-
摘要:
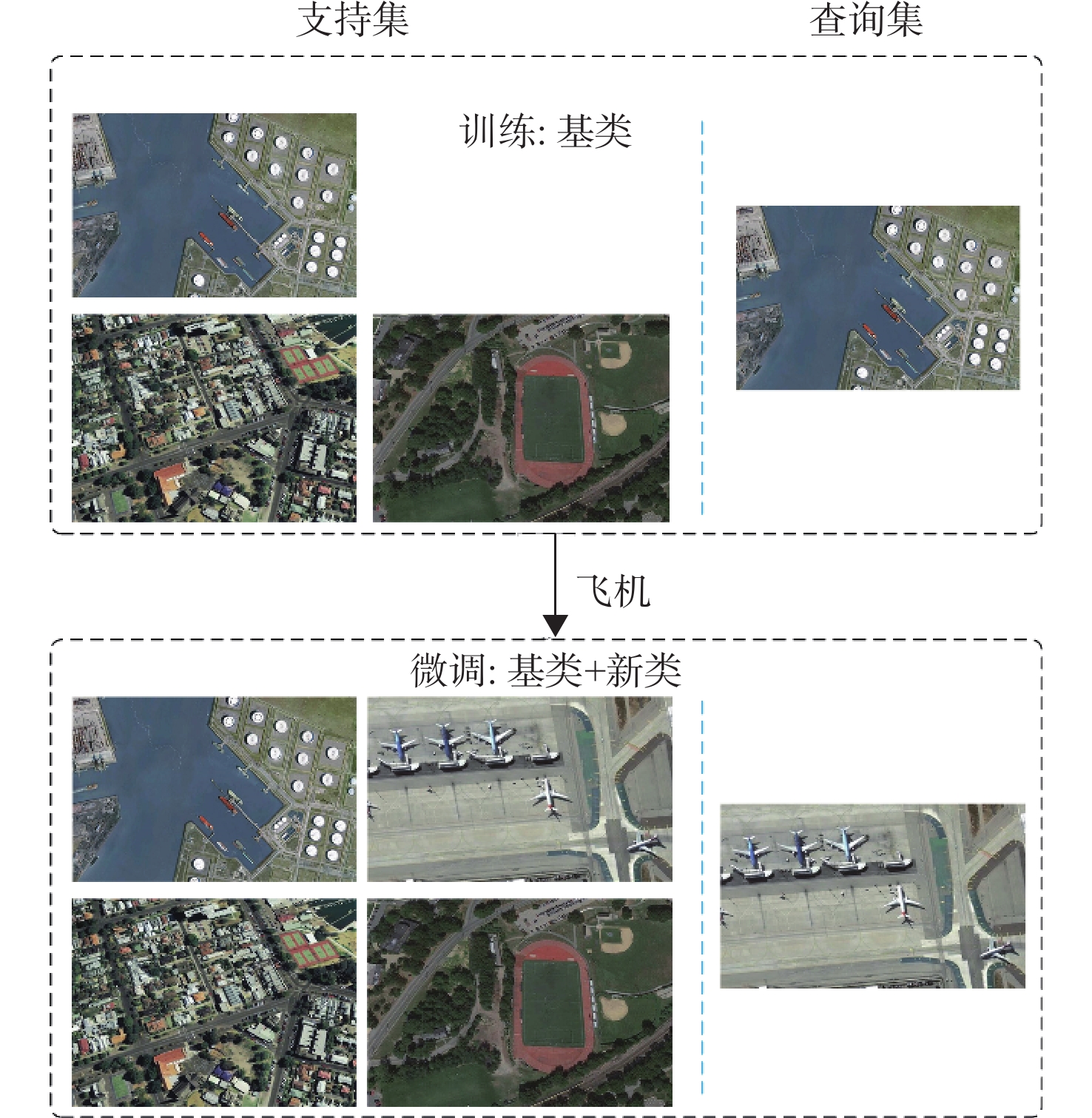
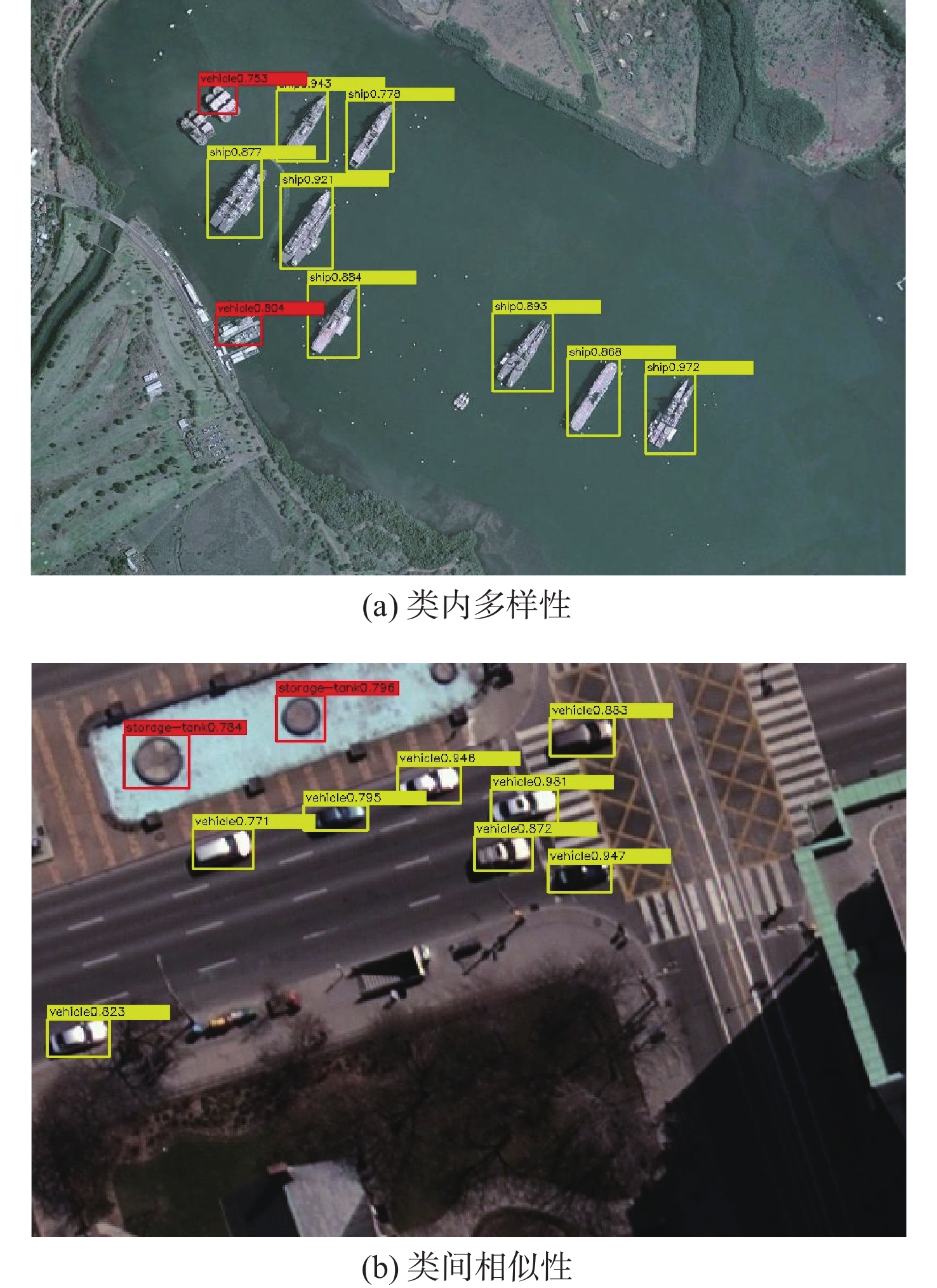
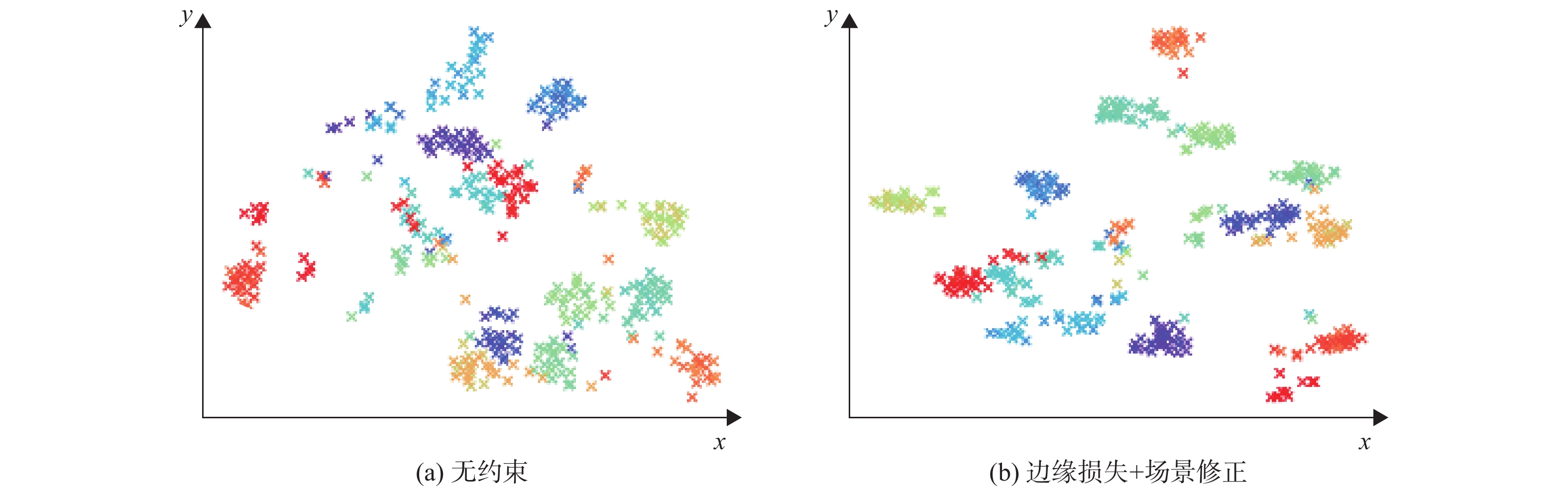
面向小样本条件下的遥感图像目标检测任务,提出一种基于元学习的小样本遥感图像目标检测算法。针对遥感图像中目标尺度变化大、小样本条件下目标与背景易混淆的问题,在特征提取部分将单尺度重加权拓展为多尺度重加权模块,充分引入支持样本的先验知识以适应不同目标的尺度变化;为解决遥感图像目标类间相似性和类内差异性的问题,利用目标对于场景的依赖性设计了场景修正模块,对检出目标类别进行修正,并引入边际损失对特征空间内不同目标的特征分布进行约束。实验结果表明:所提算法在10样本任务设定上获得了较高的检测性能,在NWPU VHR-10和DIOR数据集新类别上的平均精度(mAP)分别达到了64.18%和37.27%。
Abstract:This study introduces meta-learning technology to propose a meta-learning-based few-shot object detection algorithm for the few-shot item detection job in remote sensing photos. The object and background are easily confused under the condition of large-scale changes and small samples in remote sensing images. To solve this issue, we expand the single-scale re-weighting into a multi-scale re-weighting module in the feature extraction part, where the prior knowledge of supporting samples can be adapted to different objects. In order to solve the problem of large inter-class similarities and intra-class differences among remote sensing objects, a scene correction module is designed by leveraging the dependence relationship between the object and scene to correct the detected object’s category. In order to restrict the feature distributions of various objects, we additionally incorporate the marginal loss to the feature space. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves high detection performance on the 10-shot task setting, achieving mean average precision (mAP) of 64.18% and 37.27% on the new category of NWPU VHR-10 and DIOR datasets, respectively.
-
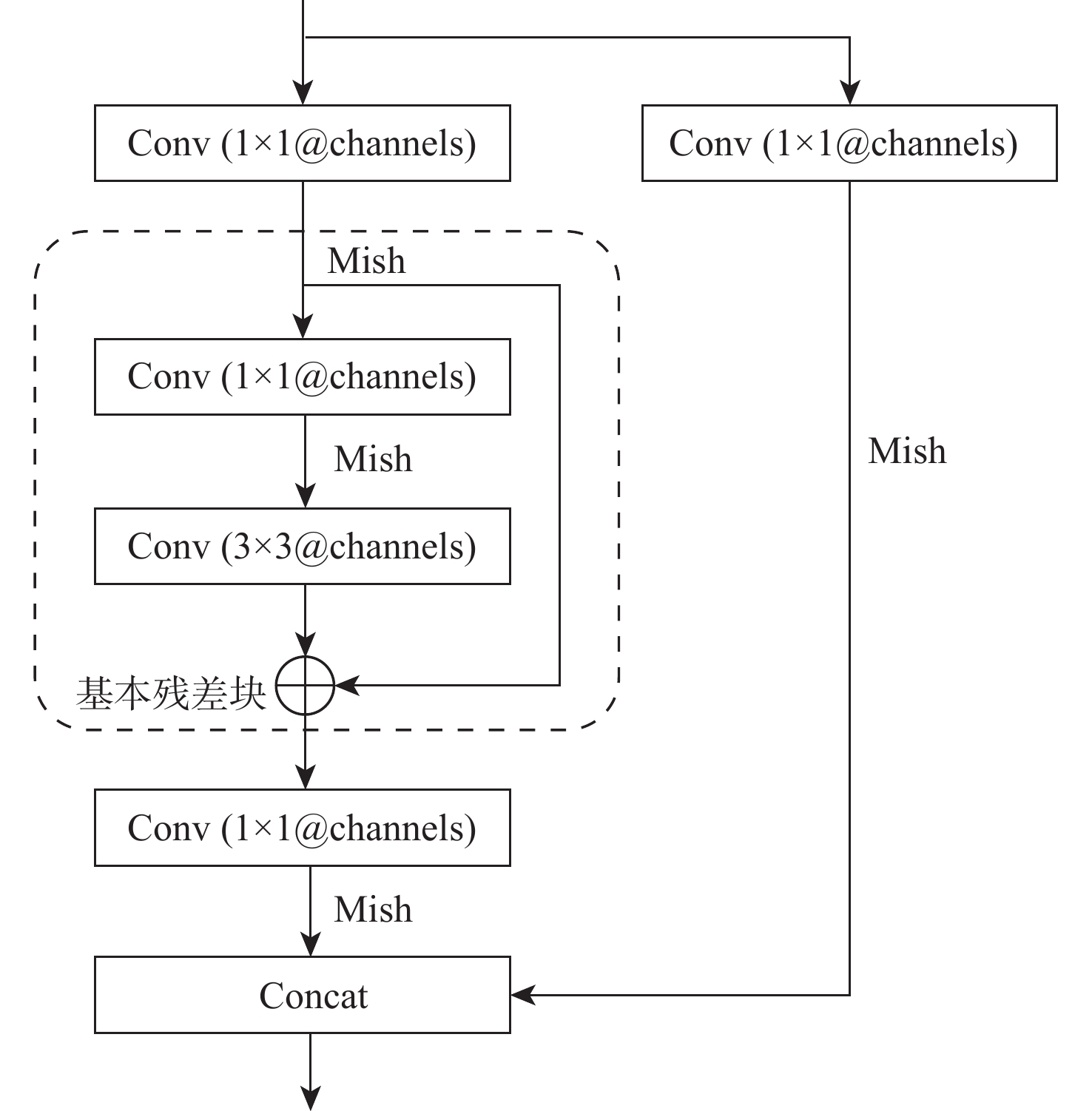
表 1 重加权向量生成网络结构
Table 1. Structure of reweighted vector generation network
网络层 输出维度 是否重加权 标志 Input 4×512×512 否 Conv1 + Maxpooling 32×256×256 否 Conv2 + Maxpooling 64×128×128 否 Conv3 + Maxpooling 128×64×64 否 Conv4 + Maxpooling 256×32×32 否 Conv5 + CAM 256×1×1 是 通道 Route from Conv4 256×32×32 否 Conv6 + SAM 256×64×64 是 空间 Route with Conv4 256×32×32 否 Conv7 + Maxpooling 512×16×16 否 Conv8 + CAM 512×1×1 是 通道 Route from Conv7 512×16×16 否 Conv9 + SAM 512×32×32 是 空间 Route with Conv7 512×16×16 否 Conv10 + Maxpooling 1024 ×8×8否 Conv11 + CAM 1024 ×1×1是 通道 Route from Conv10 1024 ×8×8否 Conv9 + SAM 1024 ×16×16是 空间 表 2 多尺度重加权的有效性验证
Table 2. Effectiveness of the multiscale reweighting
样本/个 单尺度通道
mAP/%多尺度通道
mAP/%多尺度空间+通道
mAP/%3 13.17 26.36 29.52 5 26.22 49.03 51.44 10 37.10 61.74 62.85 表 3 边际损失和场景修正的有效性验证
Table 3. Effectiveness of marginal loss and scene correction
样本/个 无约束
mAP/%边际损失
mAP/%场景修正+
边际损失mAP/%1 10.17 9.87 10.32 3 29.52 30.37 33.42 5 51.44 52.03 54.58 10 62.85 62.98 64.18 表 4 本文算法与其他算法的性能对比
Table 4. Comparison results with other algorithms
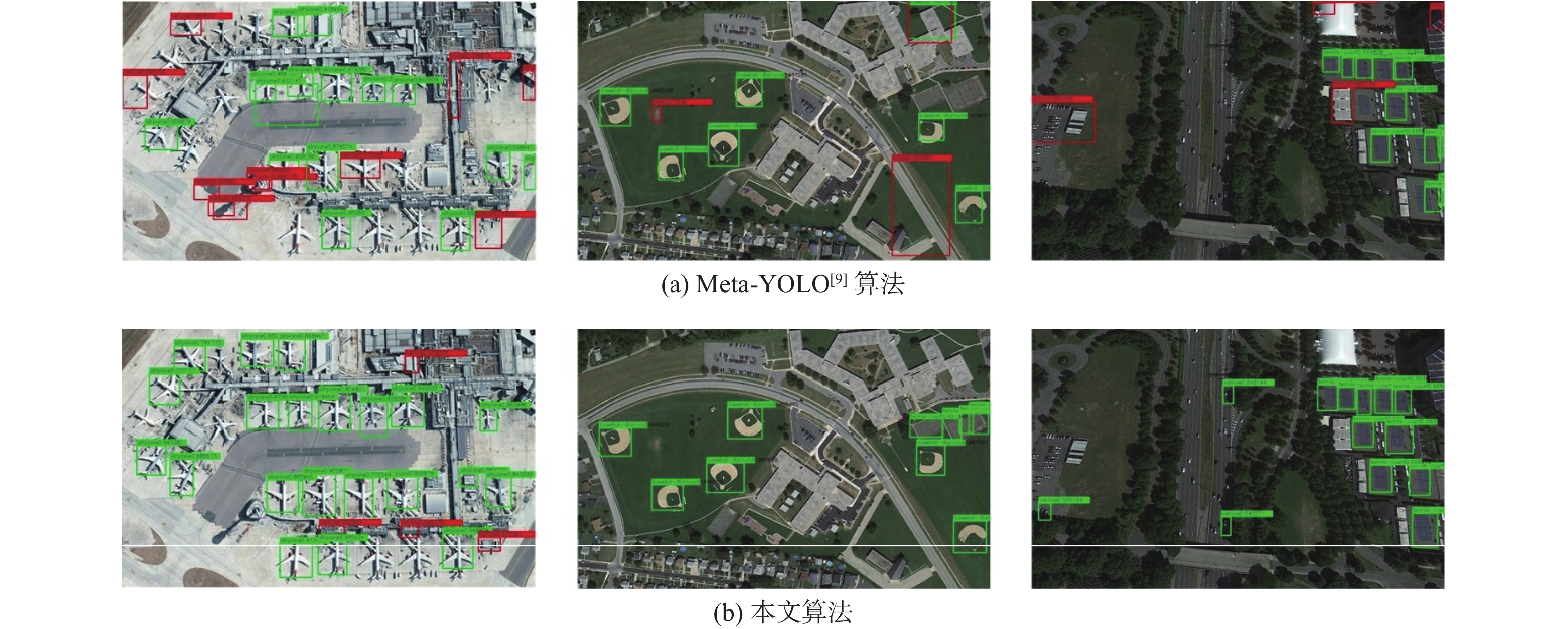
% 数据集 类别 YOLOv4[14]算法 mAP Meta-YOLO[9]算法 mAP 本文算法mAP 5样本 10样本 3样本 5样本 10样本 3样本 5样本 10样本 NWPU VHR-10[24] airplane 14.22 13.27 20.17 20.52 17.87 44.53 51.11 baseball-diamond 26.05 14.73 43.64 74.38 55.69 83.45 90.71 tennis-court 4.45 11.52 14.85 16.42 26.71 35.76 50.73 mean 14.91 13.17 26.22 37.10 33.42 54.58 64.18 DIOR[25] airplane 2.55 7.56 9.04 15.04 11.93 15.93 19.16 baseballfield 32.25 27.35 33.37 45.63 30.57 39.06 51.29 Tennis-court 29.61 40.48 47.23 54.44 57.54 63.41 65.13 trainstation 1.79 8.62 9.27 7.98 11.35 13.52 19.25 windmill 4.84 9.05 13.35 18.21 20.83 27.56 31.53 mean 14.21 18.61 22.45 28.26 26.64 32.09 37.27 -
[1] 聂光涛, 黄华. 光学遥感图像目标检测算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 1749-1768.NIE G T, HUANG H. A survey of object detection in optical remote sensing images[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1749-1768(in Chinese). [2] ZHANG R Q, SHAO Z F, HUANG X, et al. Adaptive dense pyramid network for object detection in UAV imagery[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 489: 377-389. [3] 张振伟, 郝建国, 黄健, 等. 小样本图像目标检测研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(5): 1-11.ZHANG Z W, HAO J G, HUANG J, et al. Review of few-shot object detection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(5): 1-11(in Chinese). [4] 赵永强, 饶元, 董世鹏, 等. 深度学习目标检测方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(4): 629-654.ZHAO Y Q, RAO Y, DONG S P, et al. Survey on deep learning object detection[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(4): 629-654(in Chinese). [5] 谢富, 朱定局. 深度学习目标检测方法综述[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2022, 31(2): 1-12.XIE F, ZHU D J. Survey on deep learning object detection[J]. Computer Systems and Applications, 2022, 31(2): 1-12 (in Chinese). [6] WU J X, LIU S T, HUANG D, et al. Multi-scale positive sample refinement for few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 456-472. [7] CHEN H, WANG Y L, WANG G Y, et al. LSTD: A low-shot transfer detector for object detection[J]. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 32(1): 2836-2843. [8] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [9] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 28. [10] KARLINSKY L, SHTOK J, HARARY S, et al. RepMet: Representative-based metric learning for classification and few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5192-5201. [11] KANG B Y, LIU Z, WANG X, et al. Few-shot object detection via feature reweighting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8419-8428. [12] YAN X P, CHEN Z L, XU A N, et al. Meta R-CNN: Towards general solver for instance-level low-shot learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9576-9585. [13] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6517-6525. [14] XIAO Z X, QI J H, XUE W, et al. Few-shot object detection with self-adaptive attention network for remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 4854-4865. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3078177 [15] LE JEUNE P, LEBBAH M, MOKRAOUI A, et al. Experience feedback using representation learning for few-shot object detection on aerial images[C]//Proceedings of the 20th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 662-667. [16] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. (2020-04-23) [2021-11-01]. [17] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [18] ZHAO Q J, SHENG T, WANG Y T, et al. M2Det: A single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network[J]. National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 9259-9266. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33019259 [19] LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [20] LI B H, YANG B Y, LIU C, et al. Beyond max-margin: Class margin equilibrium for few-shot object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 7359-7368. [21] ZHENG Z H, WANG P, LIU W, et al. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression[J]. AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 12993-13000. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6999 [22] LI X Y, LI H G, YU R N, et al. Few-shot scene classification with attention mechanism in remote sensing[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Engineering and Innovative Application of VR. Bristol: IOP Publishing, 2021, 1961: 012015. [23] RUBNER Y, TOMASI C, GUIBAS L J. The earth mover’s distance as a metric for image retrieval[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2000, 40(2): 99-121. doi: 10.1023/A:1026543900054 [24] LONG Y, GONG Y P, XIAO Z F, et al. Accurate object localization in remote sensing images based on convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(5): 2486-2498. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2645610 [25] LI K, WAN G, CHENG G, et al. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296-307. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.023 -








 下载:
下载: