Quality control model of CYGNSS sea surface wind speed retrieval based on ML combination
-
摘要:
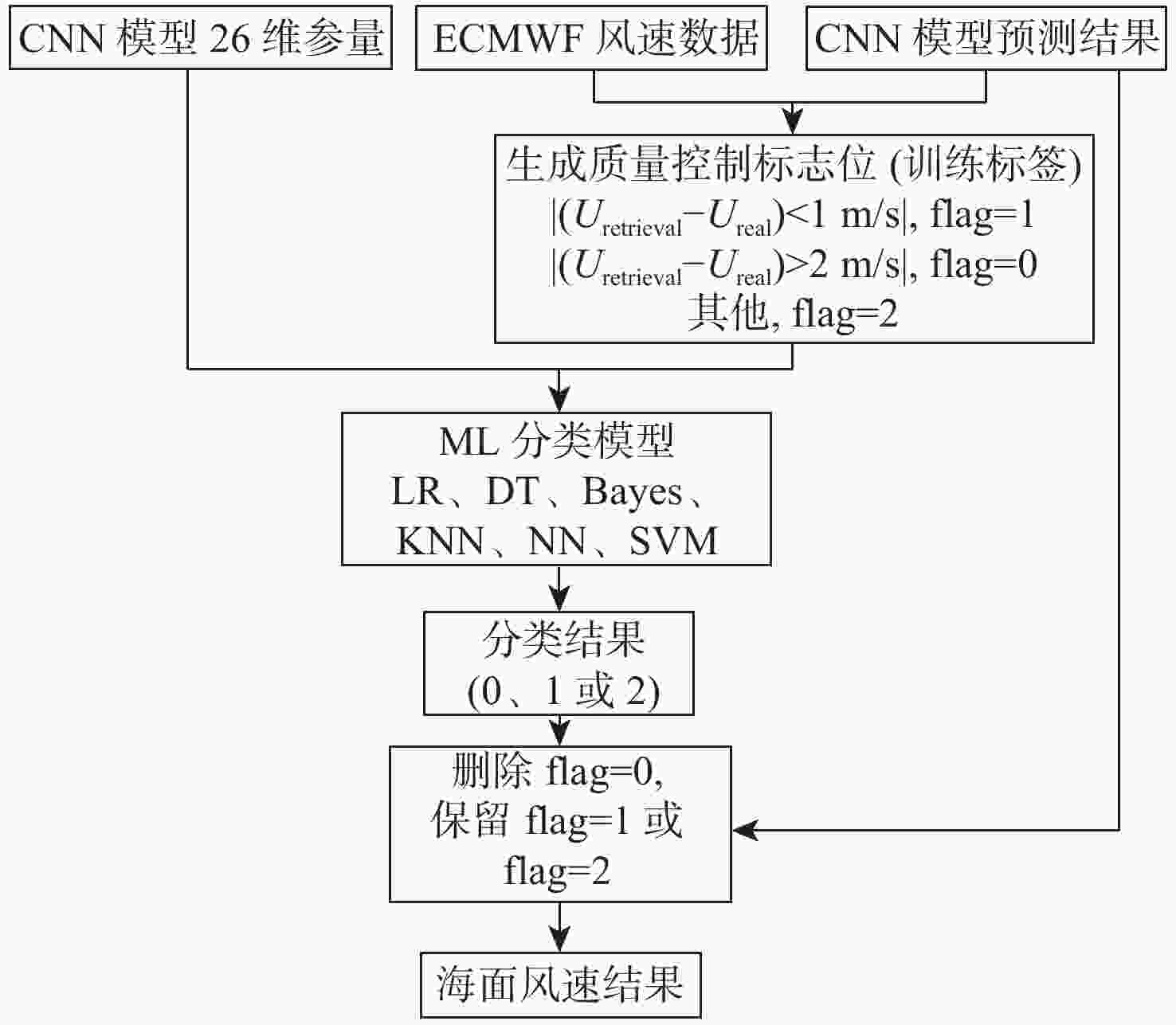
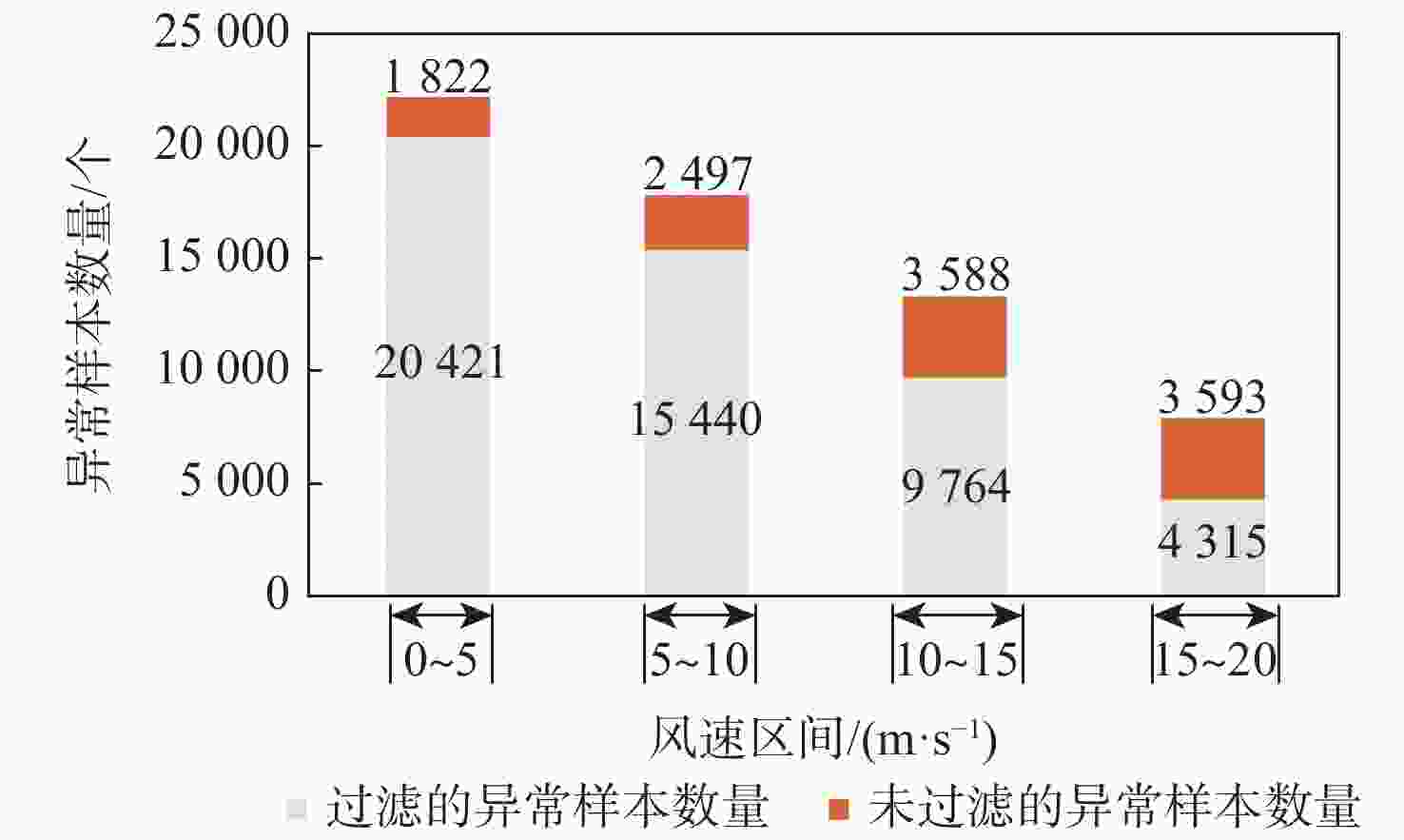
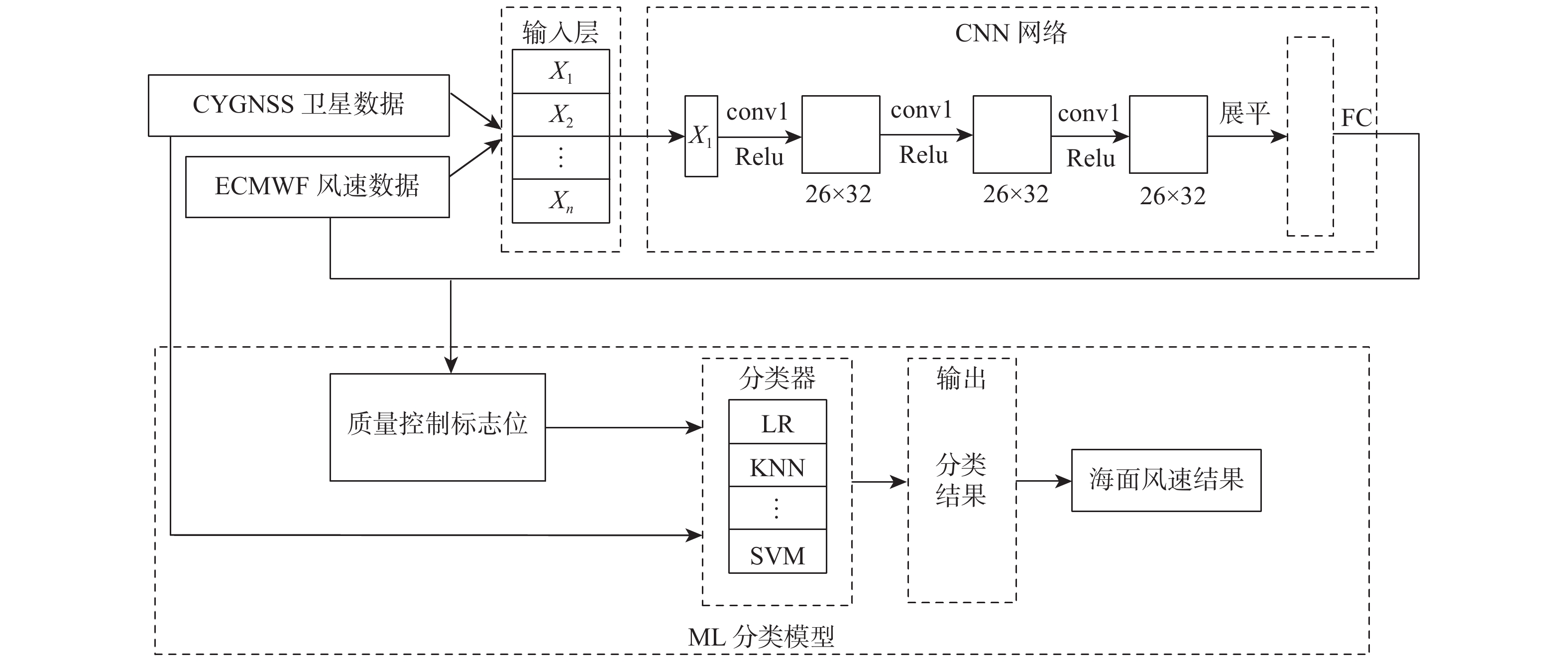
卷积神经网络(CNN)可用于气旋全球导航卫星系统(CYGNSS)的海面风速反演。虽然在模型训练前设置了质量控制指标来检测和削弱CYGNSS的异常观测数据,但CYGNSS观测数据中仍存在异常值导致模型反演精度降低,甚至出现错误反演结果。因此,提出一种基于机器学习(ML)组合的海面风速反演模型。在基于CNN回归模型的CYGNSS反演海面风速基础上,ML分类模型生成CNN回归结果的质量标志位,该标志位可以检测并删除CNN回归结果的异常值,进一步提高风速反演结果的数据质量,ML分类模型能够更好地考虑各种数据误差之间的相互作用,而不是单独使用每个条件的阈值,以达到更优的海面风速反演精度的效果。实验对比了Logistic回归(LR)、决策树(DT)、朴素贝叶斯模型、K最邻近(KNN)算法、神经网络(NN) 模型、支持向量机(SVM) 算法等6个分类模型,其中,基于KNN算法的分类模型对风速反演质量控制的效果最优。所提风速反演组合模型显著提高了反演结果的精度,在0~20 m/s区间内,异常样本过滤率为81.27%,在所有被过滤的数据中,过滤正确率为86.03%;风速反演误差的均方根误差从无ML分类模型的1.7 m/s降低到有ML分类模型的1.44 m/s,其中,训练样本为0~10 m/s的反演结果精度提升效果较为明显,证明了所提风速反演组合模型对风速质量控制的有效性。
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNN) can be used for sea surface wind speed retrieval of cyclone global navigation satellite system (CYGNSS). There are still anomalous values in the observation data of CYGNSS, despite the fact that numerous quality control indicators have been set up to detect and weaken the abnormal observation data of CYGNSS before model training, which results in a drop in model retrieval accuracy and even incorrect retrieval results. Therefore, this paper proposes a wind speed retrieval model based on machine learning (ML) combination. Based on the CYGNSS retrieval of sea surface wind speed based on the CNN regression model, the ML classification model generates the quality flag of the CNN regression result, which can detect and remove the outliers of the CNN regression results to further improve the data quality of the wind speed retrieval results, and the ML classification model can better consider the interaction between various data errors, instead of using the threshold for each condition individually, to achieve better results. The effect of retrieval accuracy of sea surface wind speed. Six classification models were compared in the experiments, including Logistic regression (LR), decision tree (DT), naive Bayes model, K-nearest neighbor (KNN) algorithm, neural network (NN) model, and support vector machine (SVM). It was ultimately determined that the classification model based on KNN algorithm had the best impact on the quality control of wind speed retrieval. The wind speed retrieval combined model significantly improves the accuracy of the retrieval results. In the range of 0−20 m/s, the filtering rate of abnormal samples is 81.27%, and in all filtered data, the filtering correct rate is 86.03%; the root mean square error of the error is reduced from 1.7 m/s for the classification model without ML to 1.44 m/s for the classification model with ML. Among them, the training sample is 0−10 m/s retrieval results, and the accuracy improvement effect is more obvious, which proves the effectiveness of the ML combination model proposed in this paper for wind speed quality control.
-
表 1 ML组合模型性能分析
Table 1. Performance analysis of ML combination model
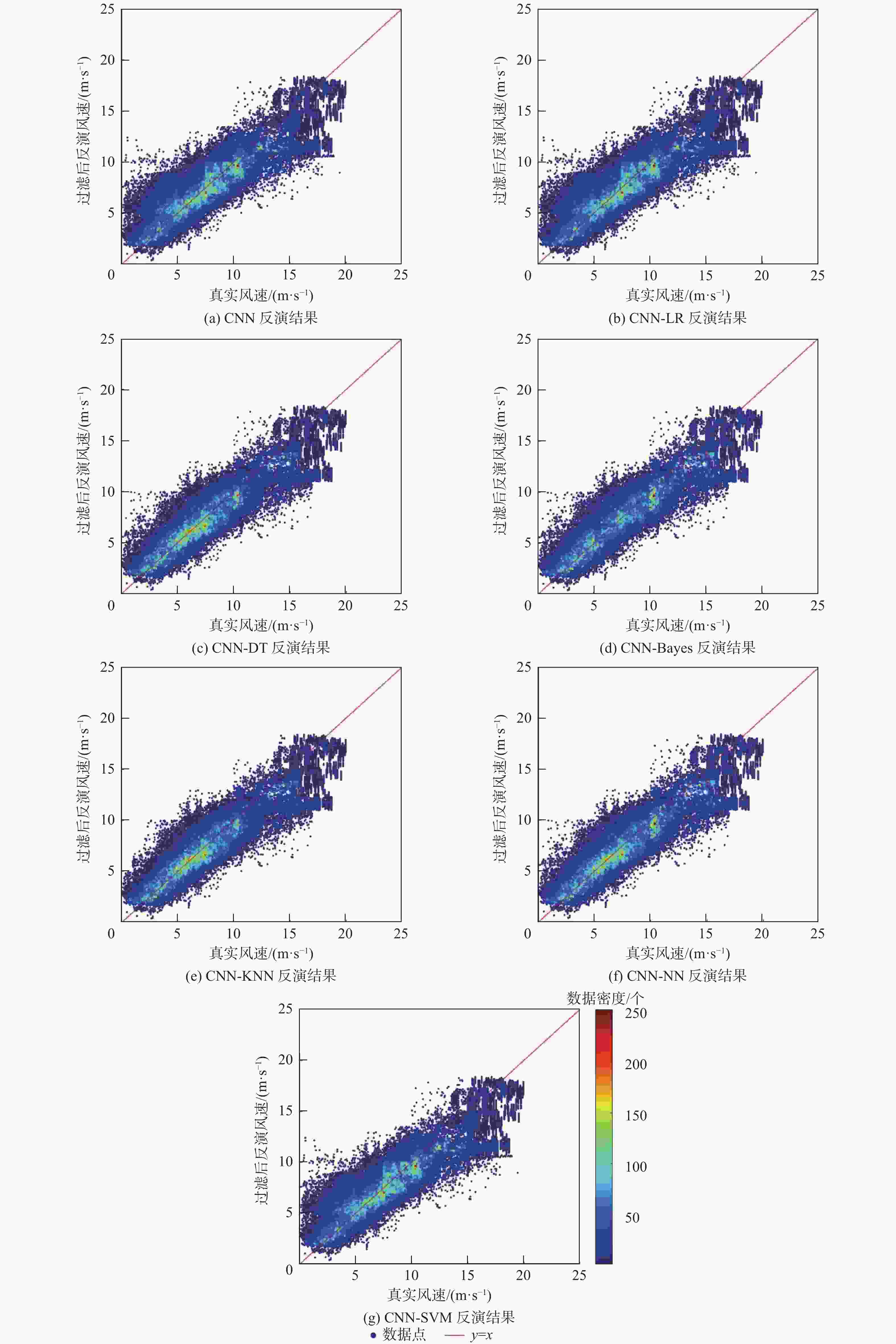
模型 M/(m·s−1) R/(m·s−1) B/(m·s−1) R2 CNN 1.47 1.70 0.21 0.69 CNN-LR 1.46 1.68 1.32 0.71 CNN-DT 1.34 1.52 0.22 0.73 CNN-Bayes 1.41 1.59 0.19 0.73 CNN-KNN 1.19 1.44 0.17 0.76 CNN-NN 1.28 1.49 0.13 0.69 CNN-SVM 1.43 1.62 1.92 0.61 表 2 分类模型过滤性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of filtering performance of classification models
分类模型 过滤正确率/% 异常样本过滤率/% 耗时/s LR 16.43 14.25 21598 DT 70.91 69.98 71153 Bayes 80.95 32.29 40426 KNN 86.03 81.27 66311 NN 81.03 80.91 29108 SVM 32.30 40.98 41803 表 3 CNN-KNN模型性能分析
Table 3. CNN-KNN model performance analysis
风速区间/(m·s−1) M/(m·s−1) R/(m·s−1) B/(m·s−1) R2 CNN CNN-KNN CNN CNN-KNN CNN CNN-KNN CNN CNN-KNN 0~5 1.51 1.01 1.85 1.16 0.97 0.78 0.58 0.78 5~10 1.12 0.97 1.24 1.2 0.24 0.13 0.72 0.75 10~15 1.67 1.69 1.86 1.77 1.3 1.18 0.57 0.59 15~20 2.94 3.02 3.41 3.31 2.15 1.98 0.18 0.19 -
[1] MASHBURN J, AXELRAD P, ZUFFADA C, et al. Improved GNSS-R ocean surface altimetry with CYGNSS in the seas of Indonesia[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6071-6087. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2973079 [2] HUANG F X, GARRISON J L, RODRIGUEZ-ALVAREZ N, et al. Sequential processing of GNSS-R delay-Doppler maps to estimate the ocean surface wind field[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10202-10217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931847 [3] ZHU Y C, TAO T Y, YU K G, et al. Sensing sea ice based on Doppler spread analysis of spaceborne GNSS-R data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 217-226. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2955175 [4] YIN C, LOPEZ-BAEZA E, MARTIN-NEIRA M, et al. Intercomparison of soil moisture retrieved from GNSS-R and from passive L-band radiometry at the Valencia anchor station[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 19(8): 1900. doi: 10.3390/s19081900 [5] CLARIZIA M P, RUF C S, JALES P, et al. Spaceborne GNSS-R minimum variance wind speed estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(11): 6829-6843. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2303831 [6] VALENCIA E, ZAVOROTNY V U, AKOS D M, et al. Using DDM asymmetry metrics for wind direction retrieval from GPS ocean-scattered signals in airborne experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 3924-3936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2278151 [7] GLEASON S, RUF C, CLARIZIA M P, et al. Calibration and unwrapping of the normalized scattering cross section for the cyclone global navigation satellite system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(5): 2495-2509. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2502245 [8] 骆黎明, 白伟华, 孙越强. 基于树模型机器学习方法的GNSS-R海面风速反演[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(4): 595-601.LUO L M, BAI W H, SUN Y Q. GNSS-R sea surface wind speed retrieval based on tree model machine learning method[J]. Journal of Space Science, 2020, 40(4): 595-601(in Chinese). [9] CARDELLACH E, NAN Y, LI W. Variational retrievals of high winds using uncalibrated CyGNSS observables[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(23): 3930. doi: 10.3390/rs12233930 [10] SAÏD F, JELENAK Z, PARK J, et al. The NOAA track-wise wind retrieval algorithm and product assessment for CyGNSS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 1-24. [11] GLEASON S. Level 1B DDM calibration : 148-0137[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 2020. [12] LI X, MECIKALSKI J R, LANG T J. A study on assimilation of CYGNSS wind speed data for tropical convection during 2018 January MJO[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(8): 1243. doi: 10.3390/rs12081243 [13] ZHANG Y, YIN J, YANG S, et al. High wind speed retrieval model of CYGNSS sea surface data based on machine learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3324. doi: 10.3390/rs13163324 [14] RUF C, CHANG P, CLARIZIA M P, et al. CYGNSS handbook[M]. Ann Arbor: Michigan Publishing, 2016. [15] HERSBACH H, BELL B, BERRISFORD P, et al. ERA5 hourly data on single levels from 1940 to present[EB/OL]. (2018-10-23)[2022-04-01]. https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-single-levels?tab=form. [16] ROSKA T, CHUA L O. The CNN universal machine: An analogic array computer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 2015, 40(3): 163-173. [17] 徐嘉兴, 李钢, 陈国良. 基于logistic回归模型的矿区土地利用演变驱动力分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(20): 247-255.XU J X, LI G, CHEN G L. Analysis of driving force of land use evolution in mining area based on logistic regression model[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(20): 247-255(in Chinese). [18] 张增伟, 吴萍. 基于朴素贝叶斯算法的改进遗传算法分类研究[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2012, 33(2): 750-753.ZHANG Z W, WU P. Research on classification of improved genetic algorithm based on naive Bayes algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2012, 33(2): 750-753(in Chinese). [19] ALIMJAN G, SUN T L, LIANG Y, et al. A new technique for remote sensing image classification based on combinatorial algorithm of SVM and KNN[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 32(7): 1859012. doi: 10.1142/S0218001418590127 [20] BOLLWEIN F, WESTPHAL S. A branch & bound algorithm to determine optimal bivariate splits for oblique decision tree induction[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51: 7552-7572. [21] ALIMJAN G, SUN T L, JUMAHUN H, et al. A hybrid classification approach based on support vector machine and K-nearest neighbor for remote sensing data[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 31(10): 1750034. doi: 10.1142/S0218001417500343 [22] BALASUBRAMANIAM R, RUF C. Neural network based quality control of CYGNSS wind retrieval[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(17): 2859. doi: 10.3390/rs12172859 [23] SUN X K, LIU L, LI C F, et al. Classification for remote sensing data with improved CNN-SVM method[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164507-164516. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952946 [24] RUF C, GLEASON S, MCKAGUE D. Assessment of CYGNSS wind speed retrieval uncertainty[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(1): 87-97. -







 下载:
下载: