-
摘要:
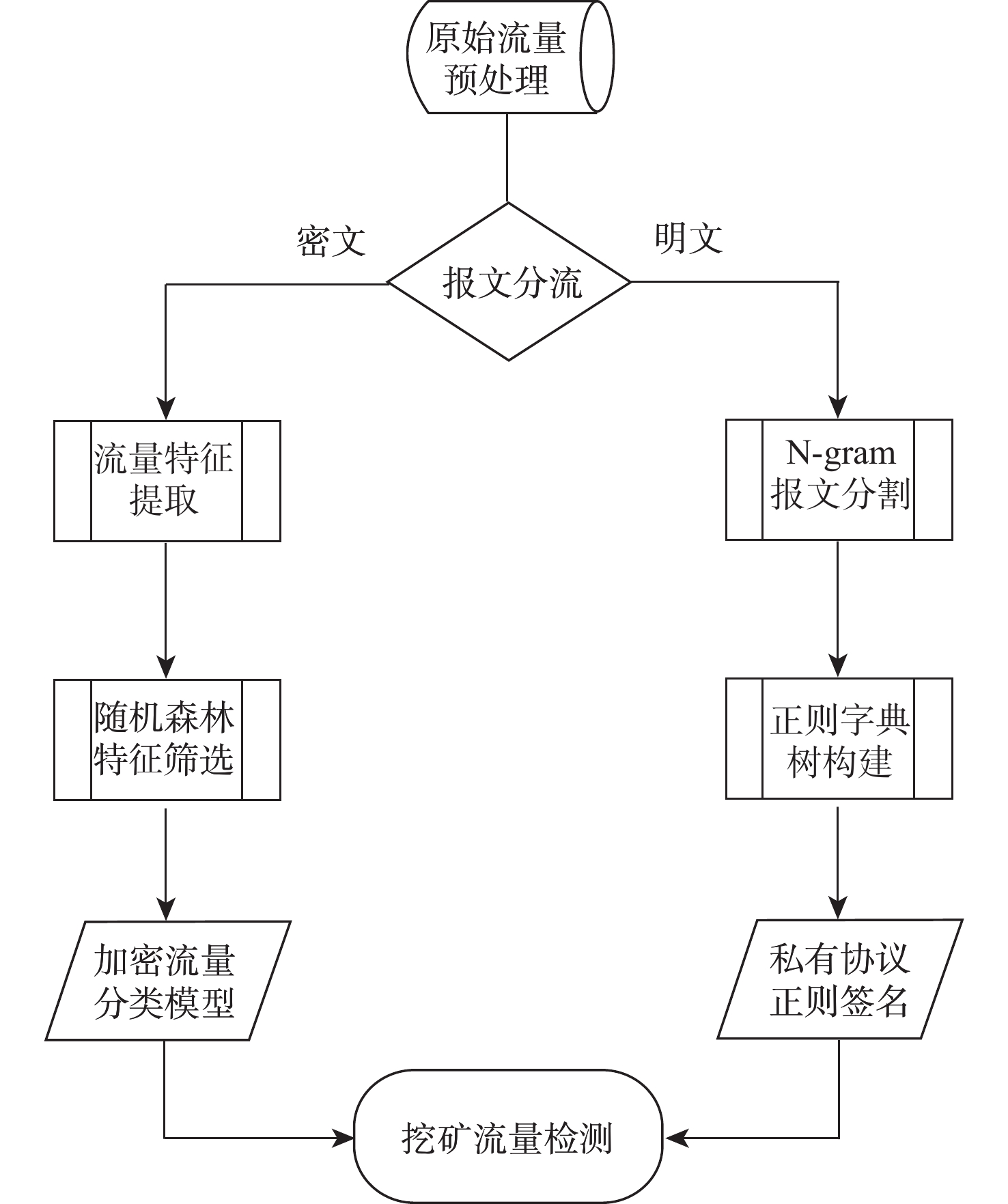
面向虚拟货币挖矿过程中私有协议流量检测识别需求,提出面向未知挖矿行为通信协议流量的自动化识别方法。改进N-gram报文格式分割算法和字典树正则表达式生成算法,实现私有协议特征签名自动化生成,对明文通信的挖矿流量进行精确匹配;基于经典加密流量分类模型,改进基于流交互特征的流量分析方法,实现轻量级的挖矿行为识别模型,对加密通信的挖矿流量进行实时检测。测试结果表明:所提方法生成的挖矿通信协议特征签名可覆盖当前3种主流明文挖矿流量,在实网验证过程中可达到0.996的识别精确率和0.985的召回率。
Abstract:To meet the demand for private protocol traffic detection and identification during cryptocurrency mining, an automated communication protocol traffic identification method for unknown mining behaviors was proposed. The N-gram message format segmentation algorithm and regular expression generation algorithm of the dictionary tree were improved, so as to automatically generate private protocol signatures and accurately match mining traffic during plaintext communications. Based on the classical encrypted traffic classification model, the traffic analysis method based on flow interaction features was improved, so as to achieve a lightweight mining behavior identification model and detect mining traffic during encrypted communications in real time. The test results show that the mining communication protocol signatures generated by the proposed method effectively cover the current three kinds of mainstream mining traffic during plaintext communications. The proposed method can achieve 0.996 identification accuracy and 0.985 recall rate in the real network verification process.
-
Key words:
- cryptocurrency /
- mining traffic /
- private protocol /
- automation /
- regular signatures /
- encrypted traffic identification
-
表 1 测试环境
Table 1. Test environment
配置 操作系统 内核版本 核心处理器 图形处理器 内存大小 性能测试主机 Arch Linux x86_64 Linux 5.18.3-arch1-1 Intel Core i7-9750H @ 12x 2.60 GHz NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 15.5 GB 数据集
捕获主机Ubuntu 20.04 focal x86_64 Linux 5.4.0-110-generic Intel Core i5-9300H @ 8x 4.1 GHz NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 15789 MB 服务端采集 Ubuntu 20.04 focal x86_64 Linux 5.4.0-94-generic Intel Xeon Platinum 8269CY @ 2x 2.5 GHz Cirrus Logic GD 5446 1879 MB -
[1] JIANG S R, LI Y Z, LU Q Y, et al. Policy assessments for the carbon emission flows and sustainability of Bitcoin blockchain operation in China[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1938. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22256-3 [2] SQUAREPANTS S. Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system[J]. SSRN Electronic Journal, 2008: 21260. [3] RUSSO M, ŠRNDIĆ N, LASKOV P. Detection of illicit cryptomining using network metadata[J]. EURASIP Journal on Information Security, 2021, 2021: 11. doi: 10.1186/s13635-021-00126-1 [4] 郑云超, 范渊, 黄进. 一种恶意挖矿行为识别方法、装置、设备及存储介质: CN113177791A[P]. 2021-07-27.ZHENG Y C, FAN Y, HUANG J. Malicious mining behavior identification method and device, equipment and storage medium: CN113177791A[P]. 2021-07-27(in Chinese). [5] 邢宝玉, 白淳升. 基于GPU恶意挖矿行为的检测方法与装置: CN202010578925. XA[P]. 2020-06-23.XING B Y, BAI C S. Method and apparatus for detecting GPU malicious mining behavior based on extracted redundant strings: CN202010578925. XA[P]. 2020-06-23(in Chinese). [6] 余文珣, 余斯聪, 钟英南, 等. 一种基于流量特征识别挖矿程序的方法和系统: CN202010123819.2[P]. 2020-10-12.YU W X, YU S C, ZHONG Y N, et al. A method and system for identifying mining programs based on traffic characteristics: CN202010123819.2[P]. 2020-10-12(in Chinese). [7] 杨家海, 张世泽, 王之梁, 等. 基于时间序列追踪的挖矿流量检测方法和装置 CN202110203327.9[P] . 2021-10-20.YANG J H, ZHANG S Z, WANG Z L, et al. Mining traffic detection method and device based on time series tracking CN202110203327.9[P]. 2021-10-20(in Chinese). [8] PERDISCI R, LEE W K, FEAMSTER N. Behavioral clustering of HTTP-based malware and signature generation using malicious network traces[C]//Proceedings of the 7th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation. New York: ACM, 2010: 26. [9] BEDDOE M A. Network protocol analysis using bioinformatics algorithms[EB/OL]. (2004-06-01)[2021-10-12]. http://phreakocious.net/PI/PI.pdf. [10] 李峻辰, 程光, 杨刚芹. 基于网络流量的私有协议逆向技术综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(1): 167-190. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202110722LI J C, CHENG G, YANG G Q. Review of private protocol reverse technology based on network traffic[J]. Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60(1): 167-190(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202110722 [11] BOSSERT G, GUIHERY F, HIET G. Towards automated protocol reverse engineering using semantic information[C]//Proceedings of the 9th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2014: 51-62. [12] 黎敏, 余顺争. 抗噪的未知应用层协议报文格式最佳分段方法[J]. 软件学报, 2013, 24(3): 604-617.LI M, YU S Z. Noise-tolerant and optimal segmentation of message formats for unknown application-layer protocols[J]. Journal of Software, 2013, 24(3): 604-617(in Chinese). [13] DE CARLI L, TORRES R, MODELO-HOWARD G, et al. Botnet protocol inference in the presence of encrypted traffic[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-9. [14] BERNAILLE L, TEIXEIRA R. Early recognition of encrypted applications[C]//Proceedings of the Passive and Active Network Measurement. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 165-175. [15] DAINOTTI A, PESCAPE A, CLAFFY K C. Issues and future directions in traffic classification[J]. IEEE Network, 2012, 26(1): 35-40. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2012.6135854 [16] VELAN P, ČERMÁK M, ČELEDA P, et al. A survey of methods for encrypted traffic classification and analysis[J]. Networks, 2015, 25(5): 355-374. [17] DRAPER-GIL G, LASHKARI A H, MAMUN M S I, et al. Characterization of encrypted and VPN traffic using time-related features[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy. Setúbal: SciTePress, 2016: 407-414. [18] 李慧慧, 张士庚, 宋虹, 等. 结合多特征识别的恶意加密流量检测方法[J]. 信息安全学报, 2021, 6(2): 129-142.LI H H, ZHANG S G, SONG H, et al. Robust malicious encrypted traffic detection based with multiple features[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2021, 6(2): 129-142(in Chinese). [19] LOTFOLLAHI M, SIAVOSHANI M J, ZADE R S H, et al. Deep packet: A novel approach for encrypted traffic classification using deep learning[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24(3): 1999-2012. doi: 10.1007/s00500-019-04030-2 [20] KONDRAK G. N-gram similarity and distance[C]//Proceedings of the String Processing and Information Retrieval. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 115-126. [21] BENOV D M. The Manhattan project, the first electronic computer and the Monte Carlo method[J]. Monte Carlo Methods and Applications, 2016, 22(1): 73-79. doi: 10.1515/mcma-2016-0102 -







 下载:
下载: