-
摘要:
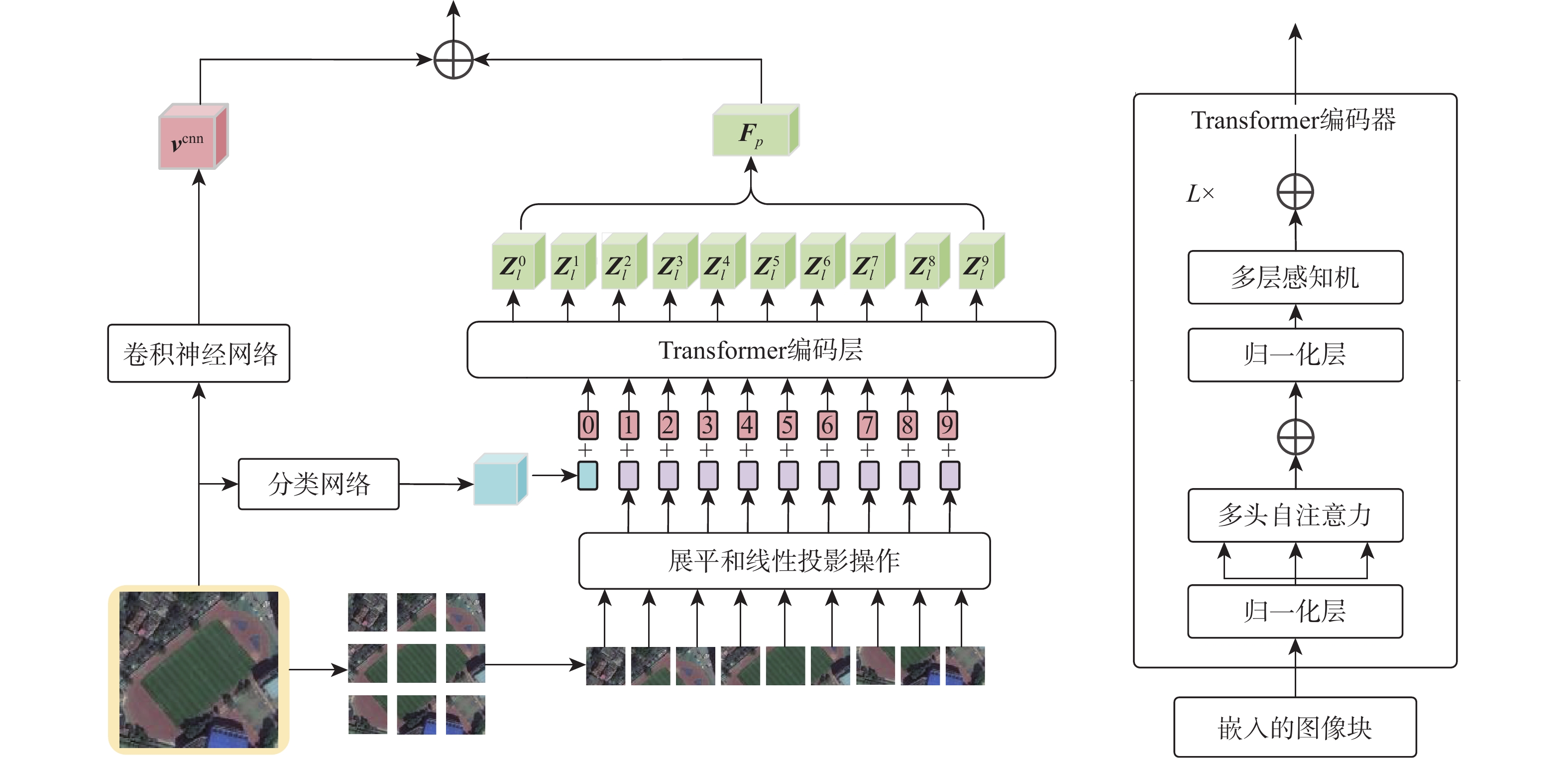
遥感图文检索可以从类别繁多、内容复杂的遥感数据中检索到有价值的信息,对环境评估、城市规划以及灾害预测具有重要意义。但是,遥感图文跨模态检索存在一个关键问题,即遥感图像的空间布局信息被忽略。其主要体现在2个方面:①遥感目标的远距离建模困难;②遥感相邻次要目标被淹没。基于以上问题,提出了一种基于布局化-语义联合表征的跨模态遥感图像文本检索(SL-SJR),主要包括主导语义监督的布局化视觉特征提取(DSSL)模块、布局化视觉-全局语义交叉指导(LV-GSCG)模块和多视角匹配(MVM)模块。DSSL模块实现主导语义类别特征监督下图像的布局化建模。LV-GSCG模块计算布局化视觉特征与文本中提取的全局语义特征的相似度来实现不同模态特征的交互。MVM模块建立跨模态特征指导的多视角度量匹配机制以消除跨模态数据之间的语义鸿沟。在4个基线遥感图像文本数据集上的实验验证,结果表明所提方法在大多数跨模态遥感图像文本检索任务中可以达到最先进的性能。
Abstract:Remote sensing image-text retrieval can retrieve valuable information from remote sensing data. It is of great significance to environmental assessment, urban planning and disaster prediction. However, there is a key problem that the spatial layout information of remote sensing images is ignored, which is mainly reflected in two aspects: one is the difficulty of long-distance modeling of remote sensing targets; the other, the submerge of the remote sensing adjacent secondary targets. Based on the above problems, this paper proposes a cross modal remote sensing image-text retrieval model based on layout semantic joint representation, which includes the dominant semantic supervison layout visual feature extraction module (DSSL), Layout visual-global semantic cross guidance (LV-GSCG) and multi-view matching (MVM). The DSSL module realizes the layout modeling of images under the supervision of dominant semantic category features. The LV-GSCG module calculates the similarity between the layout visual features and the global semantic features extracted from text to realize the interaction of different modal features. The MVM module establishes a cross-modal feature-guided multi-view metric matching mechanism to eliminate the semantic gap between the cross-modal data. Experimental validation on four baseline remote sensing image text datasets shows that the model can achieve state-of-the-art performance in most cross-modal remote sensing image text retrieval tasks.
-
表 1 RSICD数据集对比实验结果
Table 1. Comparative experimental results on RSICD
方法 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 SCAN t2i 4.42 4.02 11.20 11.54 17.68 18.60 11.24 SCAN i2t 5.90 3.86 13.21 16.83 19.96 26.49 14.38 CAMP-triplet 5.22 4.30 13.05 17.10 21.02 27.54 14.71 CAMP-bce 4.50 3.03 10.08 15.12 16.48 23.05 12.04 MTFN 5.01 4.96 12.86 12.24 21.30 29.12 14.24 AMFMN 5.39 5.05 15.32 18.19 28.82 29.70 17.07 本文 5.31 5.32 19.12 19.69 31.47 32.50 18.90 表 2 RSITMD数据集对比实验结果
Table 2. Comparative experimental results on RSITMD
方法 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 SCAN t2i 10.59 10.04 28.72 29.54 38.41 42.91 26.70 SCAN i2t 10.84 9.62 25.86 29.80 37.26 41.06 25.74 CAMP-triplet 11.82 8.69 27.40 27.17 38.12 43.60 26.13 CAMP-bce 9.21 6.81 22.56 25.65 35.73 40.05 23.34 MTFN 10.80 9.82 27.68 30.28 36.40 48.27 27.21 AMFMN 11.37 9.04 27.70 32.46 39.29 49.68 28.25 本文 13.05 9.82 29.42 35.39 39.82 52.65 30.03 表 3 UCM数据集对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparative experimental results on UCM
方法 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 SCAN t2i 13.68 11.06 40.92 48.28 63.28 69.40 41.10 SCAN i2t 12.54 11.24 42.15 46.26 65.45 74.93 42.10 CAMP-triplet 10.37 8.30 38.71 45.13 62.78 70.50 39.30 CAMP-bce 14.22 10.91 39.02 47.95 62.98 72.56 41.27 MTFN 10.89 14.06 38.16 49.38 60.05 76.22 41.46 AMFMN 11.90 13.81 41.42 45.52 61.90 70.67 40.87 本文 14.76 11.33 39.52 50.86 61.43 82.29 43.37 表 4 Sydney数据集对比实验结果
Table 4. Comparative experimental results on Sydney
方法 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 SCAN t2i 17.26 16.83 40.60 56.04 58.05 71.24 43.34 SCAN i2t 19.48 15.62 44.81 58.20 55.28 73.53 44.49 CAMP-triplet 17.80 14.50 45.28 45.63 61.44 69.55 42.37 CAMP-bce 14.26 13.41 42.53 50.32 57.35 73.86 41.96 MTFN 16.23 14.05 42.09 56.95 52.68 77.18 43.20 AMFMN 15.52 14.14 43.10 56.21 60.34 75.52 44.14 本文 15.52 16.90 50.00 55.17 67.24 80.69 47.59 表 5 消融实验结果
Table 5. Ablation experimental results
方法 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 AMFMN 10.62 8.50 27.65 33.01 40.04 51.64 28.58 AMFMN+A 11.06 9.16 27.87 34.78 42.26 54.34 29.91 AMFMN+A+B 13.05 9.82 29.42 35.39 39.82 52.65 30.03 注:加粗数值表示最优结果。 表 6 图像块个数的消融实验结果
Table 6. Ablation experimental results of number of image blocks
图像块个数 图像块大小 R1 R5 R10 Rm 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 64 32 8.85 9.42 27.21 34.07 42.04 54.38 29.33 16 64 12.83 8.19 27.88 34.12 42.26 55.53 30.13 4 128 11.73 8.72 28.98 33.89 40.93 54.03 29.71 注:加粗数值表示最优结果。 表 7 相似度度量中参数α1与α2消融实验结果
Table 7. Parameters in similarity measurement α1 and α2 ablation experimental results
(α1,α2) R1 R5 R10
Rm图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 (1,1) 0.44 0.40 2.43 2.21 4.65 3.81 2.32 (0.1,0.1) 10.62 8.89 28.10 31.02 41.15 47.70 27.91 (0.05,0.05) 10.62 9.96 28.10 34.34 41.37 49.87 29.04 (0.01,0.01) 12.83 8.19 27.88 34.12 42.26 55.53 30.13 (0.0005,0.0005) 10.37 8.27 26.55 34.25 39.38 55.00 28.97 (0.0001,0.0001) 9.96 7.92 23.67 30.49 38.05 52.30 27.06 注:加粗数值表示最优结果。 表 8 损失函数中β消融实验结果
Table 8. In the loss function β ablation experimental results
(β,1−β) R1 R5 R10
Rm图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 图像检索文本 文本检索图像 (1,0) 13.05 9.82 29.42 35.39 39.82 52.65 30.025 (0.5,0.5) 12.83 8.19 27.88 34.12 42.26 55.53 30.135 (0,1) 11.28 11.37 28.32 34.69 43.58 49.87 29.85 -
[1] LIU Y J, LI X F, REN Y B. A deep learning model for oceanic mesoscale eddy detection based on multi-source remote sensing imagery[C]// IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6762-6765. [2] ZHANG Q L, SETO K C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(9): 2320-2329. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.04.032 [3] NOGUEIRA K, FADEL S G, DOURADO I C, et al. Exploiting ConvNet diversity for flooding identification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(9): 1446-1450. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2845549 [4] CHENG Q M, ZHOU Y Z, FU P, et al. A deep semantic alignment network for cross-modal image-text retrieval in remote sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 4284-4297. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3070872 [5] YUAN Z Q, ZHANG W K, FU K, et al. Exploring a fine-grained multiscale method for cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4404119. [6] 葛芸, 马琳, 叶发茂, 等. 基于多尺度池化和范数注意力机制的遥感图像检索[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(2): 543-551.GE Y, MA L, YE F M, et al. Remote sensing image retrieval based on multi-scale pooling and norm attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(2): 543-551(in Chinese). [7] 李彦甫, 范习健, 杨绪兵, 等. 基于自注意力卷积网络的遥感图像分类[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2021, 43(10): 81-88. doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210196LI Y F, FAN X J, YANG X B, et al. Remote sensing image classification farmework based on self-attention convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2021, 43(10): 81-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.12171/j.1000-1522.20210196 [8] YUAN Z Q, ZHANG W K, TIAN C Y, et al. Remote sensing cross-modal text-image retrieval based on global and local information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 3163706. [9] RONG X E, SUN X, DIAO W H, et al. Historical information-guided class-incremental semantic segmentation in remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5622618. [10] ZHANG Z Y, HAN X, LIU Z Y, et al. ERNIE: Enhanced language representation with informative entities[C]//Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: ACL, 2019: 1441-1451. [11] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. Washington DC: ICLR, 2020: 16-28. [12] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers [C]// In European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 213-229. [13] SRINIVAS A, LIN T Y, PARMAR N, et al. Bottleneck transformers for visual recognition[C]// /IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 16514–16524. [14] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al . Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [15] LIU S L, ZHANG L, YANG X, et al. Query2Label: A simple transformer way to multi-label classification[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 661-670. [16] MESSINA N, AMATO G, FALCHI F, et al. Towards efficient cross-modal visual textual retrieval using transformer-encoder deep features[C]// 2021 International Conference on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-6. [17] GABEUR V, SUN C, ALAHARI K, et al. Multi-modal transformer for video retrieval[C]// Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 214-229. [18] MALEKI D, TIZHOOSH H R. LILE: look in-depth before looking elsewhere -- A dual attention network using transformers for cross-modal information retrieval in histopathology archives[J]. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. Virtual: PMLR, 2022: 3002-3013. [19] SHI Z W, ZOU Z X. Can a machine generate humanlike language descriptions for a remote sensing image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3623-3634. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2677464 [20] LU X Q, WANG B Q, ZHENG X T, et al. Exploring models and data for remote sensing image caption generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2183-2195. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2776321 [21] HOXHA G, MELGANI F, SLAGHENAUFFI J. A new CNN-RNN framework for remote sensing image captioning[C]//2020 Mediterranean and Middle-East Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-4. [22] LI X L, ZHANG X T, HUANG W, et al. Truncation cross entropy loss for remote sensing image captioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(6): 5246-5257. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3010106 [23] LU X Q, WANG B Q, ZHENG X T. Sound active attention framework for remote sensing image captioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1985-2000. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2951636 [24] FAGHRI F, FLEET D J, KIROS J R , et al. VSE++: improving visual-semantic embeddings with hard negatives[C]// British Machine Vision Conference. London : British Machine Vision Association, 2017: 1707-1717. [25] LEE K H, CHEN X, HUA G, et al. Stacked cross attention for image-text matching[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 212-228. [26] WANG T, XU X, YANG Y, et al. Matching images and text with multi-modal tensor fusion and re-ranking[C]// the 27th ACM International Conference. New York: ACM, 2019, 1: 12-20. [27] DEVLIN J, CHENG H, FANG H, et al. Language models for image captioning: the quirks and what works[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 2(53): 100-105. [28] ABDULLAH, BAZI, RAHHAL A, et al. TextRS: Deep bidirectional triplet network for matching text to remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): 405. doi: 10.3390/rs12030405 [29] QU B, LI X L, TAO D L, et al. Deep semantic understanding of high resolution remote sensing image[C]// International Conference on Computer. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 124-128. [30] WANG Z H, LIU X H, LI H S, et al. CAMP: Cross-modal adaptive message passing for text-image retrieval[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 5763-5772. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 钟金彦,陈俊,李宇,吴业炜,葛小青. 基于MFF-SFE的遥感图文跨模态检索方法. 中国科学院大学学报(中英文). 2025(02): 236-247 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术

