-
摘要:
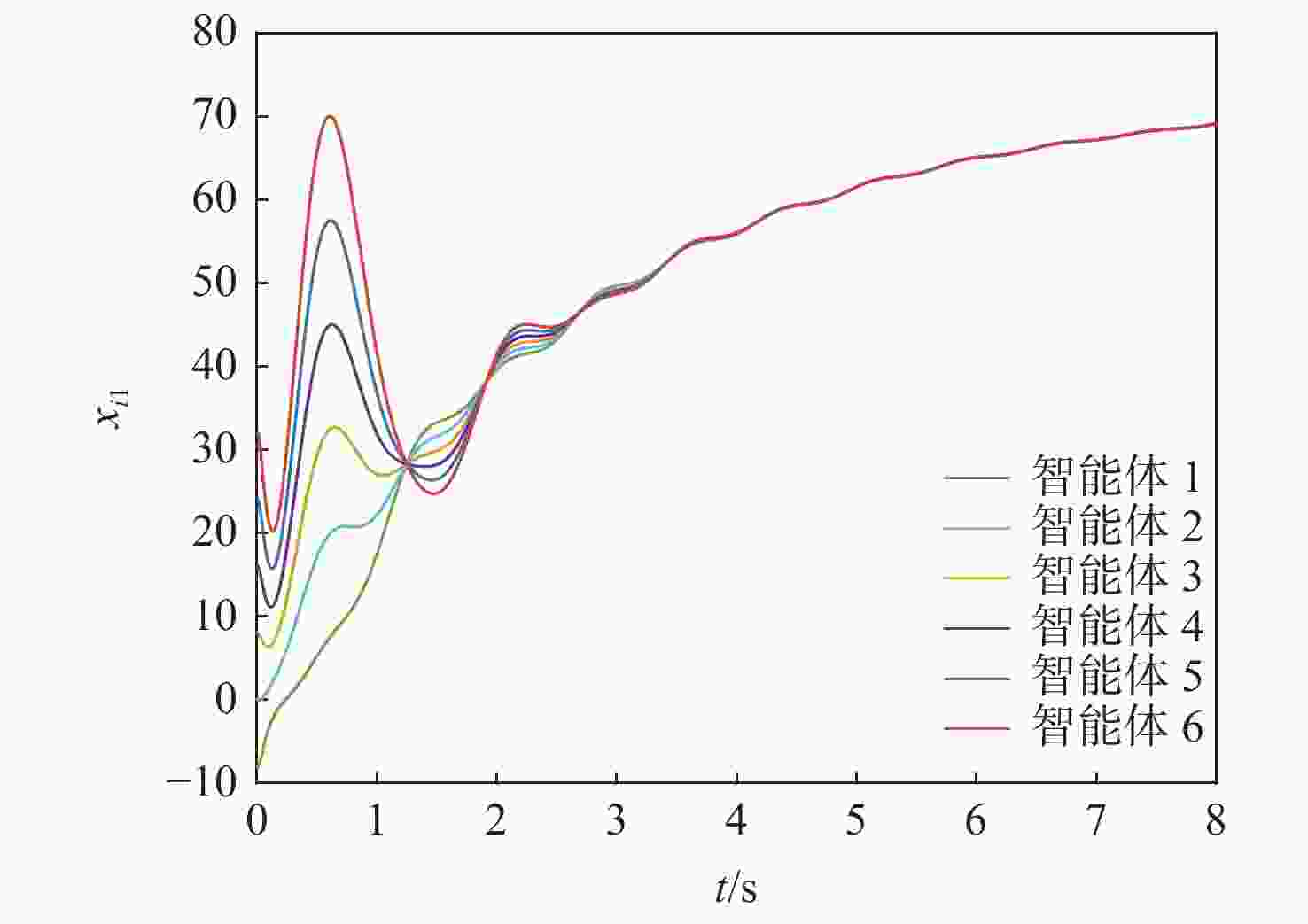
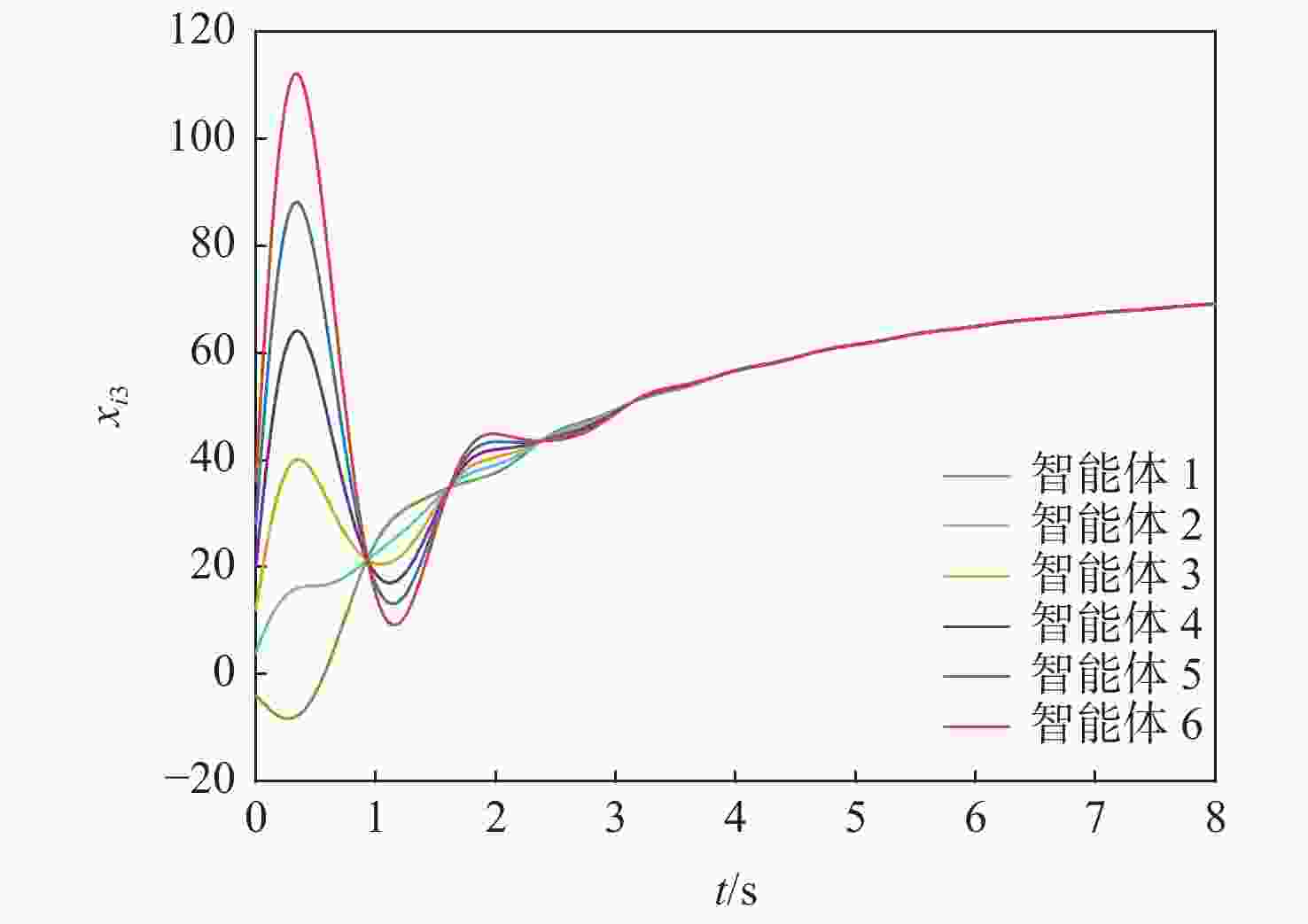
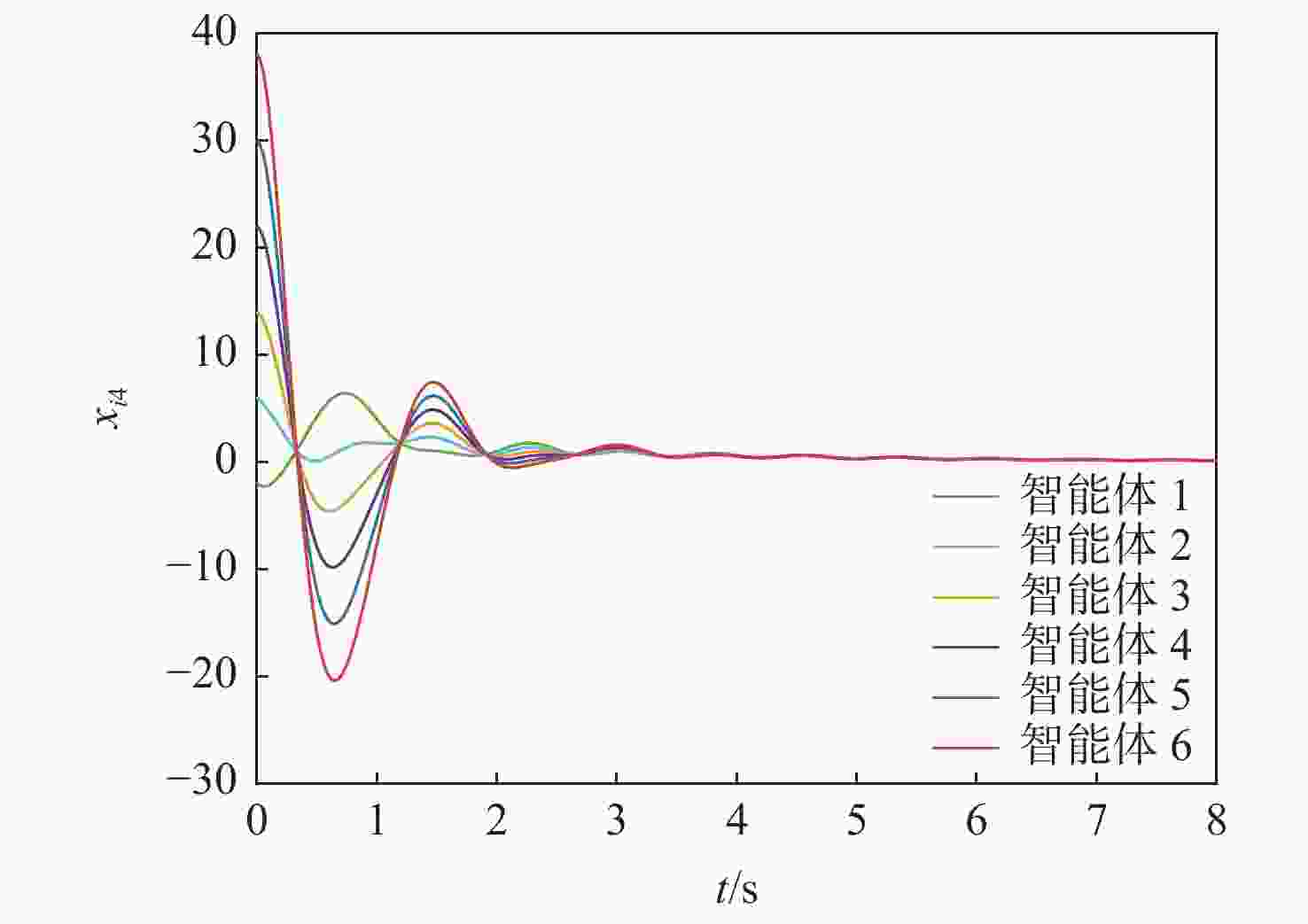
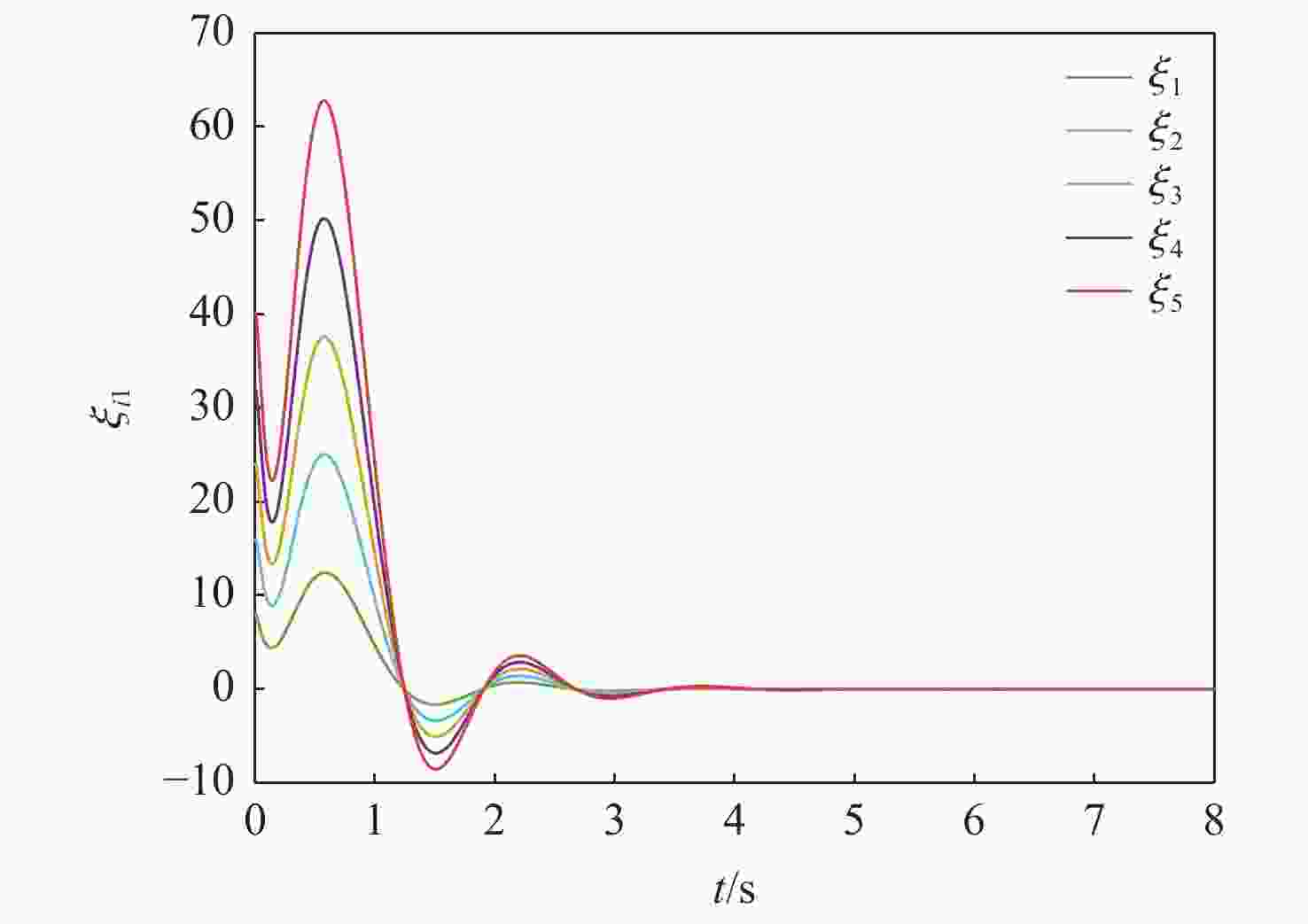
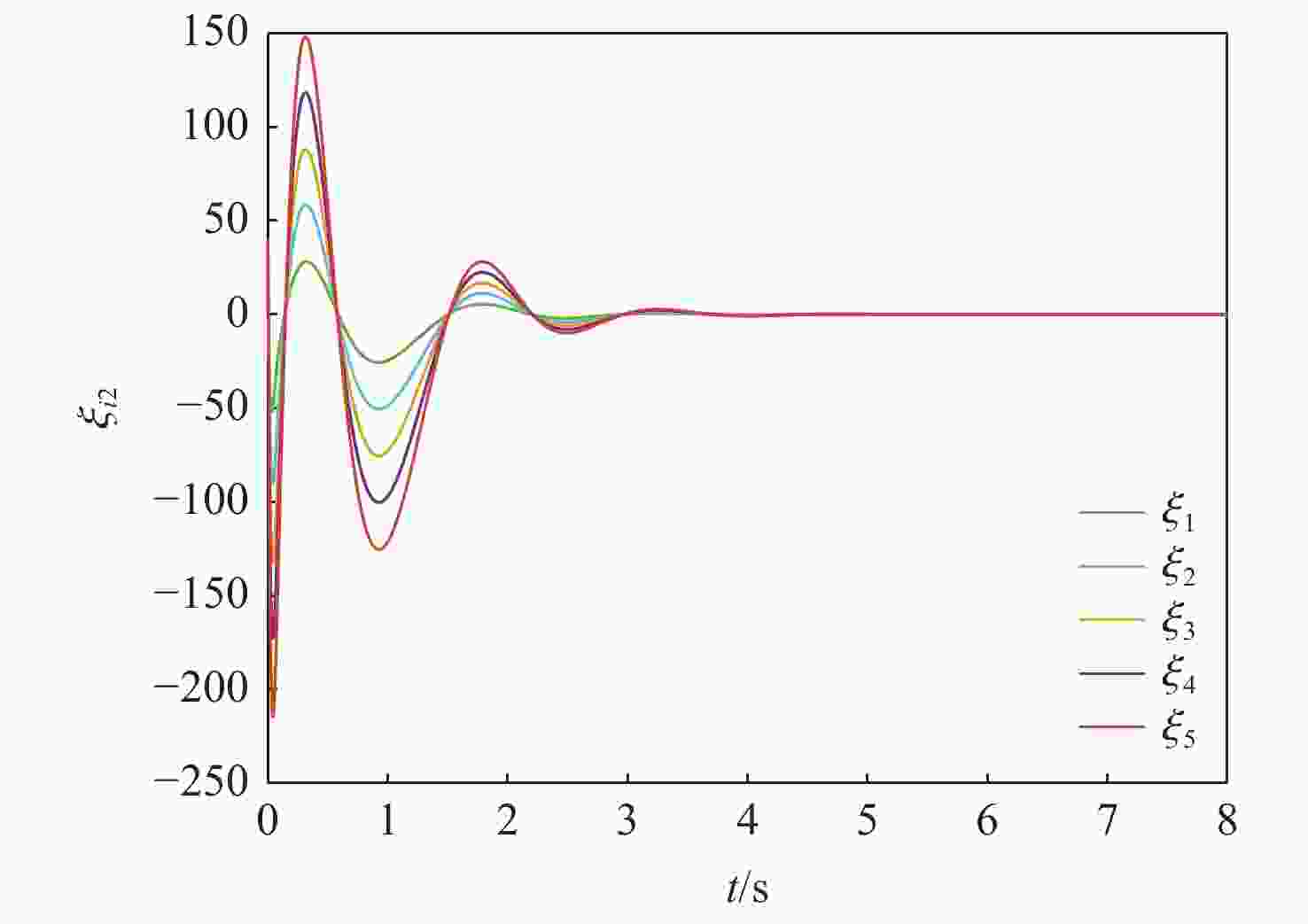
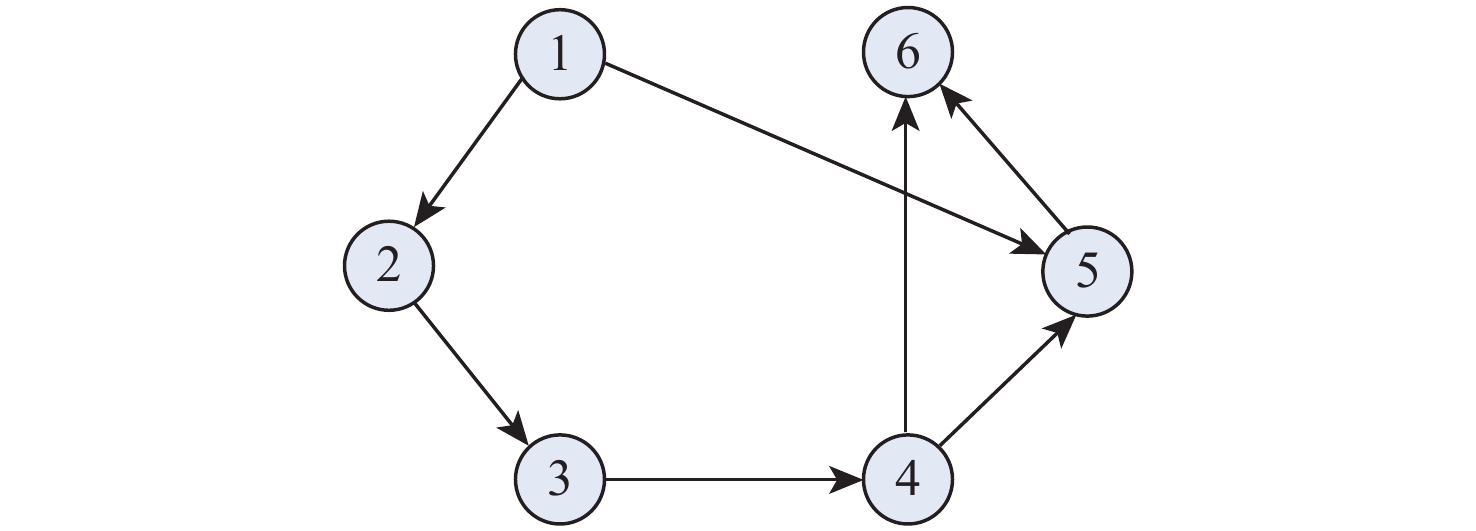
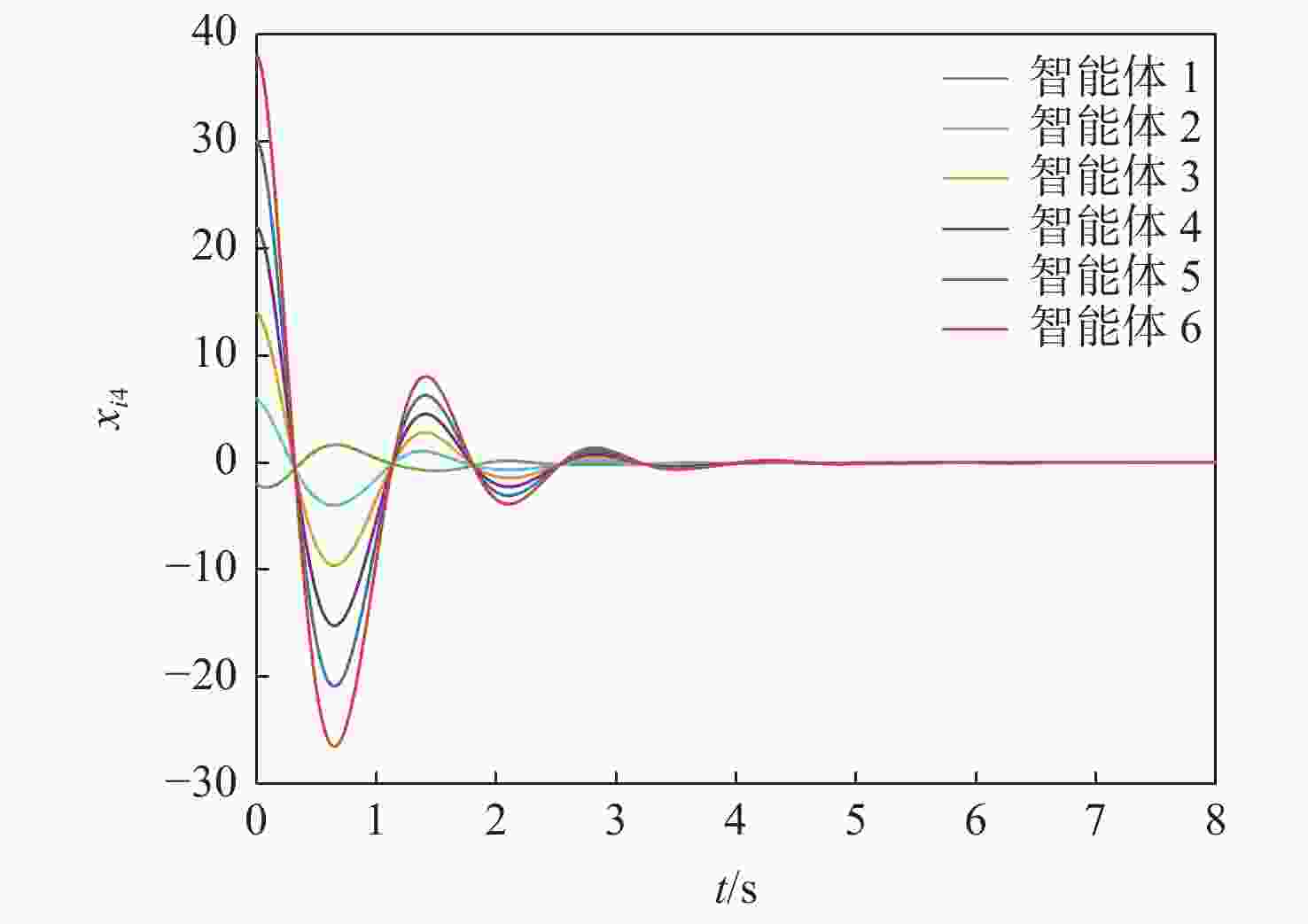
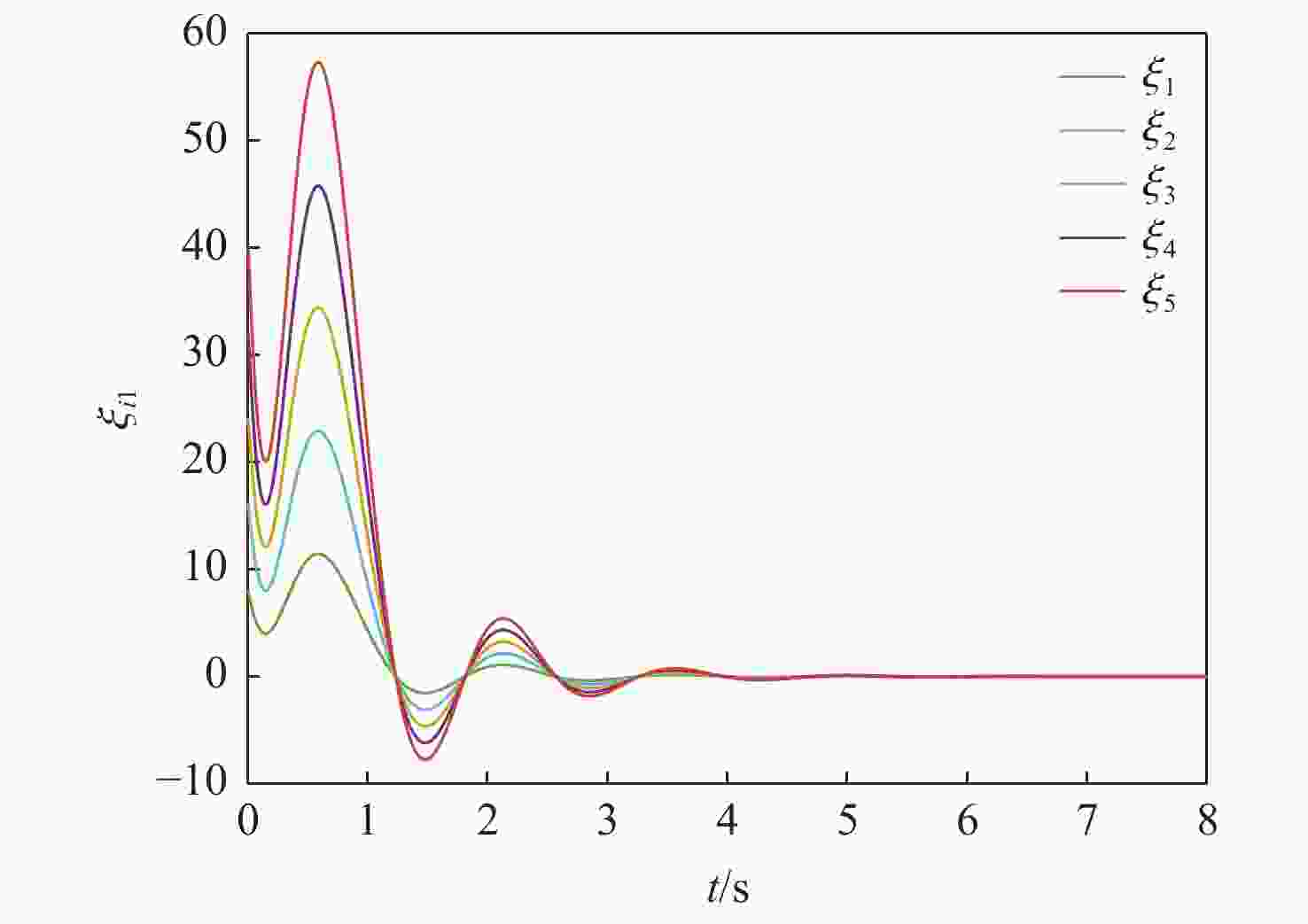
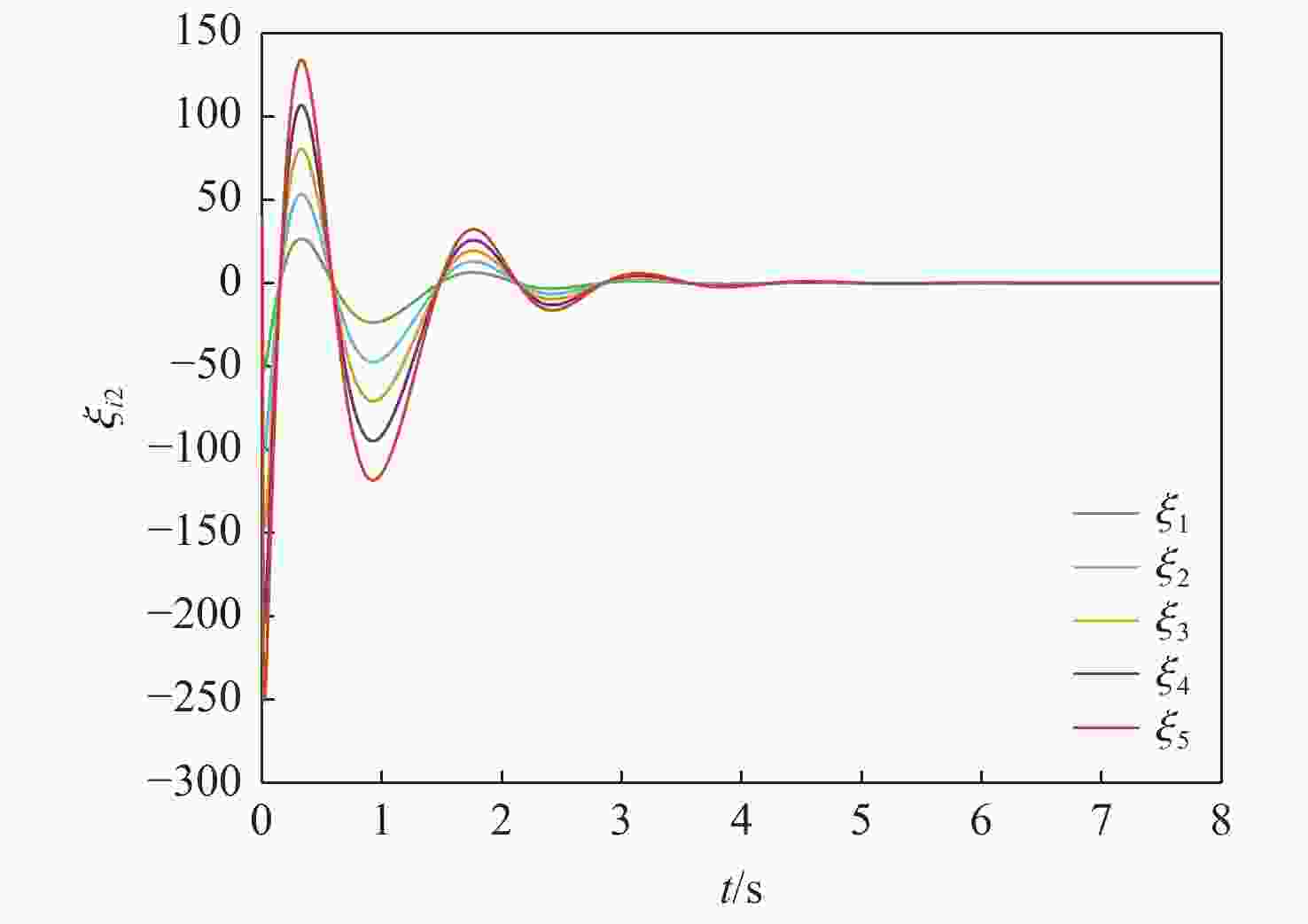
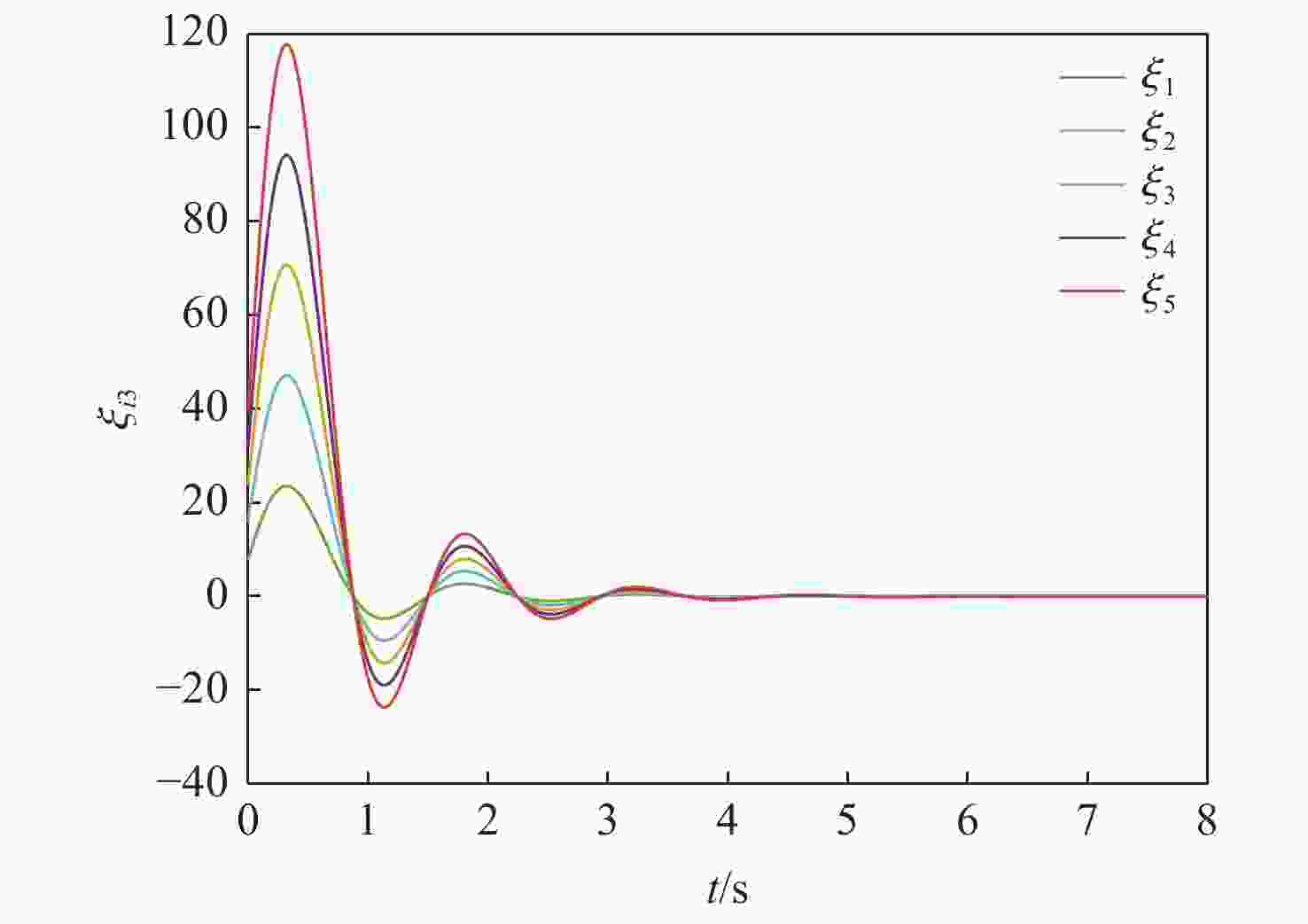
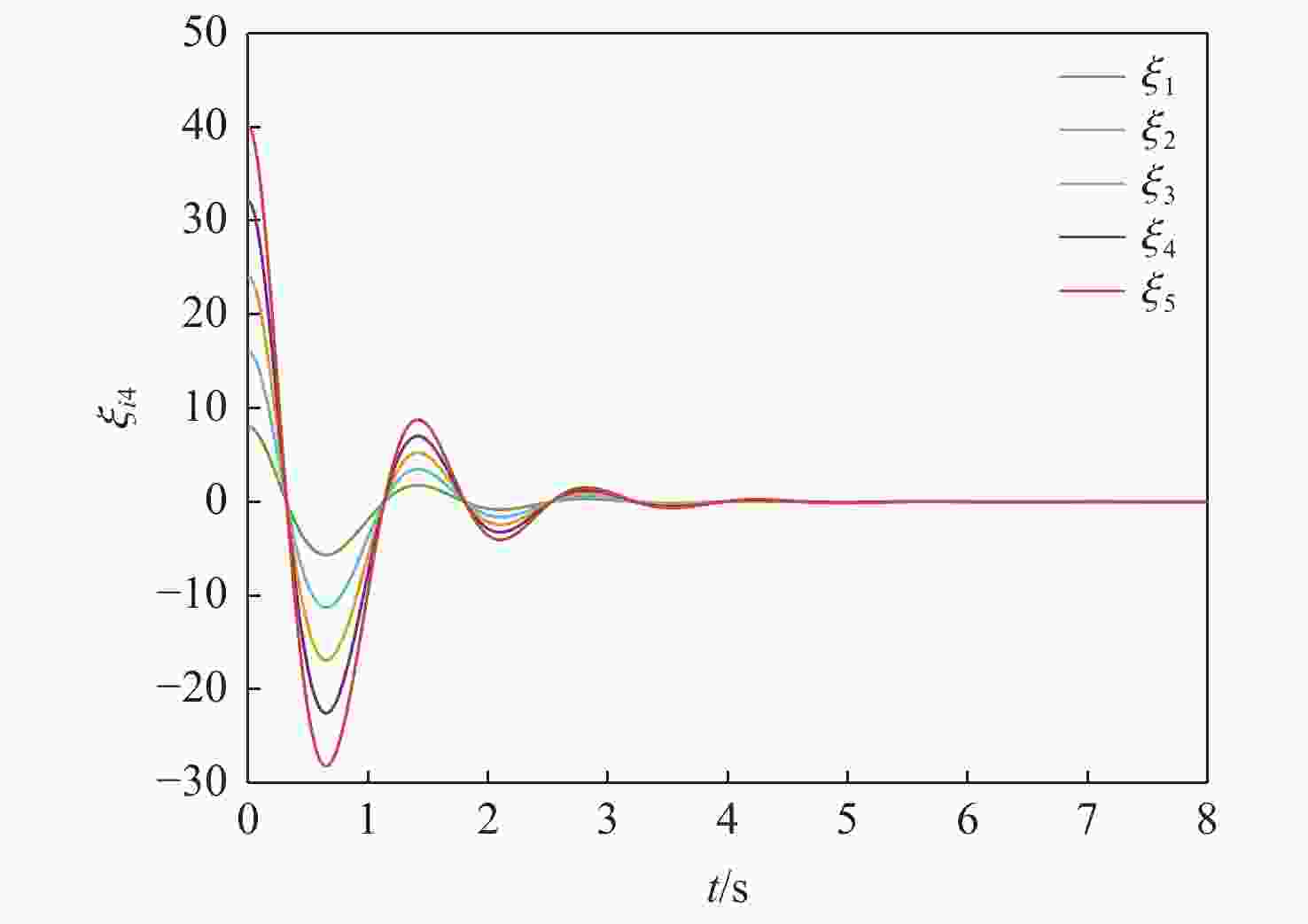
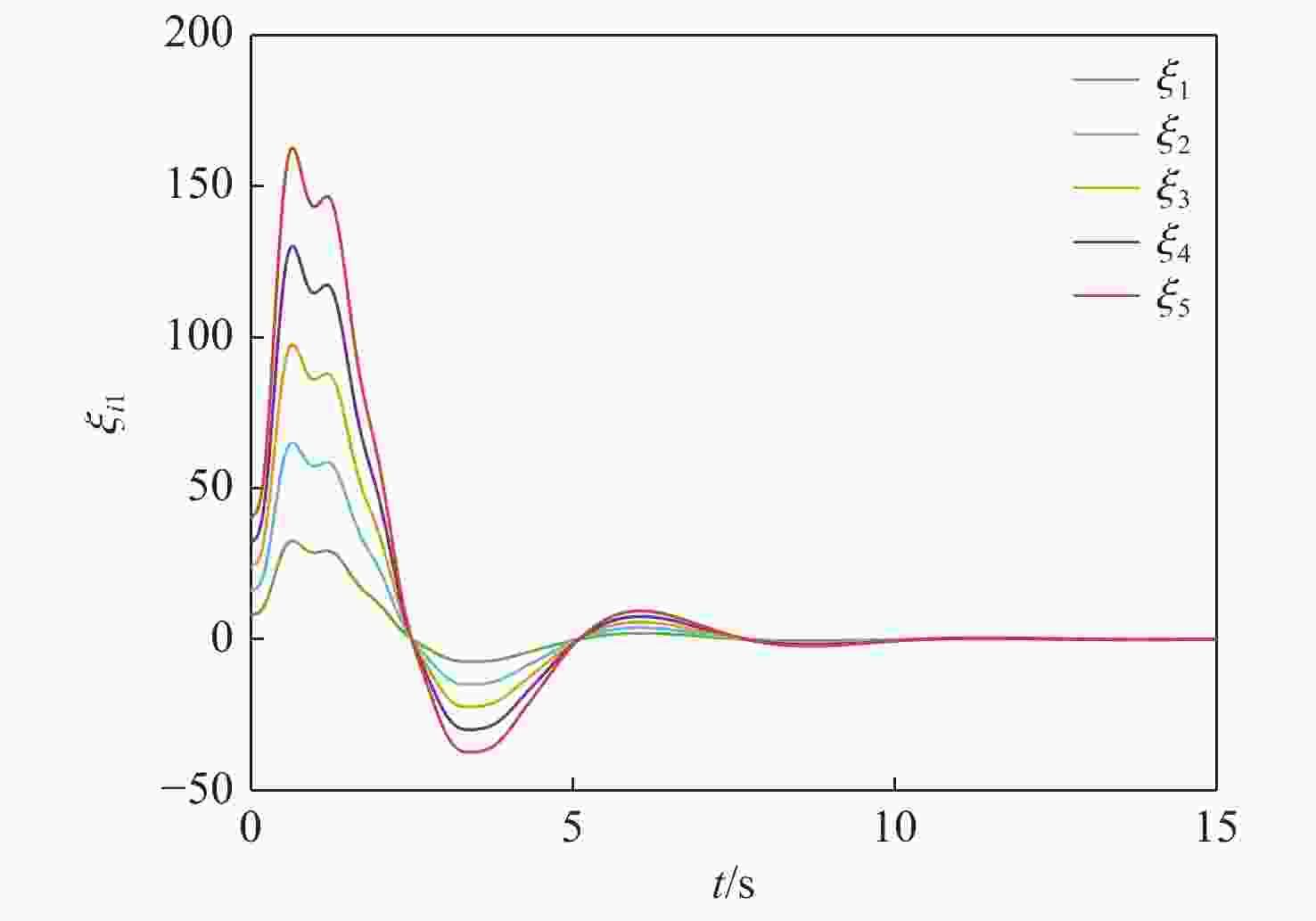
针对一类Lipschitz非线性多智能体系统的一致性控制问题,在一般有向拓扑条件下,研究了通信网络具有不确定性的一致性控制方法,设计了基于输出反馈的一致性控制器。利用拓扑图拉普拉斯矩阵的性质,克服了有向拓扑不对称性的影响,将有向拓扑条件下的一致性控制问题转化为低维非线性系统的鲁棒镇定问题;利用李雅普诺夫函数直接方法,推导系统达成一致的充分性条件,将控制器反馈矩阵的设计转化为求解线性矩阵不等式可行解问题。分别在无领导者和有领导者2种拓扑条件下进行数值仿真,结果表明:系统在通信网络存在不确定性时可以达成一致性。
Abstract:Under general directed topology conditions, a consensus control approach with uncertainty in communication networks is studied, and a consensus controller based on output feedback is built, with the aim of solving the consensus control problem of a class of Lipschitz nonlinear multi-agent systems. Based on the properties of the Laplacian matrix of a graph, the influence of asymmetric topology is overcome, and the consensus control problem under the condition of directed topology is transformed into a robust stabilization problem of a dimension-reduced nonlinear system. Using the properties of the Laplacian matrix,we overcome the influence of asymmetric topology,and convert the consensus control problem under the condition of directed topology into a resilient stabilization problem of a dimension-reduced nonlinear system. Using the Lyapunov function direct method, the sufficiency conditions for the system to achieve consensus are deduced, and the design of the feedback matrix of the controller is transformed into a feasible solution problem for solving linear matrix inequalities. Finally, numerical simulations were conducted under both leaderless and leader-following topology conditions, and the results showed that the system can achieve consensus in the presence of uncertainty in the communication network.
-
Key words:
- network uncertainty /
- consensus /
- nonlinear /
- multi-agent systems /
- output feedback
-
表 1 不同参数条件下不等式(7)可解性对比
Table 1. Comparison of solvability of inequality (7) under different parameter conditions
序号 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 $ {\delta _0} $ 可解性 1 0.006 −0.02 0.03 −0.01 0.05 −0.001 0.05 不可解 2 0.01 −0.02 0.03 −0.01 0.04 −0.001 0.02 不可解 3 0.01 −0.009 0.003 −0.006 0.01 −0.009 0.01 可解 4 0.002 −0.003 0.003 −0.001 0.002 −0.001 0.003 可解 -
[1] QIN J, MA Q, SHI Y, et al. Recent advances in consensus of multi-agent systems: A brief survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 4972-4983. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2636810 [2] WU Y, GOU J, HU X, et al. A new consensus theory-based method for formation control and obstacle avoidance of UAVs[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 107: 106332. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106332 [3] CHEN Q, SUN Y, ZHAO M, et al. Consensus-based cooperative formation guidance strategy for multiparafoil airdrop systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 2175-2184. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2020.3020558 [4] WANG N, DAI J, YING J. UAV formation obstacle avoidance control algorithm based on improved artificial potential field and consensus[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2021, 22(6): 1413-1427. doi: 10.1007/s42405-021-00407-6 [5] WANG A, LIU W, DONG T, et al. DisEHPPC: Enabling heterogeneous privacy-preserving consensus-based scheme for economic dispatch in smart grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(6): 5124-5135. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3027572 [6] LI Z, CHEN G. Fixed-time consensus based distributed economic generation control in a smart grid[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2022, 134: 107437. doi: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2021.107437 [7] HERRERA-VIEDMA E, GARCIA-LAPRESTA J L. Information fusion in consensus and decision making[J]. Information Fusion, 2014, 17: 2-3. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2013.05.005 [8] TALEBI S P, WERNER S. Distributed Kalman filtering and control through embedded average consensus information fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 4396-4403. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2897887 [9] YOO S J. Connectivity-preserving approximation-free design for synchronized tracking of uncertain networked nonaffine nonlinear multi-agent systems[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute-Engineering and Applied Mathematics, 2019, 356(11): 5781-5800. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.05.031 [10] 黄小龙, 陈阳舟, 詹璟原. 模型不确定多智能体系统的鲁棒一致性控制[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(9): 19-24.HUANG X L, CHEN Y Z, ZHAN J Y. Robust consensus control of multi-agent systems with model uncertainties[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 19-24(in Chinese). [11] NGUYEN D H, NARIKIYO T, KAWANISHI M. Robust consensus analysis and design under relative state constraints or uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(6): 1784-1790. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2752843 [12] CI C, KAN X, FRANK L L, et al. Adaptive synchronization of multi-agent systems with resilience to communication link faults[J]. Automatica, 2020, 111: 108636. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108636 [13] 刘淼, 李忠奎. 不确定通讯下的异构多智能体网络鲁棒编队控制[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2018, 44(5): 47-54.LIU M, LI Z K. Robust formation control of heterogeneous multiagent systems with uncertain communications[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2018, 44(5): 47-54(in Chinese). [14] AMINI A, ASIF A, MOHAMMADI A, et al. A robust event-triggered consensus strategy for linear multi-agent systems with uncertain network topology[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3659-3663. [15] LIU M, LI Z. Robust consensus of Lur’e networks with uncertain communications[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2017, 11(6): 877-882. [16] LI Z, CHEN J. Robust consensus of linear feedback protocols over uncertain network graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(8): 4251-4258. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2685082 [17] WANG J, LI X. Distributed event-triggered consensus for nonlinear networked robotic systems over an uncertain network[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Mechatronics Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-6. [18] GODSIL C, ROYLE G F. Algebraic graph theory[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2001: 82-96. [19] HORN R, JOHNSON C. Matrix analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1985: 33-65. [20] ZADEH L, DESOER C. Linear system theory: The state space approach[M]. Mineola: Courier Dover Publications, 2008: 25-43. [21] HAN D, CHESI G, HUNG Y S. Robust consensus for a class of uncertain multi-agent dynamical systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(1): 306-312. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2217971 [22] LIN P, JIA Y. Robust H∞ consensus analysis of a class of second-order multi-agent systems with uncertainty[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 4(3): 487-498. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2008.0492 [23] LI H, LIAO X, HUANG T, et al. Second-order global consensus in multiagent networks with random directional link failure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(3): 565-575. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2320274 [24] LIU W, ZHOU S, QI Y, et al. Leaderless consensus of multi-agent systems with Lipschitz nonlinear dynamics and switching topologies[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 173: 1322-1329. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.09.005 [25] LIU W, ZHOU S, WU Q, et al. H∞ consensus of multi-agent systems in directed networks with Lipschitz non-linear dynamics[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2017, 39(12): 1877-1884. doi: 10.1177/0142331216655395 -







 下载:
下载: