-
摘要:
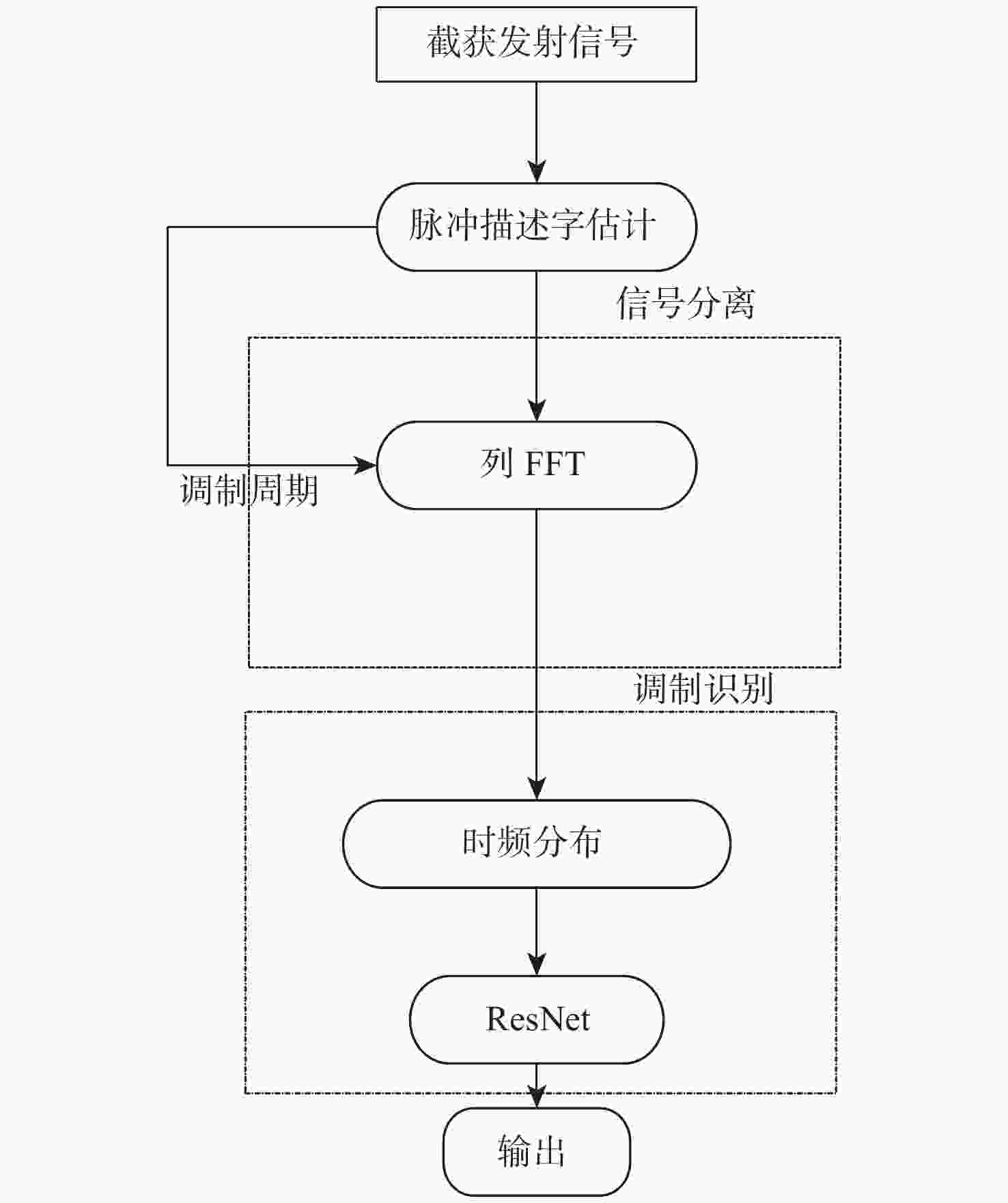
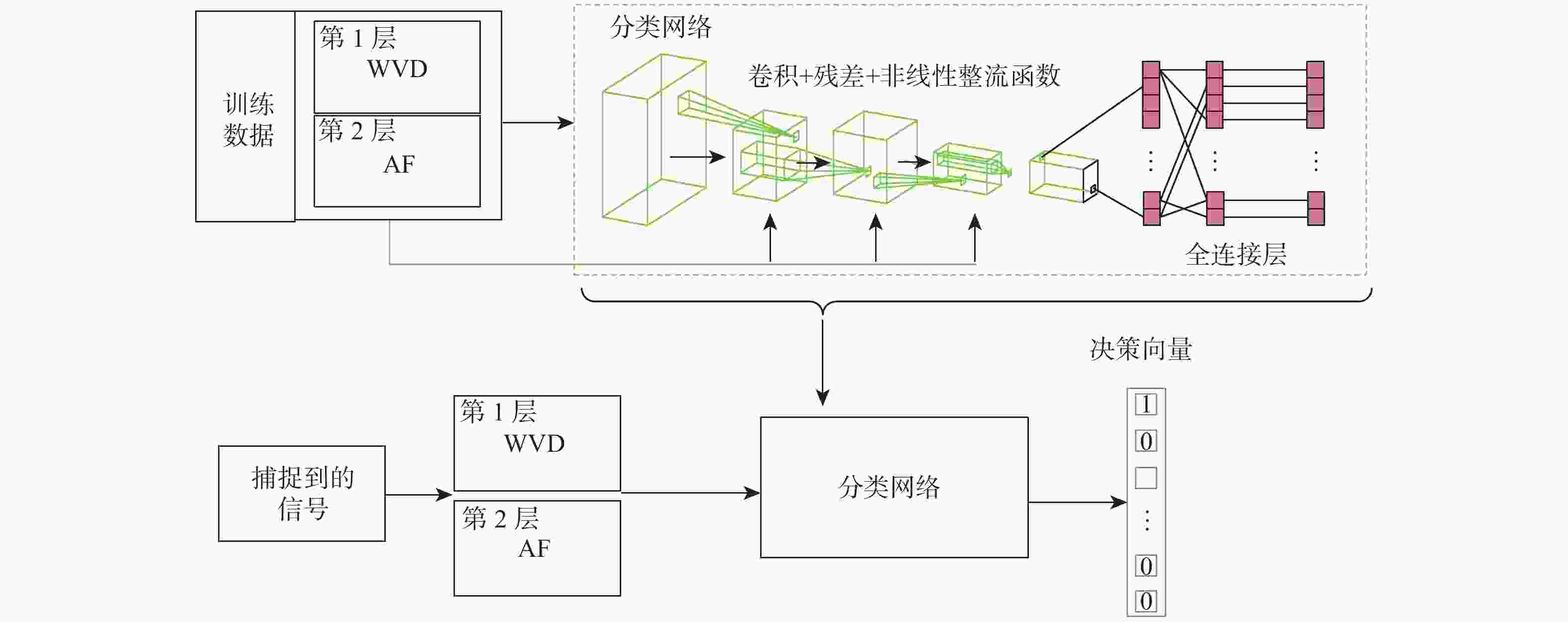
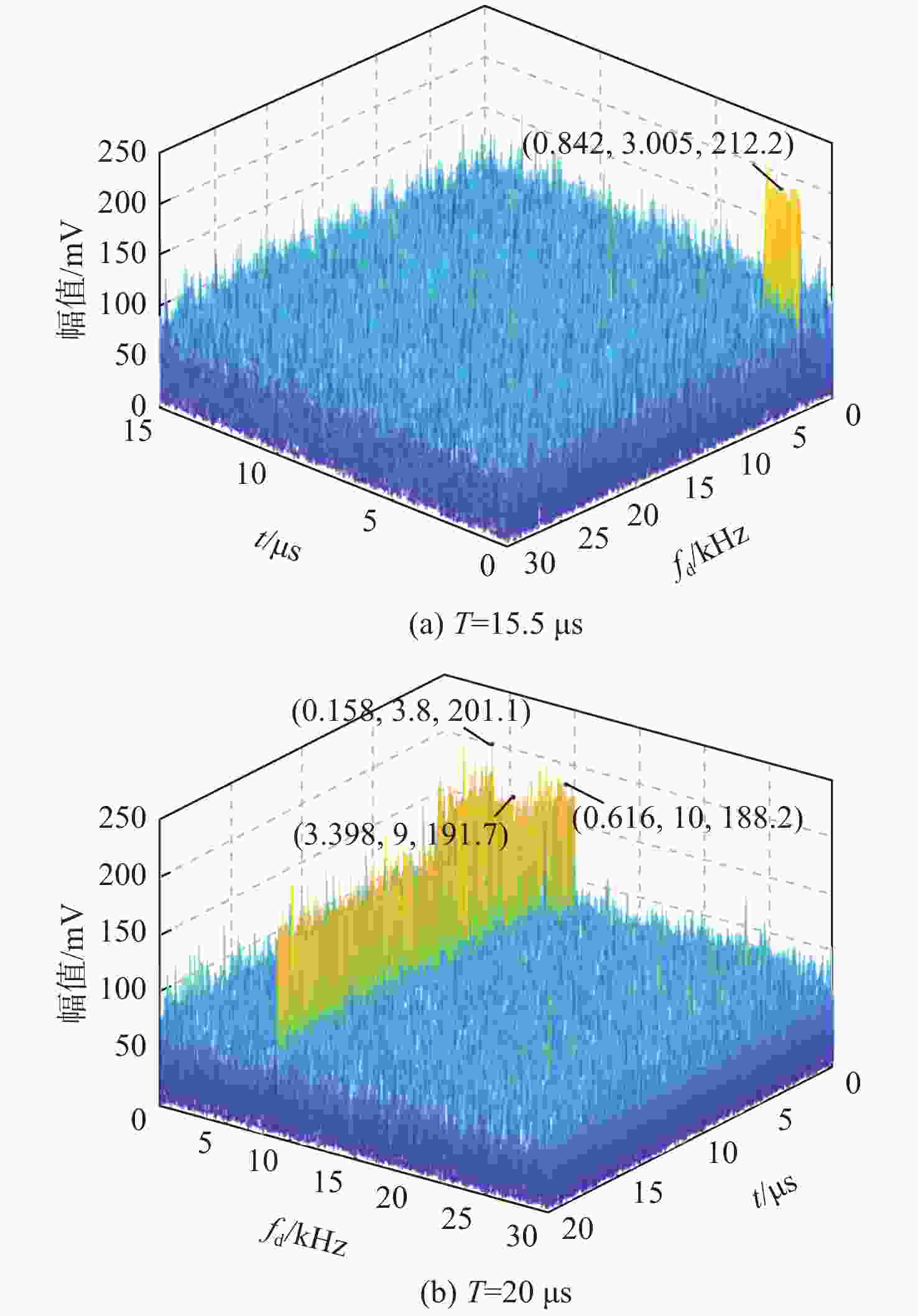
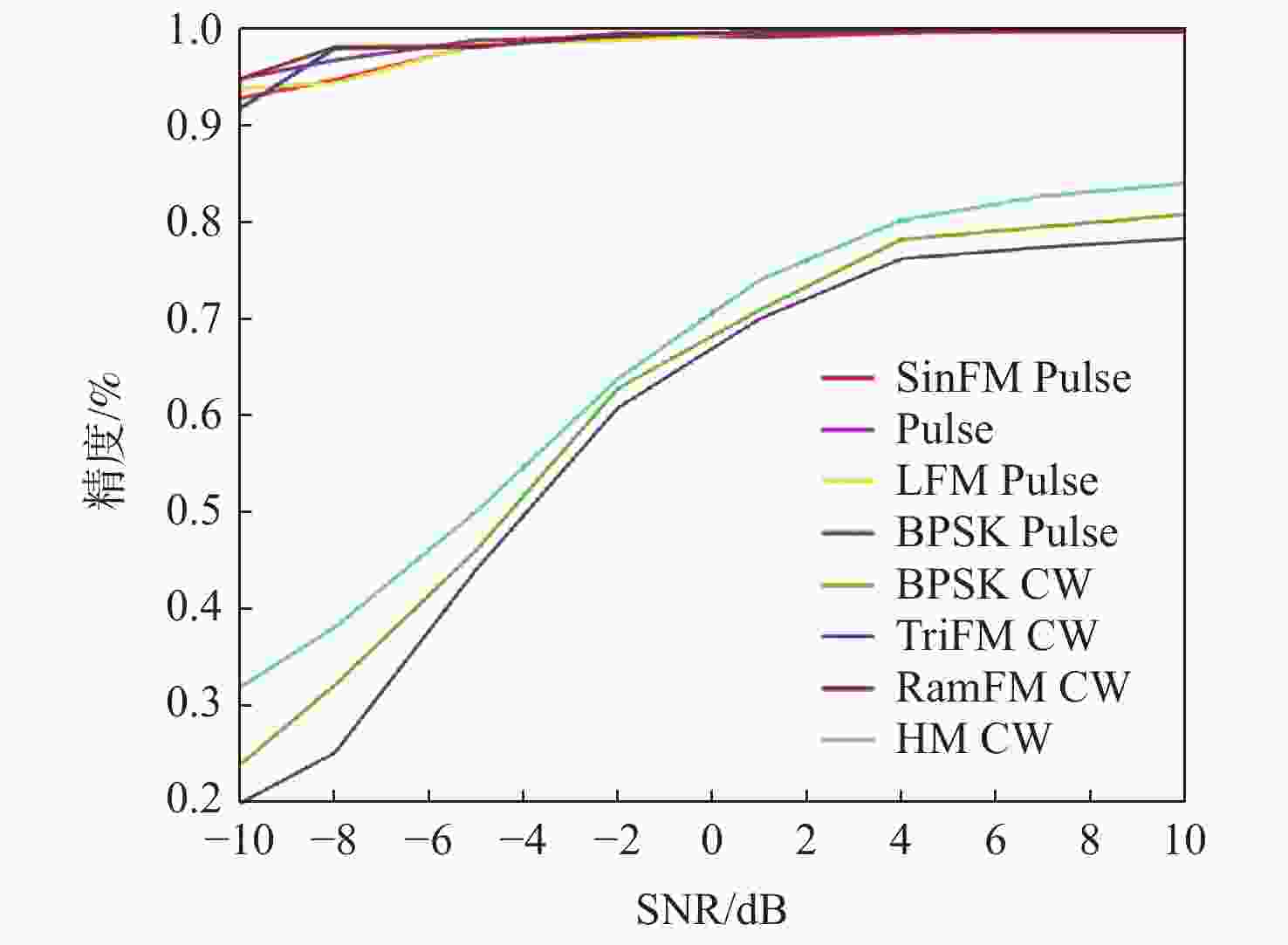
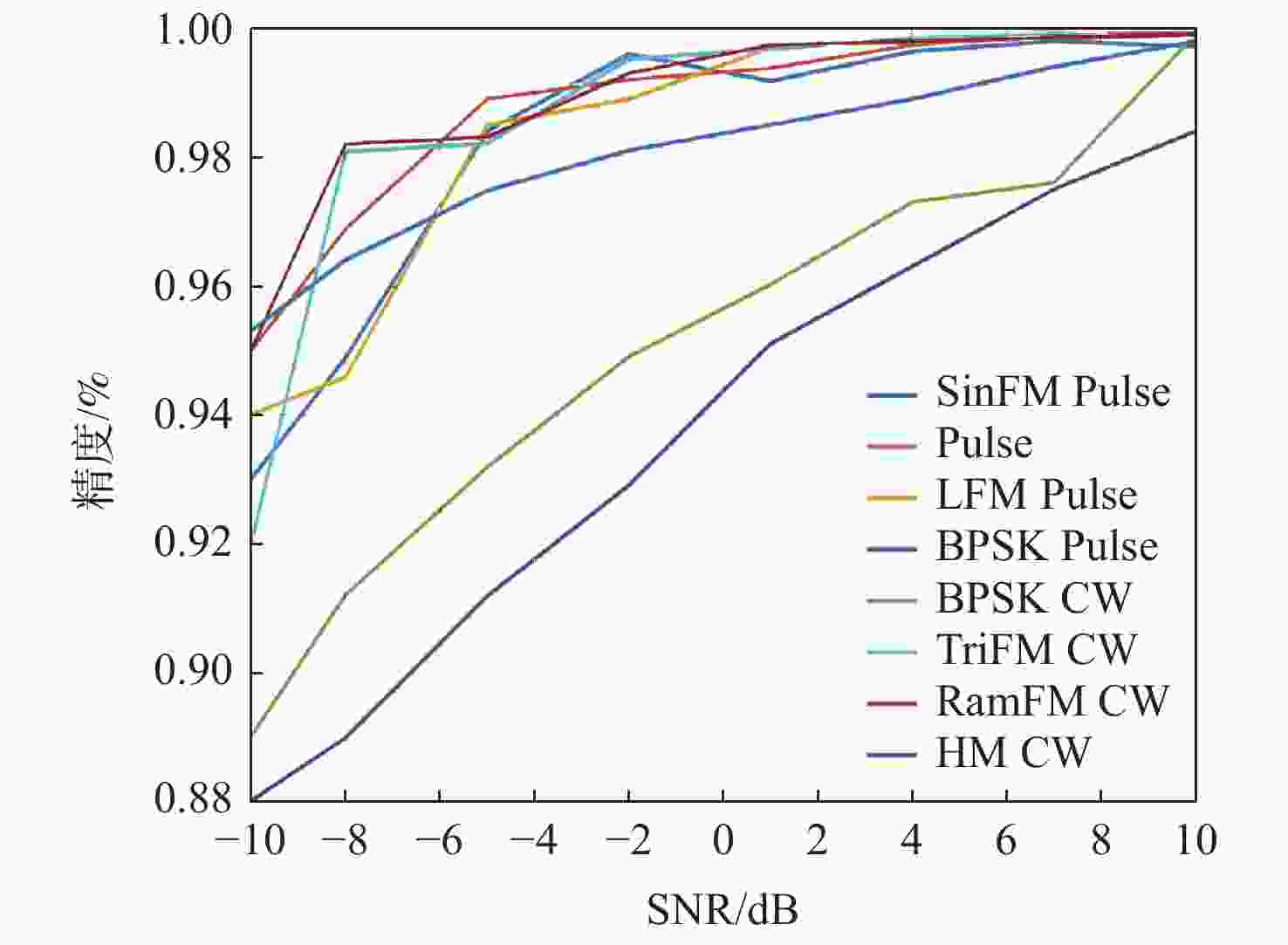
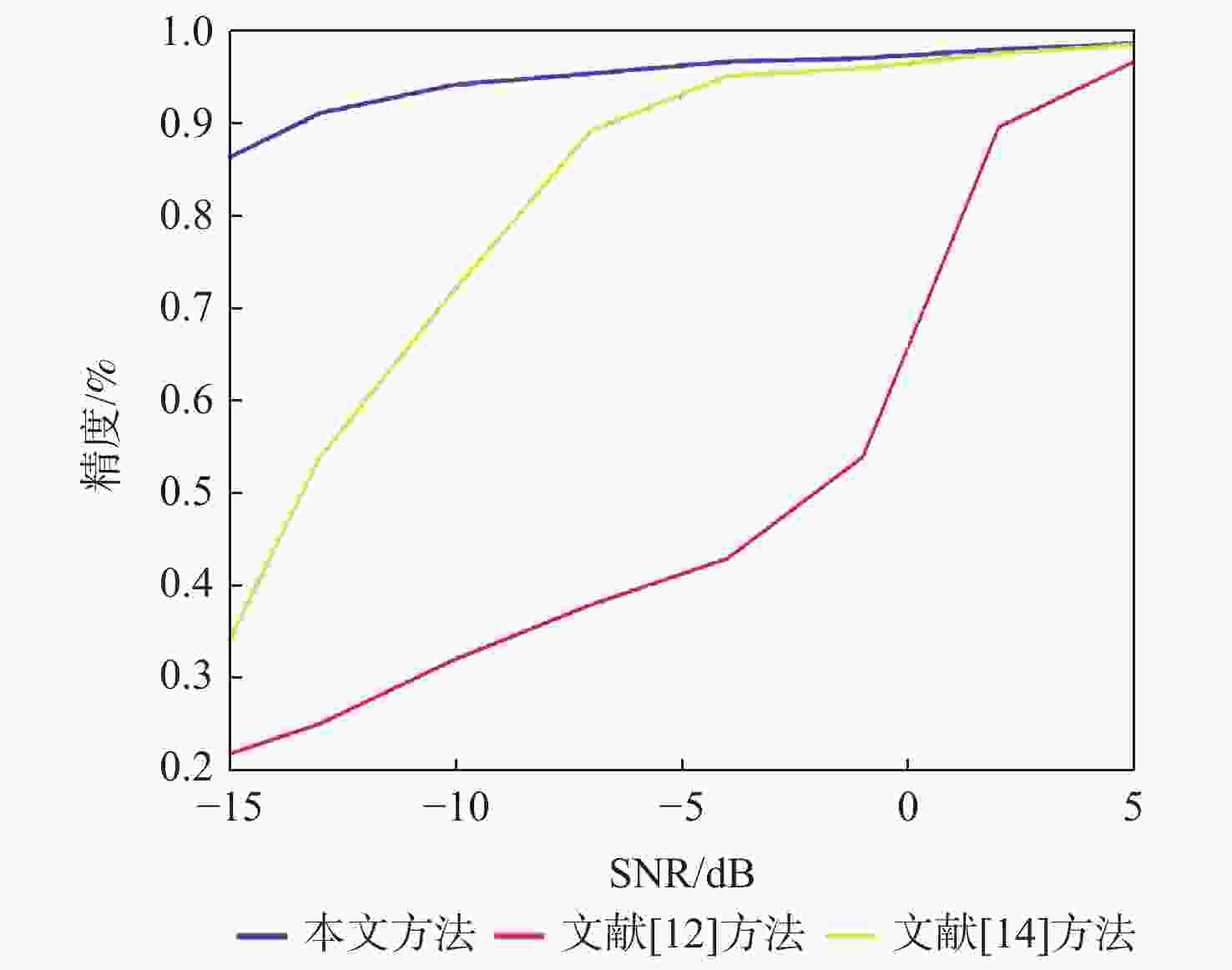
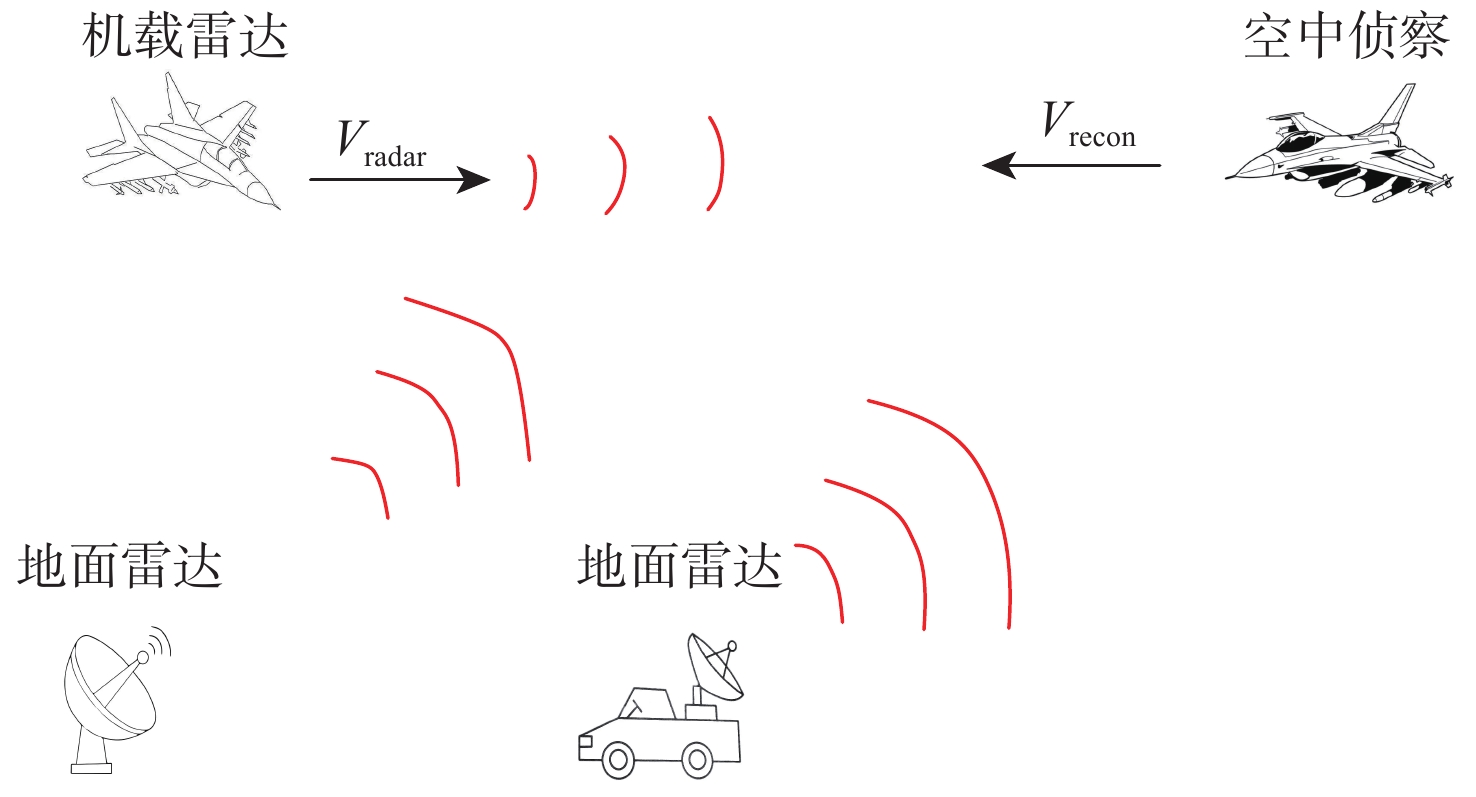
为解决复杂电磁环境中多台雷达在相似的频段上同时发射各自的信号,导致侦察接收信号在时域和频域上重叠的问题,提出一种低信噪比(SNR)下自动调制识别(MR)方法。通过接收脉冲间列快速傅里叶变换(FFT)将接收信号的能量集中在各自的多普勒频率上,以达到分离多个截获信号的目的;将每个信号的Wigner-Ville分布(WVD)和模糊函数(AF)作为一幅图像的2层同时发送到训练后的残差神经网络(ResNet),以解决某些类型的信号仅采用单一时频分布时识别精度低的问题。理论分析和仿真结果表明:所提方法不仅能有效分离时域和频域重叠的多个雷达信号,而且能在SNR为−10 dB的条件下准确识别其调制模式。
Abstract:In complex electromagnetic environments, simultaneous signal transmission of multiple radars in similar frequency bands can cause overlapping of reconnaissance’s received signals in the time and frequency domains. To address this problem, an automatic modulation recognition (MR) method with a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is proposed. The energy of the received signal is concentrated on the respective Doppler frequency through the row FFT transformation between the received pulses to achieve the separation of multiple intercepted signals. The Wigner-Ville distribution (WVD) and ambiguity function (AF) of each signal are simultaneously sent to the trained residual neural network (ResNet) as two layers of an image to solve the problem of low recognition accuracy when some types of signals only use a single time-frequency distribution. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the proposed method can not only effectively separate multiple radar signals overlapping in the time and frequency domains, but also accurately identify their modulation modes with the SNR of −10 dB.
-
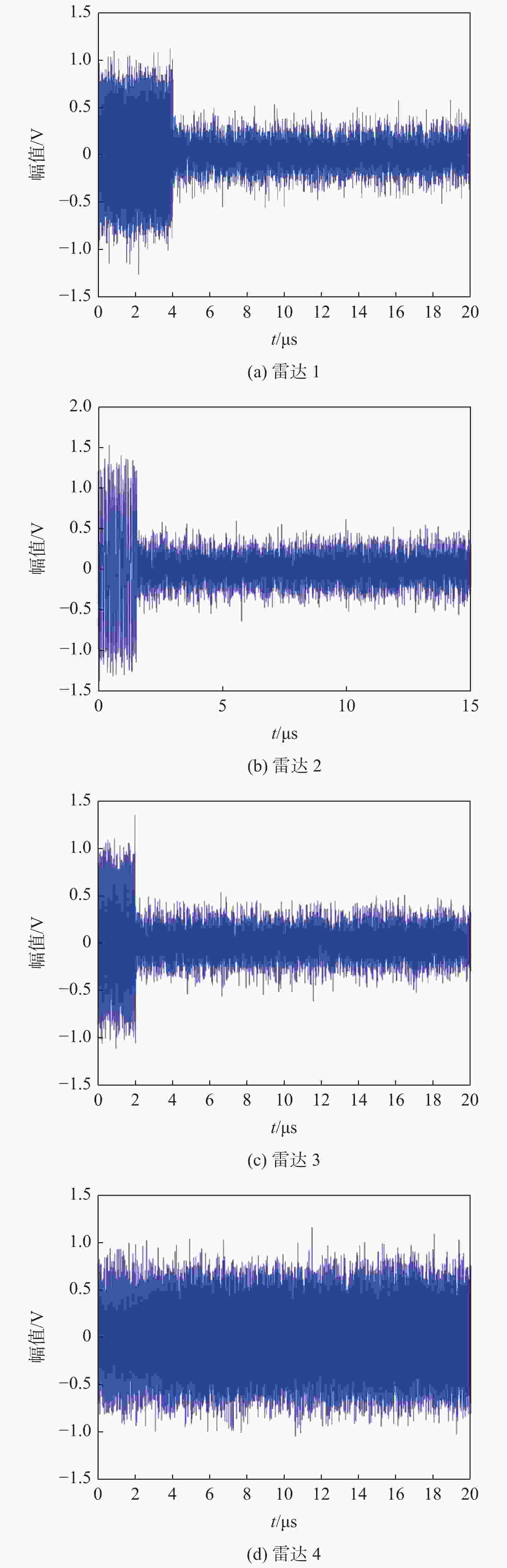
表 1 雷达信号的仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of radar signal
雷达 种类 调制
模式带宽/MHz 重复
周期/μs脉冲
宽度/μs径向速度/
( m·s−1)雷达 1 地面 LFM 50 20 4 200 雷达 2 地面 BPSK 20 15.5 1.55 150 雷达 3 空中 Pulse 0.5 20 2 500 雷达 4 空中 FMCW 30 20 450 表 2 雷达信号的仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters of radar signal
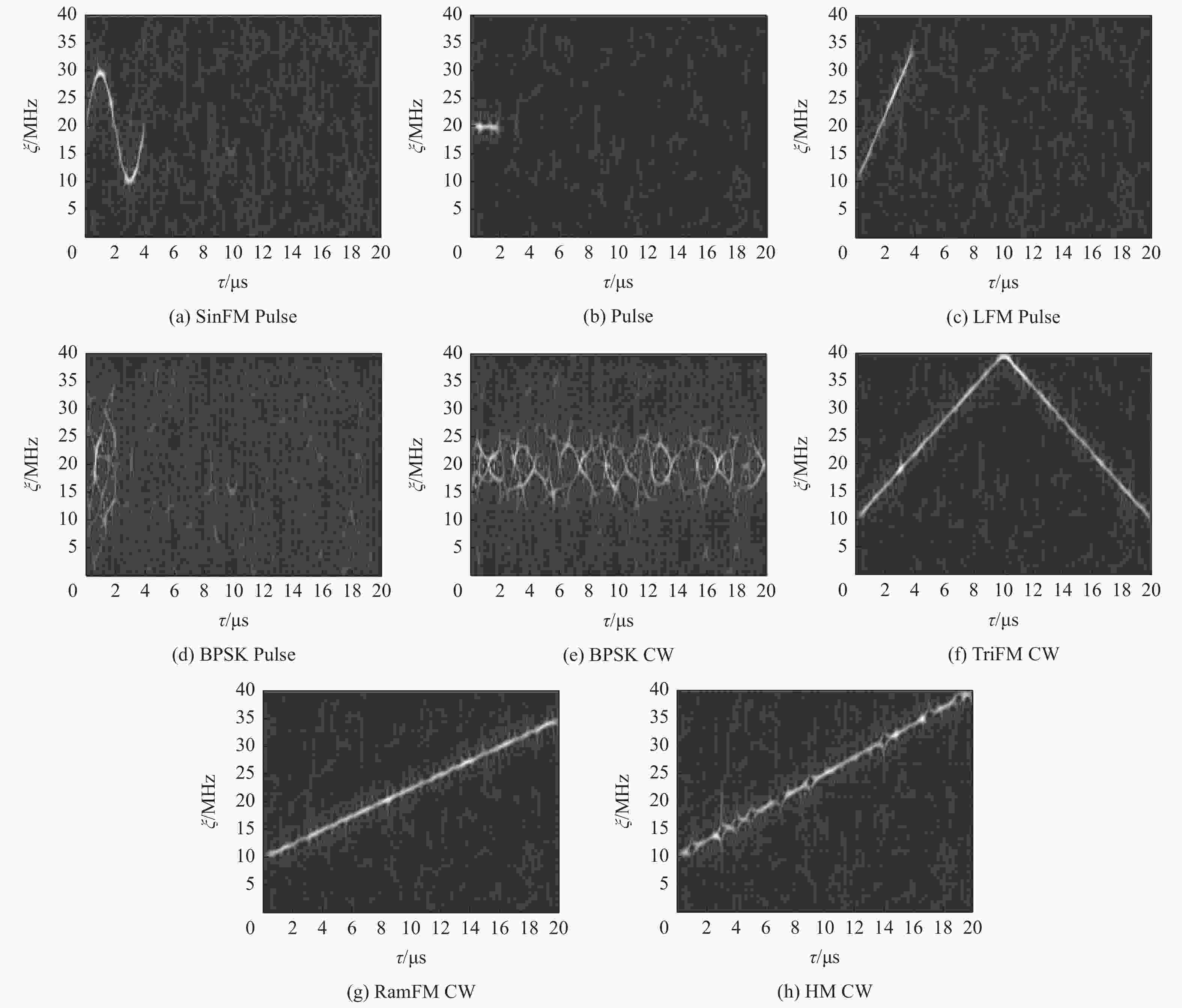
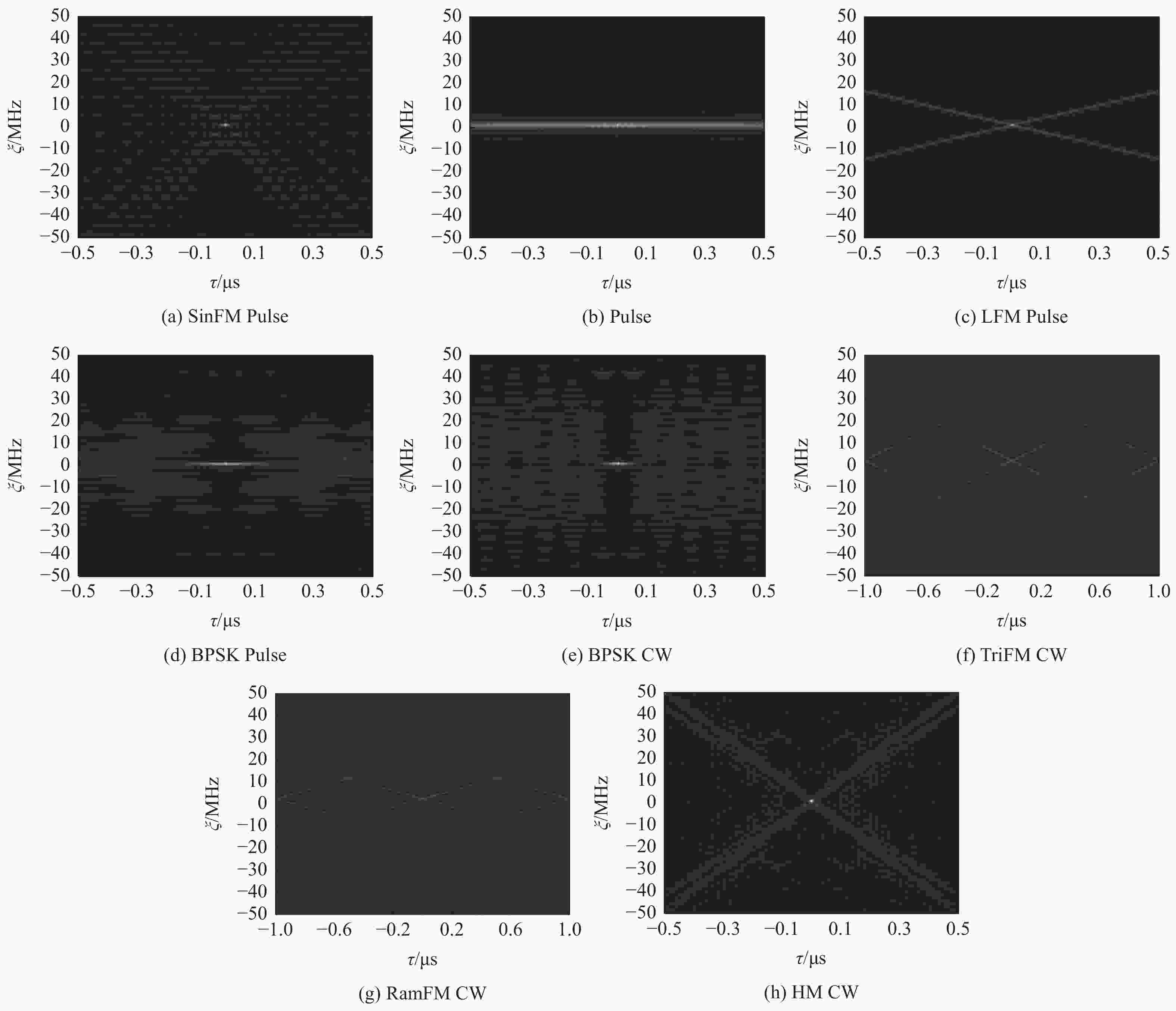
调制类型 PW/μs 带宽/MHz 频率/kHz SNR/dB SinFM
Pulse0.5~4 20~50 10~120 −10~10 Pulse 0.5~4 1~10 10~120 −10~10 LFM
Pulse0.5~4 20~50 10~120 −10~10 BPSK
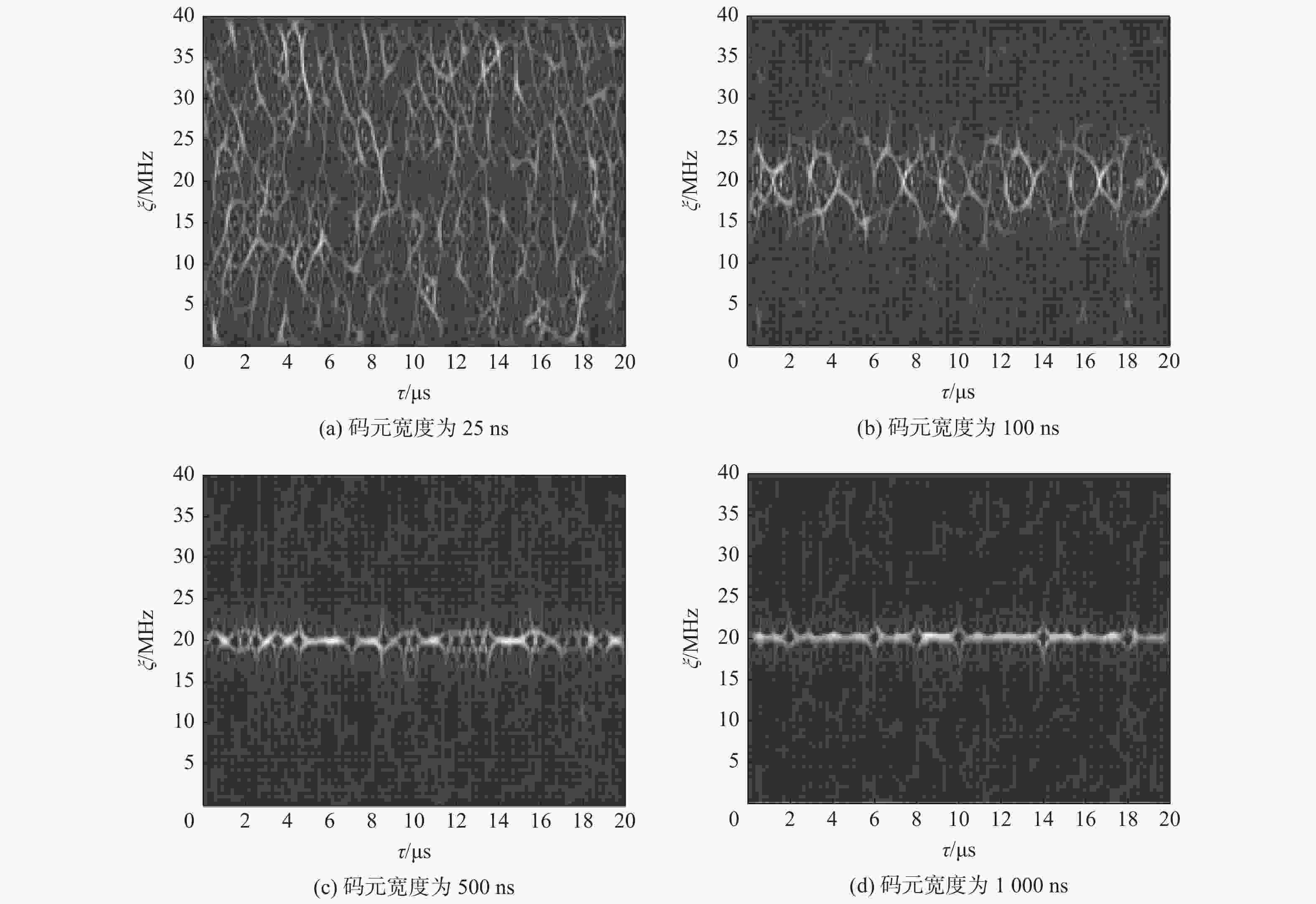
Pulse0.5~4 10~50 10~120 −10~10 BPSK
CW10~50 10~120 −10~10 TriFM
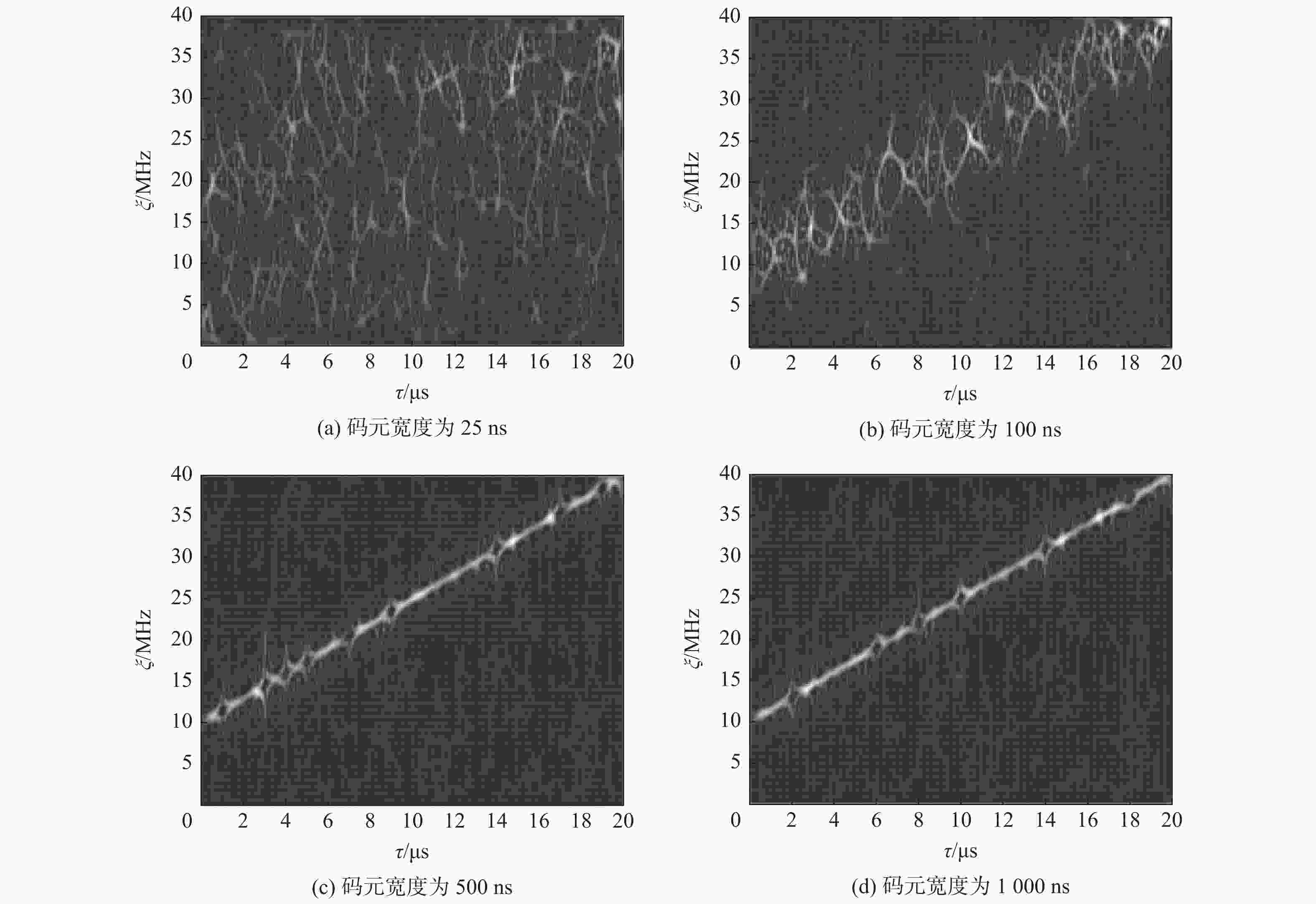
CW20~50 10~120 −10~10 RamFM
CW20~50 10~120 −10~10 HM
CW20~50 10~120 −10~10 表 3 网络模型参数
Table 3. Network model parameters
层 输入大小 输出大小 Input 128×128×2 128×128×2 Conv2D 128×128×2 128×128×32 Residual Unit1 128×128×32 128×128×32 Residual Unit2 128×128×32 64×64×32 Residual Unit3 64×64×32 64×64×32 Residual Unit4 64×64×32 64×64×32 Residual Unit5 64×64×32 32×32×32 Residual Unit6 32×32×32 32×32×32 Residual Unit7 32×32×32 32×32×32 Residual Unit8 32×32×32 32×32×32 Average Pooling2D 32×32×32 4×4×32 Flatten 4×4×32 512 Dense 512 8 Sigmoid 8 8 -
[1] HAYKIN S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30-40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335 [2] ZHANG G X, RONG H N, JIN W D, et al. Radar emitter signal recognition based on resemblance coefficient features[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Rough Sets and Current Trends in Computing. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 665-670. [3] HORNE C, RITCHIE M, GRIFFITHS H. Proposed ontology for cognitive radar systems[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1363-1370. [4] XU Z, SHI Q. Interference mitigation for automotive radar using orthogonal noise waveforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 137-141. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2777962 [5] ZHANG G X, LI X. A new recognition system for radar emitter signals[J]. Kybernetes, 2012, 41(9): 1351-1360. doi: 10.1108/03684921211275405 [6] WEST N E, O’SHEA T. Deep architectures for modulation recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [7] DANG H V, KINSNER W. An analytical multiobjective optimization of joint spectrum sensing and power control in cognitive radio networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Cognitive Informatics & Cognitive Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 39-48. [8] GRILO A, MACEDO M, SEBASTIÃO P, et al. Electronic protection and routing optimization of MANETs operating in an electronic warfare environment[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2007, 5(7): 1031-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2006.05.002 [9] KONG S H, KIM M, HOANG L M, et al. Automatic LPI radar waveform recognition using CNN[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 4207-4219. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2788942 [10] ZHANG M, LIU L T, DIAO M. LPI radar waveform recognition based on time-frequency distribution[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1682. doi: 10.3390/s16101682 [11] GRANGER E, RUBIN M A, GROSSBERG S, et al. Radar ESM with a what-and-where fusion neural network[C]//Neural Networks for Signal Processing XI: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 539-548. [12] ZAERIN M, SEYFE B. Multiuser modulation classification based on cumulants in additive white Gaussian noise channel[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2012, 6(9): 815-823. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2011.0357 [13] O’SHEA T J, ROY T, CLANCY T C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168-179. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022 [14] ZHU J D, ZHAO Y J, TANG J. Automatic recognition of radar signals based on time-frequency image character[C]//Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference. London: IET, 2013: 1-6. [15] YU H H, YAN X P, LIU S K, et al. Radar emitter multi-label recognition based on residual network[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(3): 410-417. [16] QU Z Y, HOU C F, HOU C B, et al. Radar signal intra-pulse modulation recognition based on convolutional neural network and deep Q-learning network[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 49125-49136. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980363 [17] WANG Q, DU P F, YANG J Y, et al. Transferred deep learning based waveform recognition for cognitive passive radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 155: 259-267. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.09.038 [18] ZHU M T, LI Y J, PAN Z S, et al. Automatic modulation recognition of compound signals using a deep multi-label classifier: a case study with radar jamming signals[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 169: 107393. [19] LIU S K, YAN X P, LI P, et al. Radar emitter recognition based on SIFT position and scale features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2018, 65(12): 2062-2066. [20] ZAMIR S W, ARORA A, KHAN S, et al. Multi-stage progressive image restoration[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 14816-14826. [21] PETROV N, JORDANOV I, ROE J. Radar emitter signals recognition and classification with feedforward networks[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2013, 22: 1192-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2013.09.206 [22] GOULDIEFF V, PALICOT J, DAUMONT S. Blind modulation classification for cognitive satellite in the spectral coexistence context[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(12): 3204-3217. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2688976 [23] GUO Q, NAN P L, WAN J. Signal classification method based on data mining for multi-mode radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27(5): 1010-1017. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2016.05.09 [24] CHEN K Y, ZHANG S N, ZHU L Z, et al. Modulation recognition of radar signals based on adaptive singular value reconstruction and deep residual learning[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(2): 449. doi: 10.3390/s21020449 [25] ZHOU Z W, HUANG G M, CHEN H Y, et al. Automatic radar waveform recognition based on deep convolutional denoising auto-encoders[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2018, 37(9): 4034-4048. doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0757-0 [26] PAN Z S, WANG S F, ZHU M T, et al. Automatic waveform recognition of overlapping LPI radar signals based on multi-instance multi-label learning[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1275-1279. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3009195 [27] LIU Z P, LI L C, XU H Y, et al. A method for recognition and classification for hybrid signals based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electronics Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 325-330. [28] GUO Q, SUN J, XU J F, et al. EfficientDeRain: Learning pixel-wise dilation filtering for high-efficiency single-image deraining[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washton, D. C. : AAAI, 2021: 35(2): 1487-1495. [29] BAKO S, VOGELS T, MCWILLIAMS B, et al. Kernel-predicting convolutional networks for denoising Monte Carlo renderings[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 1-14. -






 下载:
下载: