Research on toxicity of gases of thermal runaway released from ternary lithium-ion batteries featuring cyclic aging process
-
摘要:
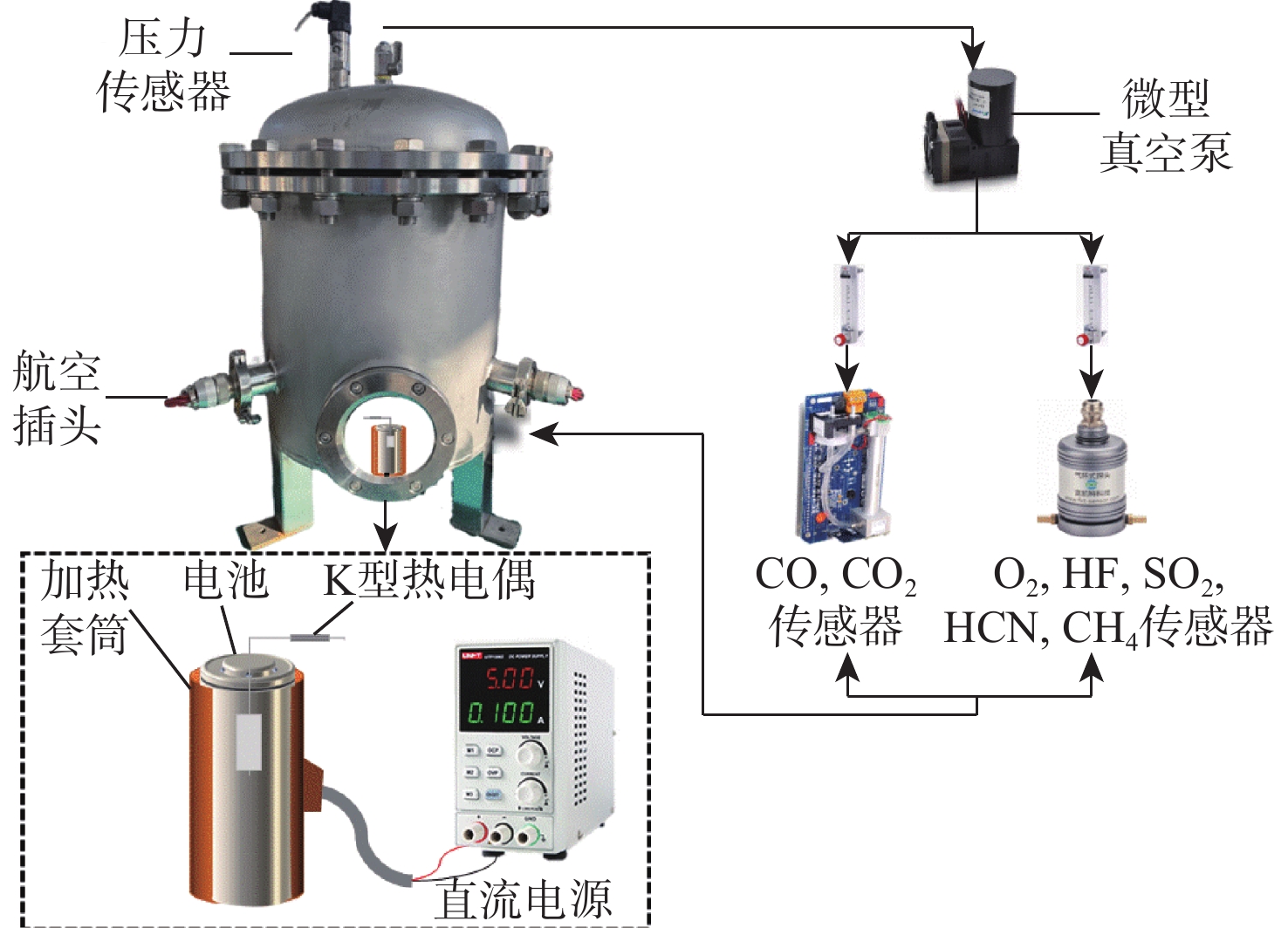
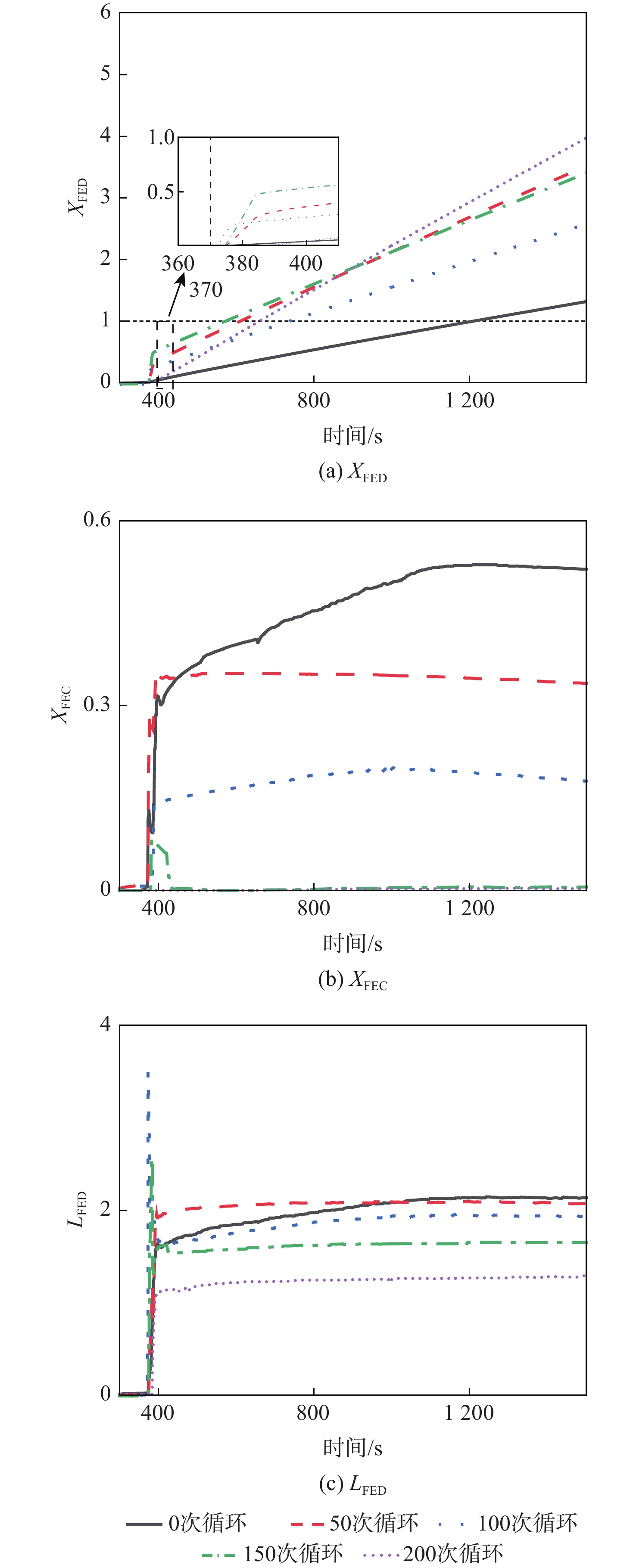
为研究高能量密度锂离子电池循环老化过程中热失控特性变化及释放气体的毒性危害,对不同循环老化程度的三元锂离子电池进行热滥用实验,利用气体传感器阵列,基于有效剂量分数模型对热失控气体毒性危害进行定量分析。结果表明,高镍含量三元锂离子电池循环性能差,200次循环老化后,电池健康状态低于70%。老化电池更容易进入热失控状态,热失控反应更剧烈但释放能量少,释放气体燃烧效率低。在密闭空间内,电池热失控释放窒息性气体危害性比刺激性气体更高,150次循环老化电池的窒息性气体毒性累积效应比新鲜电池早638 s达到临界值1。随老化程度增加,最终电池的刺激性气体毒性即时效应与气体致死毒性即时效应降低,与新鲜电池相比,100次循环老化后,电池的刺激性气体毒性即时效应降低0.34,气体致死毒性即时效应降低0.19。研究结果可为老化电池安全性评估及热失控预警提供数据支撑。
Abstract:Thermal abuse experiments were carried out on ternary lithium-ion batteries with a range of cyclic aging degrees in order to investigate the changes in thermal runaway characteristics and the harmful effects of released gases during the cyclic aging process of high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, a gas sensor array was used to carry out quantitative analysis on the toxicity of pyrolysis gases based on fraction model of effective dose. The results demonstrated that the ternary lithium-ion battery with high nickel content was equipped with poor cyclic performance since the health state of the battery was lower than 70% after 200 cycles of aging. Aging batteries tended to transform into a state of thermal runaway, which reacted more drastically with less energy released, consequently, the combustion efficiency of the released gas is low. The detriments of asphyxiating gases released during the thermal runaway of batteries were more harmful than irritating gases in a confined space, and the cumulative effect of asphyxiating gas toxicity of batteries after 150 times of cyclic aging process tended to reach the critical value, which is one, 638 s earlier than fresh batteries. With the aging degree increasing, immediate toxic effects of irritant gases and immediate effects of gas lethal toxicity weakened. Compared with fresh batteries, immediate toxic effects of irritant gases after 100 times of cyclic aging process decreased by 0.34, and immediate effects of gas lethal toxicity decreased by 0.19. The study’s findings can offer data support for the assessment of safety and the aging process’s thermal runaway warning.
-
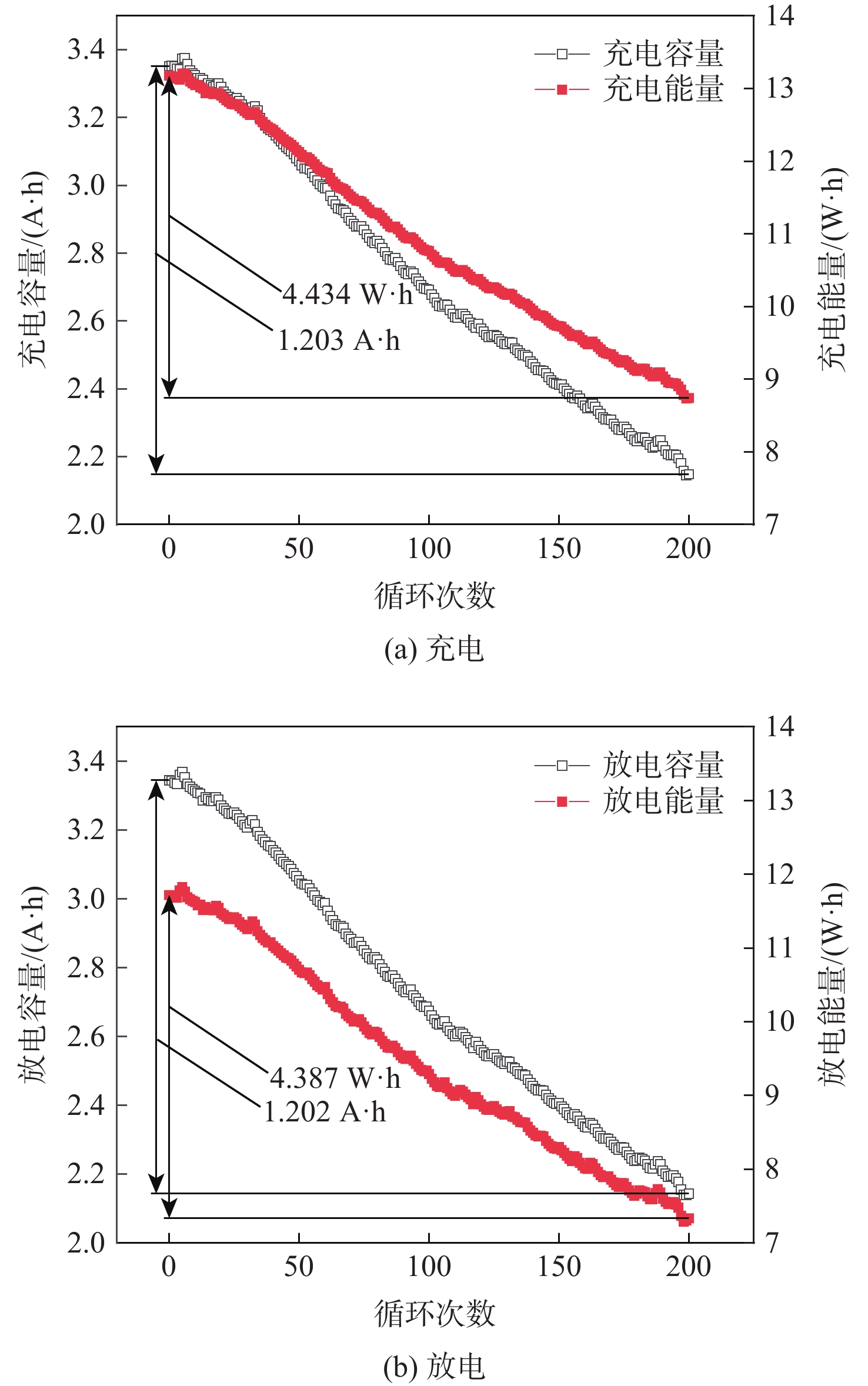
表 1 容量和能量衰减曲线的线性拟合
Table 1. Linear fitting of capacity and energy decay curves
参数 截距 斜率 R2 充电容量 3.3919 −0.00629 0.92781 放电容量 3.3823 −0.00629 0.93436 充电能量 13.3120 −0.02305 0.92683 放电能量 11.8847 −0.02317 0.93194 表 2 电池主要性能参数
Table 2. Main performance parameters of battery
循环次数 H/% ηQ/% ηE/% 内阻/mΩ 0 100.0 99.75±0.41 88.7±0.3 27.2±0.2 50 91.3±1.3 99.97±0.11 88.0 27.7±0.3 100 77.3±1.7 99.80±0.24 85.3±0.7 28.6±0.5 150 72.9±2.9 99.85±0.18 84.3±0.7 29.7±0.6 200 66.8±3.2 99.71±0.41 83.5±0.5 30.5±0.5 表 3 不同老化程度电池关键参数
Table 3. Key parameters of batteries with different aging degrees
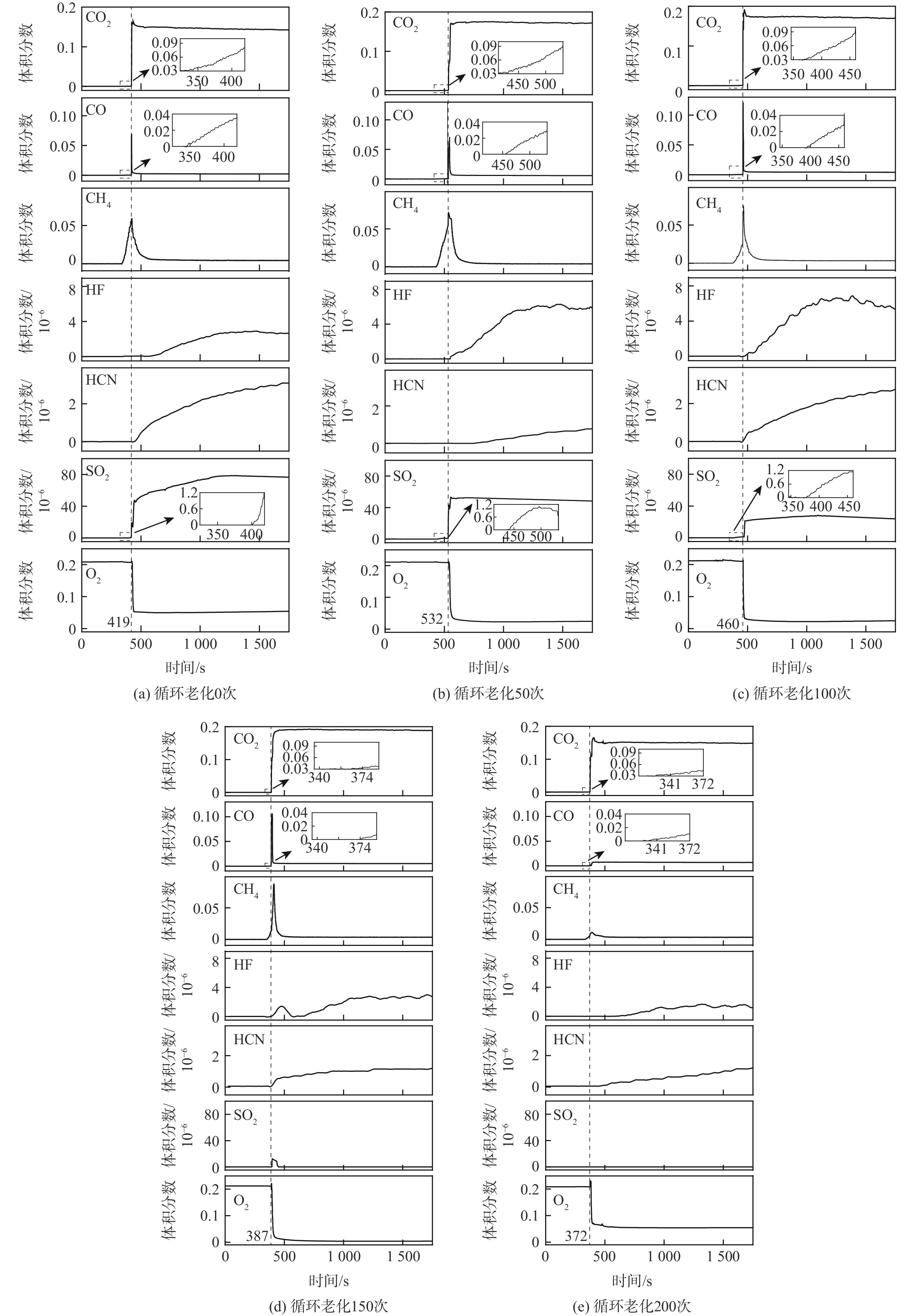
循环次数 Δt/s Tdrop/℃ Tvent/℃ TTR/℃ Tgmax/℃ Pmax/MPa ΔM/g 0 153±41 138.19±4.73 149.22±2.63 206.24±3.54 878.55±29.23 0.2787±0.0272 27.86±0.22 50 135±23 133.43±3.24 146.24±2.98 198.97±3.25 671.65±23.61 0.3002±0.0327 29.45±0.19 100 106±16 130.78±4.65 144.39±3.21 186.43±2.97 646.96±58.48 0.3064±0.0416 30.67±0.21 150 71±20 130.37±2.79 150.49±3.87 181.48±4.12 474.63±47.37 0.3174±0.0372 31.34±0.16 200 63±13 121.70±2.37 142.81±2.10 179.82±2.67 355.93±37.92 0.2871±0.0118 19.70±0.24 表 4 不同老化程度电池热失控后气体分析
Table 4. Gas analysis after thermal runaway of batteries with different aging degrees
循环次数 CCO2/10−2 CCO/10−2 CCH4/10−2 CHF/10−6 CHCN/10−6 CSO2/10−6 CO2/10−2 Cmax,CO/10−2 Cmax,CH4/10−2 0 17.29±0.82 0.28±0.07 0.52±0.08 2.61±0.29 3.06±0.24 56.34±15.66 4.13±0.85 6.87±1.49 6.12±0.34 50 18.14±0.46 0.63±0.10 0.47±0.05 6.26±0.41 1.02±0.34 34.96±13.64 2.32±0.70 7.09±1.63 7.25±0.21 100 17.71±0.43 0.44±0.14 0.41±0.01 6.59±0.65 2.57±0.22 20.95±8.52 2.27±0.30 10.44±1.59 7.50±0.47 150 19.18±0.75 0.54±0.12 0.37±0.02 2.79±0.32 1.15±0.29 <0.01 0.88±0.57 10.56±1.35 8.72±0.39 200 15.71±0.55 0.67±0.09 0.48±0.14 1.95±0.29 1.76±0.35 <0.01 4.76±0.68 2.84±0.62 1.05±0.03 -
[1] ZHANG Q S, LIU T T, WANG Q. Experimental study on the influence of different heating methods on thermal runaway of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 42: 103063. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103063 [2] 张青松, 曲奕润, 郝朝龙, 等. 三元锂离子电池热失控气体原位分析[J]. 高电压技术, 2022, 48(7): 2817-2825.ZHANG Q S, QU Y R, HAO C L, et al. In-situ analysis of thermal runaway gas in ternary lithium-ion battery[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2022, 48(7): 2817-2825(in Chinese). [3] 张青松, 赵启臣. 过充循环对锂离子电池老化及安全性影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(10): 3390-3397.ZHANG Q S, ZHAO Q C. Effects of overcharge cycling on the aging and safety of lithium ion batteries[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(10): 3390-3397(in Chinese). [4] 张青松, 刘添添, 郝朝龙, 等. 锂离子电池热失控气体快速检测及危险性方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(9): 2227-2233.ZHANG Q S, LIU T T, HAO C L, et al. Rapid analysis method of thermal runaway gas composition and risk of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(9): 2227-2233(in Chinese). [5] 张青松, 罗星娜, 程相静, 等. 基于锂离子电池温降指数的细水雾添加剂筛选方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079.ZHANG Q S, LUO X N, CHENG X J, et al. Method for screening fine water mist additive based on temperature drop index of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079(in Chinese). [6] 张青松, 刘添添, 赵子恒. 锂离子电池热失控气体燃烧对热失控传播影响的量化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(1): 17-22.ZHANG Q S, LIU T T, ZHAO Z H. Quantitative method of influence of thermal runaway gas combustion on thermal runaway propagation of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(1): 17-22(in Chinese). [7] LIU P J, LI Y Q, MAO B B, et al. Experimental study on thermal runaway and fire behaviors of large format lithium iron phosphate battery[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 192: 116949. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.116949 [8] MAO B B, LIU C Q, YANG K, et al. Thermal runaway and fire behaviors of a 300 Ah lithium ion battery with LiFePO4 as cathode[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 139: 110717. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.110717 [9] RIBIÈRE P, GRUGEON S, MORCRETTE M, et al. Investigation on the fire-induced hazards of Li-ion battery cells by fire calorimetry[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(1): 5271-5280. [10] MAO B B, CHEN H D, JIANG L, et al. Refined study on lithium ion battery combustion in open space and a combustion chamber[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 139: 133-146. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.03.037 [11] LECOCQ A, ESHETU G G, GRUGEON S, et al. Scenario-based prediction of Li-ion batteries fire-induced toxicity[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 316: 197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.02.090 [12] CHEN M Y, LIU J H, HE Y P, et al. Study of the fire hazards of lithium-ion batteries at different pressures[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 1061-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.131 [13] LARSSON F, BERTILSSON S, FURLANI M, et al. Gas explosions and thermal runaways during external heating abuse of commercial lithium-ion graphite-LiCoO2 cells at different levels of ageing[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 373: 220-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.10.085 [14] ZHANG G X, WEI X Z, CHEN S Q, et al. Revealing the impact of fast charge cycling on the thermal safety of lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(6): 7056-7068. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.2c00688 [15] 王康康, 高飞, 杨凯, 等. 不同健康状态等级的储能磷酸铁锂电池熵变系数及放电产热研究[J]. 高电压技术, 2017, 43(7): 2241-2248.WANG K K, GAO F, YANG K, et al. Research of LiFePO4/cenergy storage batteries entropy coefficient and discharge heat generation based on the state of health[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2017, 43(7): 2241-2248(in Chinese). [16] GAO Y, JIANG J C, ZHANG C P, et al. Aging mechanisms under different state-of-charge ranges and the multi-indicators system of state-of-health for lithium-ion battery with Li(NiMnCo)O2 cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 400: 641-651. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.07.018 [17] 彭继明, 陈玉华, 刘世成, 等. 不同镍钴锰比对xLi2MnO3-(1−x)LiMO2正极材料的结构和电化学性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(7): 2950-2955.PENG J M, CHEN Y H, LIU S C, et al. Effect of Ni/Co/Mn molarratio on structure and electrochemical properties of xLi2MnO3-(1−x)LiMO2 cathode material[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(7): 2950-2955(in Chinese). [18] REN D S, HSU H, LI R H, et al. A comparative investigation of aging effects on thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries[J]. eTransportation, 2019, 2: 100034. doi: 10.1016/j.etran.2019.100034 [19] DIAZ F, WANG Y, WEYHE R, et al. Gas generation measurement and evaluation during mechanical processing and thermal treatment of spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 84: 102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.11.029 [20] YANG H, ZHUANG G V, ROSS P N. Thermal stability of LiPF6 salt and Li-ion battery electrolytes containing LiPF6[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 161(1): 573-579. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.03.058 [21] WILKEN S, TRESKOW M, SCHEERS J, et al. Initial stages of thermal decomposition of LiPF6-based lithium ion battery electrolytes by detailed Raman and NMR spectroscopy[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(37): 16359-16364. doi: 10.1039/c3ra42611d [22] KAWAMURA T, OKADA S, YAMAKI J I. Decomposition reaction of LiPF6-based electrolytes for lithium ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 156(2): 547-554. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.05.084 [23] ZHANG S S. A review on electrolyte additives for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 162(2): 1379-1394. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.07.074 [24] ISO. Life-threatening components of fire-guidelines for the estimation of time to compromised tenability in fires: ISO 13571[S]. Geneva: ISO, 2012. [25] ISO. Estimation of the lethal toxic potency of fire effluents: ISO 13344[S]. Geneva: ISO, 2015. [26] PENG Y, YANG L Z, JU X Y, et al. A comprehensive investigation on the thermal and toxic hazards of large format lithium-ion batteries with LiFePO4 cathode[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 381: 120916. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120916 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 周晓猛,蔡金乐,郭一博,廖云龙. 商用锂离子电池快充降解及热失控特性研究. 中国民航大学学报. 2025(01): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 卫寿平,孙杰,李吉刚,周添,陈静,党胜男,唐娜,张帆. 锂离子电池热失控气体产物检测及分析技术研究进展. 储能科学与技术. 2024(11): 4155-4176 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-







 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

