Complex equipment troubleshooting strategy generation based on Bayesian networks and reinforcement learning
-
摘要:
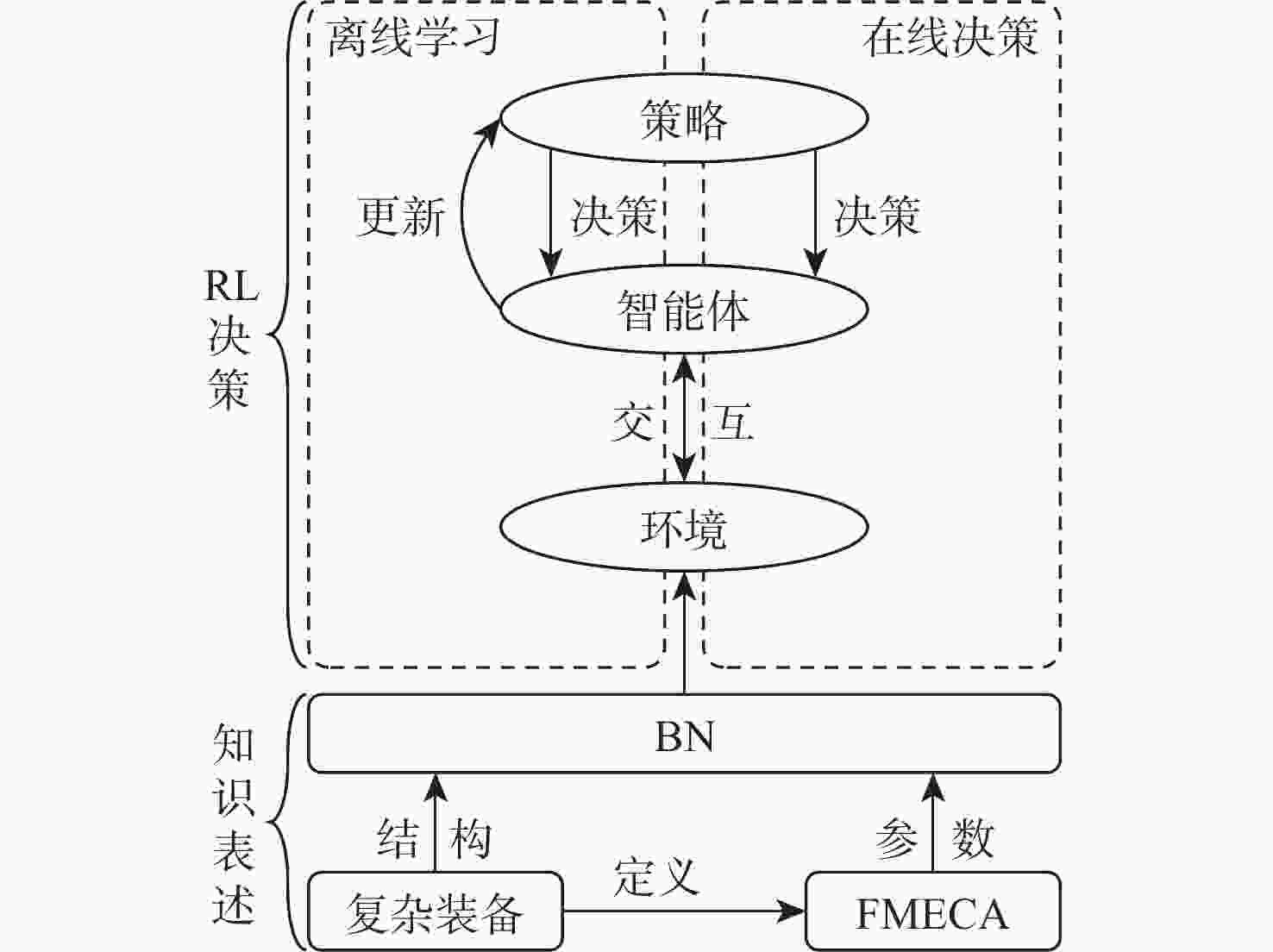
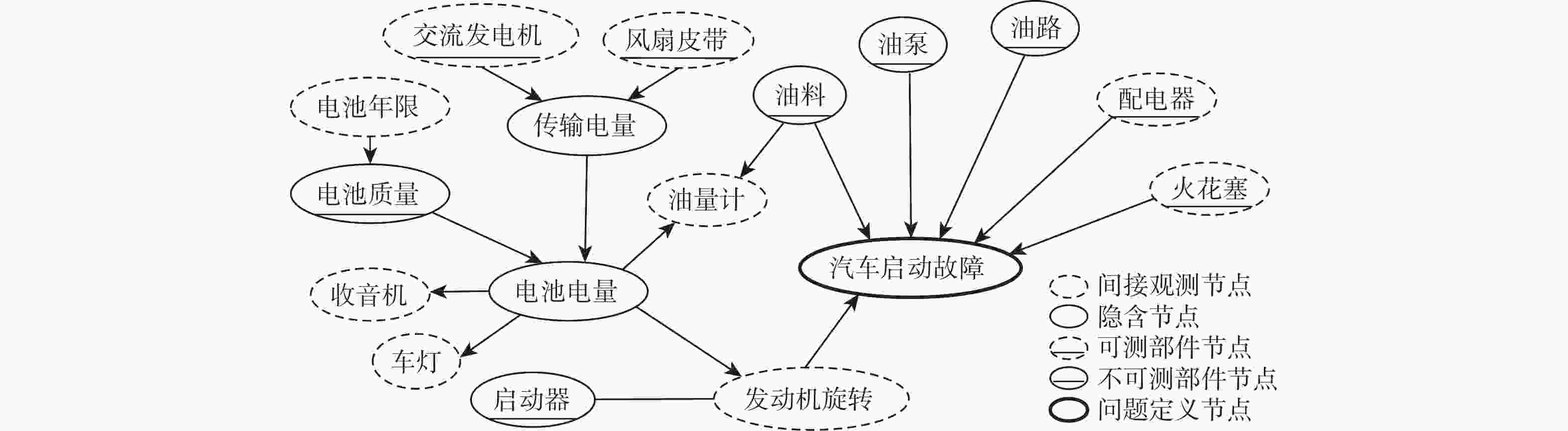
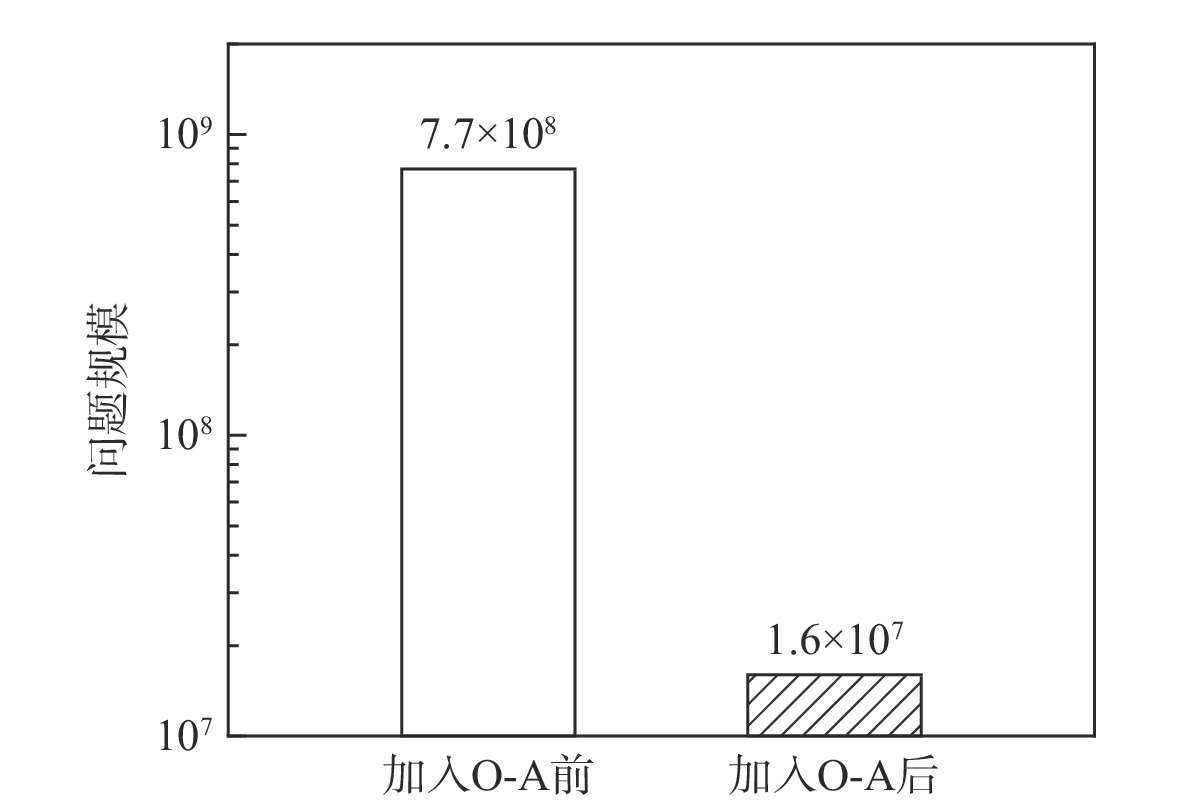
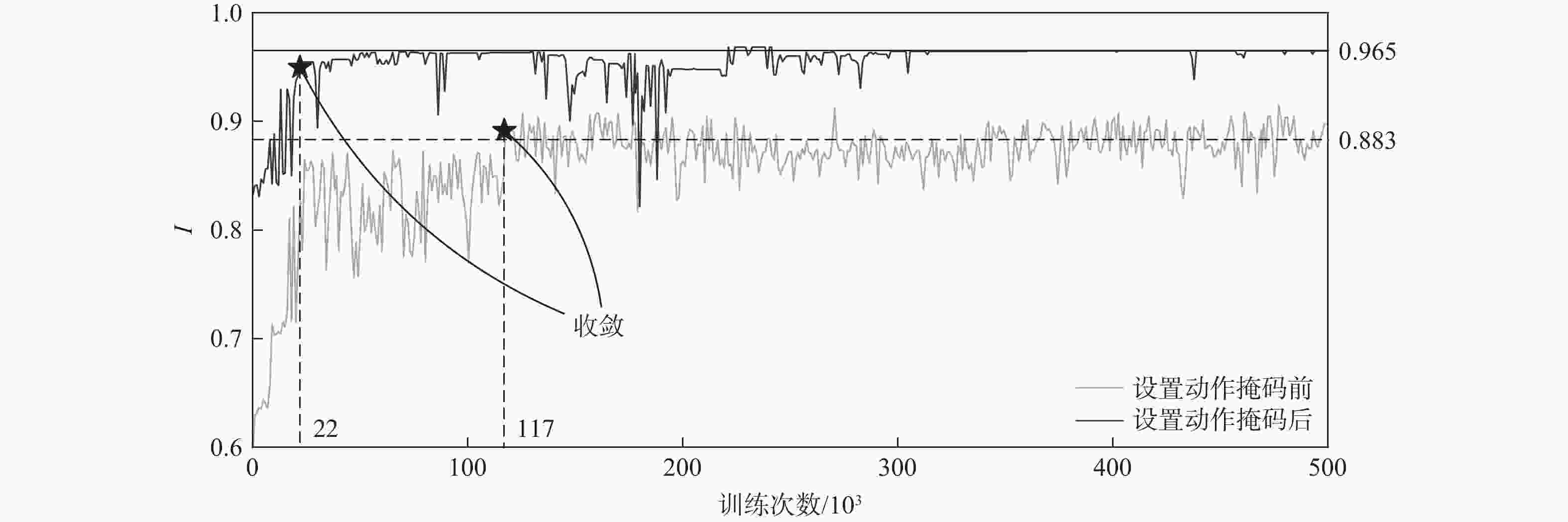
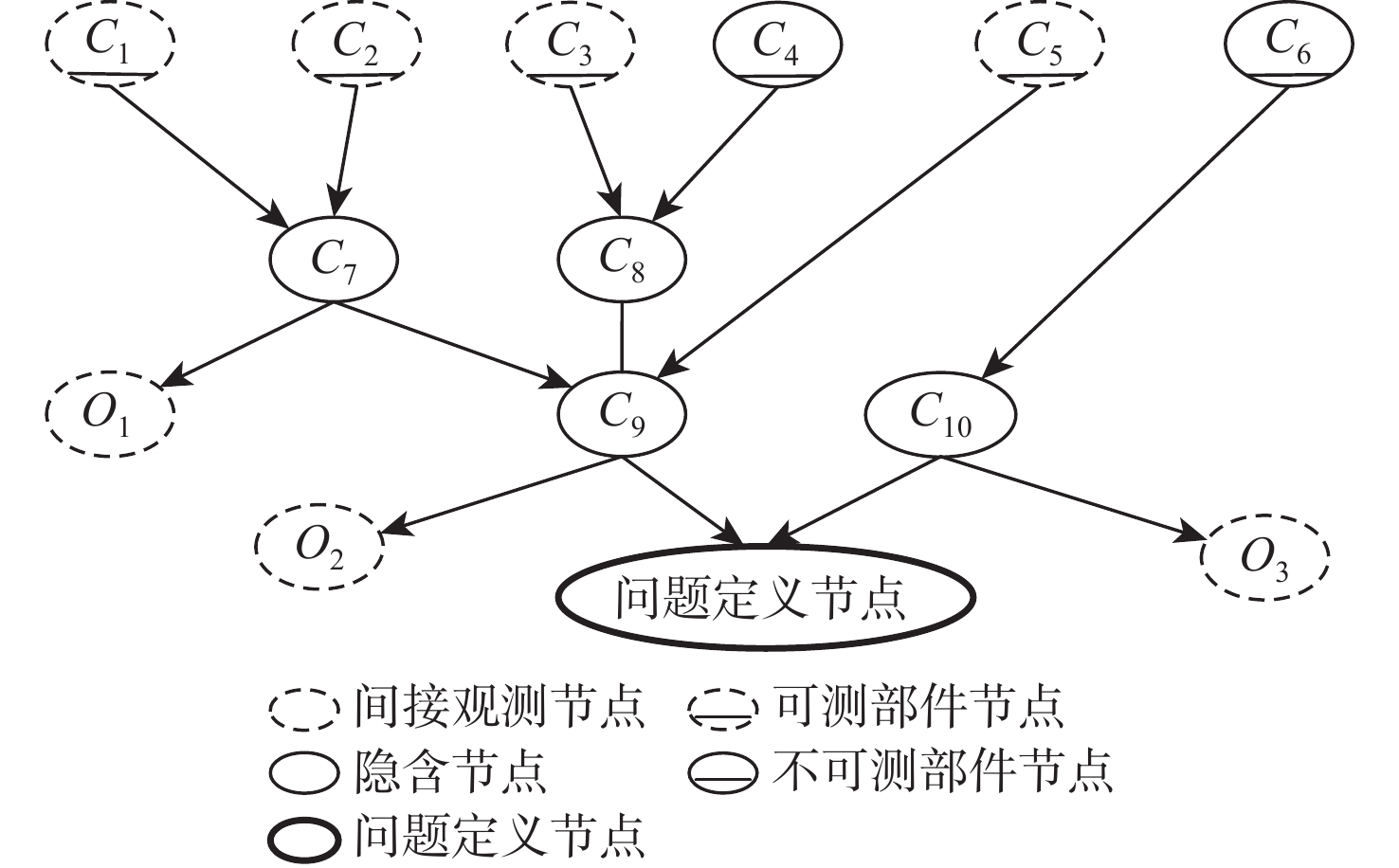
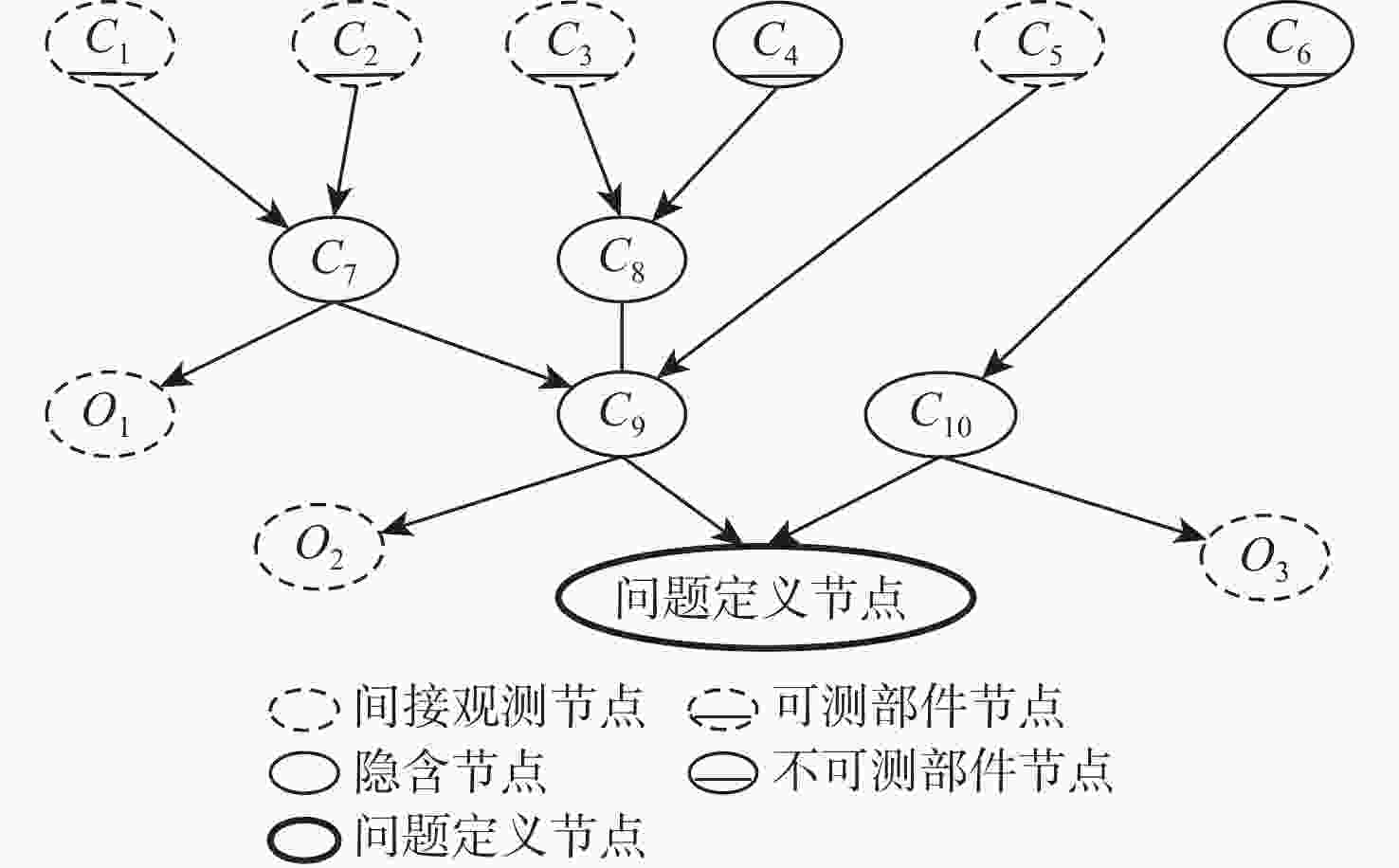
为解决传统启发式维修排故决策方法决策时间长、生成策略总成本高的问题,提出一种基于贝叶斯网络(BN)结合强化学习(RL)进行复杂装备维修排故策略生成方法。为更好地利用复杂装备模型知识,使用BN进行维修排故知识表述,并且为更加贴近复杂装备实际情况,依据故障模式、影响和危害性分析(FMECA)的故障概率,经合理转化后作为BN的先验概率;为使用RL的决策过程生成维修排故策略,提出一种维修排故决策问题转化为RL问题的方法;为更好地求解转化得到的强化学习问题,引入观测-修复动作对(O-A)以减小问题规模,并设置动作掩码处理动态动作空间。仿真结果表明:在统一的性能指标下,所提BN-RL方法较传统方法获得更高的指标值,证明该方法的有效性和优越性。
Abstract:To shorten the time spent and reduce the troubleshooting cost of traditional heuristic methods, a method of generating a troubleshooting strategy based on reinforcement learning (RL) and Bayesian networks (BN) is proposed for complex equipment. BN is used for the expression of knowledge to make better use of model knowledge of complex equipment. To get closer to the real scenario, the fault probability in the failure mode, effect, and critical analysis (FMECA) of complex equipment is converted and used as a prior probability in BN. A paradigm of converting troubleshooting problems into RL problems is proposed to generate a troubleshooting strategy by using the decision process of RL. The observation-action pair (O-A) is introduced to reduce the scale of the RL problem and the action masking is set to deal with dynamic action space. Simulation findings demonstrate the superiority of the proposed BN-RL method by demonstrating its remarkable performances compared to standard heuristic methods based on the proposed metrics.
-
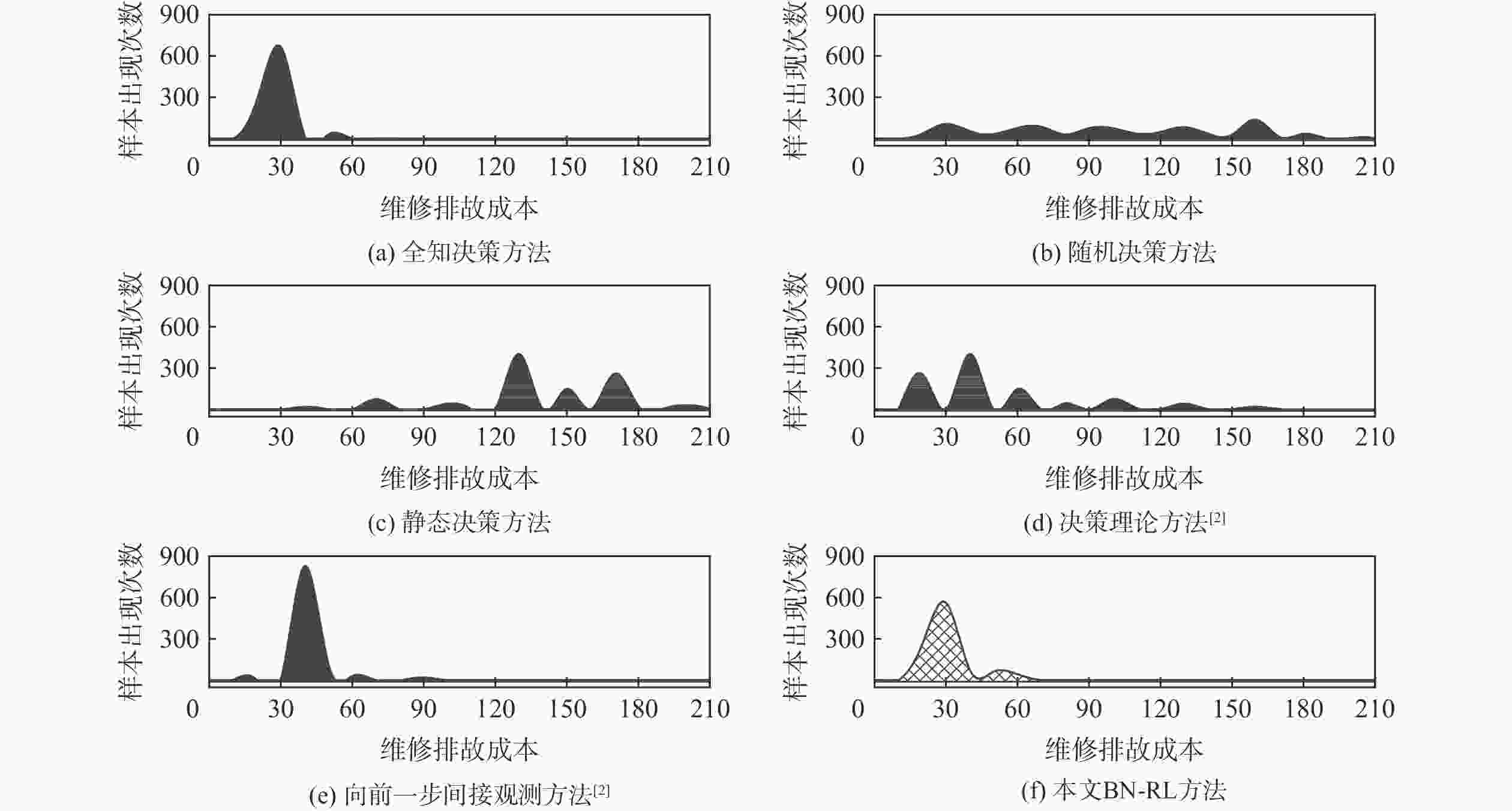
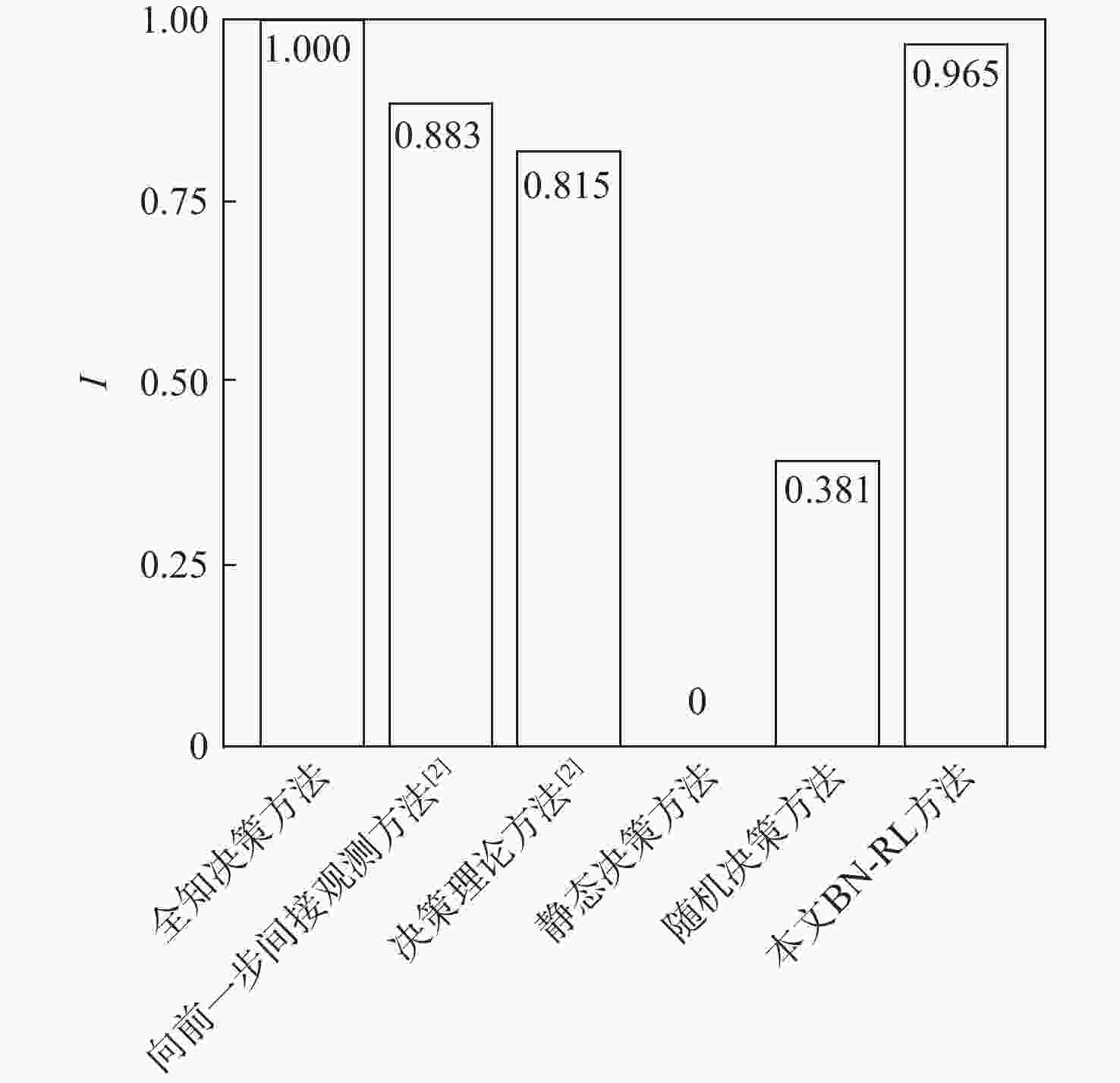
表 1 各方法耗时和维修排故成本
Table 1. Time consumed and troubleshooting costs of each method
方法 $C$ $t$ 全知决策方法 25.46 1 随机决策方法 92.83 1.67 静态决策方法 134.31 2.11 决策理论方法 45.61 37 990.20 向前一步间接观测方法 38.23 383 244.21 本文BN-RL方法 30.66 11.10 -
[1] 郭文彬, 刘东, 王宇健. 功能交联条件下飞机混合增强故障诊断方法[J]. 测控技术, 2022, 41(10): 107-113.GUO W B, LIU D, WANG Y J. Hybrid enhancement fault diagnosis method of aircraft under functional crosslink condition[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2022, 41(10): 107-113(in Chinese). [2] HECKERMAN D, BREESE J S, ROMMELSE K. Decision-theoretic troubleshooting[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1995, 38: 49-57. [3] PEARL J. Bayesian networks: A model of self-activated memory for evidential reasoning[C]//Proceedings of the 7th Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Irvine: Cognitive Science Society, 1985: 15-17. [4] SKAANNING C, JENSEN F V, KJÆRULFF U. Printer troubleshooting using Bayesian networks[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2003: 367-380. [5] JENSEN F V, KJÆRULFF U, KRISTIANSEN B, et al. The SACSO methodology for troubleshooting complex systems[J]. Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing, 2001, 15(4): 321-333. doi: 10.1017/S0890060401154065 [6] 于劲松, 刘浩, 万九卿, 等. 贝叶斯网络结合决策理论的向前多步排故策略[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(3): 298-303.YU J S, LIU H, WAN J Q, et al. Bayesian networks and decision theory-based forward multi-step troubleshooting strategy[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(3): 298-303(in Chinese). [7] HUANG Y P, WANG Y S, ZHANG R J. Fault troubleshooting using Bayesian network and multicriteria decision analysis[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 6: 282013. doi: 10.1155/2014/282013 [8] VIANNA W O L, RODRIGUES L R, YONEYAMA T, et al. Troubleshooting optimization using multi-start simulated annealing[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 Annual IEEE Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-6. [9] DE OLIVEIRA L S, RODRIGUES L R, YONEYAMA T. A comparative study of metaheuristics applied to troubleshooting optimization problems[C]//Proceedings of the XLIX Brazilian Symposium on Operational Research. Blumenau: SOBRAPO, 2017: 1783-1794. [10] COELHO D B P, RODRIGUES L R. A chaotic inertia weight TLBO applied to troubleshooting optimization problems[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-8. [11] HUANG C W, LI Y X, YAO X. A survey of automatic parameter tuning methods for metaheuristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(2): 201-216. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2921598 [12] 李凯文, 张涛, 王锐, 等. 基于深度强化学习的组合优化研究进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2521-2537.LI K W, ZHANG T, WANG R, et al. Research reviews of combinatorial optimization methods based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2521-2537(in Chinese). [13] 顾一凡. 基于强化学习的组合优化综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2021, 20(9): 74-77.GU Y F. A survey on reinforcement learning for combinatorial optimization[J]. Software Guide, 2021, 20(9): 74-77(in Chinese). [14] ZHANG Z Z, WU Z Y, ZHANG H, et al. Meta-learning-based deep reinforcement learning for multiobjective optimization problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 34(10): 7978-7991. [15] OREN J, ROSS C, LEFAROV M, et al. SOLO: Search online, learn offline for combinatorial optimization problems[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021, 12(1): 97-105. [16] ALMASAN P, SUÁREZ-VARELA J, RUSEK K, et al. Deep reinforcement learning meets graph neural networks: Exploring a routing optimization use case[J]. Computer Communications, 2022, 196: 184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2022.09.029 [17] OTTOSEN T J. Solutions and heuristics for troubleshooting with dependent actions and conditional costs[D]. Aalborg: Aalborg University, 2012: 33-43. [18] MZOUGUI I, CARPITELLA S, CERTA A, et al. Assessing supply chain risks in the automotive industry through a modified MCDM-based FMECA[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(5): 579. doi: 10.3390/pr8050579 [19] 李俊杰, 王尧, 张强, 等. 基于视情维修的涡轴发动机维修保障辅助决策体系研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2021, 29(6): 205-211.LI J J, WANG Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Research on auxiliary decision-making system of turboshaft engine maintenance support based on condition-based maintenance[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2021, 29(6): 205-211(in Chinese). [20] 邱锡鹏. 神经网络与深度学习[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2020: 328-353.QIU X P. Neural networks and deep learning[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2020: 328-353(in Chinese). [21] 张秦浩, 敖百强, 张秦雪. Q-learning强化学习制导律[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(2): 414-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.21ZHANG Q H, AO B Q, ZHANG Q X. Reinforcement learning guidance law of Q-learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(2): 414-419(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.21 [22] WATKINS C J, DAYAN P. Q-learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3): 279-292. [23] 龚铭凡, 徐海祥, 冯辉, 等. 基于改进Q-Learning的智能船舶局部路径规划[J]. 船舶力学, 2022, 26(6): 824-833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.06.004GONG M F, XU H X, FENG H, et al. Ship local path planning based on improved Q-learning[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2022, 26(6): 824-833(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2022.06.004 [24] 黄鑫陈, 陈光祖, 郑敏, 等. 基于Q-learning的飞行自组织网络QoS路由方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2022, 39(1): 134-143.HUANG X C, CHEN G Z, ZHENG M, et al. Q-learning based QoS routing for high dynamic flying Ad Hoc networks[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 39(1): 134-143(in Chinese). [25] LOW E S, ONG P, CHEAH K C. Solving the optimal path planning of a mobile robot using improved Q-learning[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 115: 143-161. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.02.013 [26] HUANG S, ONTAÑÓN S. A closer look at invalid action masking in policy gradient algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the the International FLAIRS Conference. Gainesville: Library Press, 2022, 35: 1-6. -






 下载:
下载: