-
摘要:
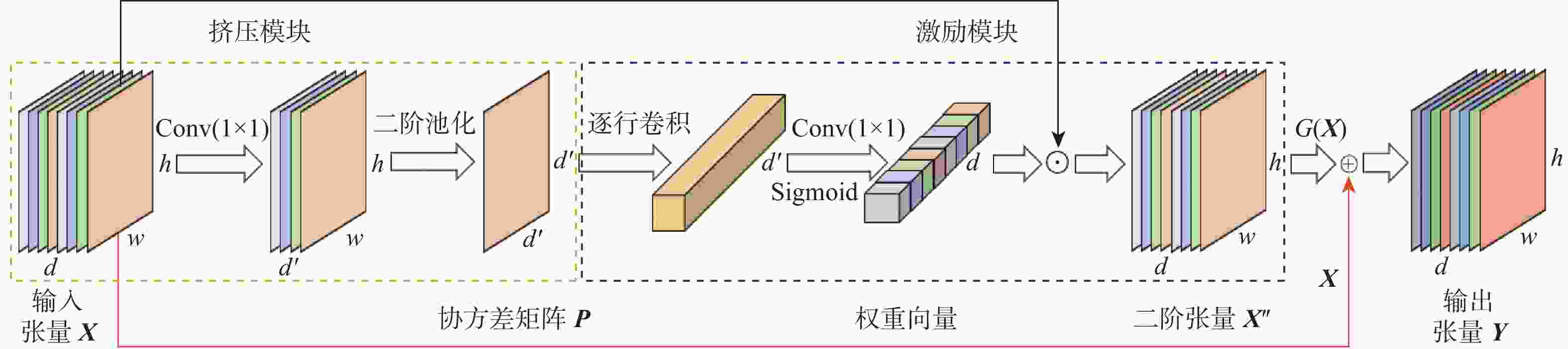
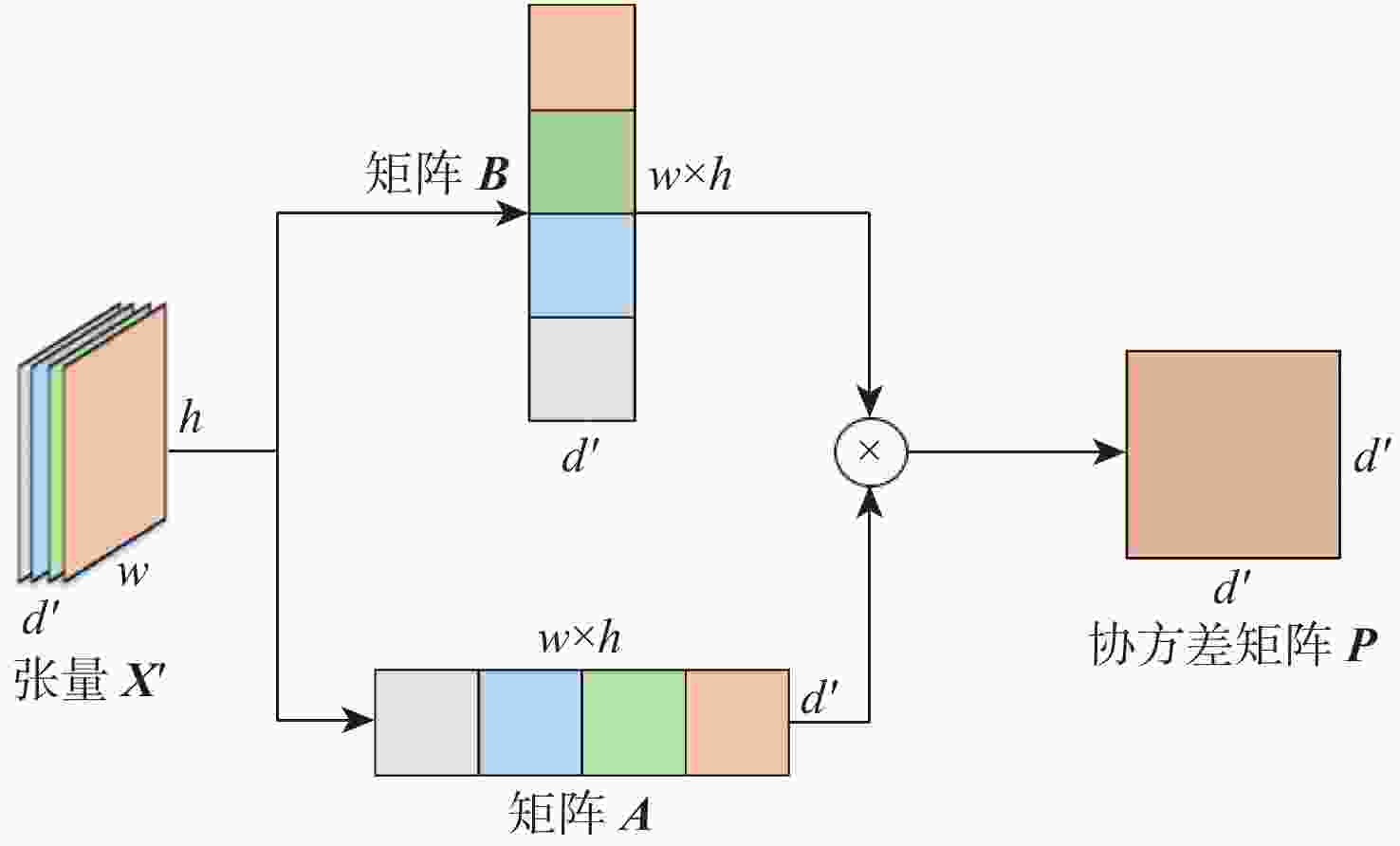
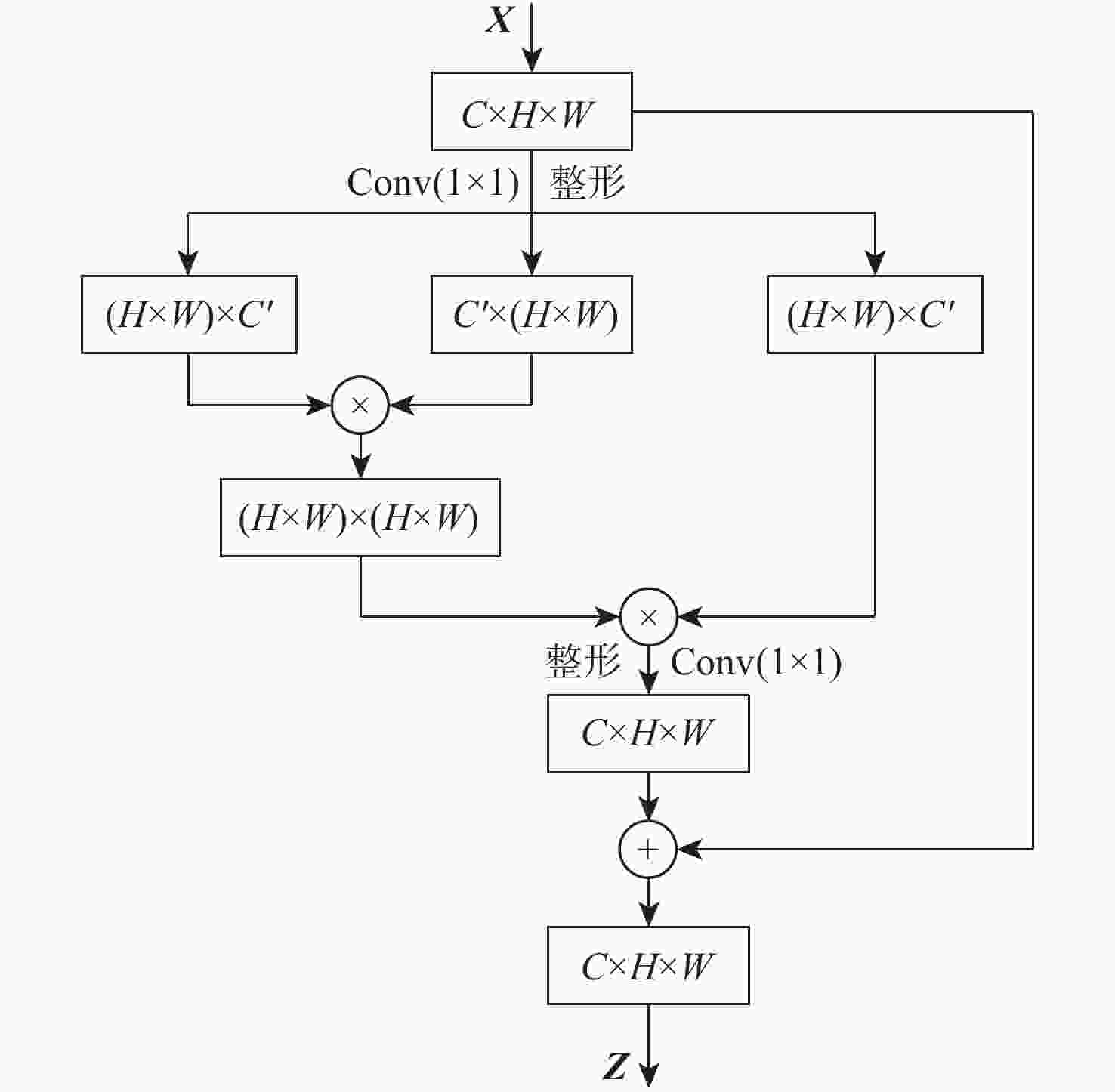
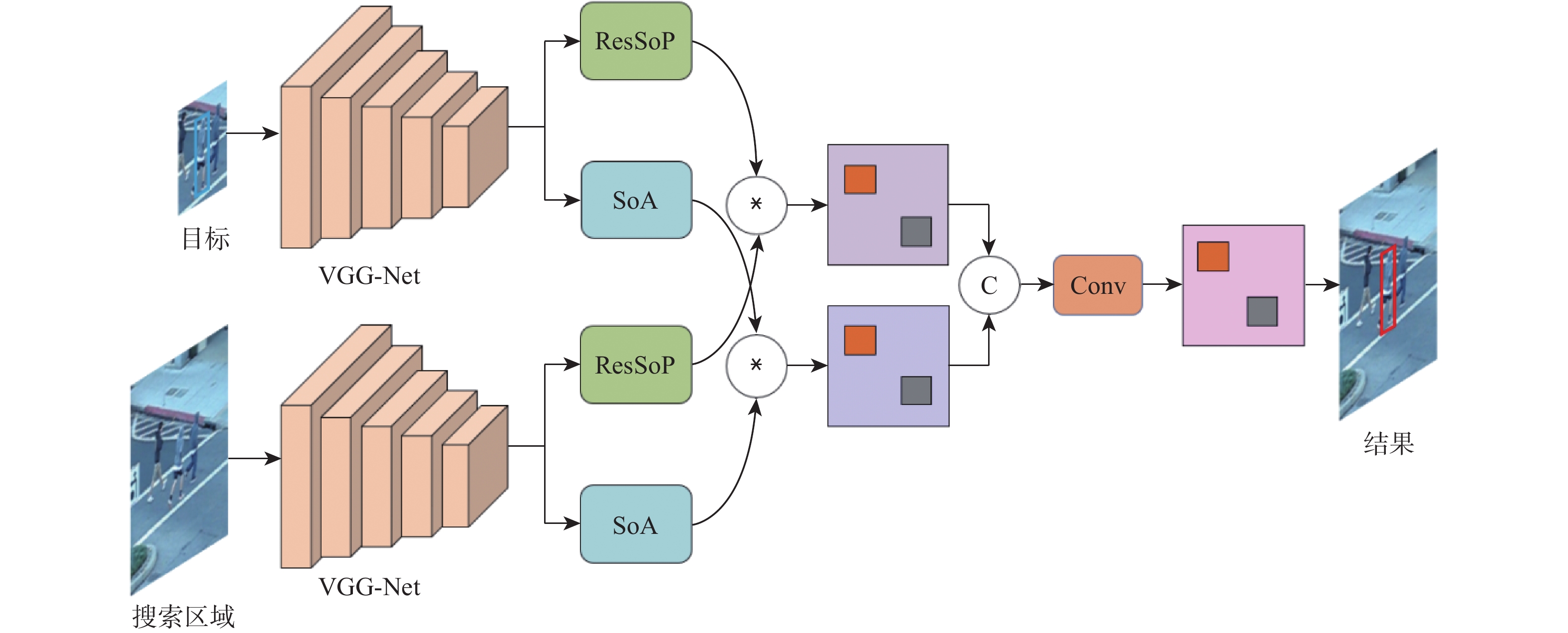
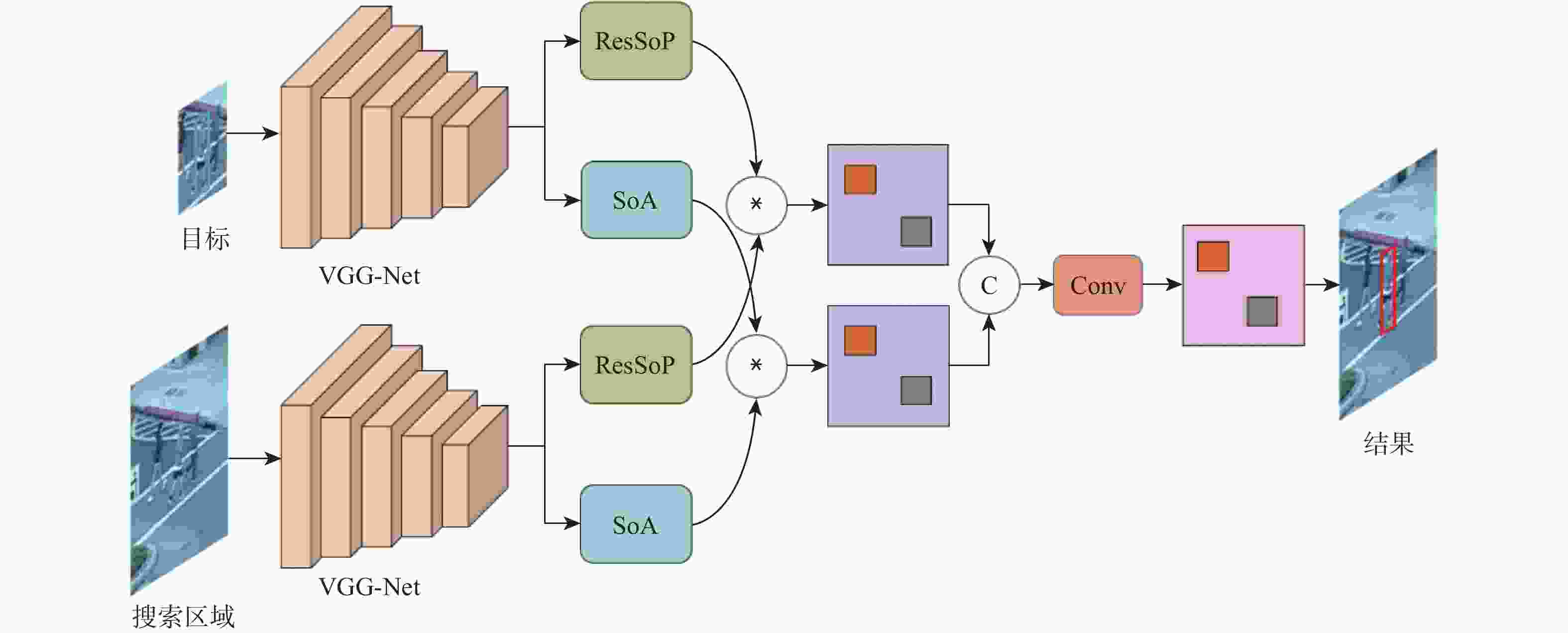
为提升基于Siamese网络视觉跟踪算法的特征表达能力和判别能力,以获得更好的跟踪性能,提出了一种轻量级的基于二阶注意力的Siamese网络视觉跟踪算法。使用轻量级VGG-Net作为Siamese网络的主干,获取目标的深度特征;在Siamese网络的末端并行使用所提残差二阶池化网络和二阶空间注意力网络,获取具有通道相关性的二阶注意力特征和具有空间相关性的二阶注意力特征;使用残差二阶通道注意力特征和二阶空间注意力特征,通过双分支响应策略实现视觉跟踪。利用GOT-10k数据集对所提算法进行端到端的训练,并在OTB100和VOT2018数据集上进行验证。实验结果表明:所提算法的跟踪性能取得了显著提升,与基准算法SiamFC相比,在OTB100数据集上,精度和成功率分别提高了0.100和0.096,在VOT2018数据集上,预期平均重叠率(EAO)提高了0.077,跟踪速度达到了48帧/s。
Abstract:To improve the feature expression ability and discriminative ability of the visual tracking algorithm based on Siamese network and obtain better tracking performance, a lightweight Siamese network visual tracking algorithm based on second-order attention is proposed. Firstly, to obtain deep features of the object, the lightweight VGG-Net is used as the backbone of the Siamese network.Secondly, the residual second-order pooling network and the second-order spatial attention network are used in parallel at the end of the Siamese network to obtain the second-order attention features with channel correlation and the second-order attention features with spatial correlation.Finally, visual tracking is achieved through a double branch response strategy using the residual second-order channel attention features and the second-order spatial attention features. The proposed algorithm is trained end-to-end with the GOT-10k dataset and validated on the datasets OTB100 and VOT2018.The experimental results show that the tracking performance of the proposed algorithm has been significantly improved. Compared with the baseline algorithm SiamFC, on dataset OTB100, the precision and the success are increased by 0.100 and 0.096, respectively; on dataset VOT2018, the expected average overlap (EAO) increased by 0.077, tracking speed reached 48 frame/s.
-
表 1 归一化参数对跟踪性能的影响
Table 1. Influence of normalization parameters on tracking performance
C 精度 成功率 0.5 0.806 0.597 0.6 0.815 0.606 0.7 0.818 0.609 0.8 0.825 0.614 0.9 0.821 0.612 1.0 0.831 0.621 2.0 0.843 0.629 3.0 0.844 0.626 4.0 0.830 0.623 5.0 0.849 0.633 6.0 0.845 0.638 7.0 0.836 0.626 8.0 0.846 0.633 9.0 0.824 0.617 10.0 0.830 0.621 表 2 细化归一化参数平衡跟踪性能
Table 2. Refinement of normalization parameters to balance tracking performance
C 精度 成功率 5.0 0.849 0.633 5.1 0.843 0.629 5.2 0.832 0.629 5.3 0.839 0.630 5.4 0.842 0.629 5.5 0.848 0.638 5.6 0.836 0.625 5.7 0.836 0.622 5.8 0.829 0.628 5.9 0.844 0.626 6.0 0.845 0.638 表 3 消融实验结果
Table 3. Ablation experiment results
SiamFC VGG-Net SoA ResSoP DBR 精度 成功率 跟踪速度/(帧·s−1) √ 0.777 0.580 58 √ √ 0.828 0.622 55 √ √ √ 0.845 0.638 53 √ √ √ 0.864 0.649 50 √ √ √ √ √ 0.877 0.676 48 表 4 不同属性下算法的跟踪成功率对比结果
Table 4. Comparison results of tracking success rate of algorithms under different attributes
算法 光照变化 平面外旋转 尺度变化 离开视野 目标形变 低分辨率 快速运动 目标遮挡 相似背景 平面内旋转 运动模糊 本文算法 0.681 0.658 0.668 0.607 0.640 0.698 0.646 0.634 0.640 0.649 0.674 SiamSE[26] 0.670 0.635 0.678 0.613 0.617 0.697 0.663 0.637 0.620 0.651 0.651 ATOM[25] 0.679 0.643 0.681 0.612 0.630 0.693 0.662 0.648 0.631 0.650 0.658 SiamDW-FC[18] 0.627 0.617 0.618 0.595 0.562 0.616 0.632 0.606 0.582 0.613 0.655 TADT[24] 0.674 0.643 0.650 0.623 0.602 0.644 0.655 0.638 0.619 0.618 0.668 GradNet[23] 0.643 0.628 0.614 0.583 0.572 0.669 0.624 0.616 0.611 0.627 0.646 DaSiamRPN[8] 0.655 0.644 0.637 0.537 0.645 0.636 0.621 0.611 0.642 0.652 0.625 SASiam[22] 0.644 0.642 0.642 0.611 0.590 0.692 0.636 0.629 0.634 0.626 0.651 SiamRPN[7] 0.652 0.628 0.621 0.548 0.619 0.663 0.603 0.589 0.598 0.632 0.624 SiamFC[6] 0.536 0.550 0.560 0.473 0.546 0.574 0.575 0.532 0.525 0.567 0.587 表 5 VOT2018数据集实验对比结果
Table 5. VOT2018 dataset experimental comparison results
算法 EAO 准确率 鲁棒性 本文算法 0.265 0.534 0.389 SiamSE[26] 0.270 0.538 0.432 GradNet[23] 0.247 0.510 0.390 SiamDW-FC[18] 0.230 0.500 0.490 SiamRPN[7] 0.243 0.560 0.340 SASiam[22] 0.236 0.500 0.459 SiamFC-tri[29] 0.212 0.483 0.526 DSiam[28] 0.196 0.512 0.646 DCFNet[27] 0.182 0.470 0.543 SiamFC[6] 0.188 0.500 0.590 -
[1] MARVASTI-ZADEH S M, CHENG L, GHANEI-YAKHDAN H. Deep learning for visual tracking: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(5): 3943-3968. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3046478 [2] 柏罗, 张宏立, 王聪. 基于高效注意力和上下文感知的目标跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(7): 1222-1232.BAI L, ZHANG H L, WANG C. Target tracking algorithm based on efficient attention and context awareness[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(7): 1222-1232(in Chinese). [3] 李玺, 查宇飞, 张天柱, 等. 深度学习的视觉跟踪算法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(12): 2057-2080. doi: 10.11834/jig.190372LI X, ZHA Y F, ZHANG T Z, et al. A survey of visual object tracking algorithms based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(12): 2057-2080(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190372 [4] 蒲磊, 李海龙, 侯志强, 等. 基于高层语义嵌入的孪生网络跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(4): 792-803.PU L, LI H L, HOU Z Q, et al. Siamese network tracking based on high level semantic embedding[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(4): 792-803(in Chinese). [5] 张成煜, 侯志强, 蒲磊, 等. 基于在线学习的Siamese网络视觉跟踪算法[J]. 光电工程, 2021, 48(4): 4-14.ZHANG C Y, HOU Z Q, PU L, et al. Siamese network visual tracking algorithm based on online learning[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(4): 4-14(in Chinese). [6] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 850-865. [7] LI B, YAN J, WU W. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8971-8980. [8] ZHU Z, WANG Q, LI B. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 101-117. [9] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [10] WANG Q, ZHANG L, WU B. What deep CNNs benefit from global covariance pooling: An optimization perspective[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10771-10780. [11] WANG Q, XIE J, ZUO W. Deep CNNs meet global covariance pooling: Better representation and generalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2582-2597. [12] GAO Z, WANG Q, ZHANG B, et al. Temporal-attentive covariance pooling networks for video recognition[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. l. ]: NeurIPS, 2021. [13] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 等. 基于二阶池化网络的鲁棒视觉跟踪算法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(8): 1472-1478.PU L, FENG X X, HOU Z Q, et al. Robust visual tracking based on second order pooling network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(8): 1472-1478(in Chinese). [14] LI Y, ZHANG X, CHEN D M. SiamVGG: Visual tracking using deeper Siamese networks[EB/OL]. (2019-02-07)[2022-05-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.02804. [15] GAO Z, XIE J, WANG Q. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3024-3033. [16] NG T, BALNTAS V, TIAN Y. SOLAR: Second-order loss and attention for image retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 253-270. [17] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2022-05-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [18] ZHANG Z, PENG H. Deeper and wider Siamese networks for real-time visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4591-4600. [19] HUANG L, ZHAO X, HUANG K. GOT-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(5): 1562-1577. [20] WU Y, LIM J, YANG M H. Object tracking benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848. [21] KRISTAN M, LEONARDIS A, MATAS J. The sixth visual object tracking VOT2018 challenge results[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-53. [22] HE A, LUO C, TIAN X. A twofold Siamese network for real-time object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4834-4843. [23] LI P, CHEN B, OUYANG W, et al. GradNet: Gradient-guided network for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6162-6171. [24] LI X, MA C, WU B. Target-aware deep tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1369-1378. [25] DANELLJAN M, BHAT G, KHAN F S. ATOM: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4660-4669. [26] SOSNOVIK I, MOSKALEV A, SMEULDERSA W M. Scale equivariance improves Siamese tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2765-2774. [27] WANG Q, GAO J, XING J. DCFNet: Discriminant correlation filters network for visual tracking[EB/OL]. (2017-04-13)[2022-05-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04057. [28] GUO Q, FENG W, ZHOU C. Learning dynamic Siamese network for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1763-1771. [29] DONG X, SHEN J. Triplet loss in Siamese network for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 459-474. -






 下载:
下载: