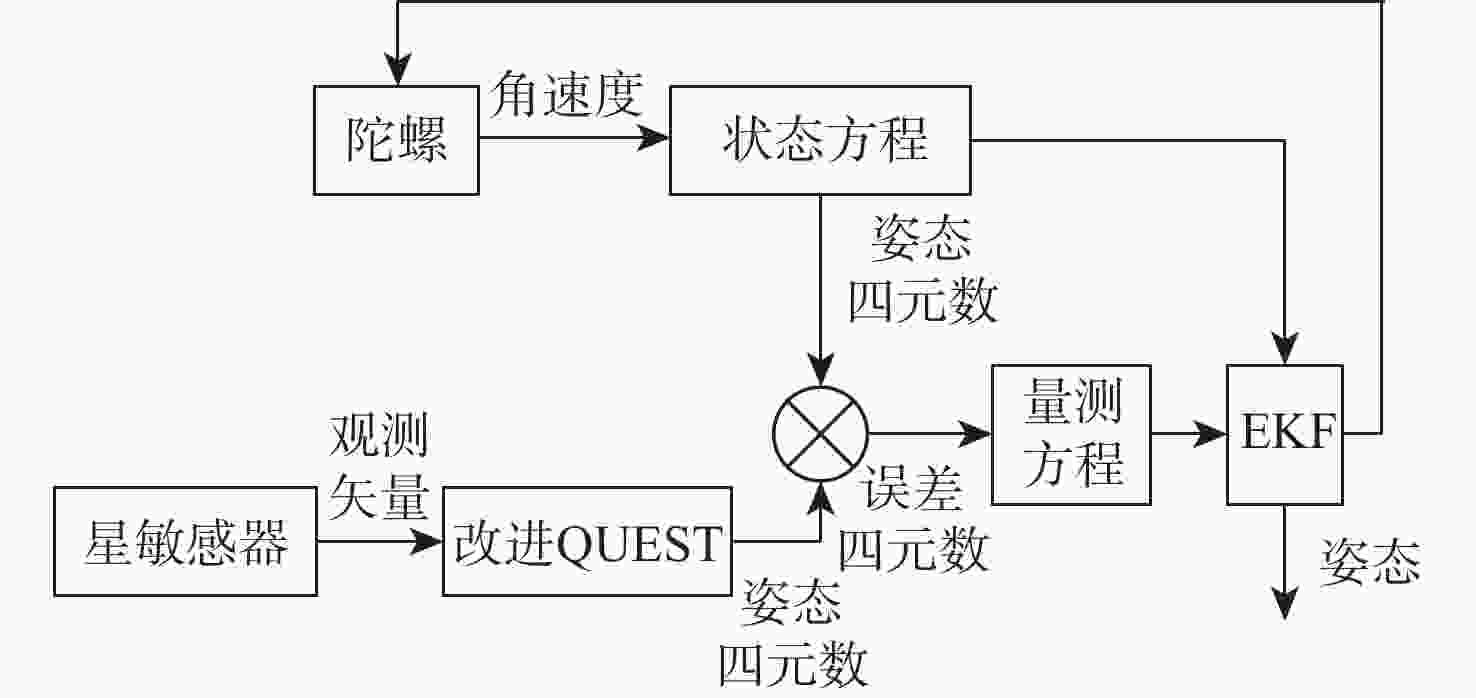
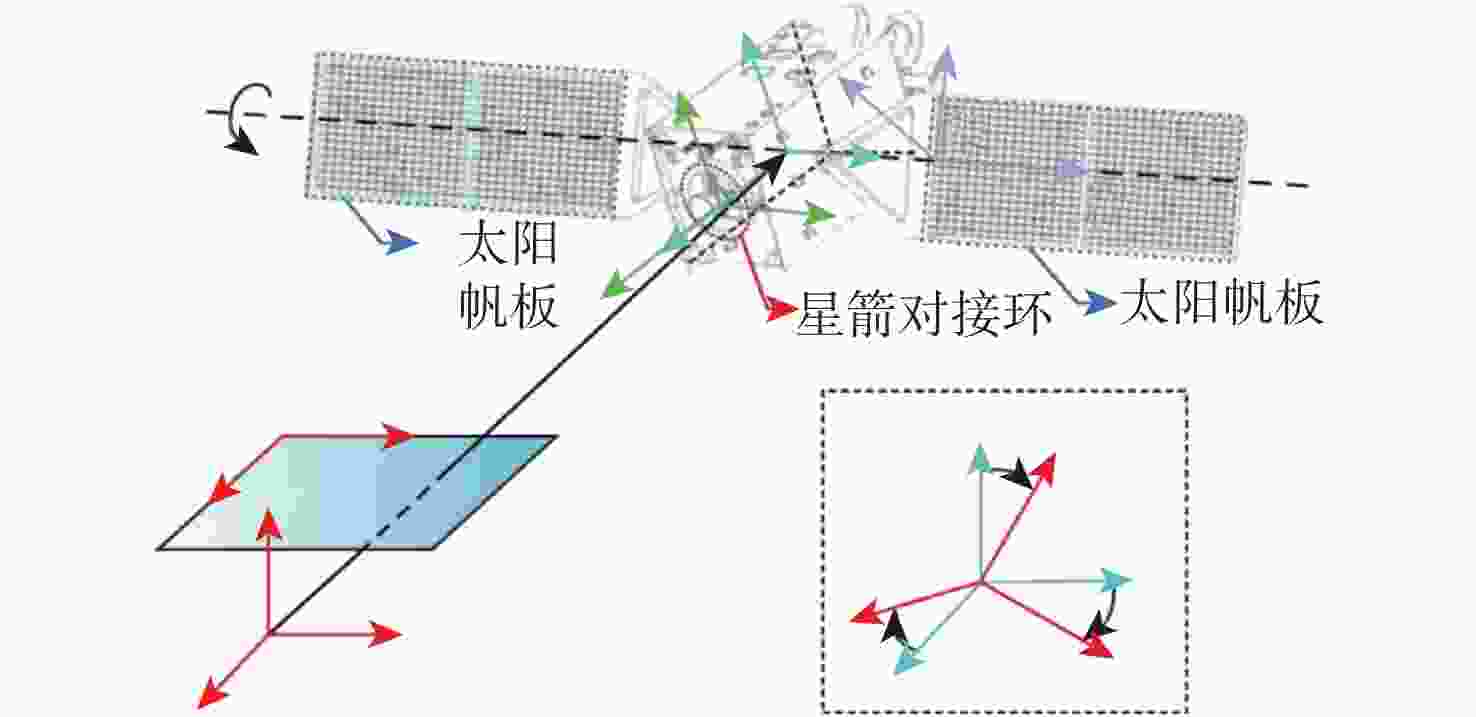
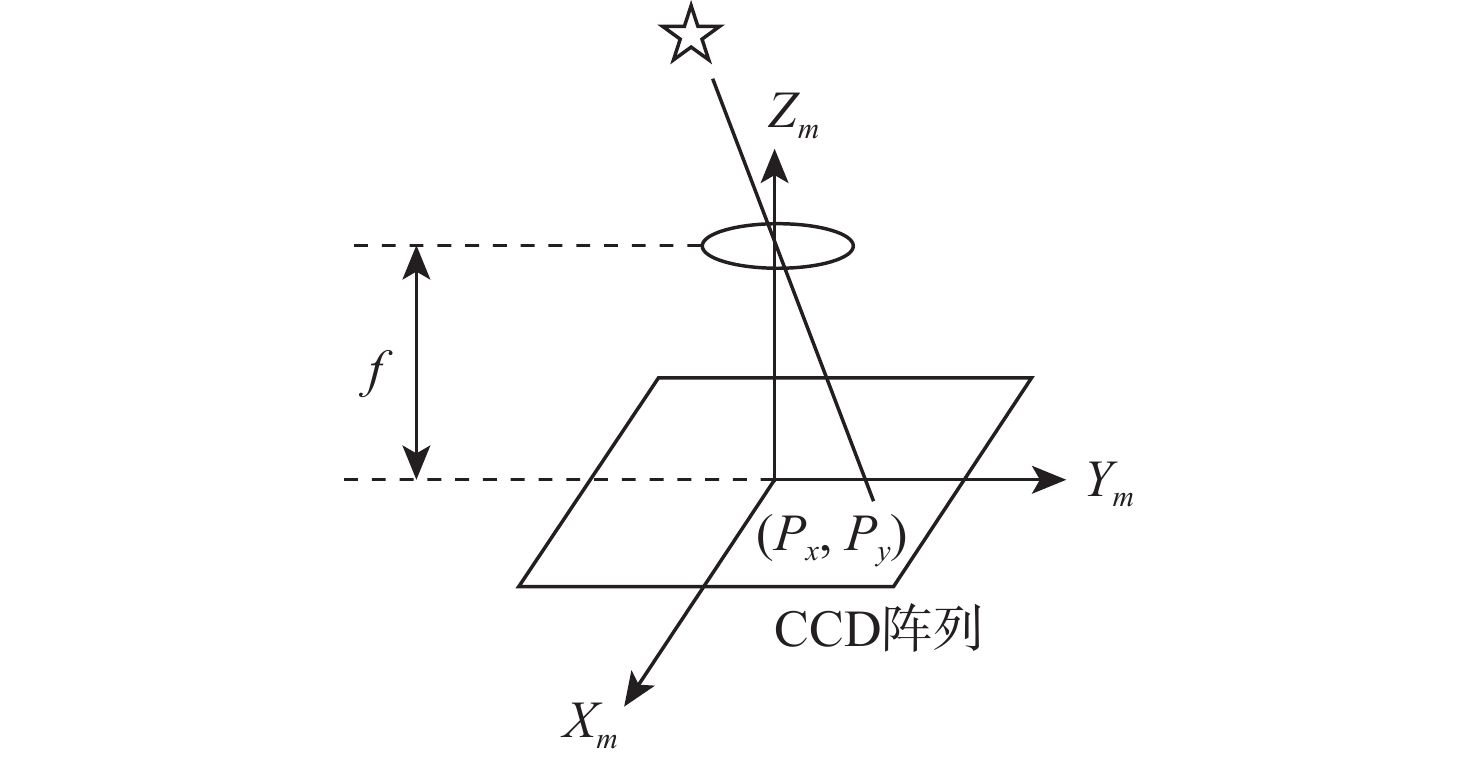
-
摘要:
将矢量测量转化为姿态测量,该问题在姿态估计中被称为Wahba问题。介绍了最小化Wahba问题的损失函数的不同算法,包括最优四元数估计器(ESOQ)、四元数估计器(QUEST)、快速最优姿态矩阵(FOAM)、矩阵的奇异值分解(SVD)等广泛使用的算法,以及基于快速线性四元数姿态估计器(FLAE)、黎曼流形等近年来提出的算法。给出了简单的计算原理与推导过程,并通过计算机仿真对照,归纳各类算法在计算旋转矩阵时的计算精度、鲁棒性。针对姿态测量算法应对当前应用场景的性能需求,简要介绍其在惯性测量单元(IMU)动态对准、协同集群视觉定姿、图像拼接等方面的适用可能和工作原理,并在此基础上简述了姿态测量算法当前的缺陷与未来的发展趋势。
Abstract:The transformation of vector measurements into attitude measurements is known as the Wahba problem in the literature of attitude estimation. This review introduces various algorithms for minimizing the Wahba’s loss function, including estimator of the optimal quaternion (ESOQ), quaternion estimator (QUEST), fast optimal attitude matrix (FOAM), singular value decomposition (SVD) as well as new algorithms proposed in recent years such as fast linear quaternion attitude estimator (FLAE) and the algorithm based on Riemannian manifold. The calculation principle and derivation process are briefly introduced. The computational accuracy and robustness of various methods in calculating rotation matrices are summarized through computer simulation. Then, this review outlines the applicability and working principles of these algorithms in inertial measurement unit (IMU) dynamic alignment, collaborative cluster visual attitude determination, and image mosaic in addressing emerging performance requirements in current applications. Finally, we describe the current limitations and development trends of attitude algorithms in the future.
-
表 1 信噪比100 dB时失准角误差
Table 1. Misalignment angle error corresponding to signal-to-noise ratio of 100 dB
10−6 向量 QUEST SVD ESOQ FLAE FOAM Davenport 1 9.4 9.6 9.85 9.41 9.53 9.39 2 10.3 10.1 10.15 10.52 NaN 10.24 3 9.56 9.55 9.91 9.65 9.57 9.38 4 10.14 10.18 10.23 10.44 NaN 10.20 5 10.0 10.0 10.0 10.29 NaN 10.43 注:NaN表示算法解算未收敛到解的可行域。 表 2 信噪比100 dB时损失函数
Table 2. Loss function with signal-to-noise ratio of 100 dB
10−6 向量 QUEST SVD ESOQ FLAE FOAM Davenport 1 6.78 6.76 7.32 6.76 6.76 6.83 2 5.49 5.40 5.28 5.41 NaN 5.41 3 6.69 6.84 6.91 6.82 6.75 6.72 4 5.44 5.33 5.48 5.38 NaN 5.45 5 5.41 5.38 5.42 5.38 NaN 5.43 注:NaN表示算法解算未收敛到解的可行域。 表 3 信噪比20 dB时失准角误差
Table 3. Misalignment angle error corresponding to Signal-to-Noise Ratio of 20 dB
向量 QUEST SVD ESOQ FLAE FOAM Davenport 1 0.154 0.09 0.349 0.147 0.152 0.09 2 0.103 0.101 0.102 0.104 NaN 0.102 3 0.154 0.09 0.349 0.136 0.151 0.09 4 0.102 0.103 0.103 0.102 NaN 0.101 5 0.101 0.102 0.102 0.103 NaN 0.104 注:NaN表示算法解算未收敛到解的可行域。 表 4 信噪比20 dB时损失函数
Table 4. Loss function with signal-to-noise ratio of 20 dB
向量 QUEST SVD ESOQ FLAE FOAM Davenport 1 0.0874 0.0680 0.1836 0.0927 0.0899 0.0675 2 0.0542 0.0541 0.0532 0.0539 NaN 0.530 3 0.0887 0.0670 0.1841 0.088 0.0939 0.0675 4 0.0543 0.0535 0.0539 0.0542 NaN 0.0544 5 0.0544 0.0530 0.0539 0.0542 NaN 0.0530 注:NaN表示算法解算未收敛到解的可行域。 -
[1] WAHBA G. A least squares estimate of satellite attitude[J]. SIAM Review, 1965, 7(3): 409. [2] HUANG W, XIE H S, SHEN C, et al. A robust strong tracking cubature Kalman filter for spacecraft attitude estimation with quaternion constraint[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2016, 121: 153-163. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.01.009 [3] BLACK H D. A passive system for determining the attitude of a satellite[J]. AIAA Journal, 1964, 2(7): 1350-1351. doi: 10.2514/3.2555 [4] MARKLEY F L, MORTARI D. Quaternion attitude estimation using vector observations[J]. Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2000, 48(2): 359-380. [5] MARKLEY F L. Attitude determination using vector observations and the singular value decomposition[C]//Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1987. [6] DAVENPORT P B. A vector approach to the algebra of rotations with applications: NASA TN D-4696[R]. Washington, D.C.: NASA, 1968. [7] SHUSTER M D, OH S D. Three-axis attitude determination from vector observations[J]. Journal of Guidance and Control, 1981, 4(1): 70-77. doi: 10.2514/3.19717 [8] MARKLEY F L. Attitude determination using vector observations: A fast optimal matrix algorithm[J]. Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 1993, 41(2): 261-280. [9] MORTARI D. ESOQ: A closed-form solution to the Wahba problem[J]. Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 1997, 45(2): 195-204. doi: 10.1007/BF03546376 [10] MORTARI D. ESOQ2 Single-point algorithm for fast optimal attitude determination[C]//Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 1997. [11] YANG Y G, ZHOU Z Q. An analytic solution to Wahbaʼs problem[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2013, 30(1): 46-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2013.07.002 [12] YANG Y. Attitude determination using Newton’s method on Riemannian manifold[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2015, 229(14): 2737-2742. [13] WU J, ZHOU Z B, GAO B, et al. Fast linear quaternion attitude estimator using vector observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(1): 307-319. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2017.2699221 [14] YAN G M, CHEN R T, WENG J. A super-fast optimal attitude matrix in attitude determination[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2021, 32(9): 095012. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ac02f5 [15] GHADIRI H, ESMAELZADEH R, ZARDASHTI R. Robust optimal attitude determination using interval analysis[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(6): 2611-2617. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.12.045 [16] 严恭敏, 陈若彤, 郭鹍. 多矢量定姿的SVD和QUEST算法等价性分析[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2019, 27(5): 568-572.YAN G M, CHEN R T, GUO K. Equivalence analysis between SVD and QUEST for multi-vector attitude determination[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2019, 27(5): 568-572(in Chinese). [17] SHMAKOV S L. A universal method of solving quartic equations[J]. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2011, 71(2): 251-259. [18] YANG Y. Globally convergent optimization algorithms on Riemannian manifolds: Uniform framework for unconstrained and constrained optimization[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2007, 132(2): 245-265. doi: 10.1007/s10957-006-9081-0 [19] SMITH S T. Optimization techniques on Riemannian manifolds[J]. Fields Institute Communications, 1994, 3: 113-136. [20] BEN-ISRAEL A, GREVILLE T N E. Generalized inverses: Theory and applications[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A, 1976, 139(1): 131-132. [21] 严恭敏, 秦永元, 卫育新, 等. 一种适用于SINS动基座初始对准的新算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(3): 634-637.YAN G M, QIN Y Y, WEI Y X, et al. New initial alignment algorithm for SINS on moving base[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(3): 634-637(in Chinese). [22] 翁浚, 秦永元, 严恭敏, 等. 车载动基座FOAM对准算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(7): 1498-1501.WENG J, QIN Y Y, YAN G M. Vehicular moving-base FOAM alignment algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(7): 1498-1501(in Chinese). [23] 刘文倩, 程向红, 曹鹏, 等. 基于多矢量定姿的动基座最优化对准算法[J]. 飞控与探测, 2021, 4(5): 27-33.LIU W Q, CHENG X H , CAO P, et al. Optimal alignment algorithm for moving base based on multi vector attitude determination[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2021, 4(5): 27-33(in Chinese). [24] 韩勇强, 王新健, 谢玲, 等. 一种车载捷联惯导行进间QUEST优化粗对准算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28(1): 41-46.HAN Y Q, WANG X J, XIE L, et al. An in-motion QUEST optimized coarse alignment algorithm for vehicle carried SINS[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28(1): 41-46(in Chinese). [25] 周月, 曾建辉, 刘猛, 等. 惯性系姿态确定的SINS晃动基座初始对准算法[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2020, 7(2): 83-89.ZHOU Y, ZENG J H, LIU M, et al. Alignment algorithm based on attitude determination in inertial frame for SINS with swaying base[J]. Navigation Positioning & Timing, 2020, 7(2): 83-89(in Chinese). [26] 洪然. 基于旋量的星敏感器姿态确定方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020.HONG R. Attitude determination of star sensor based on spinor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020(in Chinese). [27] 陈希军, 张泽, 史话. 基于恒星敏感器的姿态确定算法研究[J]. 控制工程, 2008, 15(3): 253-256.CHEN X J, ZHANG Z, SHI H. Attitude determination algorithm based on star sensor[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2008, 15(3): 253-256(in Chinese). [28] NARKIEWICZ J, SOCHACKI M, RODACKI A, et al. Comparison of algorithms for satellite attitude determination using data from visual sensors[J]. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences, 2021, 69(4): 137935. [29] 张磊, 何昕, 魏仲慧, 等. 星图分布对星敏感器最小二乘姿态精度的影响[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(6): 1836-1841.ZHANG L, HE X, WEI Z H, et al. Impact analysis of star distribution on least square attitude measuring precision in star sensor[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(6): 1836-1841(in Chinese). [30] 宋亮亮, 张涛, 梁斌, 等. 基于星敏感器的卫星姿态确定方法研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2010, 22(增刊1): 1-6.SONG L L, ZHANG T, LIANG B, et al. Research on satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2010, 22(Sup 1): 1-6(in Chinese). [31] 肖支才, 李海君, 王朕. 基于最优REQUEST/CKF组合的航天器姿态确定[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2015, 6: 1-4,8.XIAO Z C, LI H J, WANG Z. Spacecraft attitude determination of REQUEST/CKF Integration[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2015, 6: 1-4,8(in Chinese). [32] SHUSTER M D. Filter quest or request[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2009, 32(2): 643-645. doi: 10.2514/1.40423 [33] 周竹青, 李星秀, 吴盘龙. 一种星敏感器/陀螺组合卫星姿态确定算法[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(10): 187-191. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.10.030ZHOU Z Q, LI X X, WU P L. Attitude determination method of satellite based on star and gyroscope[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2021, 42(10): 187-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.10.030 [34] 张刘, 张家坤, 吕雪莹, 等. 基于粒子群寻优的高精度星敏感器在轨标定方法[J]. 飞控与探测, 2020, 3(3): 1-7.ZHANG L, ZHANG J K, LYU X Y, et al. A hight precision on or bit calibration method for star sensor based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2020, 3(3): 1-7(in Chinese). [35] 白子扬. 基于星敏感器的航天器姿态确定算法[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.BAI Z Y. Attitude determination algorithm of spacecraft based on star sensor[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [36] YANG H, CARLONE L. A quaternion-based certifiably optimal solution to the Wahba problem with outliers[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1665-1674. [37] YANG H, SHI J N, CARLONE L. TEASER: Fast and certifiable point cloud registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(2): 314-333. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2020.3033695 [38] DUAN Y B, ZHANG X Y, LI Z B. A new quaternion-based Kalman filter for human body motion tracking using the second estimator of the optimal quaternion algorithm and the joint angle constraint method with inertial and magnetic sensors[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(21): 6018. doi: 10.3390/s20216018 [39] YUN X P, BACHMANN E R. Design, implementation, and experimental results of a quaternion-based Kalman filter for human body motion tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2006, 22(6): 1216-1227. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2006.886270 [40] ZHANG X Y, XIAO W. A fuzzy tuned and second estimator of the optimal quaternion complementary filter for human motion measurement with inertial and magnetic sensors[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3517. doi: 10.3390/s18103517 [41] 马正华, 朱鸣庆, 戎海龙. 地磁组合重力矢量权值的优化算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2020, 37(4): 298-303.MA Z H, ZHU M Q, RONG H L. Optimization algorithm of the weight assigned to gravity acceleration vector used to MAG-μIMU[J]. Computer Simulation, 2020, 37(4): 298-303(in Chinese). [42] 谢启龙, 宋龙, 鲁浩, 等. 协同导航技术研究综述[J]. 航空兵器, 2019, 26(4): 23-30.XIE Q L, SONG L, LU H, et al. Review of collaborative navigation technology[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2019, 26(4): 23-30(in Chinese). [43] 高伟, 刘亚龙, 徐博. 基于双领航者的多AUV协同导航系统可观测性分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(11): 2370-2375.GAO W, LIU Y L, XU B. Observability analysis of cooperative navigation system for multiple AUV based on two-leaders[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(11): 2370-2375(in Chinese). [44] 刘晓洋, 李瑞涛, 徐胜红. 基于测距/测速信息的无人机协同导航算法研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2019(2): 73-77.LIU X Y, LI R T, XU S H. Research on cooperative navigation algorithm of UAV based on ranging/speed measurement information[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2019(2): 73-77(in Chinese). [45] 张旭, 崔乃刚, 王小刚, 等. 考虑几何约束的无人机双机编队相对姿态确定方法[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2017(1): 17-21.ZHANG X, CUI N G, WANG X G, et al. Relative attitude determination method for dual-UAVs formation with geometric constraint[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2017(1): 17-21(in Chinese). [46] 张旭, 崔乃刚, 王小刚. 基于相对视线矢量测量的多航天器编队相对姿态求解方法[J]. 北京理工大学报, 2017, 31(11): 1178-1182.ZHANG X, CUI N G, WANG X G. Relative attitude solution for multi-spacecraft formation based on relative line-of-sight vector measurement[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017, 31(11): 1178-1182(in Chinese). [47] 张旭. 基于鲁棒自适应滤波的无人机编队相对导航方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.ZHANG X. Research on relative navigation method of UAV formation based on robust adaptive filtering[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [48] 王大轶, 鄂薇, 邹元杰, 等. 利用非合作航天器双特征结构的相对姿态确定方法[J]. 飞控与探测, 2020, 3(1): 18-26.WANG D Y, E W, ZOU Y J, et al. Relative attitude determination method of non-cooperative spacecraft using dual feature structure[J]. Flight Control & Detection, 2020, 3(1): 18-26(in Chinese). [49] JACKSON B E, TRACY K, MANCHESTER Z. Planning with attitude[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 5658-5664. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3052431 [50] HOWELL T A, JACKSON B E, MANCHESTER Z. ALTRO: A fast solver for constrained trajectory optimization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7674-7679. -






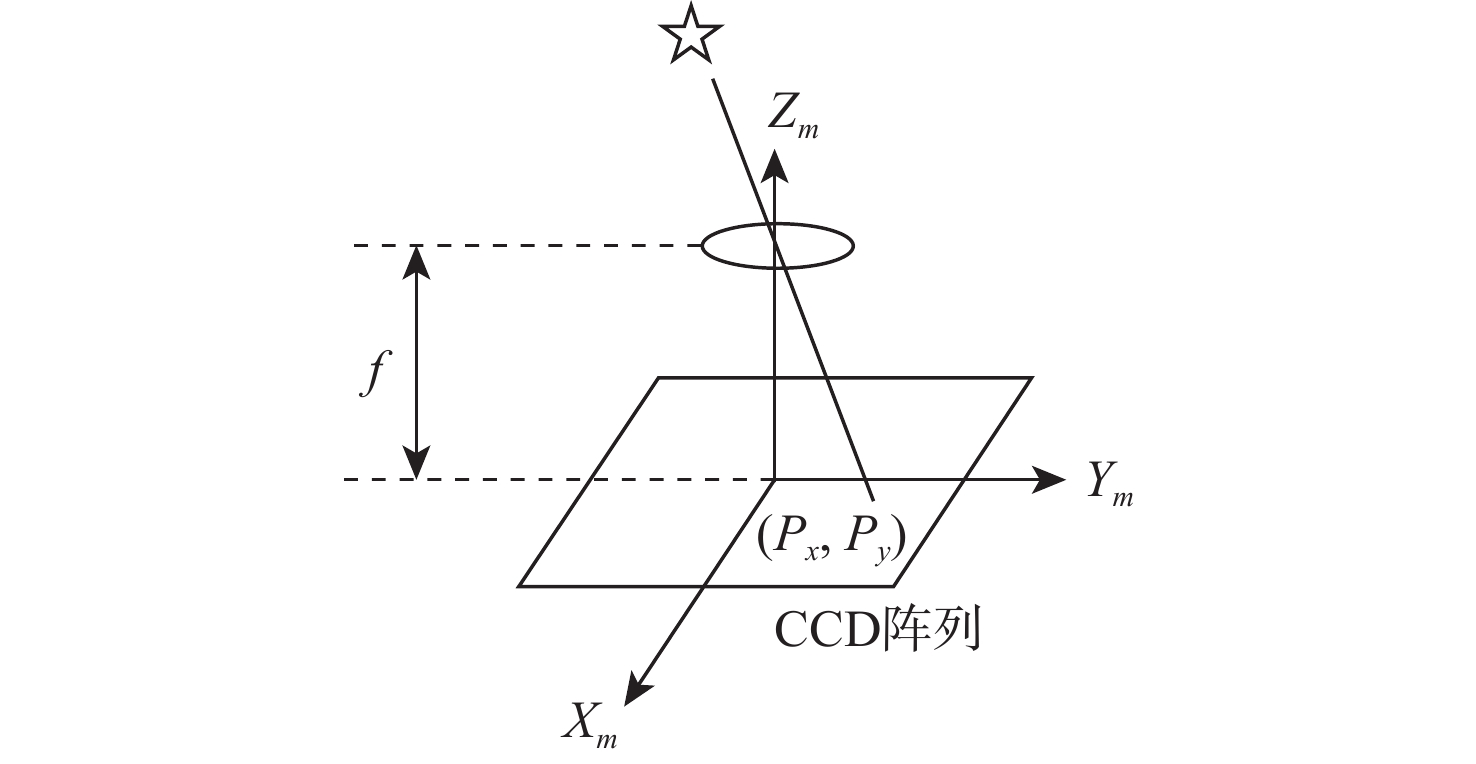
 下载:
下载: