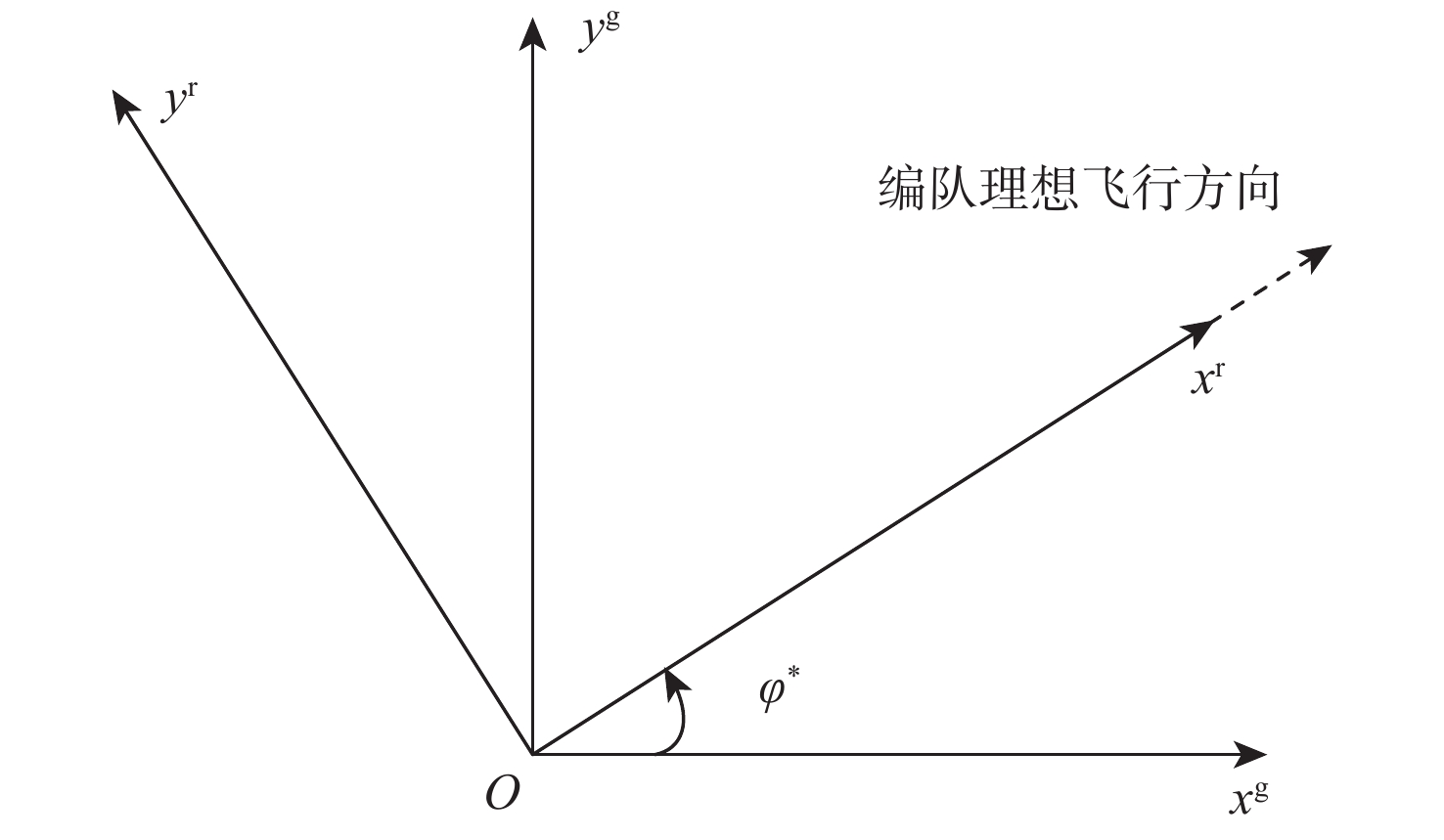
-
摘要:
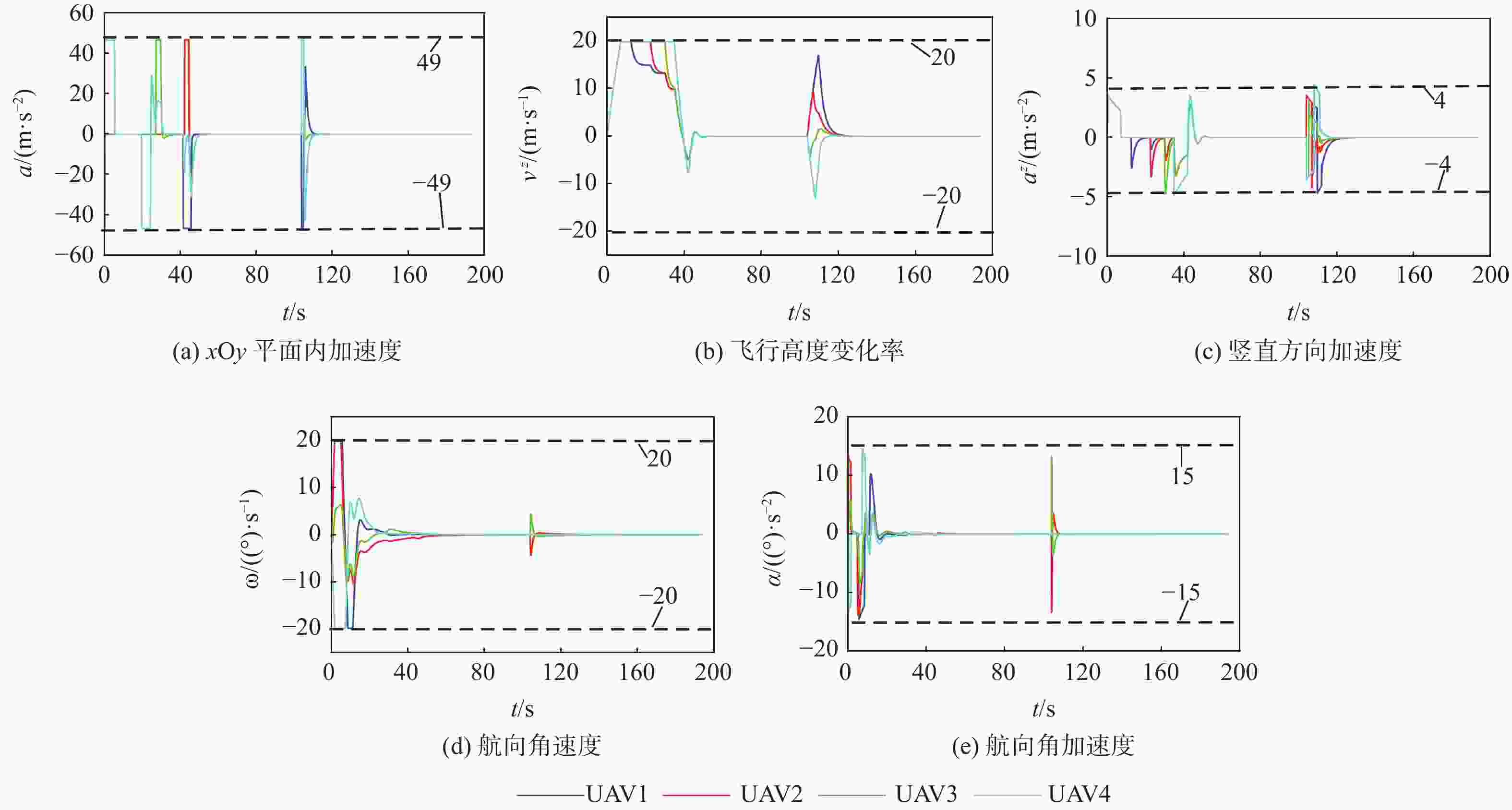
针对无人机运动学模型特点和远距离成形问题,提出一种基于改进一致性算法的无人机集结-成形策略。建立能直观描述编队队形的坐标系,根据纵向和横航向解耦的带自动驾驶仪的无人机三自由度运动学模型的特点,考虑无人机机动性能约束,对一致性算法进行改进,实现对无人机速度、航向和飞行高度的控制,提出编队队形控制算法。针对无人机初始间距大带来的调参问题,增加集结过程,并利用粒子群算法优化集结速度,避免航迹冲突,集结结束后再采用所提算法生成无人机航迹,提升算法的适应性。仿真结果表明:所提算法能使无人机在满足机动性约束的情况下,形成稳定队形;相比于直接成形法,所提策略提高改进一致性算法的适应性和安全性。
Abstract:According to the characteristics of unmanned aerial vehicle kinematics model and the problem of remote forming, an improved consensus-based algorithm was proposed to solve the gathering-forming strategy of unmanned aerial vehicle. The coordinate system which can describe the formation directly was established. According to the characteristics of the three degree-of-freedom kinematics model of unmanned aerial vehicle with autopilot decoupled from longitudinal and transverse directions and the constraints of unmanned aerial vehicle maneuvering performance, the consensus algorithm was improved to realize the control of unmanned aerial vehicle speed, heading and flight altitude. The formation control algorithm was proposed. In addressing the parameter tuning problem caused by the large initial spacing of unmanned aerial vehicle, a gathering process was added. The particle swarm optimization algorithm was used to optimize the gathering speed to avoid trajectory conflicts, and the proposed algorithm was used to generate trajectory of each unmanned aerial vehicle after the gathering, both of which improved the adaptability of the algorithm. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can make unmanned aerial vehicles form a stable formation under the condition of satisfying the maneuverability constraints. Compared with the direct forming method, the proposed strategy improves the adaptability and security of the improved consistency algorithm.
-
表 1 无人机机动性能参数
Table 1. Maneuvering performance parameters of UAV
vmax/
(m·s−1)$ \begin{array}{c} {v_{\min }}/\\ ({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}}) \end{array}$ $ \begin{array}{c} {a_{\max }}/\\ ({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}}) \end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c} {a_{\min }}/\\({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}}) \end{array}$ $ \begin{array}{c}{\omega _{\max }}/ \\ ({\mathrm{rad}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}}) \end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c} {\omega _{\min }}/ \\ ({\mathrm{rad}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}})\end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c}{\alpha _{\max }}/ \\({\mathrm{rad}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}})\end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c}{\alpha _{\min }}/ \\({\mathrm{rad}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}}) \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c} v_{\max }^{\textit{z}}/ \\({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}}) \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c} v_{\min }^{\textit{z}}/ \\({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 1}})\end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c}a_{\max }^{\textit{z}}/ \\({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}}) \end{array}$ $ \begin{array}{c}a_{\min }^{\textit{z}}/ \\({\mathrm{m}} \cdot {{\mathrm{s}}^{ - 2}})\end{array} $ 300 50 49 −49 $ \dfrac{{\text{π}}}{9} $ $ - \dfrac{{\text{π}}}{9} $ $ \dfrac{{\text{π}}}{{12}} $ $ - \dfrac{{\text{π}}}{{12}} $ 20 −20 4 −4 表 2 无人机初始位置信息
Table 2. Initial position information of UAVs
无人机 $ x/{{\mathrm{m}}} $ $ y/{{\mathrm{m}}} $ $ {\textit{z}}/{{\mathrm{m}}} $ UAV1 −3 565 −2 846 0 UAV2 4 098 3 415 0 UAV3 1 372 2 588 0 UAV4 −3 360 1 612 0 -
[1] 张军国, 闫浩, 胡春鹤, 等. 无人机在林业中的应用及前景展望[J]. 林业工程学报, 2019, 4(1): 8-16.ZHANG J G, YAN H, HU C H, et al. Application and future development of unmanned aerial vehicle in forestry[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2019, 4(1): 8-16(in Chinese). [2] 南江林. 消防无人机研究与应用前景分析[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2017, 36(8): 1105-1107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2017.08.024NAN J L. The research and application prospect analysis of fire UAV[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2017, 36(8): 1105-1107(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2017.08.024 [3] 代威, 张洪涛, 惠俊鹏. 无人机在未来海战场中的应用分析[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2018, 39(1): 21-24. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.01.005DAI W, ZHANG H T, HUI J P. Application analysis of UAV in future naval warfare field[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2018, 39(1): 21-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.01.005 [4] 韩亮, 任章, 董希旺, 等. 多无人机协同控制方法及应用研究[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2018, 5(4): 1-7.HAN L, REN Z, DONG X W, et al. Research on cooperative control method and application for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2018, 5(4): 1-7(in Chinese). [5] NO T S, KIM Y, TAHK M J, et al. Cascade-type guidance law design for multiple-UAV formation keeping[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2011, 15(6): 431-439. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2010.08.011 [6] SAIF O, FANTONI I, ZAVALA-RÍO A. Distributed integral control of multiple UAVs: Precise flocking and navigation[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 13(13): 2008-2017. [7] ASKARI A, MORTAZAVI M, TALEBI H A. UAV formation control via the virtual structure approach[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2015, 28(1): 04014047. [8] 杜永浩, 王凌, 邢立宁. 空天无人系统智能规划技术综述[J]. 系统工程学报, 2020, 35(3): 416-432.DU Y H, WANG L, XING L N. Intelligent planning technologies for unmanned aerospace system: A literature review[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2020, 35(3): 416-432(in Chinese). [9] REN W. Consensus strategies for cooperative control of vehicle formations[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2007, 1(2): 505-512. [10] GULZAR M M, RIZVI S T H, JAVED M Y, et al. Multi-agent cooperative control consensus: A comparative review[J]. Electronics, 2018, 7(2): 22. doi: 10.3390/electronics7020022 [11] 陈旿, 张鑫, 金鑫, 等. 一种多智能体协同信息一致性算法[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(12): 321222. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2017.321222CHEN W, ZHANG X, JIN X, et al. A cooperative information consensus algorithm for multi-agent system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(12): 321222(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2017.321222 [12] DU H B, ZHU W W, WEN G H, et al. Distributed formation control of multiple quadrotor aircraft based on nonsmooth consensus algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 342-353. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2777463 [13] 何吕龙, 张佳强, 侯岳奇, 等. 有向通信拓扑和时延条件下的无人机集群时变编队控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(2): 314-323.HE L L, ZHANG J Q, HOU Y Q, et al. Time-varying formation control for UAV swarm with directed interaction topology and communication delay[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(2): 314-323(in Chinese). [14] DONG X W, ZHOU Y, REN Z, et al. Time-varying formation tracking for second-order multi-agent systems subjected to switching topologies with application to quadrotor formation flying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 5014-5024. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2593656 [15] 吴宇, 梁天骄. 基于改进一致性算法的无人机编队控制[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(9): 323848. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23848WU Y, LIANG T J. Improved consensus-based algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle formation control[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(9): 323848(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.23848 [16] 张佳龙, 闫建国, 张普, 等. 基于一致性算法的无人机协同编队避障研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2018, 52(9): 168-174. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201809023ZHANG J L, YAN J G, ZHANG P, et al. Collision avoidance of unmanned aerial vehicle formation based on consensus control algorithm[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(9): 168-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201809023 [17] BEARD R W, MCLAIN T W. Small unmanned aircraft: Theory and practice[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2012: 164-172. [18] REN W, BEARD R W. Distributed consensus in multi-vehicle cooperative control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2008: 7-22. [19] SHI Y H, EBERHART R C. Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of the Evolutionary Programming VII. Berlin: Springer, 1998: 591-600. -






 下载:
下载: