-
摘要:
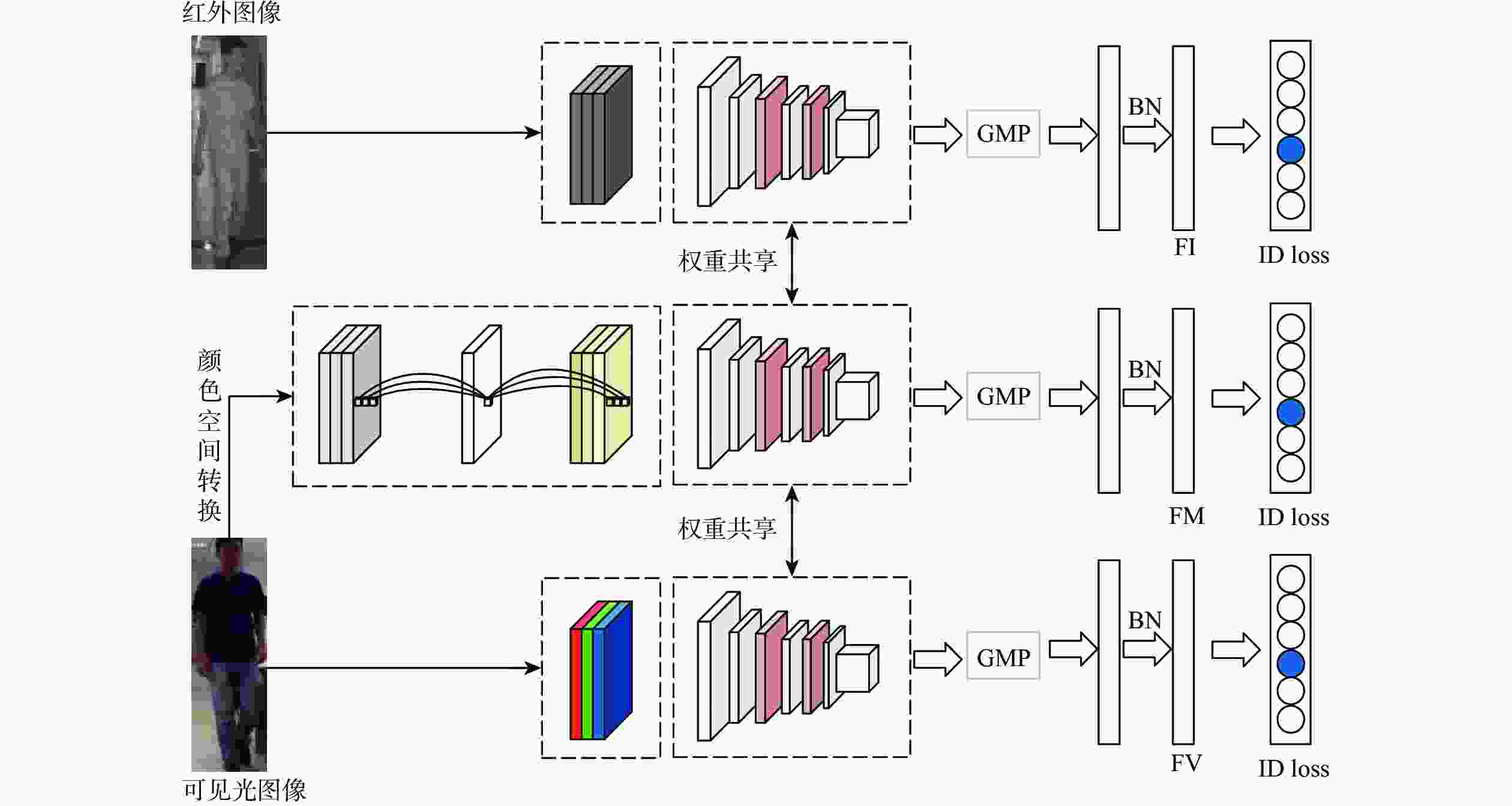
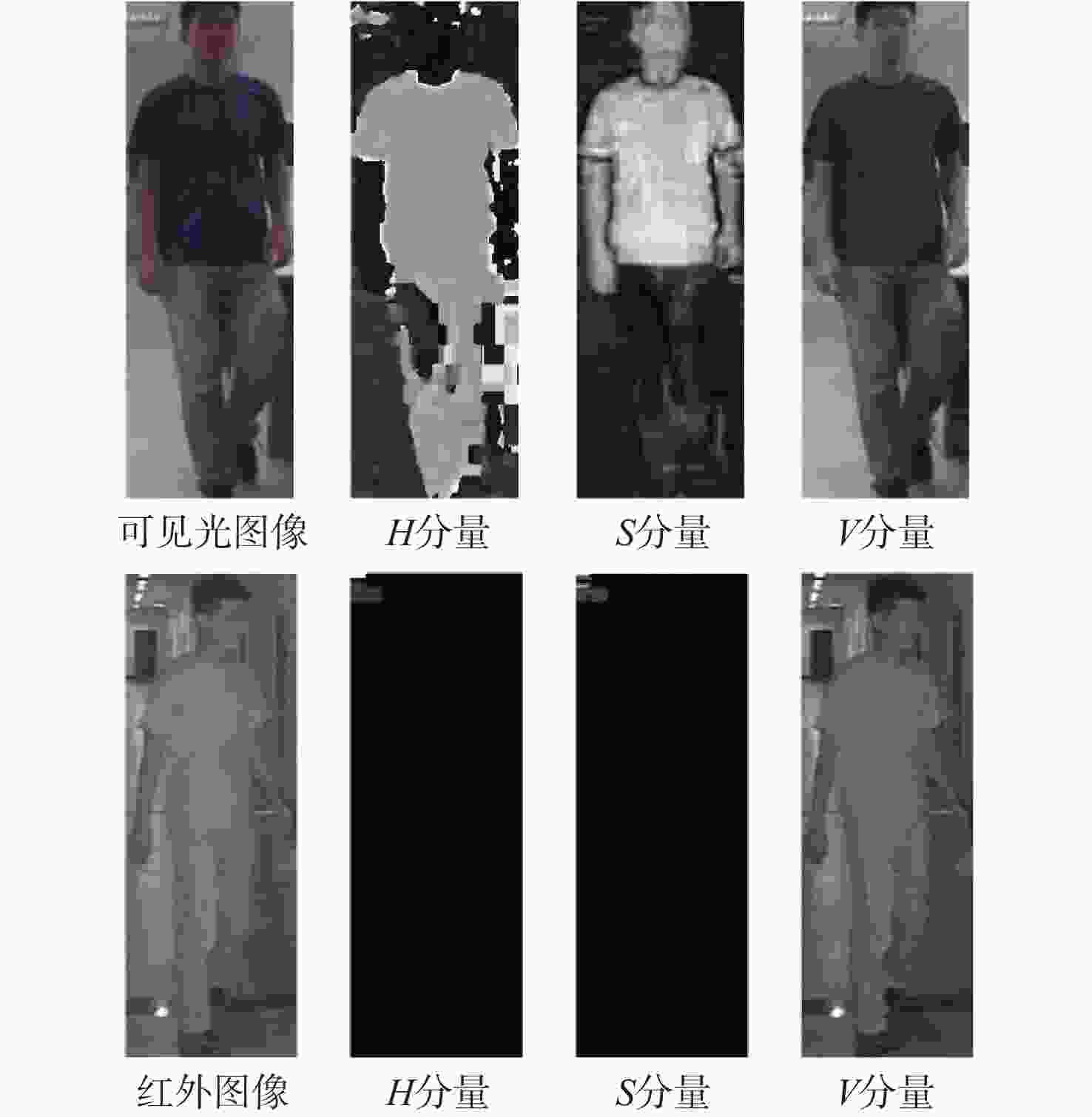
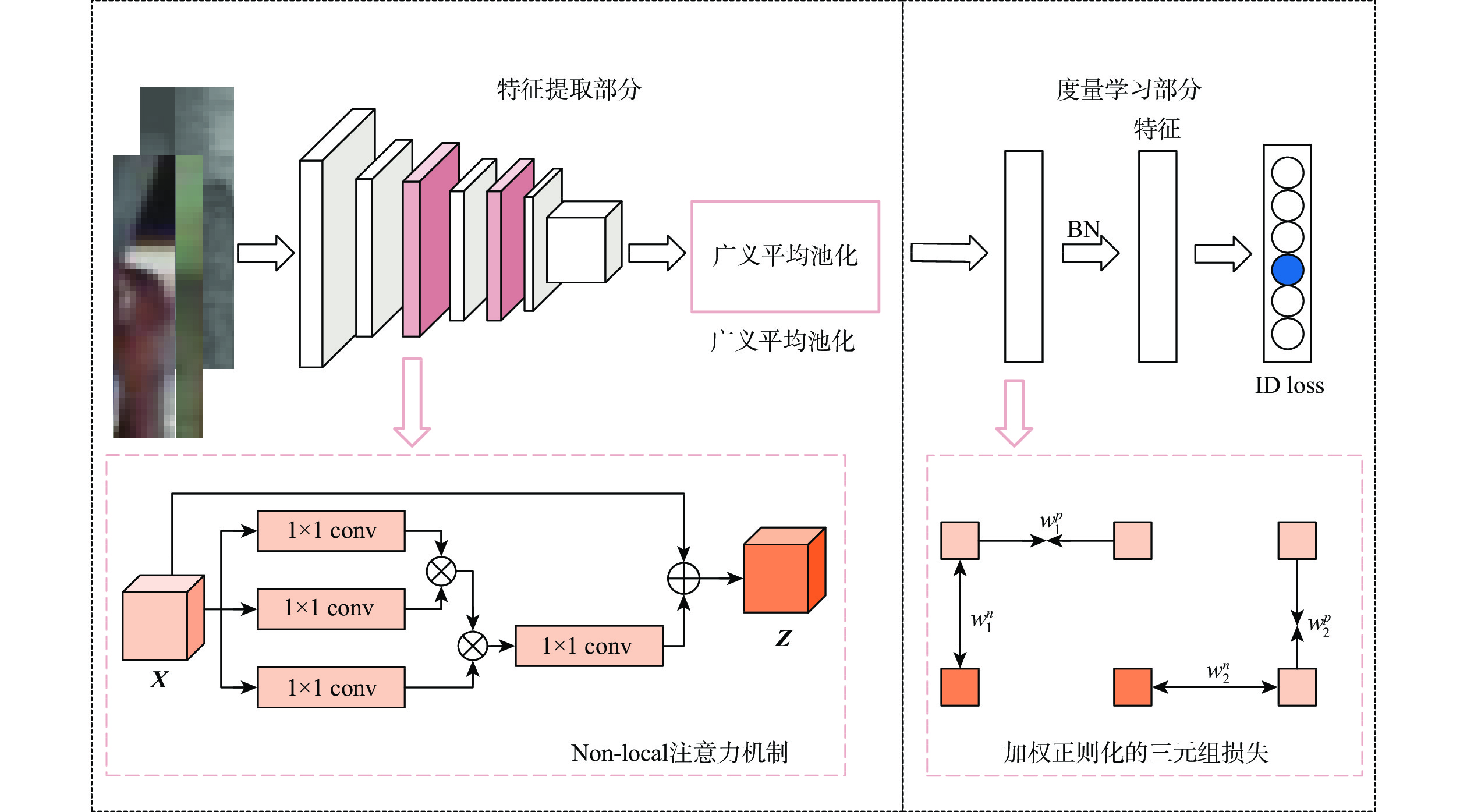
为降低模型对图像颜色的敏感度,减小可见光和红外模态间的差异,提出一种面向可见光-红外图像的跨模态行人再识别方法。将可见光图像转换到HSV颜色空间,提取只描述图像明暗信息的
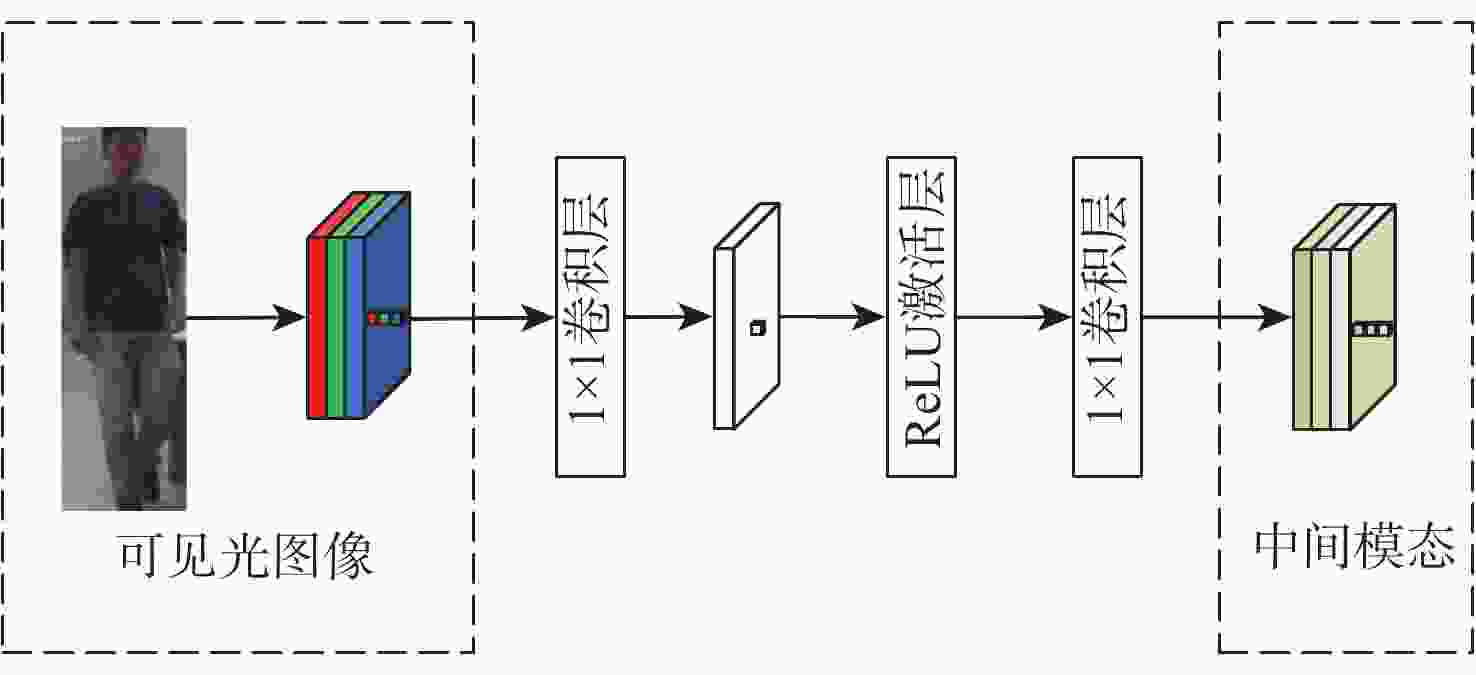
V 分量,降低模型对颜色信息的依赖性;通过轻量级网络对V 分量图像进行降维和升维,生成介于可见光和红外图像的中间模态,缩小模态间的差异性;在SYSU-MM01和RegDB数据集上进行性能评估。性能评估结果为Rank-1的数值分别增加了6.67%、1.18%,mAP的数值分别增加了6.47%、1.15%,mINP的数值分别增加了5.59%、0.42%。Abstract:We propose a cross-modality person re-identification strategy for visible-infrared images, which aims to lower the sensitivity of the model to image color information and narrow the difference between visible and infrared modalities. First, the visible image is transformed into HSV color space, and the
V component, which only describes the light and dark information of the image, is extracted to reduce the dependence of the model on color information. Second, to lessen the disparity between the modalities, a lightweight network downscales and upscales theV component image to provide an intermediate modality between visible and infrared images. Finally, evaluated on the SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets, The values of Rank-1 is improved by 6.67% and 1.18%, the values of mAP is improved by 6.47% and 1.15%, and mINP is improved by 5.59% and 0.42%, respectively. -
表 1 数据集
Table 1. Datasets
数据集 行人
数量/个可见光
摄像机
数量/个红外/热成像
摄像机
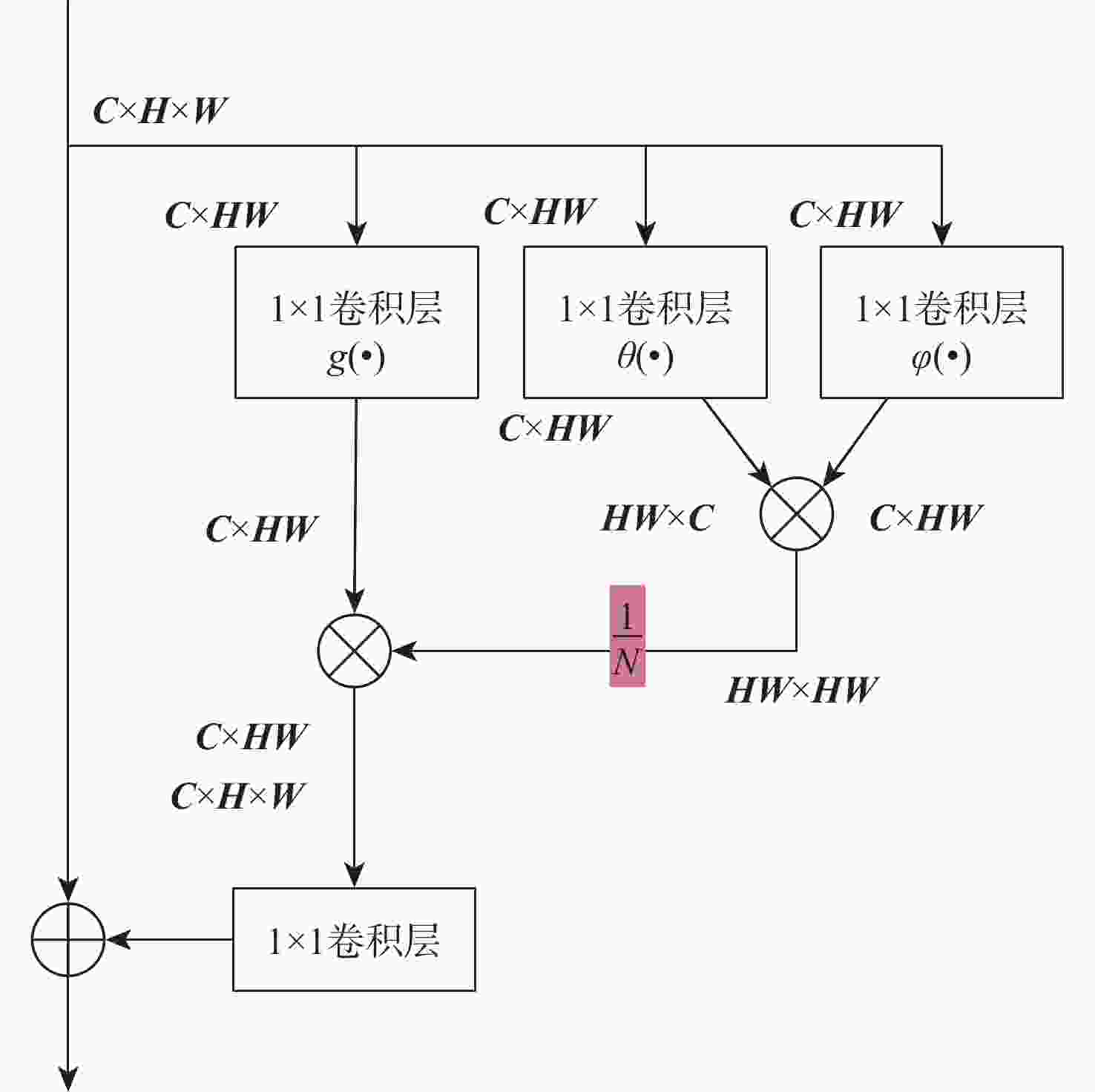
数量/个可见光
图像
数量/张红外图像
数量/张SYSU-MM01 491 4 2 30 071 15 792 RegDB 412 1 1 4 120 4 120 表 2 基于HSV颜色空间的跨模态行人再识别方法性能比较
Table 2. Performance comparison of crossmodality person re-identification method based on HSV color space
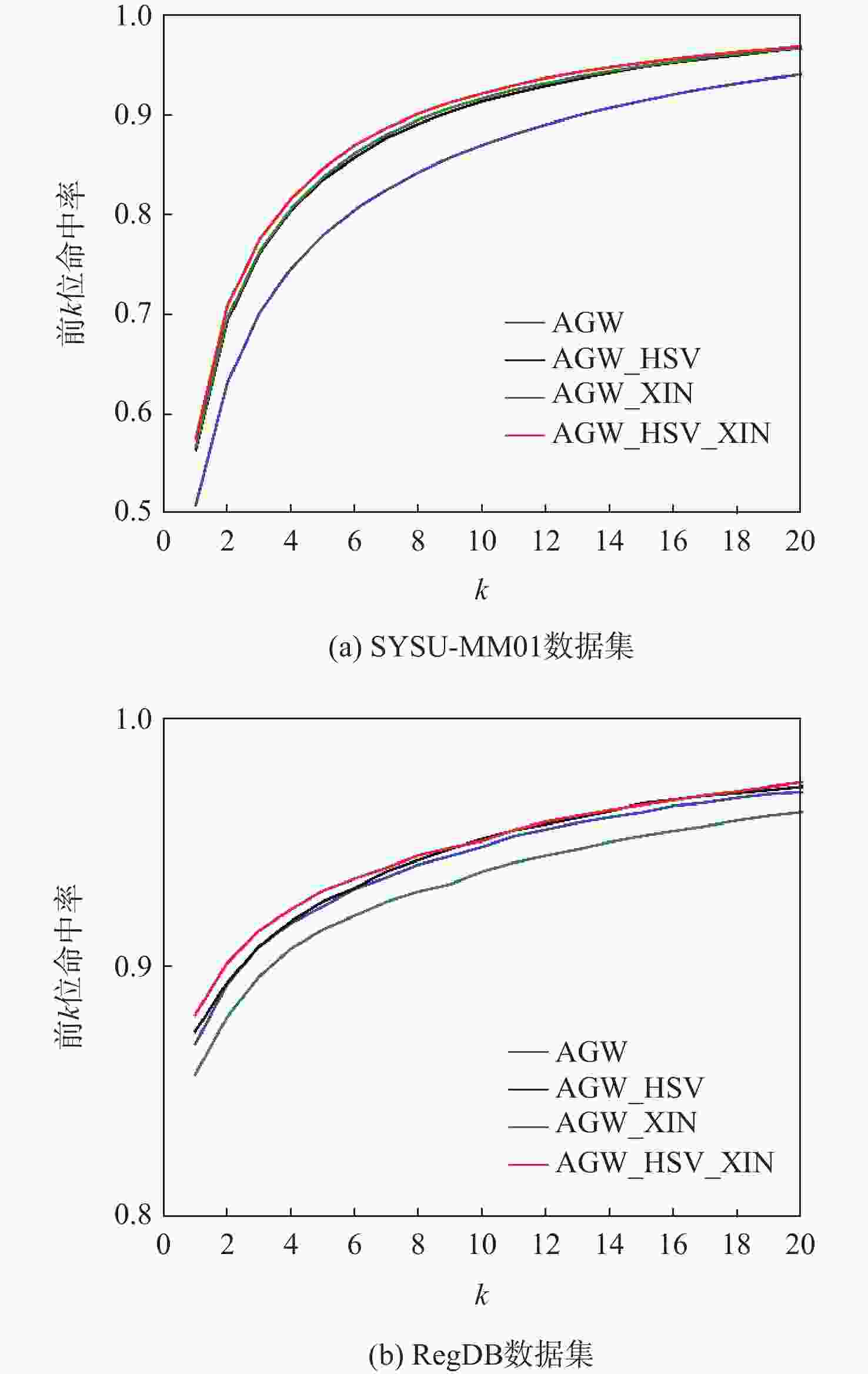
% 方法 Rank-1 mAP mINP SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB AGW(paper) 47.50 70.05 47.65 66.37 35.30 50.19 AGW 51.00 86.90 49.02 81.96 35.42 72.78 AGW_HSV 56.51 87.41 53.98 83.23 39.29 74.13 表 3 基于轻量级网络的跨模态行人再识别方法性能比较
Table 3. Performance comparison of crossmodality person re-identification method based on lightweight network
% 方法 Rank-1 mAP mINP SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB AGW(paper) 47.50 70.05 47.65 66.37 35.30 50.19 AGW 51.00 86.90 49.02 81.96 35.42 72.78 AGW_XIN 56.81 85.69 54.14 80.68 39.29 70.50 表 4 基于HSV颜色空间和轻量级网络的跨模态行人再识别方法性能比较
Table 4. Performance comparison of cross-modality person re-identification method based on HSV color space and lightweight network
% 方法 Rank-1 mAP mINP SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB AGW(paper) 47.50 70.05 47.65 66.37 35.30 50.19 AGW 51.00 86.90 49.02 81.96 35.42 72.78 AGW_HSV_XIN 57.67 88.08 55.49 83.11 41.01 73.20 表 5 不同模型性能比较
Table 5. Performance comparison of different models
% 方法 Rank-1 mAP mINP SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB SYSU-MM01 RegDB Zero-Pad[1] 14.8 17.75 15.95 18.90 HCML[18] 14.32 24.44 16.16 20.08 eBDTR[19] 27.82 34.62 28.42 33.46 HSME[20] 20.68 50.85 23.12 47.00 D2RL[6] 28.9 43.4 29.2 44.1 MAC[5] 33.26 36.43 36.22 37.03 MSR[21] 37.35 48.43 38.11 48.67 AlignG[22] 42.4 57.9 40.7 53.6 AGW(paper)[9] 47.50 70.05 47.65 66.37 35.30 50.19 AGW 51.00 86.90 49.02 81.96 35.42 72.78 AGW_HSV 56.51 87.41 53.98 83.23 39.29 74.13 AGW_XIN 56.81 85.69 54.14 80.68 39.29 70.50 AGW_HSV_XIN 57.67 88.08 55.49 83.11 41.01 73.20 -
[1] WU A C, ZHENG W S, YU H X, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5390-5399. [2] DAI P Y, JI R, WANG H B, et al. Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training [C]// Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm: IJCAI, 2018: 677-683. [3] YE M, WANG Z, LAN X, et al. Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking [C] // Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm: IJCAI, 2018: 1092-1099. [4] ZHU Y X, YANG Z, WANG L, et al. Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person re-identification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 386: 97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.100 [5] YE M, LAN X Y, LENG Q M. Modality-aware collaborative learning for visible thermal person re-identification[C]// Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2019: 347-355. [6] WANG Z X, WANG Z, ZHENG Y Q, et al. Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 618-626. [7] LING Y G, ZHONG Z, LUO Z M, et al. Class-aware modality mix and center-guided metric learning for visible-thermal person re-identification[C]// Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2020: 889-897. [8] LI D G, WEI X, HONG X P, et al. Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an X modality[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(4): 4610-4617. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5891 [9] YE M, SHEN J B, LIN G J, et al. Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 2872-2893. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775 [10] LUO H, GU Y Z, LIAO X Y, et al. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1487-1495. [11] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [12] WANG X L, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]// 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7794-7803. [13] RADENOVIC F, TOLIAS G, CHUM O. Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with No human annotation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(7): 1655-1668. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2846566 [14] HERMANS A, BEYER L, LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification [EB/OL]. (2017-03-22)[2022-06-29]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07737. [15] 赵红雨, 吴乐华, 史燕军, 等. 基于HSV颜色空间的运动目标检测方法[J]. 现代电子技术, 2013, 36(12): 45-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-373X.2013.12.014ZHAO H Y, WU L H, SHI Y J, et al. Moving target detection method based on HSV color space[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2013, 36(12): 45-48 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-373X.2013.12.014 [16] NGUYEN D T, HONG H G, KIM K W, et al. Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 605. doi: 10.3390/s17030605 [17] CHEN Y C, ZHENG W S, LAI J H, et al. An asymmetric distance model for cross-view feature mapping in person reidentification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(8): 1661-1675. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2515309 [18] YE M, LAN X Y, LI J W, et al. Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2018. [19] YE M, LAN X Y, WANG Z, et al. Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 15: 407-419. [20] HAO Y, WANG N N, LI J, et al. HSME: hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8385-8392. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018385 [21] FENG Z X, LAI J H, XIE X H. Learning modality-specific representations for visible-infrared person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2019: 3623-3632. [22] WANG G A, ZHANG T Z, CHENG J, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment[C]// 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3622-3631. -






 下载:
下载: