-
摘要:
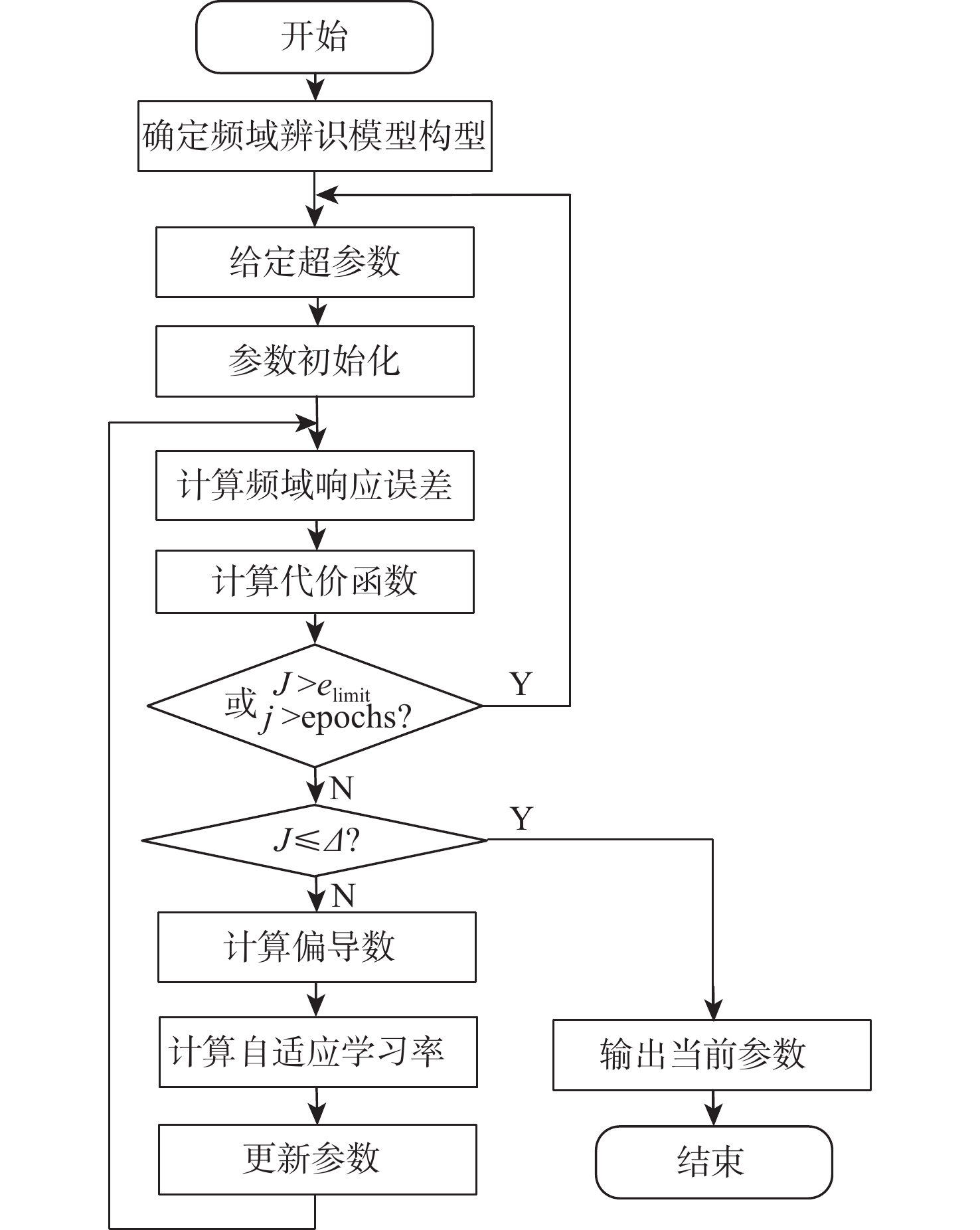
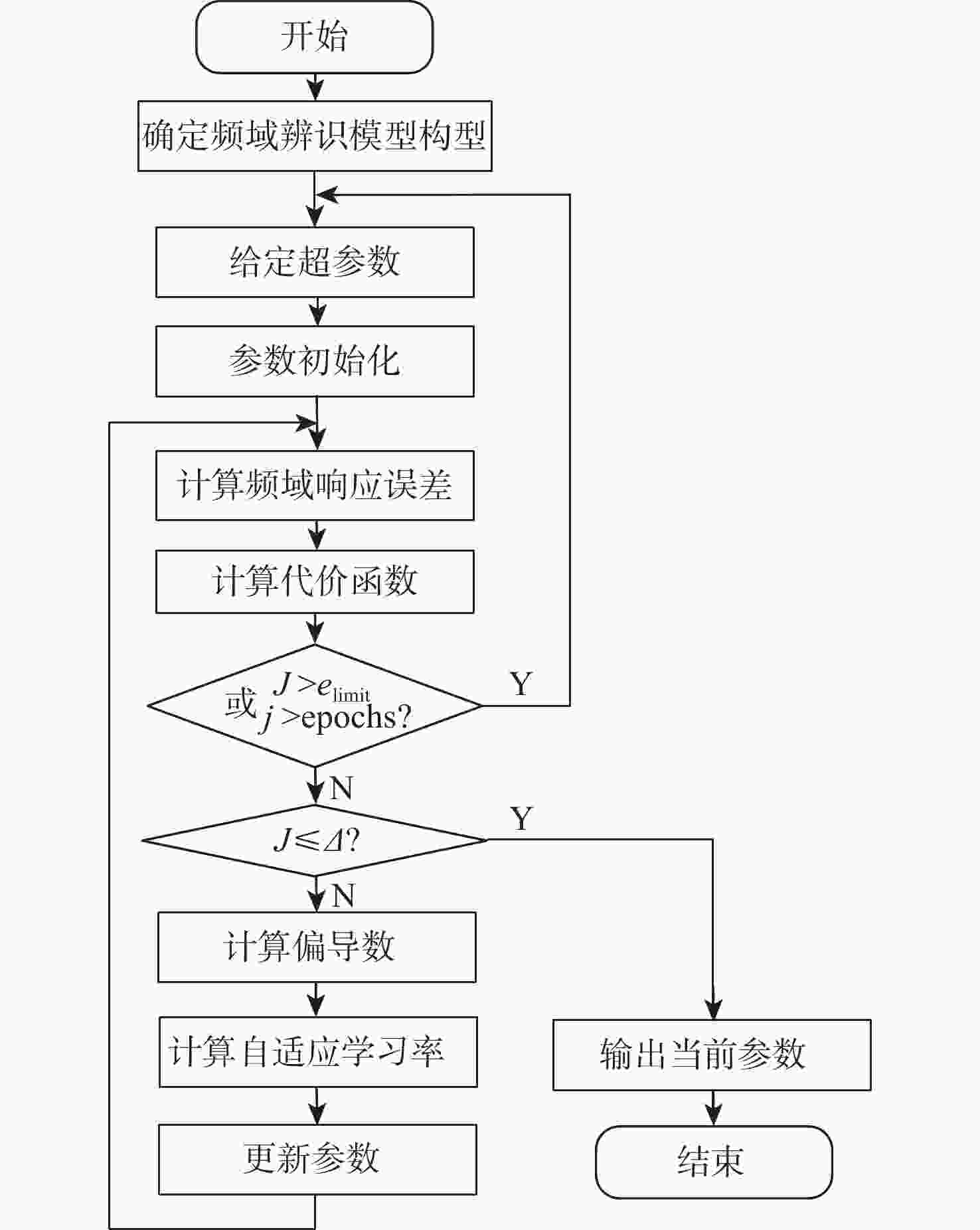
针对舰载机等复杂动力学系统的高阶时滞模型拟配难题,提出了一种基于通用化等效模型的系统频域辨识算法。建立系统辨识通用化等效模型,引入自适应学习率梯度下降法对模型进行基于样本的迭代学习训练,使模型的频域参数自动收敛,辨识得到复杂系统的高阶时滞模型。以舰载机横航向荷兰滚等效拟配模型进行验证,与传统算法对比,并分析了系统的频域与时域响应,结果表明:所提算法具有较好的辨识效果,解决了高阶时滞模型的直接拟配难题,并通用于广泛的高阶时滞模型拟配。
Abstract:This study provides a frequency domain identification approach aimed at the high-order time-delay model matching problem for complex systems like carrier aircraft. A high-order time-delay model of the complex system is ultimately identified after the generalized frequency-domain identification model is established and the model is iteratively trained by system frequency domain response data using the gradient descent method of adaptive learning rate. This allows the model’s frequency domain parameters to automatically converge.Verification is carried out with the Dutch roll equivalent model of carrier aircraft. Through the identification and comparison of high-level and low-level models, the algorithm in this paper is compared with the traditional algorithm, and the frequency domain and time domain analysis show that the algorithm in this paper has a good identification effect. It solves the problem of direct fitting of high-order time-delay models, and is suitable for universal high-order time-delay models.
-
表 1 算例频域辨识模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of arithmetic frequency domain identification model
模型 $ T $ $ Z $ $ N $ $ P $ $ Q $ 等效高阶模型 1 0 1 2 1 等效低阶模型 0 1 0 0 1 表 2 超参数
Table 2. Hyperparameters
$ \eta $ $ \rho $ $ \varepsilon $ $ \lambda $ 0.001 0.999 0.1 0.0175 表 3 等效高阶模型的频域特性参数
Table 3. Frequency domain characteristic parameters of equivalent high-order model
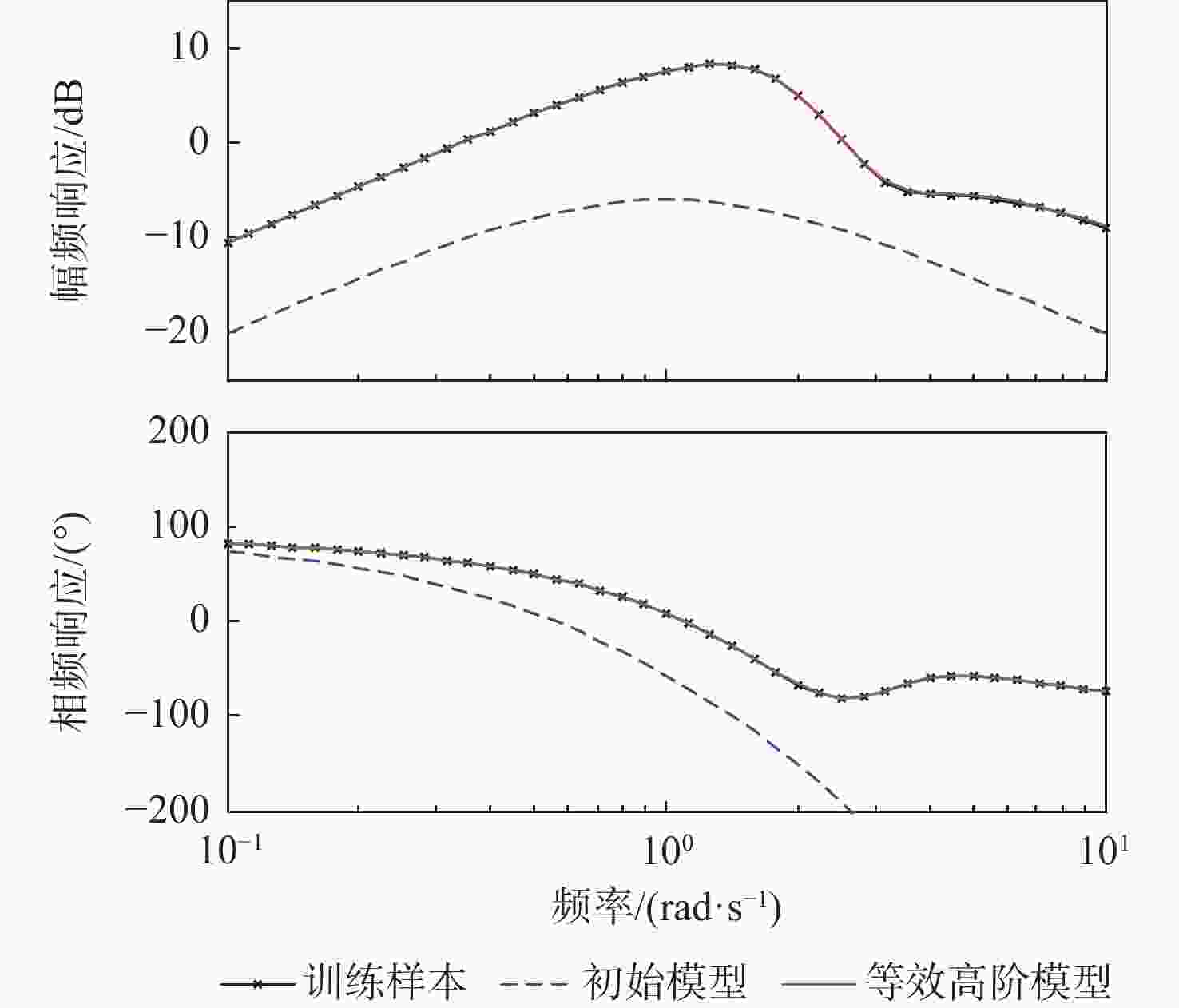
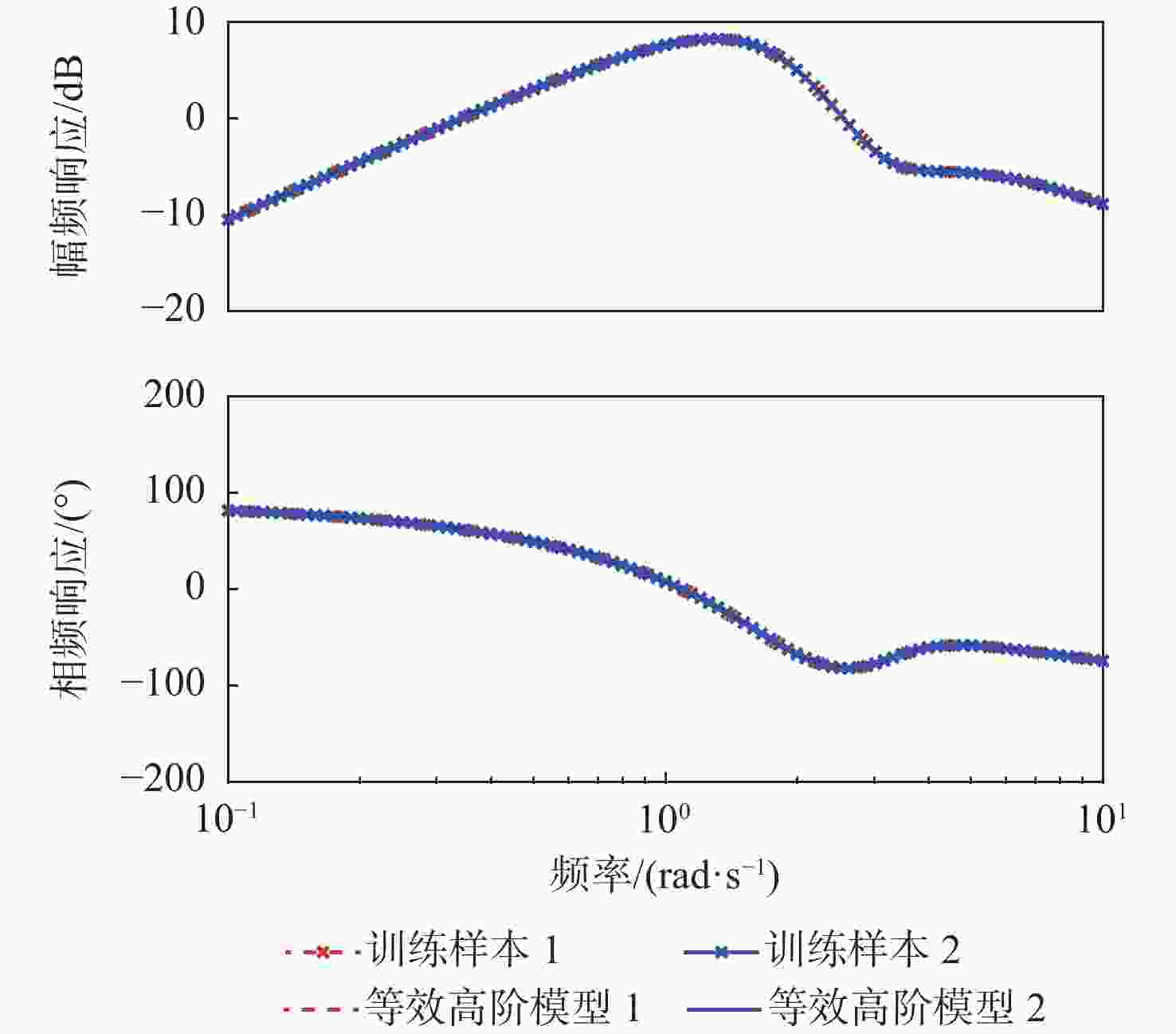
等效高阶模型 $ k $ $ b_1^{(1)} $ $ b_2^{(1)} $ $ a_0^{(1)} $ $ a_0^{(2)} $ $ a_1^{(1)} $ $ a_2^{(1)} $ $ \tau $ $ J $ 训练样本 3 0.2 0.1 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.3 0.01 初始值 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 402.8 $ 10 $次训练 1.1331 1.1353 1.1211 0.8680 0.8680 0.8601 0.8741 0.8561 271.3 $ {10^2} $次训练 1.3978 1.4102 1.1029 0.7241 0.7241 0.5794 0.9231 0.4888 89.8 $ {10^3} $次训练 2.0211 1.6973 0.7273 0.7071 0.7071 0.7864 1.0552 −0.0120 3.6 $ 5 \times {10^3} $次训练 2.9523 1.2700 0.6509 1.0063 1.0063 0.6912 0.7027 −0.0298 1.1 $ 8 \times {10^3} $次训练 3.0018 0.1999 0.1006 0.5026 0.5026 0.5955 0.2976 0.0098 6.0×10−4 $ 9 \times {10^3} $次训练 3.0003 0.2005 0.1005 0.4998 0.4998 0.5992 0.2995 0.0099 1.1×10−3 $ {10^4} $次训练 2.9995 0.1996 0.0955 0.5005 0.5005 0.6006 0.3007 0.0103 1.5×10−3 表 4 梯度下降法的等效低阶模型频域特性参数
Table 4. Frequency domain characteristic parameters of equivalent low-order model based on gradient descent method
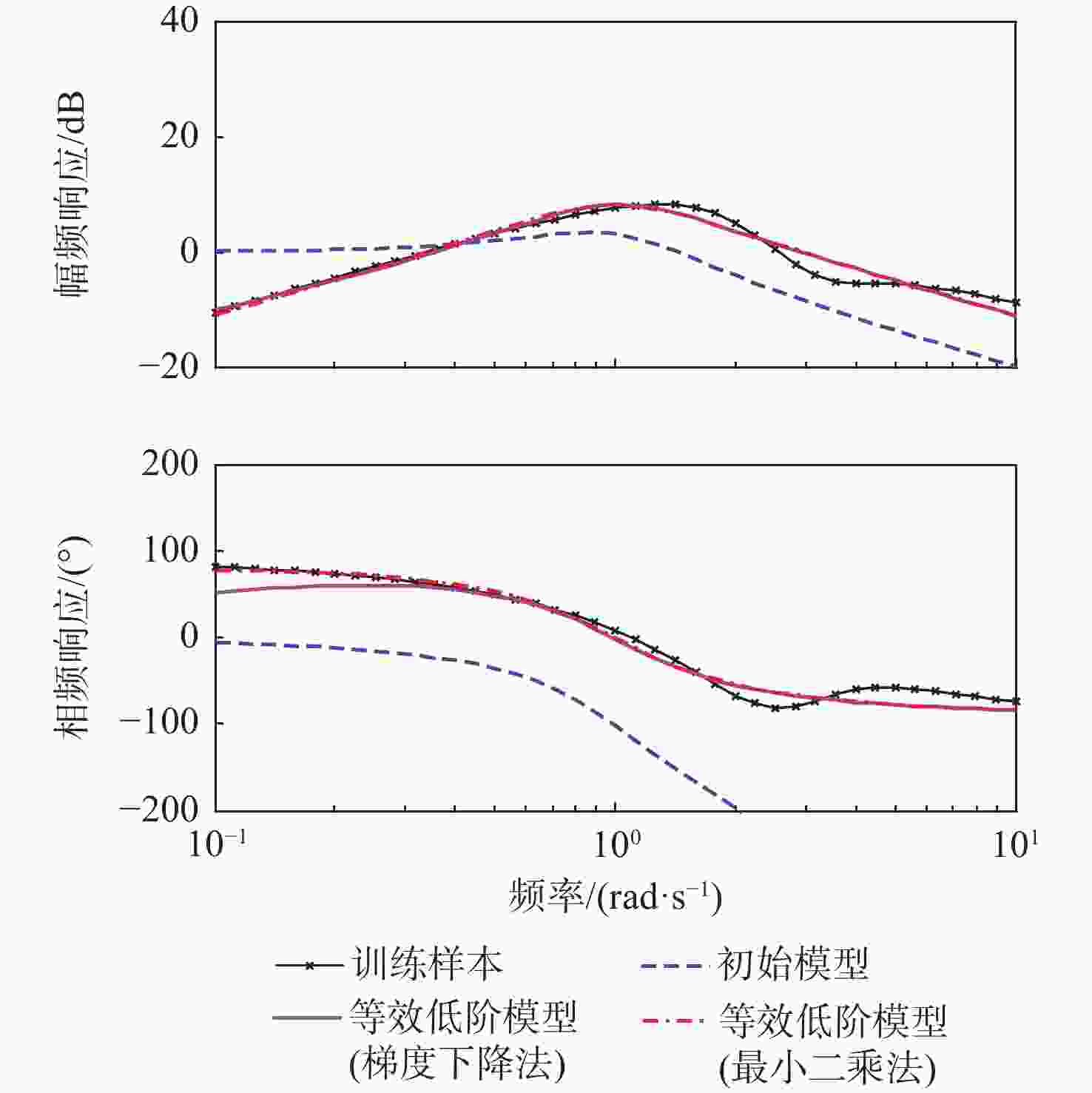
梯度下降法的等效低阶模型 $ k $ $ a_1^{(1)} $ $ a_2^{(1)} $ $ b_0^{(1)} $ $ \tau $ $ J $ 初始值 1 1 1 1 1 446.7 $ 10 $次训练 1.1084 0.8665 0.8608 1.1304 0.8554 328.6 $ {10^2} $次训练 0.8880 0.5720 0.5645 1.3620 0.4832 118.7 $ {10^3} $次训练 0.6338 0.4694 0.5553 2.0367 0 13.6 $ {10^4} $次训练 0.3146 0.8629 0.8538 7.2477 0 4.6 $ 5 \times {10^4} $次训练 0.1667 1.0386 0.9570 15.8224 0 2.5 $ {10^5} $次训练 0.1603 1.0447 0.9603 16.5260 0 2.4 表 5 最小二乘法的等效低阶模型频域特性参数
Table 5. Frequency domain characteristic parameters of equivalent low-order model based on least sqaure method
最小二乘法的等效低阶模型 $ K $ $ {\omega _0} $ $ \xi $ $ T $ $ \tau $ $ J $ 初始值 1 1 0.5 1 1 446.7 终值 0.0274 0.9996 0.5435 101.7832 0 1.7 梯度下降法$ {10^5} $次训练等效值 0.1669 1.0205 0.5119 16.5260 0 2.4 表 6 模型阶跃响应稳态值
Table 6. Steady state value of model step response
模型 单位阶跃稳态值 样本模型 0 等效高阶模型 0 等效低阶模型(梯度下降法) 0.1603 等效低阶模型(最小二乘法) 0.0274 表 7 模型阶跃响应性能指标
Table 7. Performance index of model step response
模型 峰值 峰值时间/s 调节时间/s 样本模型 1.52 1.3 4.9 等效高阶模型 1.53 1.3 4.9 等效低阶模型(梯度下降法) 1.50 1.3 6.9 等效低阶模型(最小二乘法) 1.48 1.2 7.2 -
[1] 李大伟, 徐浩军, 胡新江, 等. 基于等效系统拟配的人-机闭环系统稳定性研究[J]. 飞行力学, 2011, 29(4): 21-24.LI D W, XU H J, HU X J, et al. Research on stability of aircraft-pilot closed loop system based on matching of equivalent system[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2011, 29(4): 21-24(in Chinese). [2] 丁东杰, 王亚刚. 工业过程频域建模及控制器参数整定[J]. 控制工程, 2016, 23(11): 1714-1718.DING D J, WANG Y G. Modeling in frequency domain and controller parameter tuning for industrial processes[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2016, 23(11): 1714-1718(in Chinese). [3] 何凯, 张平. 等效系统的飞机参数辨识与快速建模[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2011, 23(8): 1545-1548.HE K, ZHANG P. Airplane aerodynamic parameters identification and fast modeling based on equivalent system[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2011, 23(8): 1545-1548(in Chinese). [4] 陈安钢, 任正云, 倪潇. 复杂高阶对象的预测PI(D)控制[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2017, 25(6): 37-40.CHEN A G, REN Z Y, NI X. Predictive PI(D) control for complex high order[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2017, 25(6): 37-40(in Chinese). [5] 杨凌宇, 柳嘉润, 申功璋. 飞控-飞机低阶等效系统的在线辨识[J]. 飞行力学, 2003, 21(2): 29-32.YANG L Y, LIU J R, SHEN G Z. Online identification of low-order equivalent system of flight control and aircraft system[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2003, 21(2): 29-32(in Chinese). [6] 周健. 一种小型无人直升机动力学模型参数辨识方法[J]. 飞行力学, 2019, 37(6): 89-96.ZHOU J. A parameter identification method for dynamic model of small unmanned helicopter[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2019, 37(6): 89-96(in Chinese). [7] MORELLI E A. Identification of low order equivalent system models from flight test data[R]. Washington, D.C.: NASA, 2000. [8] KLEIN V, MORELLI E A. Aircraft system identification: Theory and practice[M]. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [9] 程韶军, 邓建华. 飞机横航向模态模型的选择[J]. 飞行力学, 1999, 17(1): 37-41.CHENG S J, DENG J H. The model selection of aircraft lateral modes[J]. Flight Dynamics, 1999, 17(1): 37-41(in Chinese). [10] 马姝姝, 陈夕松, 杨俊. 高阶时滞系统的降阶IMC-PID控制研究[J]. 工业仪表与自动化装置, 2010(2): 5-7.MA S S, CHEN X S, YANG J. Research on IMC-PID control for the complex time-delay system reduction[J]. Industrial Instrumentation & Automation, 2010(2): 5-7(in Chinese). [11] 方振平. 航空飞行器飞行动力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2005.FANG Z P. Aircraft flight dynamics[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2005(in Chinese). [12] 方自立, 韩意新, 袁广田. 电传飞机飞行品质低阶等效系统算法研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2018, 26(11): 223-227.FANG Z L, HAN Y X, YUAN G T. Research on low-order equivalent system algorithm of fly-by-wire aircraft flight quality[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2018, 26(11): 223-227(in Chinese). [13] 崔益华, 韩意新, 陈永亮. 电传飞机低阶等效系统频域辨识新方法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 48(3): 432-437.CUI Y H, HAN Y X, CHEN Y L. A new method for frequency domain identification of low-order equivalent system of fly-by-wire aircraft[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 48(3): 432-437(in Chinese). [14] 邹瑜, 裴海龙, 刘馨, 等. 飞机模型频域辨识方法——CIFER算法研究[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(5): 46-49.ZOU Y, PEI H L, LIU X, et al. Aircraft model frequency domain identification method—CIFER algorithm research[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2010, 17(5): 46-49(in Chinese). [15] TISCHLER M B, REMPLE R K. Aircraft and rotorcraft system identification: Engineering methods with flight-test examples[M]. Reston: AIAA, 2006: 39-52. [16] 李迎博, 呼卫军, 周军. 一种基于递推最小二乘的频域辨识的新算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2014, 31(4): 269-272.LI Y B, HU W J, ZHOU J. A new algorithm of frequency domain identification based on recursive least squares[J]. Computer Simulation, 2014, 31(4): 269-272(in Chinese). [17] 陈君, 郭玉兵, 曹惠芳, 等. 基于改进的BP 神经网络算法的控制系统在线辨识方法[J]. 科技导报, 2012, 30(6): 62-65.CHEN J, GUO Y B, CAO H F, et al. On-line identification method of control system based on improved BP neural network algorithm[J]. Science and Technology Review, 2012, 30(6): 62-65(in Chinese). [18] 刘佳佳. K-平均算法的综合优化策略[J]. 知识经济, 2012(20): 106-107.LIU J J. Comprehensive optimization strategy of K-means algorithm[J]. Knowledge Economy, 2012(20): 106-107(in Chinese). [19] 国防科学技术工业委员会. 电传操纵系统飞机的飞行品质: GJB 2874—97[S]. 北京: 国防科学技术工业委员会, 1997.Commission of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense. Flying qualities standard for airplane with fly-by-wire control system: GJB 2874—97[S]. Beijing: Commission of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense, 1997(in Chinese). [20] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-441. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [21] DAUPHIN Y N, DE VRIES H , CHUNG J, et al. RMSProp and equilibrated adaptive learning rates for non-convex optimization [EB/OL]. (2015-08-29)[2022-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.04390v1. -






 下载:
下载: