Runway temperature data mechanism joint prediction based on LSTM under ice and snow
-
摘要:
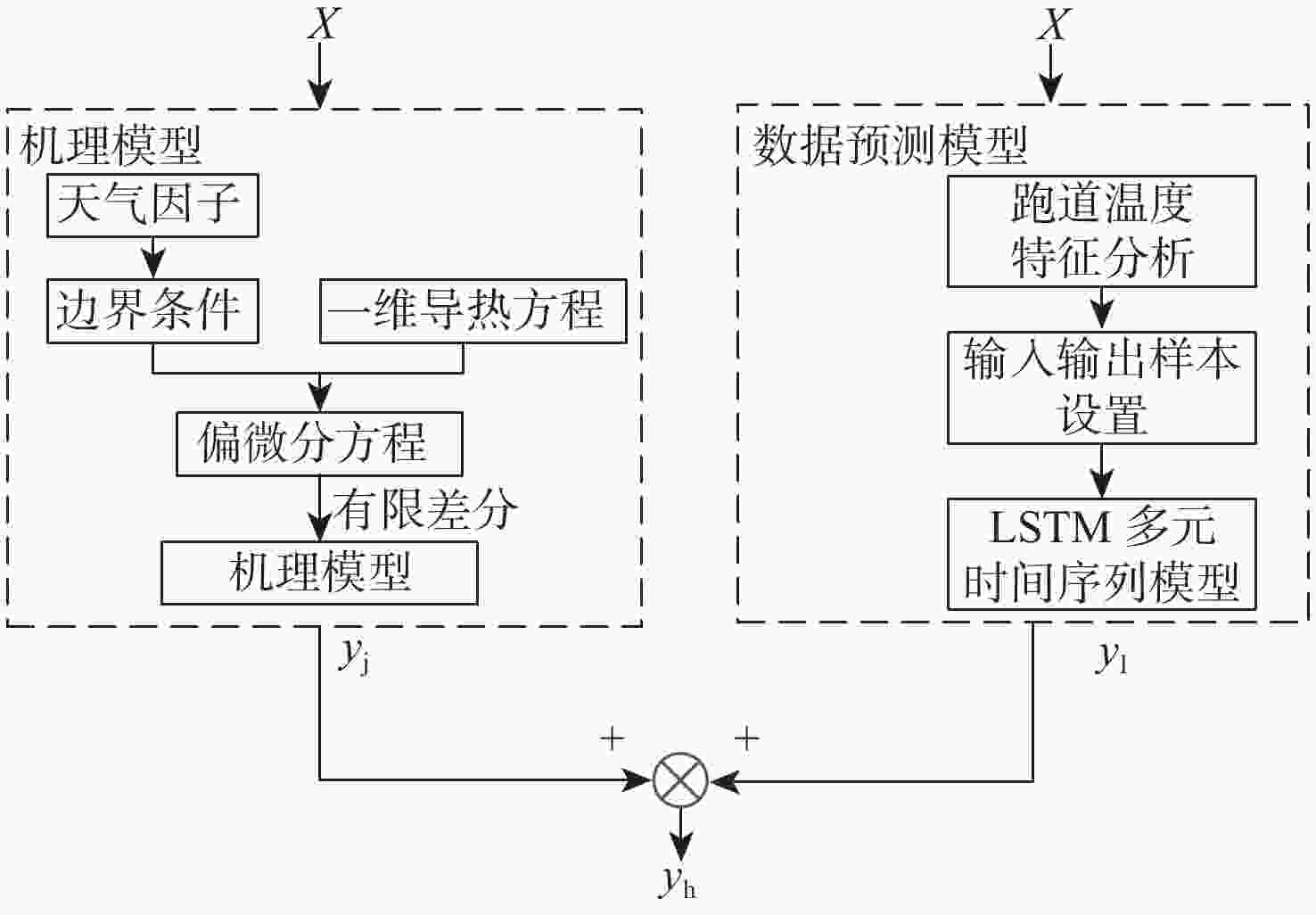
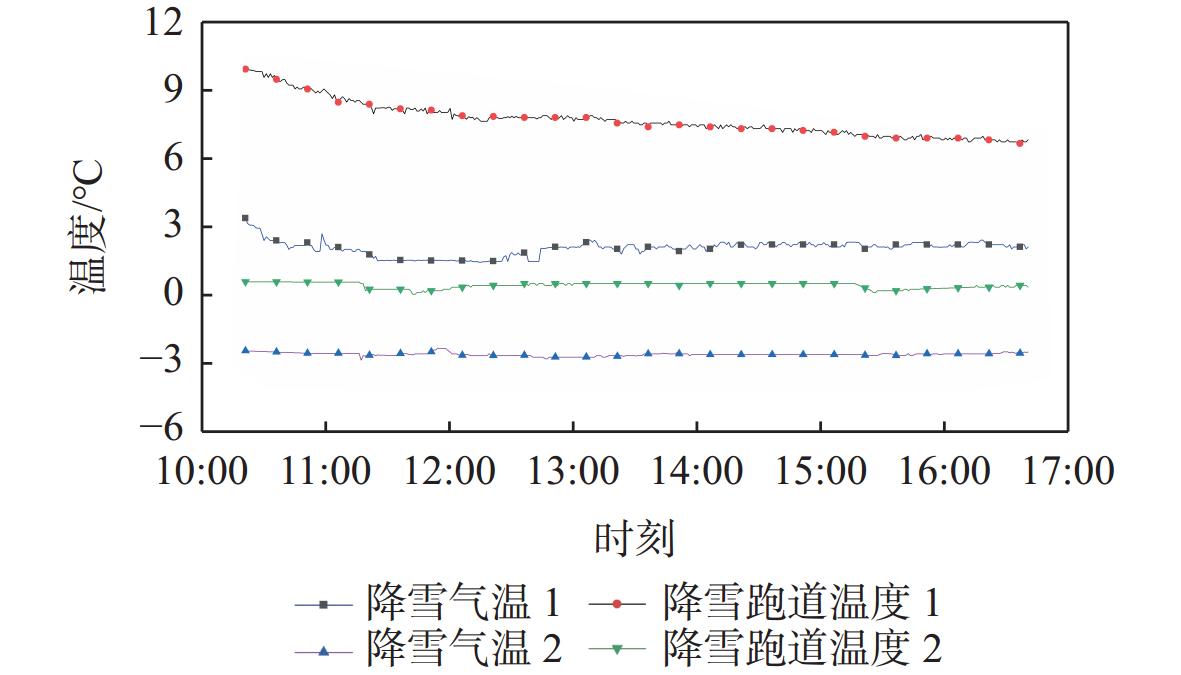
温度是跑道结冰的重要因素,针对跑道除冰运行的跑道热特性参数瞬态变化问题和温度周期序列缓慢变化特性,建立冰雪天气下基于长短时记忆(LSTM)的跑道温度数据-机理联合预测模型。通过最大信息系数法选择数据模型的输入特征变量,采用动态时间弯曲法进行跑道温度数据聚类划分,建立基于LSTM的数据预测模型;通过跑道热力学知识获取跑道温度预测机理模型,采用最小误差赋权法建立跑道温度数据-机理联合预测模型。仿真预测显示,预测时长为20 min、残差阈值为±0.5℃时,数据-机理联合预测模型优于单独的数据预测模型和机理模型,预测准确率可达99.34%;横向对比显示,在相同边界条件下,数据-机理联合预测模型优于BP神经网络、多元回归模型和支持向量机模型,平均准确率提高26.11%。研究表明,基于LSTM的跑道温度数据-机理联合预测模型契合冰雪天气下跑道除冰运行实际,可获得较好的跑道温度短时预测结果。
Abstract:Runway temperature is an important factor in runway icing. Fully considering the transient characteristics of the temperature mechanism model and the time sequence of temperature multivariate time series data, the paper has developed a joint model based on the long short term memory (LSTM) neural network and temperature mechanism model. Firstly, the influencing elements with a greater correlation with runway temperature were selected by the study using the maximum information coefficient approach to serve as the model’s input. Secondly, the paper uses the dynamic time warping method to cluster temperature data under different snowfall conditions, and then develops an LSTM model adapted to different snowfall or icing situations. Finally, to solve the disadvantage of LSTM which can not be characterized by the runway parameters that change irregularly and frequently, the paper developed a joint model based on the LSTM neural network and temperature mechanism model by using the minimum error method. The joint model’s degree of accuracy is 99.34%, which is superior than both the data model and the mechanism model, when the prediction time step is 20 minutes and the residual threshold is ±0.5°C, according to the simulation’s result based on the ice and snowfall weather condition data. With the same condition, the joint model has better accuracy than the BP model, the regression model and the support vector machine model. Average accuracy increased by 26.11%. It proved the joint model based on the LSTM neural network and temperature mechanism model has better accuracy according to the transient characteristics of the mechanism model and the periodic time sequence of the multivariate time series of pavement temperature.
-
表 1 输入变量最大信息系数值
Table 1. MIC value for input variables
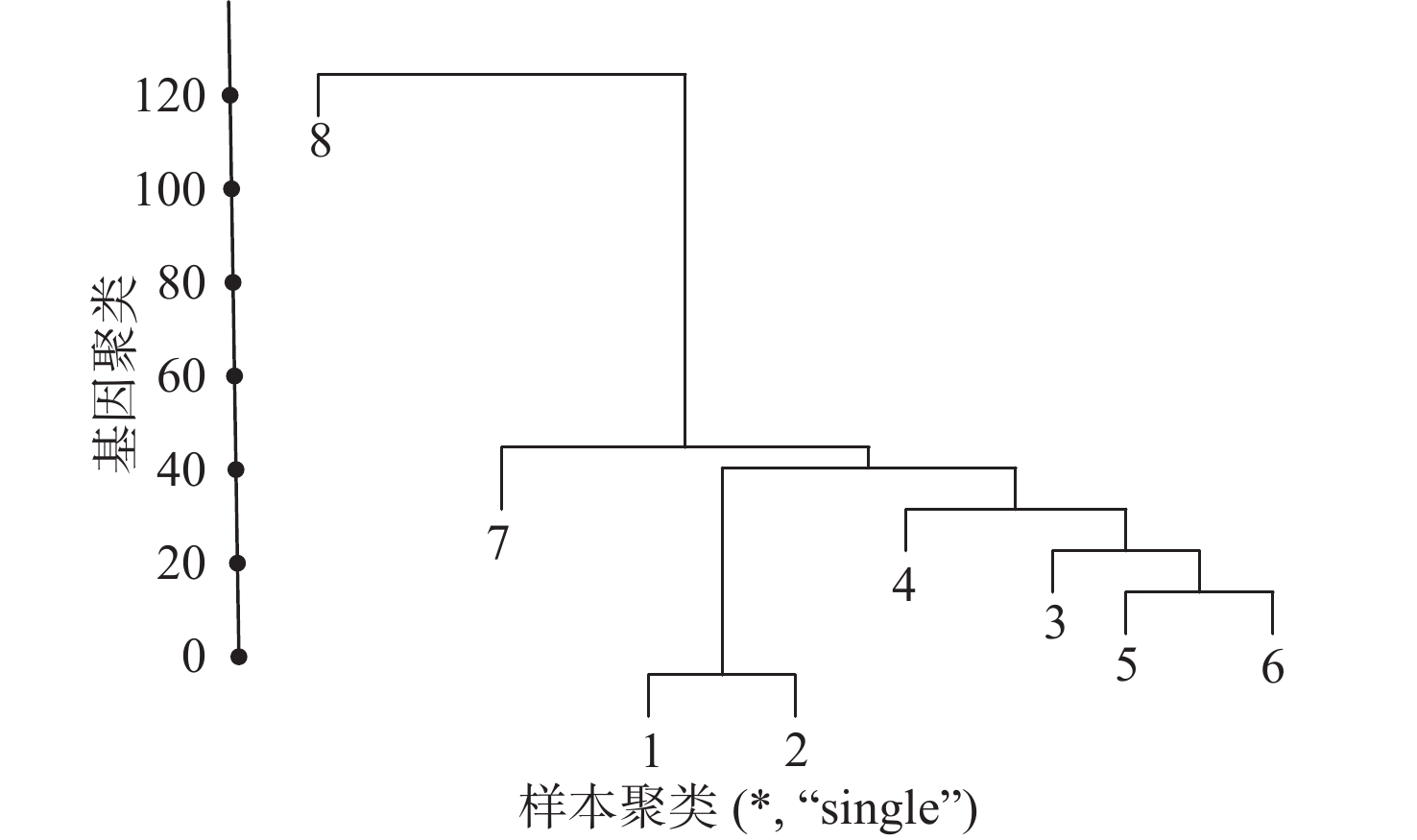
序号 影响因素 MIC值 1 大气温度 0.6820 2 露点温度 0.6815 3 大气湿度 0.6346 4 风速 0.5362 5 大气压强 0.6156 6 跑道下10 cm温度 0.6870 7 跑道下20 cm温度 0.6486 8 跑道下40 cm温度 0.5230 9 大气温度(天气预报) 0.6566 10 露点温度(天气预报) 0.6283 11 大气湿度(天气预报) 0.6021 表 2 冰雪天气下跑道温度样本分类
Table 2. Runway temperature samples classification under ice and snow
类别 样本 Ⅰ 1、2 Ⅱ 3、4、5、6 Ⅲ 7 Ⅳ 8 表 3 LSTM网络参数
Table 3. Parameters of LSTM network
参数 数值 输入层维数 10 隐藏层维数 2 输出层维数 1 每个隐藏层神经元数目 80 初始学习率 0.01 训练批次 64 迭代轮数 10 表 4 不同预测时长下的联合预测模型权重
Table 4. Weight of joint prediction model in different prediction time step
预测时长/min 机理模型权重 LSTM预测模型权重 5 0.63 0.37 10 0.55 0.45 20 0.34 0.66 30 0.33 0.67 表 5 不同模型预测值的RMSE
Table 5. RMSE of different model predictions
模型 预测时长/min RMSE 机理模型 5 0.023 10 0.32 20 0.64 30 1.02 LSTM预测模型 5 0.057 10 0.064 20 0.32 30 0.55 联合预测模型 5 0.002 10 0.037 20 0.15 30 0.21 表 6 多元模型预测值的RMSE
Table 6. RMSE of multivariate model predictions
模型 预测时长/min RMSE 准确率/% 多元回归模型 5 0.0447 86.75 10 0.5806 87.42 20 0.9807 88.08 30 1.04 88.08 BP神经网络 5 0.0699 88.08 10 0.0725 88.74 20 0.1303 88.08 30 0.11 87.42 支持向量机模型 5 0.018 71.52 10 0.2243 60.93 20 0.2549 60.93 30 0.3872 60.26 联合预测模型 5 0.002 100 10 0.037 100 20 0.15 99.34 30 0.21 99.34 -
[1] 孙立军. 沥青路面结构行为理论[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2005: 51-95.SUN L J. Theory of structural behavior of asphalt pavement[M]. Beijing: People’s Traffic Publishing House, 2005: 51-95(in Chinese). [2] NUIJTEN A D. Runway temperature prediction, a case study for Oslo Airport, Norway[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2016, 125: 72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2016.02.004 [3] NUIJTEN A D, HØYLAND K V. Modelling the thermal conductivity of a melting snow layer on a heated pavement[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2017, 140: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.04.008 [4] HERMANSSON Å. Mathematical model for calculation of pavement temperatures: Comparison of calculated and measured temperatures[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2001, 1764(1): 180-188. doi: 10.3141/1764-19 [5] HERMANSSON Å. Simulation model for calculating pavement temperatures including maximum temperature[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2000, 1699(1): 134-141. doi: 10.3141/1699-19 [6] HO C H, ROMERO P. Low design temperatures of asphalt pavements in dry-freeze regions: Predicting by means of solar radiation, transient heat transfer, and finite element method[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2009, 2127(1): 60-71. doi: 10.3141/2127-08 [7] 张丽娟, 黄建武, 许薛军. 基于拉普拉斯变换的路面一维时变温度场预测[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(11): 10-16.ZHANG L J, HUANG J W, XU X J. Prediction of time-dependent one-dimension temperature field of pavement on the basis of Laplace transform[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(11): 10-16(in Chinese). [8] 陈斌, 刘悦, 李庆真, 等. 冰雪天气下基于MFOA-KELM残差修正的跑道温度混合预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(11): 2153-2164.CHEN B, LIU Y, LI Q Z, et al. Runway temperature hybrid prediction based on MFOA-KELM residual correction under ice and snow[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(11): 2153-2164(in Chinese). [9] 孙立军, 秦健. 沥青路面温度场的预估模型[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(4): 480-483. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011SUN L J, QIN J. Prediction model on temperature field in asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2006, 34(4): 480-483(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2006.04.011 [10] NANTASAI B, NASSIRI S. Winter temperature prediction for near-surface depth of pervious concrete pavement[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2019, 20(7): 820-829. doi: 10.1080/10298436.2017.1353389 [11] LIU B, YAN S, YOU H L, et al. Road surface temperature prediction based on gradient extreme learning machine boosting[J]. Computers in Industry, 2018, 99: 294-302. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2018.03.026 [12] 邱欣, 洪皓珏, 杨青, 等. 基于APRIORI-GBDT算法的沥青路面路表温度预测[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(5): 1-10.QIU X, HONG H J, YANG Q, et al. Prediction of temperature of asphalt pavement surface based on APRIORI-GBDT algorithm[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(5): 1-10(in Chinese). [13] 魏鑫. 基于时间序列机场跑道温度预测模型[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2012.WEI X. Temperature prediction model based on time series for airport runway[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2012(in Chinese). [14] 汤筠筠, 郭忠印. 基于自回归求和移动平均的冬季路温短临预测[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 45(12): 1824-1829. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.12.012TANG J J, GUO Z Y. Pavement temperature short-impending prediction based on ARIMA in winter[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(12): 1824-1829(in Chinese). doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.2017.12.012 [15] YU M, XU F, HU W, et al. Using long short-term memory (LSTM) and Internet of things (IoT) for localized surface temperature forecasting in an urban environment[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 137406-137418. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3116809 [16] FANG Z, CRIMIER N, SCANU L, et al. Multi-zone indoor temperature prediction with LSTM-based sequence to sequence model[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2021, 245: 111053. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111053 [17] LIU J, ZHANG T, HAN G J, et al. TD-LSTM: Temporal dependence-based LSTM networks for marine temperature prediction[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3797. doi: 10.3390/s18113797 [18] 颜弋凡, 安路达, 吕志民. 基于最大互信息系数属性选择的冷轧产品机械性能预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(1): 68-75.YAN Y F, AN L D, LÜ Z M. Prediction of mechanical properties of cold rolled products based on maximal information coefficient attribute selection[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(1): 68-75(in Chinese). [19] 李正欣, 刘畅, 吴诗辉, 等. 特征点分段提取的时间序列模式匹配方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报2023, 49(7): 1593-1599.LI Z X, LIU C, W S H, et al. A time series matching method for feature point segmentation extraction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautic, 2023, 49(7): 1593-1599(in Chinese). [20] ALAEE S, MERCER R, KAMGAR K, et al. Time series motifs discovery under DTW allows more robust discovery of conserved structure[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2021, 35(3): 863-910. doi: 10.1007/s10618-021-00740-0 [21] 张慧. 深度学习中优化算法的研究与改进[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2018.ZHANG H. Research and improvement of optimization algorithms in deep learning [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018(in Chinese). [22] 顾尔祚. 流体力学中的有限差分法基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 1988.GU E Z. Fundamentals of finite difference method in fluid mechanics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 1988(in Chinese). [23] 中国民用航空局. 运输机场跑道表面状况评估程序[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局, 2022.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Runway surface condition of transport airport assessment procedure[S]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2022(in Chinese). [24] 王志刚, 王业光, 杨宁, 等. 基于LSTM的飞行数据挖掘模型构建方法[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(8): 525800.WANG Z G, WANG Y G, YANG N, et al. Construction method of flight data mining model based on LSTM[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(8): 525800(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: