Rotation binocular stereo rectification algorithm based on hierarchical spatial consistency
-
摘要:
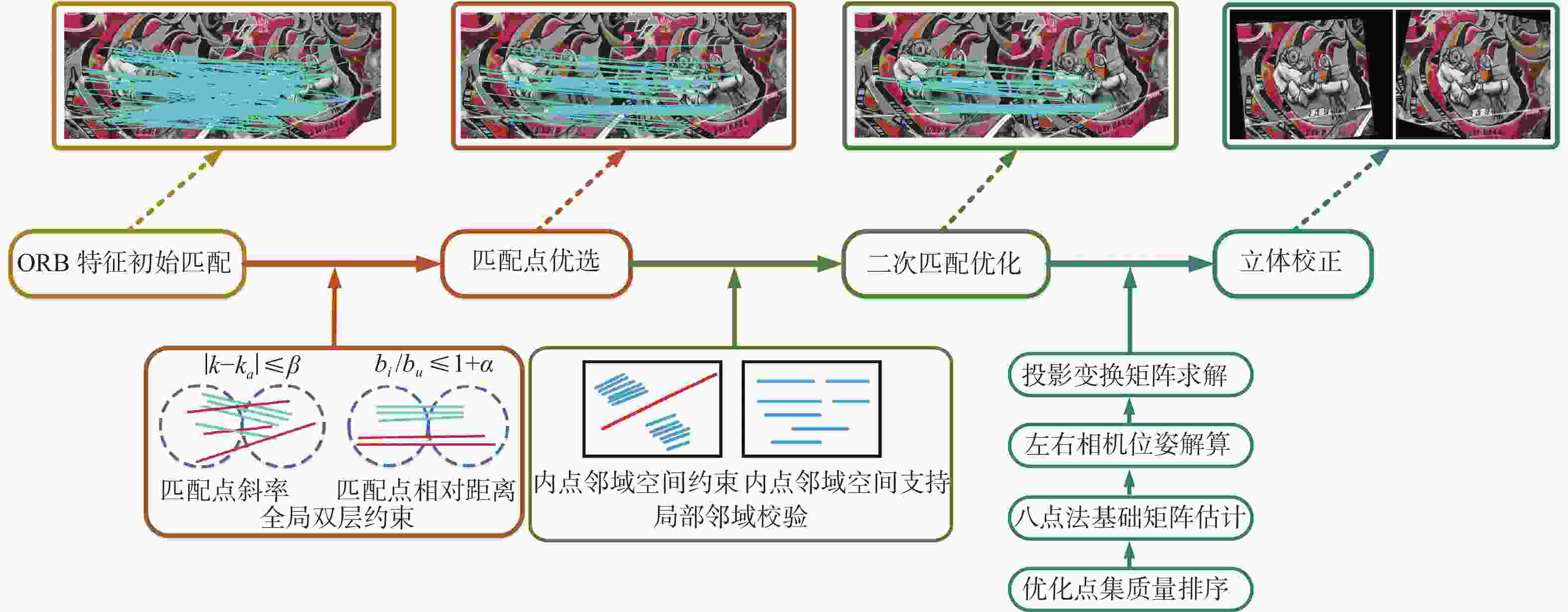
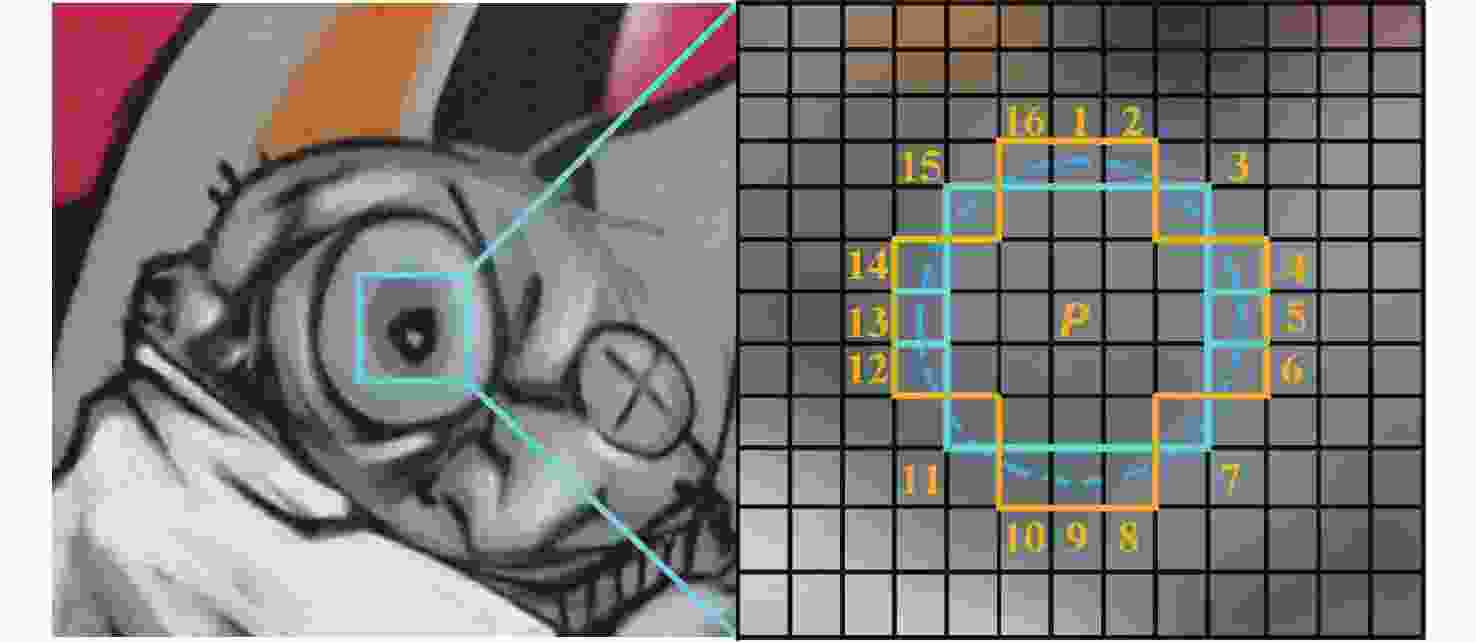
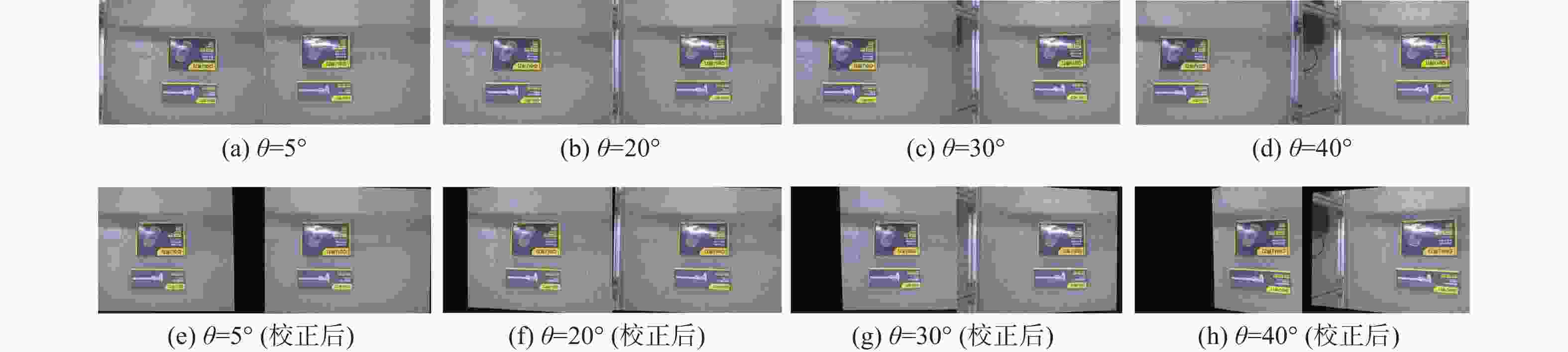
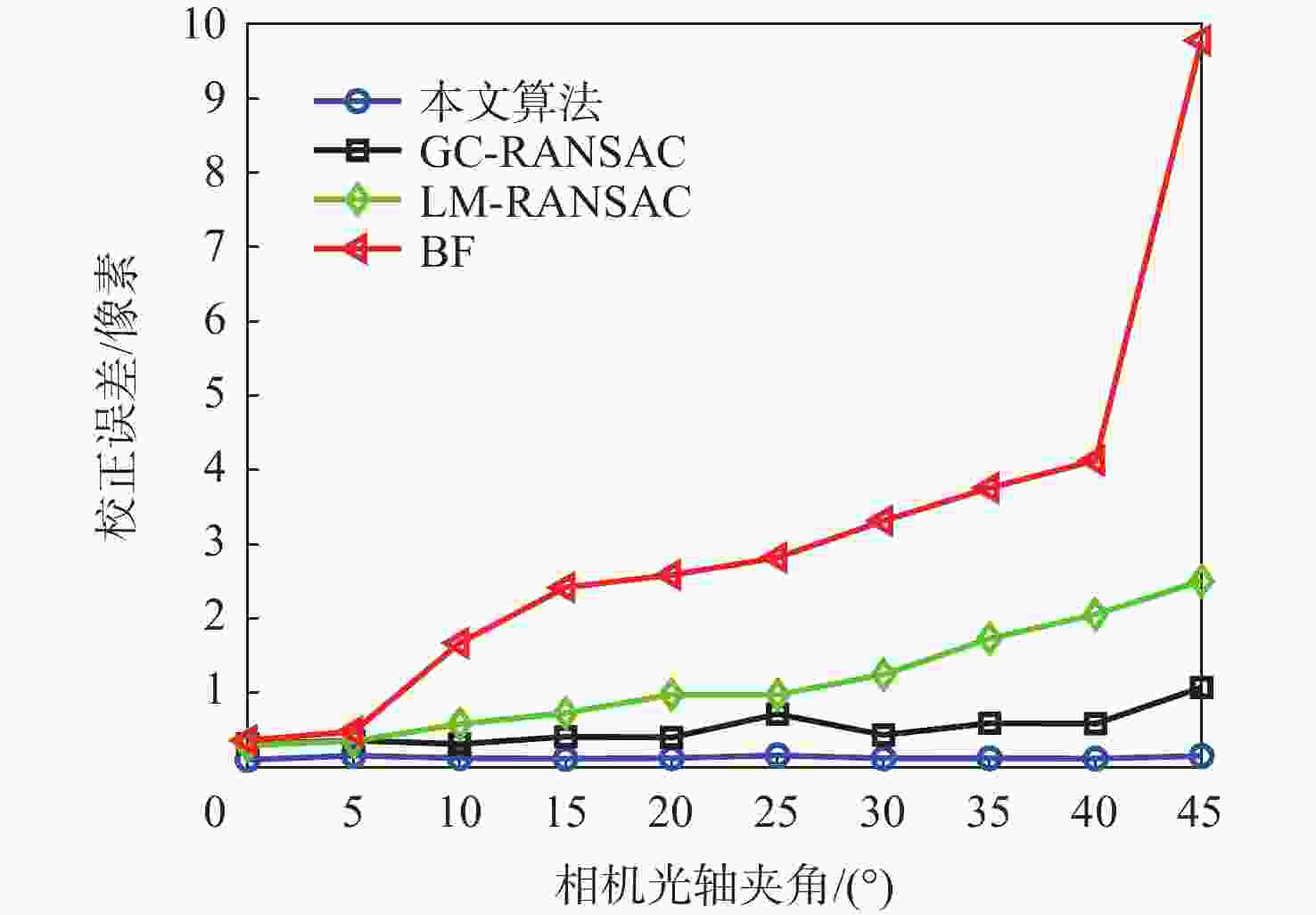
在旋转双目立体视觉系统中,转台机械间隙导致的左右相机旋转平移偏差,造成立体校正图像的严重畸变。针对该问题,提出一种基于分层空间一致性的旋转双目立体校正算法。采用ORB特征在原始左右图像中进行快速全局立体匹配,设计一种新的特征点全局双层约束,实现匹配点的优选。提出基于内点邻域空间一致性的局部校验方法,实现二次匹配优化,并利用质量排序的优化匹配点集,由八点法基础矩阵估计算法计算左右相机的精确位姿关系,以此完成图像的立体校正。在Oxford和SYNTIM数据集上的典型算法对比实验,验证了所提算法的性能。多角度立体校正实验表明:所提算法可适应光轴夹角变化,在双目最大45°夹角时保证立体校正的质量,匹配点偏差小于0.2像素。
Abstract:The mechanical gap of the turntable in the rotating binocular stereo vision system causes the left and right cameras to rotate and deviate in translation, severely distorting the stereo rectification image. To solve this problem, a rotating binocular stereo rectification algorithm based on hierarchical spatial consensus is proposed. Firstly, oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF (ORB) features are used for the fast global stereo matching in the original images, and a new global double-layer constraint of feature points is defined to realize the preferred selection of the matching points. Then, a local verification method based on the consensus of the neighborhood space of the inliers is proposed to realize the secondary matching optimizations and the matching points are optimized by quality sorting. To finish the stereo rectification of the pictures, the eight-point method-based fundamental matrix estimation algorithm determines the precise pose relationship between the left and right cameras. The comparison experiments of typical algorithms on Oxford and SYNTIM datasets verify the proposed algorithm's performance. The multi-angle stereo rectification experiment shows that the proposed algorithm can adapt to the change of optical axis angle, and ensure the quality of stereo rectification when the maximum angle of binocular is 45°. The deviation of the matching point is less than 0.2 pixels.
-
Key words:
- stereo rectification /
- rotating camera /
- fundamental matrix /
- spatial consensus /
- pose estimation
-
表 1 匹配点分层优选和优化
Table 1. Hierarchical selection and optimization of matching points
图像 初始匹配点数 匹配点优选点数 二次匹配优化点数 Graf 400 175 125 表 2 立体校正精度统计
Table 2. Stereo rectification accuracy statistics
像素 校正
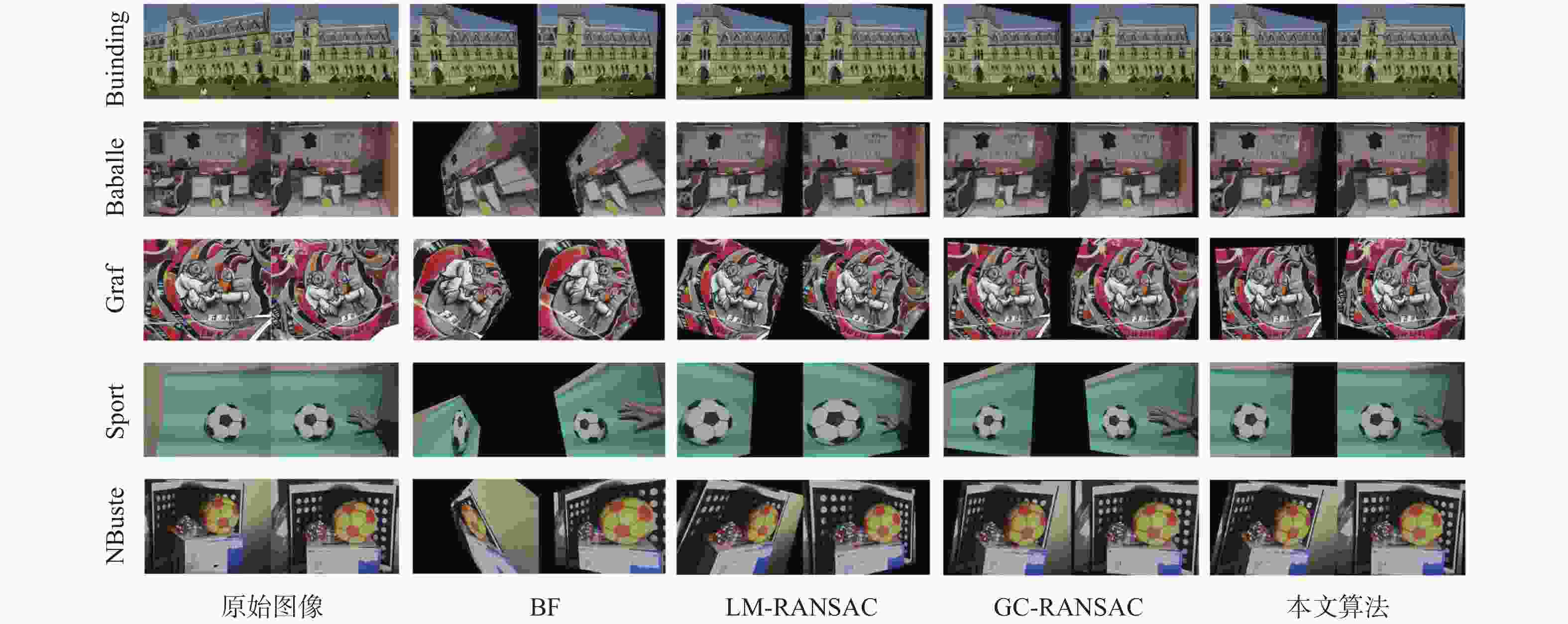
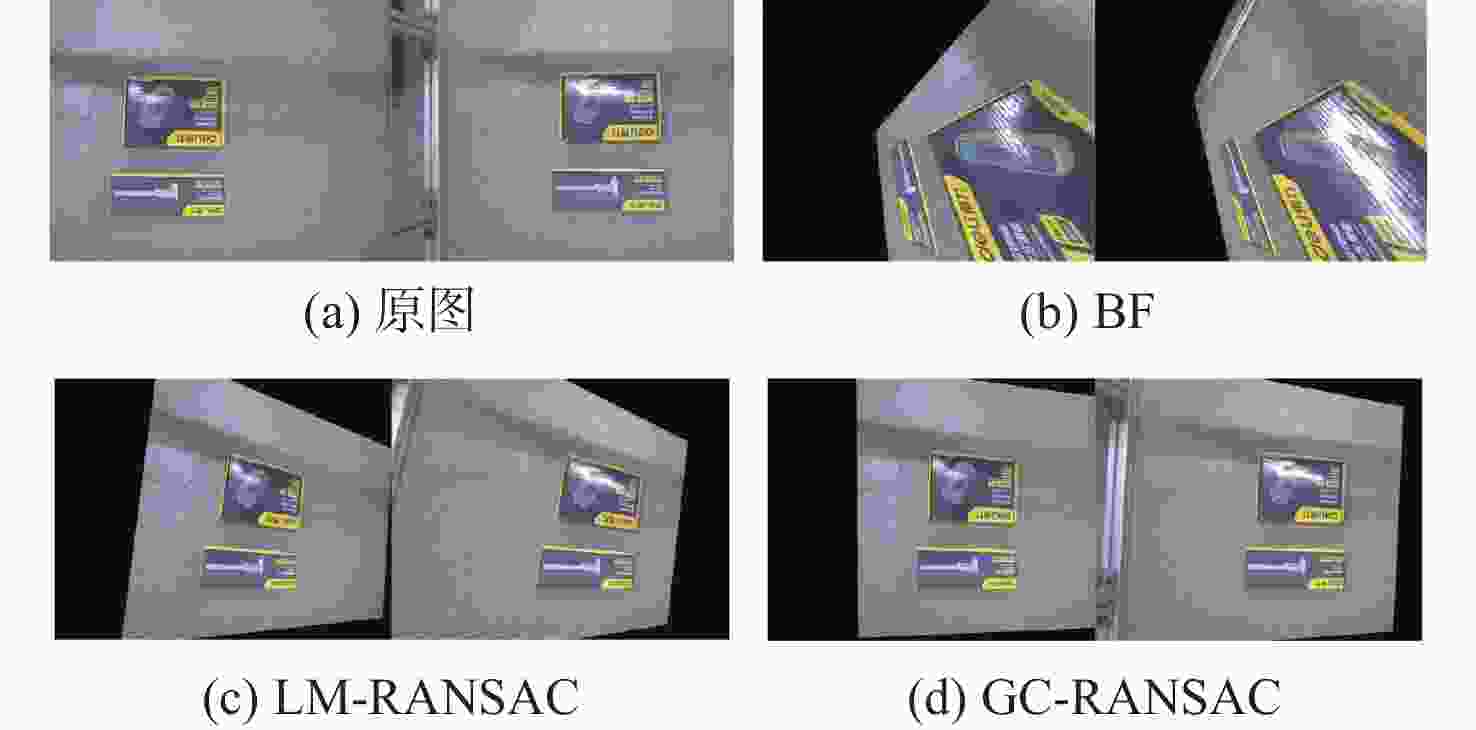
图像EH EM EV BF LM-RANSAC GC-RANSAC 本文 BF LM-RANSAC GC-RANSAC 本文 BF LM-RANSAC GC-RANSAC 本文 Building 7.4649 3.4254 3.1222 0.72 1.4629 0.4515 0.50001 0.1546 2.1609 1.2011 1.22001 0.4501 Baballe 24.4806 5.3412 5.9917 1.20001 3.2711 0.7122 0.6215 0.2056 4.4922 1.5522 1.3271 0.5132 Graf 4.728 2.5999 3.3781 0.7991 1.5077 0.4512 0.3189 0.1921 2.32 0.6801 0.6674 0.2312 Sport 212.004 12.1162 14.5999 3.33 89.3941 3.2433 2.6485 0.4975 86.458 4.1167 3.7247 1.2898 NBuste 234.3337 25.1242 22.5441 18.5327 111.9321 4.2311 2.0577 2.2262 139.2001 5.6822 3.8501 4.1999 -
[1] DINH V Q, MUNIR F, SHERI A M, et al. Disparity estimation using stereo images with different focal lengths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(12): 5258-5270. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2953252 [2] FUSIELLO A, TRUCCO E, VERRI A. A compact algorithm for rectification of stereo pairs[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 2000, 12(1): 16-22. doi: 10.1007/s001380050120 [3] 侯永宏, 王璨, 郭瑶, 等. 一种灵活的立体图像校正方法[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2016, 49(6): 555-561.HOU Y H, WANG C, GUO Y, et al. A flexible rectification for stereo images[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2016, 49(6): 555-561(in Chinese). [4] HARTLEY R I. Theory and practice of projective rectification[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1999, 35(2): 115-127. doi: 10.1023/A:1008115206617 [5] DINH V Q, NGUYEN T P, JEON J W. Rectification using different types of cameras attached to a vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing:a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2019, 28(2): 815-826. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2870930 [6] TRAN T H P, NGUYEN T P, NGUYEN H H, et al. Robust uncalibrated rectification with low geometric distortion under unbalanced field of view circumstances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(2): 1809-1818. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3060673 [7] 刘怡光, 孙柏林, 石勇涛, 等. 用于3维重建的立体图像校正[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2013, 45(3): 79-84.LIU Y G, SUN B L, SHI Y T, et al. Stereo image rectification suitable for 3D reconstruction[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2013, 45(3): 79-84(in Chinese). [8] XIAO C X, LIU M, NIE Y W, et al. Fast exact nearest patch matching for patch-based image editing and processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2011, 17(8): 1122-1134. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2010.226 [9] 黄晨威, 程景春, 潘雄, 等. 基于深度神经网络的像素级别可见光图像配准[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(3): 522-532.HUANG C W, CHENG J C, PAN X, et al. Pixel-wise visible image registration based on deep neural network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(3): 522-532 (in Chinese). [10] BARATH D, MATAS J. Graph- cut ransac[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6733-6741. [11] 郑真真, 徐爱功, 徐辛超, 等. 一种采用最小平方中值的改进极线校正方法[J]. 遥感信息, 2018, 33(2): 71-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2018.02.011ZHENG Z Z, XU A G, XU X C, et al. An improved epipolar rectification method with least Median of squares[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2018, 33(2): 71-77 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2018.02.011 [12] LI X Y, ZHANG B, SANDER P V, et al. Blind geometric distortion correction on images through deep learning[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4850-4859. [13] XUE Z C, XUE N, XIA G S, et al. Learning to calibrate straight lines for fisheye image rectification[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1643-1651. [14] NGUYEN T P, TRAN T H P, JEON J W. MultiLevel feature pooling network for uncalibrated stereo rectification in autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(10): 10281-10290. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3026307 [15] 陈天择, 葛宝臻, 罗其俊. 重投影优化的自由双目相机位姿估计方法[J]. 中国光学, 2021, 14(6): 1400-1409. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0105CHEN T Z, GE B Z, LUO Q J. Pose estimation for free binocular cameras based on reprojection error optimization[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1400-1409(in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0105 [16] XIAO R C, SUN W X, PANG J H, et al. DSR: Direct self-rectification for uncalibrated dual-lens cameras[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 561-569. [17] 王宗盛, 苏志龙, 韩永胜, 等. 基于图像特征分布优化的相机外参自标定[J]. 中国科学(技术科学), 2021, 51(11): 1410-1418. doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0499WANG Z S, SU Z L, HAN Y S, et al. External parameter calibration based on image feature distribution optimization[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2021, 51(11): 1410-1418(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SST-2020-0499 [18] 廖泓真, 王亮, 孙宏伟, 等. 一种改进的ORB特征匹配算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 344(10): 2149-2154.LIAO H Z, WANG L, SUN H W, et al. An improved ORB feature matching algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 344(10): 2149-2154(in Chinese). [19] 孙浩, 王朋. 一种基于区域划分的改进ORB算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(9): 1763-1769.SUN H, WANG P. An improved ORB algorithm based on region division[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(9): 1763-1769(in Chinese). [20] 胡立华, 左威健, 张继福. 采用逆近邻与影响空间的图像特征误匹配剔除方法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2022, 34(3): 449-458.HU L H, ZUO W J, ZHANG J F. A mismatch elimination method based on reverse nearest neighborhood and influence space[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics 2022, 34(3): 449-458(in Chinese). [21] JIANG X Y, MA J Y, JIANG J J, et al. Robust feature matching using spatial clustering with heavy outliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29(29): 736-746. [22] BARATH D, MATAS J. Graph-cut RANSAC: Local optimization on spatially coherent structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 4961-4974. -






 下载:
下载: