Martian terrain feature extraction method based on unsupervised contrastive learning
-
摘要:
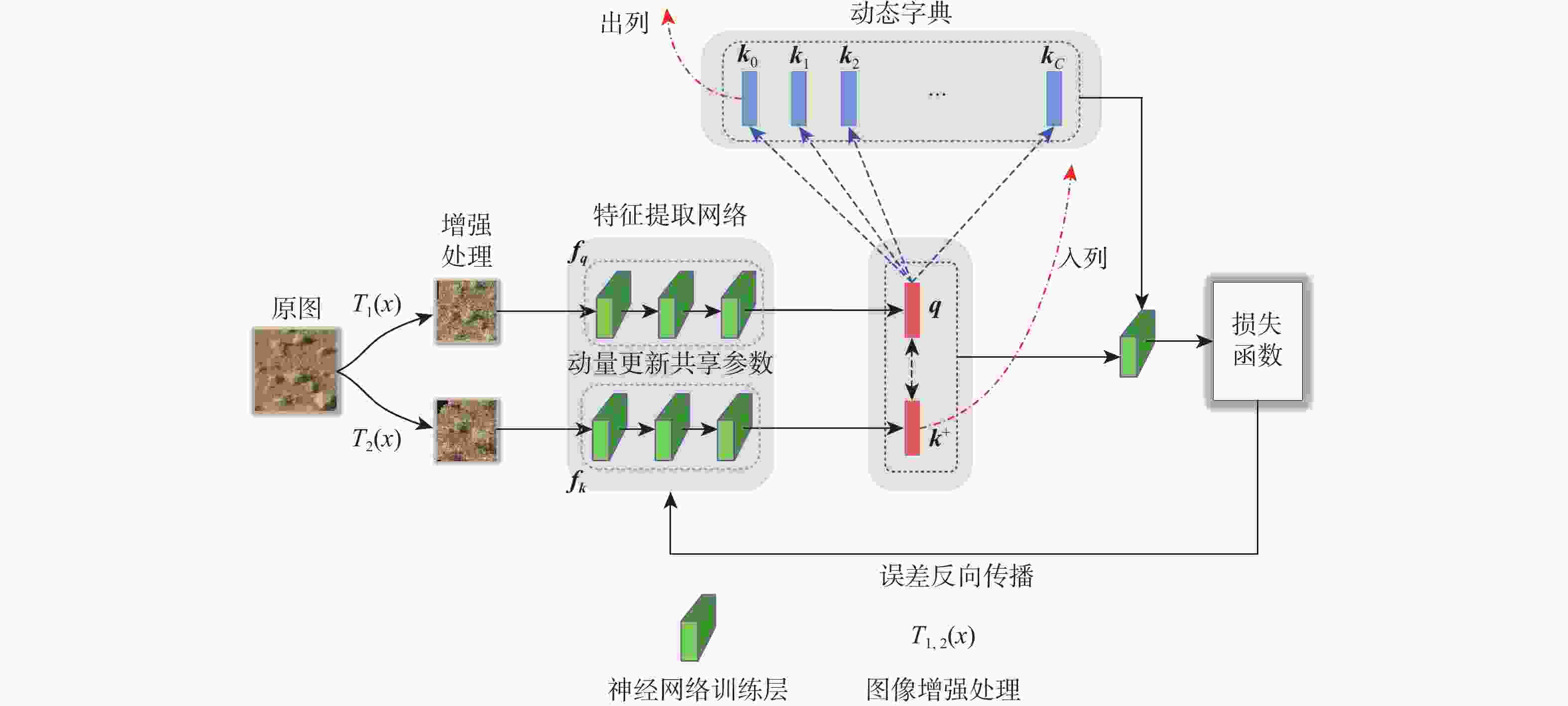
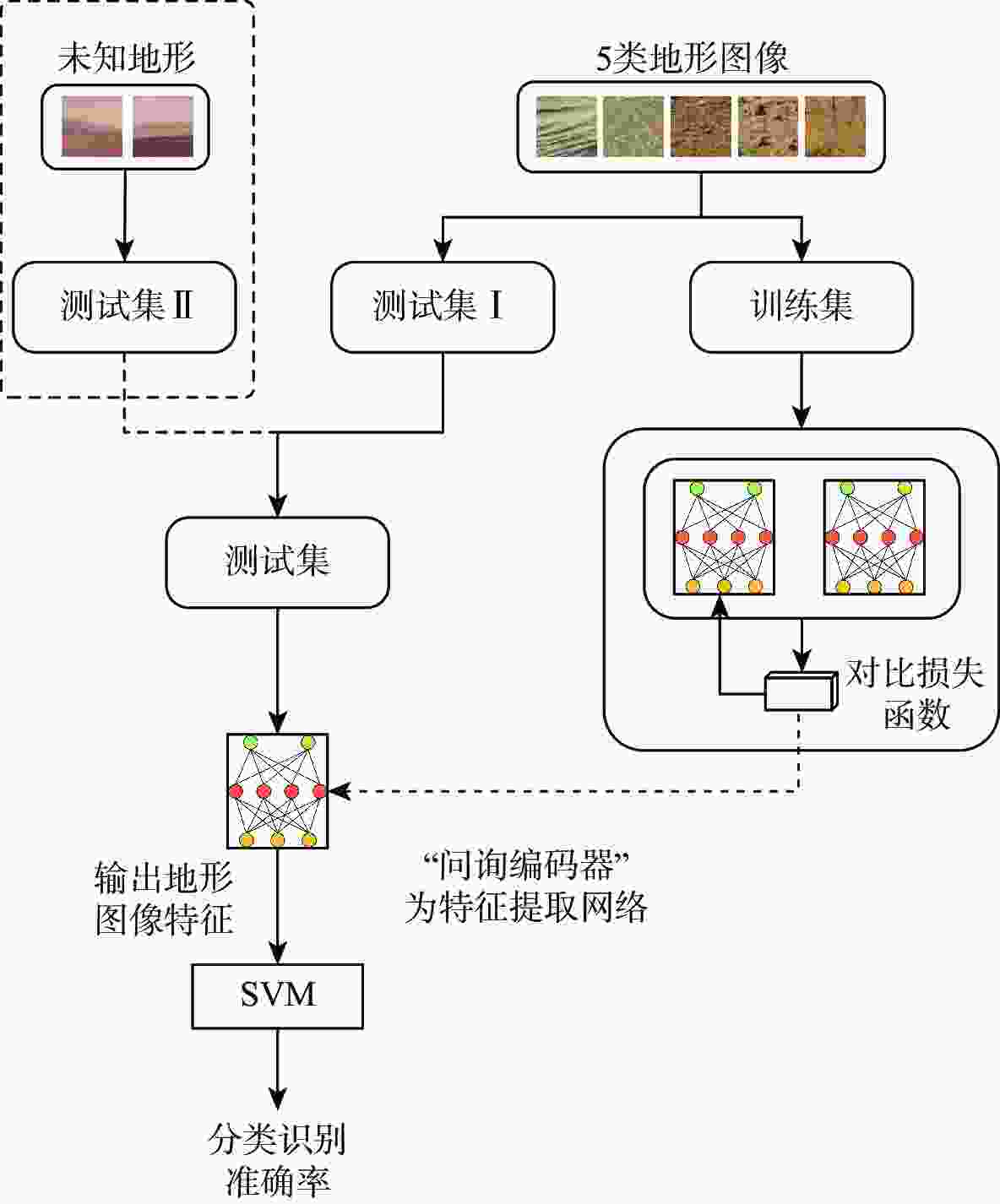
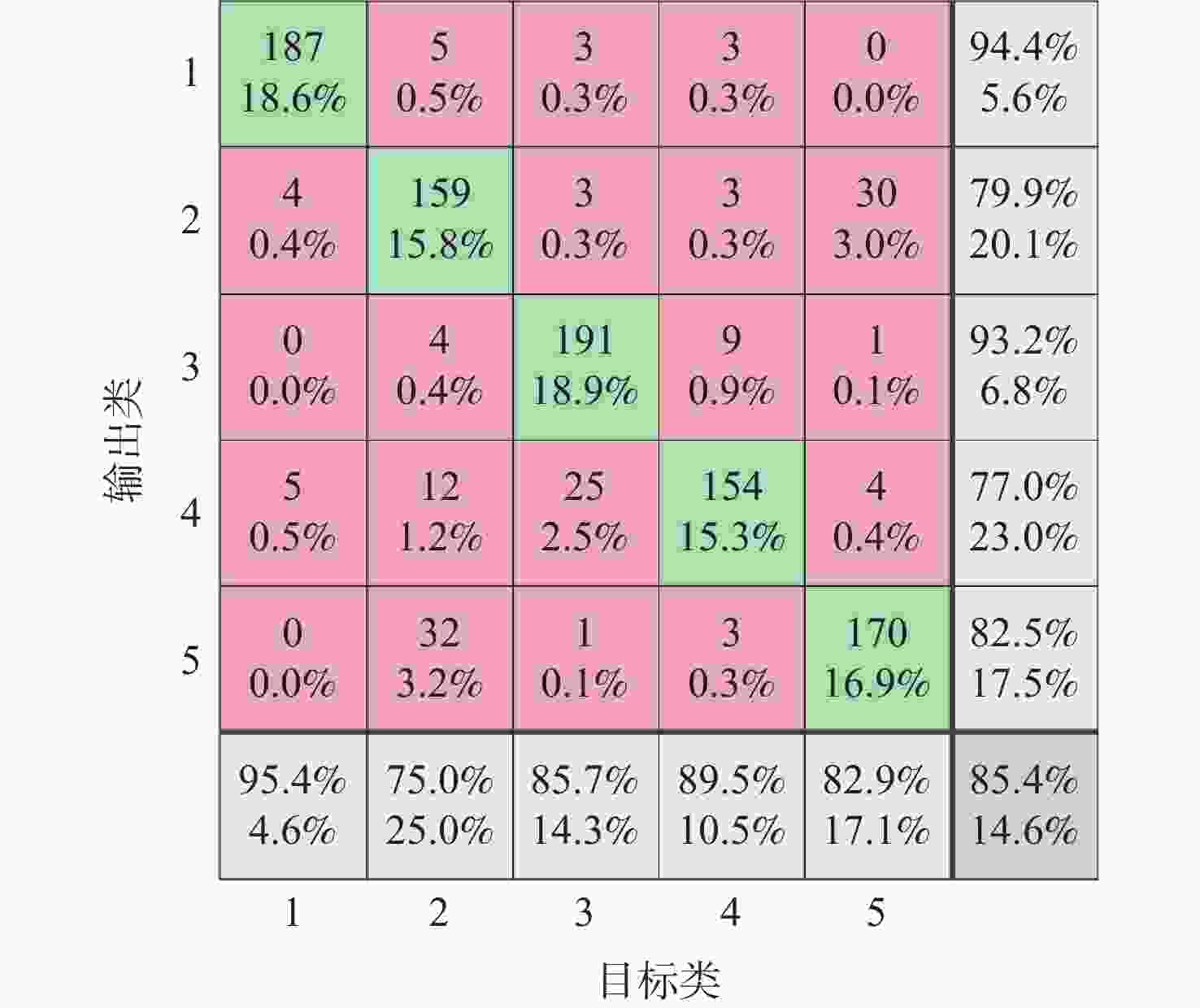
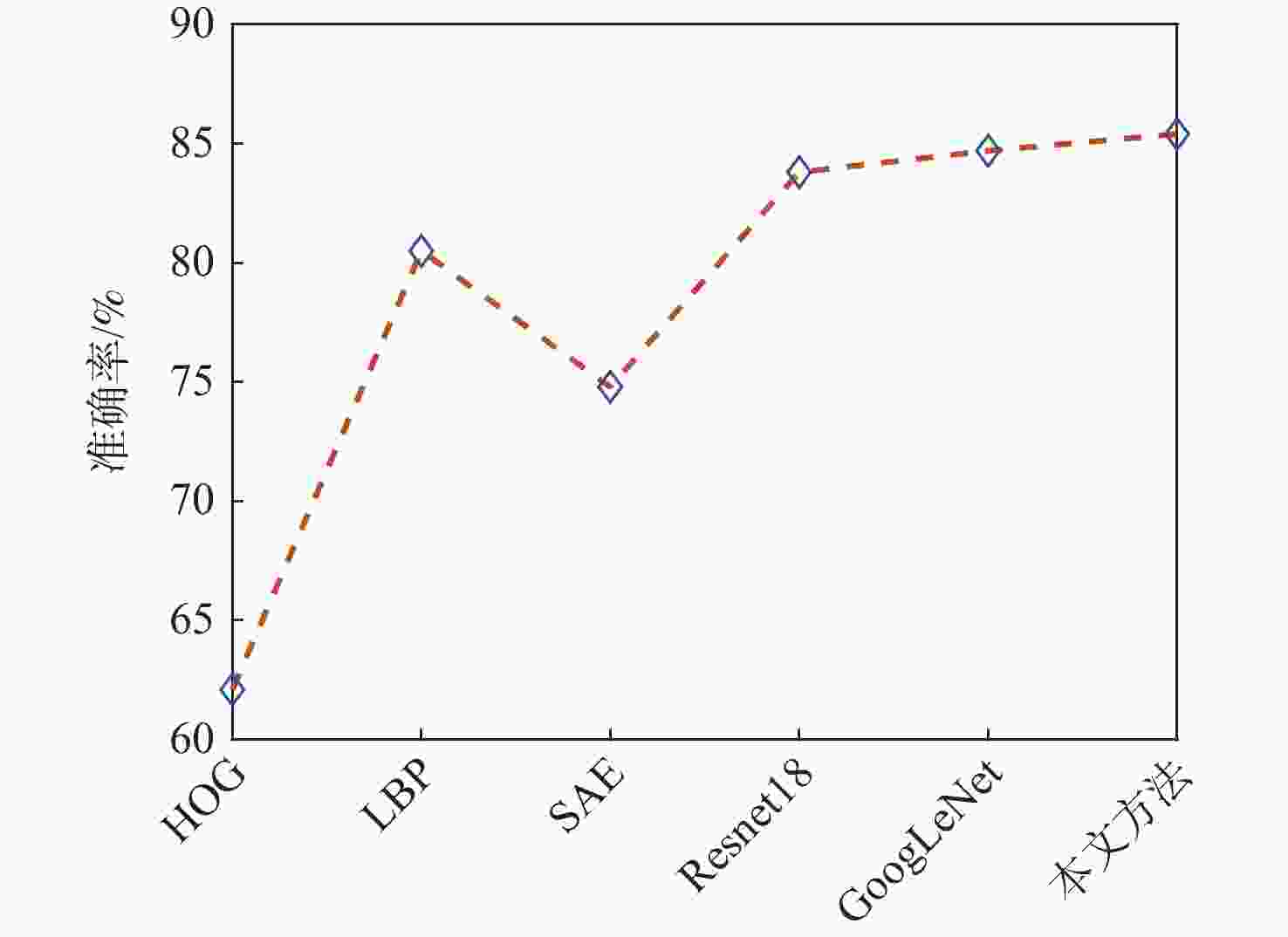
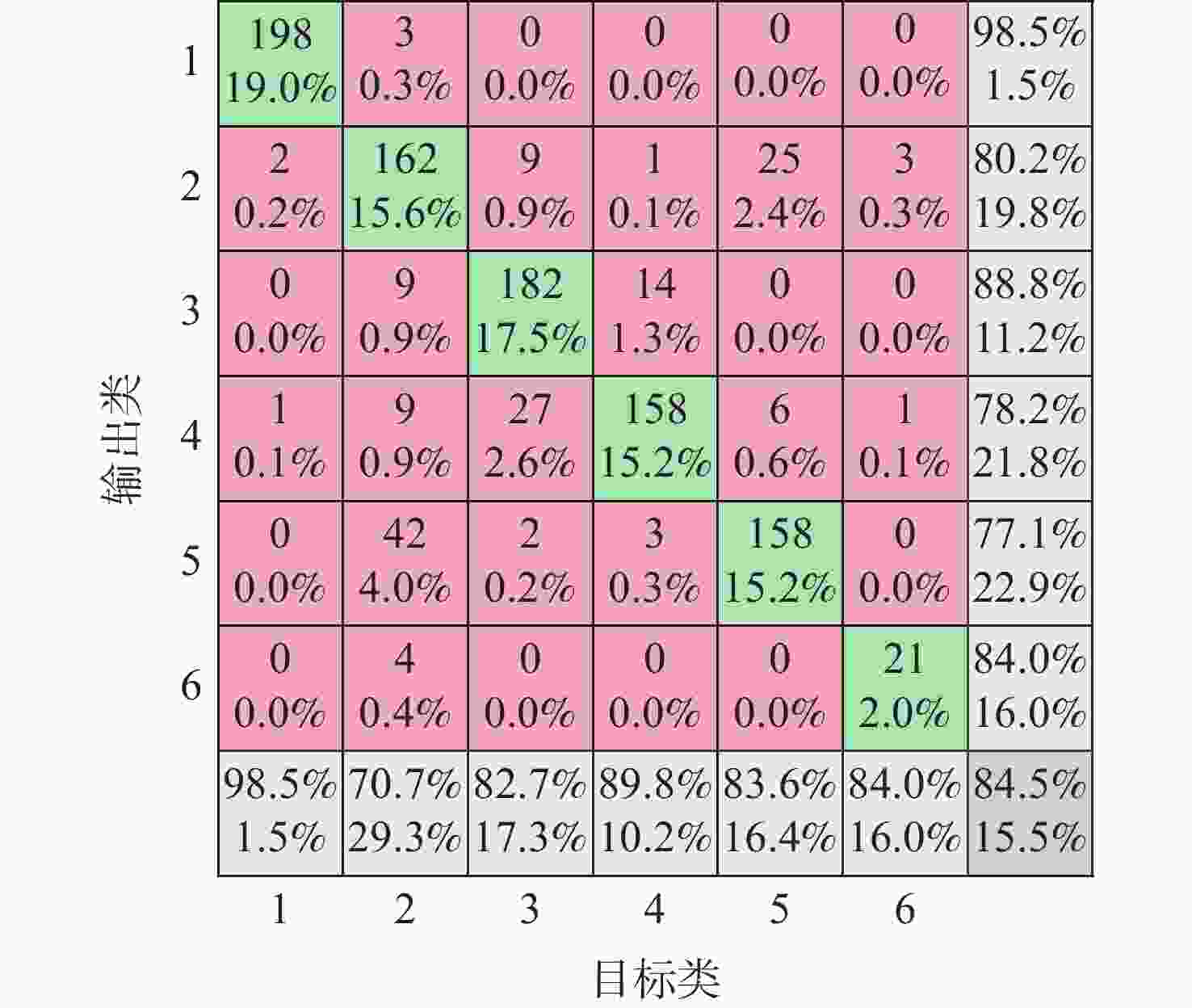
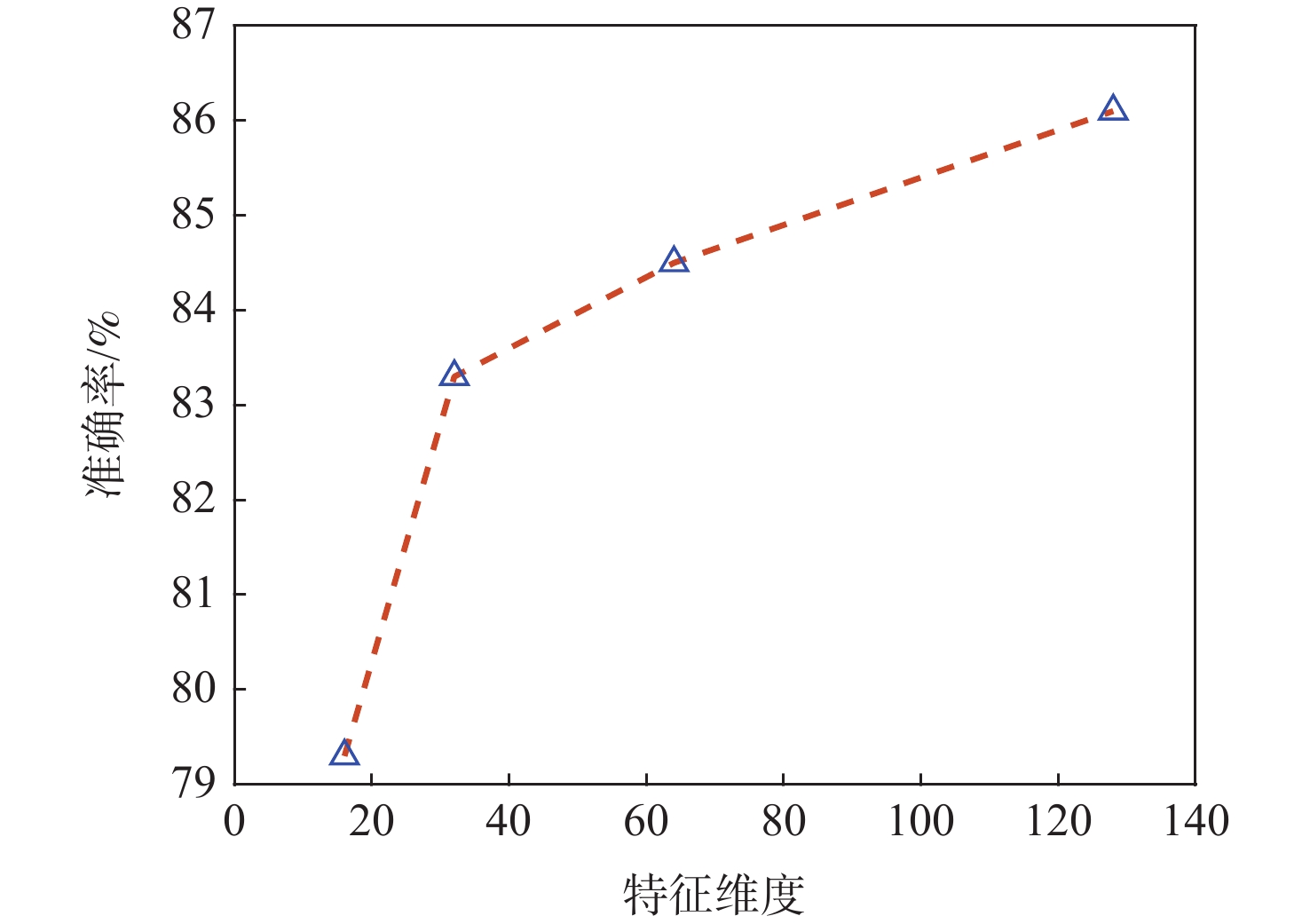
火星表面地形智能识别对火星车自主探测具有重要意义,火星地形图像的特征提取方法目前主要分为传统的浅层视觉特征提取和基于监督学习的深层特征提取2类。找回丢失图像信息、获取大量带标签数据是要解决的关键问题。为此,提出一种基于非监督对比学习的火星地形特征识别方法,通过建立图像字典数据集,用“问询”和“编码”2组神经网络分别将单个图像与“字典”数据集中其他图像进行对比,用相似度泛函作为损失函数对网络进行训练,从而实现对火星地形图像的特征识别。所提方法还具有对训练数据集之外的新类型地形图像识别能力,后续识别分类优越性突出。仿真结果表明:所提方法识别准确率为85.4%,对新类型地形图像的识别准确率为84.5%。
Abstract:Intelligent surface terrain recognition of Martian is significant for the autonomous exploration of Mars rovers. At present, the methods used for feature extraction of Martian terrain images are mainly divided into two categories: traditional shallow visual feature extraction and deep feature extraction based on supervised learning. However, these methods tend to lose image information and require a large amount of labeled data, which are key problems to be solved. A Martian terrain feature recognition method based on unsupervised contrastive learning was proposed. By establishing the image dictionary dataset, a single image was compared with other images in the dictionary dataset by using two groups of neural networks, namely “query” and “encode”. Then, the similarity function was used as the loss function to train the network, so as to realize the feature recognition of Martian terrain images. The proposed method could also recognize new types of terrain images outside the training dataset and showed superior performance in subsequent recognition and classification tasks. Simulation results show that the recognition accuracy of the proposed method is 85.4%, and the recognition accuracy of new terrain images is 84.5%.
-
Key words:
- contrastive learning /
- unsupervised /
- deep learning /
- Martian terrain /
- feature extraction
-
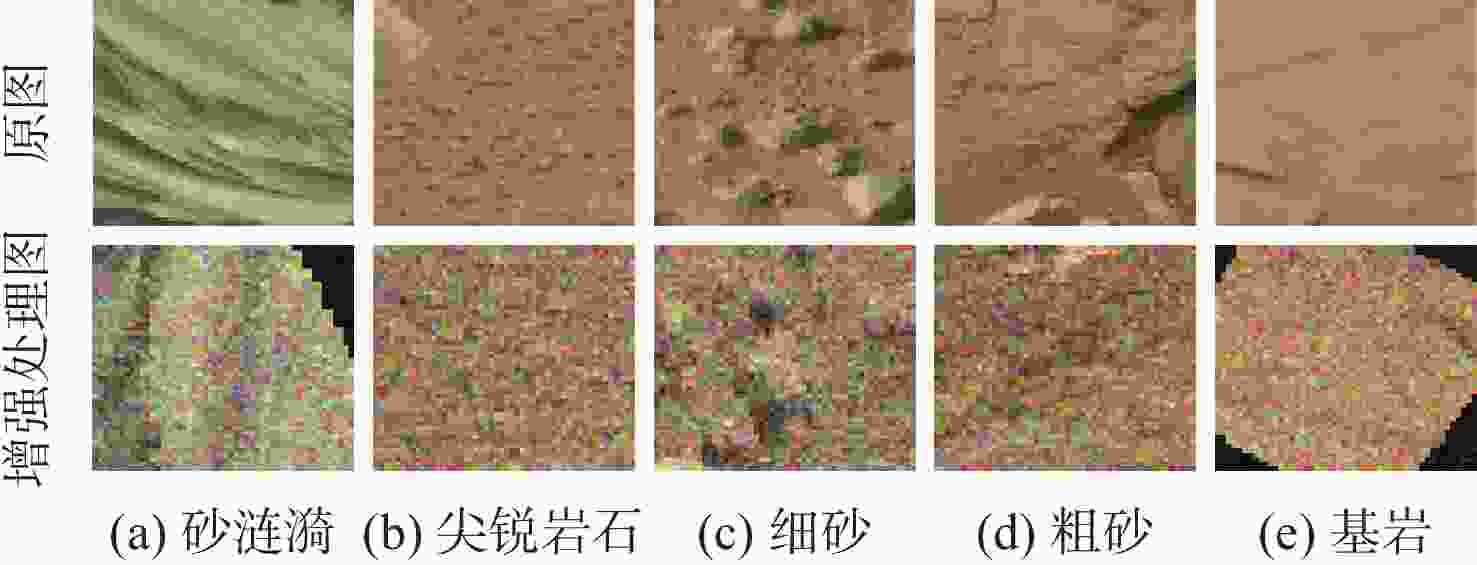
表 1 5类火星地形示例
Table 1. Examples of five types of Martian terrain
类别 典型图 影响 砂涟漪 

导致车轮陷入
沙坑无法运转尖锐岩石 

导致车轮破损 细砂 

粒度小,
车轮滑转率小粗砂 

粒度大,
车轮滑转率大基岩 

硬度大,可通行,
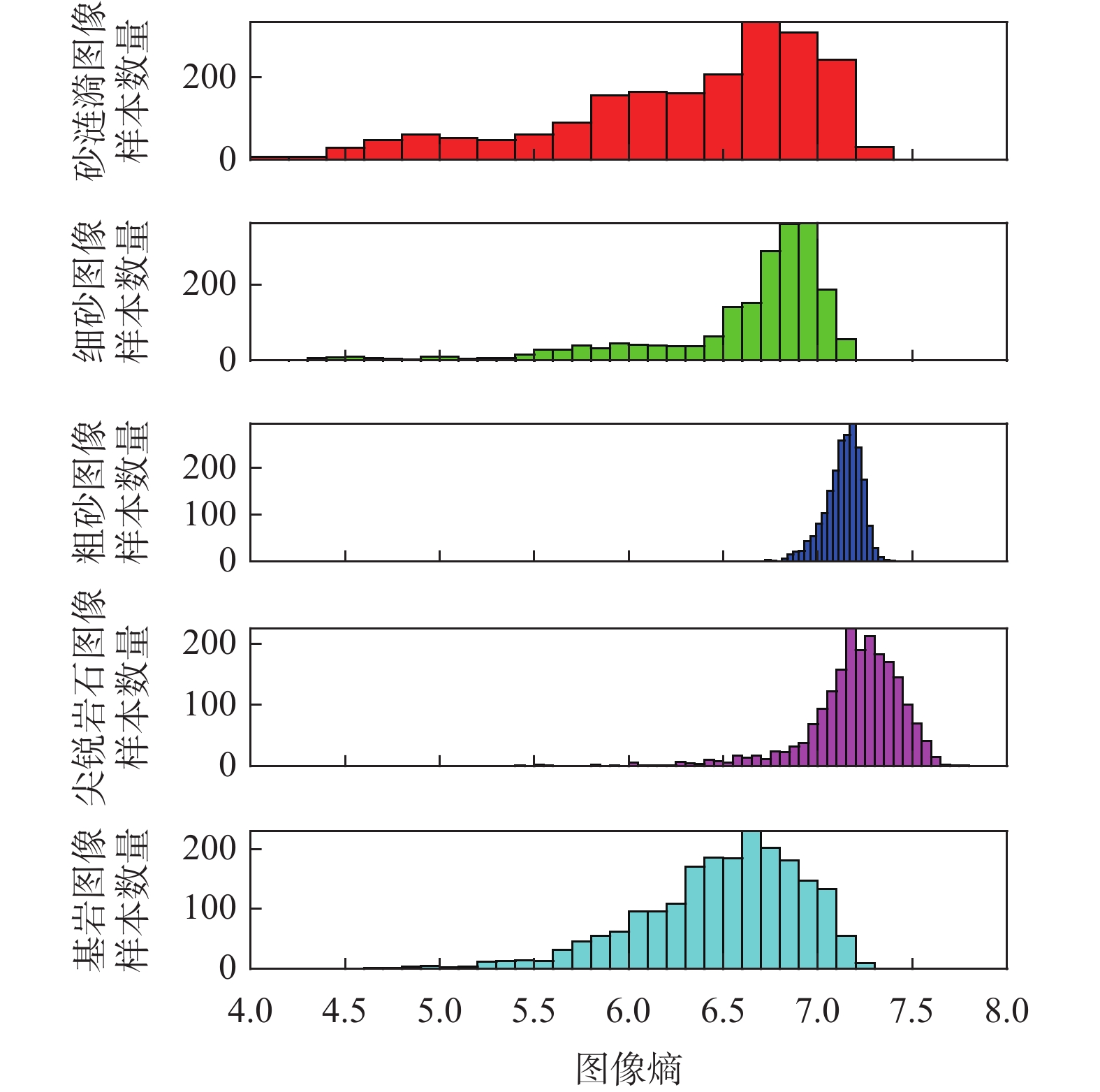
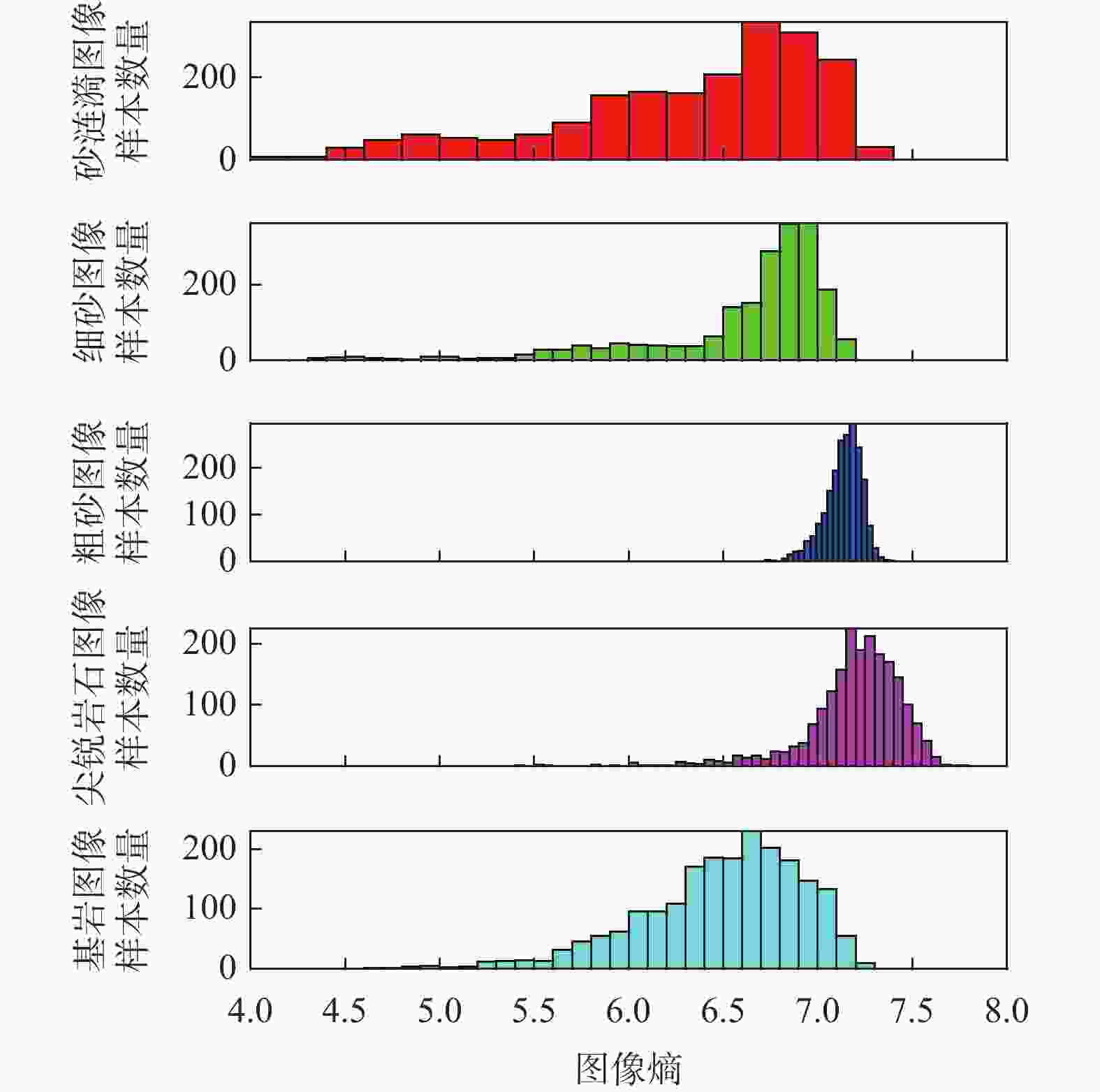
易损坏车轮表 2 火星典型地形图像熵
Table 2. Entropy of typical Martian terrain images
类别 均值 方差 砂涟漪 6.3211 0.4777 尖锐岩石 6.6011 0.2715 细砂 7.1354 0.0088 粗砂 7.1962 0.0661 基岩 6.4962 0.1772 -
[1] OJHA L, WILHELM M, MURCHIE S, et al. Spectral evidence for hydrated salts in recurring slope lineae on Mars[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(11): 829-832. [2] 张洪华, 梁俊, 黄翔宇, 等. 嫦娥三号自主避障软着陆控制技术[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2014, 44(6): 559-568. doi: 10.1360/092014-51ZHANG H H, LIANG J, HUANG X Y, et al. Autonomous hazard avoidance control for Chang’E-3 soft landing[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2014, 44(6): 559-568 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/092014-51 [3] LEE S J, CHEN T L, YU L, et al. Image classification based on the boost convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 12755-12768. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2796722 [4] JIAO L C, ZHANG F, LIU F, et al. A survey of deep learning-based object detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 128837-128868. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2939201 [5] JU J, JUNG H, OH Y, et al. Extending contrastive learning to unsupervised coreset selection[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 7704-7715. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3142758 [6] SUN Q R, LIU Y Y, CHUA T S, et al. Meta-transfer learning for few-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 403-412. [7] SHORTEN C, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning[EB/OL]. (2022-04-19)[2022-04-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08610. [8] BOWLES C, CHEN L, GUERRERO R, et al. GAN Augmentation: Augmenting training data using generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. (2018-10-25)[2022-04-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.10863. [9] FRID-ADAR M, BEN-COHEN A, AMER R, et al. Improving the segmentation of anatomical structures in chest radiographs using U-net with an ImageNet pre-trained encoder[C]//Proceedings of the International Workshop on Reconstruction and Analysis of Moving Body Organs, International Workshop on Breast Image Analysis, International Workshop on Thoracic Image Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 159-168. [10] CUI B G, CHEN X, LU Y. Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images using transfer learning and deep convolutional neural network with dense connection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 116744-116755. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003914 [11] GENG J, DENG X Y, MA X R, et al. Transfer learning for SAR image classification via deep joint distribution adaptation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5377-5392. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2964679 [12] LI H F, CUI Z Q, ZHU Z Q, et al. RS-MetaNet: Deep metametric learning for few-shot remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6983-6994. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027387 [13] VU T H, JAIN H, BUCHER M, et al. DADA: Depth-aware domain adaptation in semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 7363-7372. [14] JING L L, TIAN Y L. Self-supervised visual feature learning with deep neural networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(11): 4037-4058. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2992393 [15] MISRA I, VAN DER MAATEN L. Self-supervised learning of pretext-invariant representations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6706-6716. [16] JAISWAL A, BABU A R, ZADEH M Z, et al. A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning[J]. Technologies, 2020, 9(1): 2. doi: 10.3390/technologies9010002 [17] HJELM R D, FEDOROV A, LAVOIE-MARCHILDON S, et al. Learning deep representations by mutual information estimation and maximization[EB/OL]. (2018-08-20)[2022-04-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.06670v3. [18] HÉNAFF O J, SRINIVAS A, DE FAUW J, et al. Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding[EB/OL]. (2019-03-22)[2022-04-24].https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.09272. [19] WU Z R, XIONG Y J, YU S X, et al. Unsupervised feature learning via non-parametric instance discrimination[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3733-3742. [20] CHEN T, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]//Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2020: 1597–1607. [21] HE K M, FAN H Q, WU Y X, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 9726-9735. [22] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. -






 下载:
下载: