-
摘要:
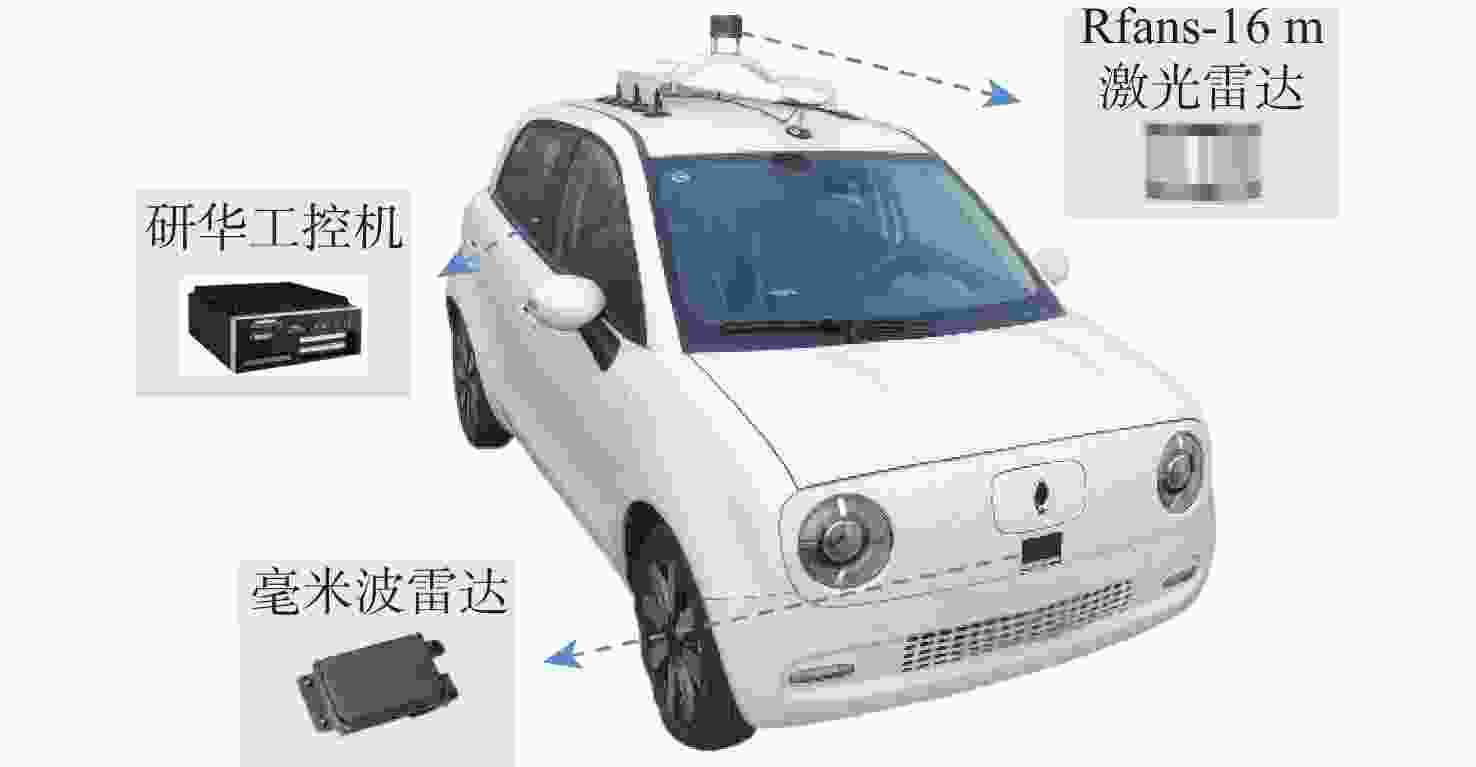
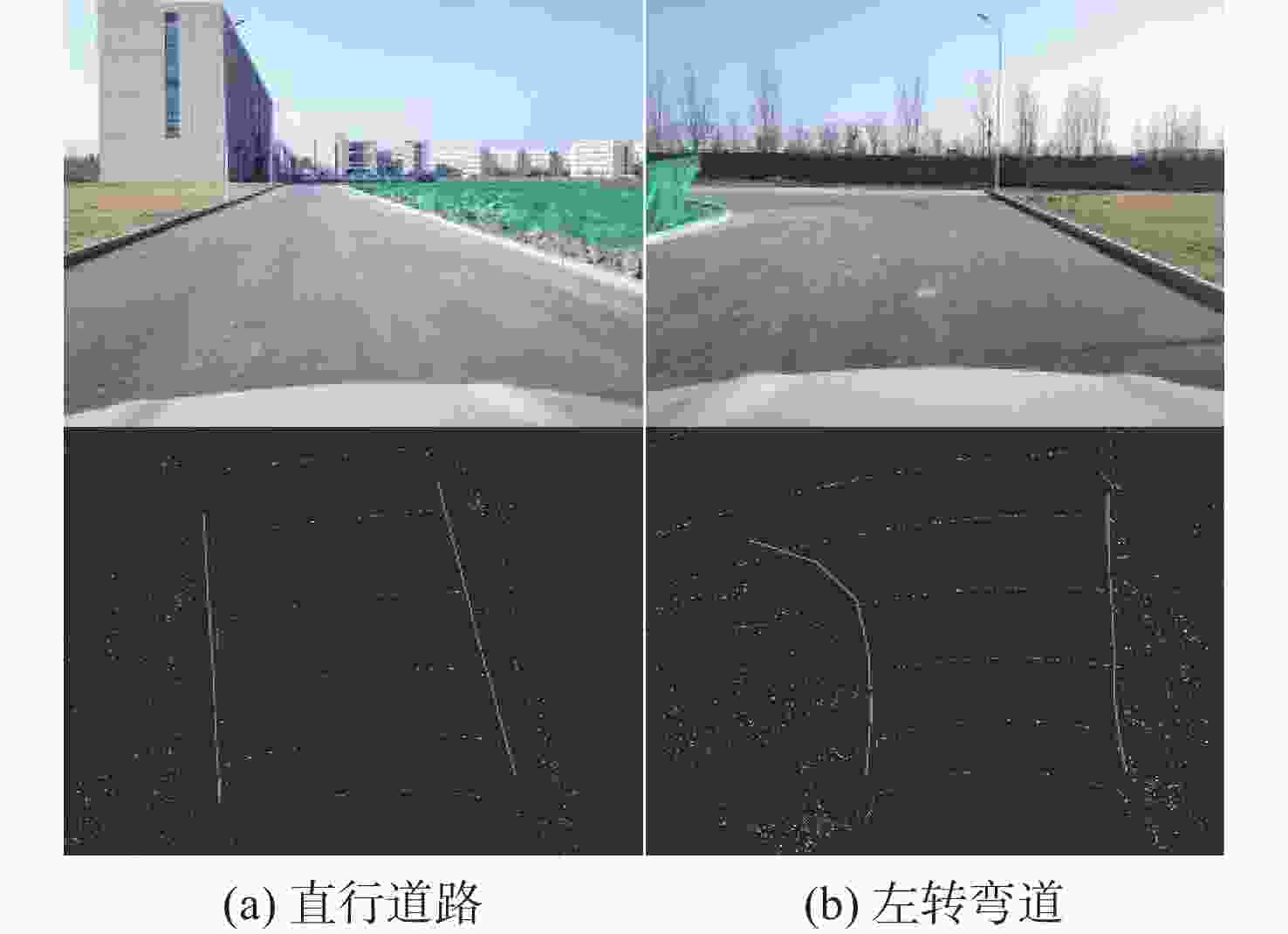
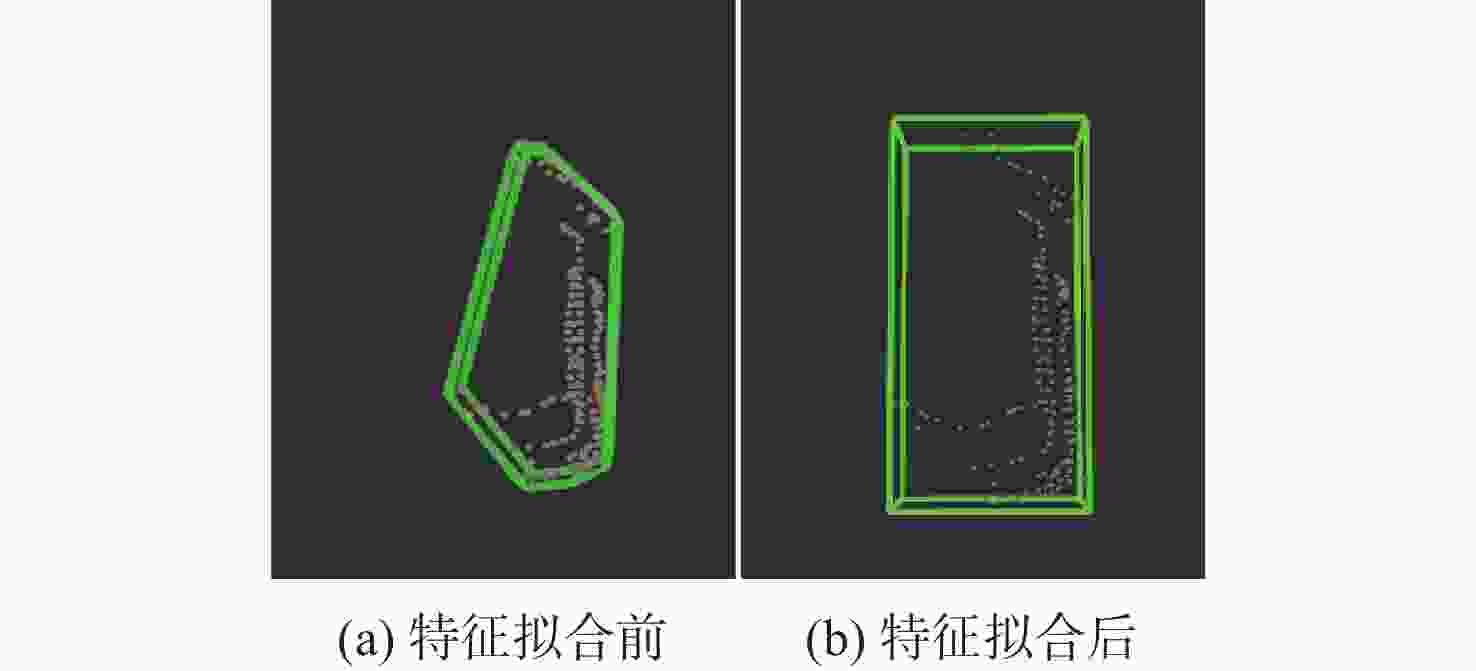
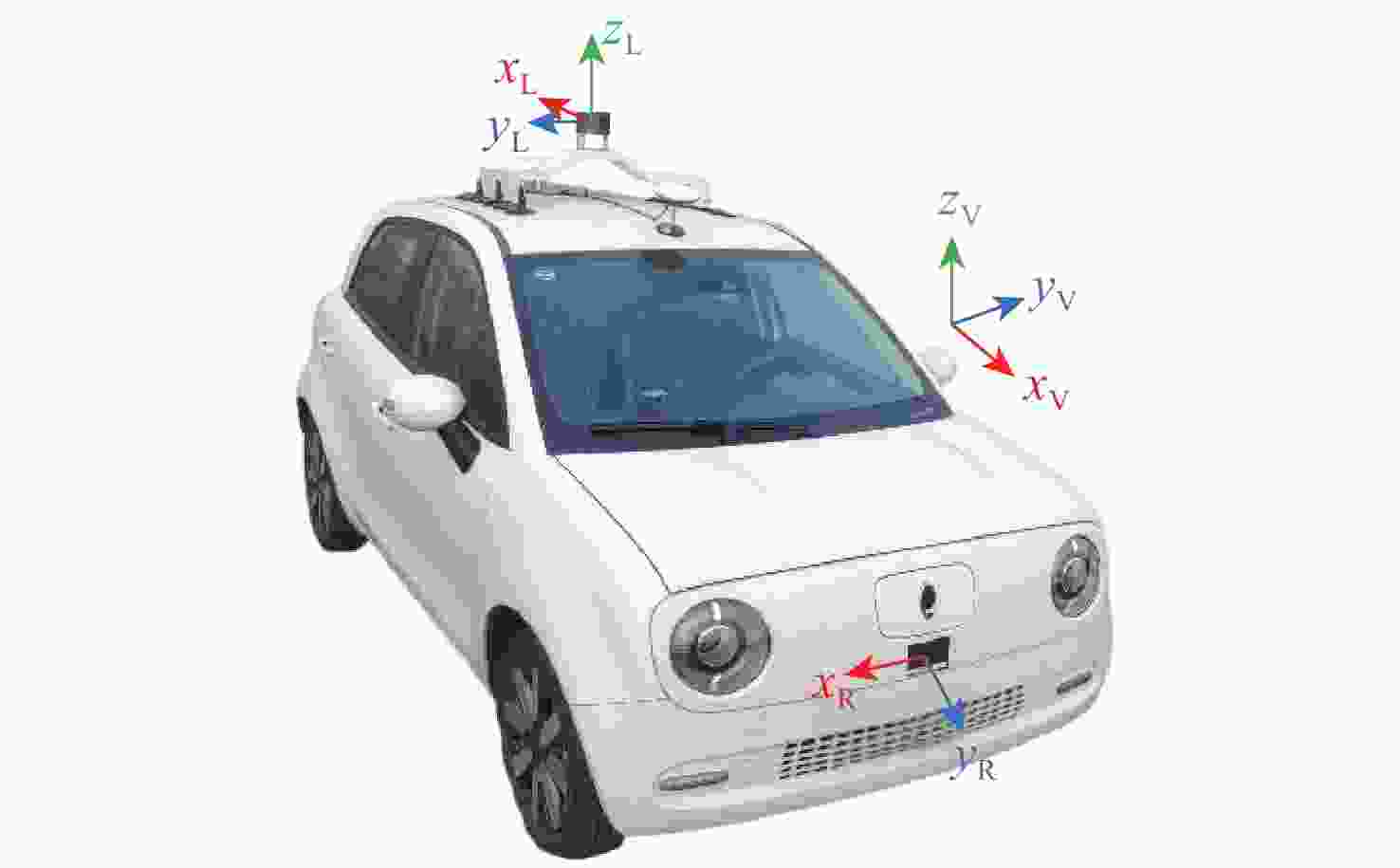
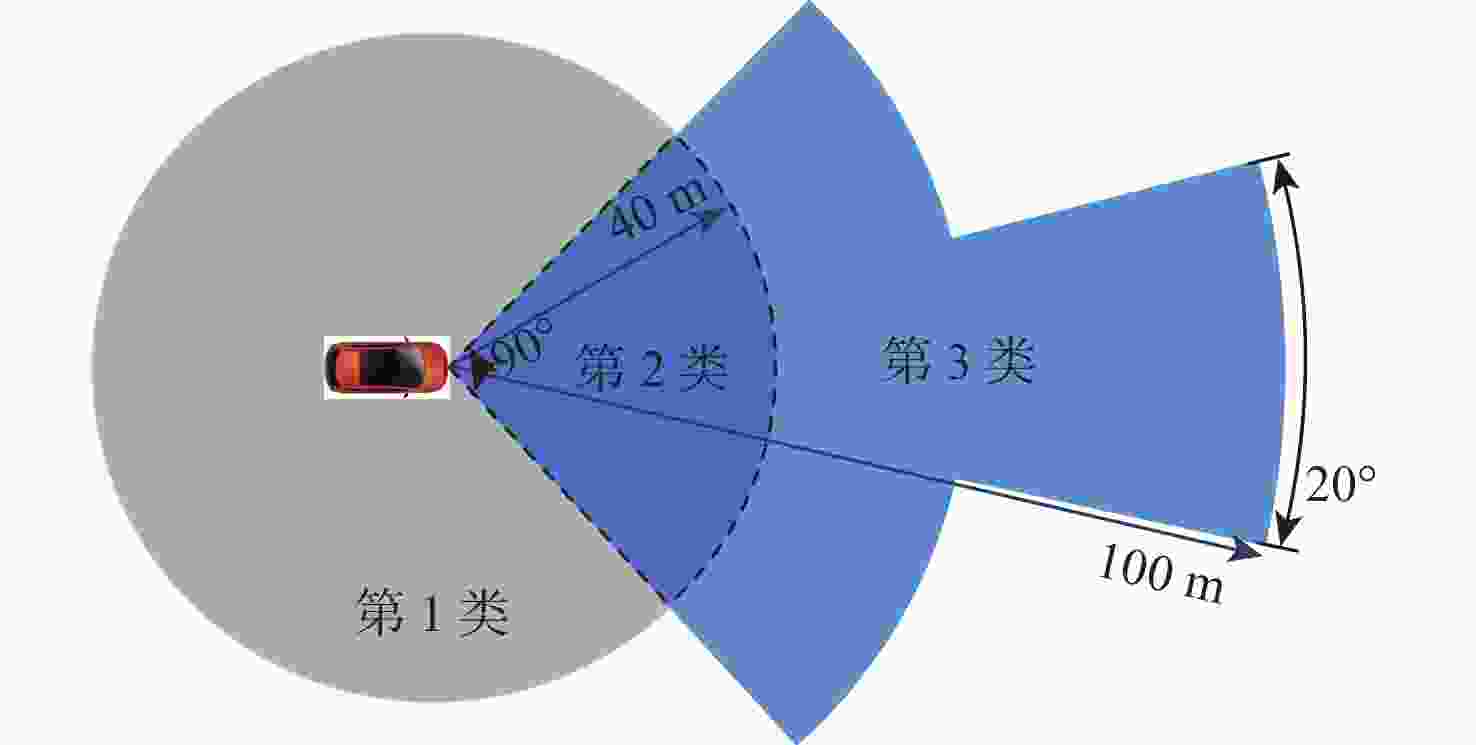
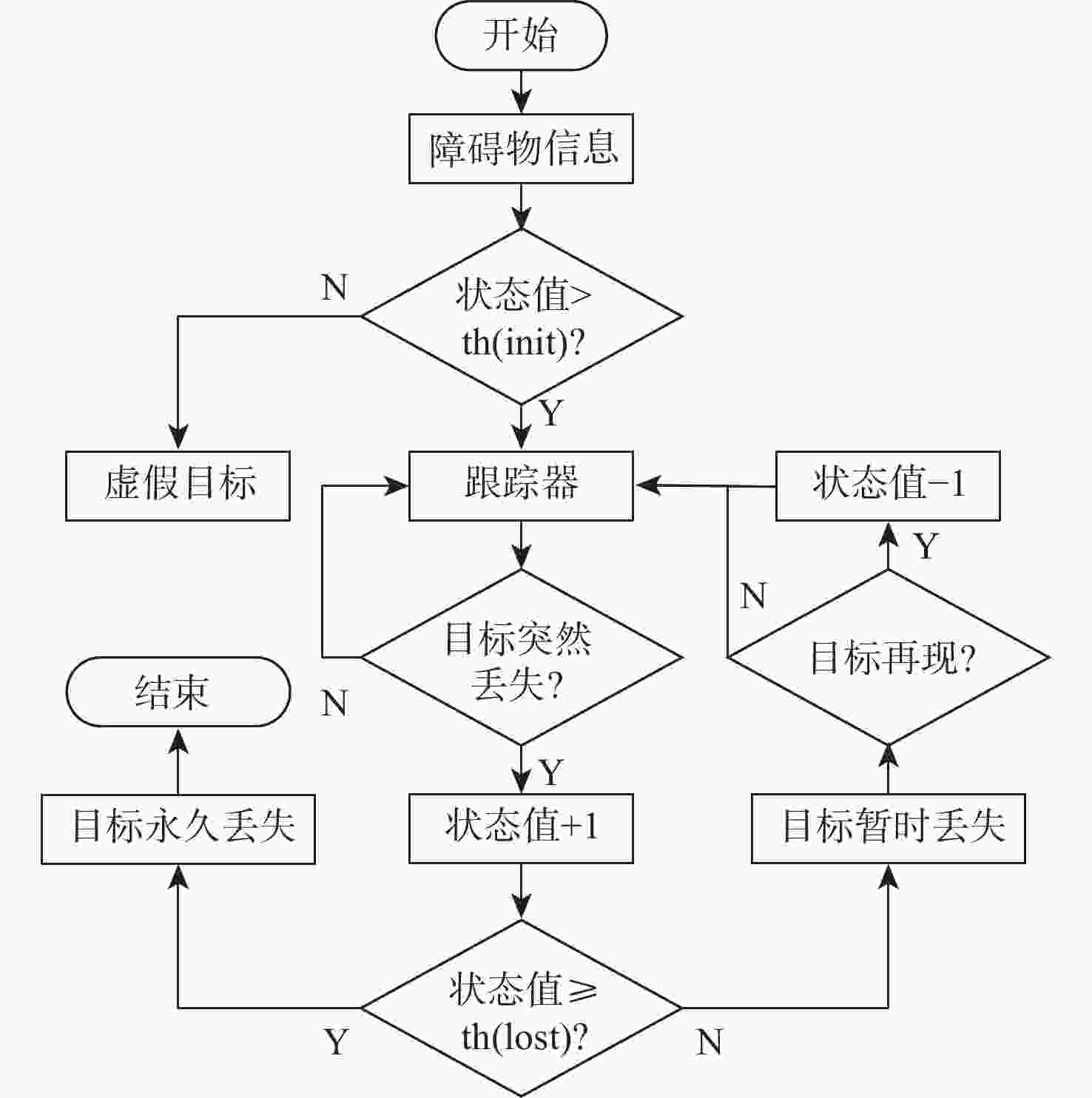
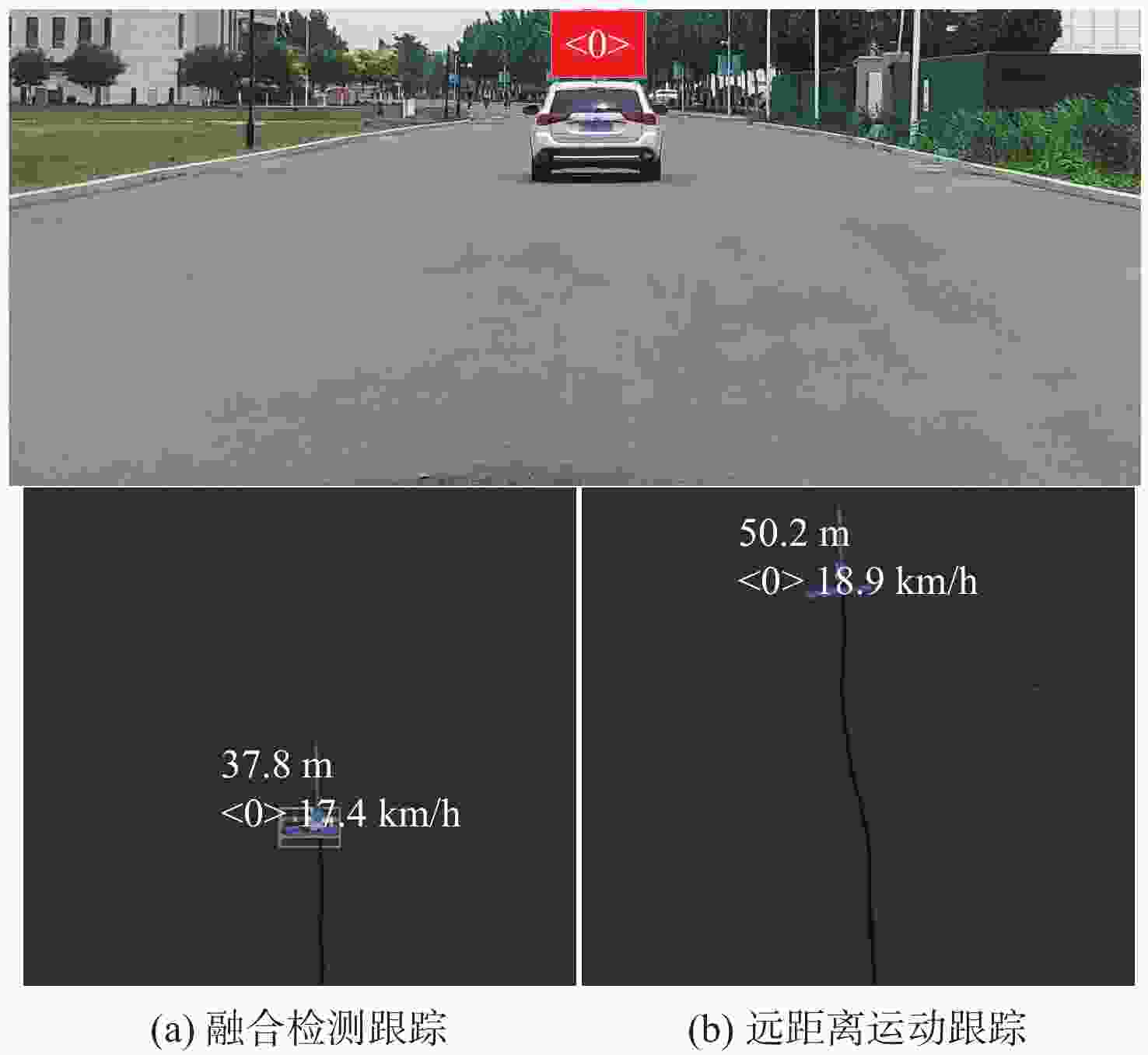
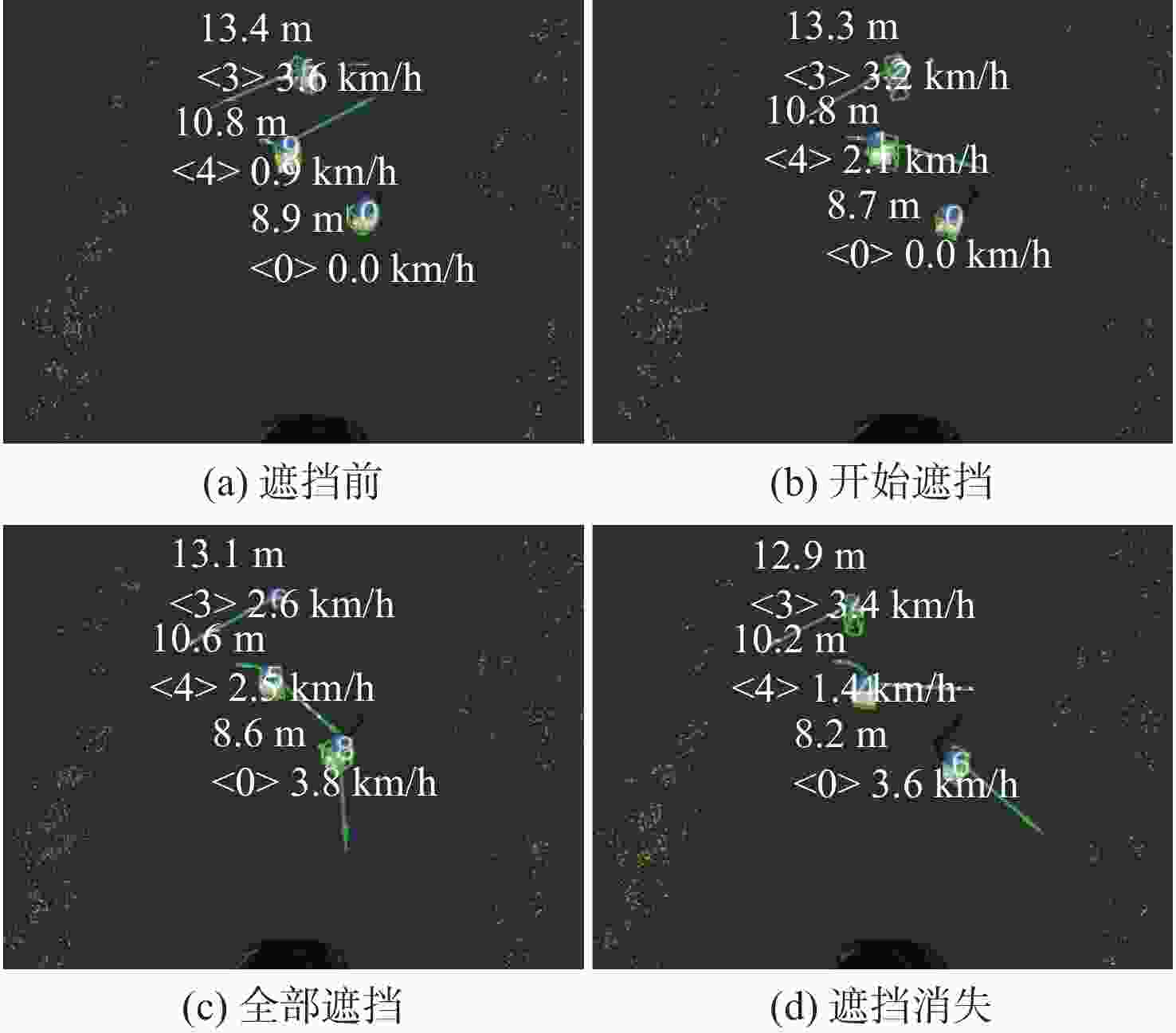
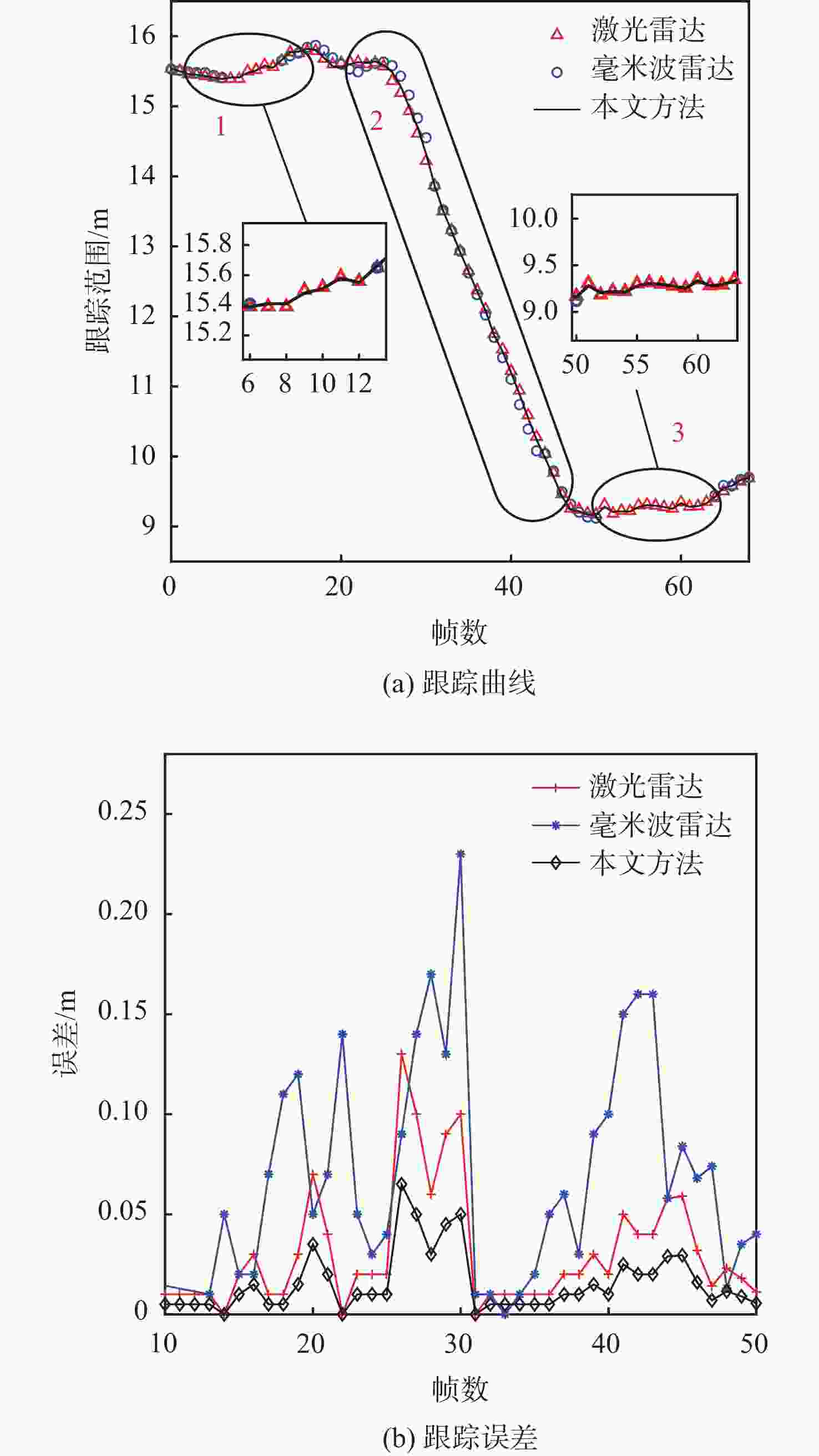
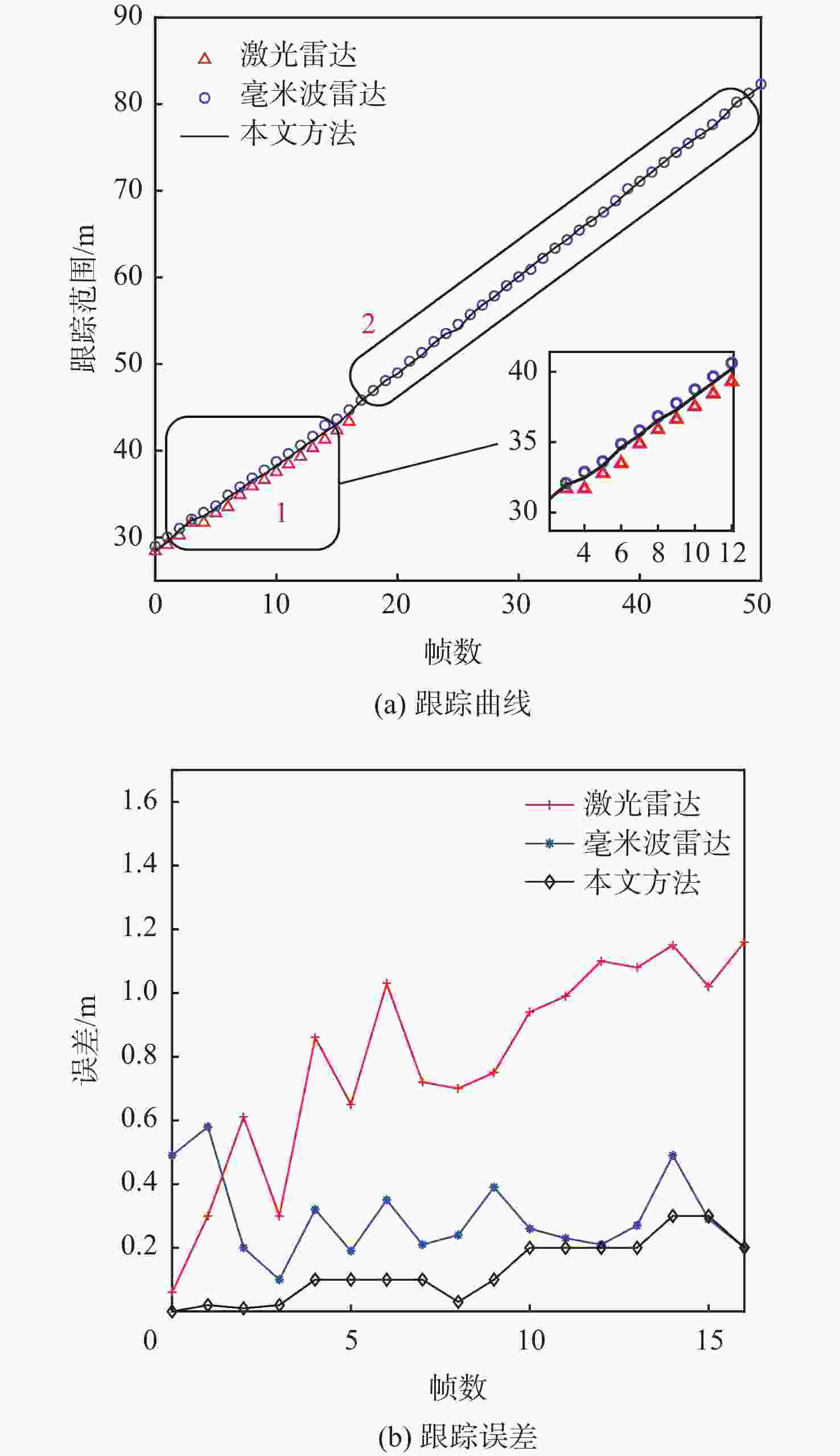
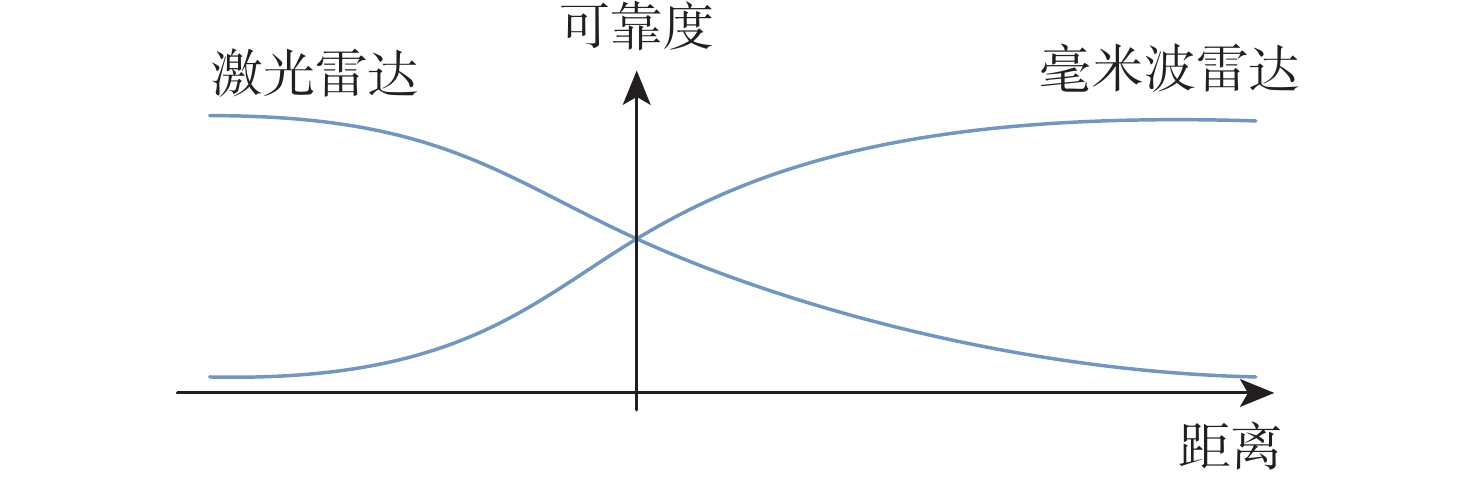
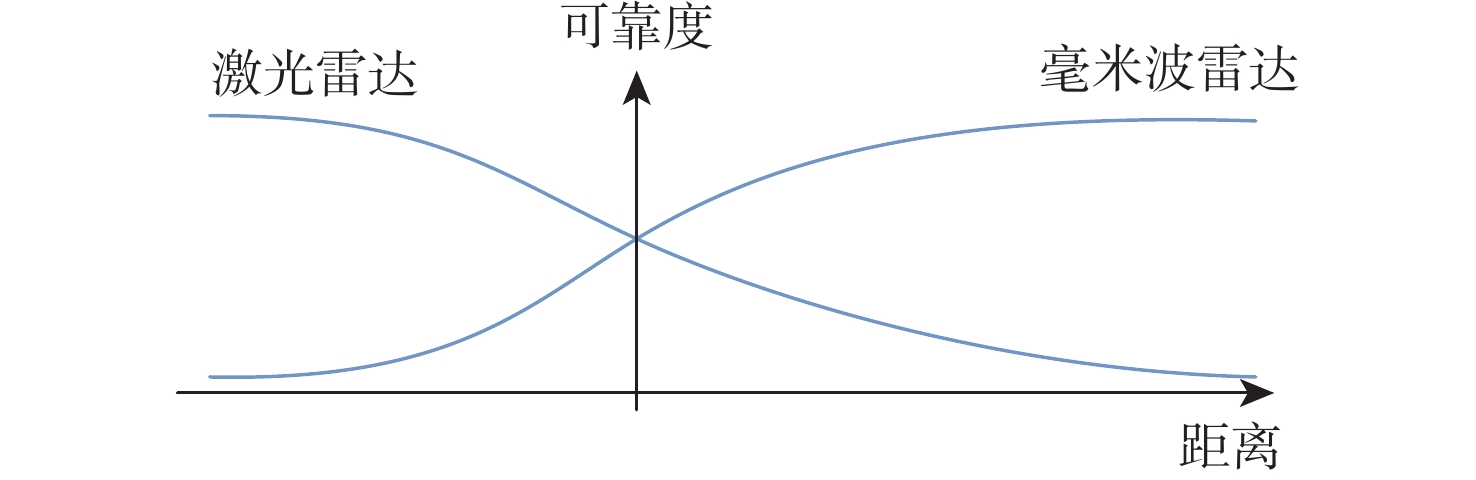
在园区环境中,无人车装载单一毫米波雷达或激光雷达传感器进行障碍物检测跟踪时存在探测范围有限、准确率低及稳定性差等问题。为此,提出一种基于毫米波雷达与激光雷达融合的多障碍物检测跟踪方法。利用改进欧氏聚类算法对道路内激光点云目标进行提取,基于信息筛选策略获得毫米波雷达数据中的有效目标;基于目标检测交并比与可靠性分析,对2种目标进行自适应融合,并利用跟踪门与联合概率数据关联(JPDA)算法完成前后帧数据匹配;应用多运动模型交互与无迹卡尔曼滤波实现障碍物跟踪。实车实验表明:相比单一毫米波雷达与激光雷达障碍物检测跟踪,所提方法有更好的准确性与稳定性。
Abstract:Limited detecting range, low precision, and poor stability are just a few of the issues with obstacle detection and tracking that arise when using a single millimeter wave radar, or LiDAR, on an unmanned vehicle in a park. An obstacle-detecting and tracking approach based on the fusion of radar and LiDAR is proposed. Firstly, the improved Euclidean clustering algorithm is adopted to extract the objects in the road boundary from LiDAR point clouds. Furthermore, effective objects can be obtained from millimeter wave radar data which is handled based on an information filtering strategy. Then, the adaptive fusion of two kinds of objects described above is carried out based on the intersection over union and reliability analysis of objectdetection. The tracking gate and the joint probabilistic data association (JPDA) algorithm are performed to match sequence frames. In order to achieve obstacle tracking, the interacting multiple model and unscented Kalman filter method are finally put into practice. The experimental results show that the proposed method has higher accuracy and stability than using a single sensor for obstacle detection and tracking.
-
Key words:
- millimeter wave radar /
- LiDAR /
- unmanned vehicle /
- sensor fusion /
- obstacle tracking
-
表 1 不同传感器跟踪结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of tracking results of different sensors
处理方法 $ {N_{{\text{MOTA}}}} $/% $ {N_{{\text{IDS}}}} $ $ {N_{{\text{FRAG}}}} $ 激光雷达 86.69 14 20 毫米波雷达 74.03 21 36 融合策略 93.58 11 19 -
[1] LI Y, IBANEZ-GUZMAN J. Lidar for autonomous driving: The principles, challenges, and trends for automotive lidar and perception systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 50-61. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2973615 [2] 郭晓旻, 李必军, 龙江云, 等. 利用激光点云的城市无人驾驶路径规划算法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(4): 182-190.GUO X M, LI B J, LONG J Y, et al. Path planning of urban autonomous driving using laser point cloud data[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(4): 182-190(in Chinese). [3] LIM W, LEE S, SUNWOO M, et al. Hierarchical trajectory planning of an autonomous car based on the integration of a sampling and an optimization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(2): 613-626. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2756099 [4] CHEN J F, WANG C C, CHOU C F. Multiple target tracking in occlusion area with interacting object models in urban environments[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 103: 68-82. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2018.02.004 [5] 蒲良, 张学军. 基于深度学习的无人机视觉目标检测与跟踪[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(5): 872-880.PU L, ZHANG X J. Deep learning based UAV vision object detection and tracking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(5): 872-880(in Chinese). [6] FENG D. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(3): 1341-1360. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2972974 [7] 李炯, 赵凯, 张志超, 等. 一种融合密度聚类与区域生长算法的快速障碍物检测方法[J]. 机器人, 2020, 42(1): 60-70.LI J, ZHAO K, ZHANG Z C, et, al. A fast obstacle detection method by fusion of density-based clustering and region growing algorithms[J]. Robot, 2020, 42(1): 60-70(in Chinese). [8] XU S, WANG R, WANG H, et al. An optimal hierarchical clustering approach to mobile LiDAR point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(7): 2765-2776. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2912455 [9] RAVINDRAN R, SANTORA M J, JAMALI M J, et al. Multi-object detection and tracking, based on DNN, for autonomous vehicles: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 5668-5677. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3041615 [10] KIM J, CHOI Y, PARK M, et al. Multi-sensor-based detection and tracking of moving objects for relative position estimation in autonomous driving conditions[J]. Journal of Supercomputing, 2020, 76(10): 8225-8247. [11] ESKANDARIAN A, WU C, SUN C. Research advances and challenges of autonomous and connected ground vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(2): 683-711. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2958352 [12] 赵万里. 基于雷达的智能车多目标检测与跟踪技术研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011.ZHAO W L. Technology research of the multi-objective detection and tracking for intelligent vehicle based on radars[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011(in Chinese). [13] LIAN H, PEI X, GUO X. A local environment model based on multi-sensor perception for intelligent vehicles[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(14): 15427-15436. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3018319 [14] HAJRI H, RAHAL M C. Real time lidar and radar high-level fusion for obstacle detection and tracking with evaluation on a ground truth[EB/OL]. (2019-07-01)[2022-05-25]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11264. [15] GOHRING D, WANG M, SCHNURMACHER M, et al. Radar/lidar sensor fusion for car following on highways[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 407-412. [16] CHO H, SEO Y W, KUMAR B V K V, et al. A multi-sensor fusion system for moving object detection and tracking in urban driving environments[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1836-1843. [17] FARAG W. Kalman-filter-based sensor fusion applied to road-objects detection and tracking for autonomous vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 2021, 235(7): 1128-1138. [18] ZERMAS D, IZZAT I, PAPANIKOLOPOULOS N. Fast segmentation of 3D point clouds: A paradigm on LiDAR data for autonomous vehicle applications[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5067-5073. -






 下载:
下载: