An automatic and real-time detection method of IoT in-the-wild vulnerability attack
-
摘要:
与互联网相连的海量物联网(IoT)设备容易被黑客攻击和利用,进而造成关键IoT应用的瘫痪。漏洞利用是一种常用的针对IoT设备的攻击方式,然而由于在野的漏洞利用形式多样、变异性和伪装性强,如何快速自动识别针对IoT设备的在野漏洞攻击极具挑战。为此,提出一种基于混合深度学习判别和开源情报关联的IoT漏洞攻击检测方法,所提检测方法可以实时判别网络流量中的IoT在野漏洞攻击行为,并且能够精准识别漏洞攻击行为的具体类别。实验结果表明:所提检测方法在大规模数据集上的判别准确率超过99.99%。所提检测方法在真实场景中应用效果显著,在不到1个月时间内发现了13种新的在野漏洞攻击。
Abstract:The vast number of Internet-connected internet of things (IoT) devices are susceptible to hacking and exploitation, which can lead to the paralysis of critical IoT applications. Vulnerability exploitation is a common method of attack on IoT devices; however, due to the diverse, mutable, and highly disguised forms of in-the-wild vulnerability exploitations, it is extremely challenging to quickly and automatically identify ongoing vulnerability attacks targeting IoT devices. To address this, a detection method for IoT vulnerability attacks based on a hybrid deep learning discrimination and open-source intelligence correlation is proposed. This detection method can identify IoT in-the-wild vulnerability attack behaviors in network traffic in real-time and accurately identify the specific categories of vulnerability attack behaviors. Experimental results show that the proposed detection method achieves an accuracy rate of over 99.99% on large-scale datasets. The application of the proposed detection method in real-world scenarios has been significant, discovering 13 new in-the-wild vulnerability attacks within less than a month.
-
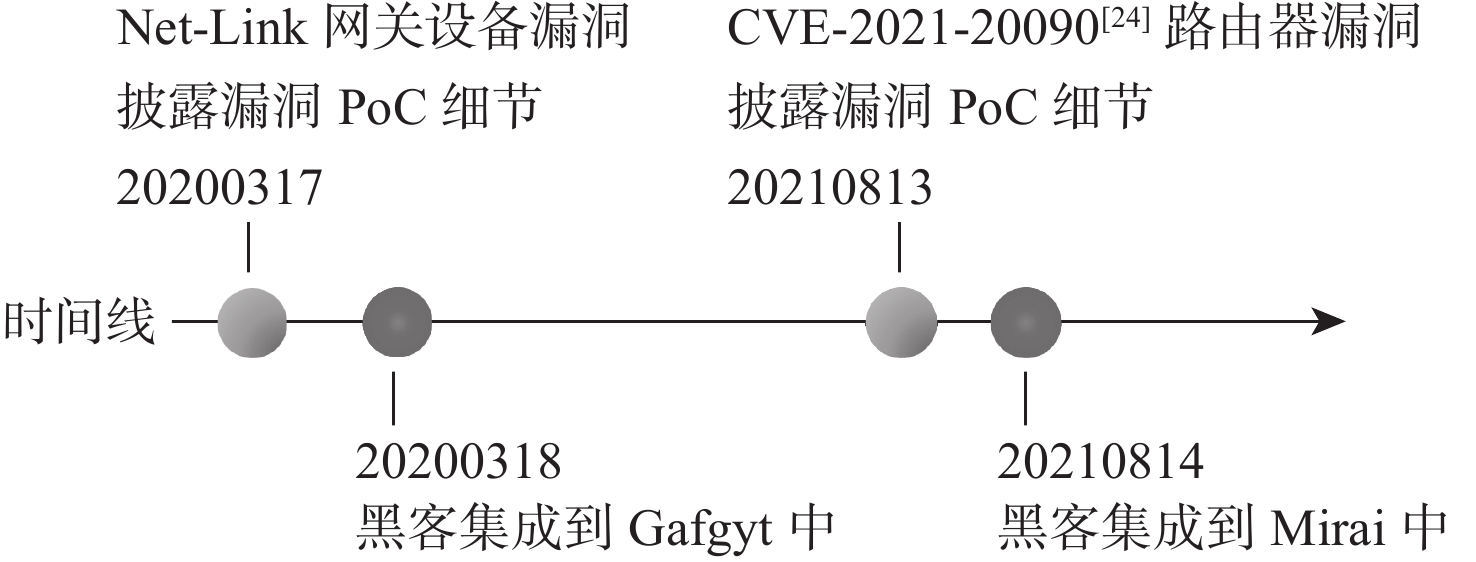
表 1 最近3年部分在野利用IoT漏洞示例
Table 1. Some inofficial IoT exploit examples in past three years
CVE编号 漏洞名称 针对设备 CVE_2021_33544 UDP_Technology_Geutebruck_IP_Cameras_Command_Injection IP摄像头 CVE_2021_33514 HTTP_Router_NetgearGC108P Netgear路由器 CVE_2021_31755 Tenda_AC11_Router_Stack_Buffer_Overflow_Vulnerability 腾达路由器 CVE_2021_28799on QNAP_NAS_Hybrid_Backup_Sync_Command_Injecti QNAP NAS设备 CVE_2021_20090 Arcadyan_Buffalo_Routers_Configuration_File_Injection Buffalo组件的路由器 CVE_2021_1497 Cisco_HyperFlex_HX_Data_Platform_Command_Execution Cisco管理平台 CVE_2020_9054_ Zyxel_NAS_RCE_Attempt_Inbound Zyxel NAS设备 CVE_2020_8949 Gocloud_Router_Remote_Code_Execution Gocloud路由器 CVE_2020_8515 DrayTek_Vigor_RCE Vigor路由器 CVE_2020_35713 Linksys_RE6500_1_0_11_001_Remote_Code_Execution Linksys路由器 CVE_2020_35576 TpLink_TLWR841N_Command_Injection Tplink路由器 CVE_2020_17456 Seowon_Route Seowon路由器 CVE_2020_13872 DLink_DIR_865L_Ax120B01_Command_Injection Dlink路由器 CVE_2020_10987 Tenda_AC15_AC1900_goform_setUsbUnload_RCE 腾达路由器 表 2 F1和ACC实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of F1 and ACC
表 3 模型每轮训练时间
Table 3. Model training time in each round
样本数量/106 训练时间/min Bert[29]模型 本文模型 1 62 71 1.5 89 102 2.5 127 146 4.5 146 167 表 4 IoT漏洞攻击中的攻击目标及攻击参数
Table 4. Attack targets and parameters in IoT exploits
漏洞编号 攻击目标 攻击参数 CVE_2021_33544 /uapi-cgi/certmngr.cgi action,createselfcert,local CVE_2021_33514 cgi/setup.cgi token CVE_2021_31755 /goform/setmac mac,wifien,wifissid CVE_2021_28799 /cgi-bin/backup/hbs_mgnt.cgi run_cmd,jisoosocoolhbsmgnt CVE_2021_20090 /images/../apply_abstract.cgi action,submit_button,action_params,arc_ping_ipaddress CVE_2021_1497 /storfs-asup action,token CVE_2020_9054 /cgi-bin/weblogin.cgi adv,username,password CVE_2020_8949 /cgi-bin/webui/admin/tools/app_ping/diag_ping/ None CVE_2020_8515 cgi-bin/mainfunction.cgi action,keypath,loginPwd CVE_2020_35713 /goform/setSysAdm AuthTimeout, admpasshint CVE_2020_35576 /cgi? maxhopcount, numberoftries, host CVE_2020_17456 /cgi-bin/system_log.cgi Command, traceMode CVE_2020_13872 /portal/__ajax_explorer.sgi Action/path/where/en CVE_2020_10987 /goform/setUsbUnload setUsbUnload 表 5 IoT漏洞攻击中常见的攻击指令
Table 5. Common attack commands in IoT exploits
攻击指令类型 关键词 样本植入 wget,curl,tftp,fetch 反弹回连 bash-i,tmp/socat exec 探测 Nc,echo,dnslog 隐藏痕迹 Rm,mv,base64,decodeHex 命令执行 chmod, system,md5sum, busybox ,exec -
[1] 绿盟科技. 2020物联网安全年报[EB/OL]. (2021-01-08)[2022-05-28]. https://www.nsfocus.com.cn/html/2021/92_0118/147.html.NSFOCUS. 2020 IoT Security annual report[EB/OL]. (2021-01-08)[2022-05-28]. https://www.nsfocus.com.cn/html/2021/92_0118/147.html(in Chinese). [2] CVE-CVE [EB/OL]. (2022-05-28) [2022-05-29]. https://cve.mitre.org/. [3] Exploit-DB - exploits for penetration testers[EB/OL]. (2022-05-28) [2022-05-29]. https://www.exploit-db.com/. [4] Packet storm-exploits the possibilities[EB/OL]. (2022-05-29) [2022-05-30]. https://packetstormsecurity.com/. [5] Snort - network intrusion detection & prevention system[EB/OL]. (2022-05-01) [2022-05-30]. https://www.snort.org/. [6] Yara-the pattern matching swiss knife for malware researchers[EB/OL]. (2022-05-01) [2022-05-30]. https://virustotal.github.io/yara/. [7] KDD cup 1999 data [EB/OL]. (2000-09-18) [2022-05-30]. http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/databases/kddcup99/kddcup99.html. [8] SHIRAVI A, SHIRAVI H, TAVALLAEE M, et al. Toward developing a systematic approach to generate benchmark datasets for intrusion detection[J]. Computers and Security, 2012, 31(3): 357-374. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2011.12.012 [9] RING M, WUNDERLICH S, GRUEDL D, et al. Technical report cidds-001 data set[EB/OL]. (2017-04-28) [2022-05-30]. https://www.hs-coburg.de/fileadmin/hscoburg/Forschung/WISENT_cidds_Technical_Report.pdf. [10] LEE W K, STOLFO S J. Data mining approaches for intrusion detection[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on USENIX Security Symposium . New York: ACM, 1998: 6. [11] KHAN L, AWAD M, THURAISINGHAM B. A new intrusion detection system using support vector machines and hierarchical clustering[J]. The VLDB Journal, 2007, 16(4): 507-521. doi: 10.1007/s00778-006-0002-5 [12] NGUYEN TTT, ARMITAGE G. A survey of techniques for Internet traffic classification using machine learning[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2008, 10(4): 56-76. [13] SOMMER R, PAXSON V. Outside the closed world: On using machine learning for network intrusion detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 305-316. [14] SUTHAHARAN S. Big data classification[C]//Proceedings of the Measurement and Modeling of Computer Systems. New York: ACM, 2014, 41(4): 70-73. [15] MA J, SAUL L K, SAVAGE S, et al. Identifying suspicious URLs: An application of large-scale online learning[C]//Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. Montreal : ICML , 2009: 681-688. [16] MA J, SAUL L K, SAVAGE S, et al. Byond blacklists: Learning to detect malicious web sites from suspicious URLs[C]//Proceedings of the Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2009: 1245-1254. [17] ZHAO P L, HOI S C H. Cost-sensitive online active learning with application to malicious URL detection[C]//Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2013: 919-927. [18] 李佳, 云晓春, 李书豪, 等. 基于混合结构深度神经网络的HTTP恶意流量检测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(1): 24-33. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019019LI J, YUN X C, LI S H, et al. HTTP malicious traffic detection method based on hybrid structure deep neural network[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(1): 24-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019019 [19] HODO E, BELLEKENS X, HAMILTON A, et al. Threat analysis of IoT networks using artificial neural network intrusion detection system[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-6. [20] THAMILARASU G, CHAWLA S. Towards deep-learning-driven intrusion detection for the Internet of Things[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(9): 1977. doi: 10.3390/s19091977 [21] AL-HAWAWREH M, MOUSTAFA N, SITNIKOVA E. Identification of malicious activities in industrial Internet of Things based on deep learning models[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2018, 41: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2018.05.002 [22] ABDEL-BASSET M, HAWASH H, CHAKRABORTTY R K, et al. Semi-supervised spatiotemporal deep learning for intrusions detection in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(15): 12251-12265. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3060878 [23] TSIMENIDIS S, LAGKAS T, RANTOS K. Deep learning in IoT intrusion detection[J]. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 2021, 30(1): 8. [24] CVE-2021-20090[EB/OL]. (2022-06-14) [2022-06-15]. https://medium.com/tenable-teblog/bypassing-authentication-on-arcad-an-routers-with-cve-2021-20090-and-rooting-some-buffalo-ea1dd30980c2. [25] IoT_Exploits_Founder[EB/OL]. (2022-1-12) [2022-06-15]. https://github.com/bennyhee/IoT_Exploits_Founder.git. [26] ZHAO Y C, WANG G T, TANG C X, et al. A battle of network structures: an empirical study of CNN, transformer, and MLP[EB/OL]. (2021-08-30) [2022-06-17]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2108.13002. [27] KIM Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[EB/OL]. (2014-08-25) [2022-06-15]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.5882. [28] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[EB/OL]. (2017-06-12) [2022-06-15]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762. [29] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[EB/OL]. (2018-10-11) [2022-06-15]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805. [30] 崔琳, 杨黎斌, 何清林, 等. 基于开源信息平台的威胁情报挖掘综述[J]. 信息安全学报, 2022, 7(1): 1-26.CUI L, YANG L B, HE Q L, et al. Survey of cyber threat intelligence mining based on open source information platform[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2022, 7(1): 1-26(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: