Deployment optimization method for missile early warning radar under complex and multi-directional missile threats
-
摘要:
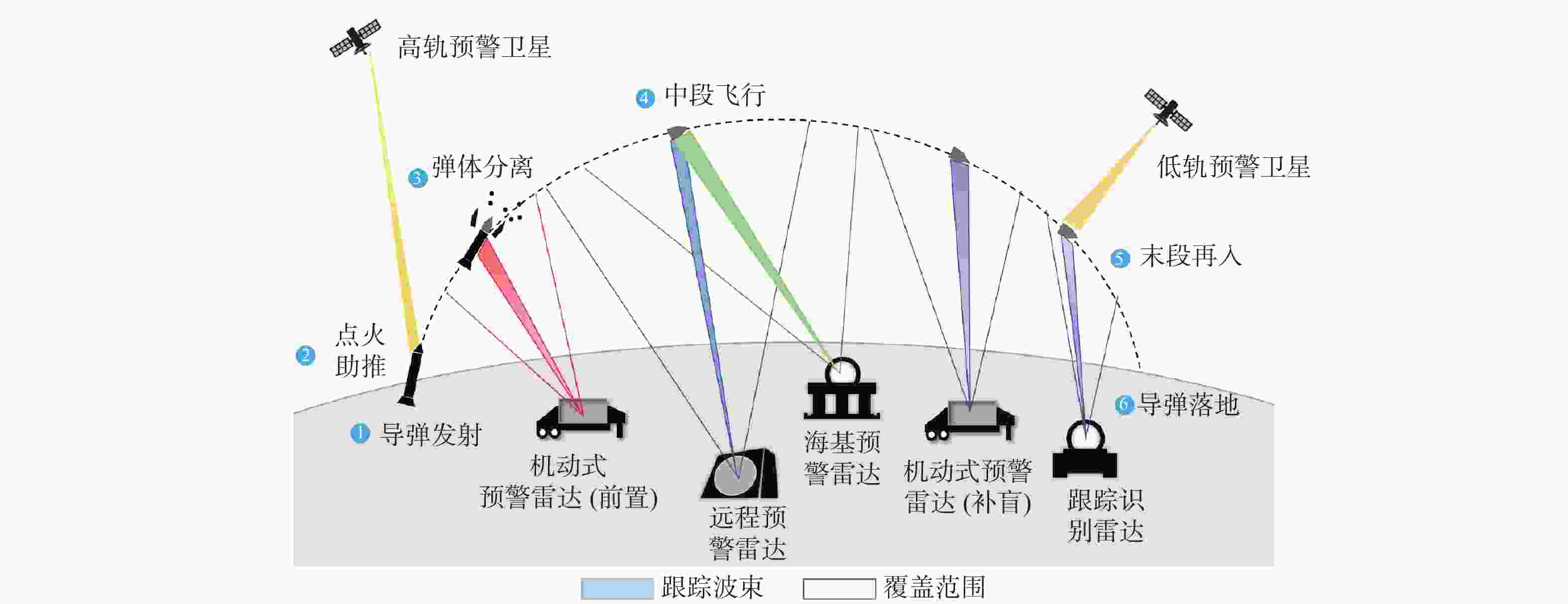
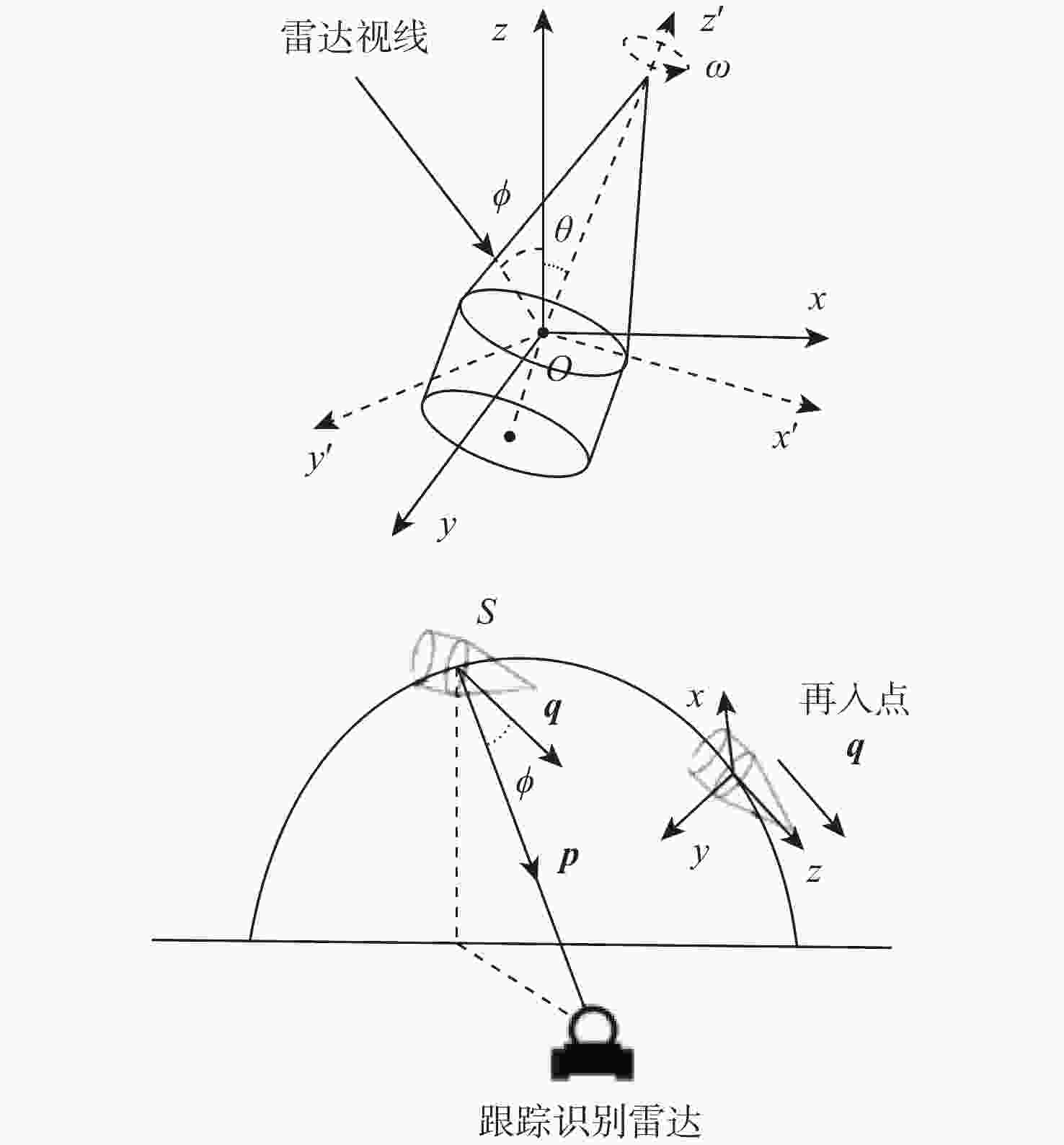
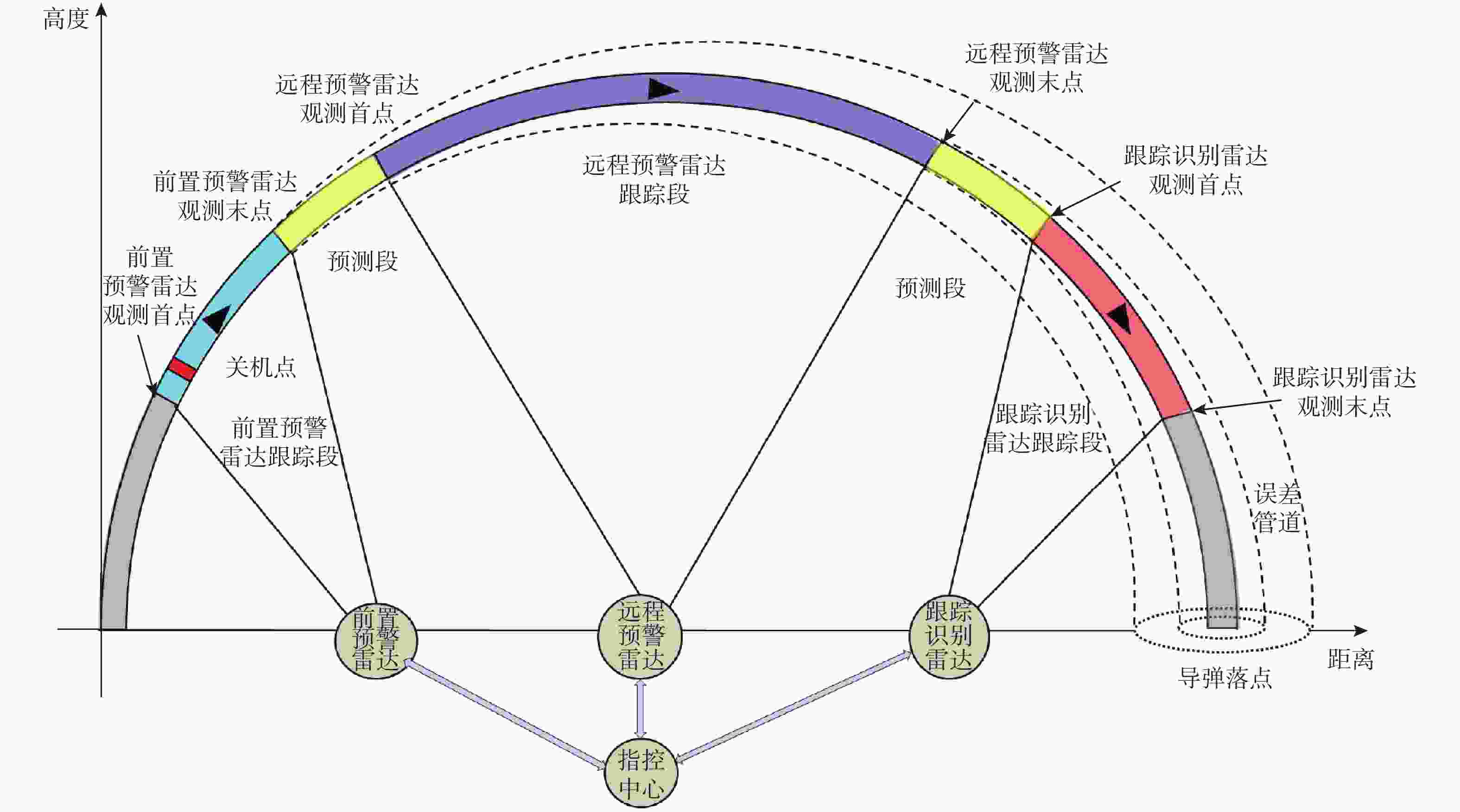
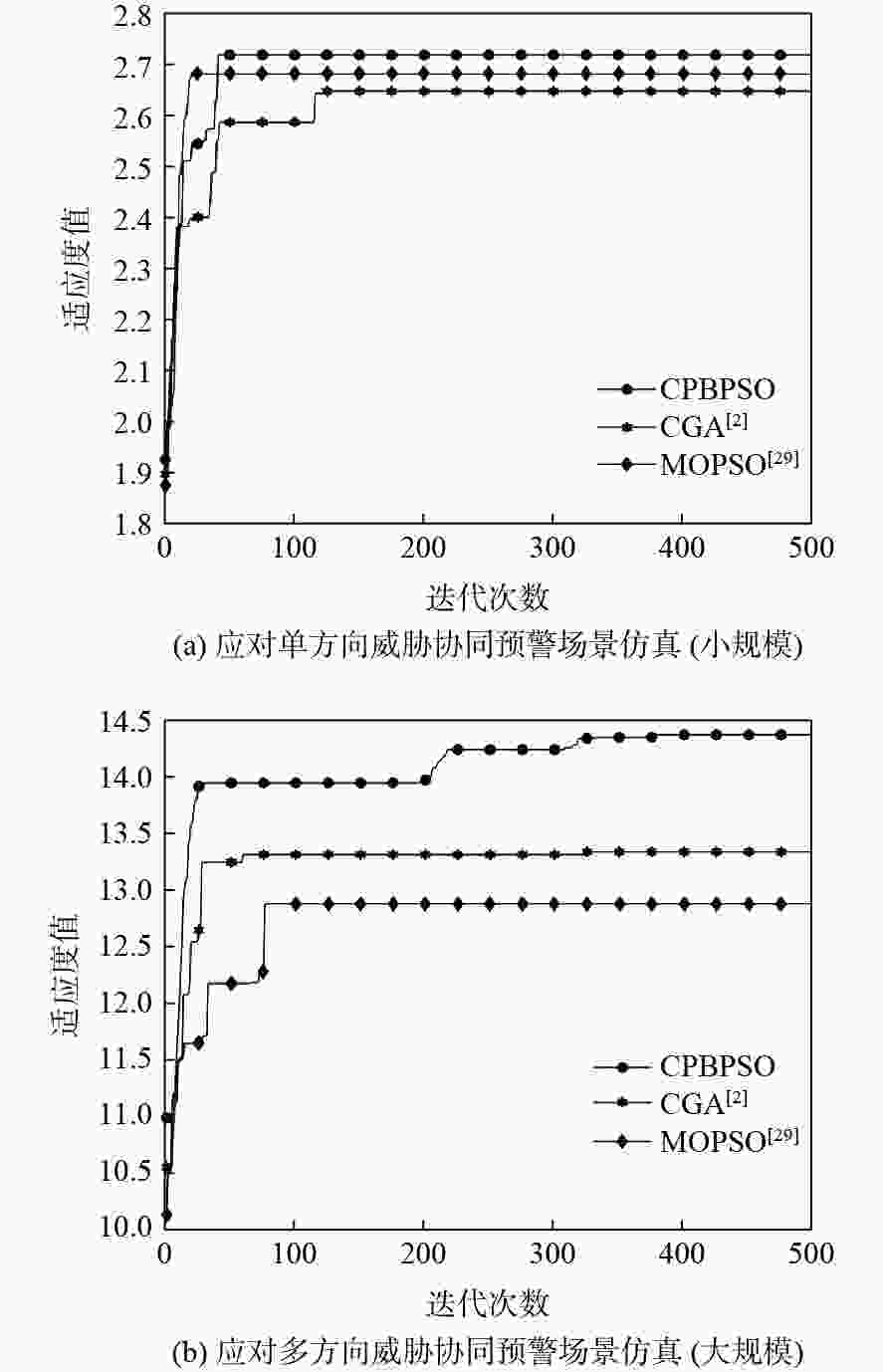
针对现有导弹预警雷达部署相对独立、协同困难,难以满足大规模对抗场景的现状,从远程预警雷达、跟踪识别雷达、机动式预警雷达不同的任务特点出发,建立应对复杂多方向威胁的多型导弹预警雷达优化部署模型,在满足最优覆盖、协同交接、目标识别等任务约束下,解决雷达协同部署问题。针对所提模型设计了一种基于云自适应的分区优化离散粒子群(CPBPSO)算法,通过设计分区编码策略缩减算法求解空间、加入云自适应变异算子提高算法全局寻优和局部跳出能力,使算法更适用于导弹预警雷达部署问题的处理。实例验证了所提模型在求解单方向、多方向威胁场景部署问题的可行性,对比分析了CPBPSO算法的有效性,基本满足导弹预警雷达最优化协同部署的需求。
Abstract:An optimized deployment model of multiple missile early warning radars is established based on the distinct mission characteristics of early warning radar, tracking and identification radar, and transportable early warning radar in order to address the situation where the deployment of existing missile early warning radars is relatively independent, difficult to cooperate with, and difficult to meet the large-scale operation scenario. Under the constraints of optimal coverage, cooperative handover, and target identification, the cooperative deployment of early warning radars is solved. A cloud adaptive partition optimization binary particle swarm optimization (CPBPSO) algorithm is designed. In order to make the algorithm more suited for solving early warning radar deployment problems, the partition coding strategy is used to shrink the algorithm’s solution space. The cloud adaptive mutation operator is then added to enhance the algorithm’s global optimization and local jumping capability.The example verifies the feasibility of the model in solving the deployment problem of single-direction and multi-direction threat scenarios and analyzes the effectiveness of the CPBPSO algorithm, which basically meets the needs of the optimal cooperative deployment of missile early warning radar.
-
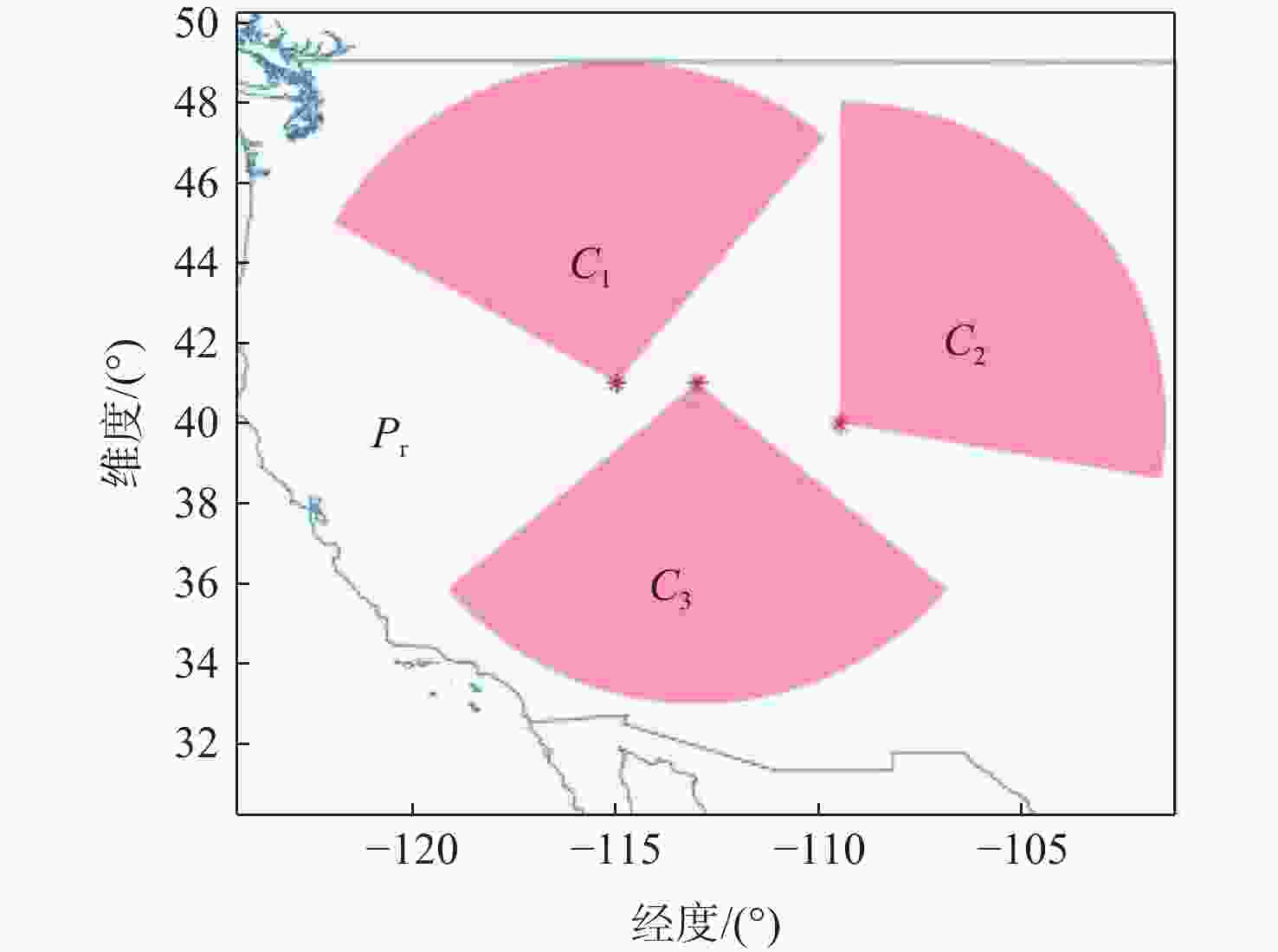
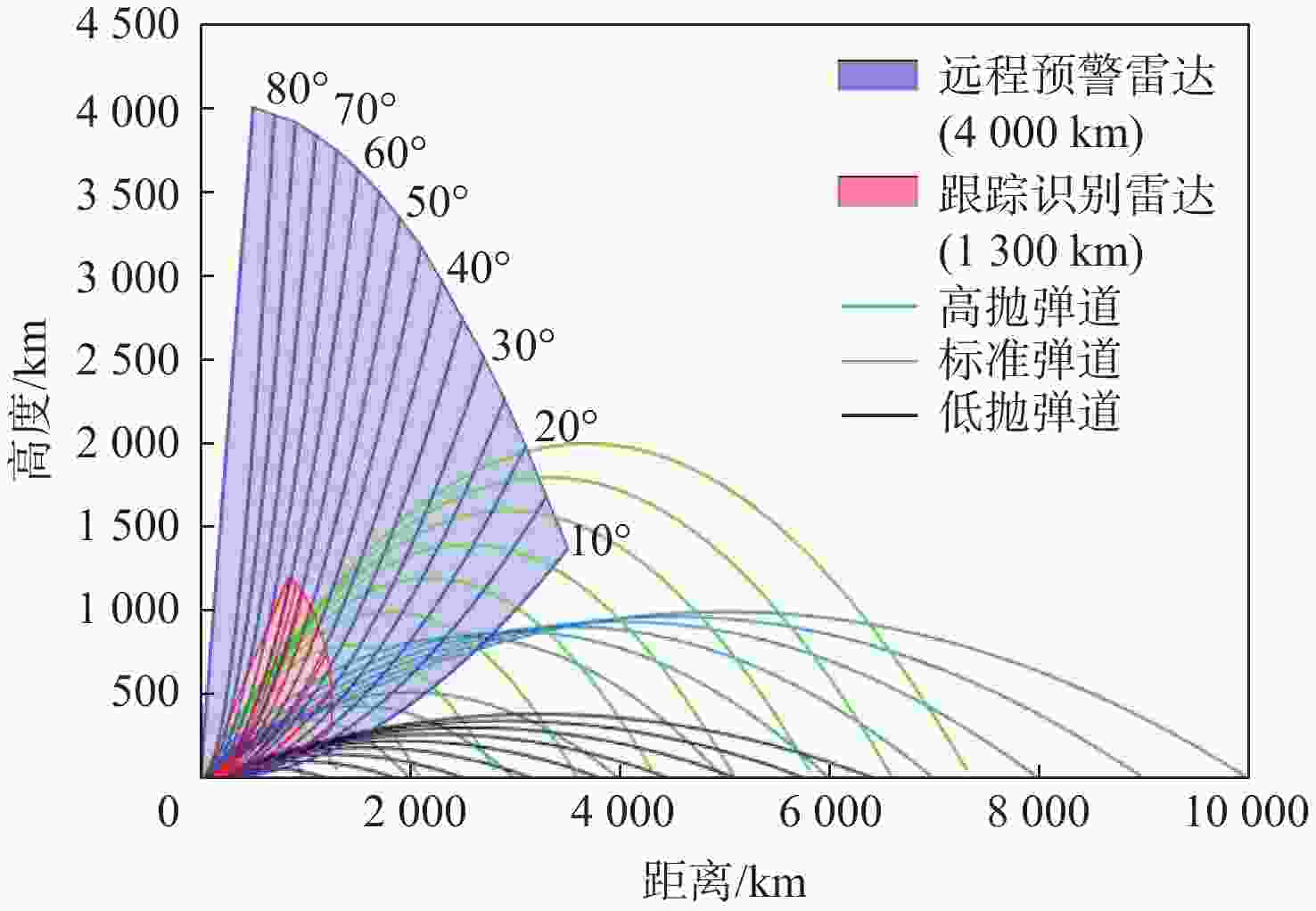
表 1 单方向威胁空域的典型弹道信息
Table 1. Typical ballistic information of single direction threat airspace
弹道序号 发点
位置/(°)落点
位置/(°)弹道
弧长/km关机点速度/
(km·s−1)飞行
时间/s1 (27.4,133.1) (41.0,80.3) 7036.7 6.534 1934.7 2 (19.2,127.8) (41.0,80.3) 7072.5 6.498 1928.3 3 (27.2,129.0) (41.0,80.3) 5140.5 5.865 1186.9 4 (23.7,127.1) (41.0,80.3) 5258.1 5.904 1203.4 表 2 雷达基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameter of radar
雷达类型 最大探测距离/km 方位范围/(°) 俯仰范围/(°) 远程预警雷达 3 000 ±60 0~85 跟踪识别雷达 500 0~360 10~90 前置预警雷达 1 500 ±53 10~85 表 3 雷达优化部署参数
Table 3. Optimal radar deployment parameter
雷达类型 部署点位 海拔/km 法向/(°) 前置预警雷达 (24.83°N 114.83°E) 0.0293 353.5 远程预警雷达 (45.62°N 116.82°E) 0.8979 148.6 跟踪识别雷达 (43.27°N 85.23°E) 3.7204 表 4 单方向威胁预警能力分析
Table 4. Analysis of single direction threat early warning capability
弹道
名称首点告警
时间/s持续跟踪
时长/s弹道覆盖
率/%高识别
时长/sBM1 T0+56.18 1831.58 94.67 71.41 BM2 T0+39.21 1601.45 83.05 56.10 BM3 T0+50.36 1117.22 94.13 113.88 BM4 T0+40.29 1106.76 92.07 100.85 注:T0为导弹发射时刻。 表 5 多方向威胁空域的典型弹道信息
Table 5. Typical ballistic information of multi-direction threat airspace
弹道序号 发点
位置/(°)落点
位置/(°)弹道
弧长/km关机点速度/
(km·s−1)飞行
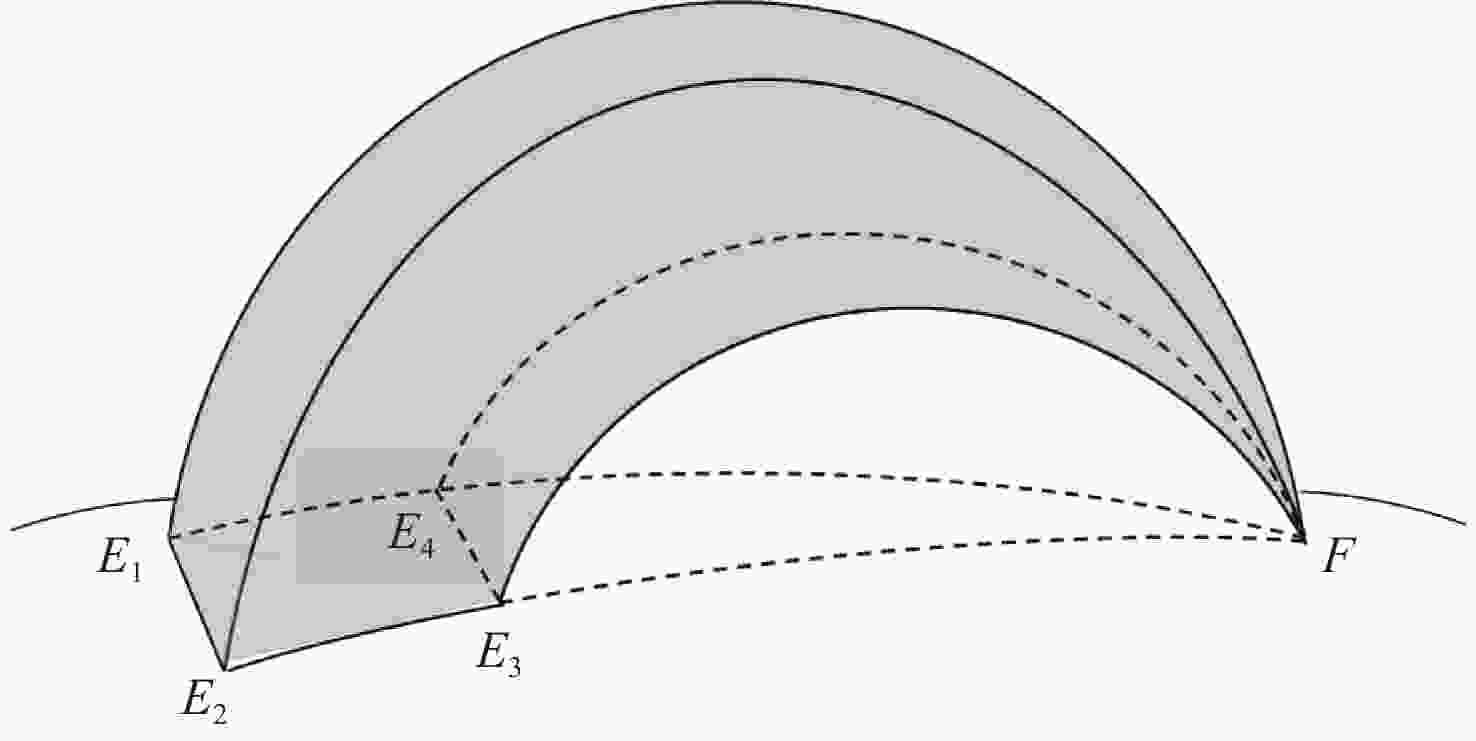
时间/s1 (56.3,123.5) (41.0,80.3) 6003.7 5.236 984.5 2 (37.0,127.0) (41.0,80.3) 4839.7 5.550 1078.9 3 (23.7,130.0) (41.0,80.3) 6083.4 5.993 1234.8 4 (13.7,105.0) (41.0,80.3) 4167.3 5.904 1607.3 5 (7.5,91.5) (41.0,80.3) 4601.5 5.392 1053.3 6 (1.6,60.0) (41.0,80.3) 5699.9 5.747 1216.6 注:为便于表示,每个空域仅选填1条典型最优能量弹道。 表 6 雷达部署及任务分配
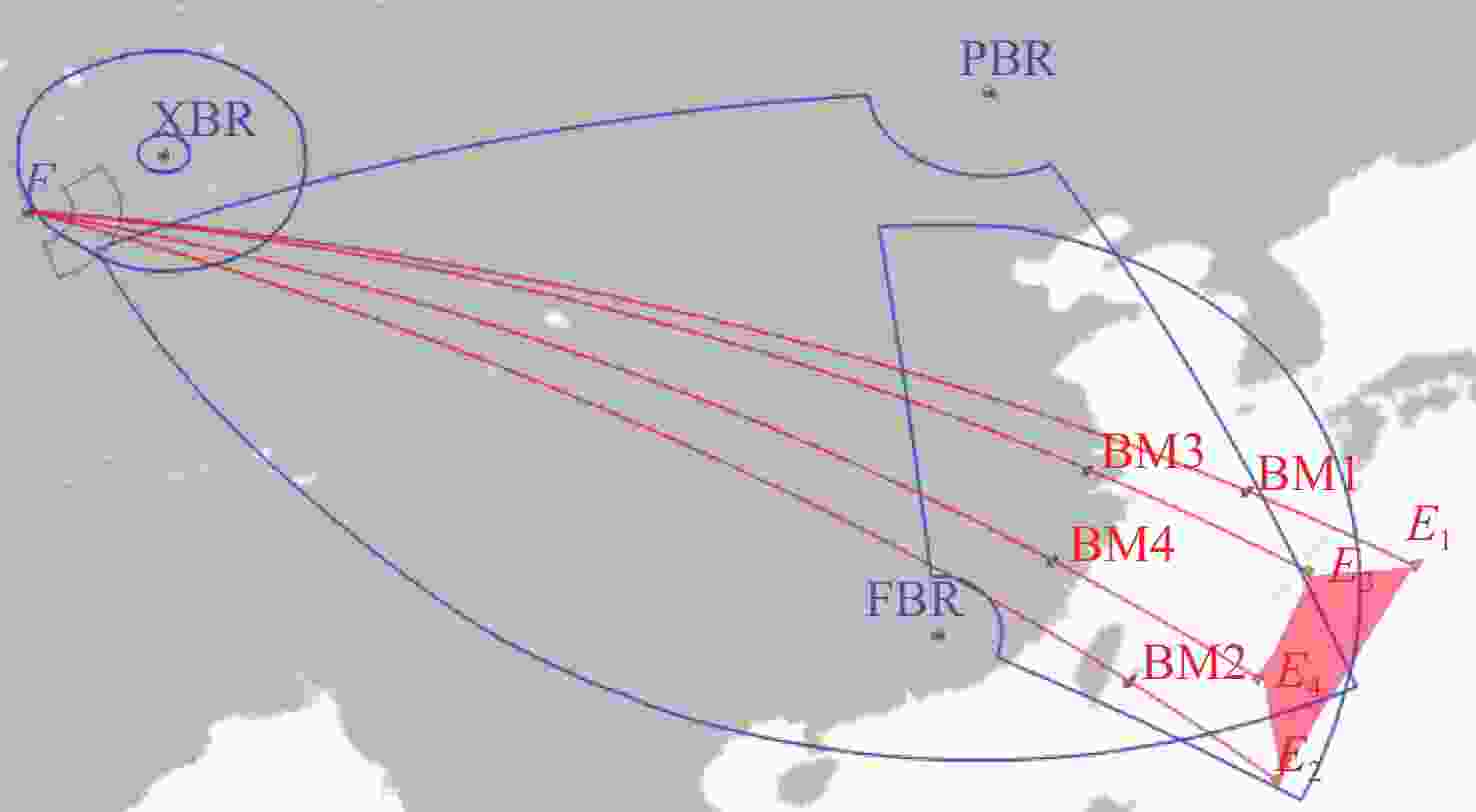
Table 6. Radar deployment and task assignment
雷达类型 名称 部署
点位/(°)高程/
km法向/
(°)E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 前置预警
雷达FBR1 (44.8,113.3) 1.278 7.2 √ √ FBR2 (25.7,119.1) 0.568 4.8 √ √ FBR3 (27.9,88.1) 4.758 88.4 √ √ 远程预警
雷达PBR1 (29.6,109.4) 0.569 304.7 √ √ √ PBR2 (38.6,90.2) 3.138 147.9 √ √ √ 跟踪识别
雷达XBR1 (42.4,81.4) 3.951 √ √ √ √ √ √ XBR2 (41.7,77.6) 5.199 √ √ √ √ √ √ 表 7 多方向威胁预警能力分析
Table 7. Analysis of mutli-direction threat early warning capability
威胁
区域首点告警
时间/s持续跟踪
时长/s弹道覆盖
率/%高识别
时长/sE1 T0+56.68 905.28 92.12 76.11 E2 T0+50.39 1049.44 97.27 111.26 E3 T0+42.07 1022.90 82.84 93.425 E4 T0+59.97 1507.16 93.77 76.96 E5 T0+51.88 980.93 93.13 77.16 E6 T0+608.46 563.16 46.29 62.55 -
[1] CHRISTIAN A. US missile defence efforts and Chinese reservation in East Asia[J]. Asian Affairs, 2020(2): 605-620. [2] WEI P, ZHENG L, HUANG F, et al. Optimal deployment of radar network based on chaos genetic algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6018- 6023. [3] LI J, DAI W, HU L. Research on intelligent station layout optimization of air defense radar network[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Robot Systems and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 39-43. [4] YANG Y, ZHANG T, YI W. Deployment of multistatic radar system using multi objective particle swarm optimization[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(5): 485-493. [5] Ma Y, JIN H B, LI H, et al. Adaptive opposition-based particle swarm optimization algorithm and application research[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 518-523. [6] RAO D V, RAVISHANKAR M. A methodology for optimal deployment and effectiveness evaluation of air defence resources using game theory[J]. Sādhanā, 2020, 45(1): 1-15. [7] YU Z, SHAN G, XU G, et al. Method of multi-sensor optimal deployment for area coverage[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 116-119. [8] 付鑫, 张峰, 冯占林. 基于并行计算的混沌遗传算法对反导预警雷达部署优化研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2016, 11(3): 276-282.FU X, ZHANG F, FENG Z L. Research of chaos genetic algorithm based on parallel computing for anti-missile warning radar disposition[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2016, 11(3): 276-282(in Chinese). [9] TIAN M, CHEN S, ZHENG X, et al. Sensors deployment optimization in multi-dimensional space based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29(5): 969-982. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2018.05.09 [10] 田桂林, 刘昌云, 高嘉乐, 等. 基于烟花算法的多传感器优化模型部署[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(8): 1742-1748.TIAN G L, LIU C Y, GAO J L, et al. Multi-sensor optimal disposition model based on fireworks algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(8): 1742-1748(in Chinese). [11] 刘伟, 刘昌云, 陈晨, 等. 反导预警装备部署方法综述[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2022, 44(3): 27-33.LIU W, LIU C Y, CHEN C, et al. Review on deployment methods of anti-missile early waring equipment[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2022, 44(3): 27-33(in Chinese). [12] KORDA M, KRISTENSEN H M. US ballistic missile defenses[J]. Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, 2019, 75(6): 295-306. [13] ZHENG Y, YAN S, QU S, et al. Research on design and evaluation method of anti-missile early warning and detection plan[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 5th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 864-867. [14] FLORES R, ALMEIDA G F, TEJERINA G R, et al. Radar coverage over irregular terrain: A practical algorithm for multipath propagation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1383-1388. [15] 徐志明, 艾小锋, 刘晓斌, 等. 基于散射中心滑动特性的双基地雷达锥体目标微动特征提取方法[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(3): 461-469.XU Z M, AI X F, LIU X B, et al. Micro-motion feature extraction of bistatic radar cone-shaped targets based on characteristic analysis of sliding scattering centers[J]. Acta Electonica Sinica, 2021, 49(3): 461-469(in Chinese). [16] 马梁. 弹道中段目标微动特性及综合识别方法[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2011: 49-68.MA L. The micro-motion characteristic and combining classification of ballistic target[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2011: 49-68(in Chinese). [17] KIM J, CHO D H, LEE W C, et al. Optimal target assignment with seamless handovers for networked radars[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(20): 4555. doi: 10.3390/s19204555 [18] 郑玉军, 田康生, 刘俊凯, 等. 早期预警雷达和多功能相控阵雷达的目标指示交接方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(1): 106-113.ZHENG Y J, TIAN K S, LIU J K, et al. The target designation and handover method of early-warning radar and multifunction phased array radar[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(1): 106-113(in Chinese). [19] FREITAS D, LOPES L G, MORGADO F. Particle swarm optimization: A historical review up to the current developments[J]. Entropy, 2020, 22(3): 362. doi: 10.3390/e22030362 [20] WANG D S, TAN D P, LIU L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(2): 387-408. doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2474-6 [21] GUO G Y, LV Y S, YANG X R, et al. Ballistic missile defense system deployment simulation based particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-4. [22] 魏法, 杨明磊, 何小静, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的平面阵同时多波束赋形方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(6): 1789-1797.WEI F, YANG M L, HE X J, et al. Simultaneous multi-beam forming method for planar array based on improved particle swarm algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1789-1797(in Chinese). [23] LIU S, HUANG F, YAN B. Optimal design of multi-missile formation based on an adaptive SA-PSO algorithm[J]. Aerospace, 2022, 9(1): 21. [24] 练青坡, 王宏健, 袁建亚, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的USV集群协同避碰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 2034-2040.LIAN Q P, WANG H J, YUAN J Y, et al. Collaborative collision avoidance method of USV cluster based on particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 2034-2040(in Chinese). [25] 黄飞腾, 翁国庆, 南余荣, 等. 基于改进云自适应粒子群的多DG配电网EV充电站优化配置[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(2): 514-525.HUANG F T, WENG G Q, NAN Y R, et al. Optimization of electric vehicle charging stations based on improved cloud adaptive particle swarm in distribution network with multiple DG[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(2): 514-525(in Chinese). [26] XIANG L I, CHEN J. A modified PSO algorithm based on cloud theory for optimizing the fuzzy PID controller[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2183(1): 012014. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2183/1/012014 [27] 陈国龙, 郭文忠, 陈羽中. 无线传感器网络任务分配动态联盟模型与算法研究[J]. 通信学报, 2009, 30(11): 48-55.CHEN G L, GUO W Z, CHEN Y Z. Research on dynamic alliance of task allocation and its algorithm in wireless sensor network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2009, 30(11): 48-55(in Chinese). [28] 韩晋山, 邢建平, 张浩, 等. 美国导弹预警系统的发展现状与趋势分析[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(4): 91-95.HAN J S, XING J P, ZHANG H, et al. Development of American missile early warning system[J]. Science Technology Review, 2019, 37(4): 91-95(in Chinese). [29] 唐嘉诚. 多功能雷达组网资源调度方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2021: 33-51.TANG J C. Research on resource scheduling method of multifunctional radar network[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021: 33-51(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: