-
摘要:
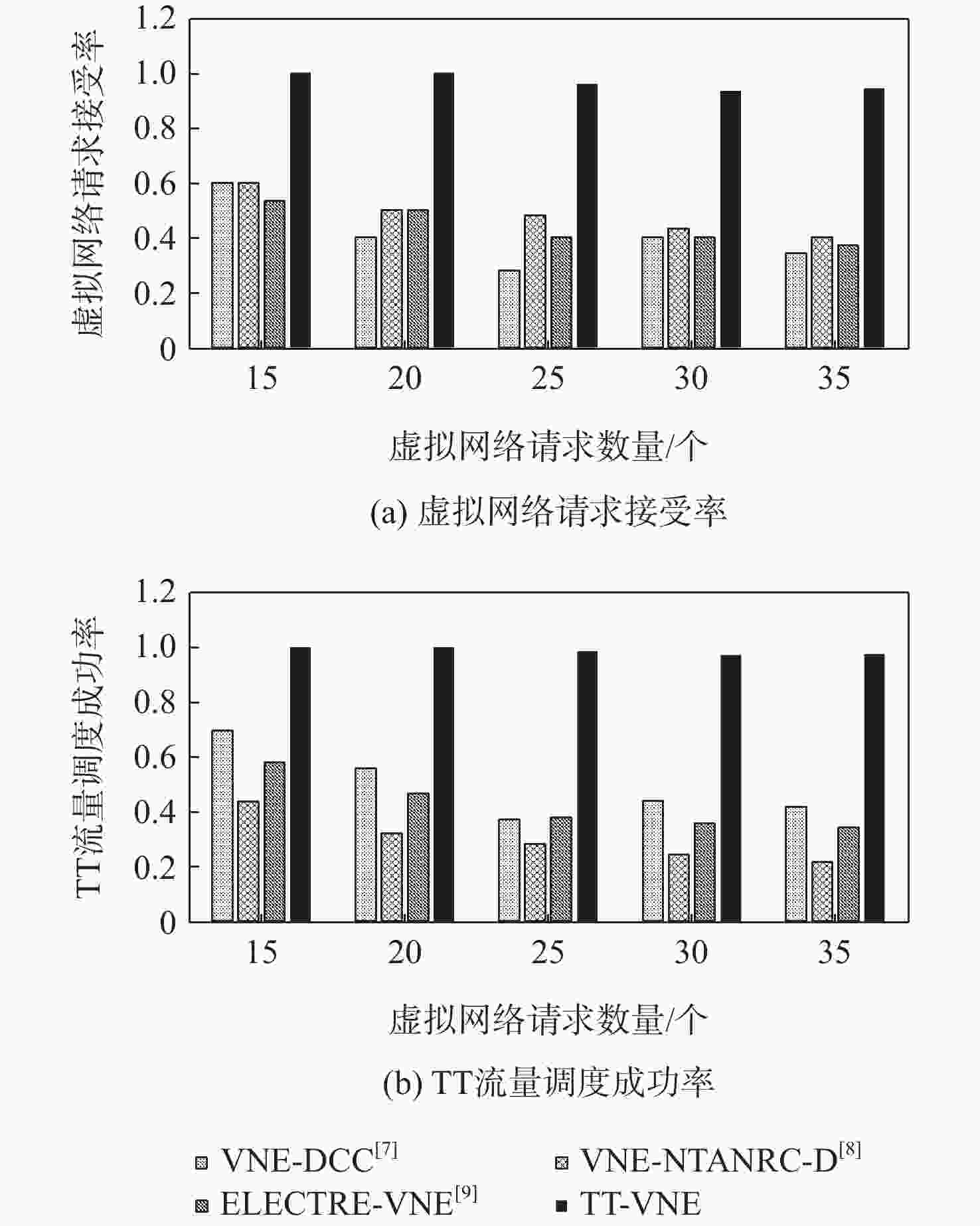
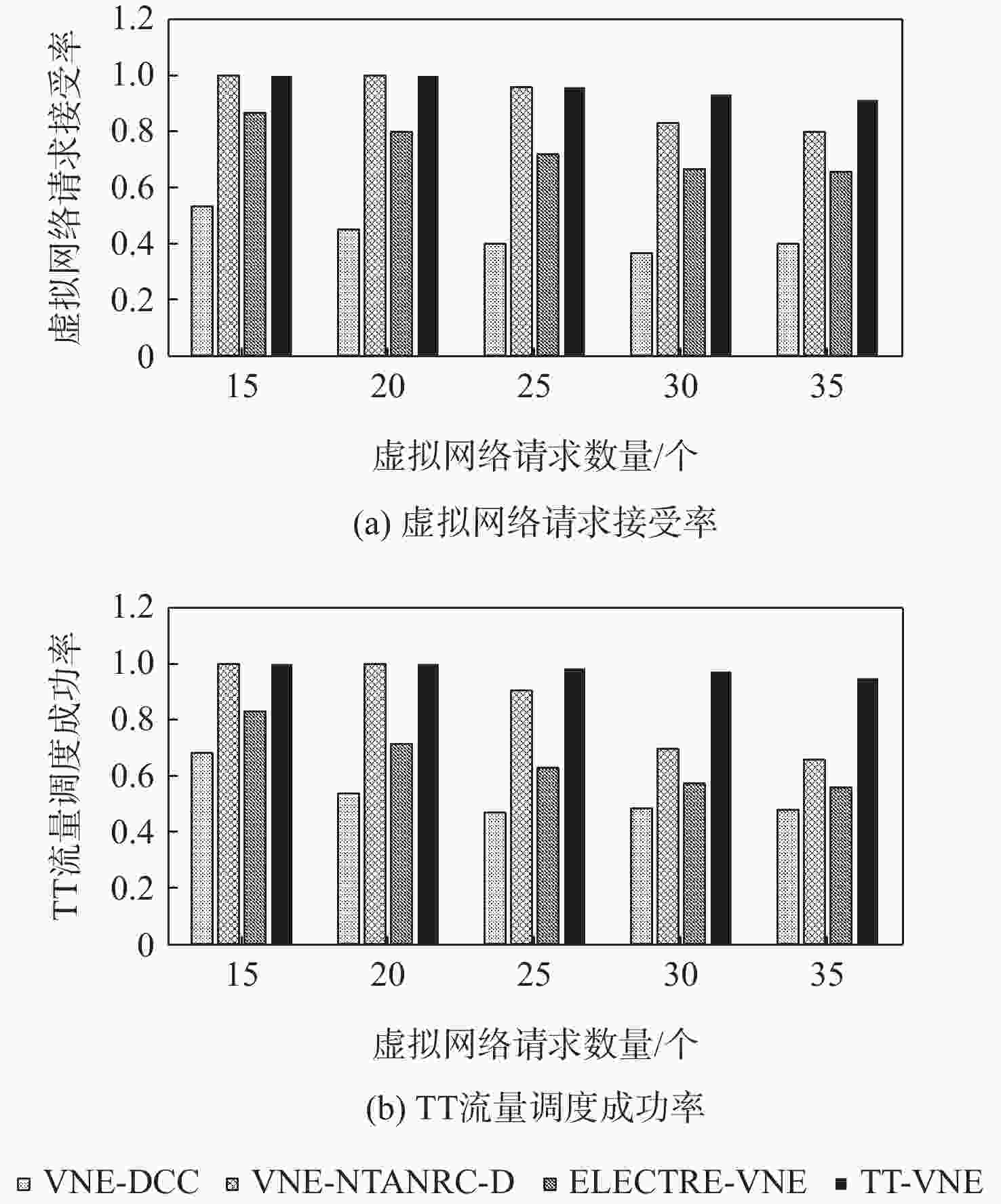
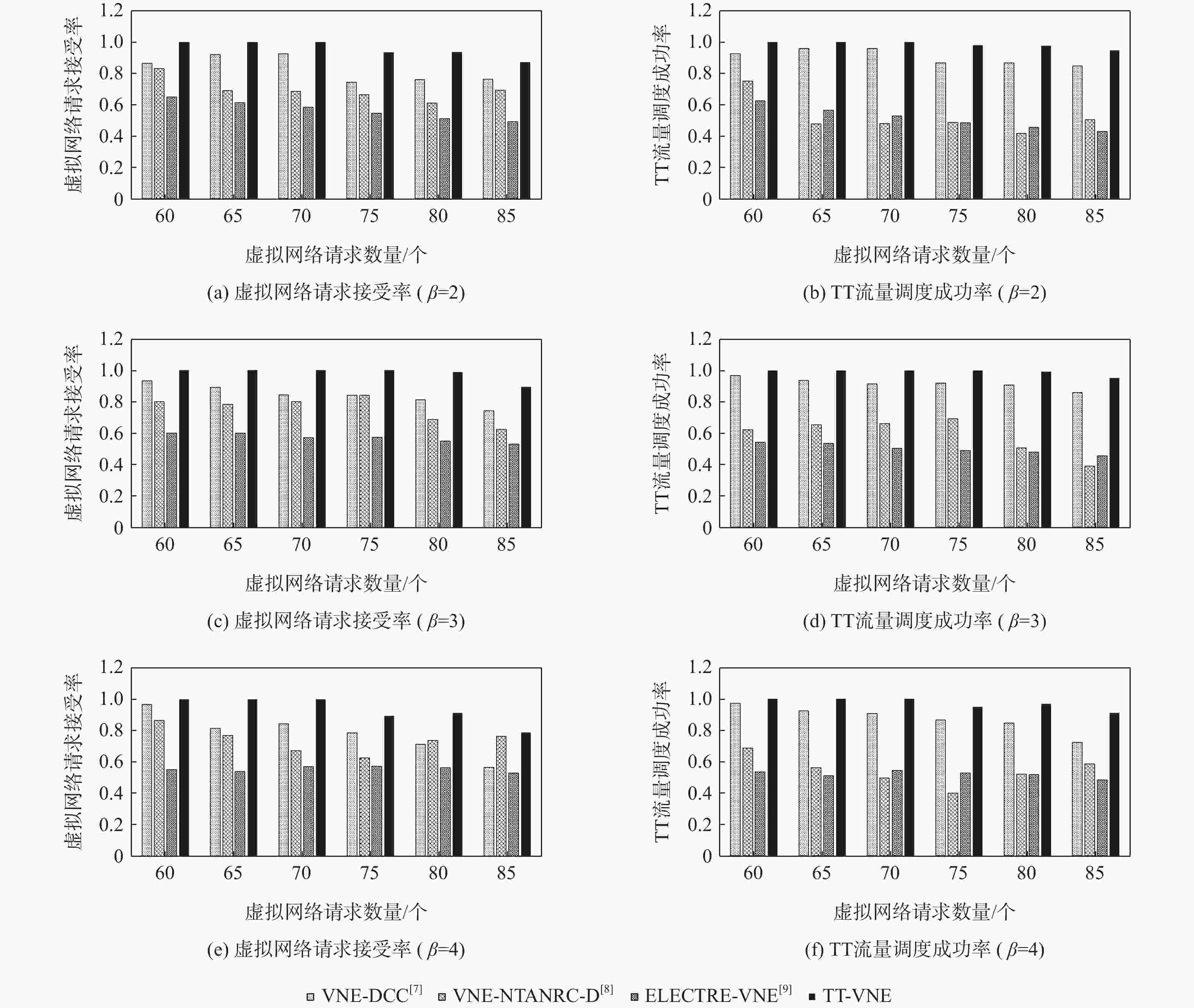
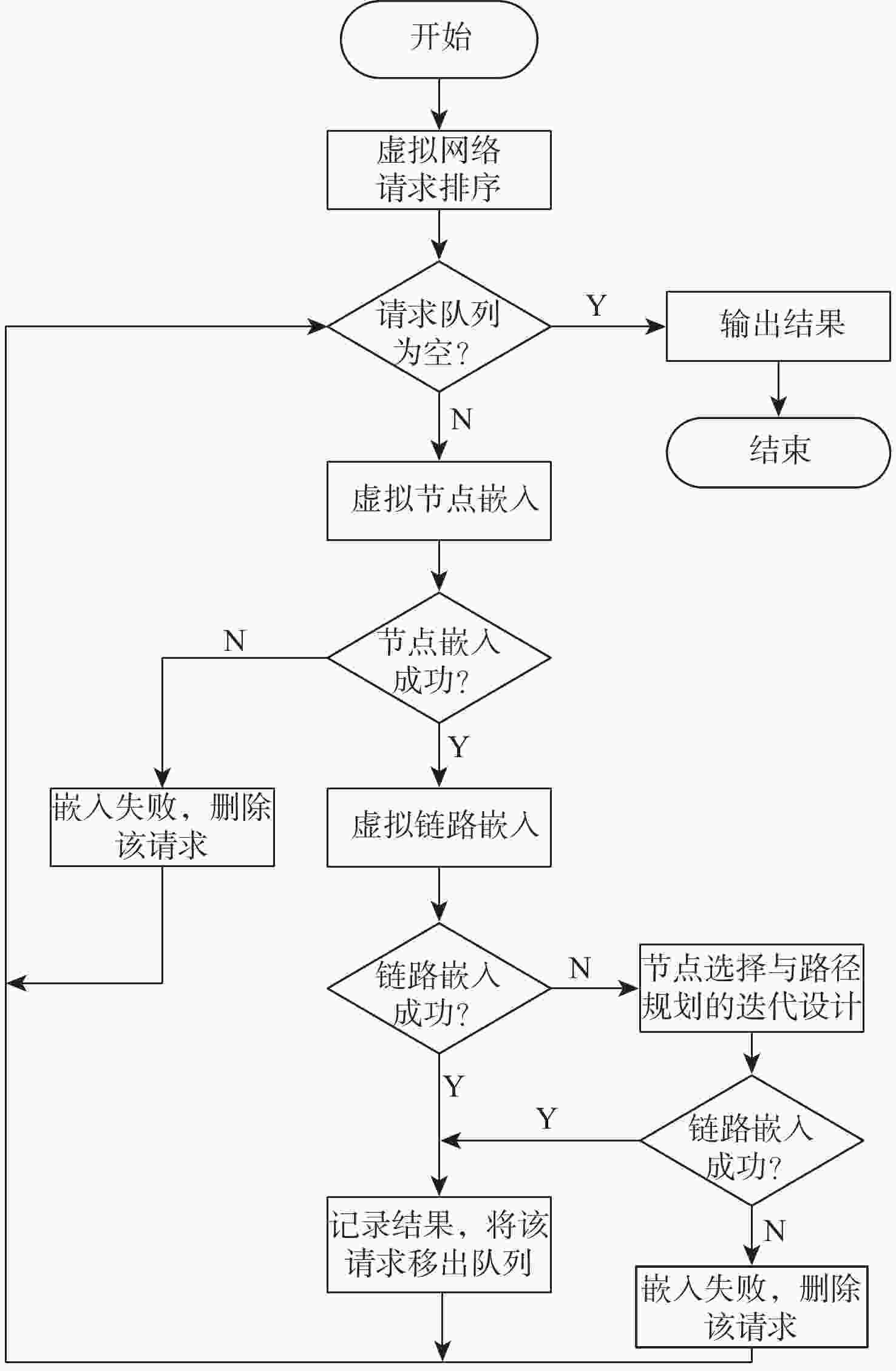
网络虚拟化技术将物理网络中的节点、链路资源进行抽象,通过虚拟网络嵌入(VNE)方法,使多个虚拟网络(VN)共享底层网络(SN)资源。对于应用于航空航天电子领域的时间触发以太网(TTE),提出一种面向时间触发流量调度的虚拟网络嵌入(TT-VNE)方法,在满足传统虚拟网络嵌入问题的总资源量限制条件的同时,保证时间触发(TT)流量的严格周期性。在求解过程中,根据与虚拟节点相连的链路中TT流量带宽需求及其总带宽资源需求对虚拟节点进行排序,利用广度优先搜索算法嵌入虚拟节点,并在候选最短路径集合中对虚拟链路进行路径规划;如果当前虚拟链路中TT流量不可调度,则进行局部虚拟节点重新嵌入与路径规划的迭代设计。仿真结果表明:TT-VNE方法的请求接受率不低于VNE-DCC、VNE-NTANRC-D、ELECTRE-VNE这3种既有方法,且当星型拓扑中虚拟网络请求数超过30时,其请求接受率比仅考虑网络拓扑属性和资源属性的VNE-NTANRC-D方法提高约14.3%。
Abstract:Network virtualization technology abstracts the nodes and links resources in the physical network and enables multiple virtual networks (VNs) to share the substrate network (SN) resources through the virtual network embedding (VNE) method. For time-triggered Ethernet (TTE) used in avionics, a time-triggered traffic scheduling-oriented VNE (TT-VNE) method was proposed. While meeting the total resource constraints of the traditional VNE problem, the method ensured the strict periodicity of time-triggered (TT) traffic. During the solution process, the method sorted the virtual nodes according to the TT traffic bandwidth requirements and the total bandwidth requirements of the links connected to the virtual nodes, embedded the virtual nodes using the breadth-first search algorithm, and planned the virtual links in candidate shortest paths. If the TT traffic in the current virtual link is not schedulable, the iterative design of local virtual node re-embedding and path planning is carried out. The simulation shows that the request acceptance rate of the TT-VNE method is not lower than that of existing methods, and when the number of virtual network requests in the star topology exceeds 30, its request acceptance rate is about 14.3% higher than the VNE-NTANRC-D method which only considers the network topology and resource attributes.
-
表 1 虚拟网络参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting of virtual networks
参数名称 取值范围 虚拟节点数 U(2,4) 虚拟节点容量需求 U(5,10) 虚拟链路数 U((n−1),n(n−1)/2) 每条虚拟链路TT消息数 U(5,10) TT消息长度/ Bytes U(64,1518) TT消息周期/ms 2x3y 虚拟链路带宽/(Mb·s−1) $ U[{b}_{\text{TT}},\beta {b}_{\text{TT}}] $ -
[1] ZHANG P Y, PANG X, BI Y X, et al. DSCD: Delay sensitive cross-domain virtual network embedding algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 2913-2925. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3005570 [2] HAERI S, TRAJKOVIC L. Virtual network embedding via Monte Carlo tree search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(2): 510-521. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2645123 [3] CAO H T, HU H, QU Z C, et al. Heuristic solutions of virtual network embedding: a survey[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(3): 186-219. doi: 10.1109/CC.2018.8332001 [4] LI Z F, LU Z B, DENG S H, et al. A self-adaptive virtual network embedding algorithm based on software-defined networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2019, 16(1): 362-373. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2018.2876789 [5] CAO H T, ZHU H B, YANG L X. Collaborative attributes and resources for single-stage virtual network mapping in network virtualization[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2019, 22(1): 61-71. [6] WU S C, YIN H, CAO H T, et al. Node ranking strategy in virtual network embedding: an overview[J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(6): 114-136. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2021.06.010 [7] ZHANG P Y, YAO H P, LIU Y J. Virtual network embedding based on the degree and clustering coefficient information[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 8572-8580. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2632421 [8] CAO H T, YANG L X, ZHU H B. Novel node-ranking approach and multiple topology attributes-based embedding algorithm for single-domain virtual network embedding[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(1): 108-120. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2773489 [9] ZHANG P Y, YAO H P, QIU C, et al. Virtual network embedding using node multiple metrics based on simplified ELECTRE method[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 37314-37327. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2847910 [10] ZHANG P Y, HONG Y R, PANG X, et al. VNE-HPSO: Virtual network embedding algorithm based on hybrid particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 213389-213400. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3040335 [11] ZHANG P Y, PANG X, KIBALYA G, et al. GCMD: Genetic correlation multi-domain virtual network embedding algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 67167-67175. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3076916 [12] STEINER W. An evaluation of SMT-based schedule synthesis for time-triggered multi-hop networks[C]// Proceedings of the 31st IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 375-384. [13] POZO F, RODRIGUEZ-NAVAS G, STEINER W, et al. Period-aware segmented synthesis of schedules for multi-hop time-triggered networks[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE 22nd International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 170-175. [14] POZO F, STEINER W, RODRIGUEZ-NAVAS G, et al. A decomposition approach for SMT-based schedule synthesis for time-triggered networks[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-8. [15] 郑重, 何锋, 李浩若, 等. 基于贪婪随机自适应搜索法的TTE通信调度算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(11): 2268-2276.ZHENG Z, HE F, LI H R, et al. Scheduling algorithm of TTE network based on greedy randomized adaptive search procedure[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(11): 2268-2276(in Chinese). [16] LOVELESS A. On time-triggered Ethernet in NASA’s Lunar Gateway[EB/OL]. (2020-1-60) [2022-05-29]. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20205005104. [17] 宋梓旭, 李峭, 汪晶晶, 等. 基于可调度性排序的时间触发调度表生成方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(11): 2388-2395.SONG Z X, LI Q, WANG J J, et al. Time-triggered scheduling table generation method based on schedulability ranking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(11): 2388-2395 (in Chinese). [18] ZHONG C M, JIA H Y, WAN H, et al. DRLS: A deep reinforcement learning based scheduler for time-triggered Ethernet[C]// Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-11. -






 下载:
下载: