studies of the deformation and breakup process[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1995, 21(2): 151-173. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(94)00069-V [14] MUNDO C, TROPEA C, SOMMERFELD M. Numerical and experimental investigation of spray characteristics in the vicinity of a rigid wall[J]. Experimental Thermal & Fluid Science, 1997, 15(3): 80-86. [15] MUNDO C, SOMMERFELD M, TROPEA C. On the modeling of liquid sprays impinging on surfaces[J]. Atomization & Sprays, 1998, 8(6): 625-652. [16] RUTKOWSKI A, WRIGHT W, POTAPCZUK M. Numerical study of droplet splashing and re-impingement[C]//41st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA 2003: 388. [17] WRIGHT W. Further refinement of the LEWICE SLD model[C]//44th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2006: 464. [18] NORDE E, HOSPERS J M, VAN DER WEIDE E, et al. Splashing model for impact of supercooled large droplets on a thin liquid film[C]//52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 2014: 738. [19] BILODEAU D R, HABASHI W, BARUZZI G, et al. An Eulerian re-impingement model of splashing and bouncing supercooled large droplets[C]// 5th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2013: 3058. [20] TRUJILLO M F, MATHEWS W S, LEE C F, et al. Modelling and experiment of impingement and atomization of a liquid spray on a wall[J]. International Journal of Engine Research, 2000, 1(1): 87-105. doi: 10.1243/1468087001545281 [21] 易贤, 李维浩, 王庄宇等. 过冷大水滴结冰过程中动力学行为的影响因素[C]//第十届全国流体力学学术会议论文摘要集. 杭州: 中国力学学会流体力学专业委员会, 2018, 1: 357.Yi Xian, Li Weihao, Wang Zhuangyu et al. Influence factors of dynamic behavior of supercooled large water droplets during icing process [C]//Abstracts of the 10th National Conference on Fluid Mechanics.Hangzhou : Fluid Mechanics Committee of Chinese Society of Mechanics, 2018, 1 : 357(in Chinese). [22] 张辰, 孔维梁, 刘洪. 大粒径过冷水滴结冰模拟破碎模型研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2013, 31(2): 144-150.ZHANG C, KONG W L, LIU H. Research on simulation crushing model of large particle size supercooled water droplets icing[J]. Journal of Aerodynamics, 2013, 31(2): 144-150(in Chinese). [23] 任靖豪, 王强, 刘宇, 等. 大型商用运输机机翼增升构型水滴撞击特性计算[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2021, 39(1): 52-58.REN J H, WANG Q, LIU Y, et al. Calculation of droplet impact characteristics of wing lift configuration for large commercial transport aircraft[J]. Journal of Aerodynamics, 2021, 39(1): 52-58 (in Chinese). [24] 周志宏, 易贤, 桂业伟, 等. 水滴撞击特性的高效计算方法[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2014, 32(5): 712-716. doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0179ZHOU Z H, YI X, GUI Y W, et al. Efficient method for calculating droplet impact characteristics[J]. Journal of Aerodynamics, 2014, 32(5): 712-716(in Chinese). doi: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2012.0179 [25] POTAPCZUK M G, TSAO J C, KING-STEEN L C. Bimodal SLD ice accretion on a NACA 0012 airfoil model[C]//9th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2017: 4478. [26] SUN F, HAN S, QIAN G, et al. A novel multi-objective optimization model for minute-in-trail strategy based on sector workload restriction[C]//2015 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation (AIMS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 65-70. [27] HSIANG L P, FAETH G M. Drop deformation and breakup due to shock wave and steady disturbances[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1995, 21(4): 545-560. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(94)00095-2 [28] OZCER I, SWITCHENKO D, BARUZZI G S, et al. Multi-shot icing simulations with automatic re-meshing: No. 2019-01-1956[R]. Montreal: SAE Technical Paper, 2019: 956-972. [29] FOULADI H, ALIAGA C N, HABASHI W G. Quasi-unsteady icing simulation of an oscillating airfoil[C]//7th AIAA Atmospheric and Space Environments Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2015: 3020. [30] WRIGHT W, CHUNG J. Correlation between geometric similarity of ice shapes and the resulting aerodynamic performance degradation-A preliminary investigation using WIND[C]//38th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA , 2000: 97. [31] BRAGG M, BROEREN A, ADDY H, et al. Airfoil ice-accretion aerodynamic simulation[C]//45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2007: 85. -






 下载:
下载: