Multiple high-speed maneuvering target detection method based on improved orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm
-
摘要:
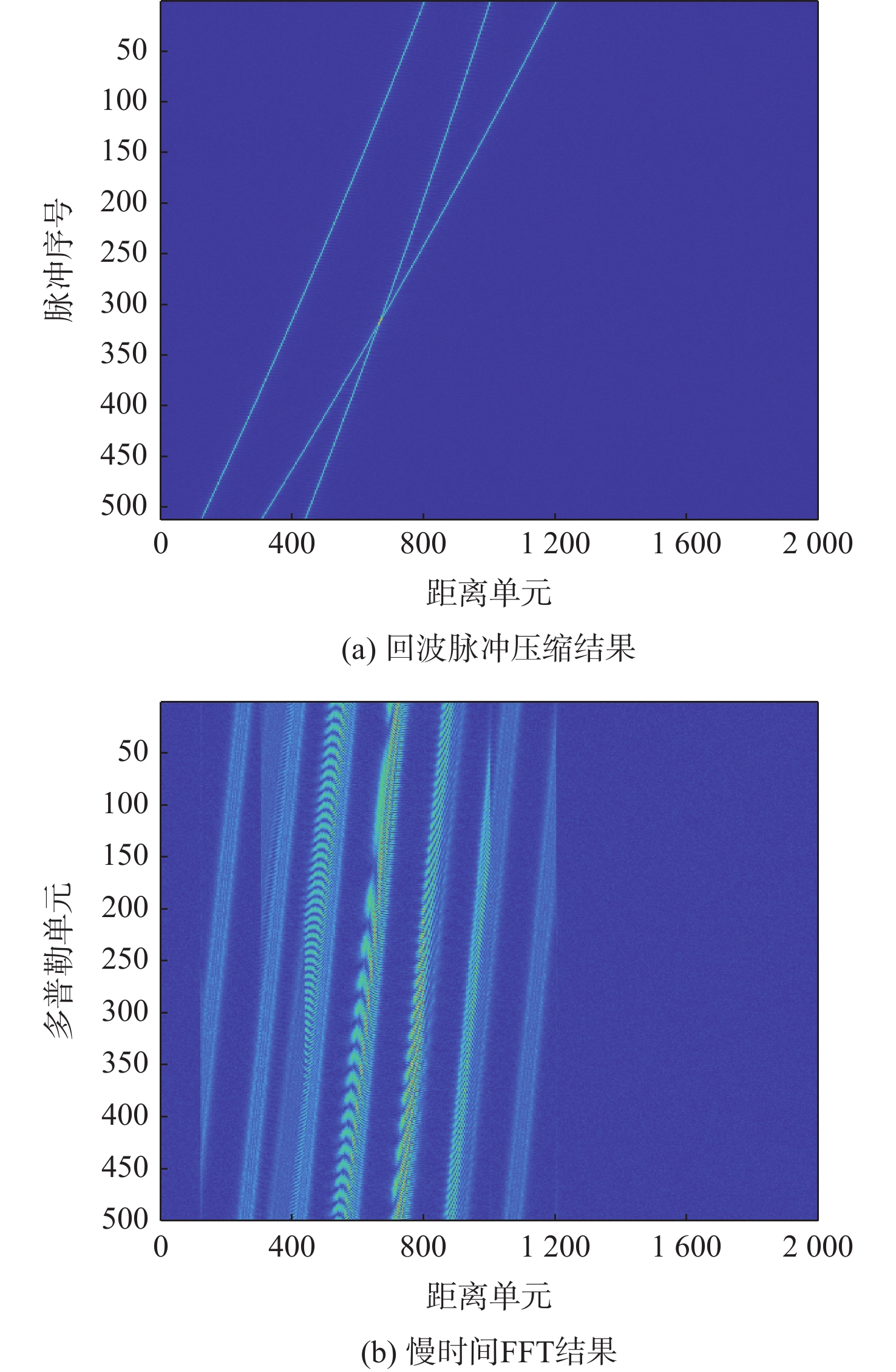
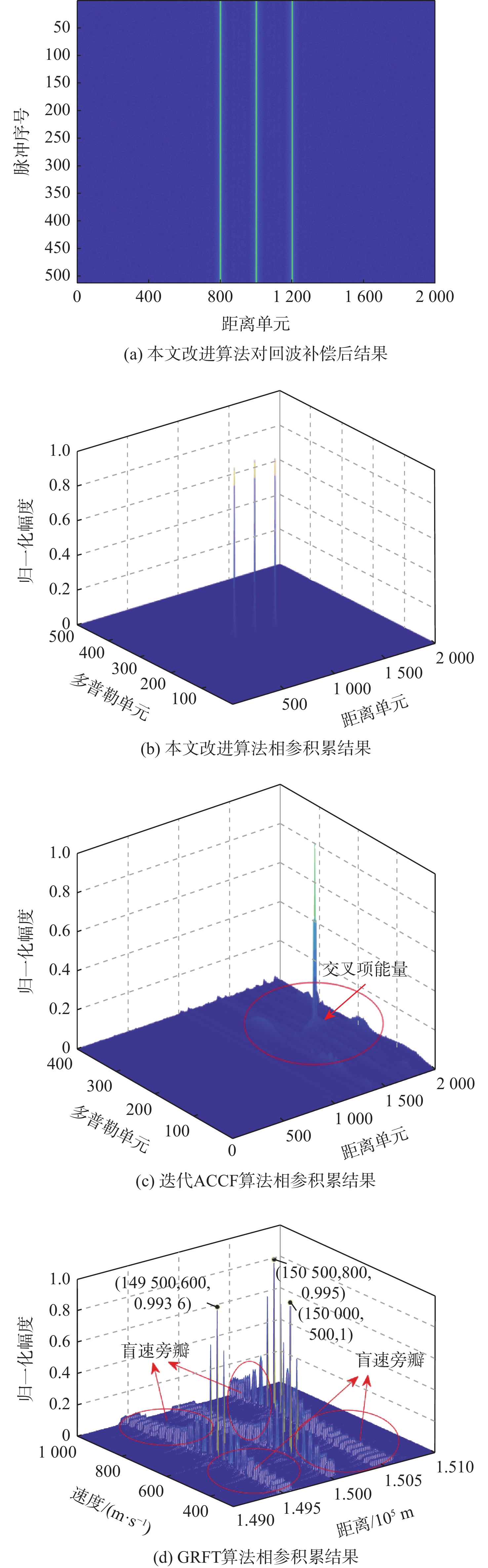
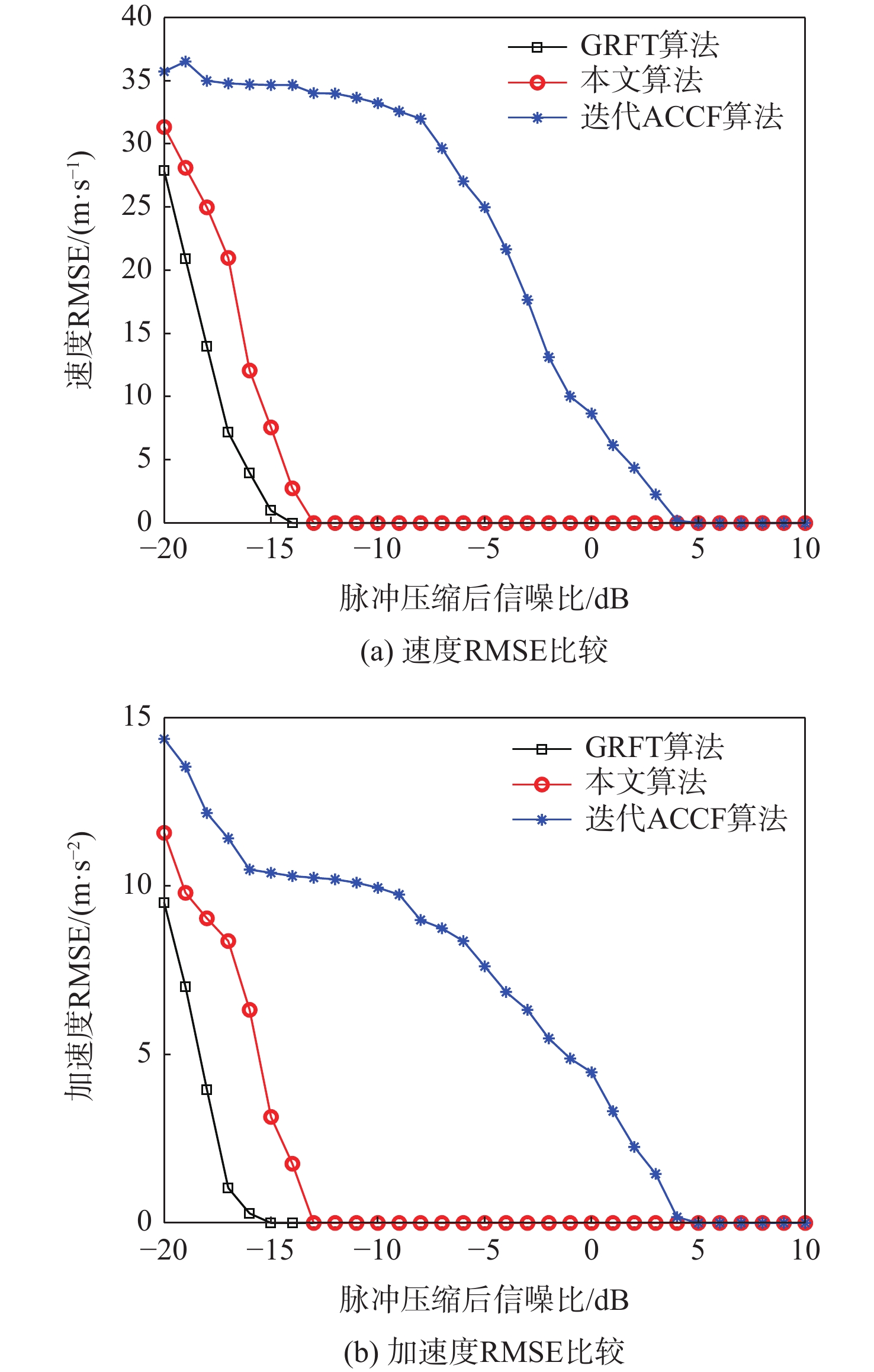
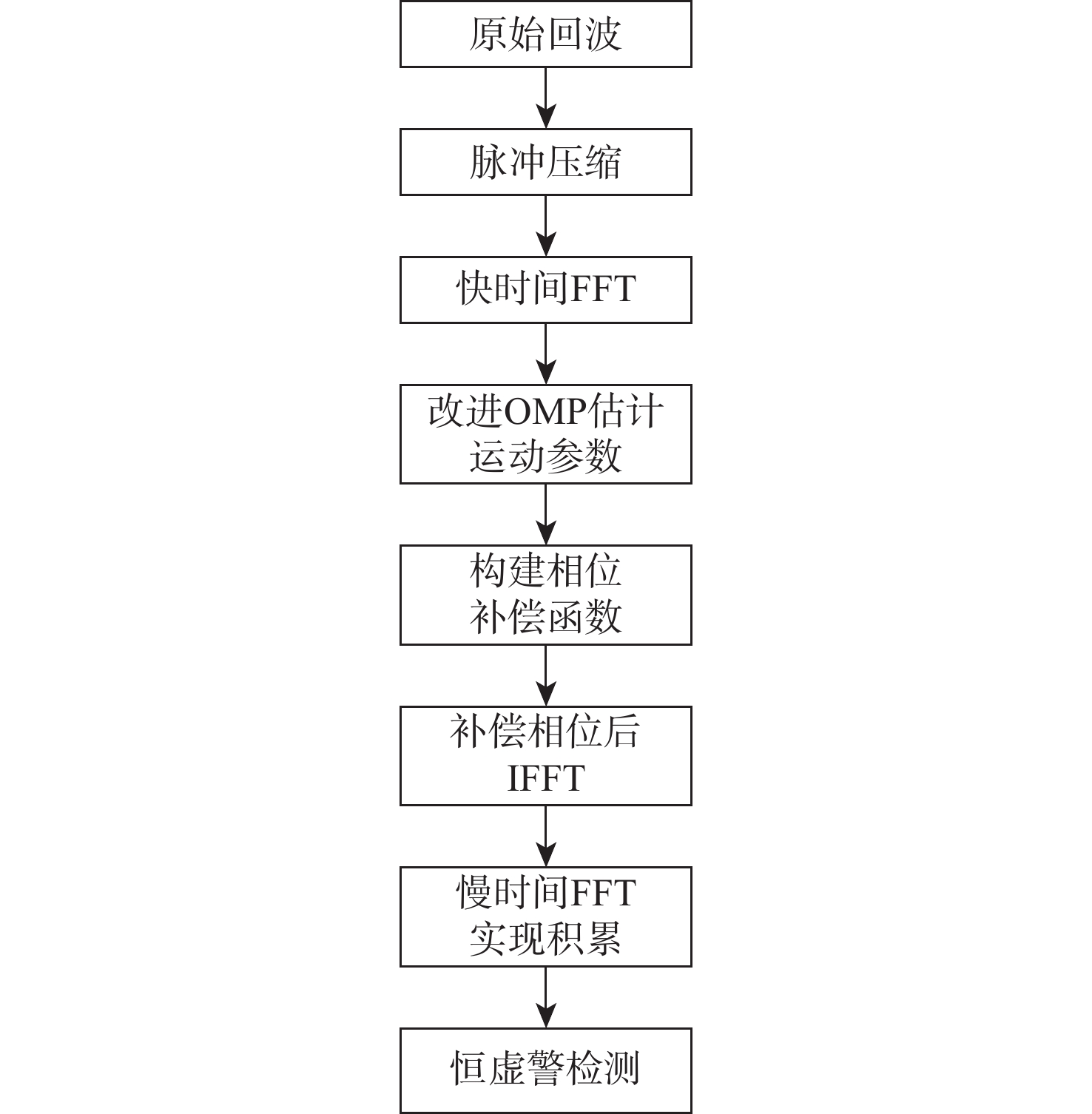
针对多目标高速机动检测问题,提出了一种基于改进正交匹配追踪(OMP)算法的多目标检测方法。根据高速机动目标运动特性建立信号模型;利用改进OMP算法对脉冲压缩后的回波信号进行运动参数估计;构建相位补偿函数对距离徙动和多普勒徙动进行校正;通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)完成相参积累,实现对多目标的检测。改进算法适用于多目标高速机动检测场景,可有效避免盲速旁瓣现象及信号交叉项的影响,且具有参数估计精度高和抗噪声能力强等优点。仿真实验验证了改进算法的有效性与可靠性。
-
关键词:
- 高速机动目标 /
- 改进正交匹配追踪算法 /
- 距离徙动 /
- 多普勒徙动 /
- 相参积累
Abstract:An improved orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm is proposed for the detection of multiple high-speed maneuvering targets. Based on the maneuvering characteristics of a high-speed target, a signal model is established at first. Then, an improved OMP algorithm is used to estimate motion parameters. In addition, a phase compensation function is constructed to correct for the range migration and Doppler migration. Finally, coherent integration can be achieved by the fast Fourier transform (FFT). The suggested technique may successfully avoid the effects of the signal cross term and blind speed side lobe in multi-target high-speed maneuver identification settings.Meanwhile, it has the advantages of high accuracy of parameter estimation and strong anti-noise robustness. The suggested algorithm’s efficacy and dependability are confirmed by the simulation results.
-
表 1 目标的运动参数
Table 1. Motion parameters of target
目标 初始径向距离/km 径向速度/(m·s−1) 径向加速度/(m·s−2) A 149.5 600 50 B 150 500 40 C 150.5 800 80 表 2 不同算法的计算复杂度比较
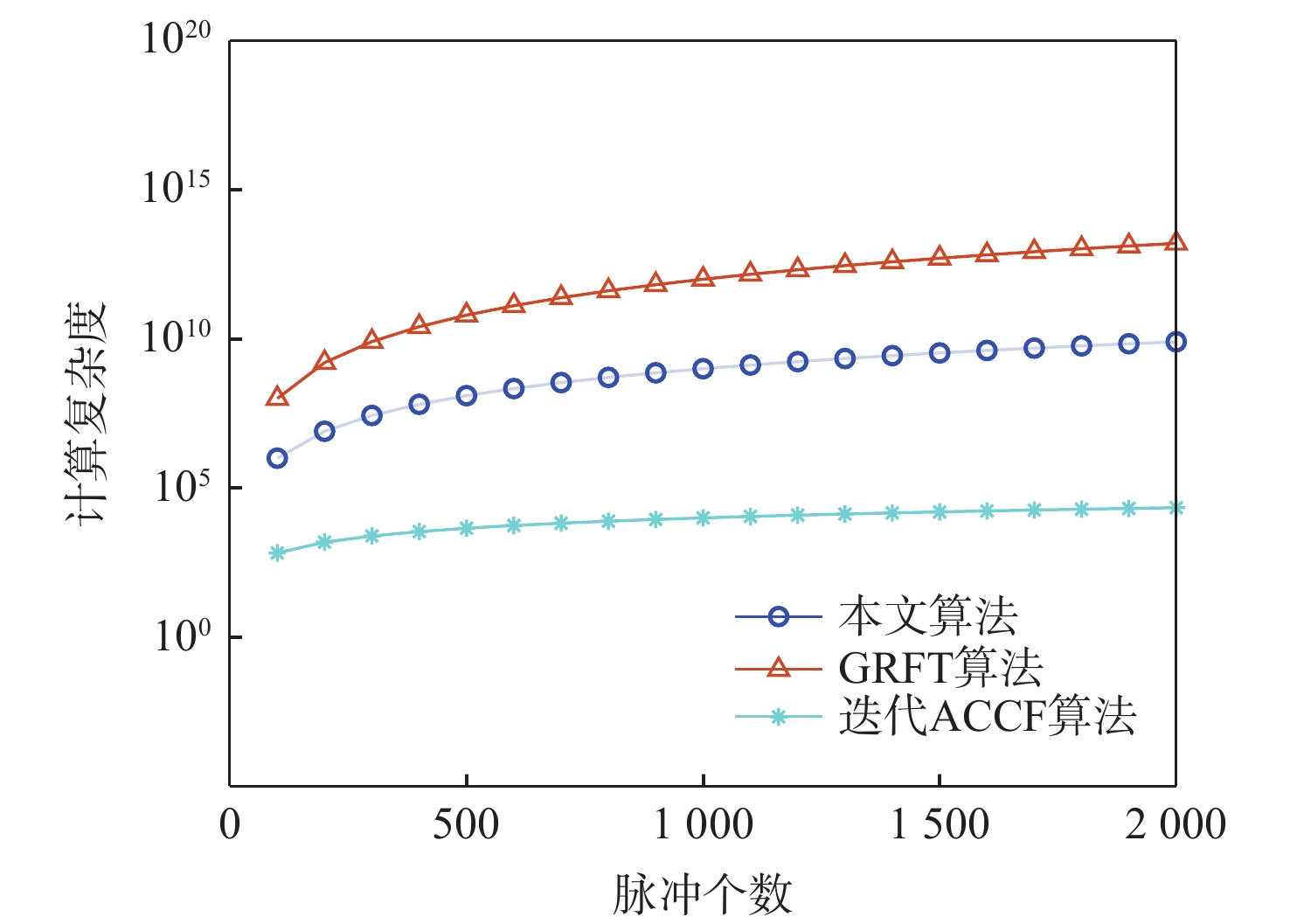
Table 2. Computational complexity comparisons between different algorithms
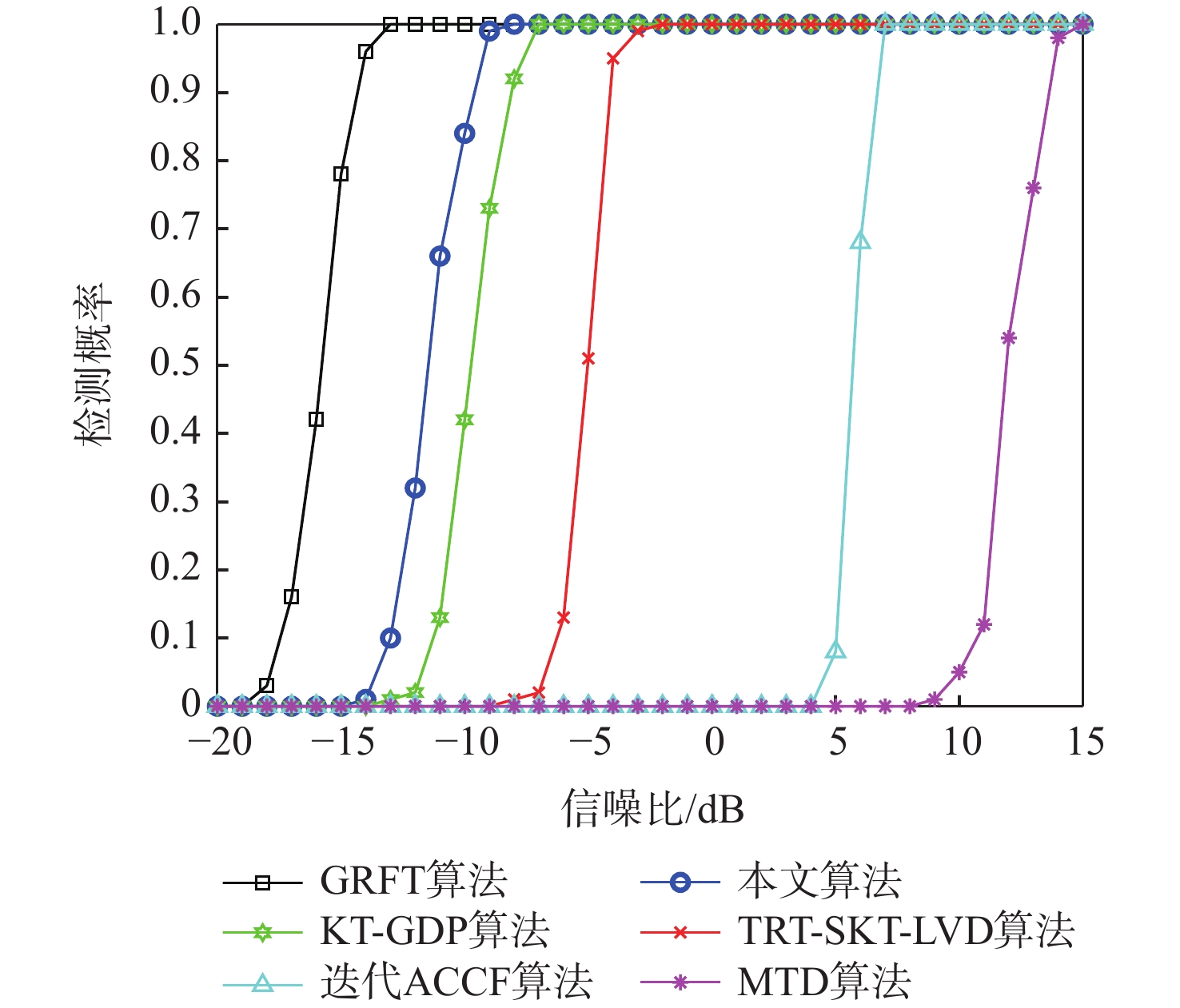
算法 计算复杂度 搜索维度 GRFT算法 O(NNdNvNa) 三维搜索 本文算法 O(NNvNa) 二维搜索 迭代ACCF算法 O(Nlog2Nd) 无须搜索 -
[1] ZHAO L X, TAO H, CHEN W J, et al. Maneuvering target detection based on subspace subaperture joint coherent integration[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(10): 1948. doi: 10.3390/rs13101948 [2] YANG J, LIU X X, YANG B, et al. Detection and speed estimation of moving target based on phase compensation and coherent accumulation using fractional Fourier transform[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1410. doi: 10.3390/s20051410 [3] YU W C, SU W M, GU H, et al. Weak maneuvering target detection in random pulse repetition interval radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 171: 107520. [4] LIN L J, SUN G H, CHENG Z Y, et al. Long-time coherent integration for maneuvering target detection based on ITRT-MRFT[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(7): 3718-3731. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2960323 [5] ZUO L, WANG J, WANG J P, et al. UAV detection via long-time coherent integration for passive bistaticradar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 112: 102997. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.102997 [6] JIN K, LAI T, WANG Y B, et al. Radar coherent detection for Doppler-ambiguous maneuvering target based on product scaled periodic Lv’s distribution[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: 107617. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107617 [7] SUN Z, LI X L, CUI G L, et al. Coherent detection method for maneuvering target with complex motions[J]. Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 8032-8036. [8] LI X L, CUI G L, YI W, et al. Sequence-reversing transform-based coherent integration for high-speed target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1573-1580. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2668018 [9] XU J, YU J, PENG Y N, et al. Radon-Fourier transform for radar target detection. I: Generalized Doppler filter bank[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1186-1202. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751251 [10] XU J, YU J, PENG Y N, et al. Space-time Radon-Fourier transform and applications in radar target detection[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(9): 846-857. [11] ZHANG S S, ZENG T, LONG T, et al. Dim target detection based on keystone transform[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 889-894. [12] RAO X, TAO H H, SU J, et al. Axis rotation MTD algorithm for weak target detection[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 26: 81-86. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2013.12.003 [13] RAO X, ZHONG T T, TAO H H, et al. Improved axis rotation MTD algorithm and its analysis[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 30(2): 885-902. doi: 10.1007/s11045-018-0588-y [14] XU J, XIA X G, PENG S B, et al. Radar maneuvering target motion estimation based on generalized Radon-Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12): 6190-6201. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2217137 [15] XIA W J, ZHOU Y, JIN X, et al. A fast algorithm of generalized Radon-Fourier transform for weak maneuvering target detection[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 2016: 4315616. [16] MA B, ZHANG S S, JIA W K, et al. Fast implementation of generalized Radon-Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3758-3767. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3082717 [17] LI X L, CUI G L, YI W, et al. Manoeuvring target detection based on keystone transform and Lv’s distribution[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(7): 1234-1242. [18] ZHENG J B, ZHU K L, NIU Z Y, et al. Generalized dechirp-keystone transform for radar high-speed maneuvering target detection and localization[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3367. doi: 10.3390/rs13173367 [19] WAN J, TAN X H, CHEN Z Y, et al. Refocusing of ground moving targets with Doppler ambiguity using keystone transform and modified second-order keystone transform for synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 177. doi: 10.3390/rs13020177 [20] LI X L, CUI G L, KONG L J, et al. Fast non-searching method for maneuvering target detection and motion parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(9): 2232-2244. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2515066 -







 下载:
下载: