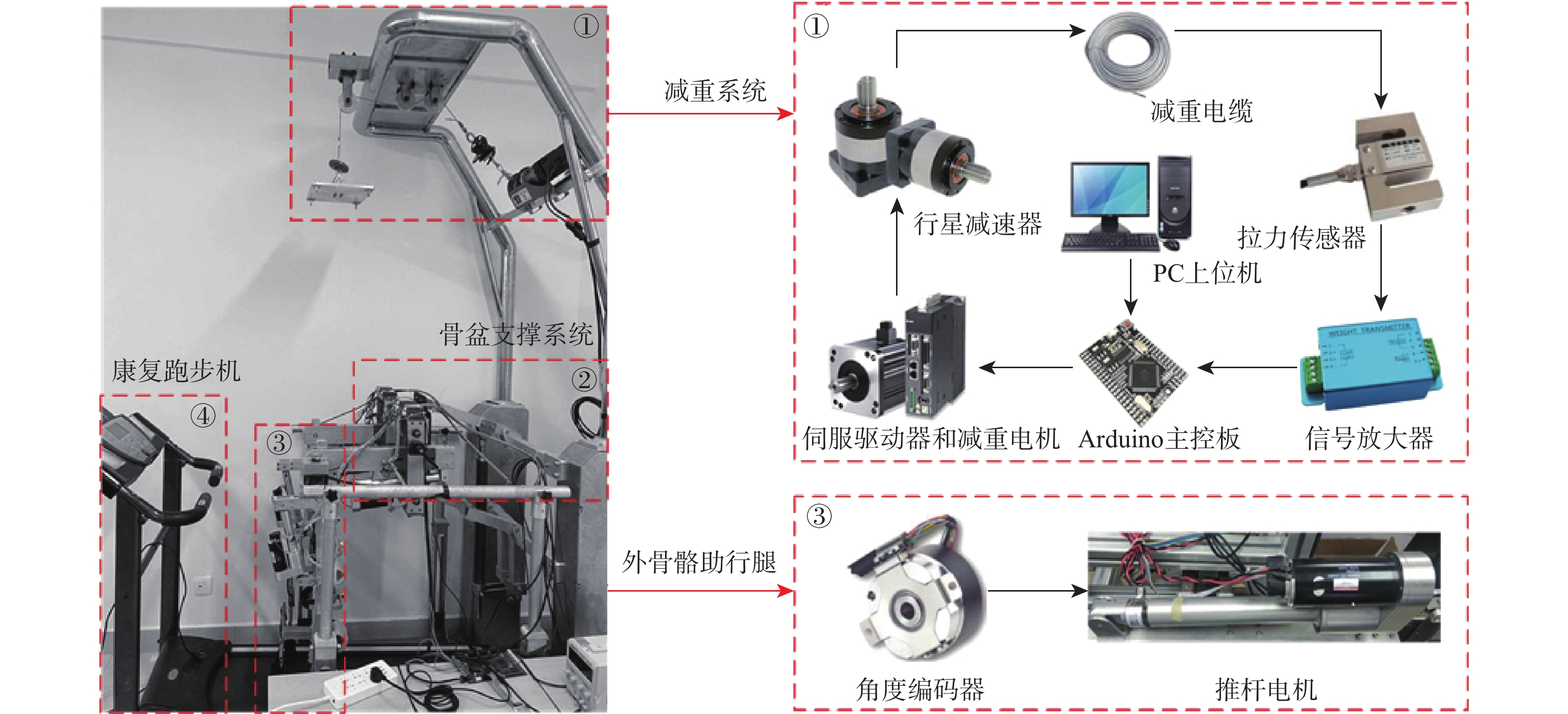
Design of suspension weight-support rehabilitation system adapted to fluctuation of human center of gravity
-
摘要:
减重系统对下肢疾病患者的行走康复训练有重要影响。现有的下肢康复外骨骼减重装置大多只考虑如何减去患者体重的百分比,而忽略了患者身体重心的起伏。由于外骨骼的骨盆支架在竖直方向运动轨迹固定,患者步态的微小变化就会导致重心高度与骨盆支架运动轨迹不符,这一差异会作用到患者的骨盆位置,影响下肢关节的活动,并产生额外的风险。针对这一问题,提出通过采集足底压力来预测重心位置变化,并利用获得的重心轨迹解算出应施加的减重力方法,为患者训练提供安全有效的减重系统。所提方法的可行性已获仿真证实,并在研发的外骨骼减重系统上获得实际验证,模糊控制器跟踪重心轨迹的误差相比PID控制减少了21.2%,稳态误差维持在±1 mm范围内,髋膝关节的活动范围相比常规减重分别增加了14.36%和13.77%。
Abstract:The training that patients undergoing lower limb rehabilitation receive in walking is significantly impacted by the body weight support system. Most of the existing lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton weight support devices only consider how to reduce the percentage of the patient's body weight and ignore the heaving of the patient's center of gravity. Since the pelvic brace of the exoskeleton has a fixed motion trajectory in the vertical direction, small changes in the patient's gait may result in a mismatch between the height of the center of gravity and the motion trajectory of the pelvic brace. This difference can be imposed on the patient's pelvic position, affecting the movement of the lower limb joints and creating additional risks. To solve this problem, plantar pressure was collected to predict the change of center of gravity position, and the obtained center of gravity trajectory was used to calculate the support force that should be applied, so as to provide safe and effective weight reduction for patient training. The feasibility of this method has been verified by simulation and practical verification of the developed exoskeleton support system. When using conventional body weight support, the fuzzy controller’s error in tracking the trajectory of the center of gravity is reduced by 21.2% compared to PID control, the steady-state error is maintained within a 1 mm range, and the range of motion of the hip and knee is increased by 14.36% and 13.77%, respectively.
-
表 1 PID模糊规则
Table 1. PID fuzzy rule
e ec NB NM NS ZO PS PM PB NB PB\NB\PS PB\NB\NS PM\NM\NB PM\NM\NB PS\NS\NB ZO\ZO\NM ZO\ZO\PS NM PB\NB\PS PB\NB\NS PM\NM\NB PS\NS\NM PS\NS\NM ZO\ZO\NS NS\ZO\ZO NS PM\NB\ZO PM\NM\NS PM\NS\NM PS\NS\NM ZO\ZO\NS NS\PS\NS NS\PS\ZO ZO PM\NM\ZO PM\NM\NS PS\NS\NS ZO\ZO\ZO NS\PS\NS NM\PM\NS NM\PM\ZO PS PS\NM\ZO PS\NS\ZO ZO\ZO\ZO NS\PS\ZO NS\PS\ZO NM\PM\ZO NM\PB\ZO PM PS\ZO\PB ZO\ZO\NS NS\PS\PS NM\PS\PS NM\PM\PS NM\PB\PS NB\PB\PB PB ZO\ZO\PB ZO\ZO\PM NM\PS\PM NM\PM\PS NM\PM\PS NB\PB\PS NB\PB\PB 表 2 受试者身体指标
Table 2. Subject physical indicators
性别 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 腿长/cm 男 25 175 62 95 女 24 165 53 88 男 27 183 72 97 表 3 0.6 m/s步速下2种控制方式误差对比
Table 3. Error comparison of two control modes at 0.6 m/s
(°) 受试者 PID控制 模糊控制 髋关节 膝关节 髋关节 膝关节 1 1.4105 3.7834 1.7395 3.1093 2 1.5154 2.6942 0.8095 0.9070 3 1.4226 3.7847 1.8142 3.2301 表 4 1.0 m/s步速下2种控制方式误差对比
Table 4. Error comparison of two control modes at 1.0 m/s
(°) 受试者 PID控制 模糊控制 髋关节 膝关节 髋关节 膝关节 1 3.6020 7.0256 3.3919 6.4750 2 3.6042 6.9877 3.3995 6.4245 3 3.5544 7.0721 3.3667 6.5273 -
[1] DONG Z H, LUCES J V S, HIRATA Y. Control and evaluation of body weight support walker for overground gait training[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 4632-4639. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3068691 [2] KOYAMA T, KAI Y. Development of a walking support system controlled by servo brakes[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-6. [3] LU Q, LIANG J X, QIAO B, et al. A new active body weight support system capable of virtually offloading partial body mass[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(1): 11-20. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2011.2160555 [4] 于宁波, 杨卓, 孙玉波, 等. 一种面向步态和平衡康复训练的单绳悬吊主动减重系统设计与控制方法研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(12): 1819-1831.YU N B, YANG Z, SUN Y B, et al. Design and control of an active gravity offloading system for rehabilitation training of gait and balance[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(12): 1819-1831(in Chinese). [5] GLAUSER M, LIN Z L, ALLAIRE P E. Modeling and control of a partial body weight support system: an output regulation approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2010, 18(2): 480-490. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2009.2016953 [6] PENNYCOTT A, WYSS D, VALLERY H, et al. Effects of added inertia and body weight support on lateral balance control during walking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-5. [7] 何秉泽, 石萍, 李新伟, 等. 一种跟随人体重心高度的骨盆支撑减重康复系统[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2022, 39(1): 175-184.HE B Z, SHI P, LI X W, et al. A pelvic support weight rehabilitation system tracing the human center of mass height[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 39(1): 175-184(in Chinese). [8] LING Y, XUE Y, XING J G, et al. Experimental studies on static postural balance using the body center of gravity test system[C]//Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Future Information and Communication Technologies for Ubiquitous HealthCare. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1-5. [9] SONG Z D, CHEN W, WANG W B, et al. Dynamic modeling and simulation of a body weight support system[J]. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2020, 2020: 2802574. [10] SHIMBA T. An estimation of center of gravity from force platform data[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 1984, 17(1): 53-60. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(84)90080-0 [11] 杨辉, 章亚男, 沈林勇, 等. 下肢康复机器人减重支撑系统的研究[J]. 机电工程, 2009, 26(7): 28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2009.07.009YANG H, ZHANG Y N, SHEN L Y, et al. Research of the BWS system for lower extremity rehabilitation robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Magazine, 2009, 26(7): 28-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2009.07.009 [12] QIN T, ZHANG L X. Coordinated control strategy for robotic-assisted gait training with partial body weight support[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(8): 2954-2962. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2831-0 [13] BENDA B J, RILEY P O, KREBS D E. Biomechanical relationship between center of gravity and center of pressure during standing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 1994, 2(1): 3-10. doi: 10.1109/86.296348 [14] 梁旭, 王卫群, 苏婷婷, 等. 下肢康复机器人的主动柔顺自适应交互控制[J]. 机器人, 2021, 43(5): 547-556.LIANG X, WANG W Q, SU T T, et al. Active compliant and adaptive interaction control for a lower limb rehabilitation robot[J]. Robot, 2021, 43(5): 547-556(in Chinese). [15] SHARMA K, PALWALIA D K. A modified PID control with adaptive fuzzy controller applied to DC motor[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Information, Communication, Instrumentation and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017, 1: 1-6. [16] KRISHNAN P H, ARJUN M. Control of BLDC motor based on adaptive fuzzy logic PID controller[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-5. [17] LIU B, YAO G, XIAO X B, et al. The research on self-adaptive fuzzy PID controller[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013(373): 1462-1465. [18] ZHANG X, LI J H, OVUR S E, et al. Novel design and adaptive fuzzy control of a lower-limb elderly rehabilitation[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(2): 1-17. [19] 陈豫生, 张琴, 熊蔡华. 截瘫助行外骨骼研究综述: 从拟人设计依据到外骨骼研究现状[J]. 机器人, 2021, 43(5): 585-605.CHEN Y S, ZHANG Q, XIONG C H. From anthropomorphic design basis to exoskeleton research status: A review on walking assist exoskeletons for paraplegics[J]. Robot, 2021, 43(5): 585-605(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: