Corrosion behavior of 2195-T8 aluminum-lithium alloy with artificial defects in 30% HNO3
-
摘要:
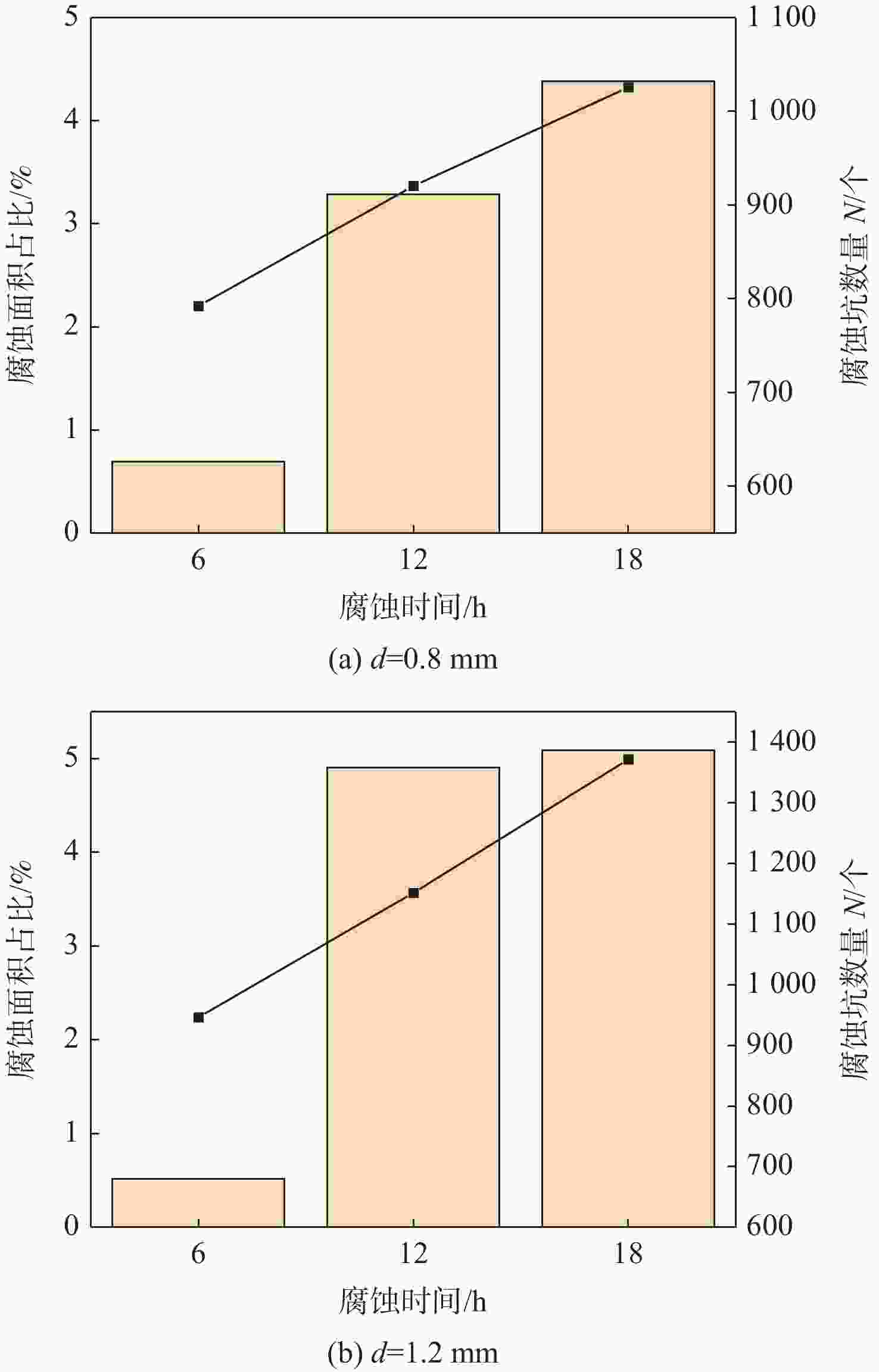
为研究2195-T8铝锂合金在酸性介质中的腐蚀性能,通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)等微观表征手段,分析2195-T8铝锂合金在30% HNO3中的腐蚀形貌。提出一种块分割和边缘检测相结合的图像处理方法,从统计的角度对2195-T8铝锂合金在30% HNO3中的腐蚀规律进行分析。结果表明:合金在浸泡不同时长后出现了典型的点蚀和晶间腐蚀形貌;人工缺陷深度会加剧腐蚀的程度;在腐蚀的初期阶段,蚀坑的数量快速增长,蚀坑面积主要集中在0~20 μm2。而在腐蚀的中后期,蚀坑的数量及面积变化不大,只有少量的蚀坑可以继续扩展形成面积大于50 μm2的蚀坑。
Abstract:To study the corrosion performance of the 2195-T8 Al-Li alloy in an acidic medium, the corrosion morphology of 2195-T8 Al-Li alloy in 30% HNO3 was analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM), scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and other microscopic characterization methods. A method for processing images that combines edge detection and block segmentation is also suggested in order to examine the corrosion law of 2195-T8 Al-Li alloy in 30% HNO3 from a statistical perspective. The results show that the typical pitting and intergranular corrosion morphologies of the alloys appear after immersion at different times. The depth of artificial defects can accelerate the progression of corrosion. While the number and area of pits fluctuate little in the middle and later phases of corrosion, only a small number can continue to expand to create etch pits with an area >50 μm2. In the early stages of corrosion, the number of pits increases rapidly, and the pit area is primarily concentrated in 0~20 μm2.
-
Key words:
- Al-Li alloy /
- HNO3 /
- artificial defects /
- localized corrosion /
- corrosion laws
-
表 1 室温下2195-T8铝锂合金的基本力学性能
Table 1. Basic mechanical properties of 2195-T8 Al-Li alloy at room temperature
材料 抗拉强度σb/MPa 屈服强度σs/MPa 断裂延伸率δ/% 弹性模量E/GPa 2195-T8 609.9 583.3 11.4 72.3 表 2 颗粒的EDS分析结果
Table 2. EDS analysis results of the particles
元素 质量分数 元素 质量分数 Cu 0.0528 Mg 0.0491 Al 0.75 Fe 0.1481 表 3 d = 0.8 mm人工缺陷试样在不同腐蚀时间的点蚀坑数量
Table 3. The number of pitting pits of d = 0.8 mm artificial defect samples at different corrosion times
腐蚀时间/h 点蚀坑数量 A1 A2 A3 A4 6 466 138 22 2 12 814 199 35 9 18 665 196 78 32 -
[1] RIOJA R J, LIU J. The evolution of Al-Li base products for aerospace and space applications[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(9): 3325-3337. doi: 10.1007/s11661-012-1155-z [2] DURSUN T, SOUTIS C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys[J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 56: 862-871. [3] LEQUEU P, SMITH K P, DANIÉLOU A. Aluminum-Copper-Lithium alloy 2050 developed for medium to thick plate[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2010, 19(6): 841-847. doi: 10.1007/s11665-009-9554-z [4] WARNER T. Recently-developed aluminium solutions for aerospace applications[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2006, 519-521: 1271-1278. [5] DANIÉLOU A, RONXIN J, NARDIN C, et al. Fatigue resistance of Al-Cu-Li and comparison with 7xxx aerospace alloys[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Aluminum Alloys. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 511-516. [6] TSIVOULAS D, ROBSON J D. Heterogeneous Zr solute segregation and Al3Zr dispersoid distributions in Al-Cu-Li alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 93(7): 73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.03.057 [7] NAYAN N, MURTY S V S N, JHA A K, et al. Processing and characterization of Al-Cu-Li alloy AA2195 undergoing scale up production through the vacuum induction melting technique[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2013, 576(8): 21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.03.054 [8] SINGH V, SATYA PRASAD K, GOKHALE A A. Effect of minor Sc additions on structure, age hardening and tensile properties of aluminium alloy AA8090 plate[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2004, 50(6): 903-908. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2003.12.001 [9] KRUG M E, SEIDMAN D N, DUNAND D C. Creep properties and precipitate evolution in Al-Li alloys microalloyed with Sc and Yb[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2012, 550(7): 300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.04.075 [10] 郭一, 常新龙, 田干, 等. 拉-拉载荷下2195-T8铝锂合金在N2O4中的预腐蚀疲劳研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2022, 51(9): 3459-3465.GUO Y, CHANG X L, TIAN G, et al. Pre-corrosion fatigue performance of 2195-T8 Al-Li alloy in N2O4 under tension-tension load[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022, 51(9): 3459-3465(in Chinese). [11] LI J F, ZHENG Z Q, REN W D, et al. Simulation on function mechanism of T1(Al2CuLi) precipitate in localized corrosion of Al-Cu-Li alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(6): 1268-1273. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(07)60005-3 [12] 李亚裕. 液体推进剂[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2011: 125-131.LI Y Y. Liquid propellant [M]. Beijing: China Aerospace Publishing House, 2011: 125-131(in Chinese). [13] LIN Y, LU C G, WEI C Y, et al. Effect of aging treatment on microstructures, tensile properties and intergranular corrosion behavior of Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 141(7): 163-168. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.04.043 [14] MA Y, ZHOU X, HUANG W, et al. Localized corrosion in AA2099-T83 aluminum-lithium alloy: The role of intermetallic particles[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 161(7): 201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.05.037 [15] DE SOUSA ARAUJO J V, DONATUS U, QUEIROZ F M, et al. On the severe localized corrosion susceptibility of the AA2198-T851 alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 133(4): 132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.01.028 [16] ZHANG X X, ZHOU X R, HASHIMOTO T, et al. Corrosion behaviour of 2A97-T6 Al-Cu-Li alloy: The influence of non-uniform precipitation[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 132(3): 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.12.010 [17] HUANG J L, LI J F, LIU D Y, et al. Correlation of intergranular corrosion behaviour with microstructure in Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 139(7): 215-226. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.05.011 [18] LIU D Y, SANG F J, LI J F, et al. The role of grain structure characteristics on the localised corrosion feature in the 1445 Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 158(12): 109981. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109981 [19] ZHANG X, ZHOU X, HASHIMOTO T, et al. The influence of grain structure on the corrosion behaviour of 2A97-T3 Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2017, 116(2): 14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.12.005 [20] LEI X W, SAATCHI A, GHANBARI E, et al. Studies on pitting corrosion of Al-Cu-Li alloys Part I: Effect of Li addition by microstructural, electrochemical, in-situ, and pit depth analysis[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(10): 1600. doi: 10.3390/ma12101600 [21] LUO C, ALBU S P, ZHOU X R, et al. Continuous and discontinuous localized corrosion of a 2xxx aluminium-copper-lithium alloy in sodium chloride solution[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 658(2): 61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.185 [22] DONATUS U, TERADA M, OSPINA C R, et al. On the AA2198-T851 alloy microstructure and its correlation with localized corrosion behaviour[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018, 131(2): 300-309. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.12.001 [23] LI M C, SEYEUX A, WIAME F, et al. Insights on the Al-Cu-Fe-Mn intermetallic particles induced pitting corrosion of Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 176(11): 109040. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2020.109040 [24] LIU D J, TIAN G, JIN G F, et al. Characterization of localized corrosion pathways in 2195-T8 Al–Li alloys exposed to acidic solution[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 25(7): 152-165. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.05.004 [25] 郭一, 田干, 刘德俊, 等. 酸性环境中的铝锂合金腐蚀行为及其元胞自动机模拟[J]. 中国机械工程, 2022, 33(8): 1001-1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2022.08.016GUO Y, TIAN G, LIU D J, et al. Corrosion behavior of aluminum lithium alloys in acidic environment and cellular automata simulation[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(8): 1001-1007(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2022.08.016 [26] TIAN G, JIN G F, ZHANG W, et al. Investigation on electrochemical corrosion characteristic of 2A14 aluminum alloy in nitric acid[J]. Surface Review and Letters, 2017, 24(S1): 1850016. [27] FENG Y B, HUANG Z, TIAN G, et al. Correlation study on general and accelerated corrosion of the welded structure of aluminum alloy 2219 in N2O4[J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2015, 62(3): 136-142. doi: 10.1108/ACMM-01-2015-1498 [28] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料 疲劳试验 变幅疲劳试验第1部分: 总则、试验方法和报告要求: GB/T 37306.1—2019[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019: 3-5.State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of of the People's Republic of China. Metallic materials-fatigue testing-variable amplitude fatigue testing Part 1: General principles, test method and reporting requirements: GB/T 37306.1—2019 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019: 3-5(in Chinese). [29] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料 疲劳试验 疲劳裂纹扩展方法: GB/T 6398—2017 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Metallic materials—Fatigue testing—Fatigue crack growth method: GB/T 6398—2017 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017(in Chinese). [30] MA Y L, ZHOU X R, MENG X M, et al. Influence of thermomechanical treatments on localized corrosion susceptibility and propagation mechanism of AA2099 Al-Li alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(6): 1472-1481. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64252-8 [31] WANG X H, WANG J H, YUE X, et al. Effect of aging treatment on the exfoliation corrosion and stress corrosion cracking behaviors of 2195 Al-Li alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 67(2): 596-605. [32] BOAG A, HUGHES A E, WILSON N C, et al. How complex is the microstructure of AA2024-T3?[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(8): 1565-1568. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2009.05.001 [33] HUGHES A E, BOAG A, GLENN A M, et al. Corrosion of AA2024-T3 Part II: Co-operative corrosion[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(1): 27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.030 [34] 李劲风, 郑子樵, 任文达. 第二相在铝合金局部腐蚀中的作用机制[J]. 材料导报, 2005, 19(2): 81-83,90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2005.02.024LI J F, ZHENG Z Q, REN W D. Function mechanism of secondary phase on localized corrosion of Al alloy[J]. Materials Review, 2005, 19(2): 81-83(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2005.02.024 [35] ZHAO K, LIU J H, YU M, et al. Through-thickness inhomogeneity of precipitate distribution and pitting corrosion behavior of Al-Li alloy thick plate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(9): 1793-1802. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65087-9 [36] GLENN A M, MUSTER T H, LUO C, et al. Corrosion of AA2024-T3 Part III: Propagation[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(1): 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.035 [37] WU P F, DENG Y L, ZHANG J, et al. The effect of inhomogeneous microstructures on strength and fatigue properties of an Al-Cu-Li thick plate[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2018, 731(7): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.06.033 [38] GHANBARI E, SAATCHI A, LEI X W, et al. Studies on pitting corrosion of Al-Cu-Li alloys Part II: Breakdown potential and pit initiation[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(11): 1786. doi: 10.3390/ma12111786 [39] BOAG A, HUGHES A E, GLENN A M, et al. Corrosion of AA2024-T3 Part I: Localised corrosion of isolated im particles[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(1): 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.009 [40] PROTON V, ALEXIS J, ANDRIEU E, et al. The influence of artificial ageing on the corrosion behaviour of a 2050 aluminium-copper-lithium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 80(3): 494-502. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.060 [41] 周松, 许良, 回丽, 等. 不同腐蚀环境下高强铝合金腐蚀行为[J]. 中国机械工程, 2017, 28(16): 2000-2007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.16.016ZHOU S, XU L, HUI L, et al. Corrosion behavior of high strength aluminum alloy under different corrosion environments[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 28(16): 2000-2007(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2017.16.016 [42] PAIK J K, LEE J M, KO M J. Ultimate shear strength of plate elements with pit corrosion wastage[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2004, 42(8): 1161-1176. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2004.03.024 -







 下载:
下载: