-
摘要:
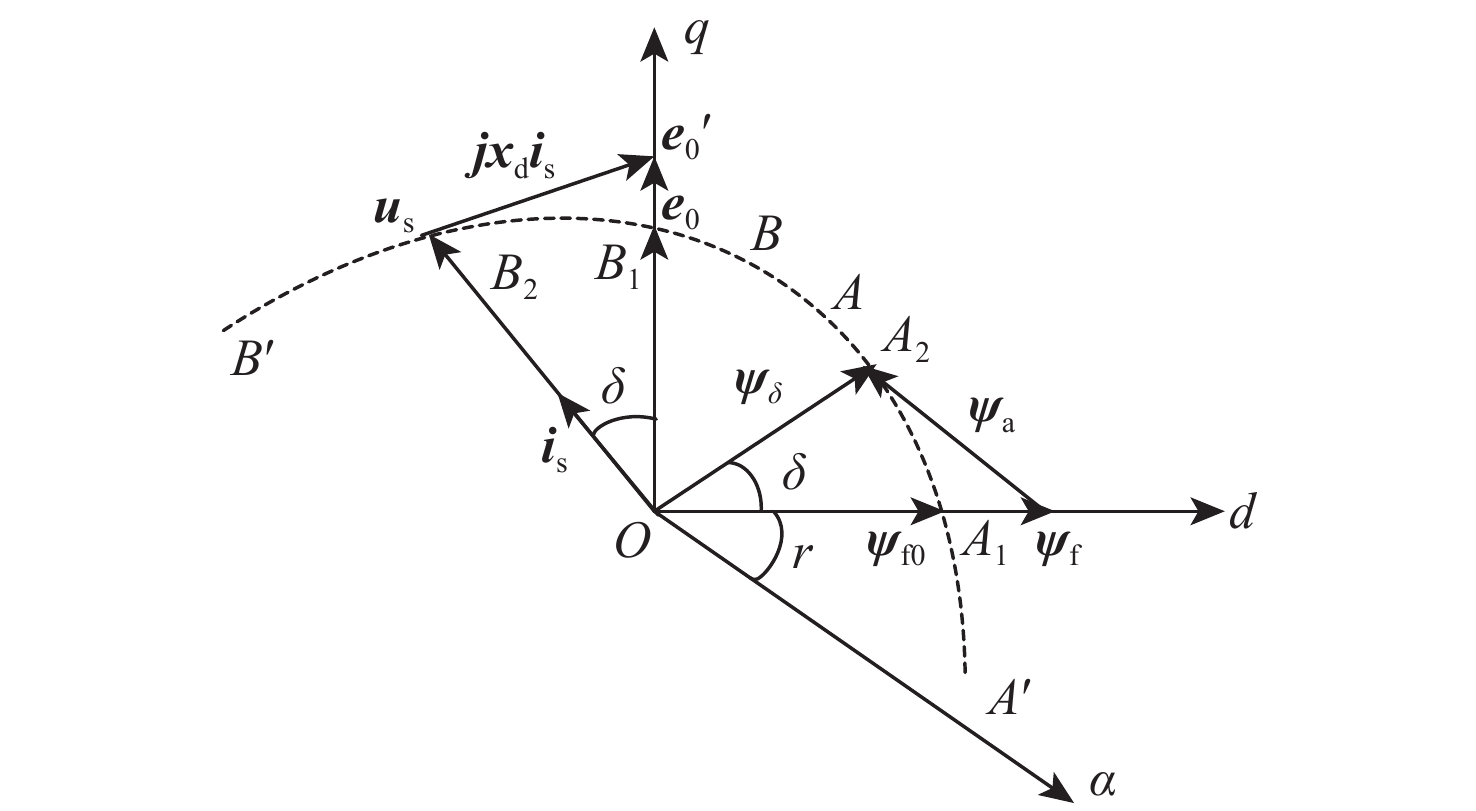
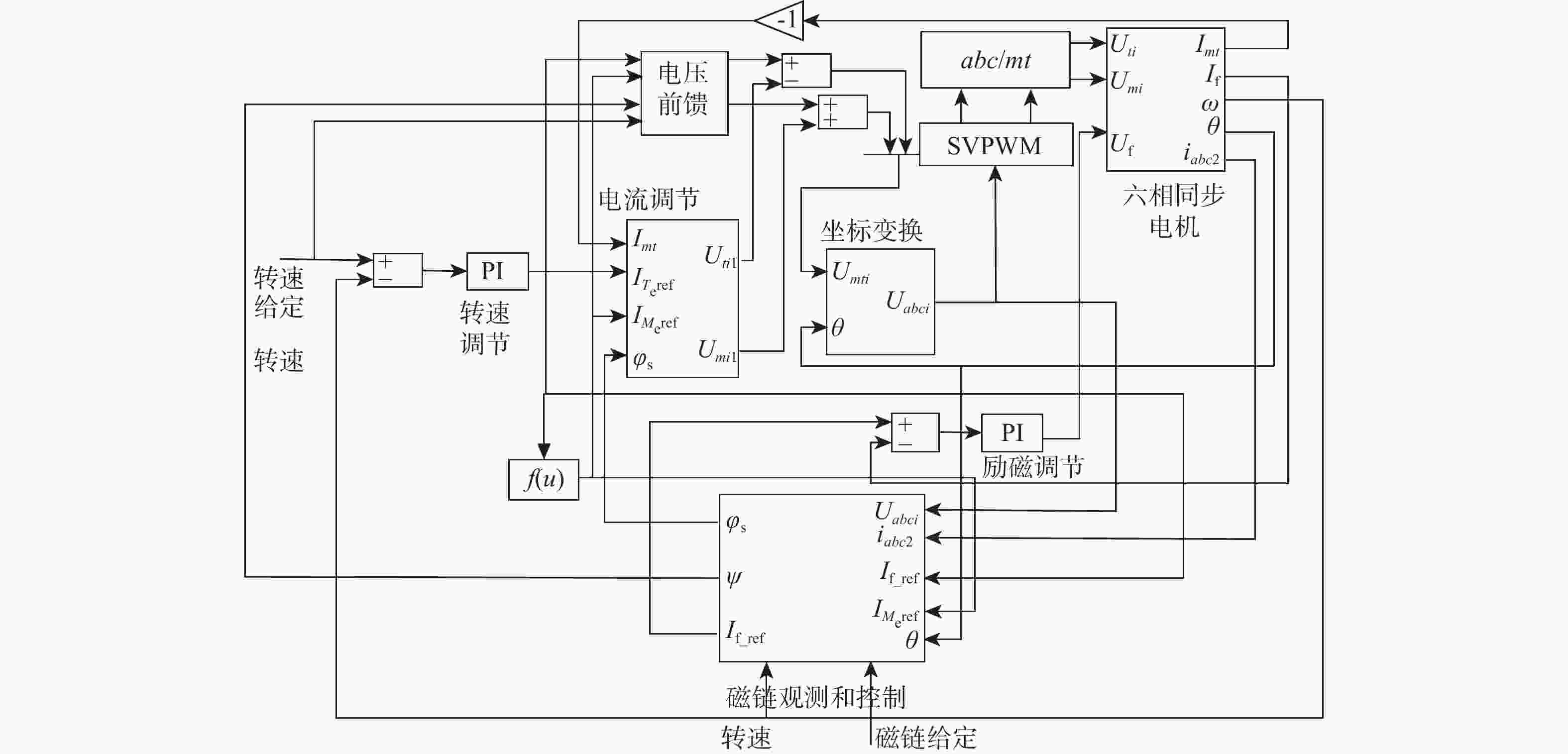
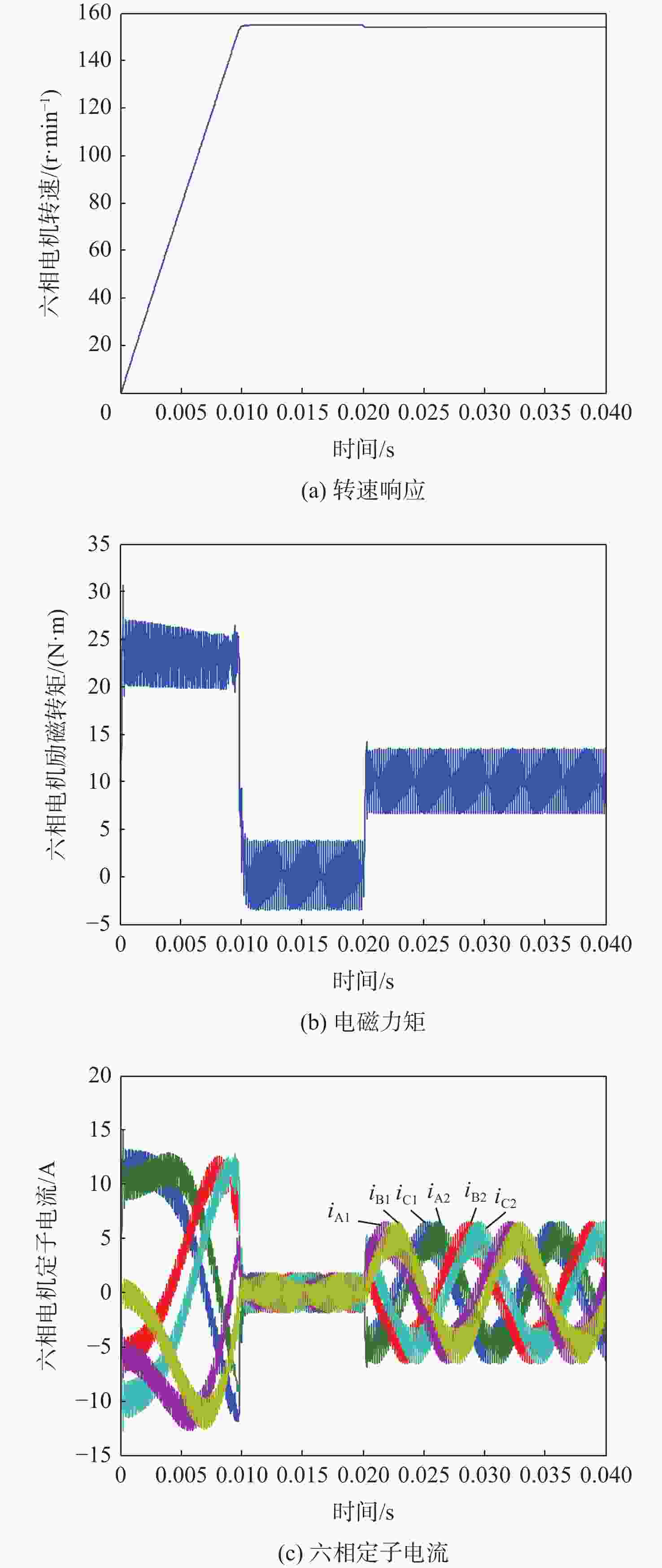
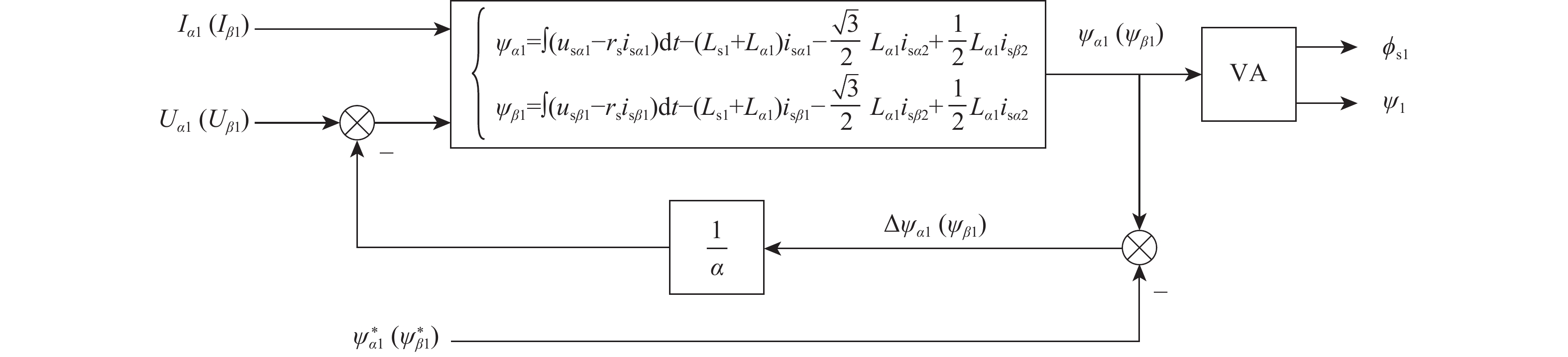
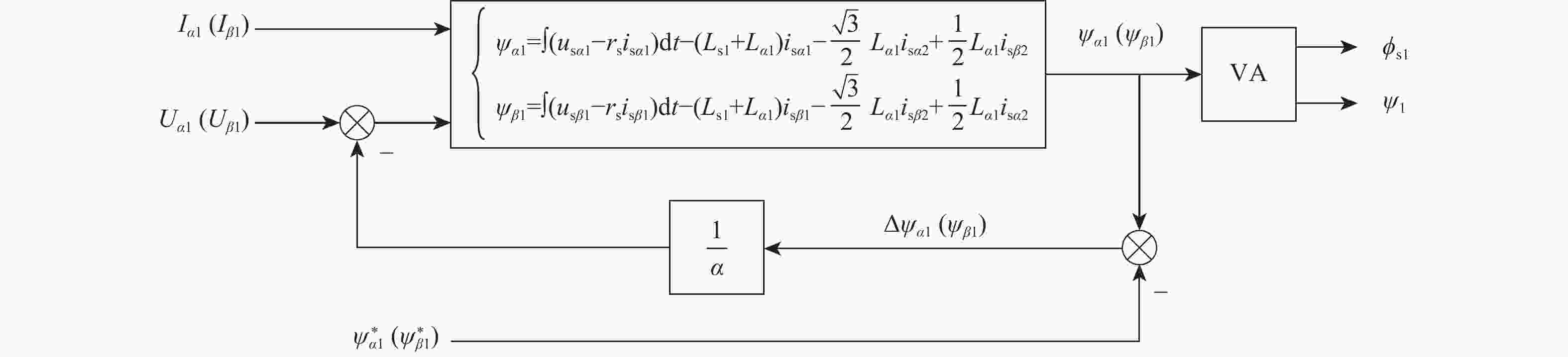
风能是中国最具潜力的可再生能源之一,而影响风能转化应用的主要因素是风力发电机的控制方法及特性。针对风能转化应用过程中遇到的风力发电机控制方法难以实现对风能的有效捕获问题,提出一种基于气隙磁链定向的矢量控制技术,通过6s/2r矢量变换得到旋转坐标系下电机的数学模型;对气隙磁链定向矢量控制技术进行研究,设计电机电流电压混合磁链观测模型,实现对电机转矩与磁通的独立控制;以双Y移30°六相同步电机为例进行仿真分析。结果表明:所提技术在电机空载启动与突加负载时具有较好的稳态性能和动态性能,解决多相电机控制的非线性和耦合性,提高模型的通用性和快速性。
Abstract:Wind energy is one of the most promising renewable energy sources in China, and the main factors affecting the application of wind energy conversion are the control method and characteristics of wind turbines. This study proposes a vector control technique based on air gap flux orientation, addressing the problem that the wind turbine control method is difficult to achieve effective capture of wind energy in wind energy conversion. We obtain the mathematical model in the rotating coordinate system through ${6{\mathrm{s}}/2{\mathrm{r}}}$ vector transformation. The vector control technique of directional air gap flux is studied, the observation model of the motor-current-voltage hybrid flux linkage is designed, and the torque and flux of the motor are controlled independently. The double Y-shift $ 30^{\circ} $six-phase synchronous motor is taken as an example for simulation analysis. Results show that the proposed technique has good steady-state performance and dynamic performance when the motor is started without load and with sudden load. The proposed technique solves the nonlinearity and coupling of polyphase motor control, and improves the universality and rapidity of the model.
-
表 1 转速仿真的性能指标
Table 1. Performance index of speed simulation
仿真情况 超调量/% 上升
时间/s调整
时间/s恢复
时间/s稳态
误差/%理想空载启动 1 0.01 0.011 0 突加负载 1 0.01 0.011 0.000 5 0.67 -
[1] 李毅. 变桨距变速风力发电机组的智能控制研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2007: 1-4.LI Y. Study on intelligent control of variable-pitch variable-speed wind turbines[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2007: 1-4(in Chinese). [2] DEVASHISH, THAKUR A, PANIGRAHI S, et al. A review on wind energy conversion system and enabling technology[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Power and Energy Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 527-532. [3] 温嘉斌, 郭晗, 荆超, 等. 电动车用永磁同步电机转子结构对弱磁调速性能分析[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2019, 24(6): 73-78.WEN J B, GUO H, JING C, et al. Analysis of the speed adjusting ability with field weakening of rotor structure of permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2019, 24(6): 73-78(in Chinese). [4] 胡维昊, 王跃, 李明烜, 等. 基于MRAS的多相永磁直驱型风力发电系统无速度传感器控制策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(23): 118-124.HU W H, WANG Y, LI M X, et al. Research on sensorless control strategy of direct drive multi-phase PMSG wind power generation system based on MRAS[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(23): 118-124(in Chinese). [5] 刘胜, 郭晓杰, 张兰勇. 六相永磁同步电机鲁棒自适应反步滑模容错控制[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2020, 24(5): 68-78.LIU S, GUO X J, ZHANG L Y. Robust adaptive backstepping sliding mode control for six-phase PMSM system with open phases[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2020, 24(5): 68-78(in Chinese). [6] 姚钢, 杨浩猛, 周荔丹, 等. 大容量海上风电机组发展现状及关键技术[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(21): 33-47. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20210416003YAO G, YANG H M, ZHOU L D, et al. Development status and key technologies of large-capacity offshore wind turbines[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(21): 33-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20210416003 [7] 刘剑, 苏健勇, 杨贵杰, 等. 六相永磁同步发电机容错控制的谐波补偿研究[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2014, 18(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-449X.2014.01.001LIU J, SU J Y, YANG G J, et al. Study of harmonic compensation for six-phase PMSG in fault tolerant control[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2014, 18(1): 1-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-449X.2014.01.001 [8] ZHANG C, YIN Z D, YANG L, et al. Model-free adaptive iterative learning control for six-phase propulsion PMSM[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1889-1893. [9] 朱元, 肖明康, 陆科, 等. 电动汽车永磁同步电机转子温度估计[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2021, 25(6): 72-81.ZHU Y, XIAO M K, LU K, et al. Rotor temperature estimation for permanent magnet synchronous motors in electric vehicles[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(6): 72-81(in Chinese). [10] KUMAR R R, CHETRI C, DEVI P, et al. Design and analysis of novel dual stator hybrid operational six-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine for wind power application[J]. GMSARN International Journal, 2021, 15: 211-216. [11] WANG B. Simulation of field oriented control algorithm of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on SVPWM[J]. Mobile Information Systems, 2022(10): 1839488. [12] 张敬南. 船舶电力推进六相同步电动机控制系统研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2009: 52-56.ZHANG J N. Six-phase synchronism motor control system for the ship electric propulsion[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2009: 52-56(in Chinese). [13] 林桦, 邹云屏. 采用气隙磁链定向控制的十二相同步电动机数学模型[J]. 中小型电机, 2004, 31(2): 21-27.LIN H, ZOU Y P. Mathematical models of 12-phase synchronous machine with air gap flux-oriented control[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2004, 31(2): 21-27(in Chinese). [14] LEVI E, JONES M, VUKOSAVIC S N. A series-connected two-motor six-phase drive with induction and permanent magnet machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2006, 21(1): 121-129. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2005.853737 [15] 李昊洋, 邱鑫, 李思祥, 等. 永磁同步电机直接转矩和矢量控制运行稳定性对比研究[J]. 南京师范大学学报(工程技术版), 2018, 18(1): 30-36.LI H Y, QIU X, LI S X, et al. Comparative study on operating stability of direct torque control and vector control using in permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 18(1): 30-36(in Chinese). [16] WOLDEGIORGIS A T, GE X L, WANG H M, et al. A new frequency adaptive second-order disturbance observer for sensorless vector control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(12): 11847-11857. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3047065 [17] 张庆宇, 涂群章, 周建波, 等. 永磁同步电机气隙磁场定向控制仿真分析[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2019, 40(12): 105-109. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.12.021ZHANG Q Y, TU Q Z, ZHOU J B, et al. Simulation analysis of air-gap field oriented control for permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2019, 40(12): 105-109(in Chinese). doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2019.12.021 [18] 顾聪, 王晓琳, 邓智泉. 一种基于双重锁相环的高速永磁同步电机转子位置估计误差全补偿方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(3): 962-970.GU C, WANG X L, DENG Z Q. A rotor position estimated error correction method for high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor based on dual-phase-locked-loop[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(3): 962-970(in Chinese). [19] 韩坤, 孙晓, 刘秉, 等. 一种永磁同步电机矢量控制SVPWM死区效应在线补偿方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(2): 620-627.HAN K, SUN X, LIU B, et al. Dead-time on-line compensation scheme of SVPWM for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system with vector control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(2): 620-627(in Chinese). [20] ZHANG A L, CHEN Z F, GAO R Z, et al. Crowbarless symmetrical low-voltage ride through based on flux linkage tracking for brushless doubly fed induction generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(9): 7606-7616. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2944096 -






 下载:
下载: