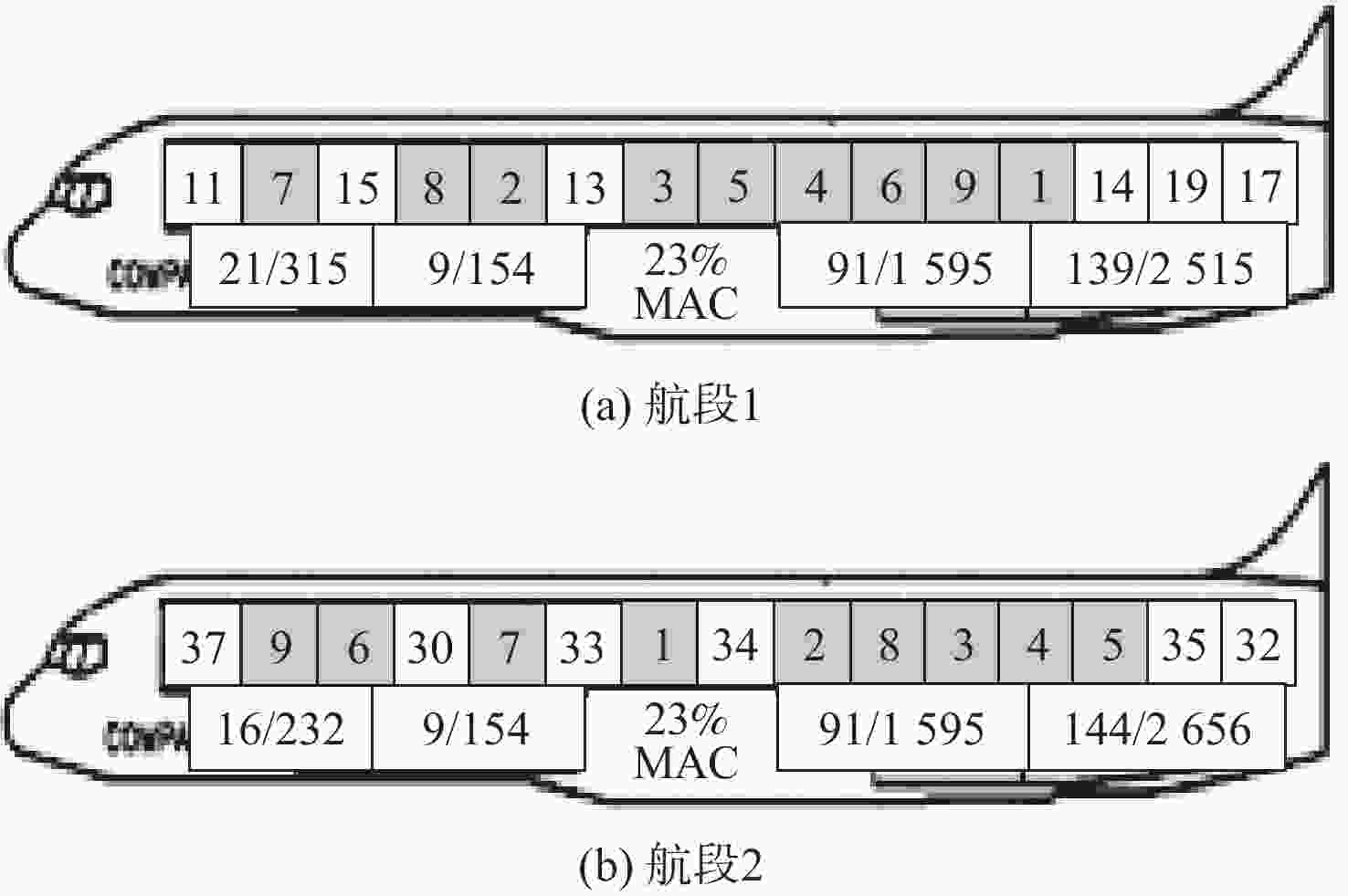
Cooperating loading balance optimization for medium-sized aircraft with multiple flight legs based on loading and unloading sequence
-
摘要:
多航段、多经停的航空货运航班,飞行过程中需要合理控制飞机的重心(CG)位置,保持平衡状态,中转站装卸操作过程中需要避免额外装卸操作,减少时间和劳力浪费,因此,研究多航段航班的协同配载问题具有重要现实意义。根据航空器自身特点与集装器(ULD)装卸顺序,结合各航段飞机装载平衡与过站机场ULD装卸操作要求,通过协调分配各航段ULD和散货位置,建立了中型机联程航班多目标整数线性规划模型。模型考虑了ULD和散货的质量、体积及与舱位的匹配限制,航空器限重、舱位限重、舱位及区域累积限重、上下舱联合限重和CG位置的平衡限制,以及前后航段ULD和散货的连接性约束。根据造成中间机场额外装卸操作的2种原因,基于装卸顺序,提出装卸优化模型,通过ULD的舱内平移,优化了CG,减少了装卸次数。以B757-200F机型为例,在两装一卸、一装两卸和两装两卸3种场景下,采用商用求解器Gurobi,分别针对3种不同目标函数组合进行求解和分析对比。实验表明:所提模型可以有效协调过站货物的额外装卸次数,优化前后两航段的CG位置。
Abstract:For air cargo flights with multiple legs and multiple stops, it is necessary to reasonably control the center of gravity (CG) position of the aircraft , and maintain a balanced state during the flight; during the loading and unloading operation at intermediate airports, it is important to avoid extra loading and unloading operations, so as to reduce waste of time and labor. Therefore, studying the cooperating loading balance problem of multiple flight legs flights was of great practical significance. In this paper, according to the aircraft’s characteristics and the sequence of unit load device (ULD) loading and unloading, and combined with the loading and unloading operation requirements for the aircraft loading balance in each flight leg and ULD in the over-station airport, a multi-objective integer linear programming model for connecting flights is constructed by cooperating and distributing the positions of ULD and bulk cargo in each flight leg. The model takes into account the weight, volume and matching restrictions of the ULD and bulk cargo. It considered the constraints of aircraft weight limitation, cabin weight limitation, cabin and regional cumulative weight limitation, upper and lower cabins combined weight limitation, and the CG location balance limit. Additionally, the model considers the connectivity constraints of ULD and bulk cargoes in the front and rear legs. According to the two reasons of the extra loading and unloading operation of the intermediate airports, and based on the loading and unloading sequence, the loading and unloading optimization model is established, the CG is optimized and the number of loading and unloading is reduced through the translation of the ULD in the cabin. Taking the B757-200F model as an example, the commercial solver Gurobi was used for the three scenarios of two loadings and one unloading, one loading and two unloadings and two loadings and two unloadings. For three different combinations of objective functions are solved, analyzed and compared. Experimental results show that the model can effectively cooperate and optimize additional loading and unloading operations and CG location of the front and rear legs.
-
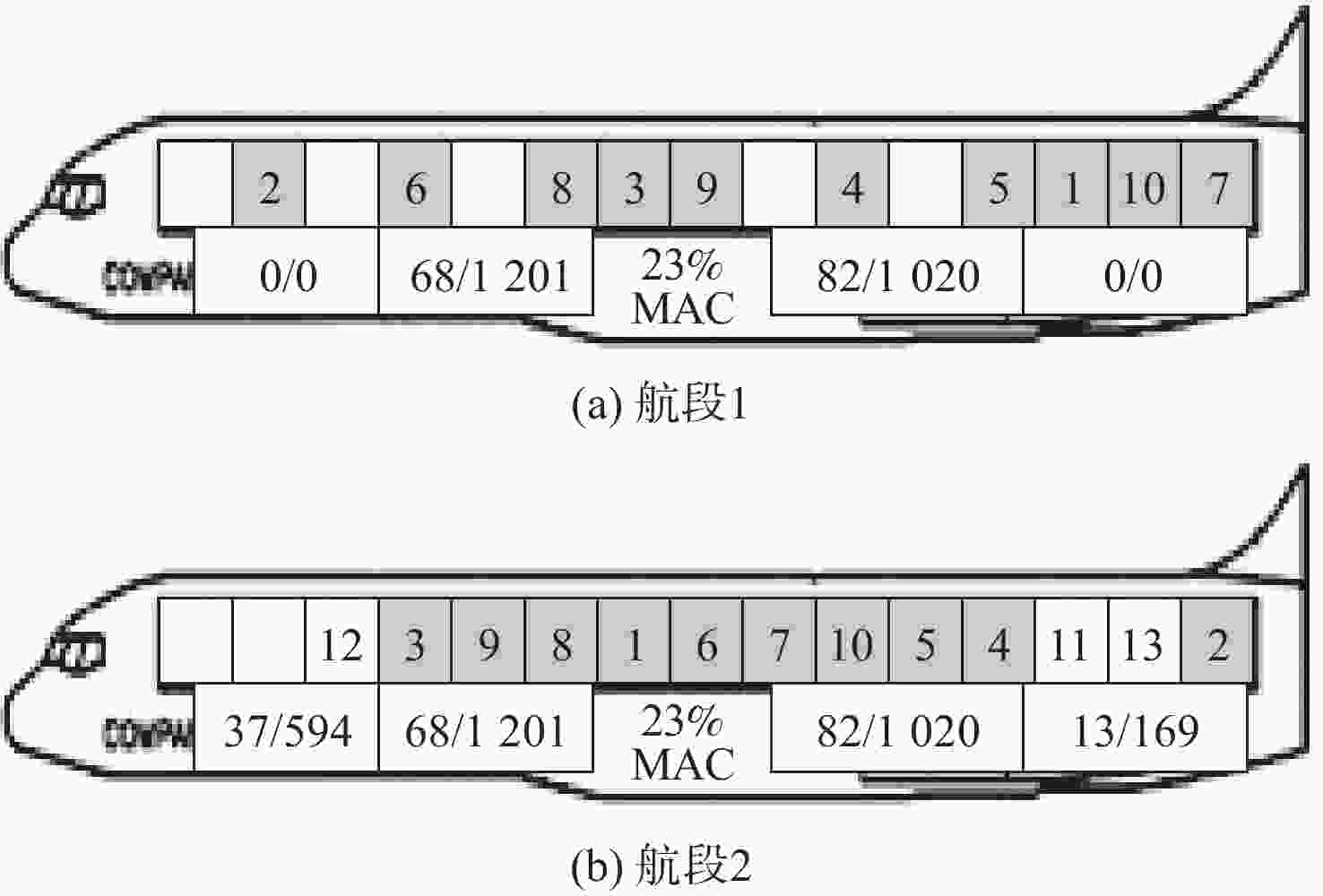
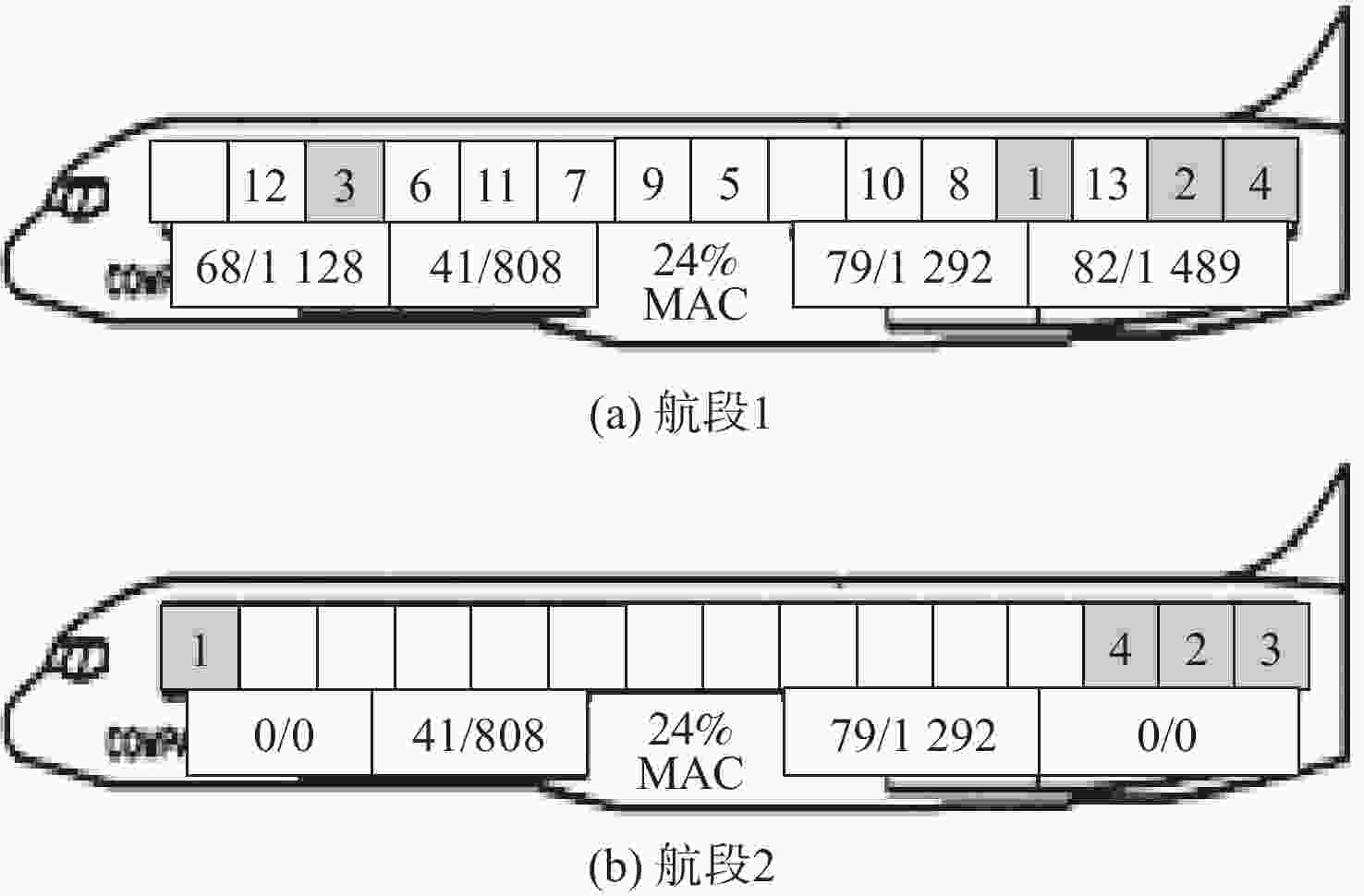
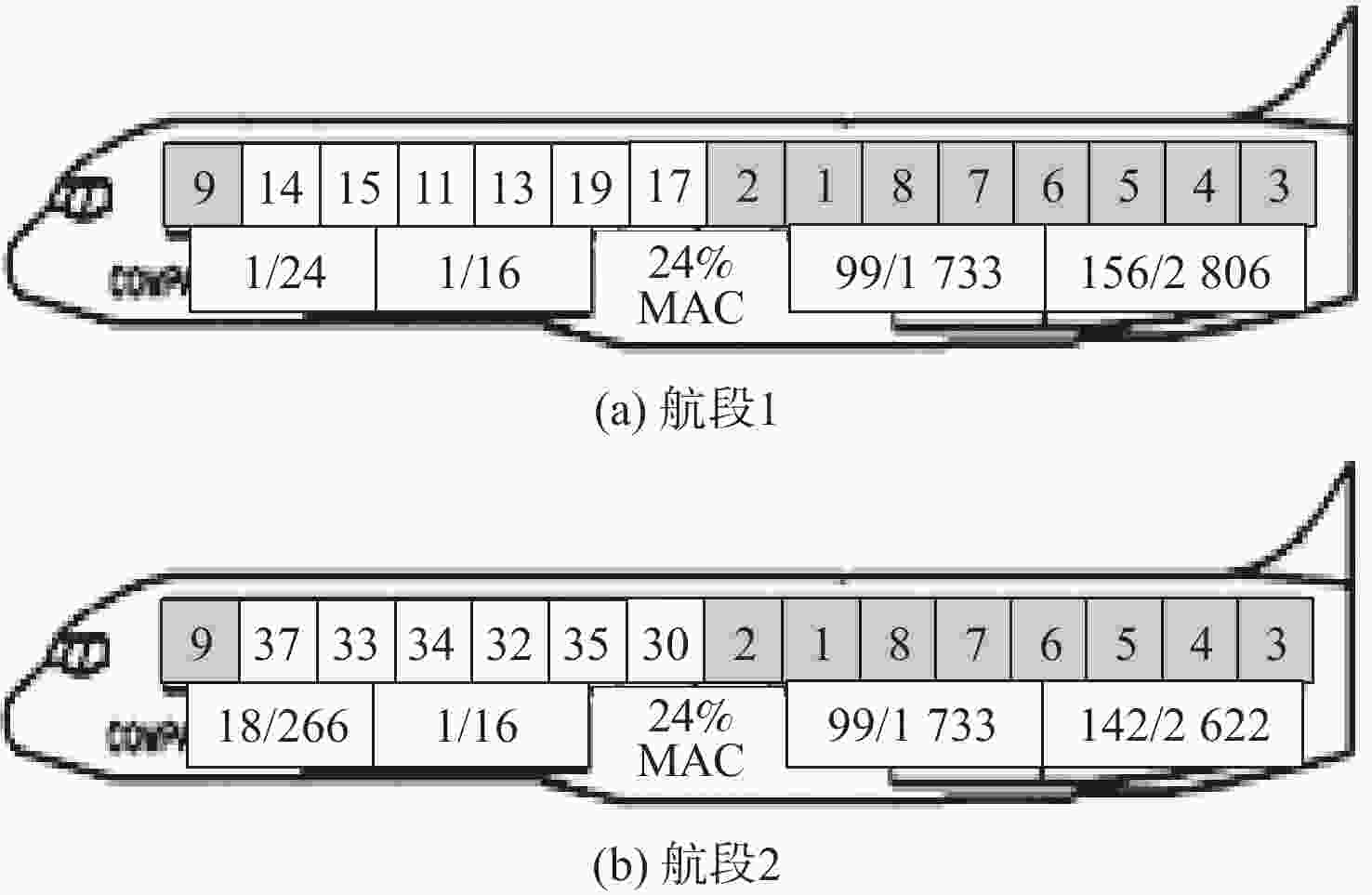
表 1 上下舱联合区间限重
Table 1. Combined weight limit of upper and lower cabins
区间 实际区间联合载量计算公式 区间限重/kg CZL CL1 C15 2716 CL2 CL1+C2+D1×10% 4360 CL3 CL2+C1+D1×80% 7871 CL4 CL3+C3+D1×10%+D2×40% 11557 CL5 CL4+C4+D2×40% 14043 CL6 CL5+C5+D2×20% 15893 CL7 CL6+C6 17712 CZR CR8 CR7+C7 23748 CR7 CR6+C8 21909 CR6 CR5+C9+D3×20% 20102 CR5 CR4+C10+D3×50% 18257 CR4 CR3+C11+D3×30%+D4×10% 15733 CR3 CR2+C12+D4×40% 11969 CR2 CR1+C13+D4×30% 8239 CR1 C14+D4×20% 3476 表 2 B757-200F基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of B757-200F
WOEW/kg WMTOW/kg WMZFW/kg BMAC/m CD/m IOEW WMLDW/kg PCGT,l /MAC BLEMAC/m ε 52752 108862 83460 5.07 26.36 31.3 95254 23 25.19 70000 表 3 主货舱舱位约束
Table 3. Main cargo space constraints
舱位 力臂/m 最大载荷/kg 最大高度/m 分区载荷 C15 9.91 2716 2 C15、C2、C1、C3和
C4质量和
不超过18000 kgC2 12.17 2948 2 C1 14.43 2948 2 C3 16.69 2948 2 C4 18.95 2948 2 C5 21.21 2948 2 C5~C9质量和
不超过24000 kgC6 23.47 2948 2 C7 25.73 4264 2 C8 27.99 4264 2 C9 30.25 2948 2 C10 32.51 2948 2 C10~C14质量和
不超过29000 kgC11 34.77 2948 2 C12 37.03 2948 2 C13 29.29 2948 2 C14 41.55 2948 1.95 表 4 下货舱舱位约束
Table 4. Lower cargo hold space constraints
下货舱舱位 舱位限重/kg 舱位累积限重/kg 力臂/m 可用体积/m3 D1 2496 4672 13.58 4.9 D2 4672 4672 18.64 13.9 D3 3773 7393 32.73 14.2 D4 5606 7393 38.29 16.7 表 5 油量指数
Table 5. Fuel index
F/kg I F/kg I F/kg I 500 +0.1 1000 +0.2 1500 +0.3 2000 +0.4 2500 +0.5 3000 +0.7 3500 +0.8 4000 +1.0 4500 +1.2 5000 +1.4 5500 +1.6 6000 +1.8 7000 +2.3 7500 +2.6 8000 +2.9 8500 +3.2 9000 +3.6 9500 +4.0 10000 +4.5 10500 +5.0 11000 +5.6 11500 +6.2 12500 +7.6 15000 +7.5 15500 +7.1 16000 +6.7 17000 +5.9 18000 +5.1 19000 +4.3 20000 +3.5 24000 +0.6 26000 −0.8 26500 −1.2 27000 −1.6 27500 −1.9 表 6 货物装载清单
Table 6. Cargo loading list
测试
场景ULD
规模算例
序号U1/
(kg(个))U2/
(kg(个))U3/
(kg(个))B1/
(kg(个))B2/
(kg(个))B3/
(kg(个))WTOF,1/
kgWRFW,1/
kgWMPL,1/
kgWTOF,2/
kgWRFW,2/
kgWMPL,2/
kg两装
一卸< 1-1 0 4634(3) 15092(10) 0 763(50) 2221(150) 7000 500 30708 15000 2500 30708 1-2 0 6054(5) 13971(9) 0 1028(70) 1996(140) 8000 1000 30708 16000 2000 30708 1-3 0 11271(7) 9599(6) 0 1355(90) 1184(80) 7500 1000 30708 15500 2500 30708 = 1-4 0 15618(10) 6848(5) 0 2361(150) 1521(100) 8500 1500 30708 16000 2000 30708 1-5 0 18655(12) 4588(3) 0 2752(180) 2353(150) 8000 1000 30708 17000 3000 30708 1-6 0 14071(9) 7952(6) 0 2400(160) 3078(200) 9000 1000 30708 15500 2000 30708 1-7 0 4568(4) 18306(11) 0 3080(200) 3629(240) 9000 1500 30708 24000 4000 30708 > 1-8 0 30540(20(10)) 7220(5) 0 2166(150) 1635(100) 8500 1000 30708 26500 5000 29610 1-9 0 25170(18(6)) 13178(9) 0 1545(100) 2043(130) 9500 2000 30708 27500 5500 28610 1-10 0 10869(7) 13134(10(8)) 0 1513(100) 2324(150) 8000 500 30708 26000 5000 30110 一装
两卸< 2-1 2672(2) 0 18155(11) 1398(80) 0 2801(160) 16000 3000 30708 7000 500 30708 2-2 6111(4) 0 11424(8) 2062(120) 0 2604(150) 15000 2500 30708 7500 1000 30708 2-3 13034(9) 0 6604(4) 2617(150) 0 2100(120) 15500 2000 30708 8000 1000 30708 = 2-4 10438(6) 0 14426(9) 1685(100) 0 2665(150) 17000 3000 30708 8500 1500 30708 2-5 11036(8) 0 9902(7) 2275(130) 0 2023(110) 26500 5000 29610 9000 2000 30708 2-6 11742(9) 0 8548(6) 2560(150) 0 1824(100) 27500 6000 28610 9500 2000 30708 2-7 17643(11) 0 6349(4) 2891(160) 0 2118(120) 27000 5500 29110 9500 1000 30708 > 2-8 29946(20(9)) 0 10087(6) 3540(200) 0 1757(100) 18000 3500 30708 10000 2000 30708 2-9 22490(15(8)) 0 10603(7) 2773(160) 0 2144(120) 19000 4000 30708 11000 2000 30708 2-10 10863(7) 0 18568(13(8)) 2118(120) 0 2522(140) 20000 4500 30708 11500 2000 30708 两装
两卸< 3-1 2587(2) 8018(5) 15230(10) 60/947 1499(100) 1729(120) 10500 2500 30708 10500 3000 30708 3-2 11246(7) 11627(8) 10205(7) 1834(120) 2330(140) 1757(120) 11000 3000 30708 9500 1500 30708 3-3 12059(8) 7074(5) 10593(7) 2023(140) 1490(100) 1804(120) 10500 3000 30708 10000 2000 30708 = 3-4 3078(2) 2836(2) 21057(13) 1513(60) 2271(80) 4242(160) 9500 1500 30708 11000 3000 30708 3-5 8074(5) 6568(5) 14278(10) 1851(100) 1587(100) 1711(100) 10000 2000 30708 10000 2000 30708 3-6 13753(9) 10177(6) 9400(6) 4415(150) 3032(110) 2964(110) 11000 3000 30708 12500 2500 30708 3-7 19430(12) 16475(12) 3827(3) 5059(180) 5028(180) 2242(80) 10500 3000 30708 9500 1500 30708 > 3-8 16679(10(6)) 16320(10(6)) 13056(9) 2830(160) 2888(160) 1749(100) 12500 2500 30708 10000 2000 30708 3-9 7563(5) 11576(8(5)) 23684(15(10)) 2778(100) 2765(100) 2844(100) 9500 1500 30708 10000 2000 30708 3-10 10022(7) 12273(9(7)) 17413(13(8)) 2732(120) 2689(120) 3102(140) 10000 2000 30708 11000 3000 30708 注:表中数据形式Z(X(Y))和Z(X)中,X表示各场景下待装ULD或散货数量,Z表示待装质量,Y为当前航空器可装载ULD数量,仅当X>Y时表示为X(Y)。 表 7 各航段业载分配
Table 7. Payload distribution of each leg
算例
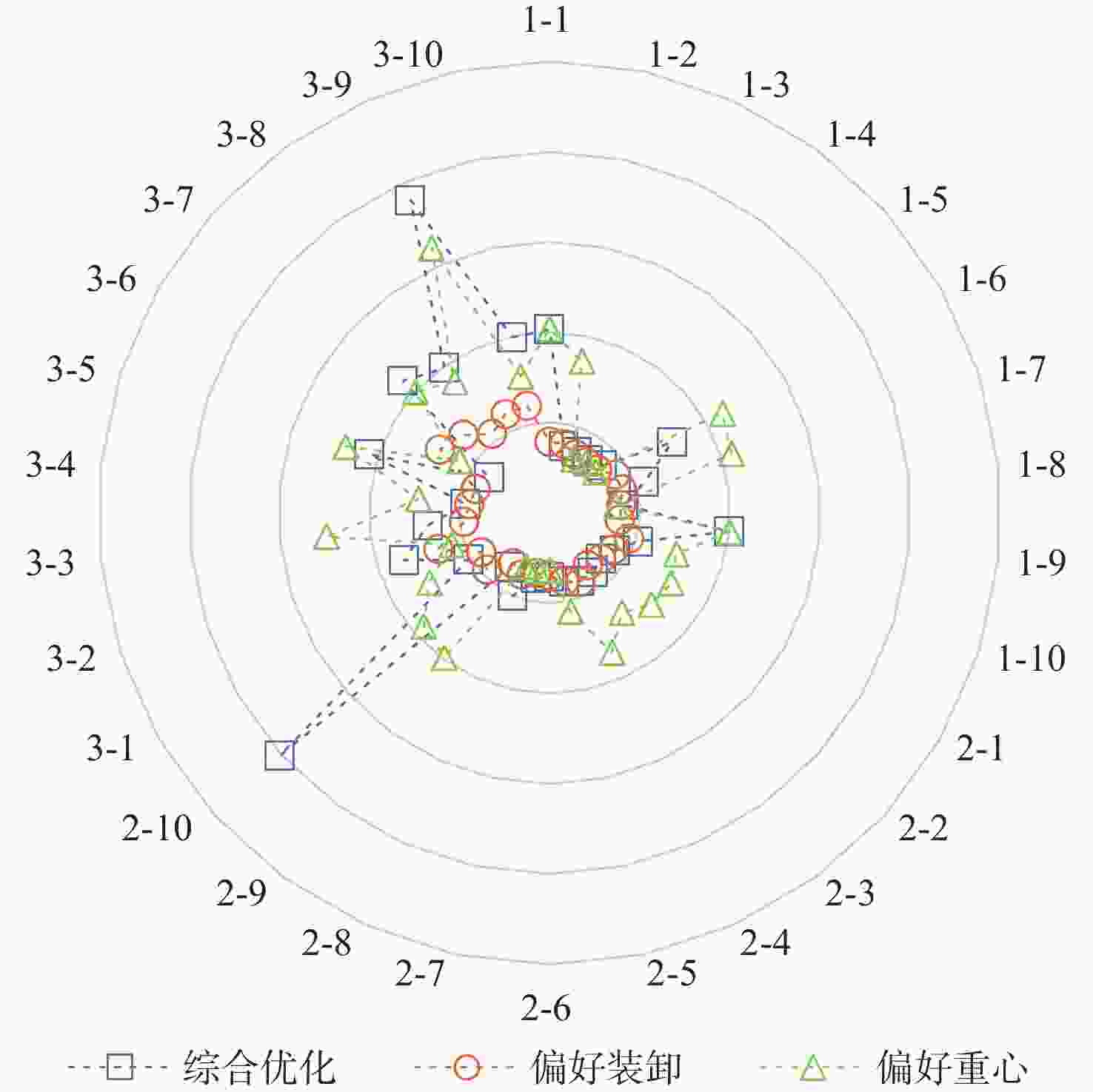
序号U/个 B/件 WPL,l /kg l=1 l=2 l=1 l=2 l=1 l=2 1-1 10 13 150 220 17313 22710 1-2 9 14 140 210 15967 23049 1-3 6 13 80 170 10783 23389 1-4 5 15 100 250 8369 26348 1-5 3 15 150 330 6941 28348 1-6 6 15 200 360 11030 27501 1-7 11 15 240 440 21935 29583 1-8 5 15 100 250 8855 28217 1-9 9 15 130 230 15221 27231 1-10 8 15 150 250 13303 25685 2-1 13 11 240 160 25026 20956 2-2 12 8 270 150 22201 14028 2-3 13 4 270 120 24355 8704 2-4 15 9 250 150 29214 17091 2-5 15 7 240 110 25236 11925 2-6 15 6 250 100 24674 10372 2-7 15 4 280 120 29001 8467 2-8 15 6 300 100 30704 11844 2-9 15 7 280 120 29199 12747 2-10 15 8 260 140 28638 15657 3-1 12 15 180 220 20493 26476 3-2 14 15 240 260 25042 25919 3-3 15 12 260 220 26479 20961 3-4 15 15 220 240 29890 30406 3-5 15 15 200 200 25914 24144 3-6 15 15 260 220 30442 25573 3-7 15 15 260 260 30558 27572 3-8 15 15 260 260 28637 29910 3-9 15 15 200 200 30312 30703 3-10 15 15 260 260 27153 27103 表 8 重心偏差
Table 8. Center of gravity deviation
算例
序号|ΔCMAC,l|/%MAC
(综合优化)|ΔCMAC,l|/%MAC
(偏好装卸)|ΔCMAC,l|/%MAC
(偏好重心)l=1 l=2 l=1 l=2 l=1 l=2 1-1 0.894 0.759 4.960 7.336 0.439 0.372 1-2 0.898 0.748 2.165 0.282 0.441 0.366 1-3 0.394 0.745 0.843 1.741 0.496 0.324 1-4 0.512 0.708 0.079 0.852 0.579 0.663 1-5 1.538 0.878 2.658 1.090 1.538 1.056 1-6 0.975 0.404 10.176 8.362 0.480 0.351 1-7 1.652 1.271 7.025 3.508 0.403 0.314 1-8 0.312 0.663 3.927 1.517 0.484 0.311 1-9 0.889 0.637 9.953 5.567 0.437 0.311 1-10 0.028 0.517 5.711 3.374 0.458 0.320 2-1 0.514 0.832 4.045 3.528 0.398 0.375 2-2 0.146 0.897 1.665 4.501 0.410 0.413 2-3 0.363 0.489 2.986 4.616 0.773 0.994 2-4 0.370 0.910 3.557 2.669 0.339 0.432 2-5 0.183 0.491 3.370 0.193 0.655 0.936 2-6 0.210 0.949 6.829 0.700 0.602 0.135 2-7 0.629 0.976 4.772 8.388 0.581 0.453 2-8 0.675 0.924 3.432 4.481 0.644 0.911 2-9 0.011 0.795 3.701 2.530 0.332 0.443 2-10 0.450 0.850 3.975 2.854 0.607 0.853 3-1 0.852 0.388 2.502 1.894 0.403 0.375 3-2 0.811 0.805 3.963 3.991 0.379 0.382 3-3 0.766 0.822 3.922 2.374 0.375 0.403 3-4 0.396 0.388 4.117 0.671 0.364 0.357 3-5 0.802 0.791 3.968 4.049 0.380 0.388 3-6 0.198 0.631 3.111 0.708 0.357 0.370 3-7 0.358 0.375 1.619 2.887 0.358 0.375 3-8 0.737 0.741 7.375 5.180 0.358 0.363 3-9 0.363 0.360 0.773 1.454 0.363 0.360 3-10 0.179 0.055 4.302 2.786 0.179 0.054 表 9 额外装卸次数
Table 9. Number of extra operations
算例
序号Eunload 时间/s 综合优化 偏好装卸 偏好重心 综合优化 偏好装卸 偏好重心 1-1 0 0 10 8.39 0.48 8.46 1-2 9 8 9 0.39 0.45 5.21 1-3 2 6 6 0.33 0.25 0.12 1-4 4 4 5 0.28 0.22 0.19 1-5 0 0.27 0 3 0.45 0.19 1-6 0 0 6 4.05 0.64 10.75 1-7 0 0 11 1.57 0.63 9.48 1-8 3 1 5 0.58 0.5 0.34 1-9 0 0 9 7.98 0.46 8.07 1-10 8 8 9 1.27 0.91 3.46 2-1 10 11 11 0.63 0.56 3.98 2-2 4 7 7 0.41 0.41 3.72 2-3 0 0 4 0.57 0.29 2.79 2-4 8 8 9 0.58 0.62 5.02 2-5 6 7 7 0.47 0.44 1.61 2-6 6 5 6 0.27 0.23 0.08 2-7 4 4 4 0.34 0.2 0.12 2-8 6 4 6 1.19 0.37 0.1 2-9 6 6 7 0.35 0.21 7.81 2-10 7 8 8 100.75 0.94 6.69 3-1 1 1 10 1.32 0.74 3.87 3-2 7 7 7 5.05 2.45 1.73 3-3 7 7 7 2.79 1 15.53 3-4 0 0 13 0.94 0.81 3.4 3-5 1 0 10 9.17 0.69 13.44 3-6 6 6 6 0.44 3.04 1.78 3-7 0 0 3 10.4 2.4 8.05 3-8 0 0 9 7.81 1.48 5.9 3-9 0 0 10 76.79 1.97 38.45 3-10 0 0 8 7.87 2.03 3.94 -
[1] FENG B, LI Y Z, SHEN Z J M. Air cargo operations: Literature review and comparison with practices[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2015, 56: 263-280. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.03.028 [2] AMIOUNY S V, BARTHOLDI J J, VANDE VATE J H, et al. Balanced loading[J]. Operations Research, 1992, 40(2): 238-246. doi: 10.1287/opre.40.2.238 [3] WODZIAK J R, FADEL G M. Packing and optimizing the center of gravity location using a genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Computers in Industry, 1994, 11: 2-14. [4] MATHUR K. An integer-programming-based heuristic for the balanced loading problem[J]. Operations Research Letters, 1998, 22(1): 19-25. doi: 10.1016/S0167-6377(97)00044-8 [5] HEIDELBERG K R, PARNELL G S, AMES J E. Automated air load planning[J]. Naval Research Logistics, 1998, 45(8): 751-768. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6750(199812)45:8<751::AID-NAV1>3.0.CO;2-R [6] DAHMANI N, KRICHEN S. On solving the bi-objective aircraft cargo loading problem[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Modeling, Simulation and Applied Optimization. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-6. [7] KRICHEN S, DAHMANI N. Solving a load balancing problem with a multi-objective particle swarm optimisation approach: Application to aircraft cargo transportation[J]. International Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 27(1/2): 62. doi: 10.1504/IJOR.2016.078455 [8] 谷润平, 贾旭颖, 赵向领, 等. 民航货机装载优化准确建模仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(3): 20-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.03.005GU R P, JIA X Y, ZHAO X L, et al. Research on loading, optimization and accurate modeling and simulation of civil aviation cargo aircraft[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(3): 20-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2019.03.005 [9] 赵向领, 杜有权. 基于遗传算法的民用航空器配载问题[J]. 中国科技论文, 2021, 16(8): 849-854. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2021.08.009ZHAO X L, DU Y Q. Civil aircraft stowage based on genetic algorithm[J]. China Science Paper, 2021, 16(8): 849-854(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2021.08.009 [10] BROSH I. Optimal cargo allocation on board a plane: A sequential linear programming approach[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1981, 8(1): 40-46. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(81)90027-8 [11] THOMAS C, CAMPBELL K, HINES G, et al. Airbus packing at federal express[J]. Interfaces, 1998, 28(4): 21-30. doi: 10.1287/inte.28.4.21 [12] MONGEAU M, BES C. Optimization of aircraft container loading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(1): 140-150. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1188899 [13] KALUZNY B L, SHAW R H A D. Optimal aircraft load balancing[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2009, 16(6): 767-787. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-3995.2009.00723.x [14] LIMBOURG S, SCHYNS M, LAPORTE G. Automatic aircraft cargo load planning[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2012, 63(9): 1271-1283. doi: 10.1057/jors.2011.134 [15] VERSTICHEL J, VANCROONENBURG W, SOUFFRIAU W, et al. A mixed integer programming approach to the aircraft weight and balance problem[J]. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2011, 20: 1051-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.08.114 [16] VANCROONENBURG W, VERSTICHEL J, TAVERNIER K, et al. Automatic air cargo selection and weight balancing: A mixed integer programming approach[J]. Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review, 2014, 65: 70-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2013.12.013 [17] ZHAO X L, YUAN Y, DONG Y, et al. Optimization approach to the aircraft weight and balance problem with the centre of gravity envelope constraints[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2021, 15(10): 1269-1286. doi: 10.1049/itr2.12096 [18] LARSEN O, MIKKELSEN G. An interactive system for the loading of cargo aircraft[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1980, 4(6): 367-373. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(80)90187-3 [19] LURKIN V, SCHYNS M. The airline container loading problem with pickup and delivery[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2015, 244(3): 955-965. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2015.02.027 [20] BRANDT F. The air cargo load planning problem[D]. Karlsruher: Karlsruher Instituts für Technologie, 2017: 61-70. [21] CHEN C S, LEE S M, SHEN Q S. An analytical model for the container loading problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1995, 80(1): 68-76. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(94)00002-T [22] LIU D S, TAN K C, HUANG S Y, et al. On solving multiobjective bin packing problems using evolutionary particle swarm optimization[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2008, 190(2): 357-382. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2007.06.032 [23] YAN S Y, SHIH Y L, SHIAO F Y. Optimal cargo container loading plans under stochastic demands for air express carriers[J]. Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review, 2008, 44(3): 555-575. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2007.01.006 [24] LI Y Z, TAO Y, WANG F. A compromised large-scale neighborhood search heuristic for capacitated air cargo loading planning[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 199(2): 553-560. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2008.11.033 [25] TANG C H. A scenario decomposition-genetic algorithm method for solving stochastic air cargo container loading problems[J]. Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review, 2011, 47(4): 520-531. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2010.11.013 [26] PAQUAY C, SCHYNS M, LIMBOURG S. Three dimensional bin packing problem applied to air cargo[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Systems, Logistics and Supply Chain. Quebec: Scientific Congresses and Symposiums, 2012: 1-6. [27] PAQUAY C, SCHYNS M, LIMBOURG S. A mixed integer programming formulation for the three-dimensional bin packing problem deriving from an air cargo application[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2016, 23(1-2): 187-213. doi: 10.1111/itor.12111 [28] PAQUAY C, LIMBOURG S, SCHYNS M. A tailored two-phase constructive heuristic for the three-dimensional multiple bin size bin packing problem with transportation constraints[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2018, 267(1): 52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2017.11.010 [29] PAQUAY C, LIMBOURG S, SCHYNS M, et al. MIP-based constructive heuristics for the three-dimensional bin packing problem with transportation constraints[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2018, 56(4): 1581-1592. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2017.1355577 -






 下载:
下载: