Differential positioning with Doppler measurements from Iridium satellite signals of opportunity based on lines of sight correction
-
摘要:
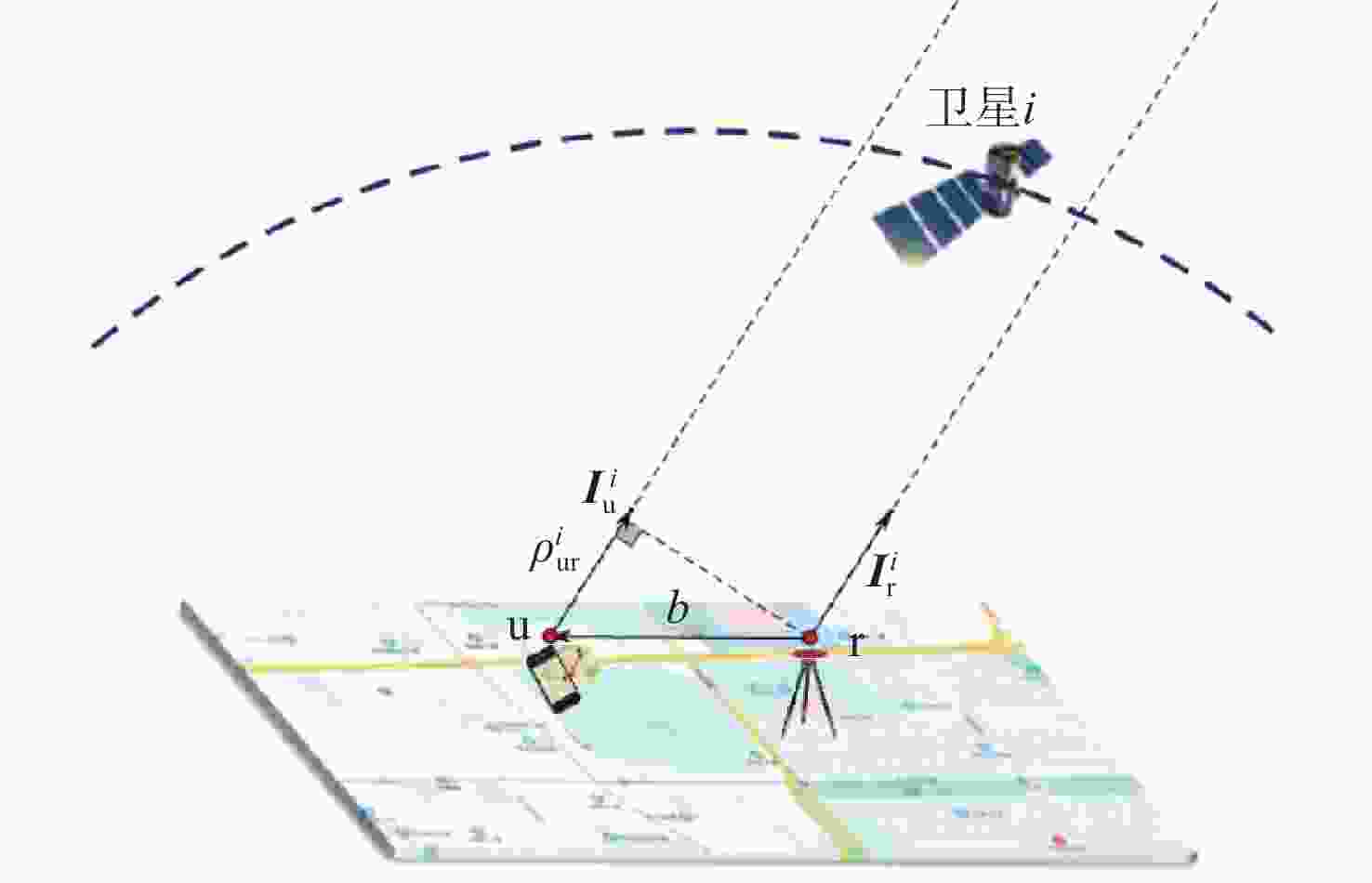
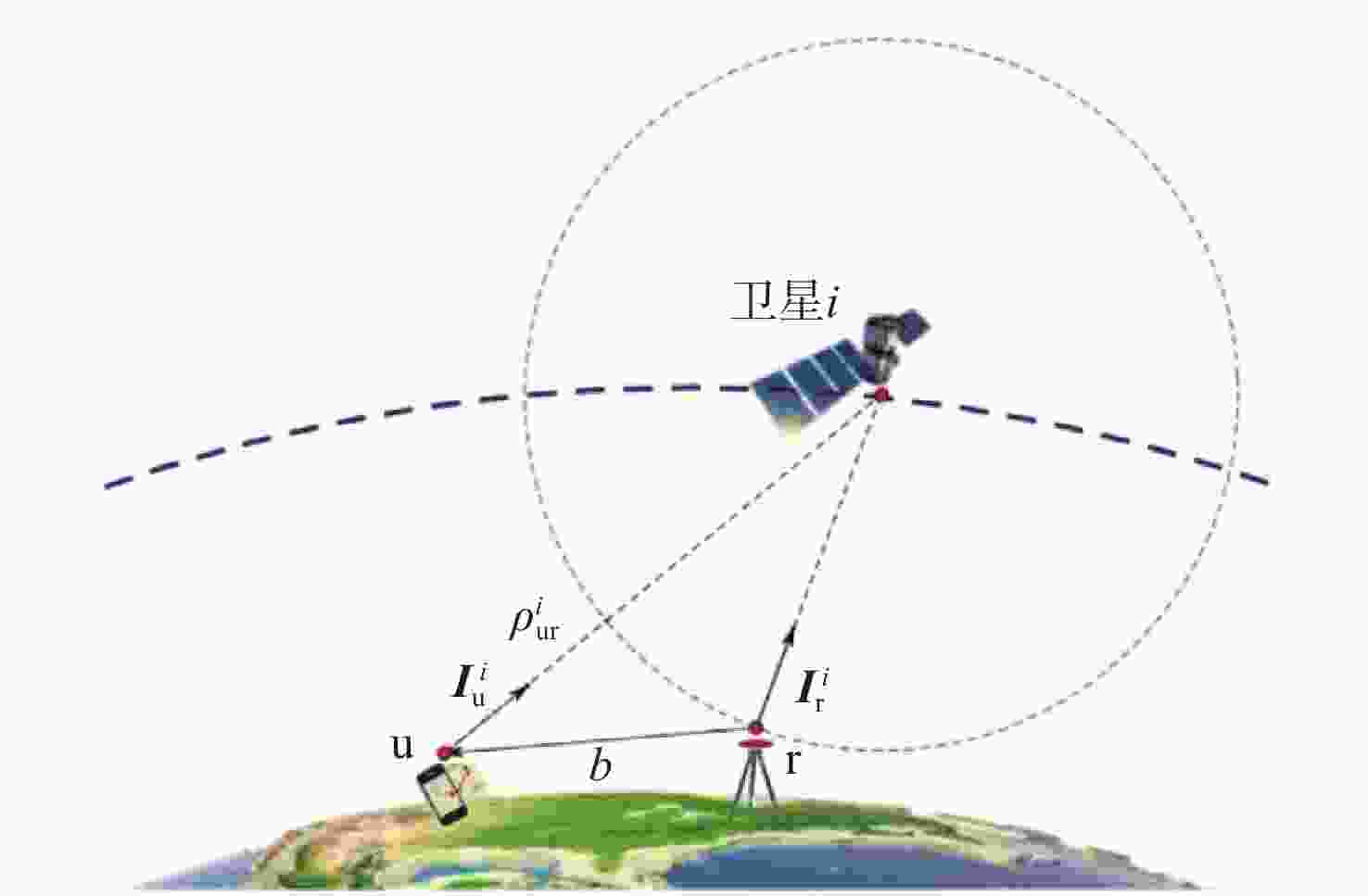
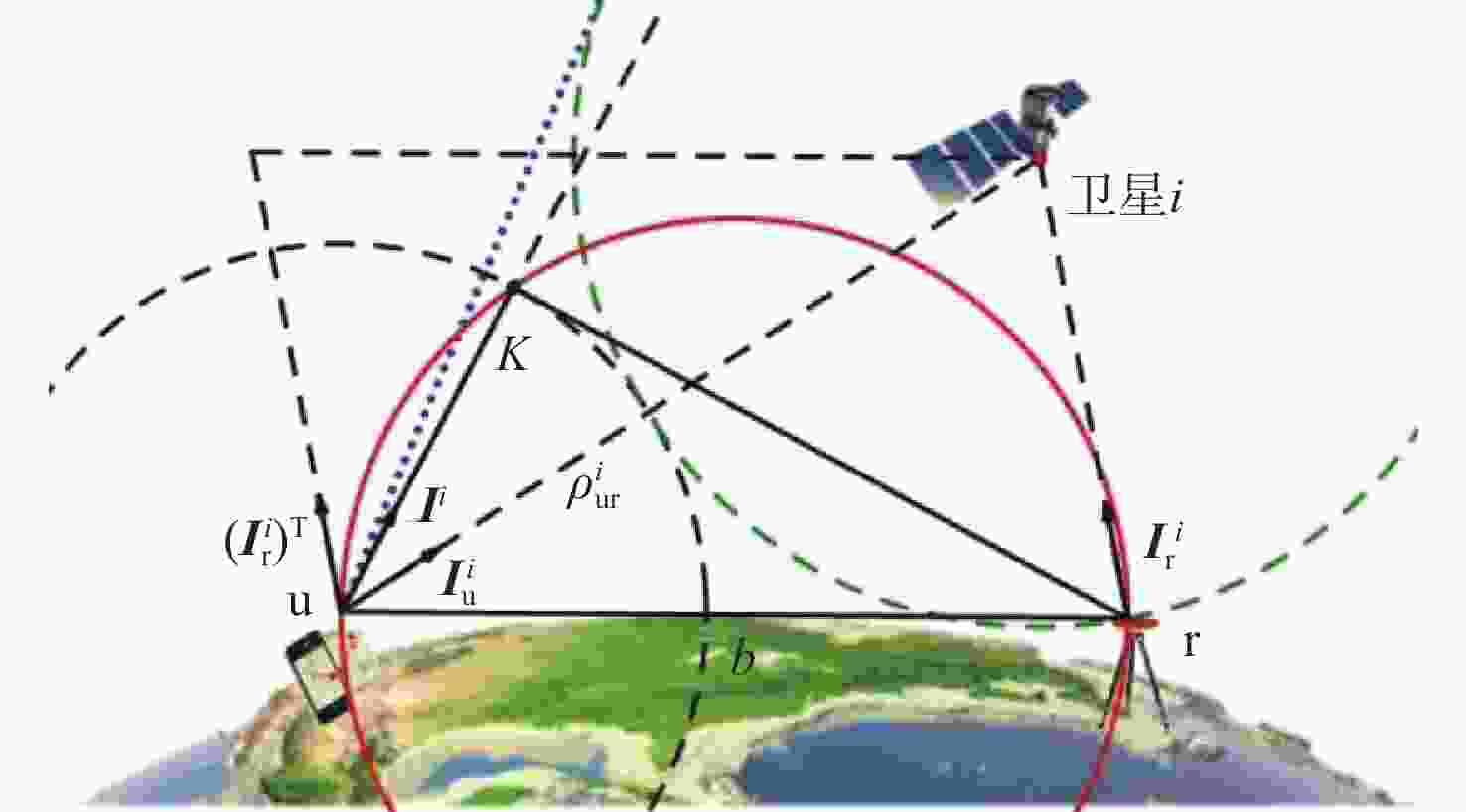
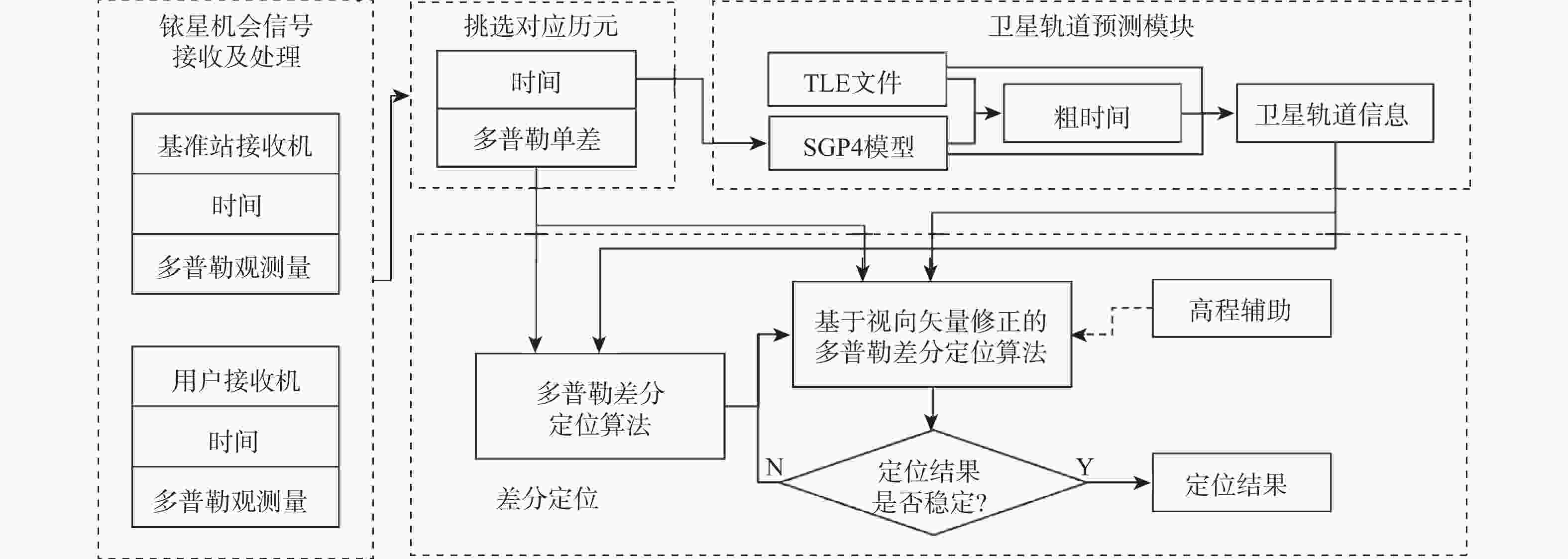
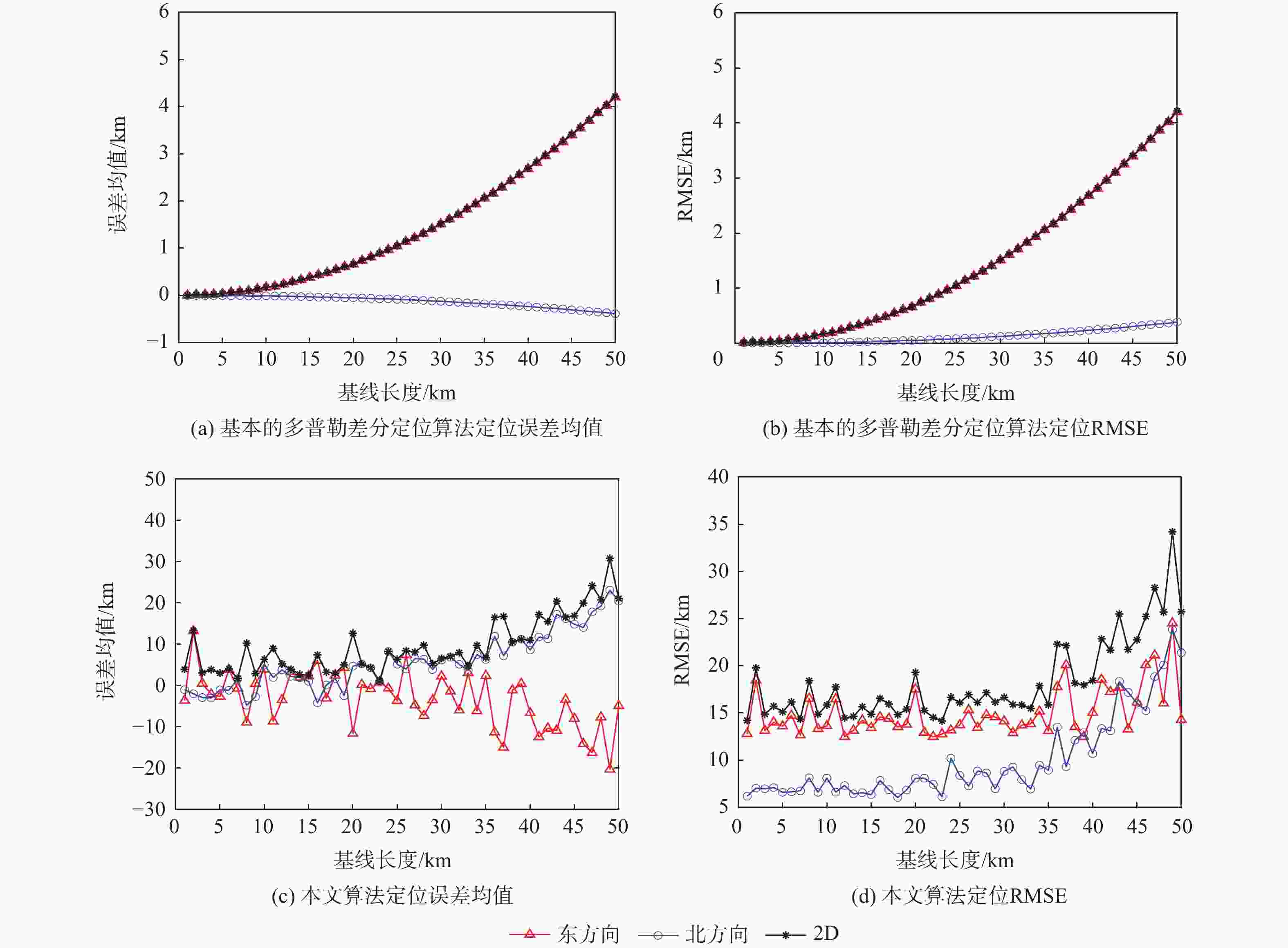
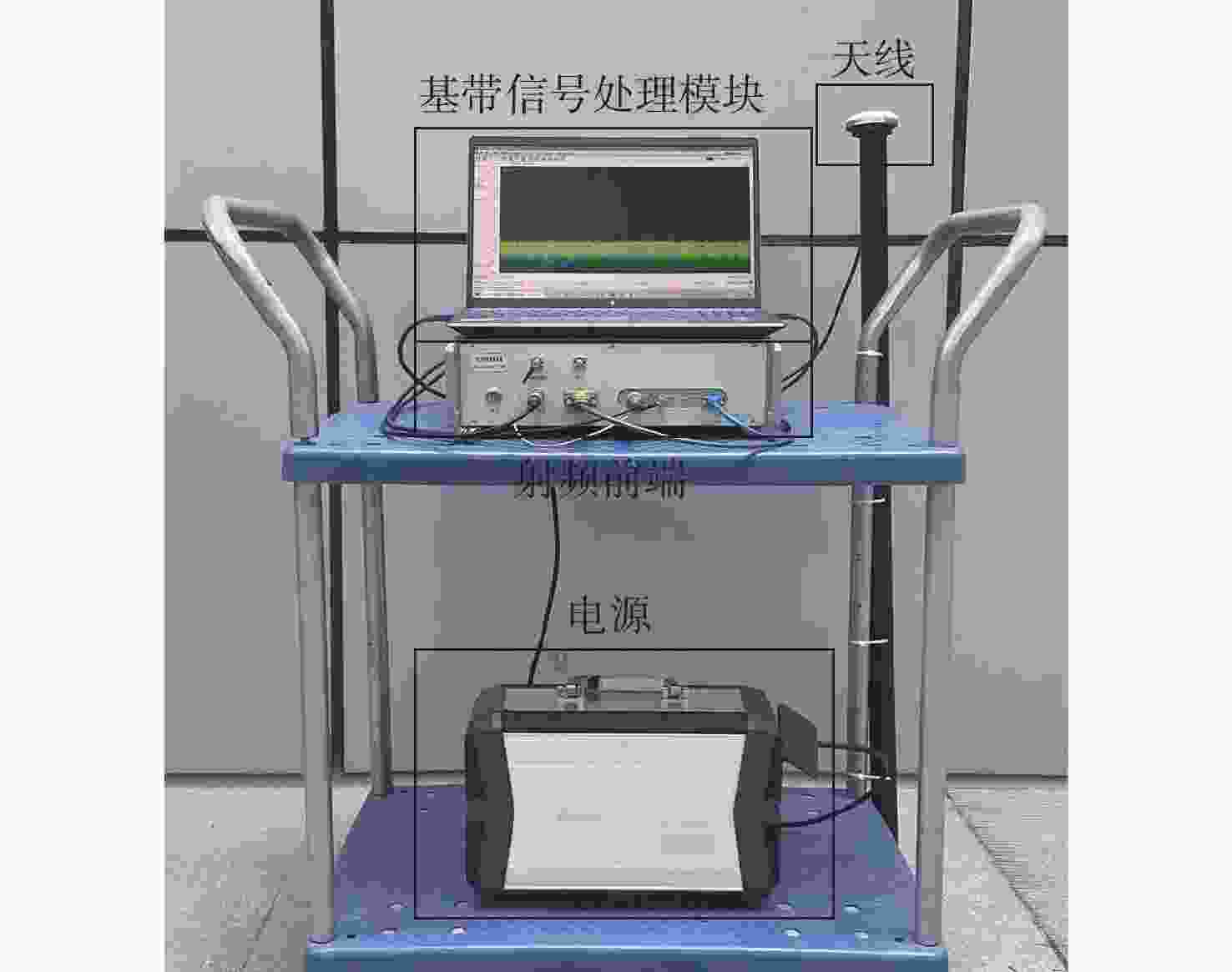
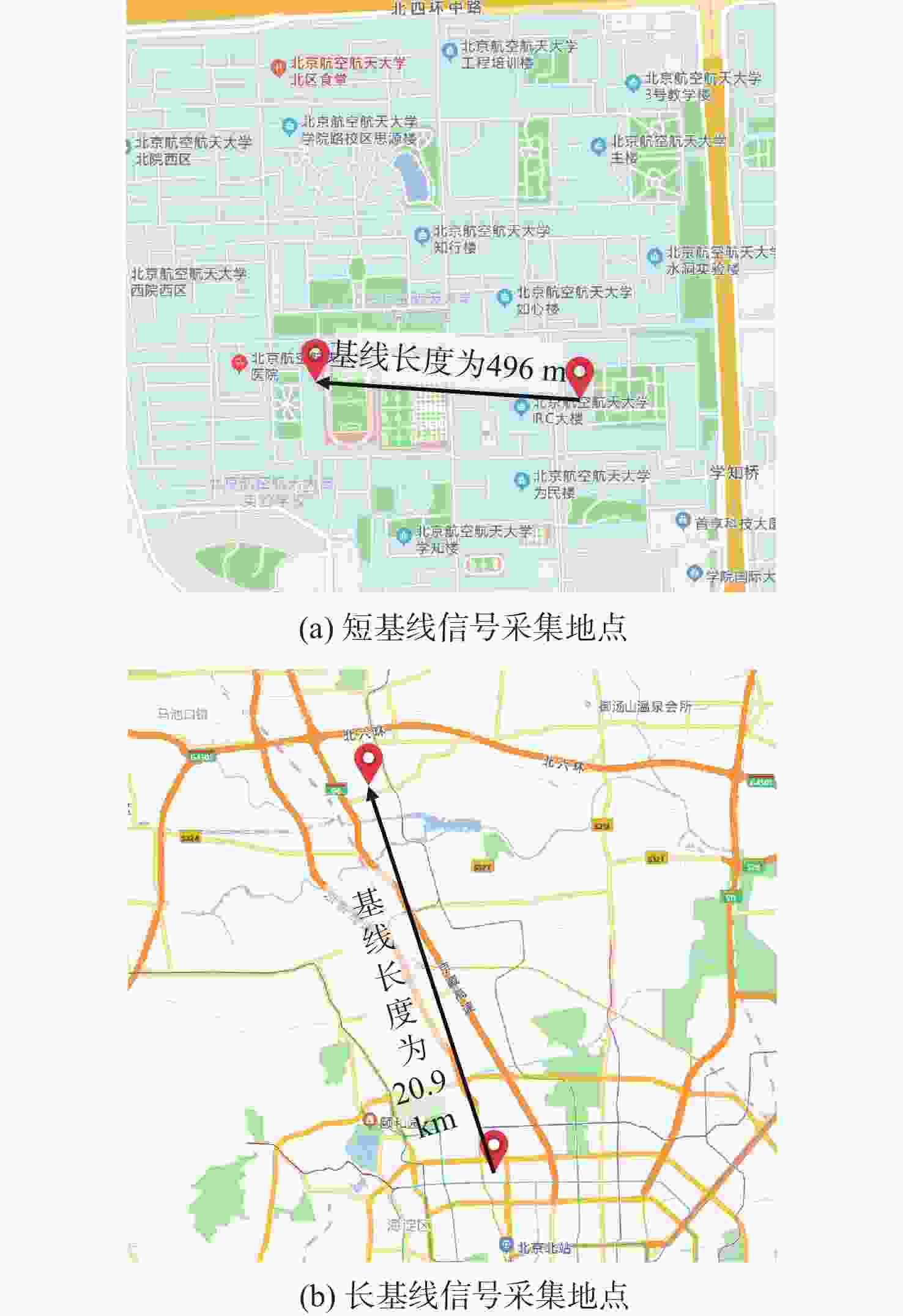
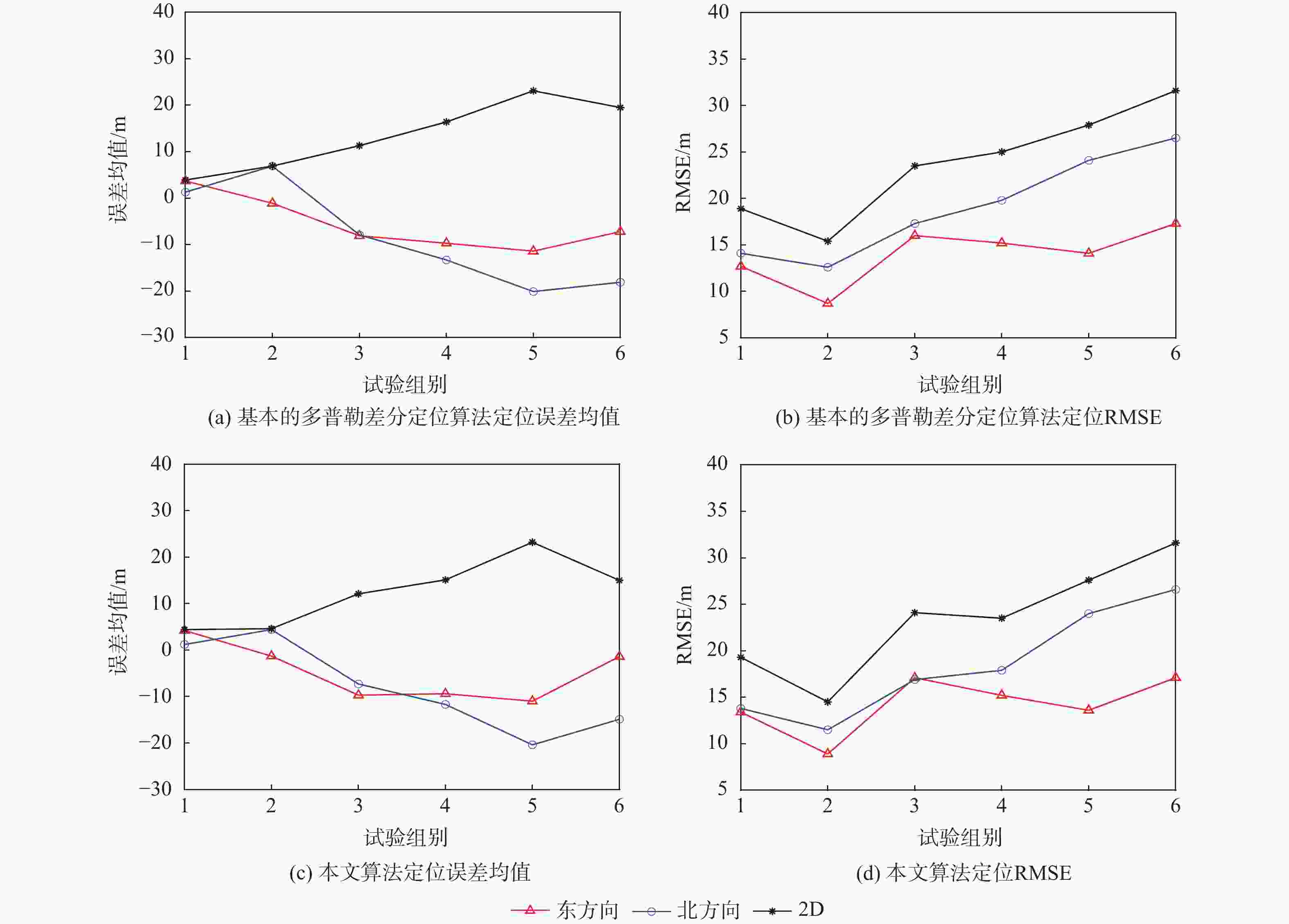
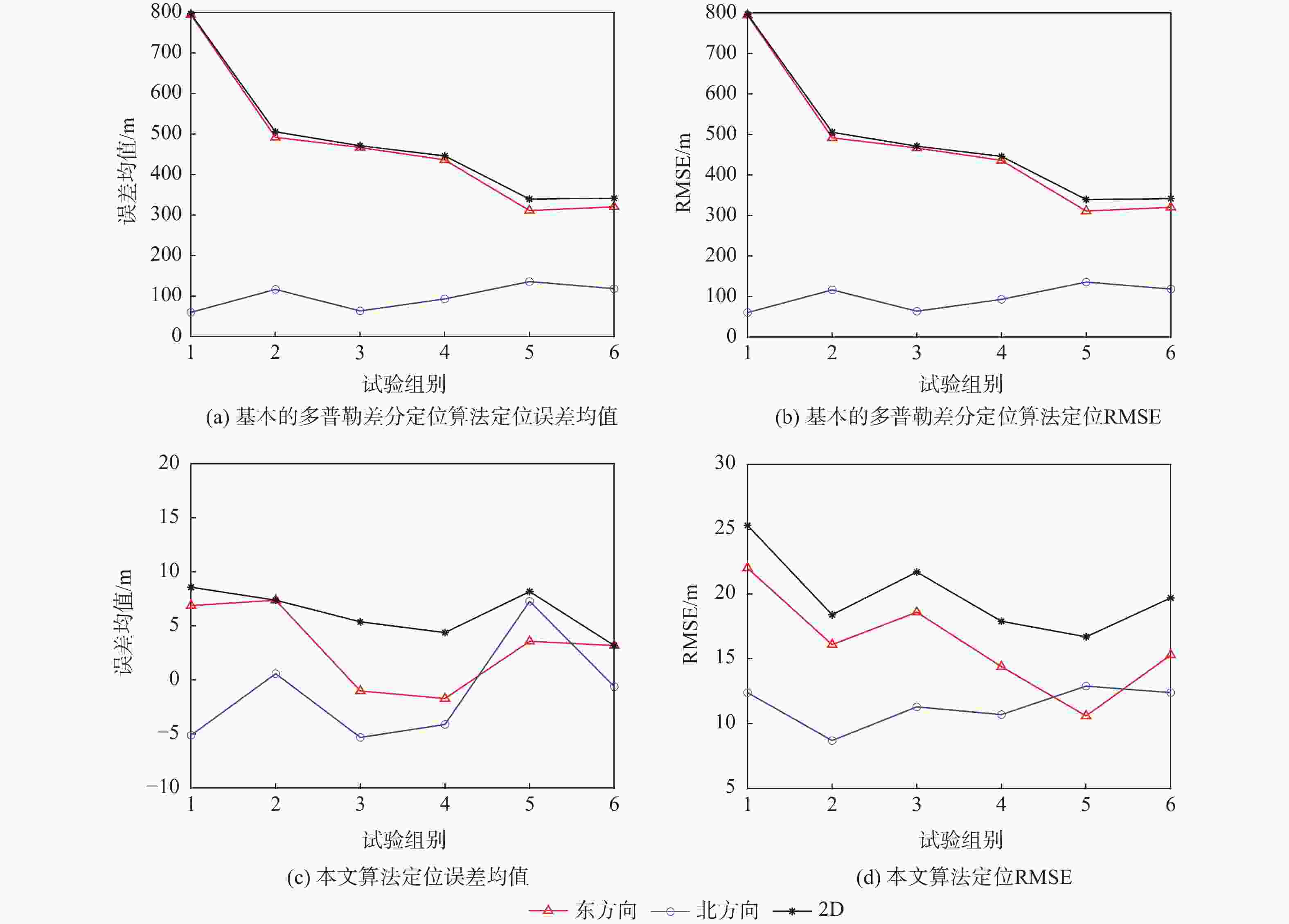
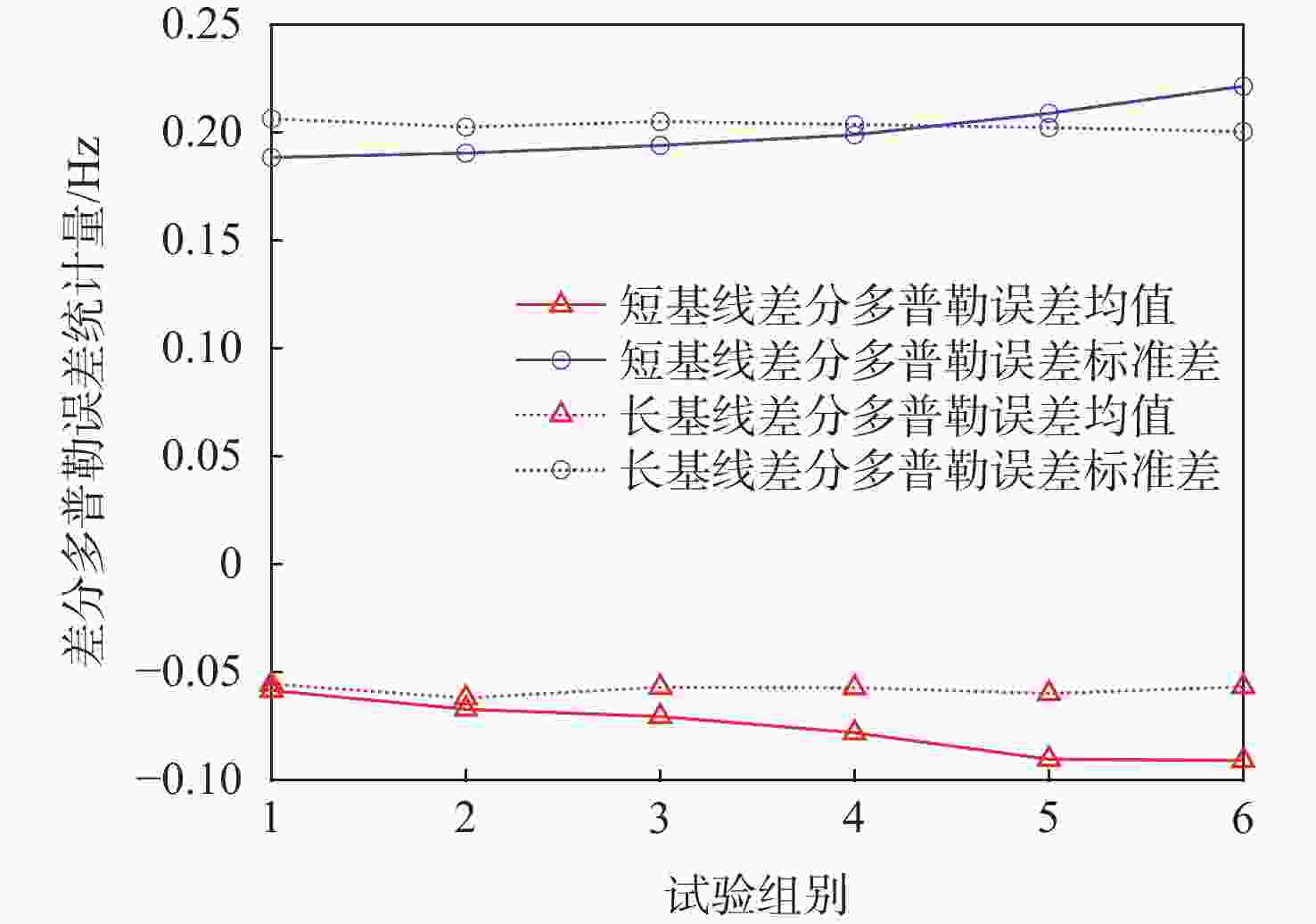
低地球轨道(LEO)卫星机会信号定位技术是全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)的有效补充和备份定位手段。LEO卫星机会信号定位误差主要因素是具有时空相关性的卫星星历和星钟误差,差分定位方法虽然可以有效降低该误差,但LEO卫星轨道较低使长基线定位误差仍然较大。针对这一问题,提出基于视向矢量修正的多普勒差分定位算法。通过仿真试验验证了在长基线情况下所提算法的定位精度明显优于基本算法,同时利用实际铱星信号多普勒差分定位试验验证了所提算法的有效性。
Abstract:Positioning technology based on signals of opportunity (SOP) from low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites is an effective complement and backup positioning solution of global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The major sources of errors to be considered in the positioning technology based on SOPs from LEO satellites are ephemeris and satellite clock errors with space-time relevance. Although the differential positioning technology can effectively reduce the above-mentioned errors, positioning error is still large in the long baseline positioning scenario due to the low orbit of the satellites. To address the afore-mentioned challenge, a differential positioning algorithm with Doppler measurements based on lines of sight correction is proposed. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has significantly better positioning accuracy than the basic algorithm in long baseline positioning experiments, and the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified by differential positioning experiments with Doppler measurements using actual signals from Iridium satellites.
-
Key words:
- signal of opportunity /
- Iridium satellite /
- long baseline /
- differential positioning /
- Doppler
-
-
[1] 秦红磊, 谭滋中, 丛丽, 等. 基于ORBCOMM卫星机会信号的定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(11): 1999-2006.QIN H L, TAN Z Z, CONG L, et al. Positioning technology based on ORBCOMM signals of opportunity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(11): 1999-2006(in Chinese). [2] LEVANON N. Quick position determination using 1 or 2 LEO satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(3): 736-754. doi: 10.1109/7.705883 [3] REID T, NEISH A M, WALTER T F, et al. Leveraging commercial broadband LEO constellations for navigation[C]//Proceedings of the 29th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Portland : Institute of Navigation, 2016: 2300-2314. [4] BENZERROUK H, NGUYEN Q, FANG X X, et al. LEO satellites based Doppler positioning using distributed nonlinear estimation[J]. IFAC, 2019, 52(12): 496-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.11.292 [5] BENZERROUK H, NGUYEN Q, FANG X X, et al. Alternative PNT based on iridium next LEO satellites doppler/INS integrated navigation system[C]//Proceedings of the 26th Saint Petersburg International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-10. [6] MORALES J J, KHALIFE J, CRUZ U S, et al. Orbit modeling for simultaneous tracking and navigation using LEO satellite signals[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation . Portland : Institute of Navigation, 2019: 2090-2099. [7] KHALIFE J J, KASSAS Z M. Receiver design for Doppler positioning with Leo satellites[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5506-5510. [8] MORALES J, KHALIFE J, KASSAS Z M. Simultaneous tracking of orbcomm LEO satellites and inertial navigation system aiding using Doppler measurements[C]//Proceedings of the 89th Vehicular Technology Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-6. [9] ARDITO C T, MORALES J J, KHALIFE J, et al. Performance evaluation of navigation using LEO satellite signals with periodically transmitted satellite positions[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation. Portland : Institute of Navigation, 2019: 206-318. [10] 秦红磊, 谭滋中, 丛丽, 等. 基于铱星机会信号的定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(9): 1691-1699.QIN H L, TAN Z Z, CONG L, et al. Positioning technology based on IRIDIUM signals of opportunity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(9): 1691-1699 (in Chinese). [11] 秦红磊, 赵超, 杜岩松, 等. 基于铱星/INS组合定位技术在船舶中的应用研究[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2020, 7(2): 35-41.QIN H L, ZHAO C, DU Y S, et al. Research on the application of iridium/INS integrated positioning technology in ship[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2020, 7(2): 35-41 (in Chinese). [12] 秦红磊, 李志强, 赵超. Iridium/ORBCOMM机会信号融合定位技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(10): 1845-1853.QIN H L, LI Z Q, ZHAO C. Fusion positioning based on Iridium /ORBCOMM signals of opportunity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(10): 1845-1853 (in Chinese). [13] LENG M, QUITIN F, TAY W P, et al. Anchor-aided joint localization and synchronization using SOOP: Theory and experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(11): 7670-7685. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2606099 [14] KHALIFE J, KASSAS Z M. Assessment of differential carrier phase measurements from orbcomm LEO satellite signals for opportunistic navigation[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Portland : Institute of Navigation, 2019: 4053-4063. [15] KHALIFE J, NEINAVAIE M, KASSAS Z M. Navigation with differential carrier phase measurements from megaconstellation LEO satellites[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1393-1404. [16] BRUNT P. Iridium-overview and status[J]. Space Communications, 1996, 14(2): 61-68. [17] 闵士权. 卫星通信系统工程设计与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 352-361.MIN S Q. Engineering design and application of satellite communication system[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2015: 352-361 (in Chinese). [18] 孙桂宇, 秦红磊, 赵超. 基于铱星机会信号定位的首次定位时间研究[C]//第十一届中国卫星导航年会论文集——S13自主导航. 北京: CSNO-AEC, 2020: 39-45.SUN G Y, QIN H L, ZHAO C. Research on time to first fix of a space-based positioning technology based on Iridium signals of opportunity[C]//Proceedings of the 11st China Satellite Navigation Conference-S13 Technologies for Navigation of Autonomous Systems. Beijing: CSNO-AEC, 2020: 39-45 (in Chinese). [19] 谢钢. GPS原理与接收机设计[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017.XIE G. Principles of GPS and receiver design[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017 (in Chinese). [20] 王萌, 马利华, 张丽荣, 等. 区域定位系统中高程辅助三星定位算法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2012, 46(10): 1647-1651.WANG M, MA L H, ZHANG L R, et al. Three-satellite positioning algorithm with altitude aiding for regional navigation satellite system[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2012, 46(10): 1647-1651 (in Chinese). [21] 孙靖, 胡松杰, 平劲松. 低轨道空间目标TLE及SGP4轨道计算精度分析[C]//测绘科学前沿技术论坛摘要集. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2008: 692-696.SUN J, HU S J, PING J S. Analysis on orbit calculation accuracy of low orbit space target TLE and SGP4 model[C]//Proceedings of Forum on Frontier Technology of Surveying and Mapping Science. Beijing: Sinomap Press, 2008: 692-696(in Chinese). -






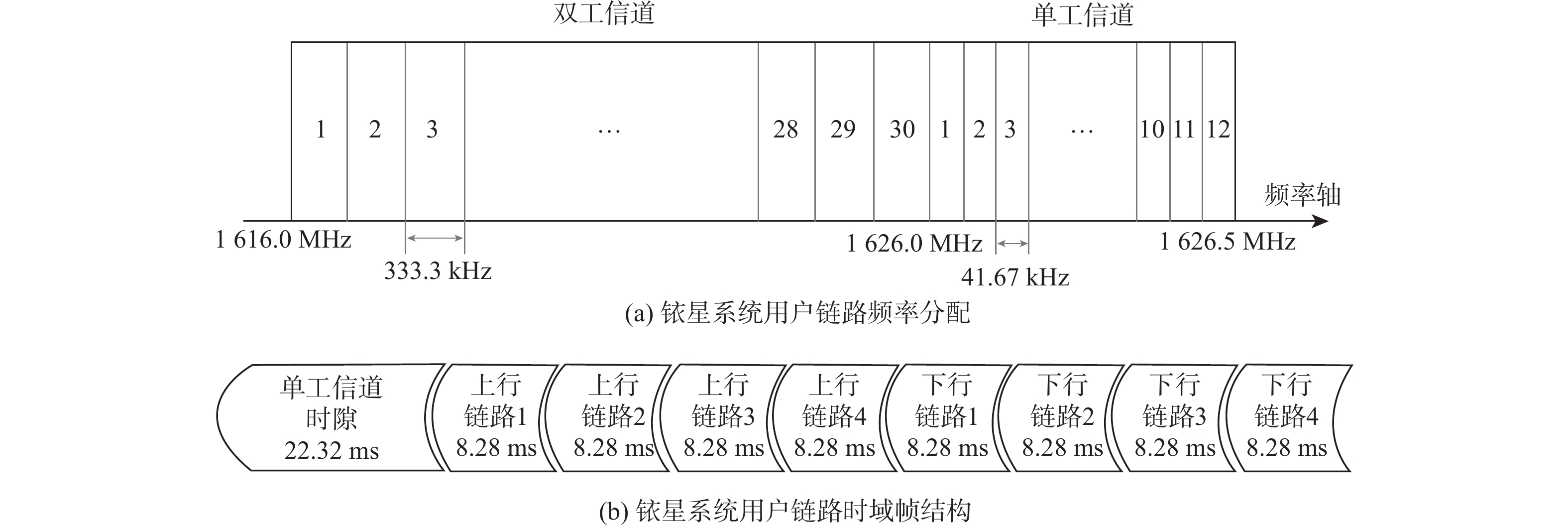
 下载:
下载: