-
摘要:
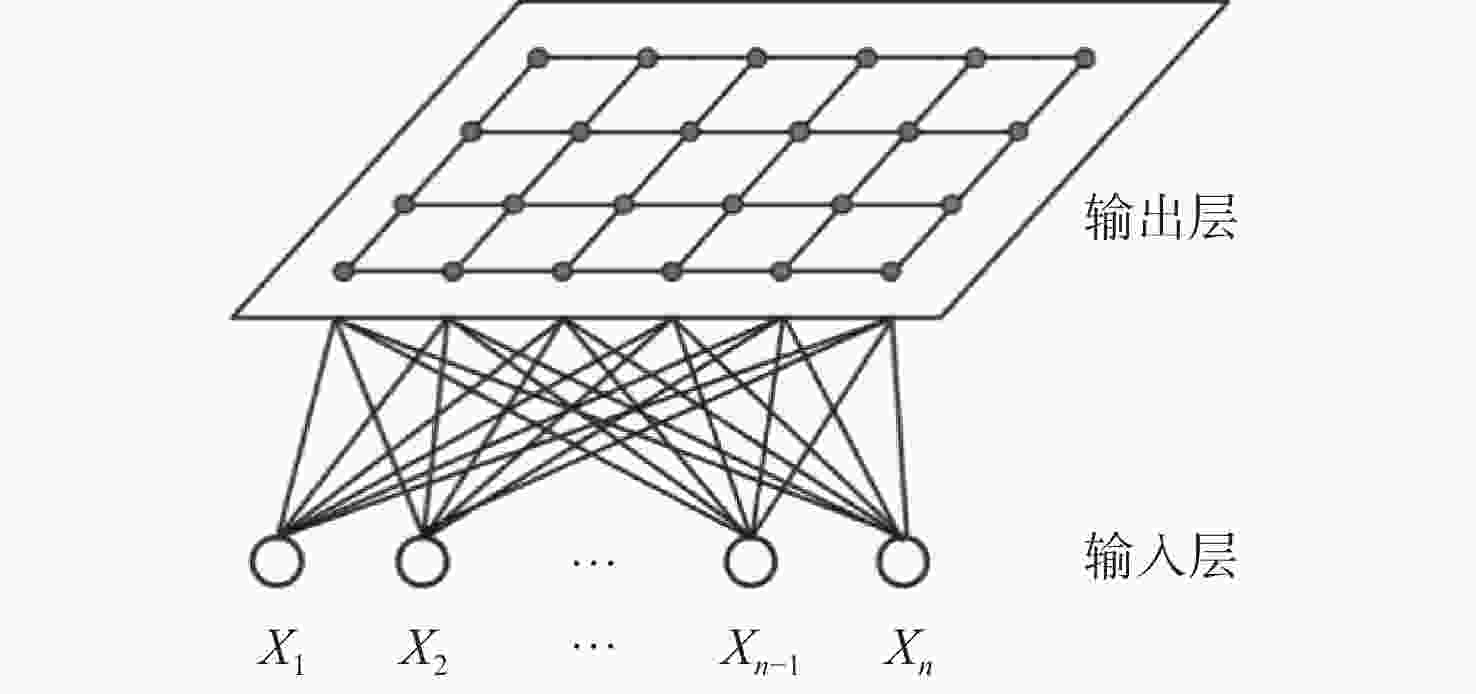
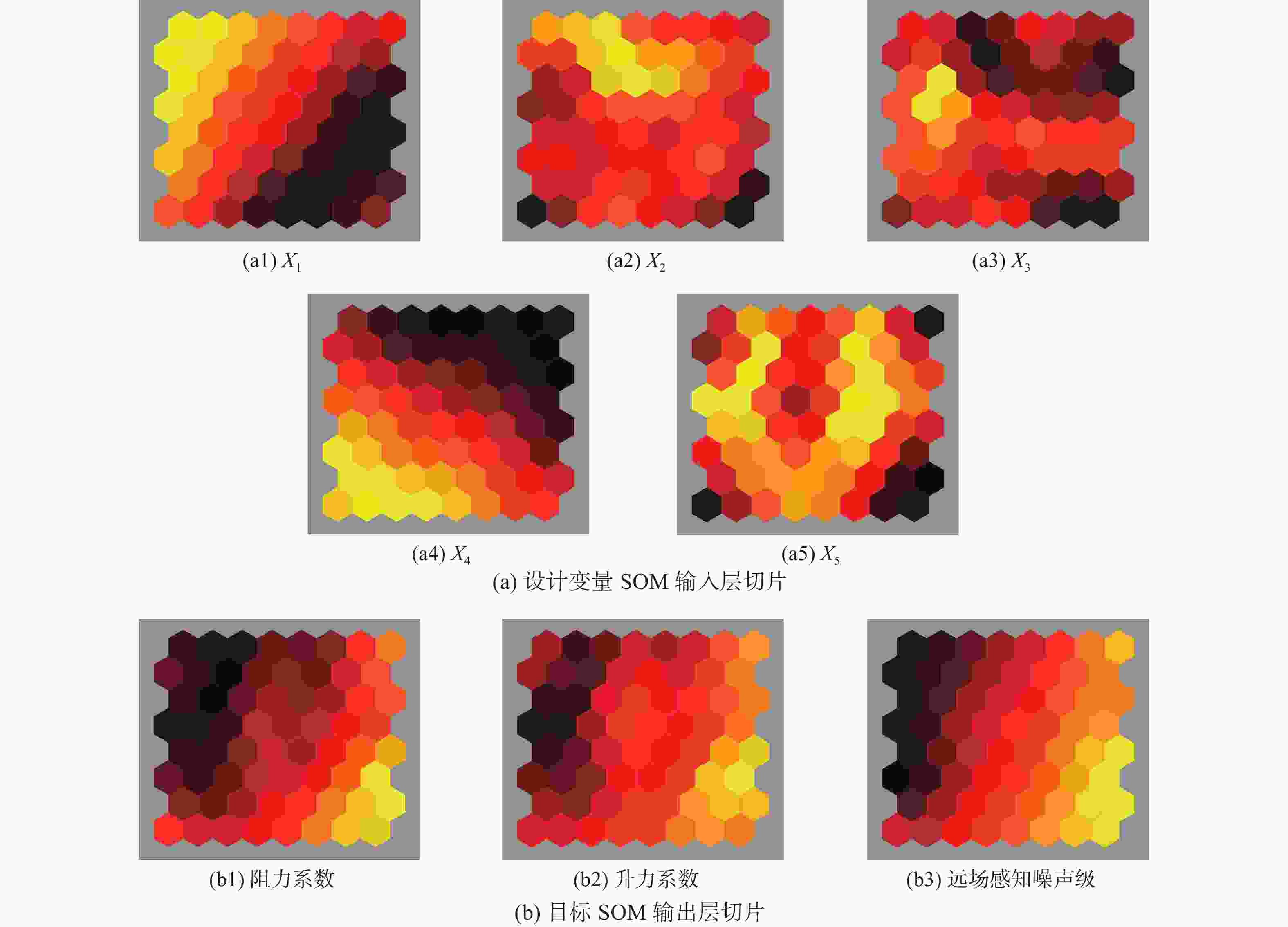
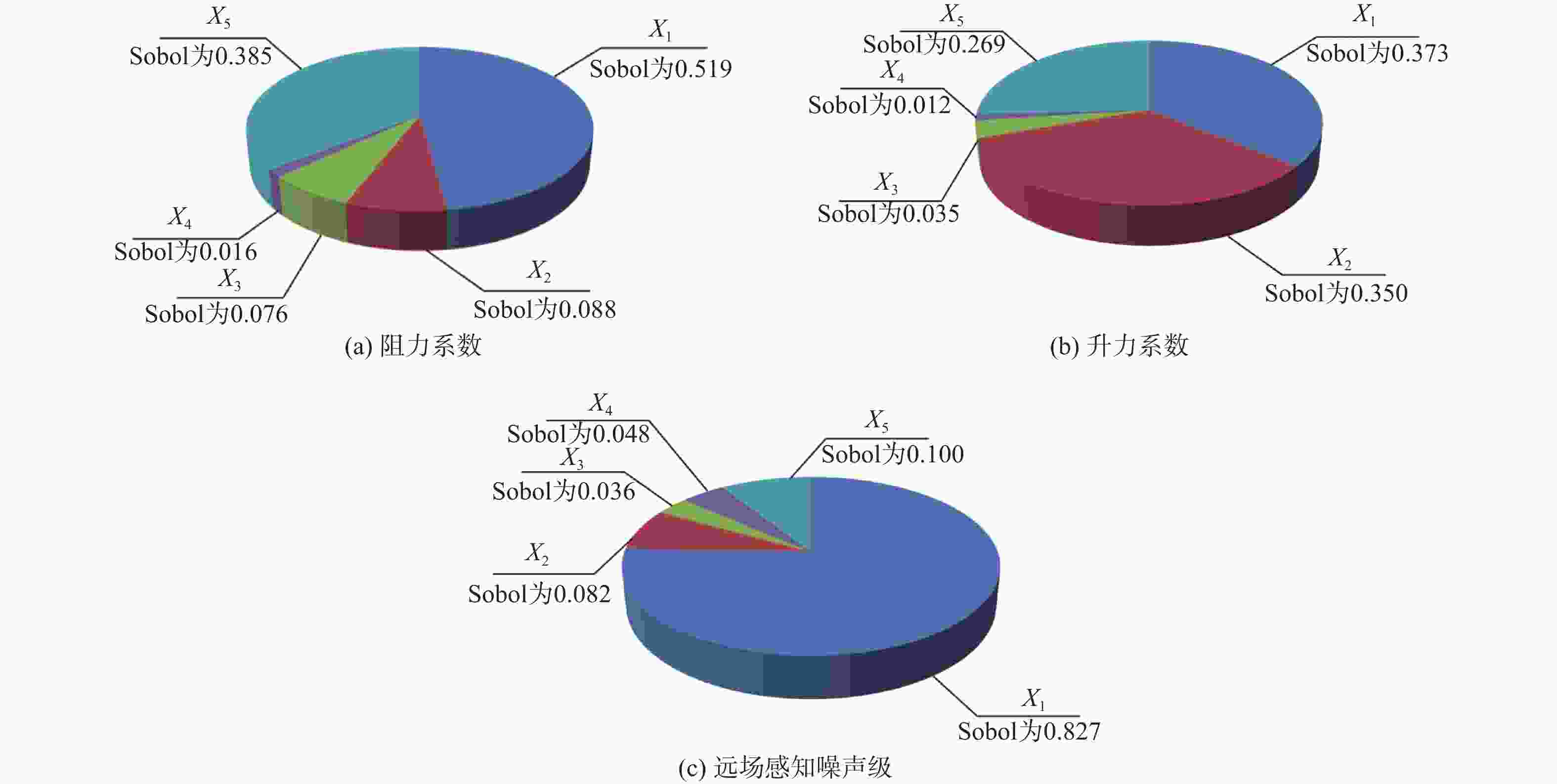
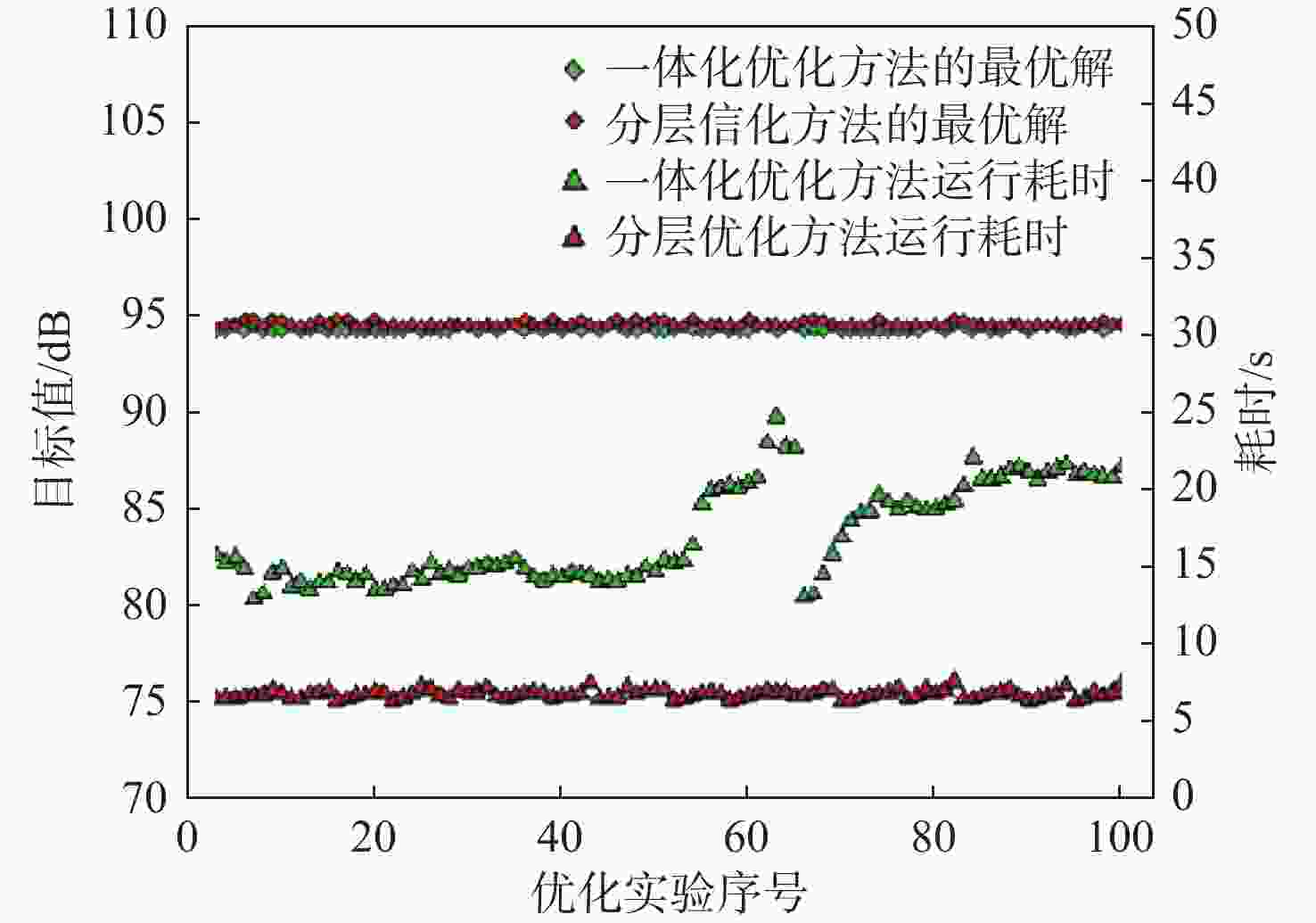
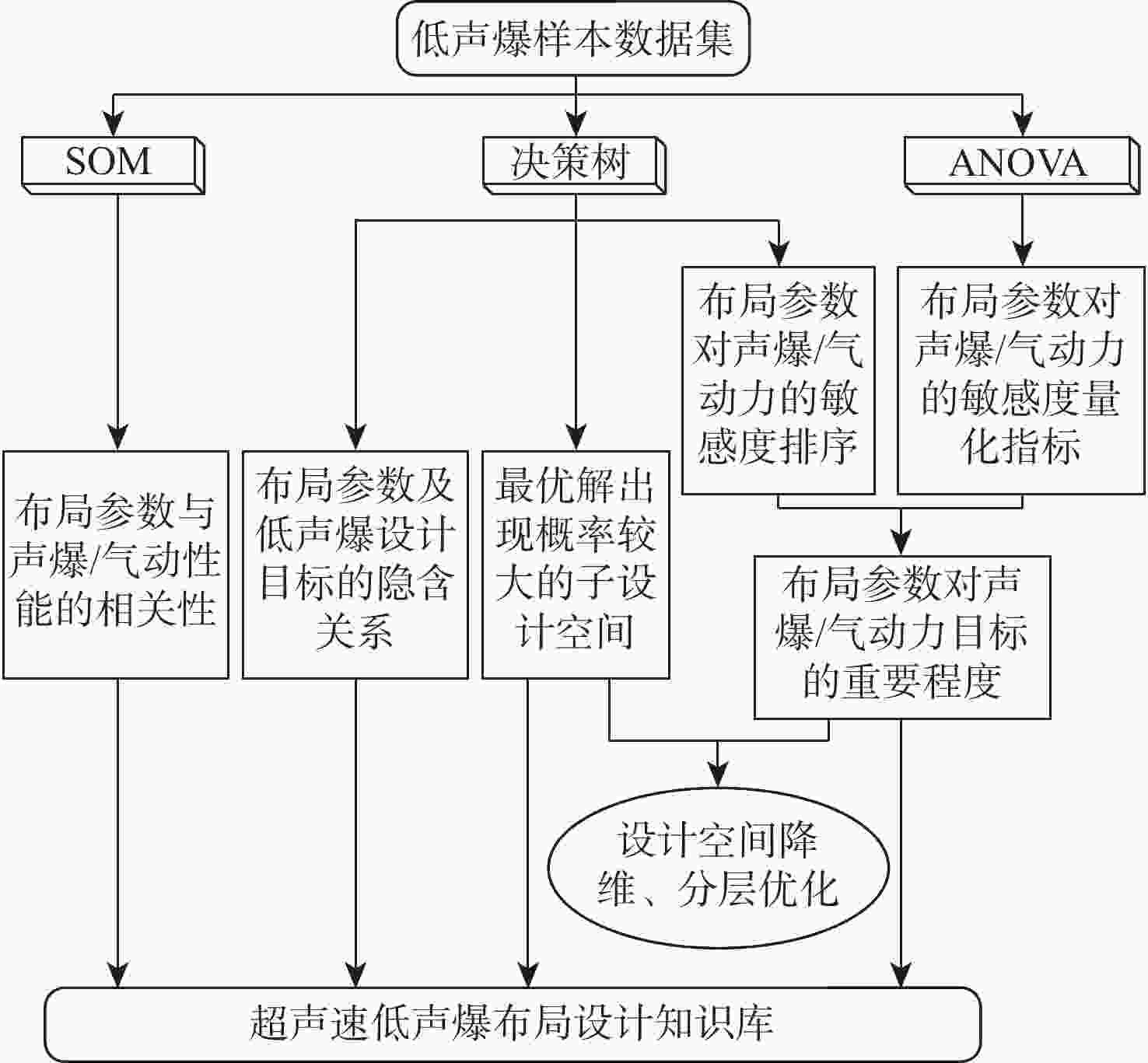
声爆抑制是发展新一代超声速民机必须突破的关键技术。飞行器总体布局参数对其声爆特性有重要影响。数据挖掘(DM)可以从大量的数据中通过算法搜索隐藏的信息,是飞行器设计知识提取的有力工具。选取后掠角、展弦比、梢根比、上反角、机身长细比5个总体布局参数作为设计变量,目标函数定义为远场感知噪声级,同时计算升、阻力系数作为气动力衡量指标。基于总变差分析(ANOVA)、决策树算法、自组织映射(SOM)网络组成的数据挖掘体系提取低声爆设计知识库。获得所选设计变量与声爆/气动力的相关度,并实现对设计变量的分层与降维。后掠角有最高设计优先级,长细比、上反角重要程度次之,展弦比与梢根比为低敏感变量。对于算例中的飞行器,在合理区间内选择较大的后掠角、上反角能够使声爆最小化的同时,设计适于超声速巡航的小展弦比布局。
Abstract:Sonic boom suppression is a key technology in the development of a new generation of supersonic civil aircraft. The configuration parameters of aircraft have an important influence on its sonic boom characteristics. Data mining (DM) can search hidden information from a large amount of data through algorithms, thus becoming a powerful tool to extract aircraft design knowledge. Five configuration parameters, including the sweep angle, aspect ratio, taper ratio, dihedral angle and fuselage slenderness ratio, are selected as design variables. The objective function is defined as the perceived noise level, and the lift and drag coefficients are calculated as aerodynamic measurement indexes. The knowledge base of low sonic boom design is extracted based on the data mining system composed of analysis of variance (ANOVA), decision tree and self-organizing feature map (SOM). The method obtains the correlation between the selected design variables and sonic boom/aerodynamic force, realizing the stratification and dimensionality reduction of design variables. The sweep angle has the first design priority, the slenderness ratio and the dihedral angle the second, and the aspect ratio and taper ratio are low sensitive variables. For the aircraft of the example in this paper, choosing a larger sweep angle and dihedral angle in a reasonable range can minimize the sonic boom and design a small aspect ratio configuration suitable for supersonic cruises.
-
Key words:
- supersonic civil aircraft /
- sonic boom suppression /
- configuration design /
- data mining /
- knowledge base
-
表 1 设计变量取值区间
Table 1. Value ranges of design variables
后掠角X1/(°) 展弦比X2 梢根比X3 上反角X4/(°) 机身长细比X5 60~70 0.7 ~ 1.2 0.02 ~ 0.2 −3~8 12 ~ 17 表 2 决策树样本标签
Table 2. Labels of decision tree samples
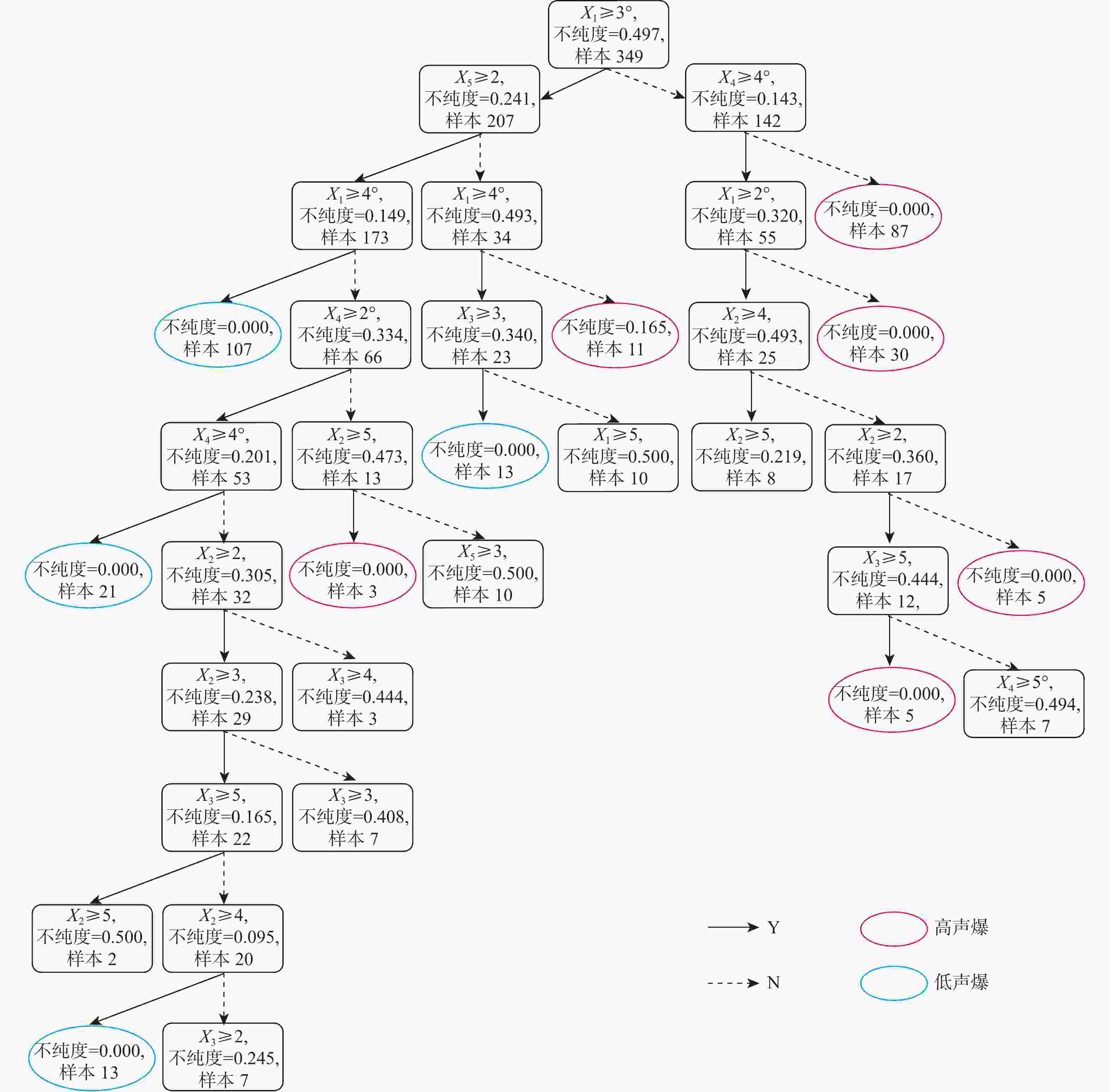
标签 X1/(°) X2 X3 X4/(°) X5 目标函数 1 [60,62) [0.7,0.8) [0.02,0.06) [−3.0,−0.8) [12,13) (−$ \mathrm{\infty } $,99.67] 2 [62,64) [0.8,0.9) [0.06,0.09) [−0.8,1.4) [13,14) (99.67,+$ \mathrm{\infty } $) 3 [64,66) [0.9,1.0) [0.09,0.13) [1.4,3.6) [14,15) 4 [66,68) [1.0,1.1) [0.13,0.16) [3.6,5.8) [15,16) 5 [68,70) [1.1,1.2) [0.16,0.20) [5.8,8.0) [16,17) 表 3 决策树设计知识提取
Table 3. Design knowledge extracted from decision tree
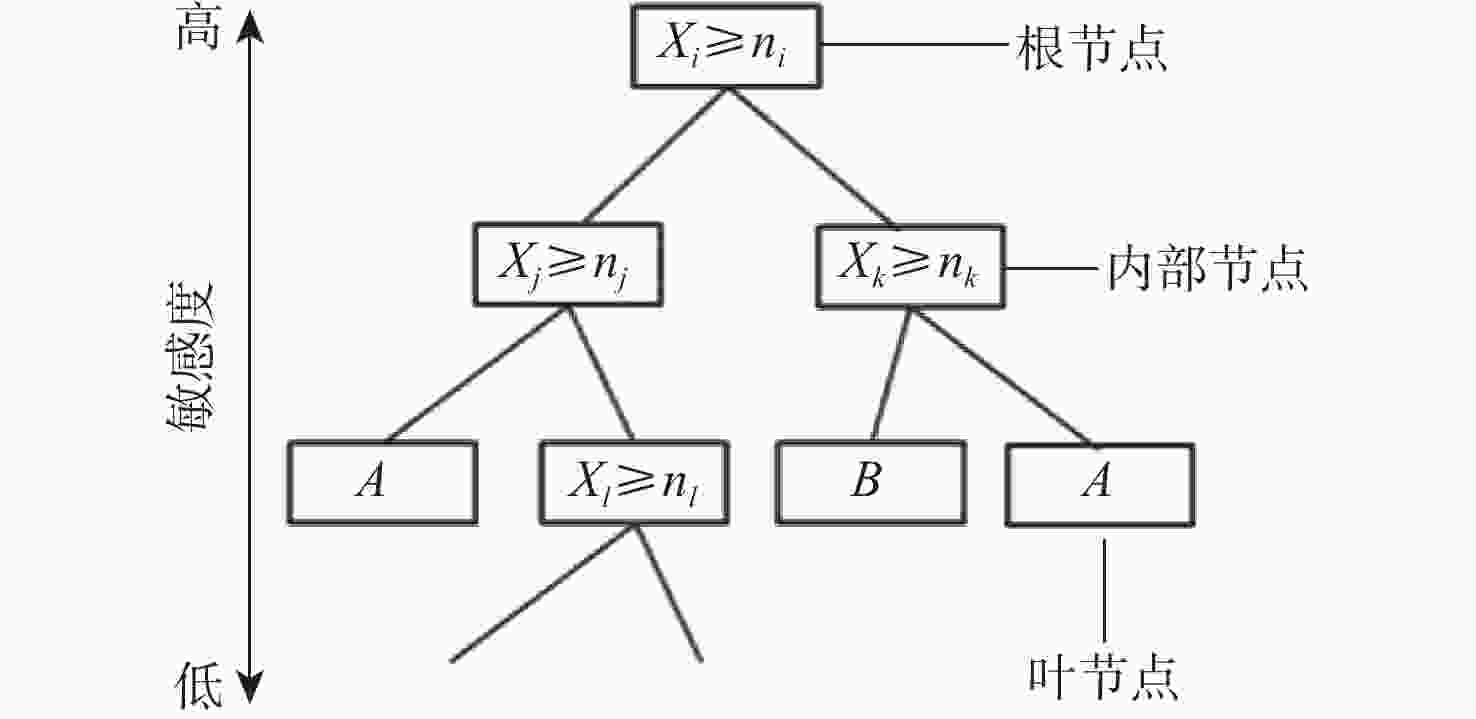
序号 样本数 设计知识 1 107 X1≥66°, X5≥13。 2 13 X1≥66°,X3≥0.09,X5<13。 3 21 64°≤X1<66°,X4≥3.6°,X5≥13。 4 13 64°≤X1<66°,X2≥1.0, X3<0.16。
−0.8°≤X4<3.6°, X5≥13。表 4 设计变量分层信息
Table 4. Hierarchical information of design variables
分层情况 变量 原区间 新空间 第1层 X1/(°) 60~70 64~70 第2层 X4/(°) −3~8 3.6~8 X5 12 ~ 17 13 ~ 17 第3层 X2 0.7 ~ 1.2 0.7 ~ 1.2 X3 0.02 ~ 0.20 0.02 ~ 0.20 -
[1] 但聃, 杨伟. 超音速公务机声爆计算与布局讨论[J]. 航空工程进展, 2012, 3(1): 7-15.DAN D, YANG W. Supersonic business jet sonic boom computation and layout discussion[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(1): 7-15(in Chinese). [2] PLOTKIN K J. State of the art of sonic boom modeling[J]. Journal of Acoustical Society of America, 2002, 111(2): 530-536. [3] 庾晋, 周洁, 白木. “协和”号: 世界上唯一运营的超音速客机[J]. 交通与运输, 2003, 19(2): 26-27.YU J, ZHOU J, BAI M. Concorde: The only supersonic airliner operating in the world[J]. Traffic& Transportation, 2003, 19(2): 26-27 (in Chinese). [4] 冯晓强, 宋笔锋, 李占科, 等. 超声速飞机低声爆布局混合优化方法研究[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(8): 1768-1777.FENG X Q, SONG B F, LI Z K, et al. Hybrid optimization approach research for low sonic boom supersonic aircraft configuration[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(8): 1768-1777(in Chinese). [5] 俞元亮, 胡章伟, 陈玉清, 等. 航空声学[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 1986: 77-110.YU Y L, HU Z W, CHEN Y Q, et al. Aviation acoustics[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 1986: 77-110(in Chinese). [6] LANDAU L D. On shock waves at large distances from the place of their origin[EB/OL]. (2013-11-17)[2021-12-02]. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-010586-4.50065-1. [7] HENNE P A, HOWE D C, WOLZ R R, et al. Supersonic aircraft with spike for controlling and reducing sonic boom: US20100012777[P]. 2010-01-21. [8] GOETHERT B H. Fundamental research on advanced techniques for sonic boom suppression[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1973, 54(6): 12-15. [9] ZHA G C, IM H, ESPINAL D. Toward zero sonic-boom and high efficiency supersonic flight, part I: A novel concept of supersonic Bi-directional flying wing[C]//Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2010. [10] ESPINAL D, LEE B, SPOSATO H, et al. Supersonic Bi-directional flying wing, part II: Conceptual design of a high speed civil transport[C]//Proceedings of the 48th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2010. [11] HORINOUCHI S. Variable forward swept wing supersonic aircraft having both low-boom characteristics and low-drag characteristics: US20050230531[P]. 2005-10-20. [12] KUSUNOSE K, MATSUSHIMA K, MARUYAMA D. Supersonic biplane—a review[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2011, 47(1): 53-87. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2010.09.003 [13] CHEUNG S, EDWARDS T A. Supersonic airplane design optimization method for aerodynamic performance and low sonic boom[EB/OL]. (2013-08-15)[2021-11-15]. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19920076743. [14] KIRZ J. Surrogate based shape optimization of a low boom axisymmetric body[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Applied Aerodynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018. [15] 乔建领, 韩忠华, 宋文萍. 基于代理模型的高效全局低音爆优化设计方法[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(5): 121736.QIAO J L, HAN Z H, SONG W P. An efficient surrogate-based global optimization for low sonic boom design[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(5): 121736 (in Chinese). [16] REUTHER J, JAMESON A. Supersonic wing and wing-body shape optimization using an adjoint formulation[EB/OL]. (1995-07-01)[2022-02-10]. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19960003026. [17] RALLABHANDI S K, NIELSEN E J, DISKIN B. Sonic-boom mitigation through aircraft design and adjoint methodology[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2014, 51(2): 502-510. doi: 10.2514/1.C032189 [18] 黄江涛, 张绎典, 高正红, 等. 基于流场/声爆耦合伴随方程的超声速公务机声爆优化[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(5): 122505.HUANG J T, ZHANG Y D, GAO Z H, et al. Sonic boom optimization of supersonic jet based on flow/sonic boom coupled adjoint equations[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(5): 122505 (in Chinese). [19] RALLABHANDI S K, MAVRIS D N. Sonic boom minimization using inverse design and probabilistic acoustic propagation[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2006, 43(6): 1815-1828. doi: 10.2514/1.20457 [20] 马创, 黄江涛, 刘刚, 等. 超声速飞行器近场声爆信号反演技术[J/OL]. 空气动力学学报, 2021: 1-10. (2021-12-20)[2022-03-23]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1192.TK.20211216.1743.002.html.MA C, HUANG J T, LIU G, et al. Inversion technology of near-field sonic boom signal of supersonic aircraft[J/OL]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2021: 1-10. (2021-12-20)[2022-03-23]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1192.TK.20211216.1743.002.html(in Chinese). [21] PLOTKIN K. Review of sonic boom theory[C]//Proceedings of the 12th Aeroacoustic Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1989. [22] SIMPSON T, TOROPOV V, BALABANOV V, et al. Design and analysis of computer experiments in multidisciplinary design optimization: A review of how far we have come - or not[C]//Proceedings of the 12th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2008. [23] 郭振东, 宋立明, 李军, 等. 基于子元模型的全局优化与设计空间知识挖掘方法[J]. 推进技术, 2015, 36(2): 207-216.GUO Z D, SONG L M, LI J, et al. Meta model-based global design optimization and exploration method[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2015, 36(2): 207-216 (in Chinese). [24] CHIBA K, JEONG S, OBAYASHI S, et al. Knowledge discovery in aerodynamic design space for flyback-booster wing using data mining[C]//Proceedings of the 14th AIAA/AHI Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [25] CHIBA K, OYAMA A, OBAYASHI S, et al. Multidisciplinary design optimization and data mining for transonic reyigional-jet wing[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(4): 1100-1112. doi: 10.2514/1.17549 [26] 刘深深, 陈江涛, 桂业伟, 等. 基于数据挖掘的飞行器气动布局设计知识提取[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 524708.LIU S S, CHEN J T, GUI Y W, et al. Knowledge discovery for vehicle aerodynamic configuration design using data mining[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 524708(in Chinese). [27] JEONG S, SHIMOYAMA K. Review of data mining for multi-disciplinary design optimization[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2011, 225(5): 469-479. [28] JEONG S, CHIBA K, OBAYASHI S. Data mining for aerodynamic design space[J]. Journal of Aerospace Computing, Information, and Communication, 2005, 2(11): 452-469. doi: 10.2514/1.17308 [29] 邱亚松. 基于数据降维技术的气动外形设计方法[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2014: 33-132.QIU Y S. Aerodynamic shape design methods based on data dimension approaches[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2014: 33-132(in Chinese). [30] 汪伟, 莫蓉, 张岩. 叶片气动优化仿真数据的数据挖掘应用研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2013, 49(12): 11-15.WANG W, MO R, ZHANG Y. Applied research on simulation data of blade optimization designing based on data mining[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2013, 49(12): 11-15(in Chinese). [31] PARK M, AFTOSMIS M, CAMPBELL R, et al. Summary of the 2008 NASA fundamental aeronautics program sonic boom prediction workshop[C]//Proceedings of the 51st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Reston: AIAA, 2013. [32] PARK M A, MORGENSTERN J M. Summary and statistical analysis of the first AIAA sonic boom prediction workshop[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2016, 53(2): 578-598. doi: 10.2514/1.C033449 [33] PARK M A, NEMEC M. Near field summary and statistical analysis of the second AIAA sonic boom prediction workshop[C]//Proceedings of the 35th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2017. -






 下载:
下载: