-
摘要:
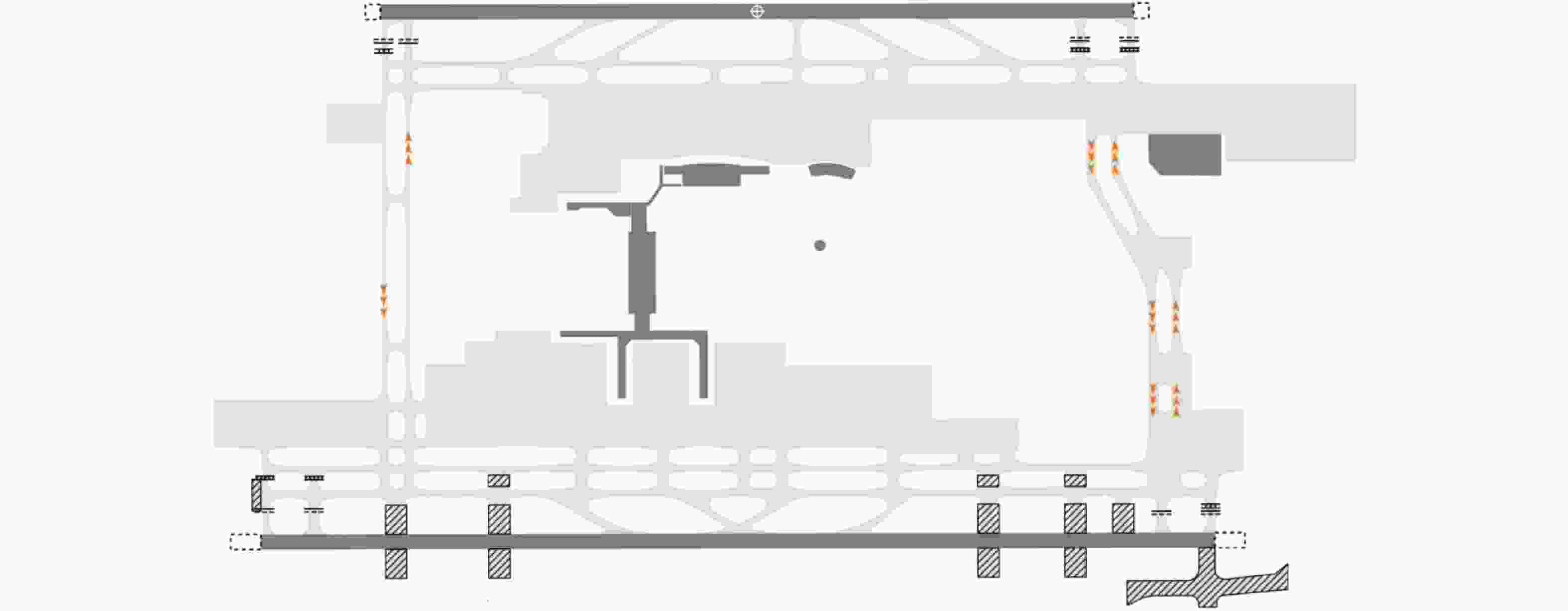
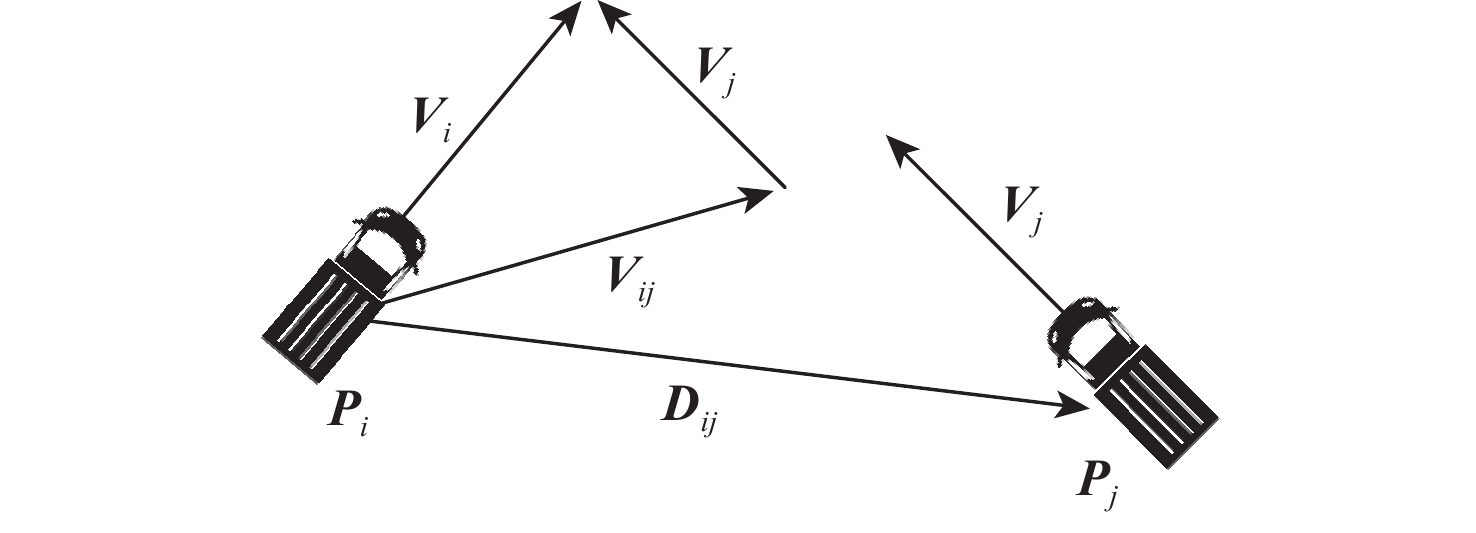
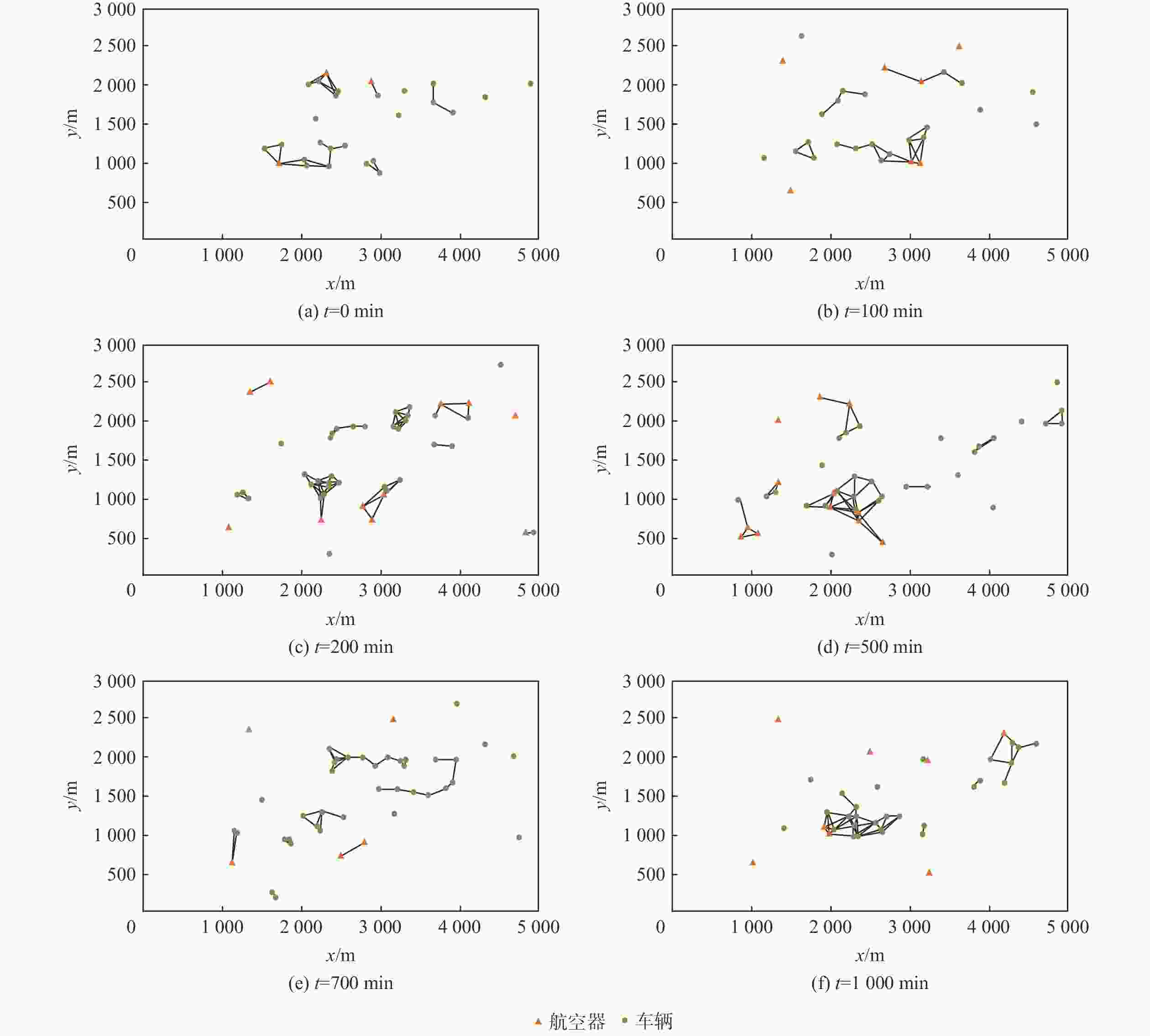
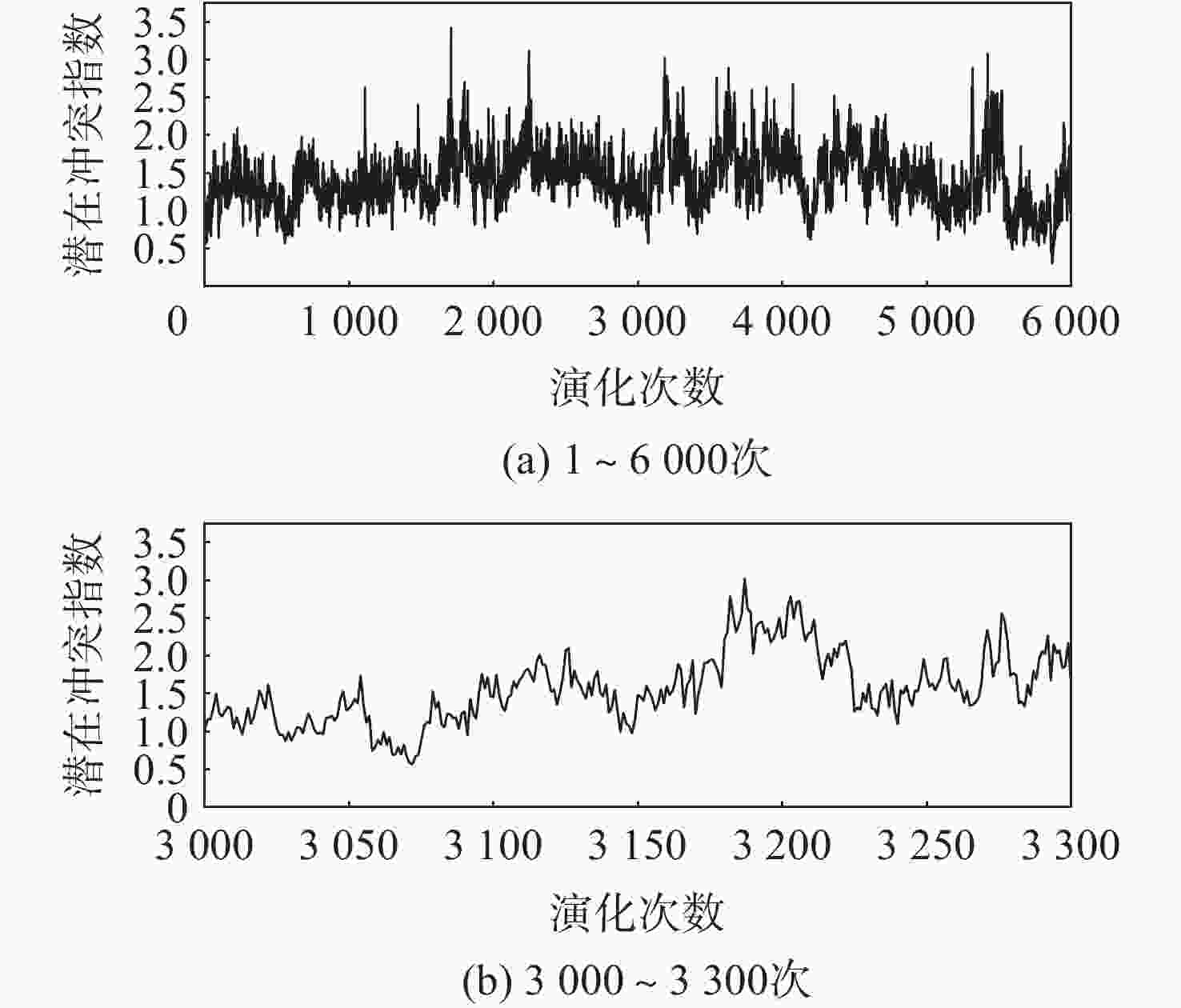
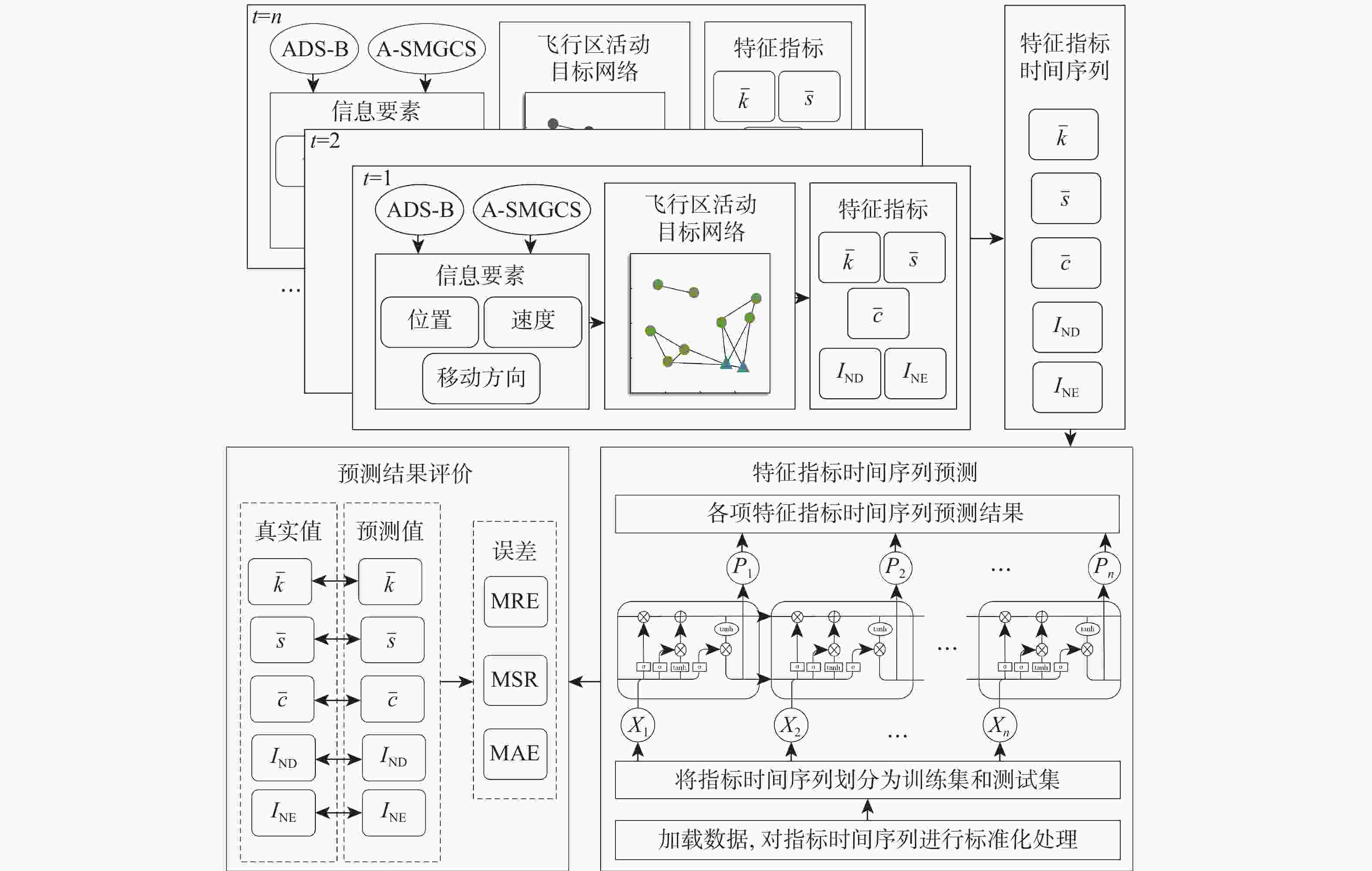
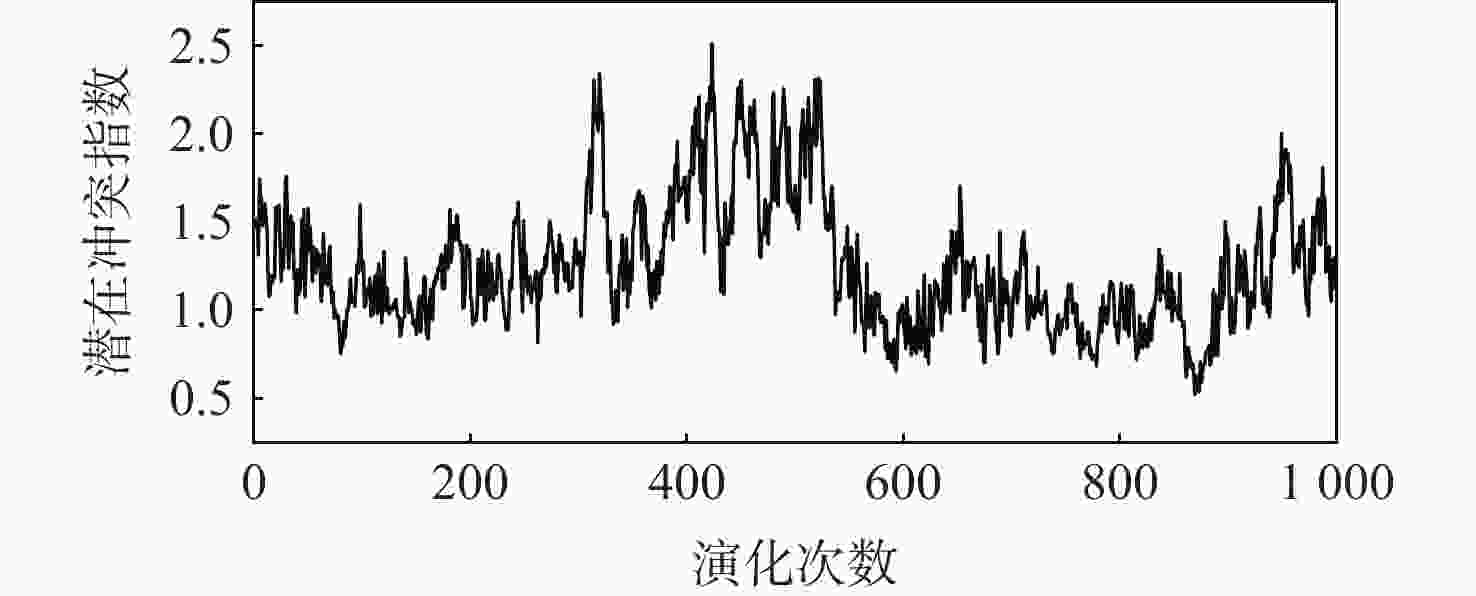
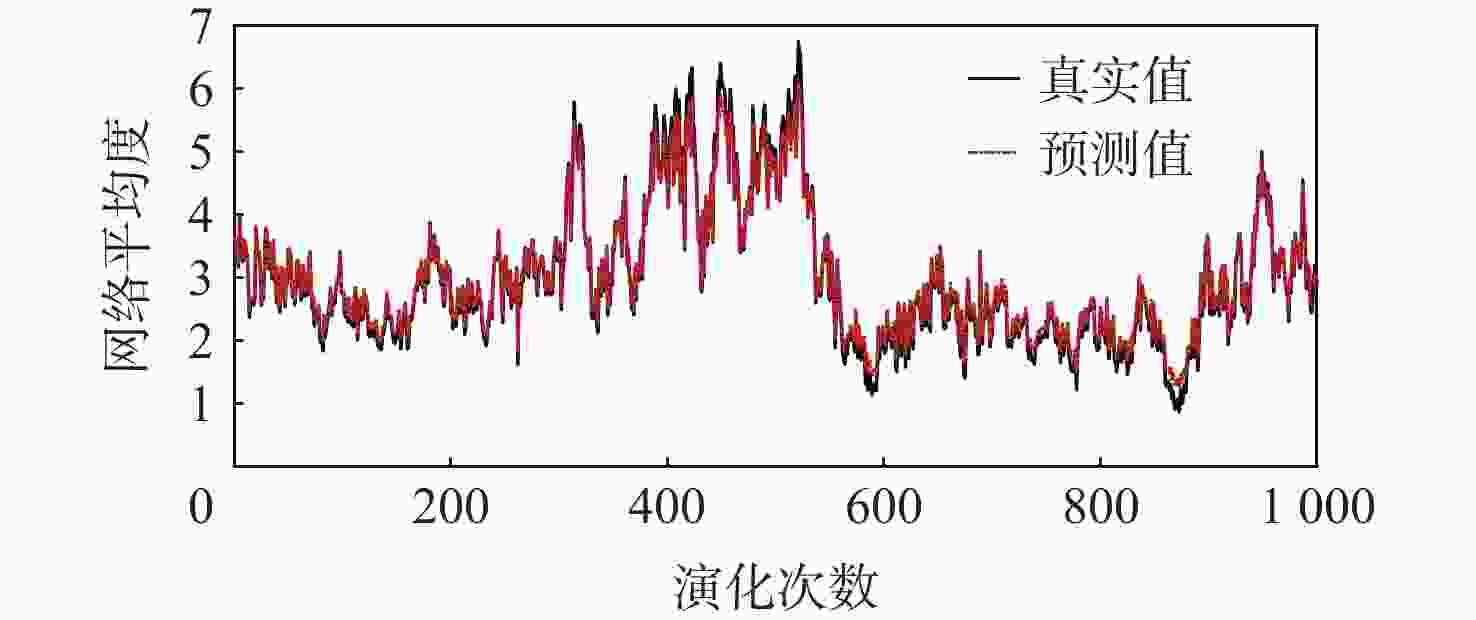
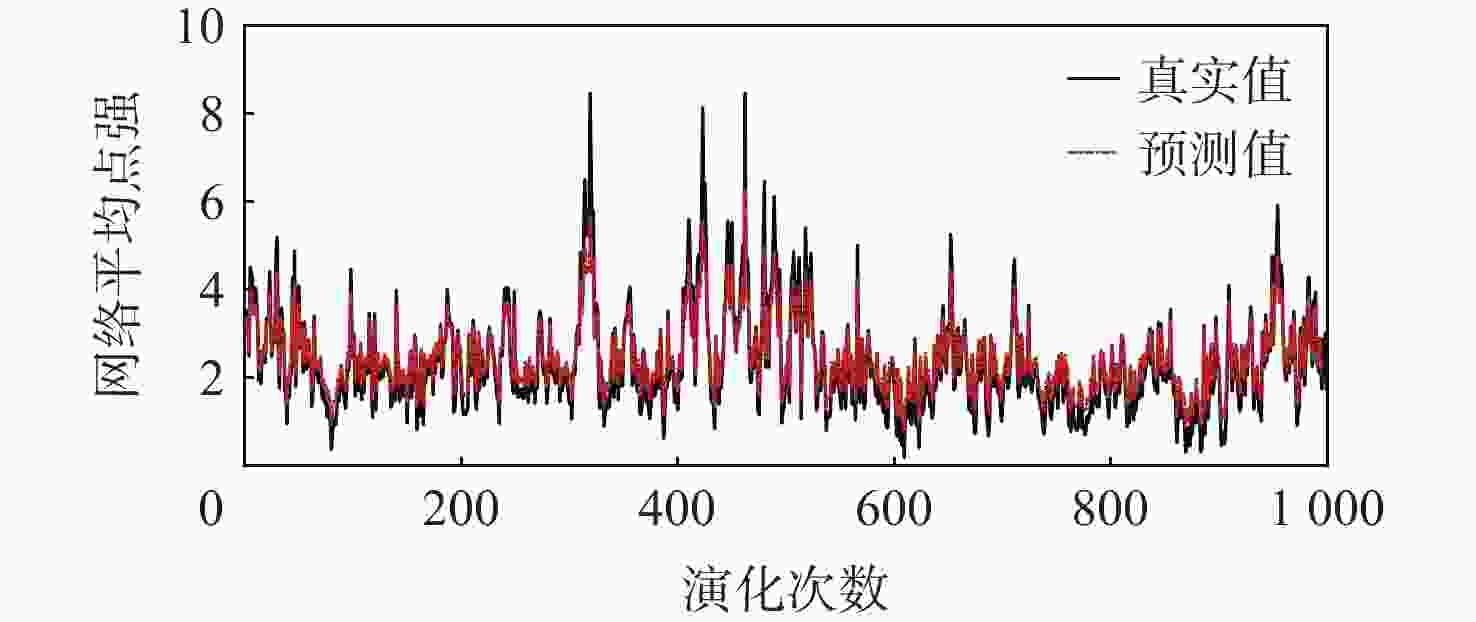
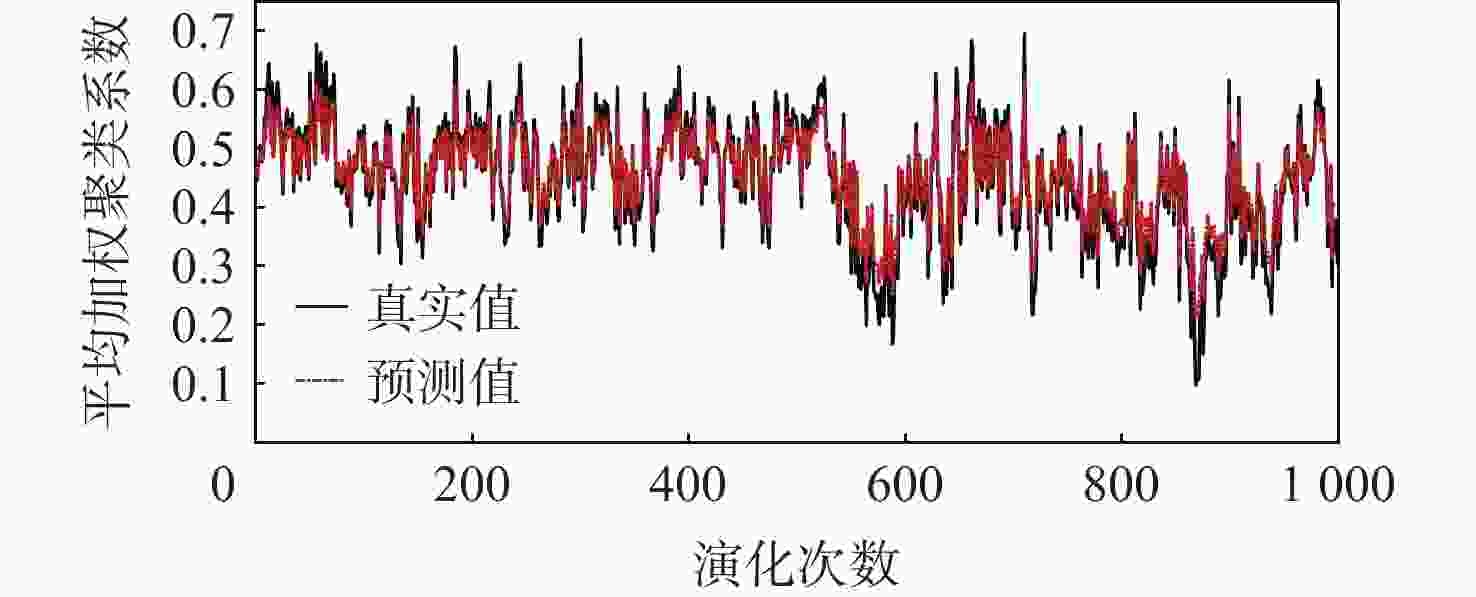
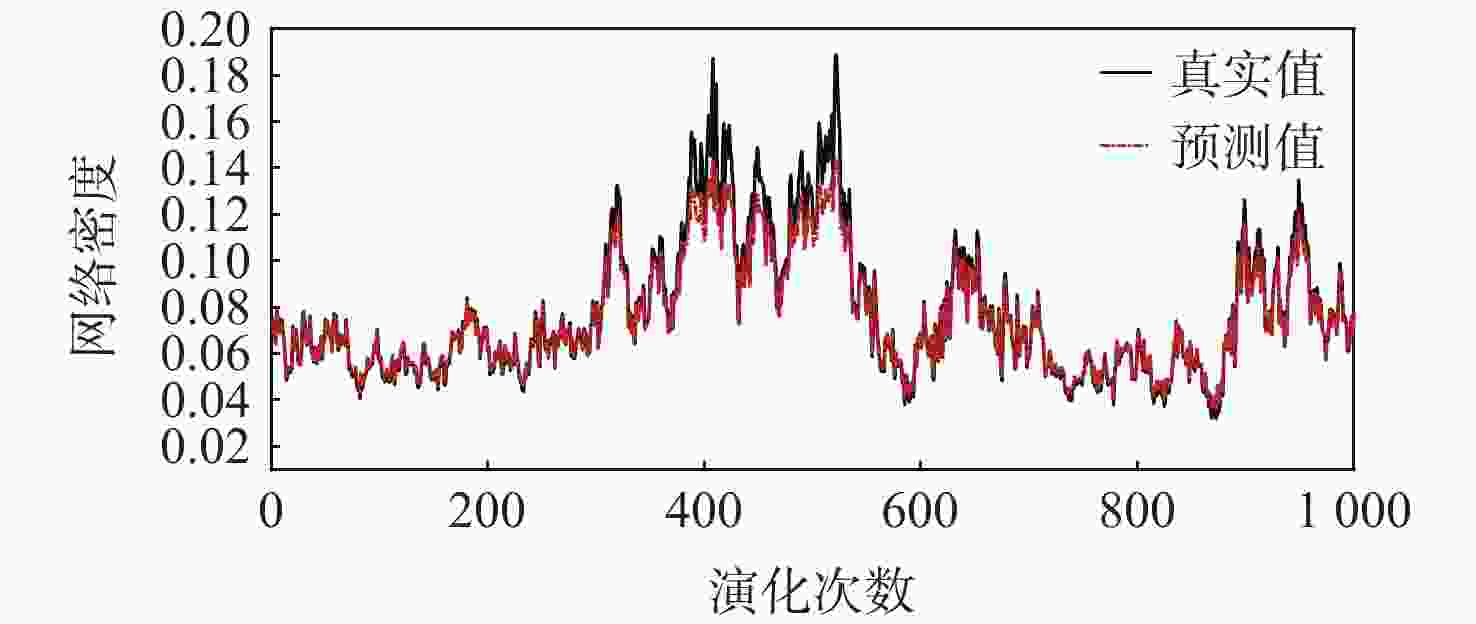
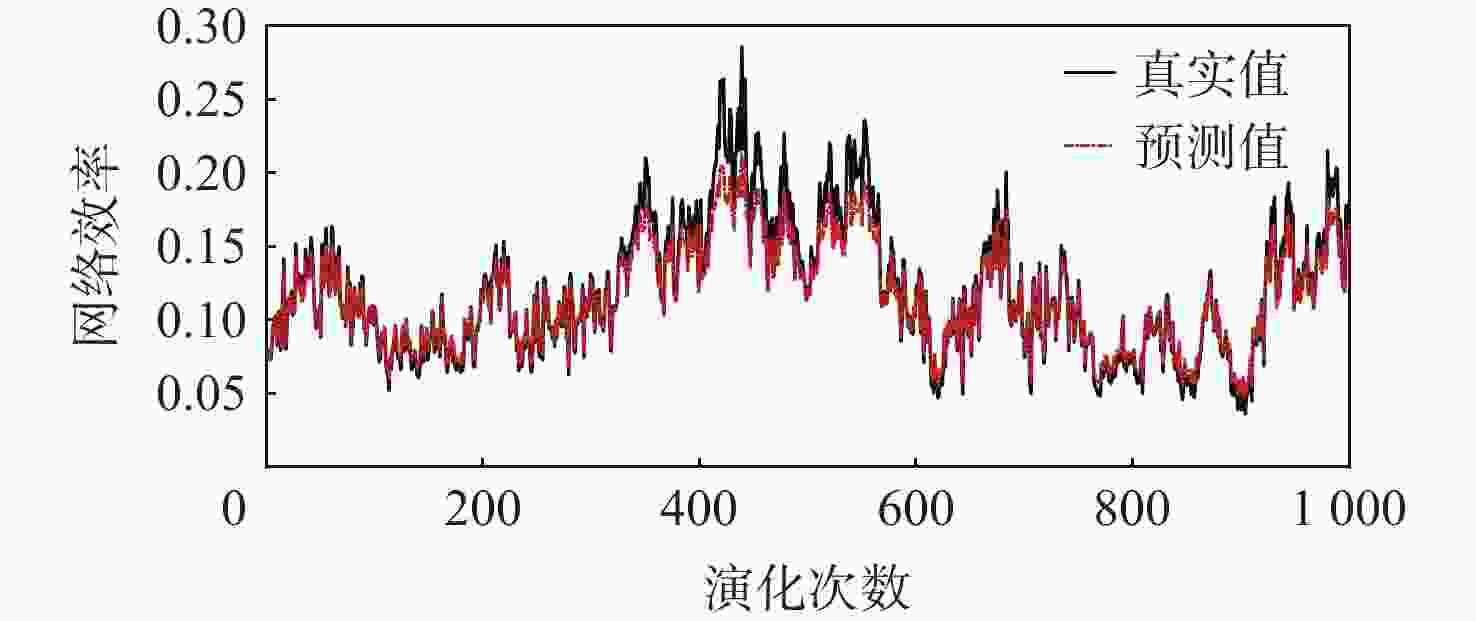
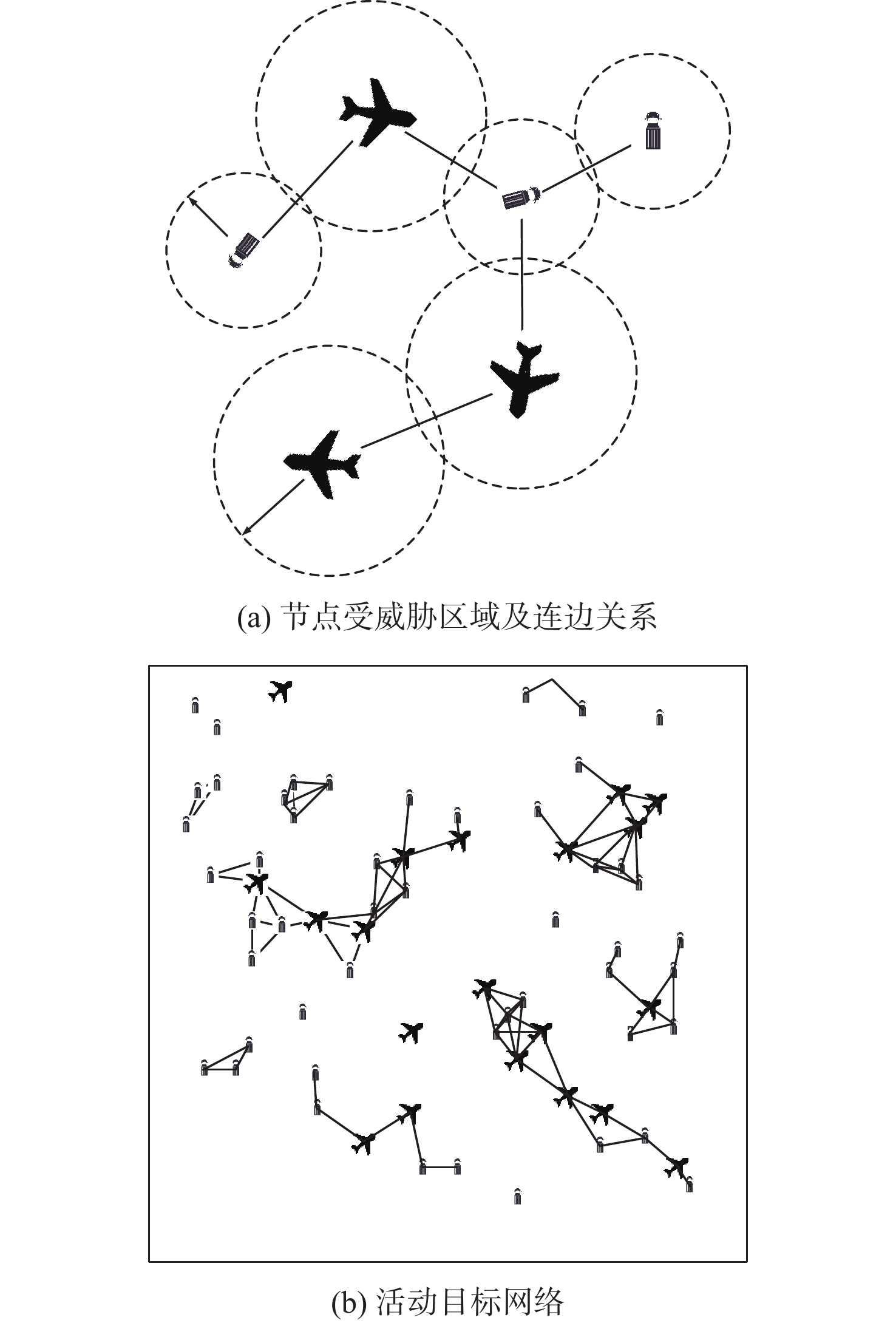
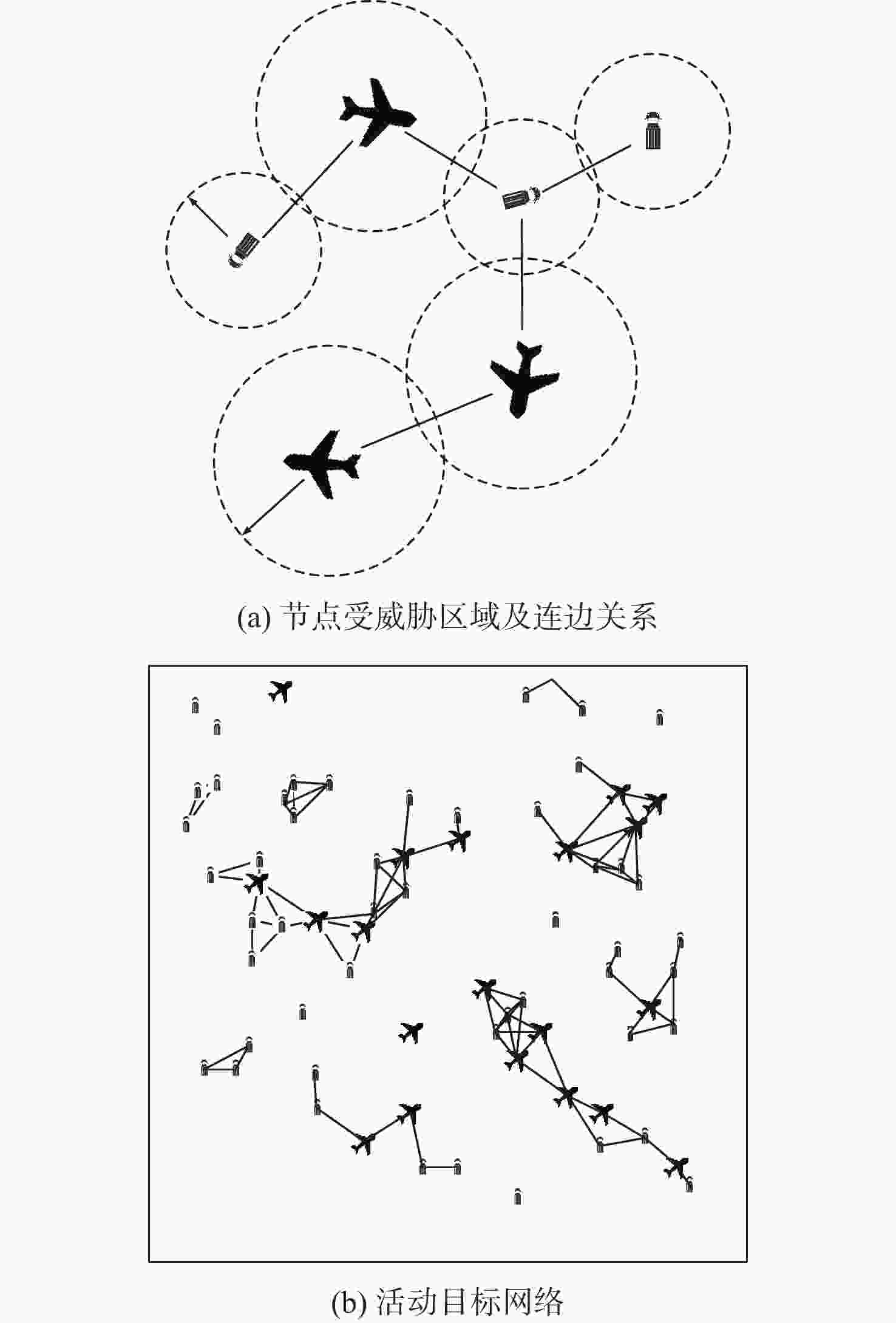
针对机场飞行区冲突不断的问题,提出一种基于长短期记忆(LSTM)网络预测机场飞行区活动目标潜在冲突的方法。根据复杂网络理论,以航空器和车辆2类活动目标为研究对象,建立飞行区活动目标网络,设置网络动态演化模型,输入运行数据计算多个网络特征指标,对指标时间序列进行主成分分析,拟合成潜在冲突指数;利用Keras框架搭建LSTM网络模型,将指标时间序列输入LSTM网络进行训练和预测,并与其他预测方法对比;用西安咸阳机场实际运行数据进行实验,将预测值与真实值进行对比,各项指标预测均方误差分别为1.608%、13.126%、0.072%、0.004%、0.014%。结果表明:通过建立飞行区活动目标网络模型,可以用网络特征指标从不同角度刻画潜在冲突;LSTM网络可以有效预测飞行区活动目标网络的潜在冲突,提醒相关人员预防冲突发生,降低冲突概率。
Abstract:In view of the problem of frequent conflicts in airfield areas, a method to predict the potential conflicts of mobile targets in airfield areas based on long short-term memory (LSTM) network was proposed. According to the complex network theory, aircraft and vehicles were taken as the research objects, and the network of mobile targets in the airfield area was established. The dynamic evolution model of the network was set, and the operation data was input to calculate multiple characteristic indicators of the network. In addition, the principal component analysis of the indicator time series was carried out to synthesize the potential conflict indicator. A LSTM network model was built by using the Keras framework, and the indicator time series were input into LSTM network for training and prediction and compared with other prediction methods. The actual operation data of Xi’an Xianyang Airport were used for experiments. The predicted values were compared with the real values. The mean square errors of the predicted results of each indicator were 1.608%, 13.126%, 0.072%, 0.004%, and 0.014%, respectively. The results show that the potential conflicts can be described from different perspectives by using characteristic indicators of the network after the network model of mobile targets in the airfield area is built. LSTM network can effectively predict the potential conflicts in the network of mobile targets in the airfield area, remind relevant personnel to prevent conflicts, and reduce the probability of conflicts.
-
表 1 网络演化特征指标
Table 1. Characteristic indicators of network evolution
演化
次数网络
平均度网络
平均点强平均加权
聚类系数网络
密度网络
效率1 1.8666 1.4084 0.4166 0.0643 0.0953 2 1.9310 1.4798 0.4459 0.0689 0.1014 3 2.0000 2.3478 0.3919 0.0714 0.0927 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 6000 2.9230 2.9339 0.3452 0.0769 0.1253 表 2 KMO和Bartlett的检验
Table 2. Testing of KMO and Bartlett
KMO值 近似卡方 df p 0.578 107.190 10 0.000 表 3 主成分及其贡献率
Table 3. Principal components and their contribution
编号 特征根 方差解释率/% 累积方差解释率/% 1 2.595 51.899 51.899 2 1.197 23.947 75.846 3 0.772 15.445 91.292 4 0.294 5.881 97.173 5 0.141 2.827 100.000 表 4 载荷系数和公因子方差
Table 4. Load factors and common factor variances
指标 载荷系数 公因子方差 主成分1 主成分2 网络平均度 0.950 0.076 0.908 网络平均点强 0.590 0.414 0.519 平均加权聚类系数 0.223 0.875 0.816 网络密度 0.818 −0.165 0.696 网络效率 0.791 −0.476 0.853 表 5 成分得分系数
Table 5. Component score coefficient
指标 成分得分系数 主成分1 主成分2 网络平均度 0.366 0.064 网络平均点强 0.227 0.346 平均加权聚类系数 0.086 0.731 网络密度 0.315 −0.138 网络效率 0.305 −0.398 表 6 飞行区活动目标网络特征指标预测值
Table 6. Predicted value of characteristic indicators of network of mobile targets in airfield area
演化
次数网络
平均度网络
平均点强平均加权
聚类系数网络
密度网络
效率1 3.3325 3.3504 0.4710 0.0697 0.0780 2 3.5974 3.2623 0.4788 0.0709 0.0735 3 3.2061 2.6007 0.4992 0.0645 0.0735 $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ $\vdots $ 1000 2.9230 2.9339 0.3452 0.0769 0.1643 表 7 LSTM网络预测结果误差
Table 7. Errors of LSTM network prediction results
% 指标 ${e_{{\mathrm{MAE}}}}$ ${e_{{\mathrm{MRE}}}}$ ${e_{{\mathrm{MSE}}}}$ 网络平均度 9.900 4.160 1.608 网络平均点强 27.820 16.914 13.126 平均加权聚类系数 2.072 5.822 0.072 网络密度 0.317 3.051 0.004 网络效率 0.724 5.385 0.014 -
[1] CAI C T, WU K J, YAN Y J. Rapid detection and social media supervision of runway incursion based on deep learning[J]. International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications, 2018, 9(2): 98-106. doi: 10.1504/IJICA.2018.092600 [2] SONG I, CHO I, TESSITORE T, et al. Data-driven prediction of runway incursions with uncertainty quantification[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2018, 32(2): 04018004. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000733 [3] 朱新平, 汤新民, 韩松臣. A-SMGCS滑行道冲突预测与避免控制[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 43(4): 504-510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2011.04.012ZHU X P, TANG X M, HAN S C. Conflict prediction and avoidance control for A-SMGCS taxiway[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2011, 43(4): 504-510 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2011.04.012 [4] 肖琴, 罗帆. 机场场面交通冲突风险演化的SD模型研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(6): 187-193.XIAO Q, LUO F. SD model of risk evolution for airport surface traffic conflict[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(6): 187-193(in Chinese). [5] ZHU X P, TANG X M, HAN S C. Aircraft intersection collision conflict detection and resolution under the control of A-SMGCS[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Modelling. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 626-631. [6] XIA Z H, ZHENG B, WAN J, et al. Recognition algorithm and risk assessment of airport hotspots[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University (Science), 2019, 24(6): 769-774. doi: 10.1007/s12204-019-2110-6 [7] CAI K Q, ZHANG J, DU W B, et al. Analysis of the Chinese air route network as a complex network[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(2): 028903. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/2/028903 [8] 王兴隆, 苗尚飞. 空域扇区网络结构特性分析及韧性评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(5): 904-911.WANG X L, MIAO S F. Structural characteristics analysis and resilience assessment of airspace sector network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(5): 904-911 (in Chinese). [9] 王岩韬, 刘毓. 基于复杂网络的航班运行风险传播分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(1): 198-205.WANG Y T, LIU Y. Flight operation risk propagation based on complex network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(1): 198-205 (in Chinese). [10] 黄洋, 汤俊, 老松杨. 基于复杂网络的无人机飞行冲突解脱算法[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(12): 322222.HUANG Y, TANG J, LAO S Y. UAV flight conflict resolution algorithm based on complex network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(12): 322222 (in Chinese). [11] 曾航, 张红梅, 任博, 等. 基于改进LSTM模型的航空安全预测方法研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(2): 569-576. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.26ZENG H, ZHANG H M, REN B, et al. Aviation safety prediction method research based on improved LSTM model[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 569-576 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.02.26 [12] 李昂, 聂党民, 温祥西, 等. 管制-飞行状态相依网络演化过程[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(9): 324726.LI A, NIE D M, WEN X X, et al. Evolution process of control-aircraft state interdependent network[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 324726 (in Chinese). [13] 李忠斌. 基于深度学习的机场场面延误的预测研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020: 49-63.LI Z B. Research on airport scene delay prediction based on deep learning[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020: 49-63(in Chinese). [14] 李小伟. P/H机场坐标系与2000国家大地坐标系的转换[J]. 林业科技情报, 2020, 52(2): 108-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2020.02.043LI X W. Conversion between P/H airport coordinate system and CGCS2000[J]. Forestry Science and Technology Information, 2020, 52(2): 108-109 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2020.02.043 [15] DING C, HE X F. Cluster structure of K-means clustering via principal component analysis[C]//Proceedings of the Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 414-418. [16] TAKASE S, SUZUKI J, NAGATA M. Input-to-output gate to improve RNN language models[C]//Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Taipei: A sian Tederation of Natural Language Processing, 2017, 2: 43-48. [17] ROMANUKE V. ARIMA model optimal selection for time series forecasting[J]. Maritime Technical Journal, 2022, 224(1): 28-40. doi: 10.2478/sjpna-2022-0003 -






 下载:
下载: