Evaluation index of accumulated water-film on asphalt pavement considering safety of aircraft hydroplaning
-
摘要:
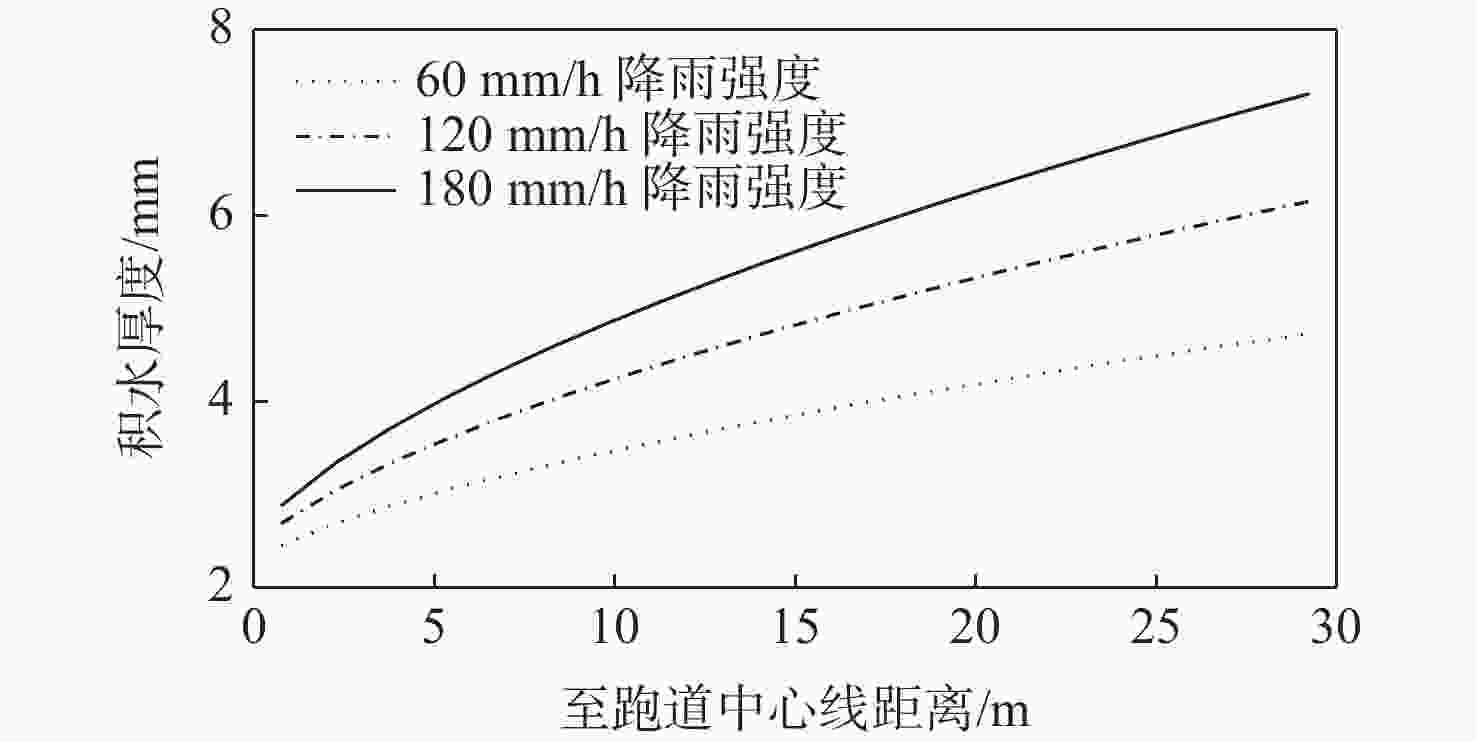
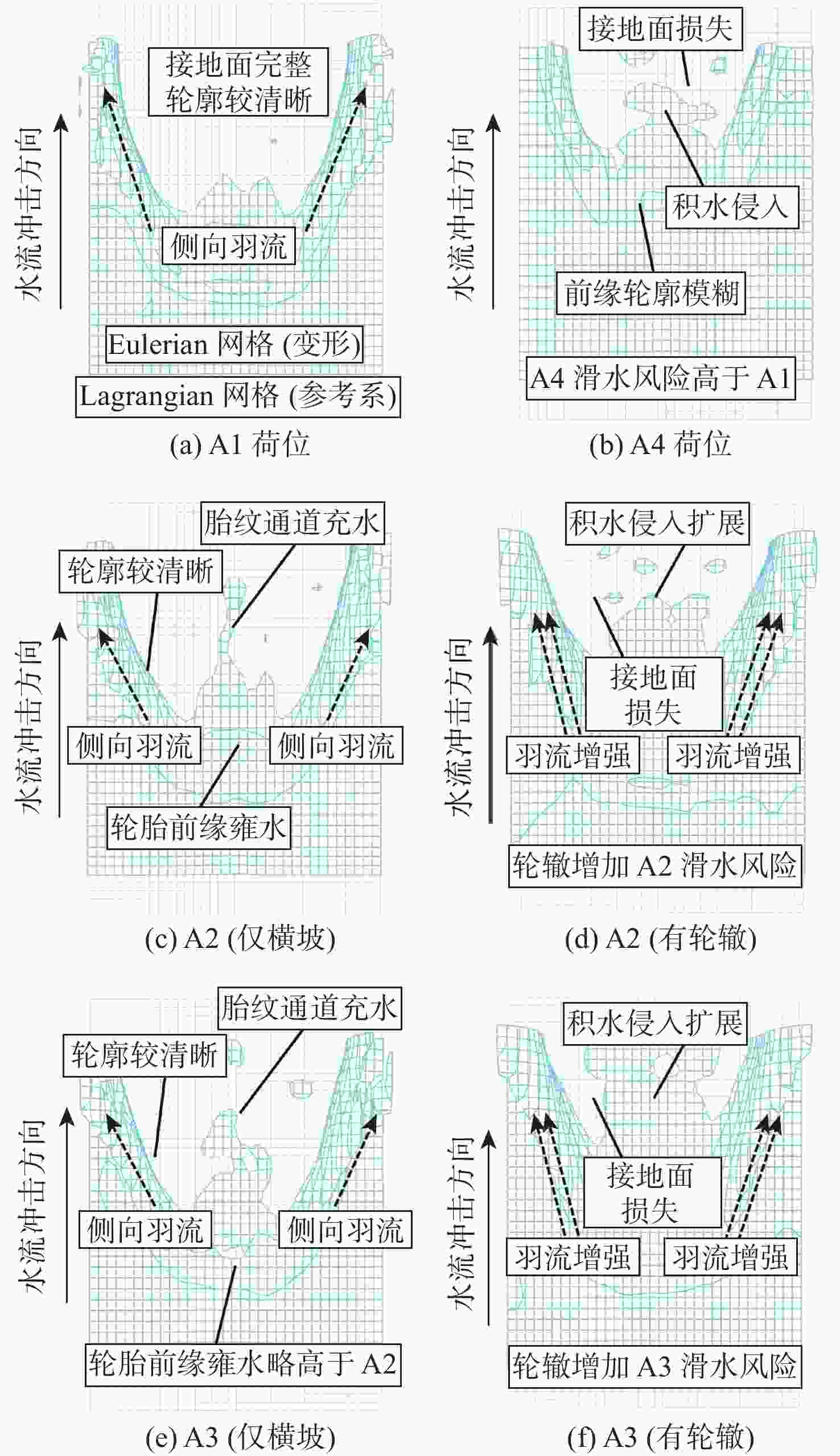
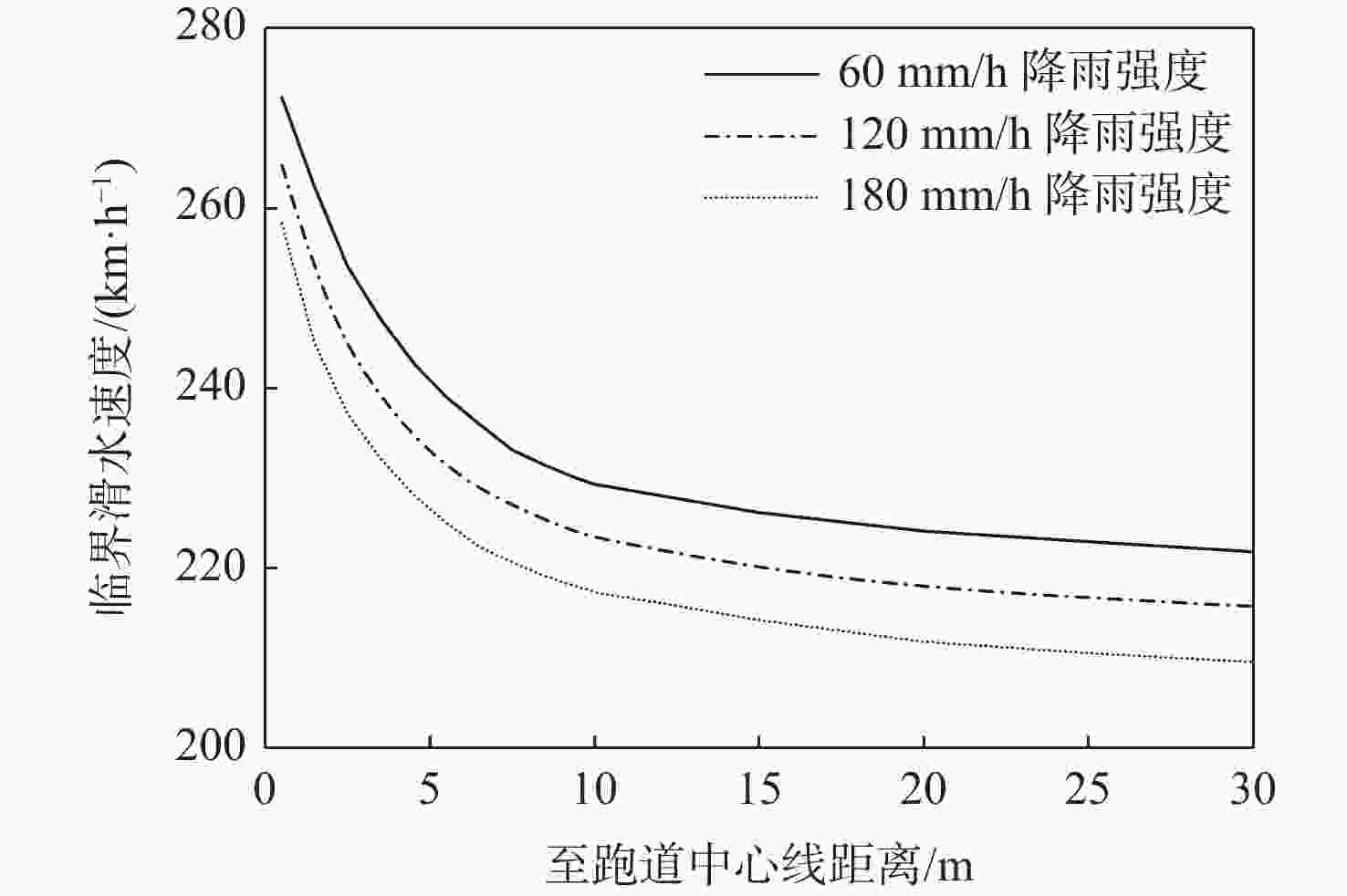
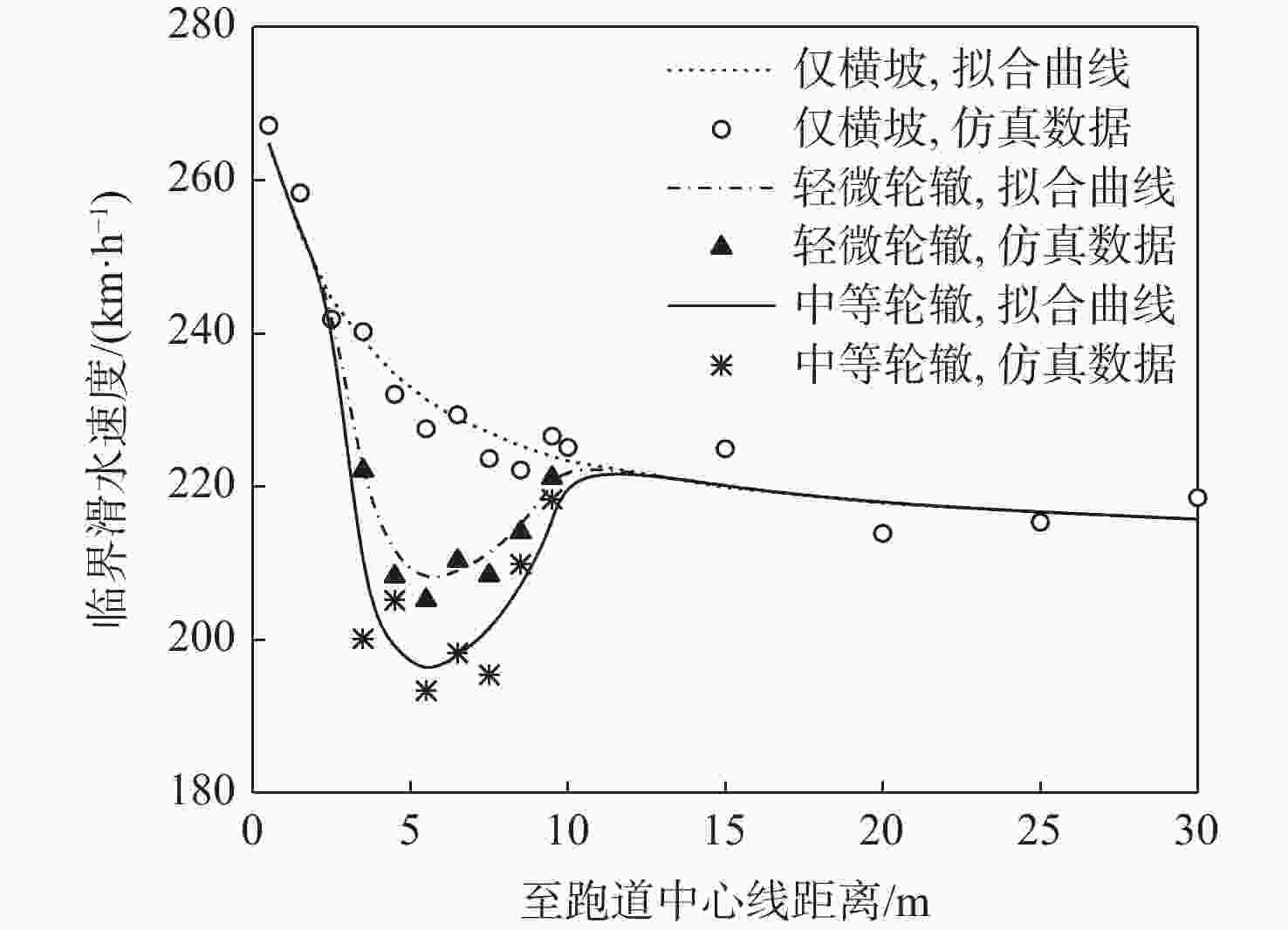
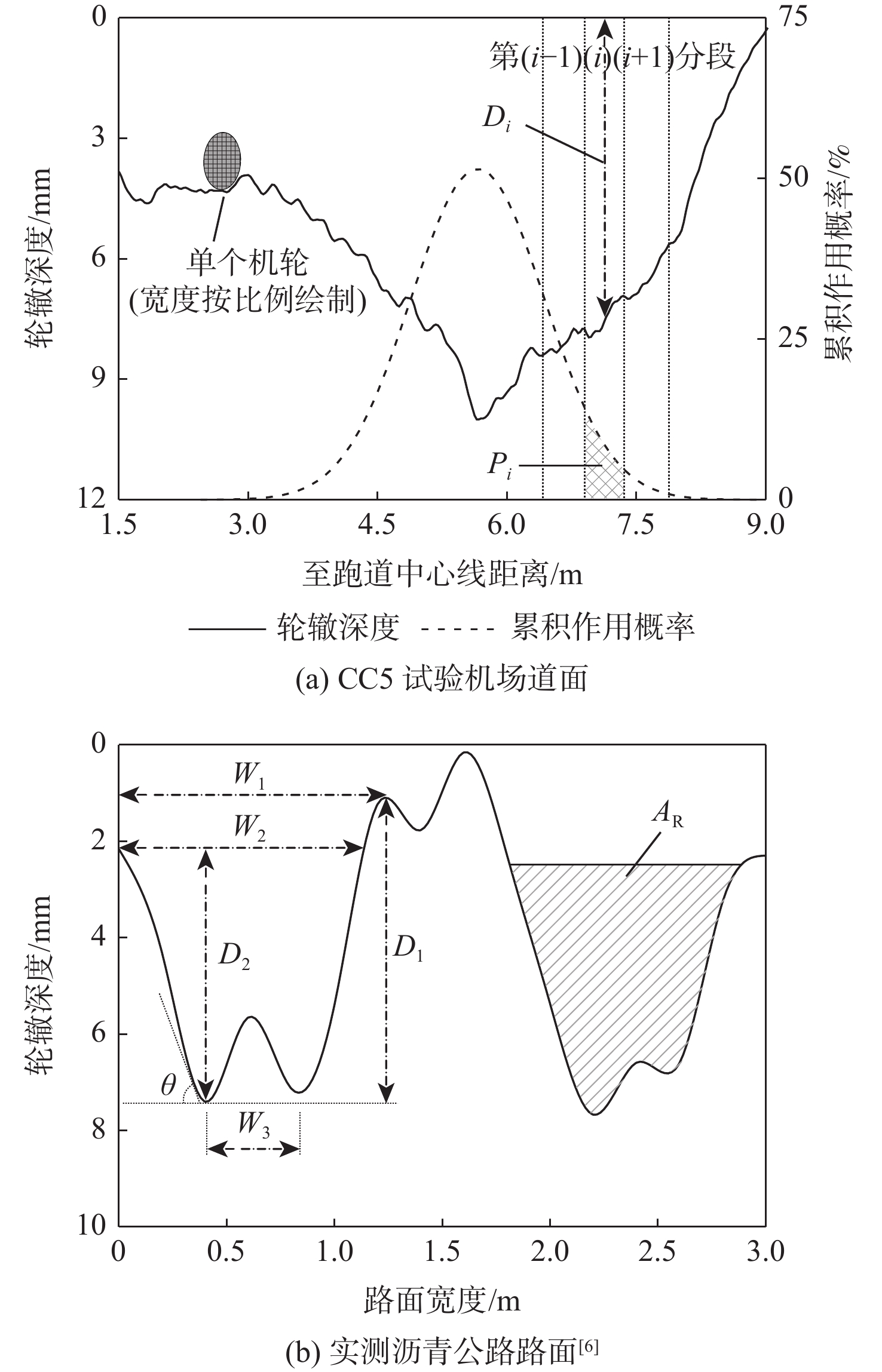
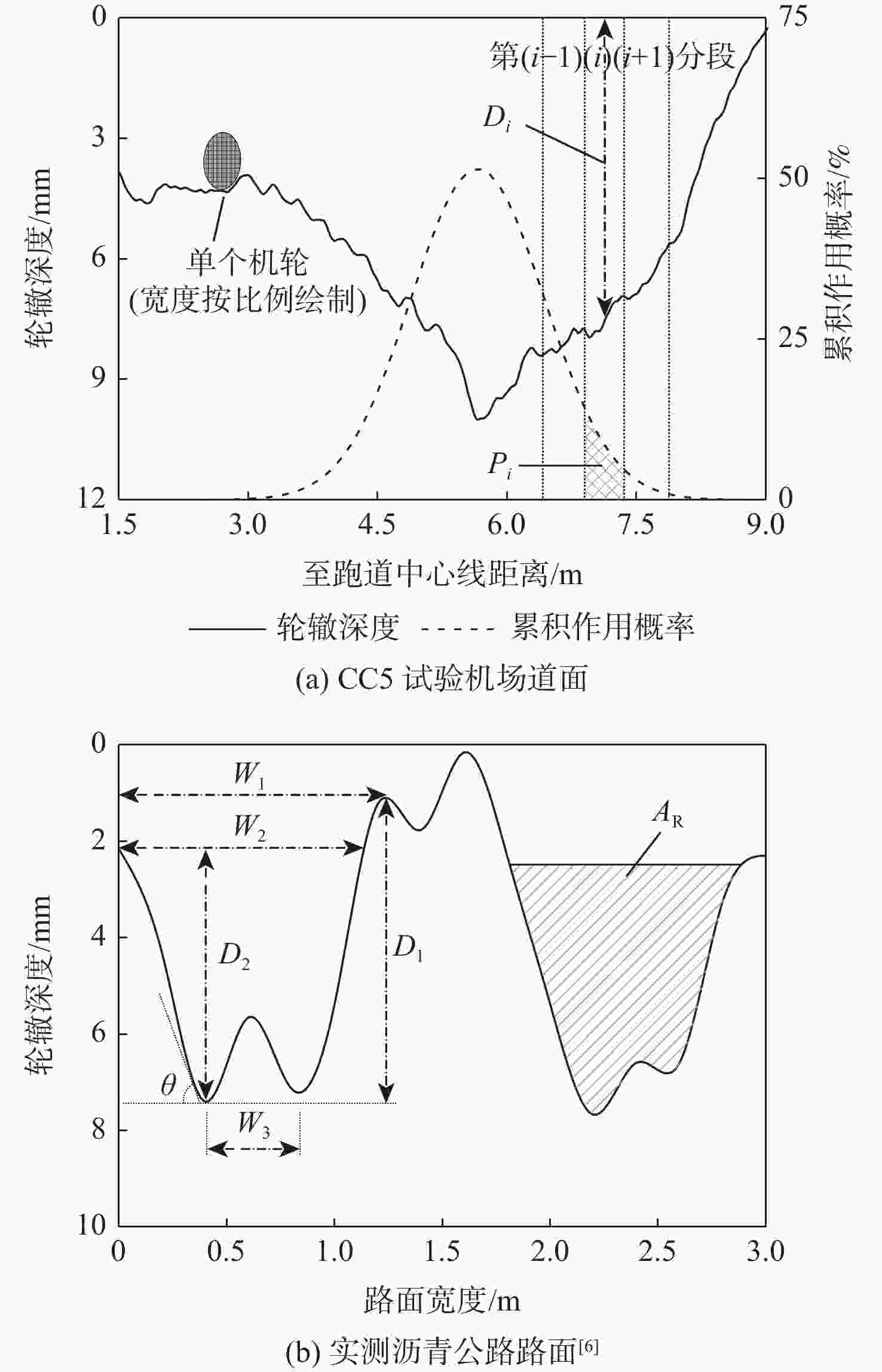
沥青道面积水深度受横坡与轮辙变形共同影响分布复杂,是诱发飞机轮胎滑水事故的重要条件。当前,仅针对飞机起降运行给出污染跑道积水厚度范围,积水评价方式与实际运行环境脱节。基于轮辙横断面变形特征分析,提出一种考察飞机轮载横向累积作用概率分布的当量水膜厚度(EWT)指标。根据道面不同区域积水条件,分段建立轮胎滑水仿真分析模型,探讨滑水行为差异及轮辙积水影响机理,验证EWT的合理性与适用范围。结果表明:轮辙内部积水引起局部水膜增厚,当飞机滑行经过时,积水侵入轮胎底部,轮胎前缘轮廓模糊且接地面积降低;当前分段临界滑水速度减小,降幅与轮载累积作用概率正相关;轮辙变形导致轮胎“最不利”滑行位置自跑道边缘向中心线内移;EWT对应表征安全接地宽度更大,覆盖轮载累积作用概率约为平均水膜厚度(AWT)的2倍,滑水风险指标仅为AWT的36%~81%。所提评价指标克服了最大水膜厚度(MWT)取值过于严格的缺陷,更适用于机场管理实践,可为起降条件保障和滑水风险分级提供量化参照。
Abstract:The primary causes of aircraft tire hydroplaning accidents were rut deformation and cross slope on asphalt pavement, which had a notable impact on the distribution of accumulated water-film depth. At present, an acceptable range of water-film thickness of contaminated runway was given in the regulations considering aircraft take-off and landing process. The evaluation procedure of accumulated water-film was not consitant with reality. Based on feature analysis of the rut section, an equivalent water-film thickness (EWT) evaluation index was proposed in this paper considering the transverse distribution of the cumulative probability of aircraft wheel load. A series of simulation models of tire hydroplaning were then established according to accumulated water-film conditions at different runway segmentations. The difference in hydroplaning behavior between segmentations and the mechanism of rutting impact was fully discussed. The feasibility and applicable range of EWT were then examined and verified. Study results indicate that accumulated water within the rut section caused the increase of overall water-film thickness, which can seriously invade the tire print interface when aircraft tire taxing through. The outline at the tire frontier blurred and the contact area was reduced consequently. At such segmentations, the essential hydroplaning speed dropped, and the cumulative probability of aircraft wheel load was positively correlated with the reduction’s magnitude. The most unfavorable taxing segmentation shifted from the edge of the runway to the area near the central line due to rut deformation. The hydroplaning risk of EWT was only 36% to 81% of that of average water-film thickness (AWT), and the cumulative likelihood of aircraft wheel load involved in EWT was up to twice that of AWT due to the greater representative breadth of safety taxing of EWT. The proposed EWT index may overcome the defection of the maximum water-film thickness (MWT) index that can be too strict to apply. Therefore, EWT is considered more suitable in airport management practice, which can be used as a quantitative reference for runway operation safeguard and hydroplaning risk ranking.
-
Key words:
- aircraft tire /
- tire hydroplaning /
- water-film evaluation /
- pavement rutting /
- hydroplaning risk
-
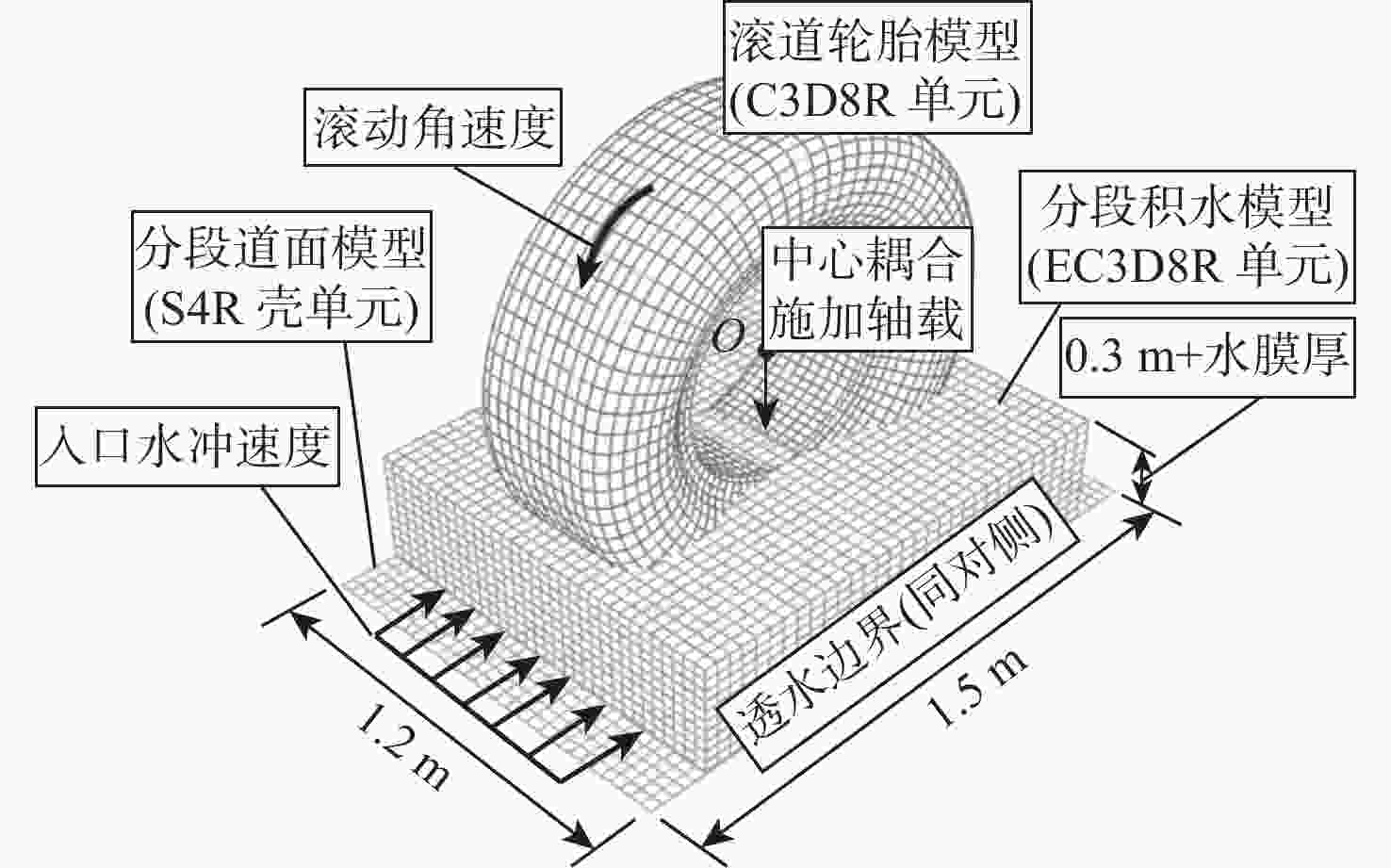
外径/cm 内径/cm 宽度/cm 胎压/kPa 轴载/kN 沟槽宽度/cm 沟槽深度/cm 橡胶正定常数
C10/MPa橡胶正定常数
C01/MPa橡胶不可
压缩系数Q1116.8 50.8 43.2 1140 154.5 1.0 0.8 9.9 8.8 10−7 注:橡胶材料参数匹配Mooney-Rivlin本构模型[20]。 表 2 积水评价指标与临界滑水速度
Table 2. Water-film evaluation index and critical hydroplaning speed
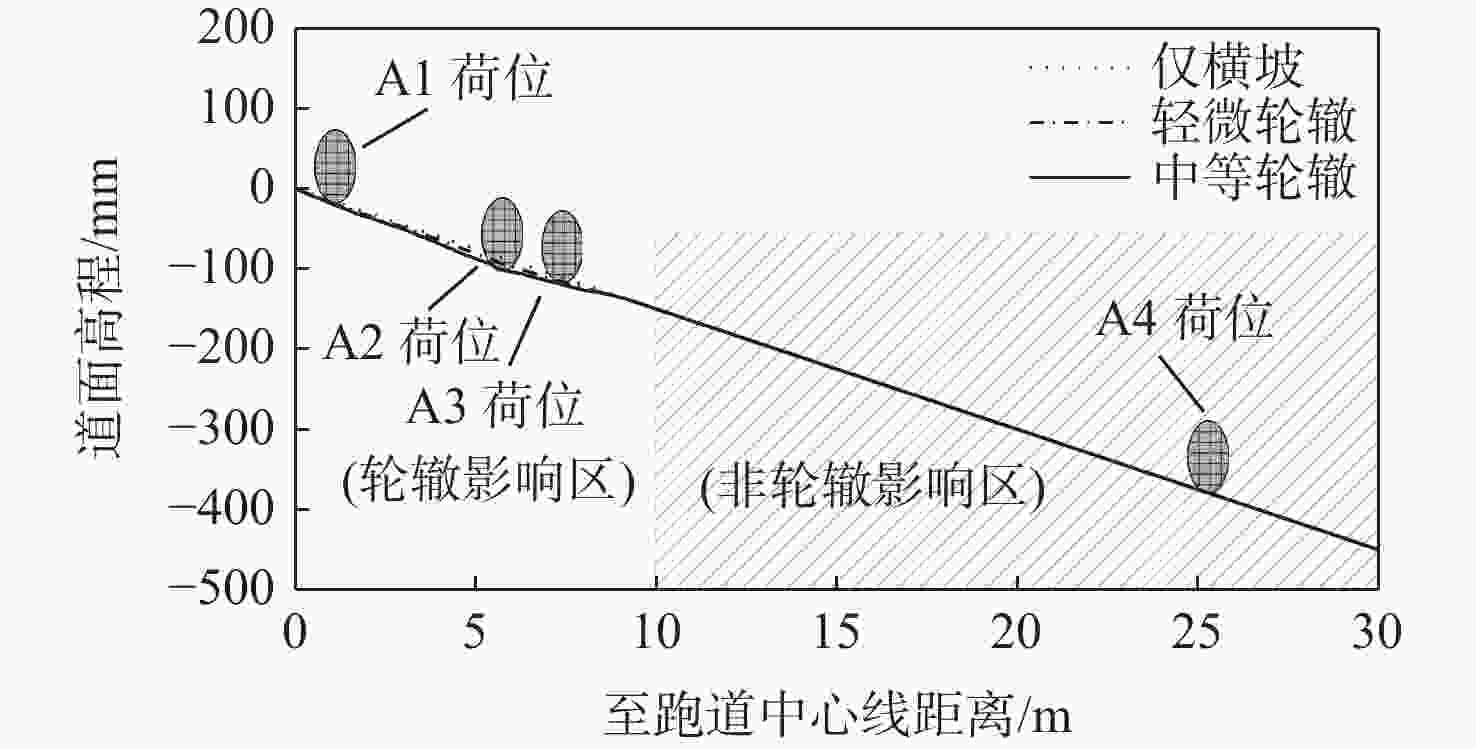
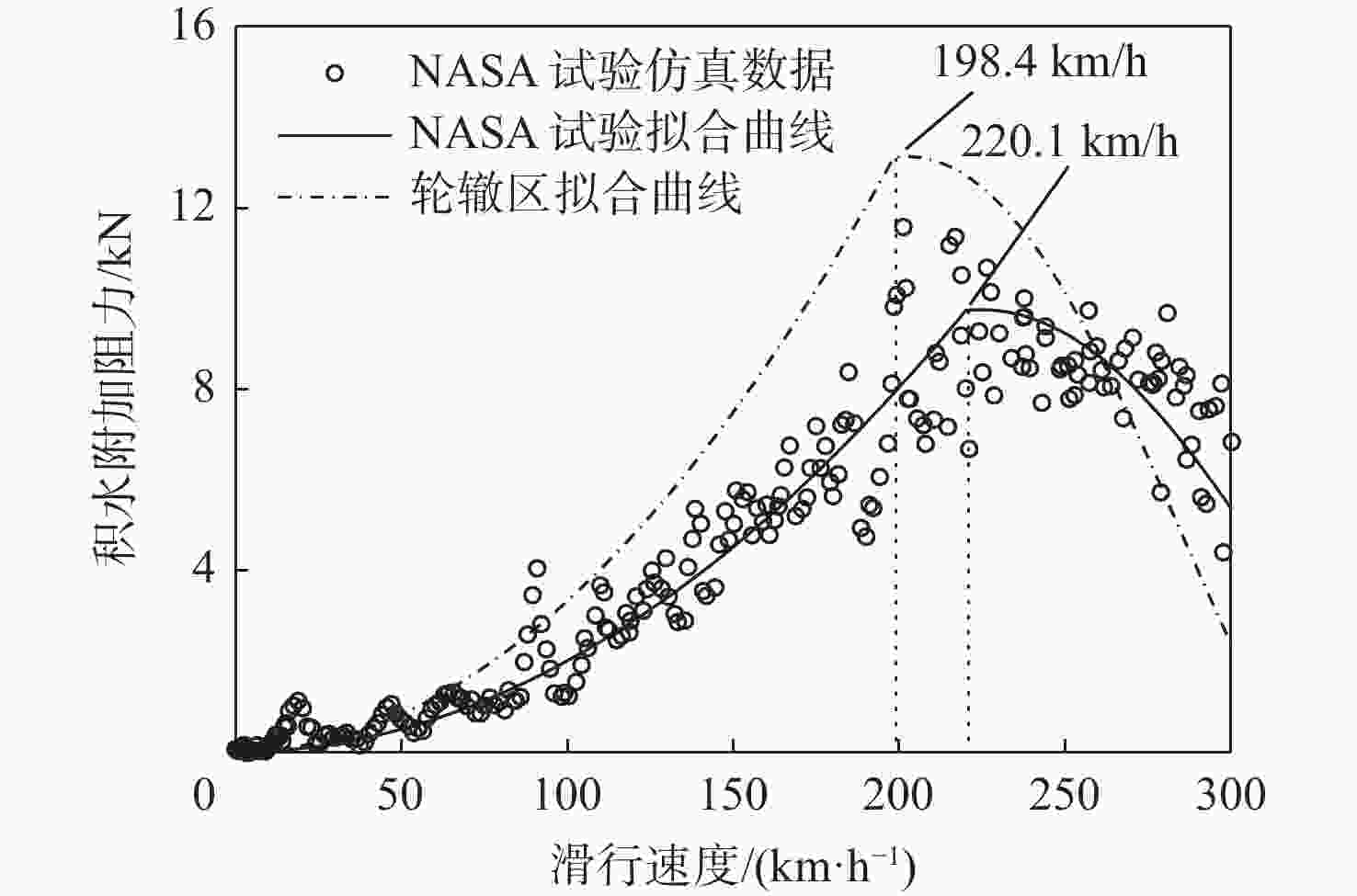
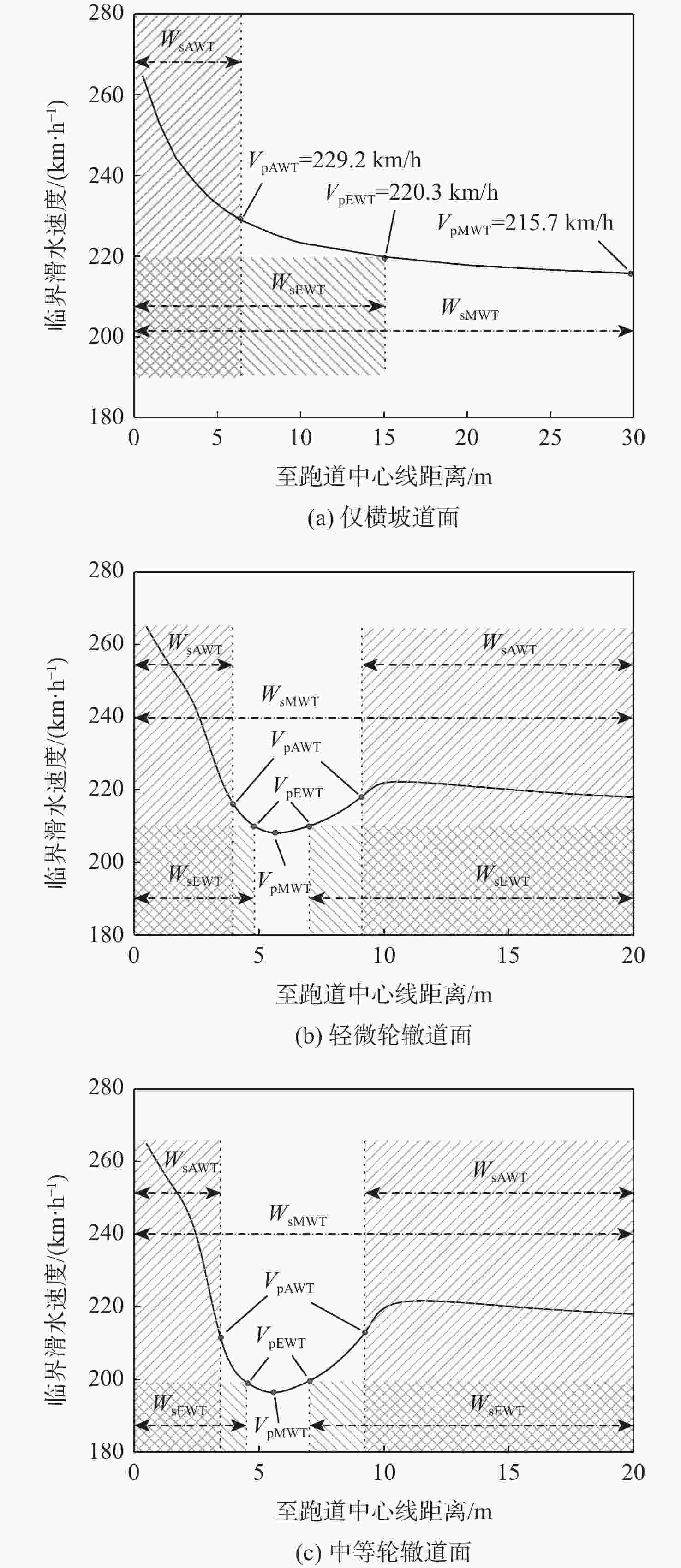
道面条件 dAWT/mm dMWT/mm dEWT/mm VpAWT/(km·h−1) VpMWT/(km·h−1) VpEWT/(km·h−1) 仅横坡道面 4.7 6.2 5.1 229.2 215.7 220.3 轻微轮辙道面 5.9 11.6 10.0 217.5 207.5 209.8 中等轮辙道面 6.9 18.5 16.0 212.6 195.5 199.2 表 3 安全接地宽度内轮载累积作用概率
Table 3. Cumulative probability of aircraft wheel load within safety grounding width
% 道面条件 αAWT αEWT αMWT 仅横坡道面 58.5 92.4 98.3 轻微轮辙道面 30.2 64.1 98.3 中等轮辙道面 20.2 51.2 98.3 表 4 滑行速度峰值安全概率
Table 4. Safety probability of peak taxing speed
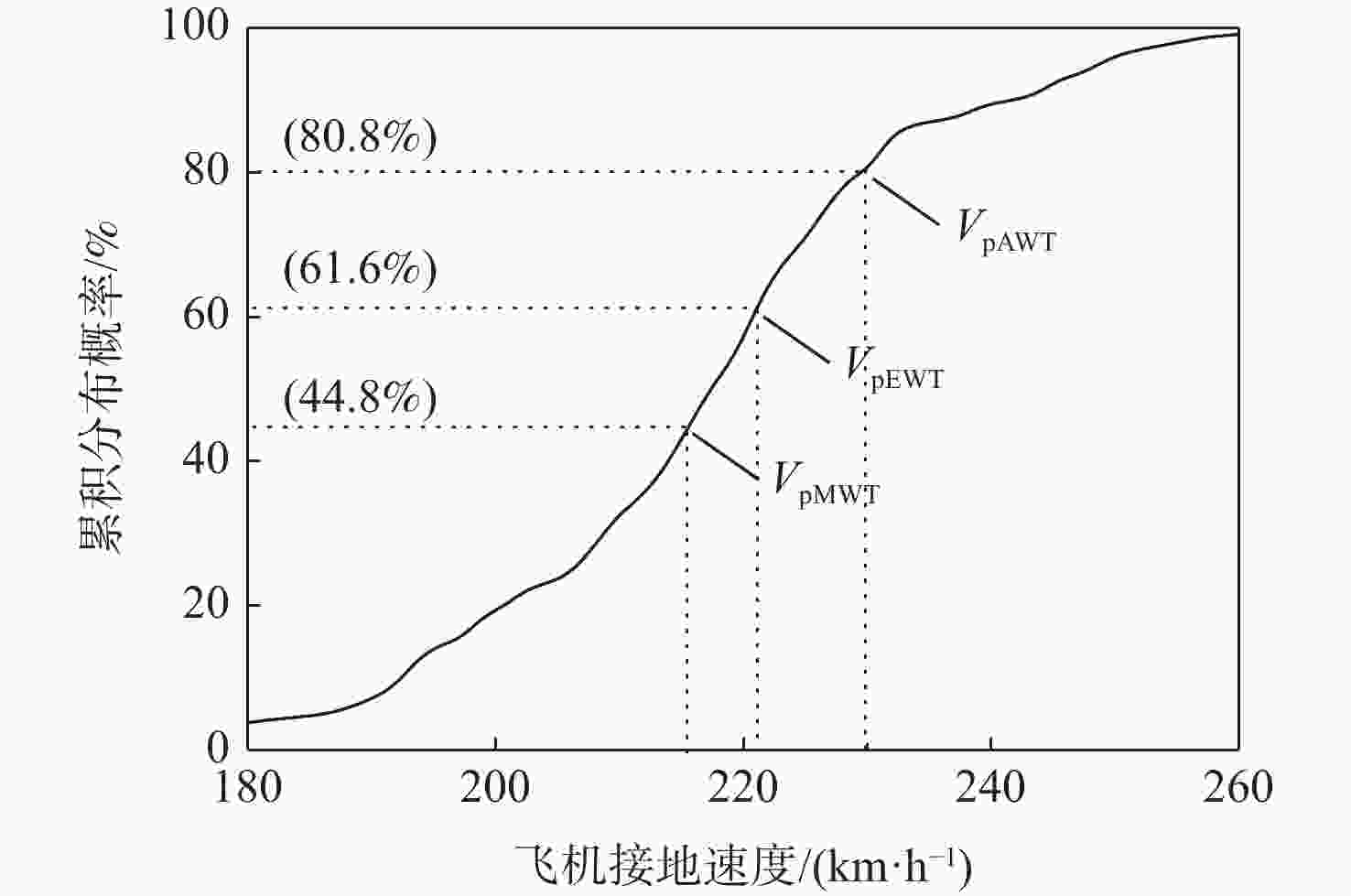
% 道面条件 βAWT βEWT βMWT 仅横坡道面 80.8 61.6 44.8 轻微轮辙道面 50.4 32.8 24.8 中等轮辙道面 39.2 20.0 14.4 表 5 轮胎滑水风险指标
Table 5. Risk indicators of tire hydroplaning
% 道面条件 RAWT REWT RMWT 仅横坡道面 8.0 2.9 0.1 轻微轮辙道面 34.6 24.2 1.3 中等轮辙道面 48.5 39.1 1.5 -
[1] VAN ES G W H, ROELEN A L C, KRUIJSEN E A C, et al. Safety aspects of aircraft performance on wet and contaminated runways: NLR-TP-2001-216[R]. Amsterdam: NLR, 2001. [2] ZHANG Q Y, WU S X. Three-dimensional study on touch down zone of steel catenary riser under cyclic loading in saturated seabed[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 190(15): 106411. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106411 [3] FWA T F, ONG G P. Wet-pavement hydroplaning risk and skid resistance: Analysis[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2008, 134(5): 182-190. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2008)134:5(182) [4] 燕姣, 李岩, 惠冰. 车辙断面非均匀积水对车辆安全性影响的仿真分析[J]. 汽车技术, 2019, 47(11): 47-51.YAN J, LI Y, HUI B. Simulation analysis of rutting section unevenness with respect to vehicle driving safety[J]. Automobile Technology, 2019, 47(11): 47-51(in Chinese). [5] 罗又元. 公路沥青路面车辙病害养护标准及养护对策研究[J]. 西部交通科技, 2019, 18(10): 61-63.LUO Y Y. Study on maintenance standard and maintenance countermeasures for rutting disease of highway asphalt pavement[J]. Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2019, 18(10): 61-63(in Chinese). [6] 侯相深, 马松林, 王彩霞. 基于行车安全的沥青路面车辙测量与评价指标的研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006, 23(8): 14-17.HOU X S, MA S L, WANG C X. Research on measurement and evaluation of asphalt pavement rutting based-on traffic safety[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006, 23(8): 14-17(in Chinese). [7] 徐世法. 沥青路面的车辙深度与行车安全性[J]. 北京建筑工程学院学报, 1994, 10(1): 47-51.XU S F. Pavement rutting depth related to vehicle travel safety[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 1994, 10(1): 47-51(in Chinese). [8] 李岳, 赵夫朋, 蔡靖. 飞机轮载作用下轮辙断面特征与评价指标研究[J]. 中国民航大学学报, 2020, 38(3): 18-22.LI Y, ZHAO F P, CAI J. Rutting profile characteristics and evaluation indices under aircraft wheel load[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation University of China, 2020, 38(3): 18-22(in Chinese). [9] FWA T F, PASINDU H R, ONG G P. Critical rut depth for pavement maintenance based on vehicle skidding and hydroplaning consideration[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(4): 423-429. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)TE.1943-5436.0000336 [10] YAN J, ZHANG H W, HUI B. Driving safety analysis using grid-based water-filled rut depth distribution[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 2021: 5568949. [11] MAMLOUK M, VINAYAKAMURTHY M, UNDERWOOD B S, et al. Effects of the international roughness index and rut depth on crash rates[J]. Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2018, 2672(40): 418-429. doi: 10.1177/0361198118781137 [12] ZHU X Y, YANG Y, ZHAO H D, et al. Effects of surface texture deterioration and wet surface conditions on asphalt runway skid resistance[J]. Tribology International, 2021, 153(10): 106589. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106589 [13] 中国民用航空局. 航空承运人湿跑道和污染跑道运行管理规定: AC-121-FS-33R1[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局, 2021.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Regulations for the management of wet runway and contaminated runway operation by air carriers: AC-121-FS-33R1[S]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2021(in Chinese). [14] HAYHOE G F, GARG N, DONG M. Permanent deformations during traffic tests on flexible pavements at the national airport pavement test facility[C]//Proceedings of the Airfield Pavements specialty conference. Reston: ASCE Press, 2003: 147-169. [15] ONG G P, FWA T F. Wet-pavement hydroplaning risk and skid resistance: Modeling[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2007, 133(10): 590-598. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2007)133:10(590) [16] 李岳, 蔡靖, 宗一鸣. 湿滑道面飞机轮胎临界滑水速度数值仿真[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2017, 17(5): 90-101.LI Y, CAI J, ZONG Y M. Numerical simulation of critical hydroplaning speed of aircraft tire under wet pavement condition[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2017, 17(5): 90-101(in Chinese). [17] 中国民用航空局. 民用机场道面评价管理技术规范: MH/T 5024—2019[S]. 北京:中国民航出版社,2019.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Specifications for pavement evaluation and management of civil airports: MH/T 5024—2019[S]. Beijing: China Civil Aviation Pubishing House, 2019(in Chinese). [18] 韩英锋. 基于降水强度的道面表面性能及滑水安全研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2021: 22-30.HAN Y F. Study on pavement surface performance and water skiing safety based on precipitation intensity[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2021: 22-30(in Chinese). [19] 许诤. 考虑道面平整度的飞机轮胎滑水安全问题研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2019: 26-27.XU Z. Safety research of hydroplaning of aircraft tire considering roughness quality of pavement[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2019: 26-27(in Chinese). [20] 蔡靖, 李岳, 宗一鸣. 湿滑道面飞机轮胎临界滑水速度计算方法比较[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(7): 220798.CAI J, LI Y, ZONG Y M. Comparasion of prediction methods for critical hydroplaning speed of aircraft tire on wet pavement[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(7): 220798(in Chinese). [21] 倪明. 大型客机污染跑道起降性能适航审定方法研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2019:36-37.NI M.Study on airworthiness certification method of large passenger aircraft taking off and landing on polluted runway[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019: 36-37(in Chinese). [22] HORNE W B, DREHER R C. Phenomena of pneumatic tire hydroplaning: NASA TN D-2056[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1963: 3-17. [23] 雷电, 赵鸿铎, 吴璨. 飞机轮迹横向分布测试系统的比选分析[J]. 西部交通科技, 2012(10): 63-68.LEI D, ZHAO H D, WU C. The analysis and selection for aircraft deviation test system[J]. Western China Communication Science & Technology, 2012(10): 63-68(in Chinese). [24] HOSANG V A. Field survey and analysis of aircraft distribution on airport pavements: 113286686[R]. Washington, D.C.: FAA, 1978: 84-86. [25] 李岳, 胡宇祺, 蔡靖, 等. 湿滑道面飞机着陆滑水风险量化分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1144.LI Y, HU Y Q, CAI J, et al. Quantitative analysis of water-skiing risk for aircraft landing on wet skid surface[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 54(6): 1138-1144(in Chinese). [26] KANG Y S, NAZARI A, CHEN L, et al. A probabilistic approach to hydroplaning potential and risk[J]. SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical Systems, 2019, 12(1): 63-70. doi: 10.4271/06-12-01-0005 -






 下载:
下载: