-
摘要:
针对基于知识的贝叶斯网络(BN)构建方法存在不完全和不精确的缺点,提出一种基于知识引导和数据挖掘的BN结构构建方法。针对单一信号故障诊断结果不精确的问题和故障信息中存在的不确定性问题,将电流信号与振动信号融合建立BN的特征节点,分别提取2种信号的故障特征参数,利用区分度指标法进行特征筛选,将其作为BN结构特征层的节点。将专家知识构建的初始BN结构结合自适应精英结构遗传算法(AESL-GA)进行结构优化,通过自适应限制进化过程中的搜索空间,减少自由参数的数量,提高其全局搜索能力,得到最优BN结构。通过MQY5585溢流型球磨机滚动轴承实测数据和Paderborn University轴承数据集对所提方法进行验证,结果证明了所提方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 贝叶斯网络 /
- 故障诊断 /
- 自适应精英结构遗传算法 /
- 滚动轴承 /
- 信号融合
Abstract:To address the imperfect and imprecise shortcomings of the knowledge-based Bayesian network (BN) construction method, this paper proposes a BN structure construction method based on knowledge guidance and data mining. Firstly, aiming at the problem of inaccurate fault diagnosis results of a single signal and the uncertainty in fault information, the current signal and the vibration signal are fused to establish the characteristic nodes of the BN. The fault characteristic parameters of the two kinds of signals are extracted respectively, and the feature selection is carried out by the distinguish index method, which is used as the node of the feature layer of the BN structure. Secondly, the initial BN structure constructed by expert knowledge is combined with the adaptive elite-based structure learner using genetic algorithm (AESL-GA) to optimize the structure. By adaptively restricting the search space in the evolution process, reducing the number of free parameters and improving its global search ability, we obtain optimal BN structure. Finally, the method is verified by the measured data of the ball mill rolling bearing of Jinchuan Company and the data set of Paderborn University, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 振动信号特征参数D值
Table 1. Characteristic parameter D value of vibration signal
运行工况 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 C1 4.82 3.21 1.77 1.69 1.46 3.44 4.95 1.38 2.15 1.58 C2 3.53 2.37 1.21 1.22 1.80 3.27 3.62 1.44 2.04 2.25 C3 2.51 2.89 2.07 2.73 0.65 2.11 2.20 2.04 1.33 1.31 表 2 电流信号特征参数D值
Table 2. Characteristic parameter D value of current signal
运行工况 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 C1 3.65 2.16 1.87 1.22 1.18 3.31 2.06 1.42 1.14 1.78 C2 2.85 1.69 1.59 2.06 2.25 2.56 1.71 2.16 2.17 1.96 C3 2.14 0.31 2.76 1.14 0.97 2.94 1.95 1.97 1.56 0.65 表 3 推理测试结果
Table 3. Reasoning test results
测试
序号测试故障 与故障相关的
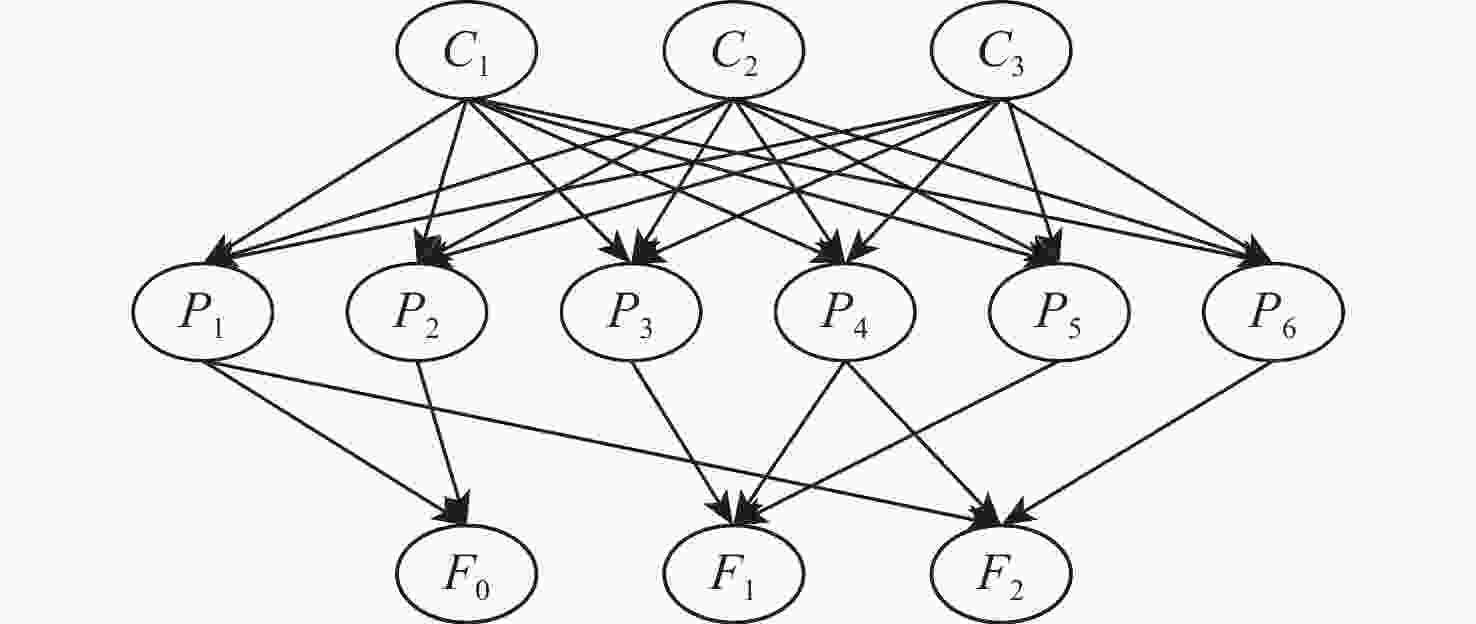
异常征兆故障类型 后验概率% 1 内圈 P3(高),P4(高),P5(低) 内圈故障 94.25 2 外圈 P1(高),P4(低),P6(高) 外圈故障 92.18 3 正常 P1(高),P2(高) 正常状态 97.42 表 4 基于本文方法的球磨机数据故障识别率
Table 4. Fault recognition rate of ball mill data based on the proposed method
工况 故障类型 识别率% C1 正常状态 98.43 内圈故障 97.72 外圈故障 98.55 C2 正常状态 98.56 内圈故障 97.83 外圈故障 98.43 C3 正常状态 98.66 内圈故障 98.17 外圈故障 98.50 表 5 数据集故障描述
Table 5. Dataset fault description
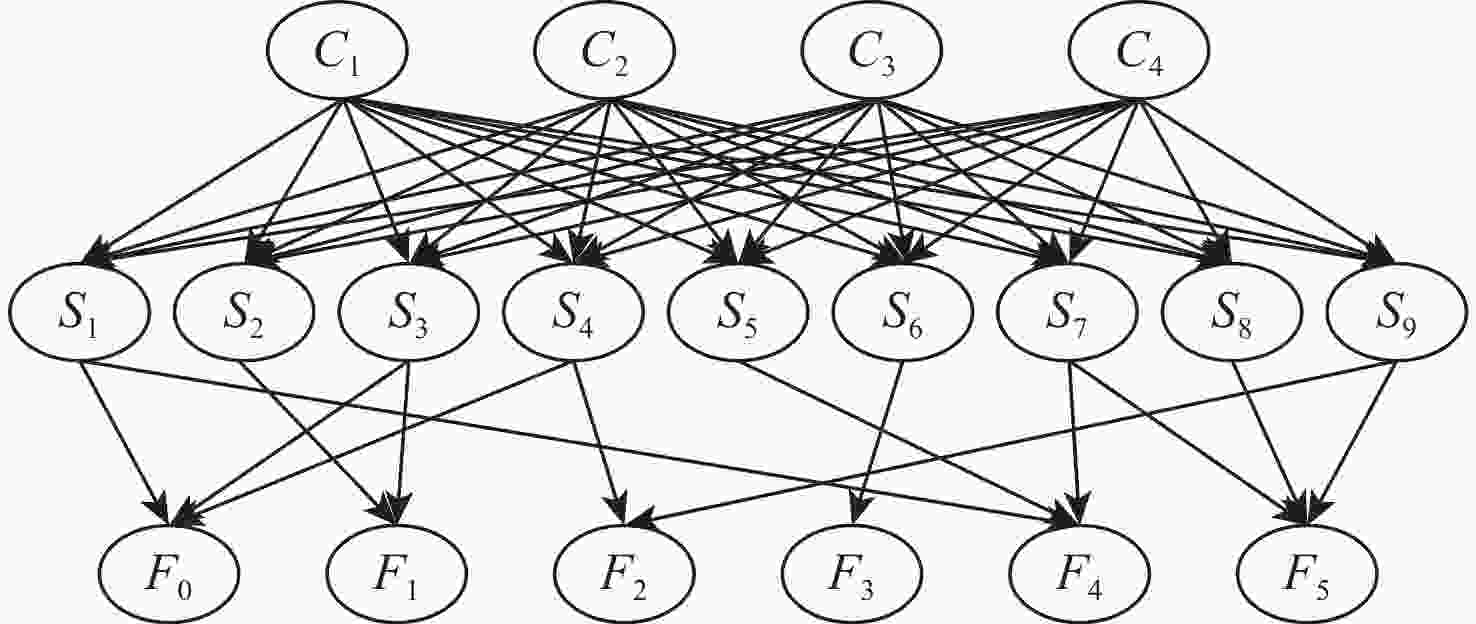
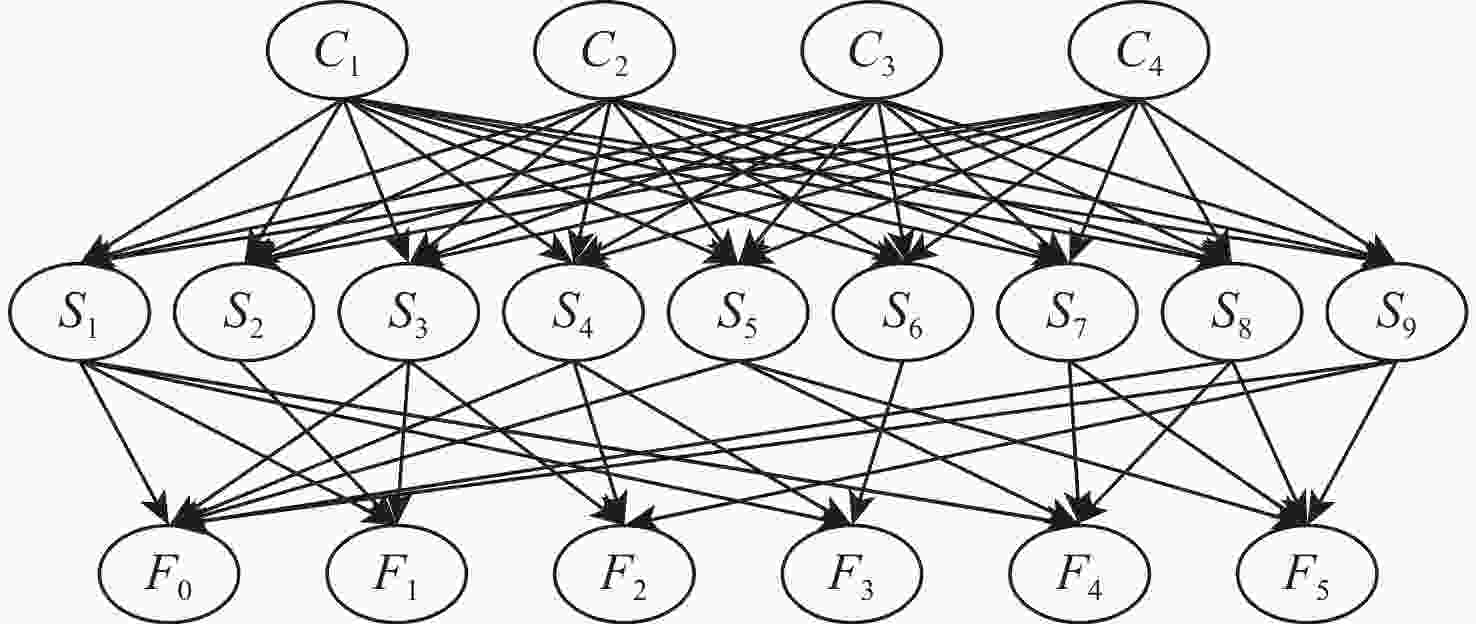
故障节点标签 故障类型 F0 正常(Nor) F1 外圈钻孔(OD) F2 内圈电雕刻(IE),外圈电雕刻(OE) F3 内圈放电沟槽 (IEDM),外圈放电沟槽(OEDM) F4 外圈塑化(OP) F5 内圈点蚀(IFP),外圈点蚀(OFP) 表 6 特征量筛选结果
Table 6. Feature selection results
故障节点标签 筛选出的特征 F0 S1,S3,S4,S5,S8,S9 F1 S1,S2,S3 F2 S3,S4,S9 F3 S1,S4,S6 F4 S1,S4,S7,S8 F5 S5,S7,S8,S9 表 7 Paderborn University数据集下4种工况条件时的故障识别率
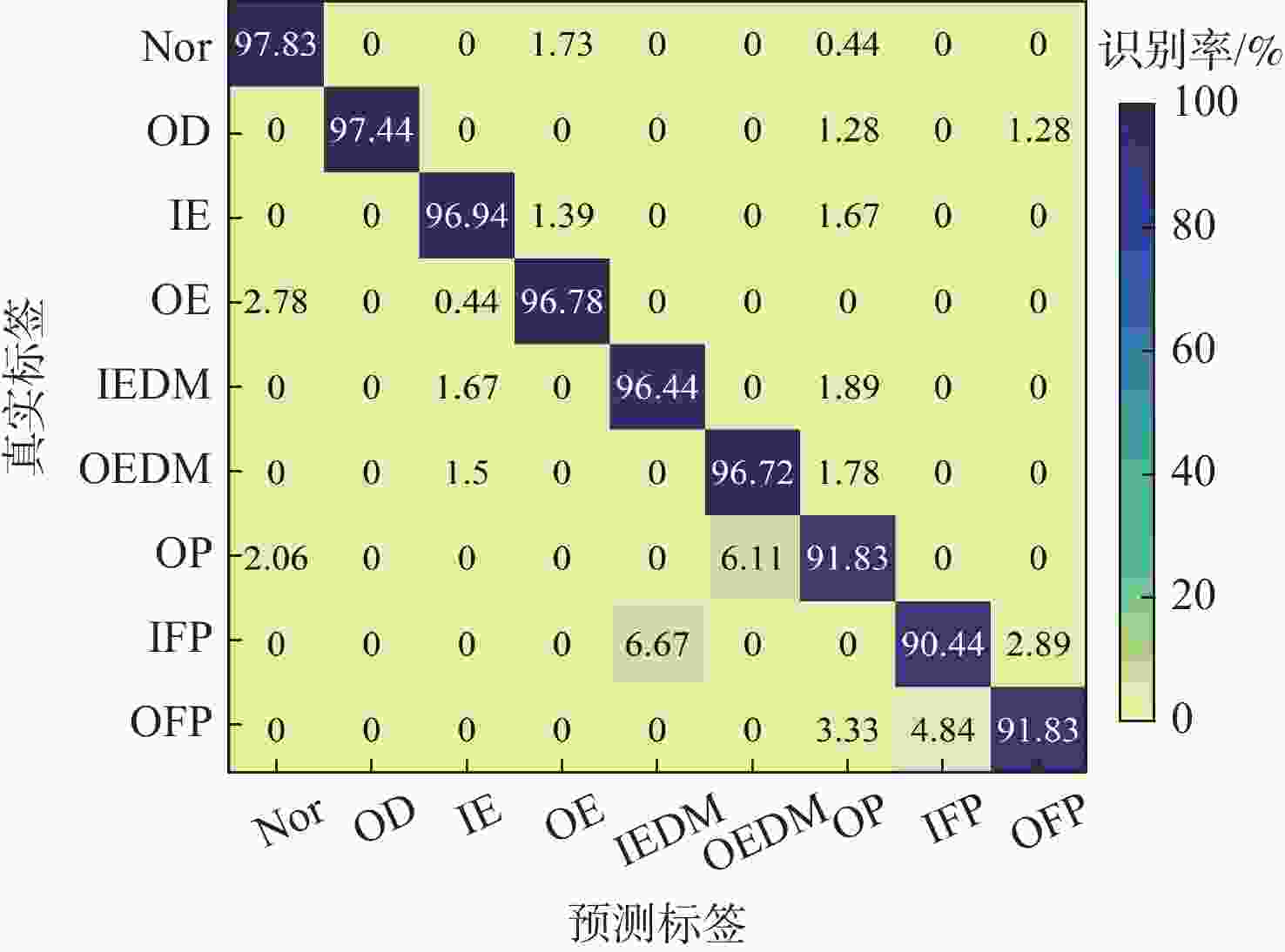
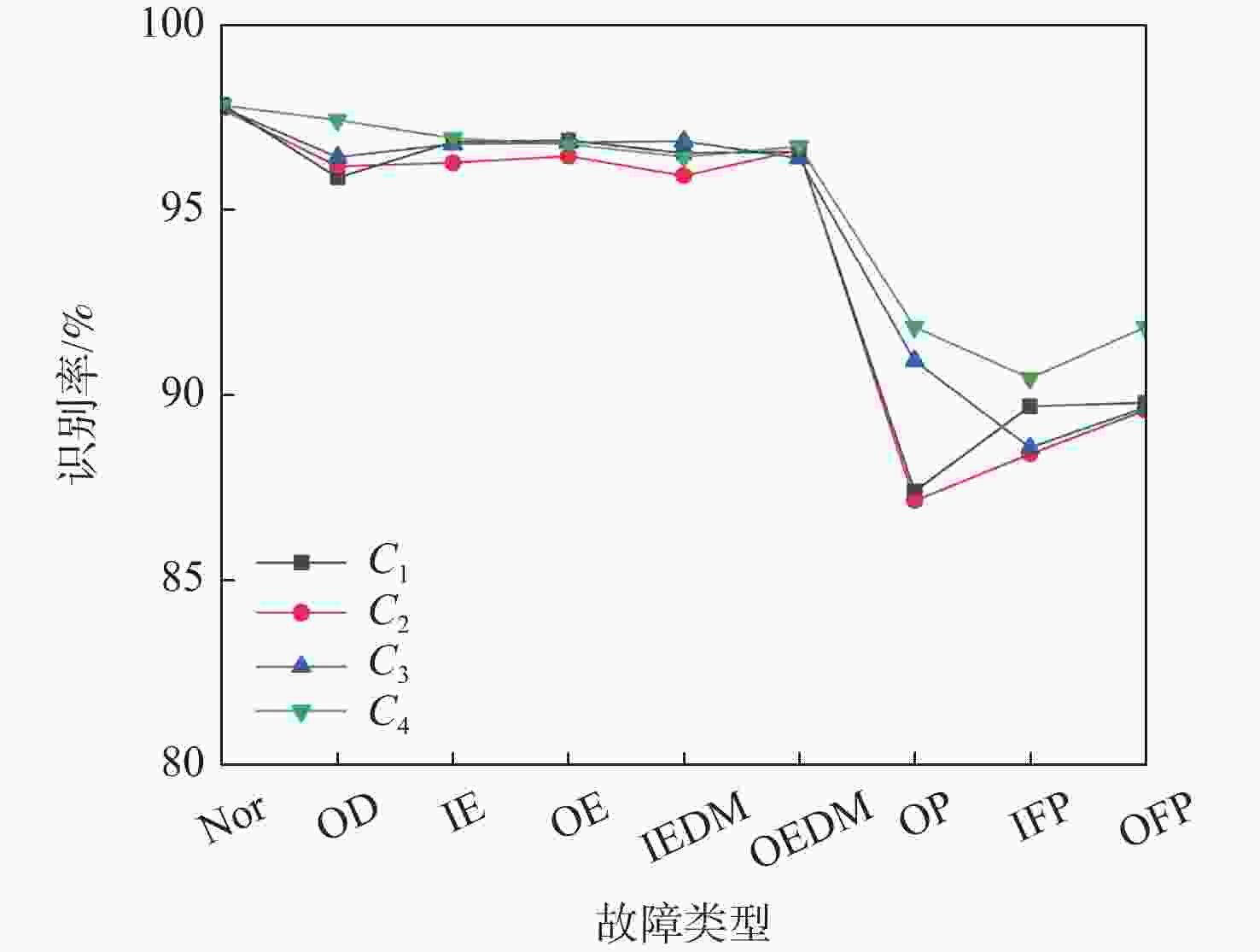
Table 7. Fault recognition rate under 4 working conditions in Paderborn University dataset
% 故障类型 C1 C2 C3 C4 正常 97.86 97.73 97.77 97.83 外圈钻孔 95.88 96.18 96.43 97.44 内圈电雕刻 96.85 96.28 96.79 96.94 外圈电雕刻 96.89 96.46 96.83 96.78 内圈放电沟槽 96.54 95.93 96.87 96.44 外圈放电沟槽 96.58 96.63 96.40 96.72 外圈塑化 87.38 87.13 90.92 91.83 内圈点蚀 89.68 88.39 88.57 90.44 外圈点蚀 89.78 89.58 89.65 91.83 -
[1] DAI X W, GAO Z W. From model, signal to knowledge: A data-driven perspective of fault detection and diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4): 2226-2238. doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2243743 [2] BARTLETT L M, HURDLE E E, KELLY E M. Integrated system fault diagnostics utilising digraph and fault tree-based approaches[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2009, 94(6): 1107-1115. [3] BEN ALI J, FNAIECH N, SAIDI L, et al. Application of empirical mode decomposition and artificial neural network for automatic bearing fault diagnosis based on vibration signals[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2015, 89(9): 16-27. [4] ZHANG W D, ZHANG F, CHEN W, et al. Fault state recognition of rolling bearing based fully convolutional network[J]. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2019, 21(5): 55-63. [5] XU G W, LIU M, JIANG Z F, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis method based on deep convolutional neural network and random forest ensemble learning[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(5): 1088. doi: 10.3390/s19051088 [6] PEARL J. Bayesian networks: A model cf self-activated memory for evidential reasoning[C]//Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Irvine: University of California, 1985: 15-17. [7] CAI B P, LIU H L, XIE M. A real-time fault diagnosis methodology of complex systems using object-oriented Bayesian networks[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 80(1): 31-44. [8] 鞠萍华, 柯磊, 冉琰, 等. 基于动作单元的机电产品故障溯源诊断方法[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(2): 60-66.JU P H, KE L, RAN Y, et al. Method of fault root causes tracing analysis for electro-mechanical products based on action unit[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 47(2): 60-66(in Chinese). [9] SAHU A R, PALEI S K. Real-time fault diagnosis of HEMM using Bayesian network: A case study on drag system of dragline[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2020, 118(12): 104917. [10] WANG J X, WANG Z W, STETSYUK V, et al. Exploiting Bayesian networks for fault isolation: A diagnostic case study of diesel fuel injection system[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 86(5): 276-286. [11] XIAO Y, PAN W G, GUO X M, et al. Fault diagnosis of traction transformer based on Bayesian network[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(18): 4966. doi: 10.3390/en13184966 [12] CAI B P, LIU Y H, FAN Q, et al. Multi-source information fusion based fault diagnosis of ground-source heat pump using Bayesian network[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 114(2): 1-9. [13] CHEN B, XIE L, LI Y Z, et al. Acoustical damage detection of wind turbine yaw system using Bayesian network[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 160(7): 1364-1372. [14] 朱彦沛, 邢宁哲, 纪雨彤, 等. 基于交互式主动探测的电力综合数据网故障定位算法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41(4): 35-40.ZHU Y P, XING N Z, JI Y T, et al. Fault location algorithm of integrated data network for power system based on interactive active detection[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(4): 35-40(in Chinese). [15] 王金鑫, 王忠巍, 马修真, 等. 柴油机燃油系统多故障的解耦与诊断技术[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(10): 2249-2255.WANG J X, WANG Z W, MA X Z, et al. Decoupling and diagnosis of multi-fault of diesel engine fuel system[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2249-2255(in Chinese). [16] CAI B P, HUANG L, XIE M. Bayesian networks in fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(5): 2227-2240. doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2695583 [17] 刘浩然, 马明, 李世昭, 等. 一种应用于故障诊断中的高效推理算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(11): 2033-2040.LIU H R, MA M, LI S Z, et al. An effective inference algorithm for fault diagnosis[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(11): 2033-2040(in Chinese). [18] 王双成, 唐海燕, 刘喜华. 用于风险管理的贝叶斯网络学习[J]. 控制与决策, 2007, 22(5): 569-572. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2007.05.019WANG S C, TANG H Y, LIU X H. Learning Bayesian networks in risk management[J]. Control and Decision, 2007, 22(5): 569-572(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2007.05.019 [19] 王海羽, 刘浩然, 张力悦, 等. 基于节点块序列约束的局部贝叶斯网络结构搜索算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1210-1219.WANG H Y, LIU H R, ZHANG L Y, et al. Local Bayesian network structure searching using constraint of node chunk sequence[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1210-1219(in Chinese). [20] 刘浩然, 孙美婷, 李雷, 等. 基于蚁群节点寻优的贝叶斯网络结构算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(1): 143-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.01.019LIU H R, SUN M T, LI L, et al. Study on Bayesian network structure learning algorithm based on ant colony node order optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(1): 143-150(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.01.019 [21] HUANG W C, KOU X Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Operational failure analysis of high-speed electric multiple units: A Bayesian network-K2 algorithm-expectation maximization approach[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 205(2): 107250. [22] SPIRTES P, GLYMOUR C, SCHEINES R. Causation, prediction, and search[M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 2001. [23] LIU M K, TRAN M Q, WENG P Y. Fusion of vibration and current signatures for the fault diagnosis of induction machines[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019: 7176482. [24] 赵志宏. 基于振动信号的机械故障特征提取与诊断研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2012.ZHAO Z H. Research on vibration signal based machinery fault feature extraction and diagnosis[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2012 (in Chinese). [25] LI K, CHEN P, WANG S M. An intelligent diagnosis method for rotating machinery using least squares mapping and a fuzzy neural network[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(5): 5919-5939. doi: 10.3390/s120505919 [26] CONTALDI C, VAFAEE F, NELSON P C. Bayesian network hybrid learning using an elite-guided genetic algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52(1): 245-272. doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-9615-5 [27] LI T T, ZHAO Y, ZHANG C B, et al. A knowledge-guided and data-driven method for building HVAC systems fault diagnosis[J]. Building and Environment, 2021, 198(5): 107850. [28] LESSMEIER C, KIMOTHO J K, ZIMMER D, et al. Condition monitoring of bearing damage in electromechanical drive systems by using motor current signals of electric motors: A benchmark data set for data-driven classification[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society. New York: PHM Society, 2016: 1-17. [29] HOANG D T, KANG H J. A motor current signal-based bearing fault diagnosis using deep learning and information fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(6): 3325-3333. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2933119 -






 下载:
下载: