Robust adaptive position algorithm for GNSS/IMU based on pseudorange residual and innovation
-
摘要:
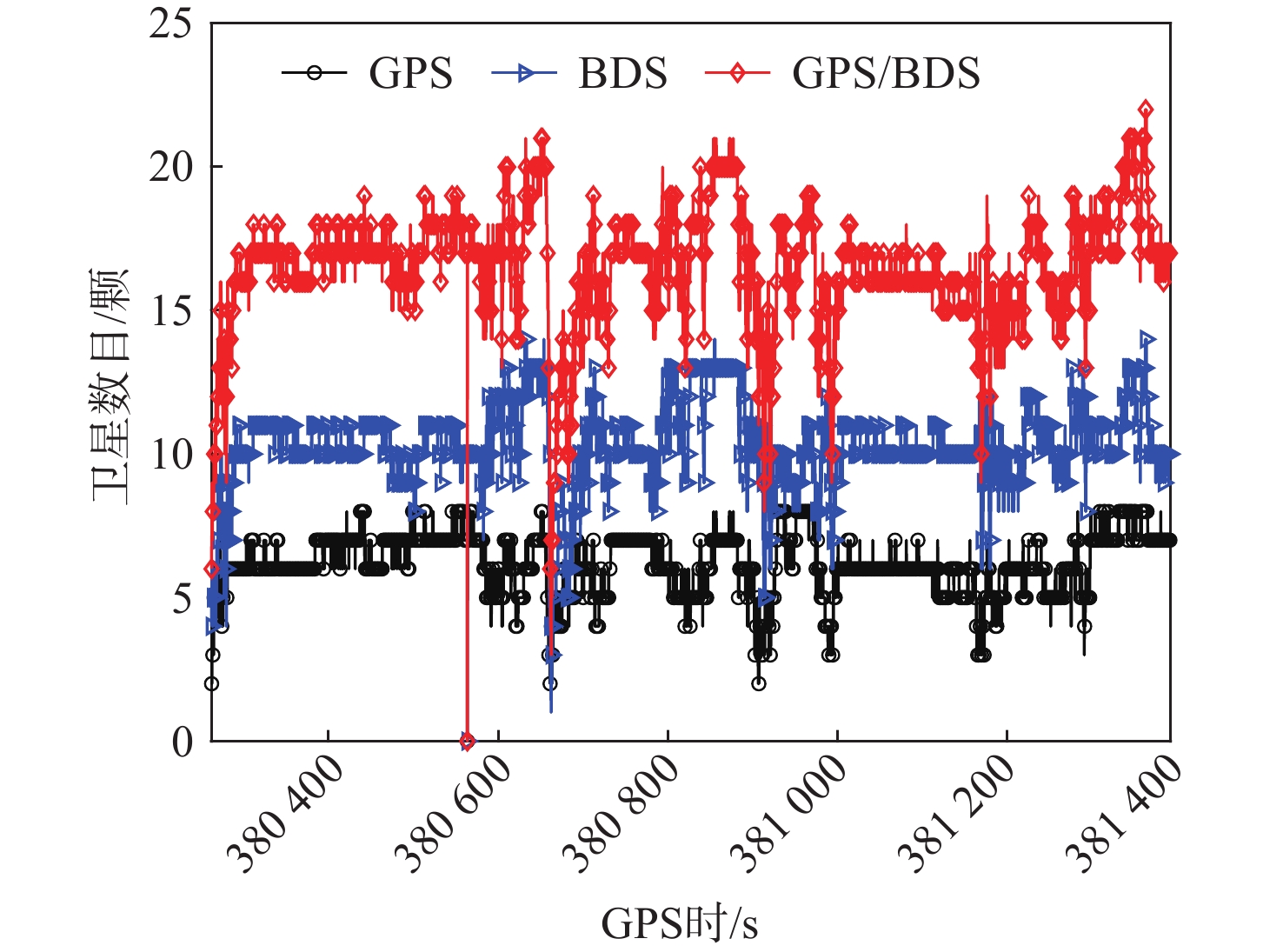
在全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)和惯性测量元件(IMU)组合导航系统中,抗差滤波和自适应滤波常被用于提高组合导航的定位精度。但是抗差滤波和自适应滤波所适用的条件不同,使用不当反而可能会降低组合导航的定位精度,针对此问题,提出基于伪距残差和新息的GNSS/IMU抗差自适应定位算法。所提算法基于伪距残差评估GNSS的定位质量,选择合适的滤波算法进行GNSS/IMU组合导航解算。在长时间GNSS定位质量较差时,基于新息和伪距残差判断是否IMU运动学推算误差大于GNSS观测值误差,从而根据判断的结果选择是否采用抗差因子。结果表明:所提算法相对于扩展卡尔曼滤波算法在东、北和天方向上分别提高36.05%、22.71%和56.22%的定位精度。
-
关键词:
- 伪距残差 /
- 新息 /
- 抗差滤波 /
- 自适应滤波 /
- GNSS/IMU组合导航
Abstract:Algorithms of robust filtering and adaptive filtering are commonly used to improve the positioning accuracy of the navigation system integrating global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and inertial measurement units (IMU). However, the conditions applicable to robust filtering and adaptive filtering are different, and improper use of the filter may reduce the positioning accuracy of the integrated system. To solve this problem, a robust adaptive position algorithm for GNSS/IMU is proposed based on pseudorange residual and innovation. The positioning quality of GNSS is evaluated based on pseudorange residuals. The appropriate filtering algorithm is selected to solve the GNSS/IMU integrated navigation. Innovation and pseudorange residuals are then used to determine whether the IMU kinematic estimation error is greater than the GNSS observation error in long-time low quality GNSS. The robust factor is used based on the determined results. Experimental results show that the positioning accuracy of the proposed algorithm is improved by 36.05%, 22.71%, and 56.22% in the east, north and up directions, respectively, compared with the results from the extended Kalman filter algorithm.
-
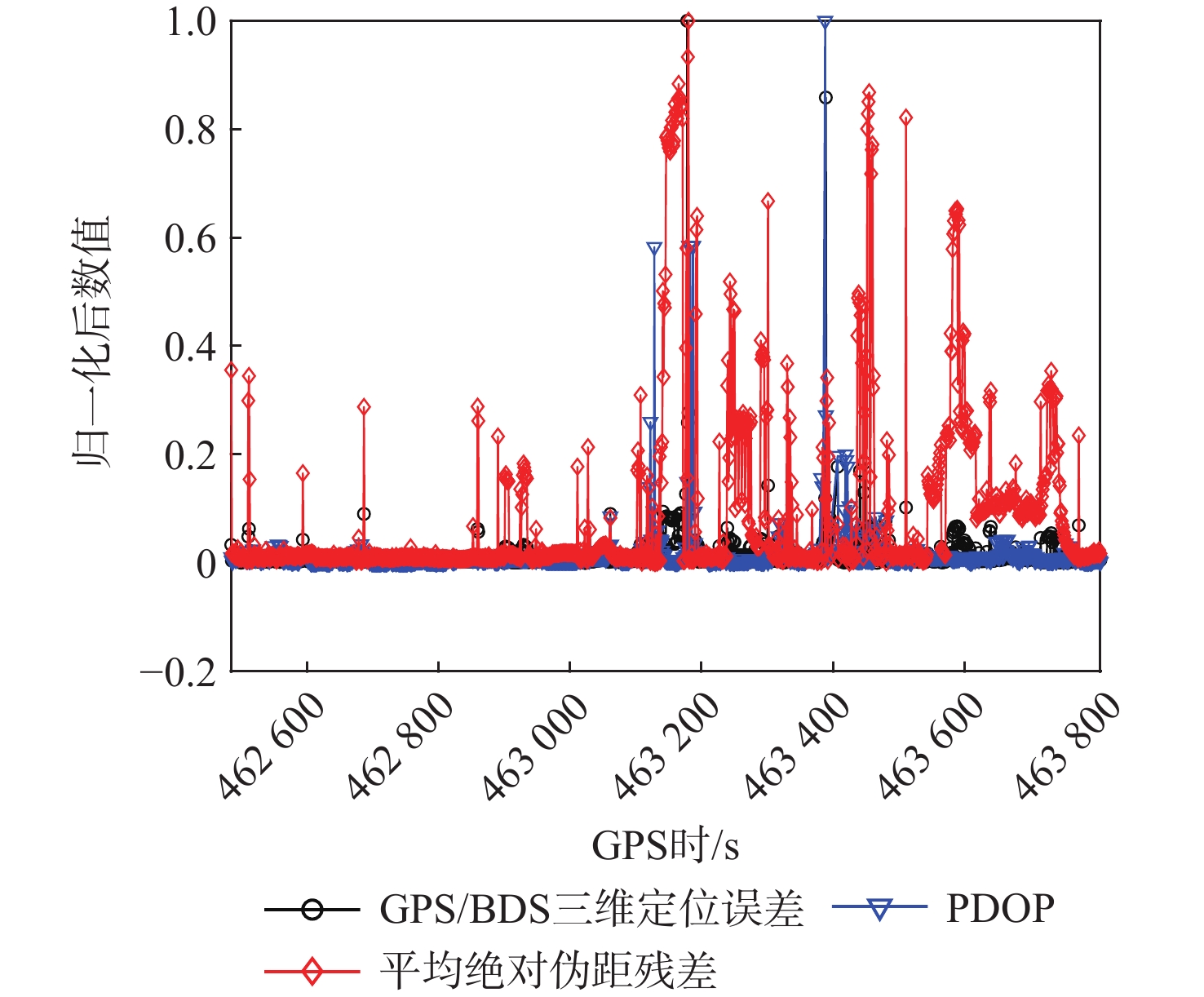
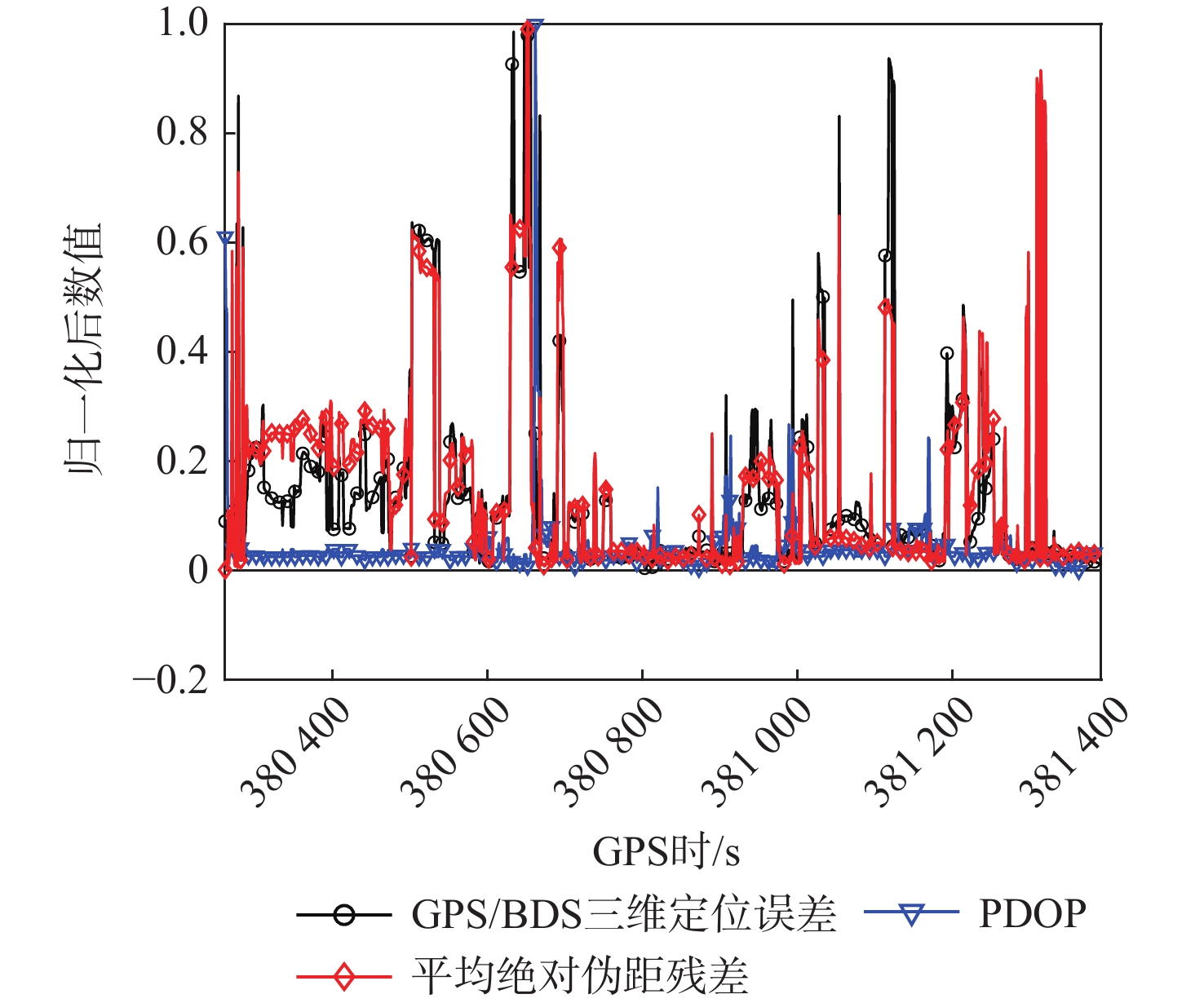
表 1 实验1中斯皮尔曼等级相关系数
Table 1. Spearman rank correlation coefficients in experiment 1
PDOP与GPS/BDS
三维定位误差平均绝对伪距残差与
GPS/BDS三维定位误差−0.03 0.58 表 2 实验2中斯皮尔曼等级相关系数
Table 2. Spearman rank correlation coefficients in experiment 2
PDOP与GPS/BDS
三维定位误差平均绝对伪距残差与GPS/BDS
三维定位误差−0.24 0.91 |ρ| 相关程度 0.00~0.19 很弱 0.20~0.39 弱 0.40~0.59 中等 0.60~0.79 强 0.80~1.0 很强 表 5 实验1中各算法均方根误差
Table 5. Root mean square error of each algorithm in experiment 1
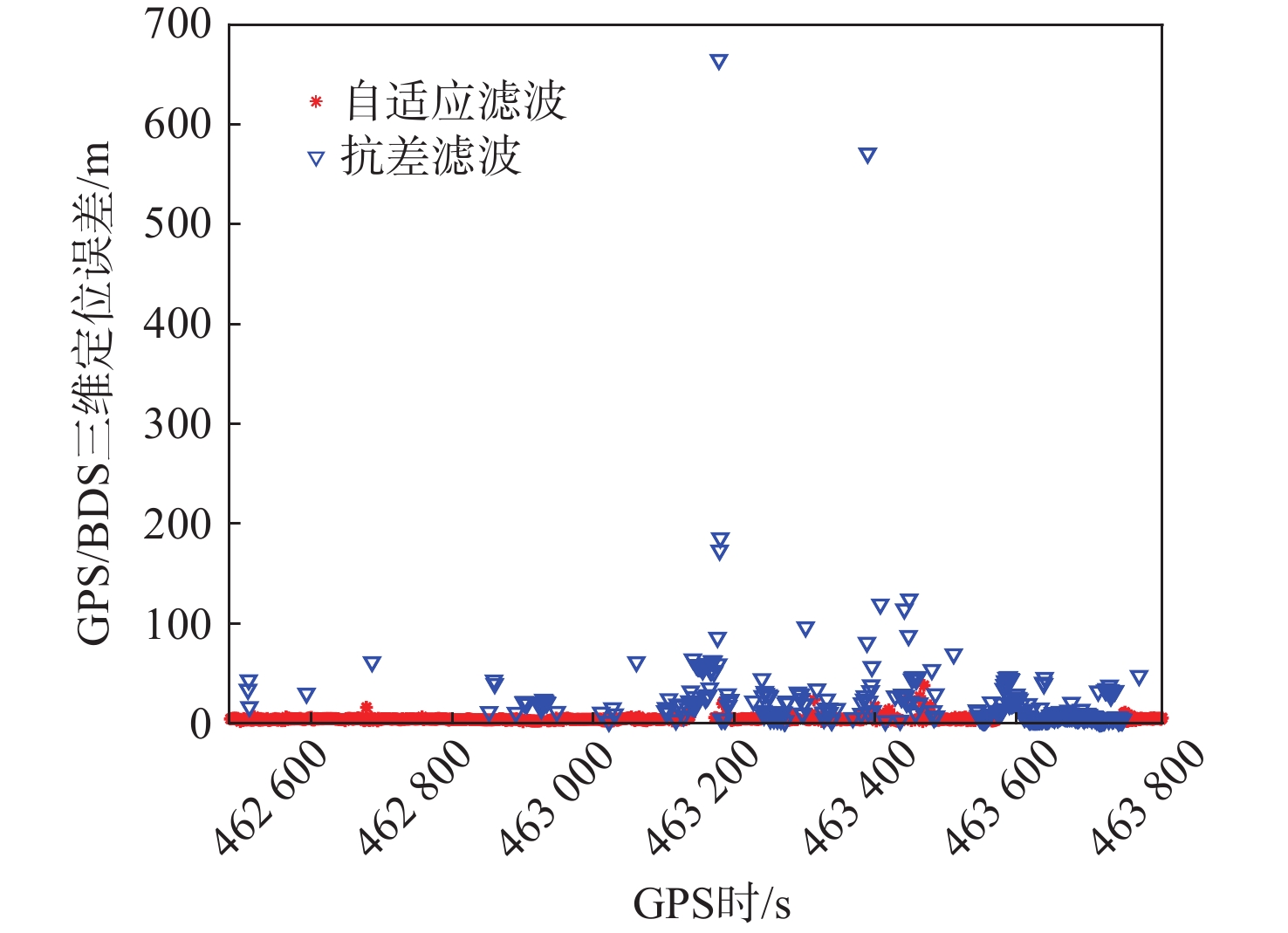
m 算法 东 北 天 2D 3D 扩展卡尔曼滤波算法 7.99 6.12 9.64 10.06 13.94 抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波算法 9.40 6.80 5.27 11.60 12.74 算法1 5.13 4.80 4.19 7.03 8.18 本文算法 5.11 4.73 4.22 6.96 8.14 表 4 实验1中本文算法滤波类型选择结果
Table 4. Selection results of the proposed algorithm filter type in Experiment 1
滤波类型 采用该滤波的
总时长/sGPS/BDS三维定位
误差平均值/mGPS/BDS三维定位
误差中位数/m自适应滤波 911 4.22 3.88 抗差滤波 399 23.26 11.36 表 6 实验1中各算法相对于扩展卡尔曼滤波提升率
Table 6. Improvement rate of each algorithm relative to extended Kalman filter in Experiment 1
% 算法 东 北 天 2D 3D 抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波算法
卡尔曼滤波算法−17.65 −11.11 45.33 −15.27 8.57 算法1 35.79 21.57 56.54 30.20 41.30 本文算法 36.05 22.71 56.22 30.82 41.58 表 8 实验2中各算法均方根误差
Table 8. Root mean square error of each algorithm in experiment 2
m 算法 东 北 天 2D 3D 扩展卡尔曼滤波算法 6.48 4.42 13.66 7.84 15.75 抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波算法 7.72 4.82 12.60 9.10 15.54 算法1 6.10 4.20 11.14 7.40 13.37 本文算法 5.84 4.30 8.73 7.25 11.35 表 7 实验2中本文算法滤波类型选择结果
Table 7. The proposed algorithm filter type selection results in experiment 2
滤波类型 采用该滤波的
总时长/sGPS/BDS三维定位
误差平均值/mGPS/BDS三维
定位误差中位数/m自适应滤波 537 2.97 2.44 抗差滤波 593 17.82 11.36 表 9 实验2中各算法相对于扩展卡尔曼滤波提升率
Table 9. Improvement rate of each algorithm relative to extended Kalman filter in experiment 2
% 算法 东 北 天 2D 3D 抗差扩展卡尔曼滤波算法 −19.14 −9.05 7.76 −16.03 1.32 算法1 5.86 4.98 18.45 5.58 15.08 本文算法 9.88 2.71 36.09 7.54 27.95 -
[1] YANG L, LI Y, WU Y L, et al. An enhanced MEMS-INS/GNSS integrated system with fault detection and exclusion capability for land vehicle navigation in urban areas[J]. GPS Solutions, 2014, 18(4): 593-603. doi: 10.1007/s10291-013-0357-1 [2] LI B X, CHEN G W, SI Y B, et al. GNSS/INS integration based on machine learning lightGBM model for vehicle navigation[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(11): 5565. doi: 10.3390/app12115565 [3] YUE S,CONG L, QIN H L, et al. A robust fusion methodology for MEMS-based land vehicle navigation in GNSS-Challenged environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 44087-44099. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2977474 [4] LYU Z T, GAO Y. An SVM based weight scheme for improving kinematic GNSS positioning accuracy with low-cost GNSS receiver in urban environments[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(24): 7265. doi: 10.3390/s20247265 [5] ZHANG G H, XU P H, XU H S, et al. Prediction on the urban GNSS measurement uncertainty based on deep learning networks with long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(18): 20563-20577. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3098006 [6] SUN R, HSU L T, XUE D B, et al. GPS signal reception classification using adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy inference system[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2019, 72(3): 685-701. doi: 10.1017/S0373463318000899 [7] WANG J, HAN H Z, MENG X L, et al. Robust wavelet-based inertial sensor error mitigation for tightly coupled GPS/BDS/INS integration during signal outages[J]. Survey Review, 2017, 49(357): 419-427. doi: 10.1080/00396265.2016.1190162 [8] CHANG G B. Robust Kalman filtering based on Mahalanobis distance as outlier judging criterion[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2014, 88(4): 391-401. doi: 10.1007/s00190-013-0690-8 [9] ZHANG Q, NIU X J, SHI C. Impact assessment of various IMU error sources on the relative accuracy of the GNSS/INS systems[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(9): 5026-5038. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2966379 [10] 杨元喜. 动态系统的抗差Kalman滤波[J]. 解放军测绘学院学报, 1997, 14(2): 79-84.YANG Y X. Robust Kalman filter for dynamic systems[J]. Journal of the PLA Institute of Surveying and Mapping, 1997, 14(2): 79-84(in Chinese). [11] 王坚, 刘超, 高井祥, 等. 基于抗差EKF的GNSS/INS紧组合算法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2011, 36(5): 596-600.WANG J, LIU C, GAO J X, et al. GNSS/INS tightly coupled navigation model based on robust EKF[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(5): 596-600(in Chinese). [12] JIANG C, ZHANG S B, LI H, et al. Performance evaluation of the filters with adaptive factor and fading factor for GNSS/INS integrated systems[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(4): 130-141. doi: 10.1007/s10291-021-01165-4 [13] 吴富梅, 杨元喜. 基于小波阈值消噪自适应滤波的GPS/INS组合导航[J]. 测绘学报, 2007, 36(2): 124-128.WU F M, YANG Y X. GPS/INS integrated navigation by adaptive filtering based on wavelet threshold denoising[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2007, 36(2): 124-128(in Chinese). [14] GAO B B, HU G G, ZHONG Y M, et al. Cubature Kalman filter with both adaptability and robustness for tightly-coupled GNSS/INS integration[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(13): 14997-15011. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3073963 [15] CHANG G B. Kalman filter with both adaptivity and robustness[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(3): 81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2013.12.017 [16] YANG Y, HE H, XU G. Adaptively robust filtering for kinematic geodetic positioning[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2001, 75(2-3): 109-116. doi: 10.1007/s001900000157 [17] 杨元喜, 任夏, 许艳. 自适应抗差滤波理论及应用的主要进展[J]. 导航定位学报, 2013, 1(1): 9-15.YANG Y X, REN X, XU Y. Main progress of adaptively robust filter with applications in navigation[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2013, 1(1): 9-15(in Chinese). [18] 谭兴龙, 王坚, 韩厚增. 支持向量回归辅助的GPS/INS组合导航抗差自适应算法[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(6): 590-597.TAN X L, WANG J, HAN H Z. SVR aided adaptive robust filtering algorithm for GPS/INS integrated navigation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2014, 43(6): 590-597(in Chinese). [19] NING Y P, WANG J, HAN H Z, et al. An optimal radial basis function neural network enhanced adaptive robust Kalman filter for GNSS/INS integrated systems in complex urban areas[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 3091. doi: 10.3390/s18093091 [20] 高为广, 陈谷仓. 结合自适应滤波和神经网络的GNSS/INS抗差组合导航算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2014, 39(11): 1323-1328.GAO W G, CHEN G C. Integrated GNSS/INS navigation algorithms combining adaptive filter with neural network[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(11): 1323-1328(in Chinese). [21] ZHANG C, ZHAO X B, PANG C L, et al. Improved fault detection method based on robust estimation and sliding window test for INS/GNSS integration[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2020, 73(4): 1-21. [22] ATIA M, WASLANDER S. Map-aided adaptive GNSS/IMU sensor fusion scheme for robust urban navigation[J]. Measurement, 2019, 131: 615-627. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.08.050 [23] WANG L, GROVES P, ZIEBART M. Multi-constellation GNSS performance evaluation for urban canyons using large virtual reality city models[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2012, 65(3): 459-476. doi: 10.1017/S0373463312000082 [24] HSU L T, TOKURA H, KUBO N, et al. Multiple faulty GNSS measurement exclusion based on consistency check in urban canyons[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(6): 1909-1917. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2654359 [25] SUN R, FU L X, WANG G Y, et al. Using dual-polarization GPS antenna with optimized adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system to improve single point positioning accuracy in urban canyons[J]. Navigation, 2021, 68(1): 41-60. doi: 10.1002/navi.408 [26] BEST D, ROBERTS D. The upper tail probabilities of Spearman's Rho[J]. Applied Sratistics, 1975, 24(3): 377-379. doi: 10.2307/2347111 -








 下载:
下载: