-
摘要:
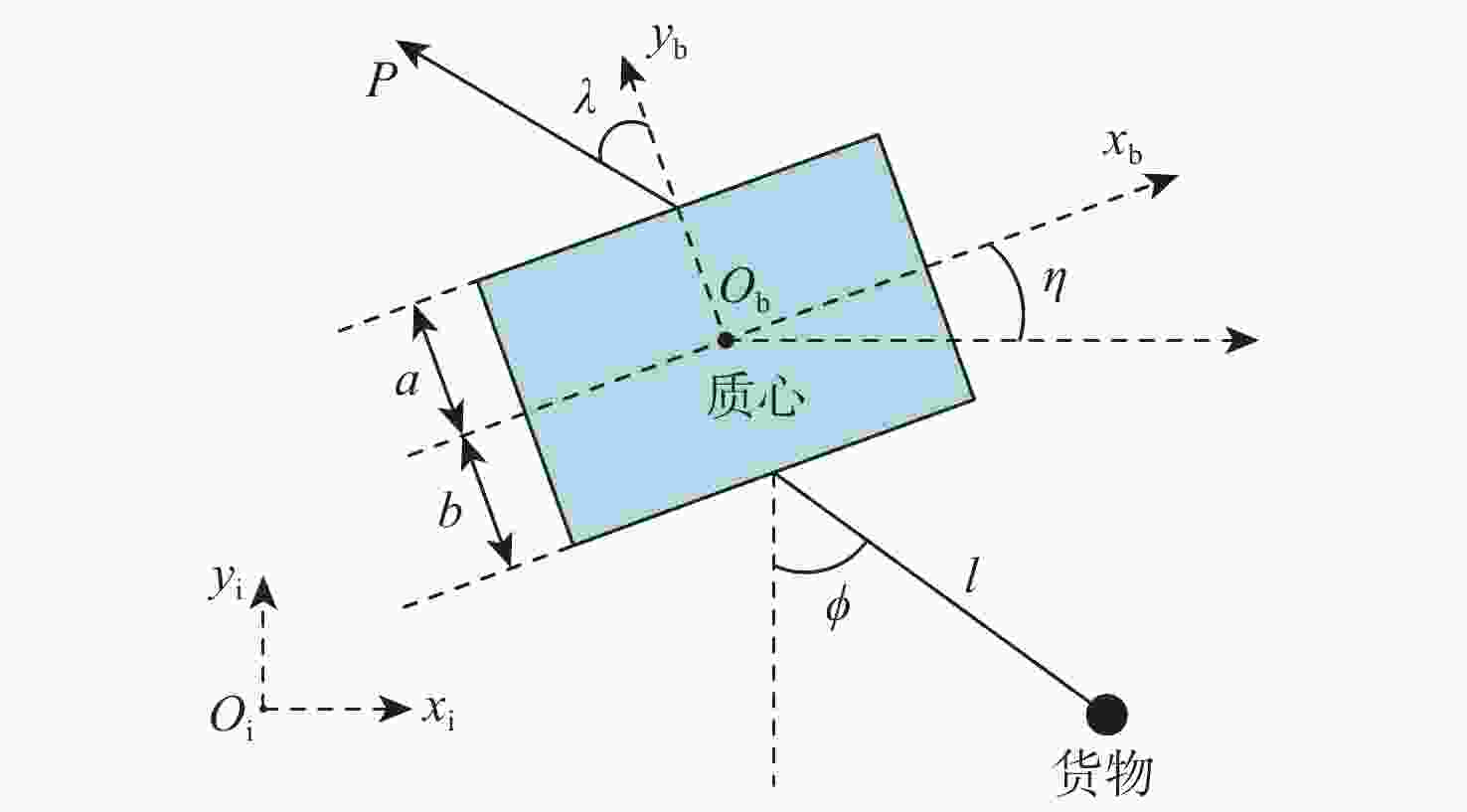
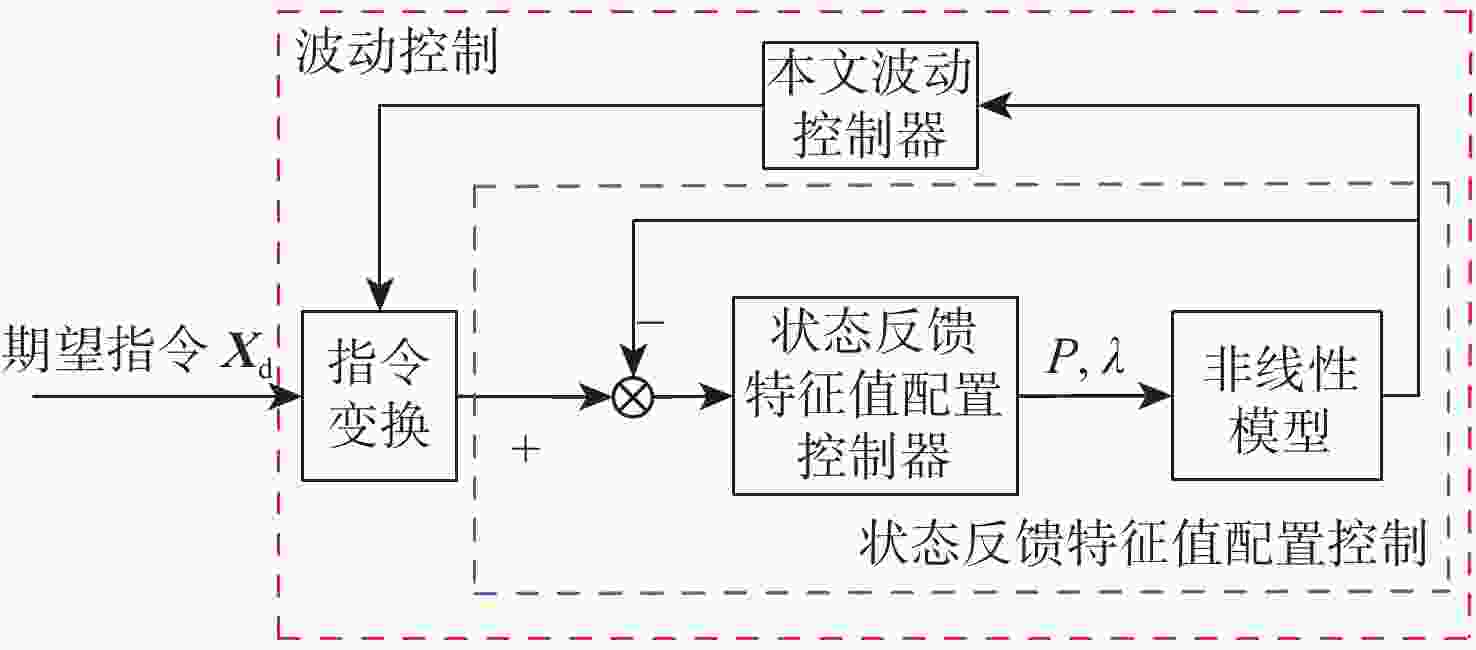
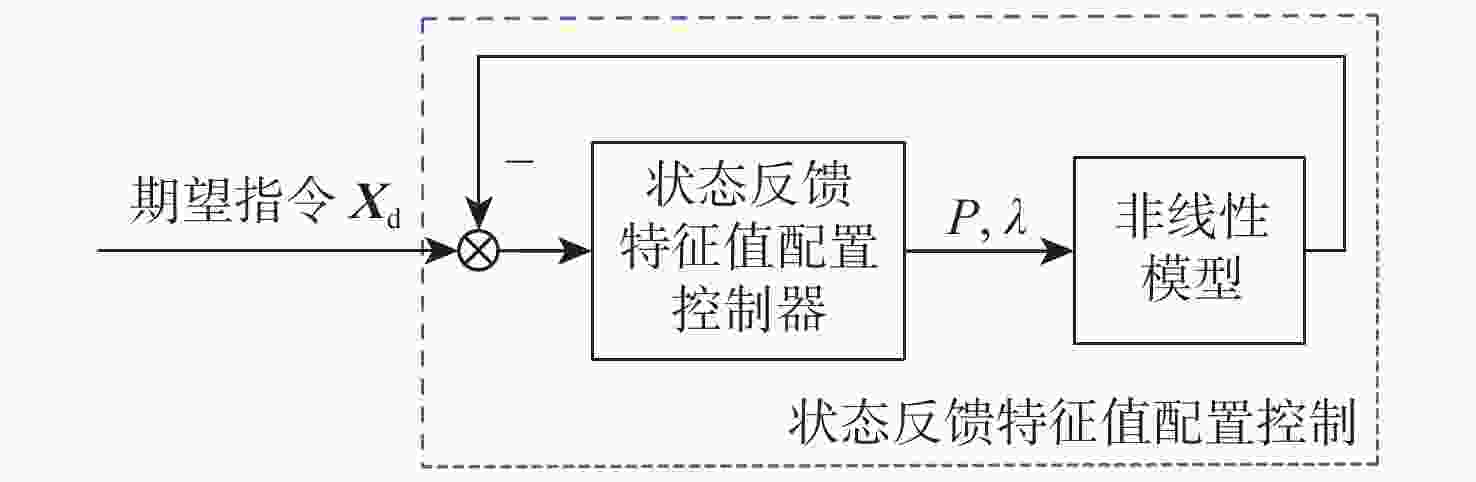
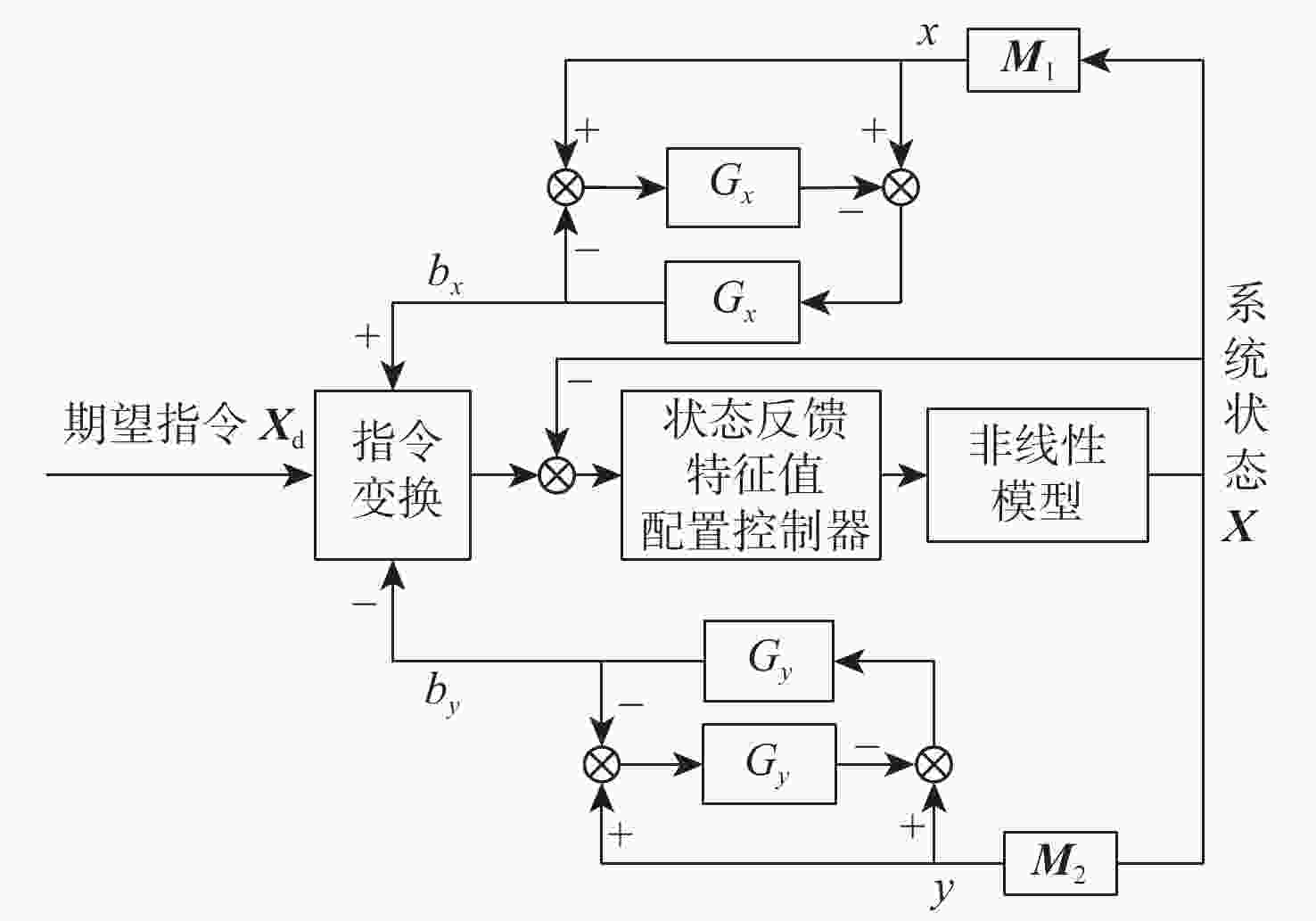
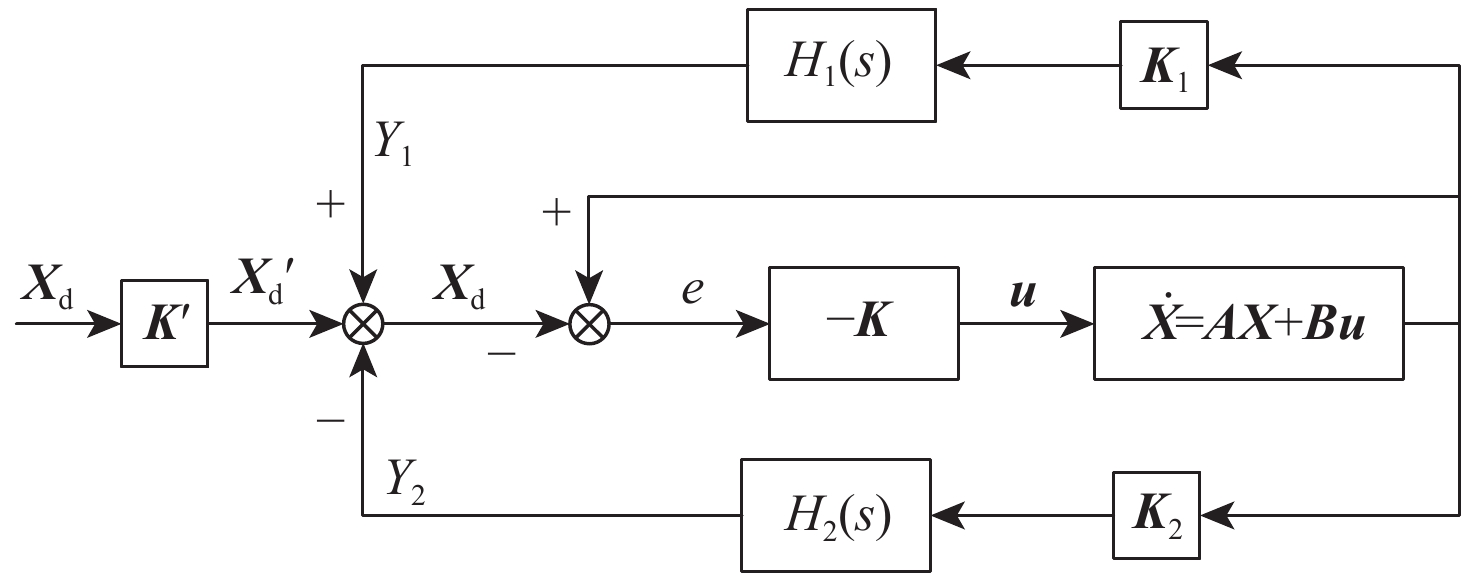
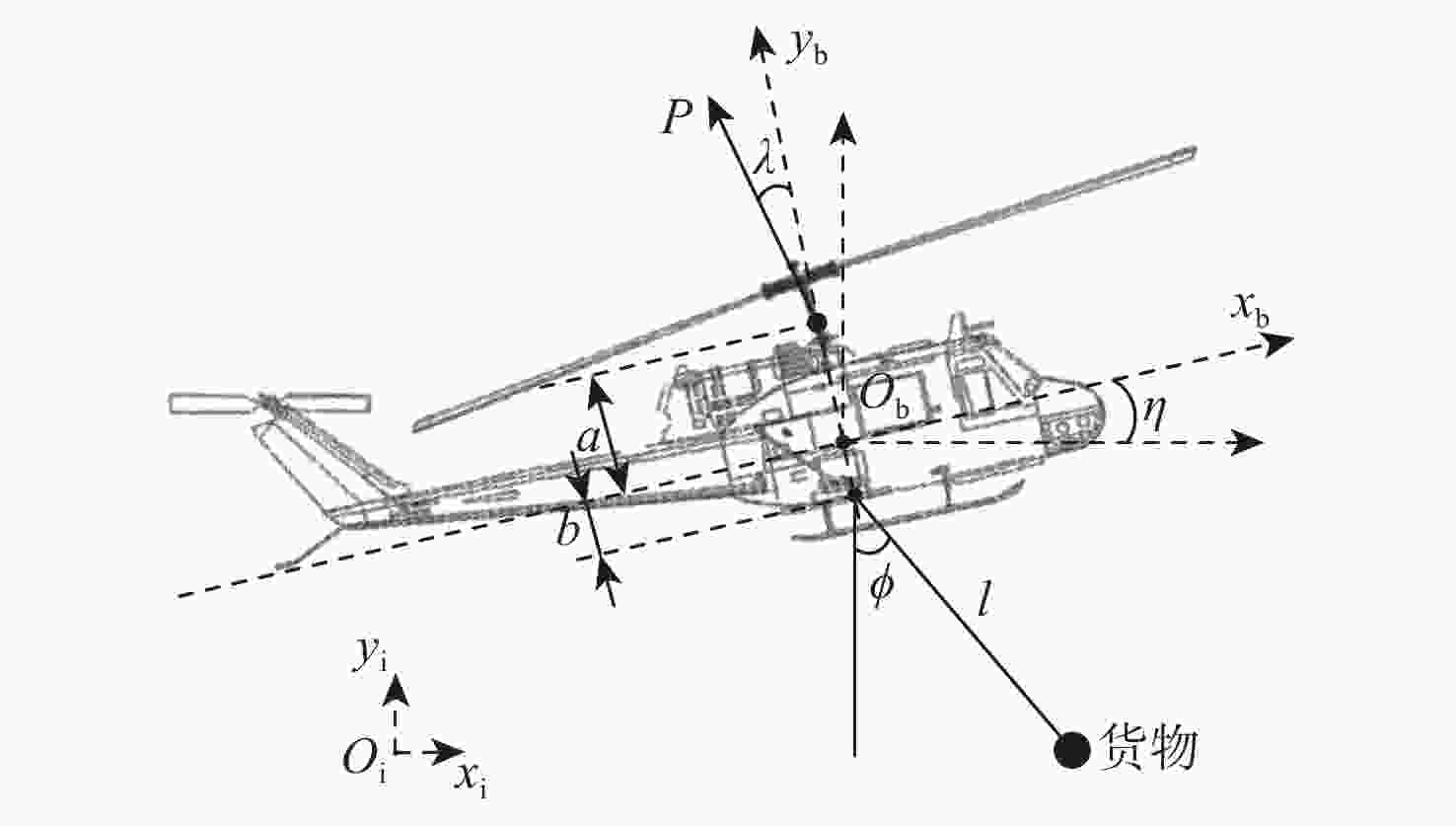
直升机在运输重型货物从平飞到悬停的机动过程中,会产生许多稳定性问题,减小吊挂摆角幅度具有重要意义。基于波动控制的方法为直升机吊挂系统设计一种减摆控制器;采用拉格朗日分析力学法,建立直升机吊挂耦合系统四自由度非线性纵向运动模型,采用小扰动的方法在平衡点处对所建模型进行线性化;在此基础上,基于特征值配置法设计状态反馈控制器;设计波动控制器来减小摆角控制具有良好的动态性能和稳态性能。在仿真中对吊挂载荷质量进行拉偏,证明所设计波动控制器具有较强的鲁棒性,结果表明:所设计波动控制器有效。
Abstract:Application of helicopter to transport heavy and bulky loads creates various stability problems especially during maneuvering from level flight to hovering; thus, it is significant to reduce the swing amplitude of suspended loads. An anti-swing controller is designed for a helicopter with slung loads by using wave control method. A nonlinear mathematical model with four degrees of freedom for the helicopter is developed by applying Lagrangian analysis method. Then the developed model is linearized by little disturbance method in equilibrium operating points. On this basis, a state feedback controller is designed with eigenvalue configuration method. An anti-swing wave controller is then designed to reduce the pendulum angle. The simulation shows that the control of the pendulum angle and helicopter position has good dynamic performance and stability. Different biases of slung-load mass in the simulation verify that the designed wave controller has strong robustness, thus demonstrating the effectiveness of the designed wave controller.
-
Key words:
- helicopter slung load system /
- dynamical model /
- state feedback /
- wave control /
- anti-swing controller
-
表 1 仿真入口参数
Table 1. Simulation entry parameters
m1/kg m2/kg l/m g/(m·s−2) a/m b/m J/(kg·m2) $ x $/m $ y $/m vx/(m·s−1) vy/(m·s−1) $ \phi $/(°) $ \eta $/(°) 400 200 10 9.8 2 0.5 210 0 5 5 0 10 5 表 2 特征值参数
Table 2. Eigenvalue parameters
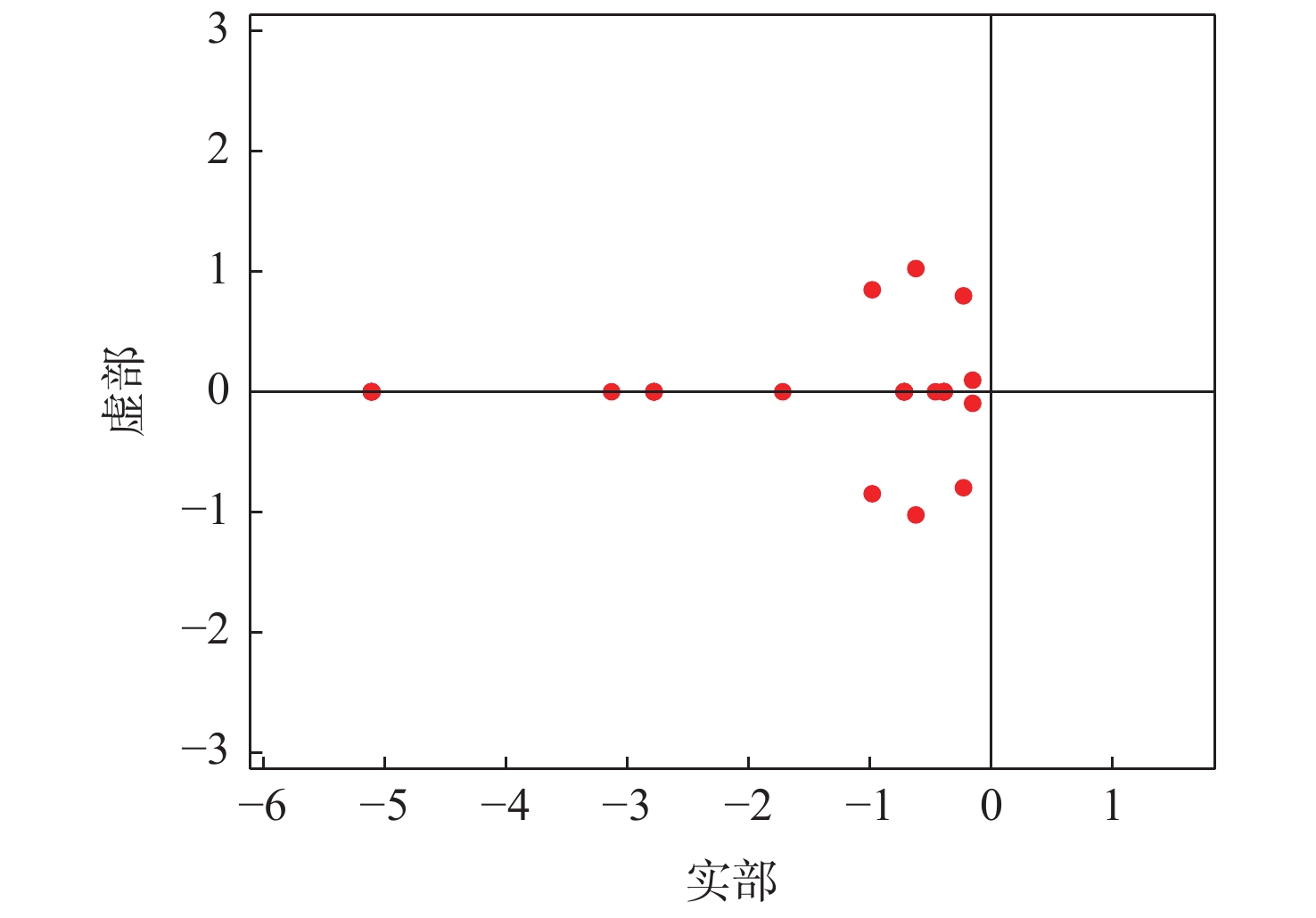
s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6 s7 s8 −0.4+0.798i −0.4+0.798i −0.5+0.455i −0.5−0.455i −0.6+0.3i −0.6−0.3i −1.2 −1.2 表 3 各状态量最大幅值
Table 3. Maximum amplitude of each state variable
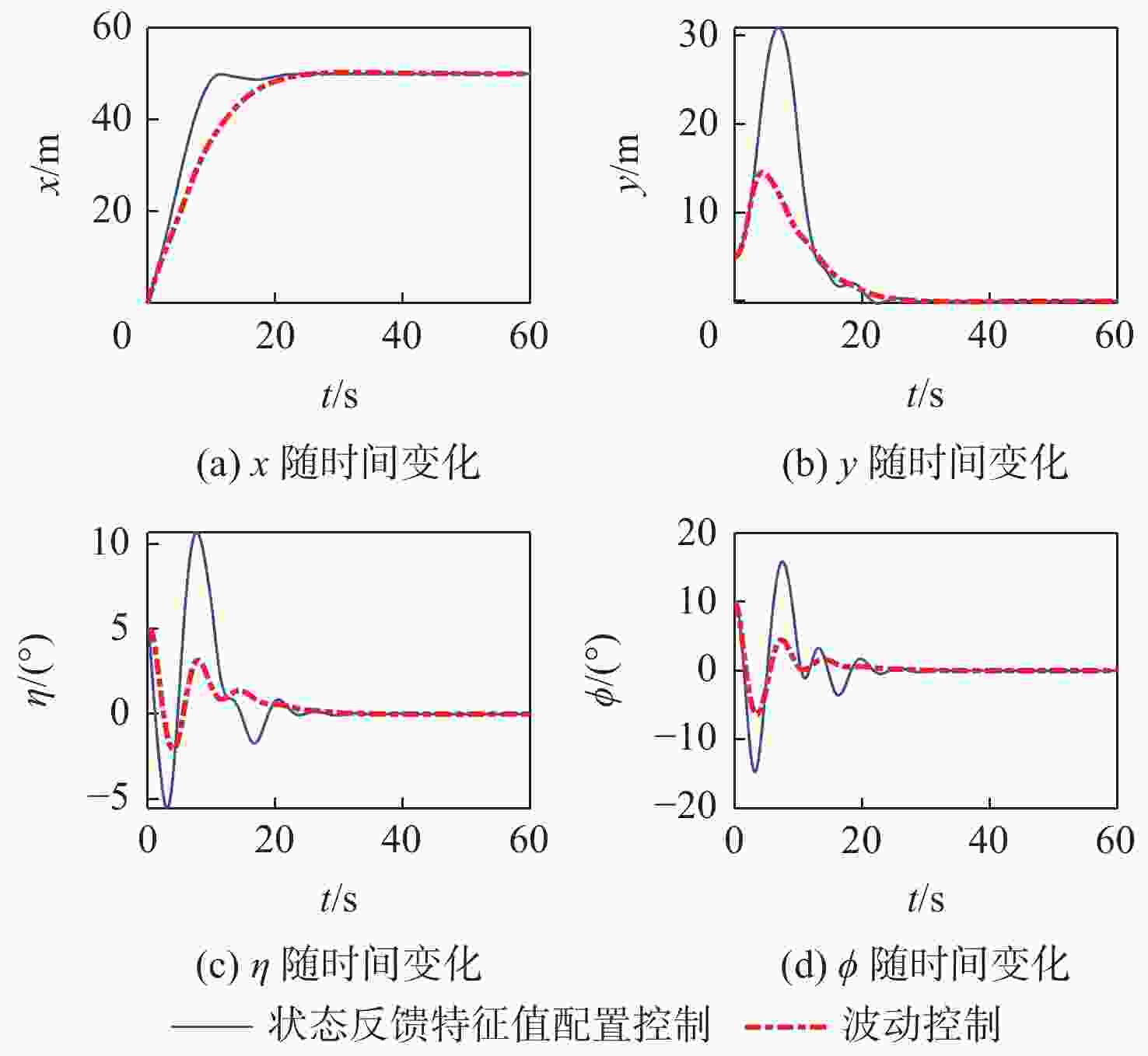
控制方法 x/m y/m $\eta $/(°) $\phi $/(°) 状态反馈特征值
配置控制50.02 12.23 9.84 12.65 波动控制 50.35 10.57 2.32 4.28 表 4 各状态量调节时间
Table 4. Adjustment time for each state variable
s 状态量 状态反馈特征值
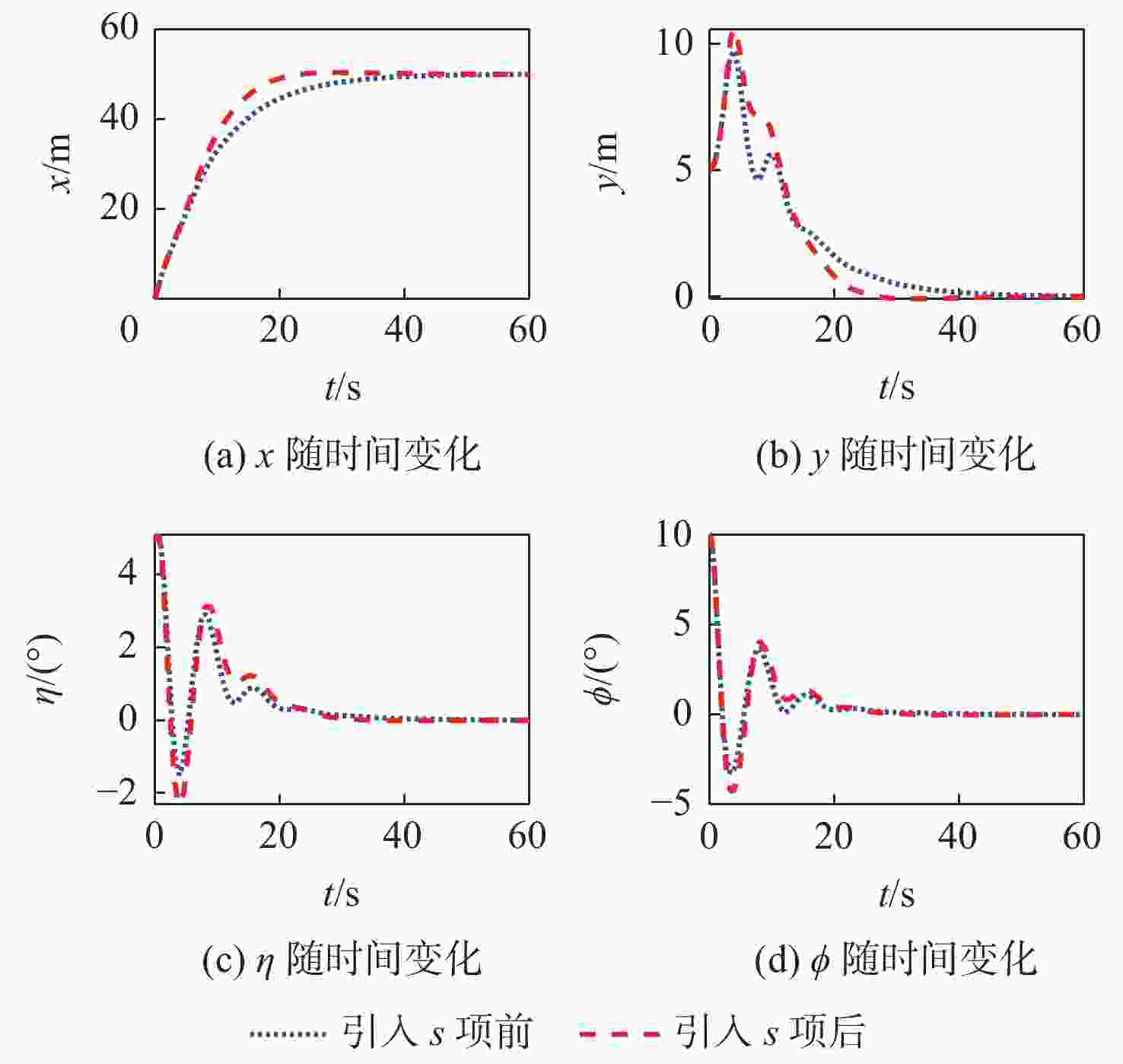
配置控制波动控制 x 8.98 17.26 y 18.40 23.26 $\eta $ 21.12 24.69 $\phi $ 16.22 19.36 表 5 引入s项前后各状态量调节时间表
Table 5. Adjustment time table for each state variable before and after introducing term s
状态量 调节时间/s 减小幅度/% 引入s项前 引入s项后 $x$ 26.82 17.26 35.65 $y$ 36.16 23.26 35.67 $\eta $ 25.36 24.69 2.64 $\phi $ 18.10 19.36 −6.96 -
[1] BERGERON K, GRUBB A L, WILKS A L, et al. Quasi-static and prescribed motion simulations for helicopter sling loads[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 2018: AIAA2018-0779. [2] GURSOY G, TARIMCI O, YAVRUCUK I. Helicopter slung load simulations using heli-dyn+[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2012: AIAA2012-4851. [3] 万绍峰, 曹义华, 黄磊. 基于Kane方法的直升机-柔性绳索-吊挂系统动力学建模[J]. 航空动力学报, 2016, 31(4): 934-940.WAN S F, CAO Y H, HUANG L. Dynamic modeling of helicopter-flexible rope-slung load system based on Kane s method[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2016, 31(4): 934-940(in Chinese). [4] SANSAL K, CALISKAN A, KARGIN V. Investigation of the effects of slung load coupled dynamics on helicopter controllability and handling quality[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2021: AIAA2021-0594. [5] 曹龙, 曹义华, 李春华. 直升机-吊挂耦合系统平衡特性和稳定性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(9): 1219-1224.CAO L, CAO Y H, LI C H. Equilibrium characteristics and stability analysis of helicopter-slung-load coupling system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(9): 1219-1224(in Chinese). [6] 王照瑞, 曹义华. 吊挂物为刚体模型的直升机外吊挂飞行平衡与稳定性分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 47(2): 296-303.WANG Z R, CAO Y H. Equilibrium characteristics and stability analysis of helicopter with rigid-body modeling slung-load[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2015, 47(2): 296-303(in Chinese). [7] 朱笑宇, 曹义华, 曹龙. 重型直升机-吊挂耦合系统闭环飞行品质分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(7): 1550-1556.ZHU X Y, CAO Y H, CAO L. Heavy helicopter-slung-load coupling system flying qualities in closed-loop state[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(7): 1550-1556(in Chinese). [8] 何荣荣, 陈谋, 吴庆宪, 等. 无人直升机吊挂系统滑模反步减摆控制[J]. 航空兵器, 2020, 27(5): 100-106. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0117HE R R, CHEN M, WU Q X, et al. Sliding mode backstepping anti-swing control of unmanned helicopter slung-load system[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2020, 27(5): 100-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0117 [9] 张松, 马钊, 张辉. 直升机吊挂飞行中载荷摆动控制方法研究[J]. 航空工程进展, 2022(2): 57-63.ZHANG S, MA Z, ZHANG H. Research on slung-load swing control method in helicopter suspension flight[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2022(2): 57-63(in Chinese). [10] POTTER J, SINGHOSE W, COSTELLOY M. Reducing swing of model helicopter sling load using input shaping[C]//Proceedings of the 2011 9th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 348-353. [11] OMAR H M. Designing anti-swing fuzzy controller for helicopter slung-load system near hover by particle swarms[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2013, 29(1): 223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2013.03.006 [12] EL-FERIK S, SYED A H, OMAR H M, et al. Nonlinear forward path tracking controller for helicopter with slung load[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 69: 602-608. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.07.028 [13] REN Y, LI K, YE H. Modeling and anti-swing control for a helicopter slung-load system[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2020, 372: 124990. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2019.124990 [14] ENCIU K, ROSEN A. Nonlinear dynamical characteristics of fin-stabilized underslung loads[J]. AIAA Journal, 2015, 53(3): 723-738. doi: 10.2514/1.J053241 [15] O’CONNOR W, LANG D. Position control of flexible robot arms using mechanical waves[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1998, 120(3): 334-339. doi: 10.1115/1.2805406 [16] O’CONNOR W J. A gantry crane problem solved[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2003, 125(4): 569-576. doi: 10.1115/1.1636198 [17] O’CONNOR W J. Wave-based analysis and control of lump-modeled flexible robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2007, 23(2): 342-352. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2007.895061 [18] HABIBI H, O’CONNOR W. Wave-based motion and slewing control of a double-appendage, flexible system with ungrounded actuator through development of direct actuator force control[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 137: 106175. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.05.059 [19] O’CONNOR W J, RAMOS DE LA FLOR F, MCKEOWN D J, et al. Wave-based control of non-linear flexible mechanical systems[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2009, 57(1): 113-123. [20] O’CONNOR W J, FUMAGALLI A. Refined wave-based control applied to nonlinear, bending, and slewing flexible systems[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2009, 76(4): 041005. doi: 10.1115/1.3086434 -






 下载:
下载: