-
摘要:
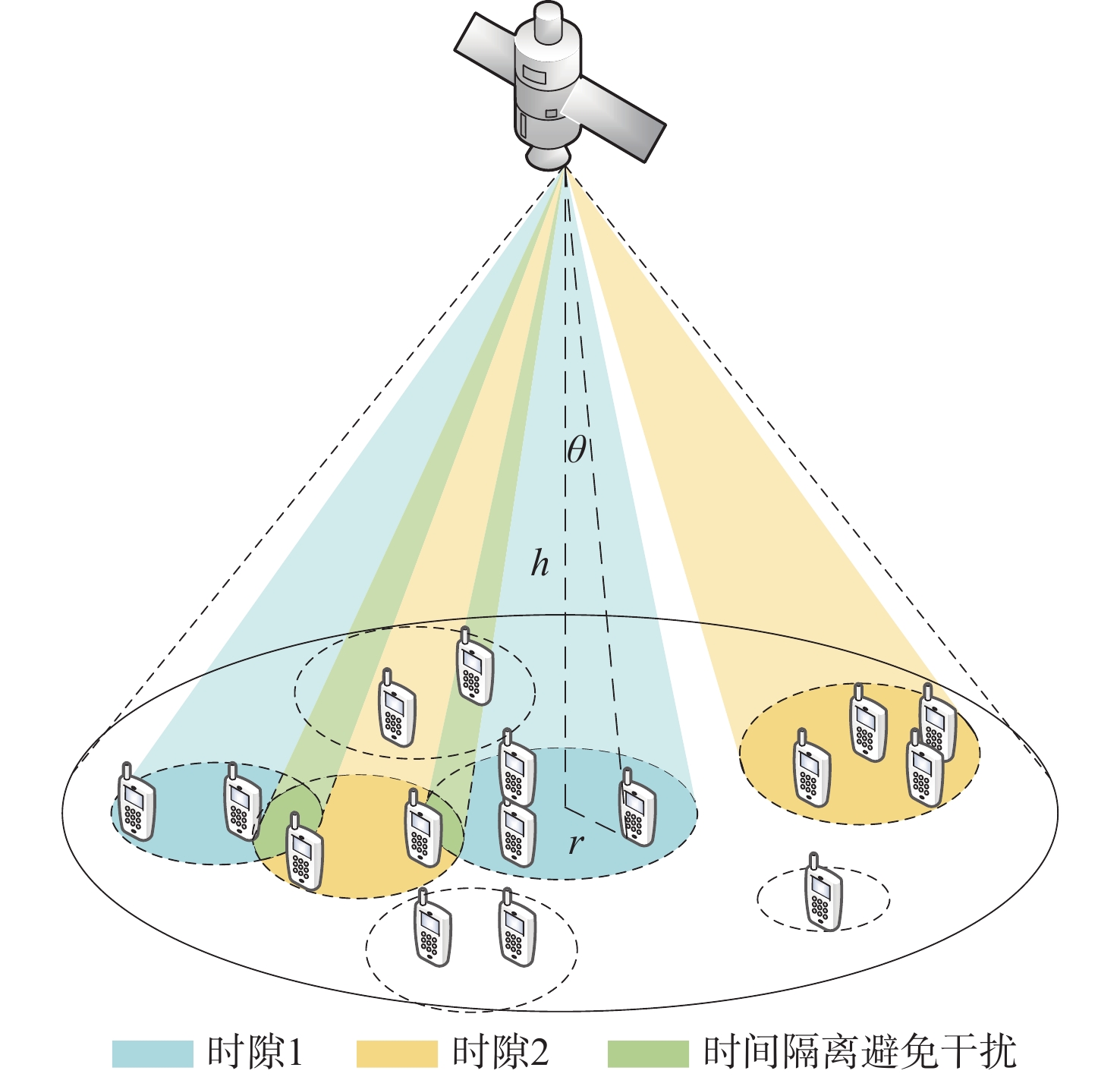
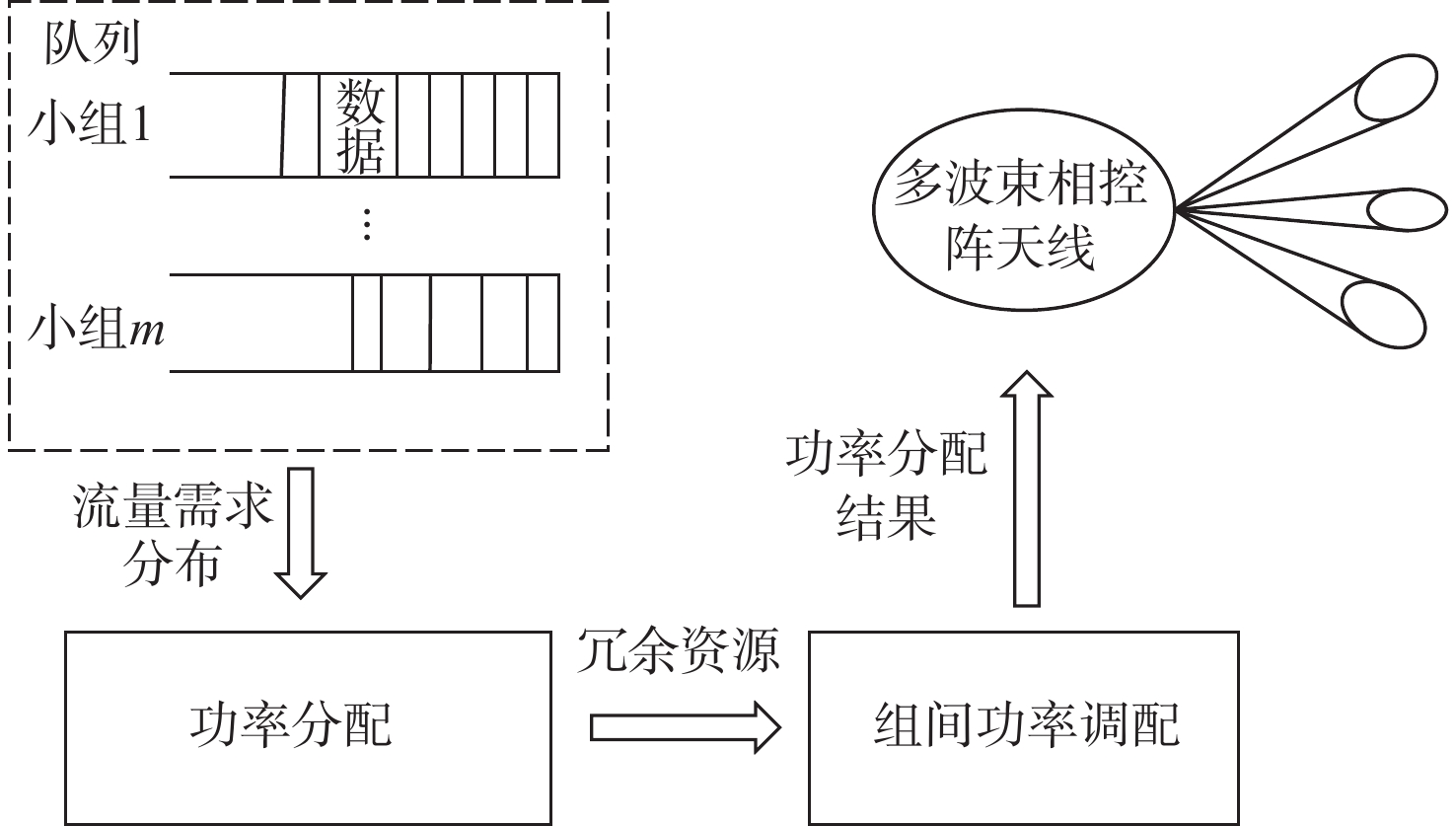
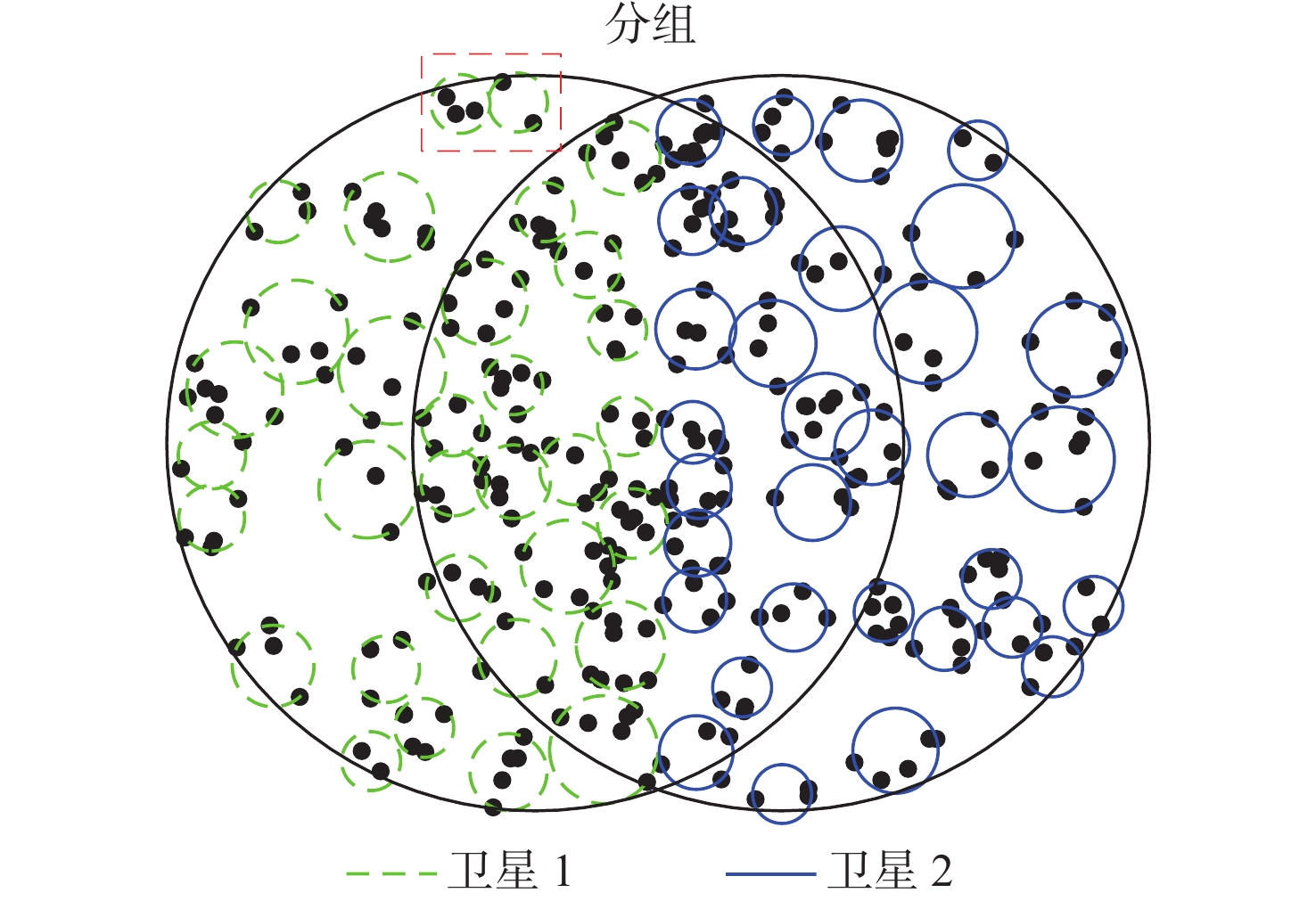
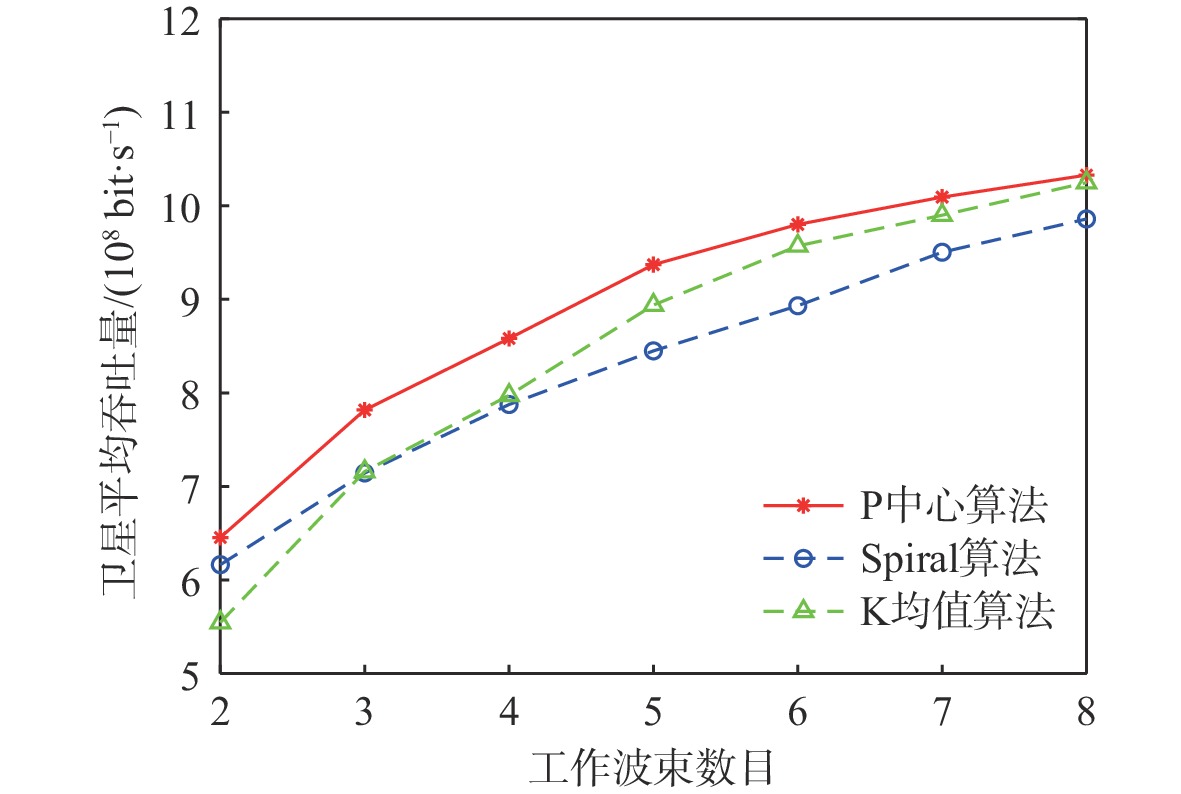
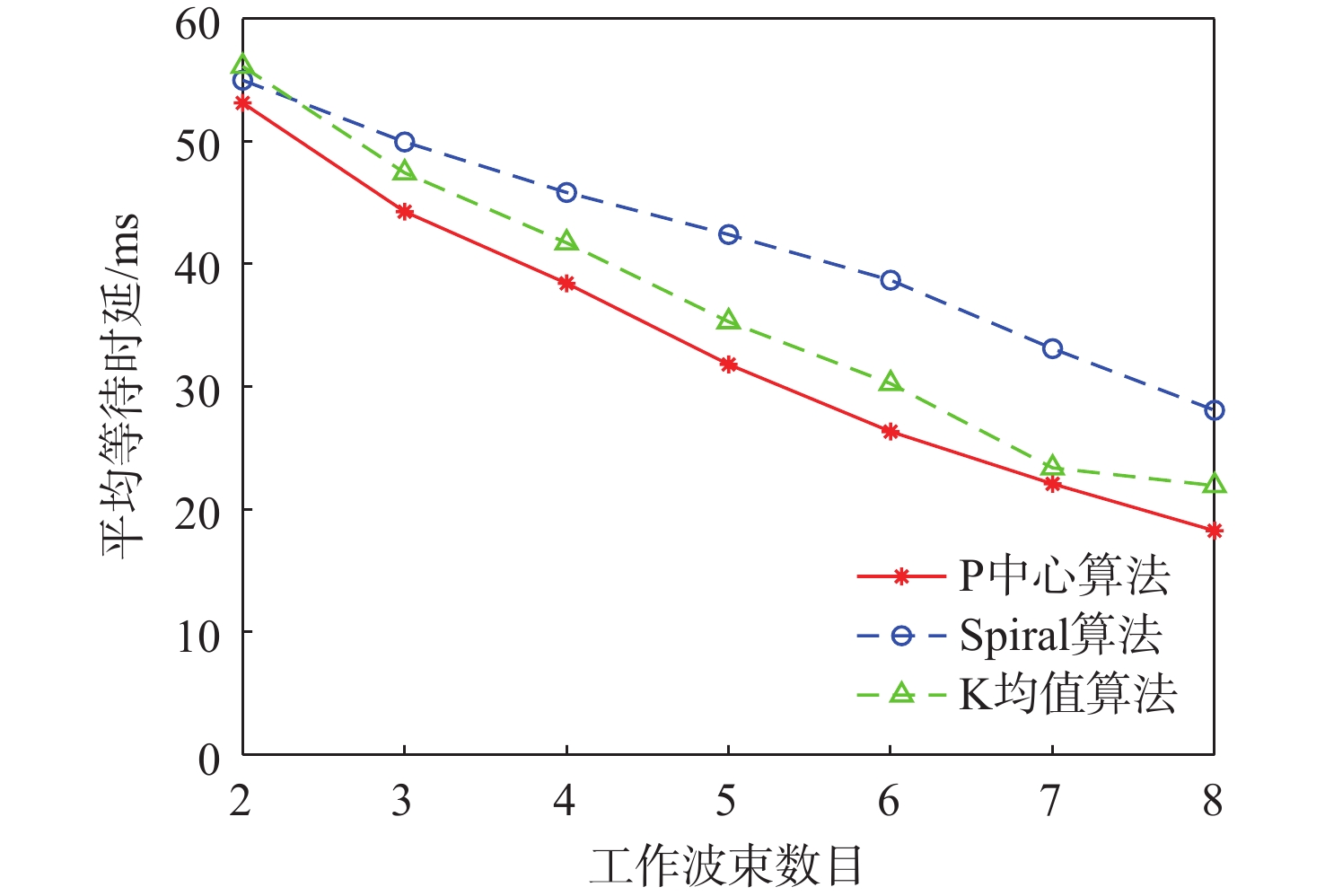
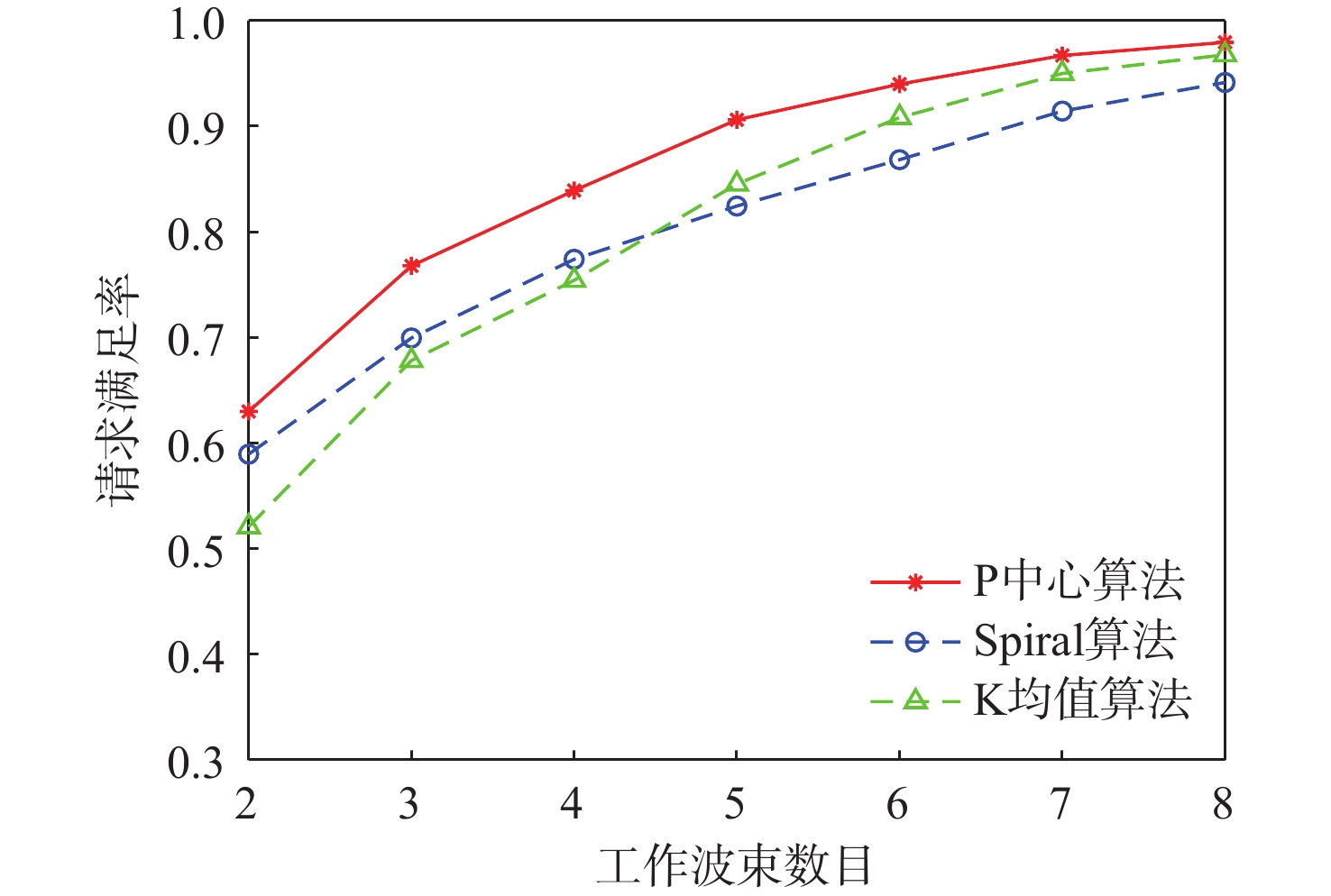
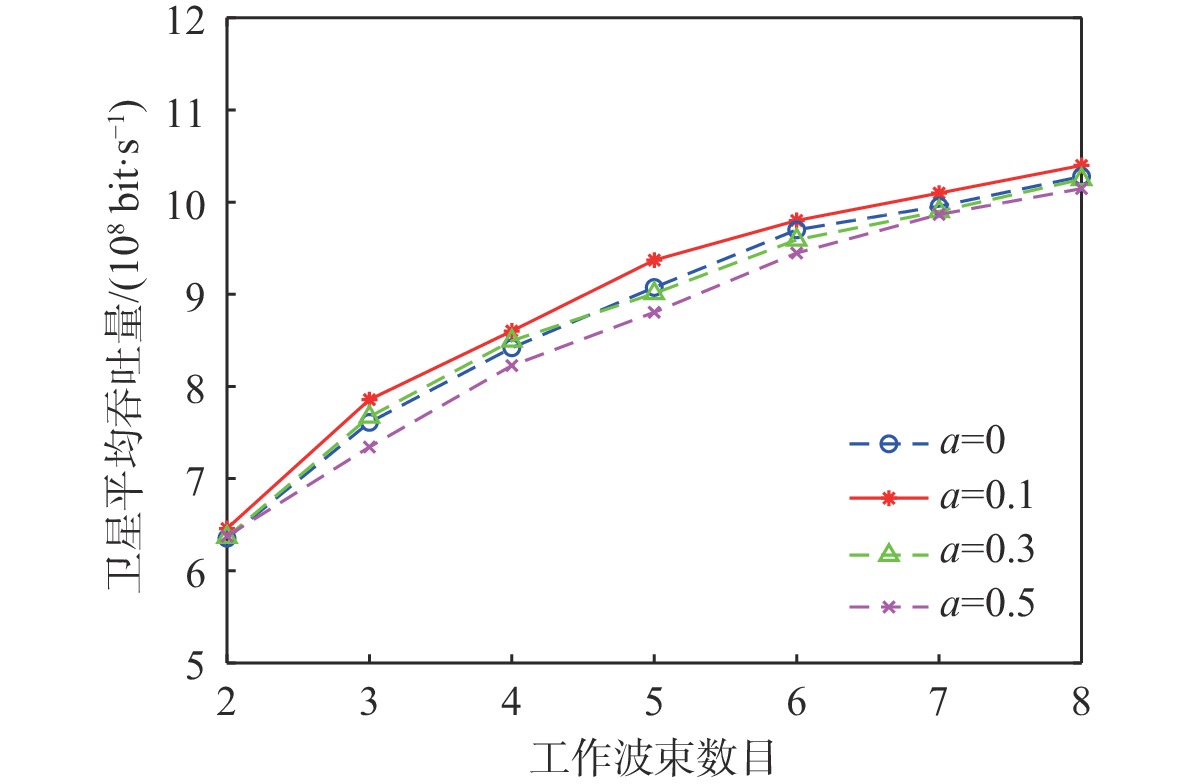
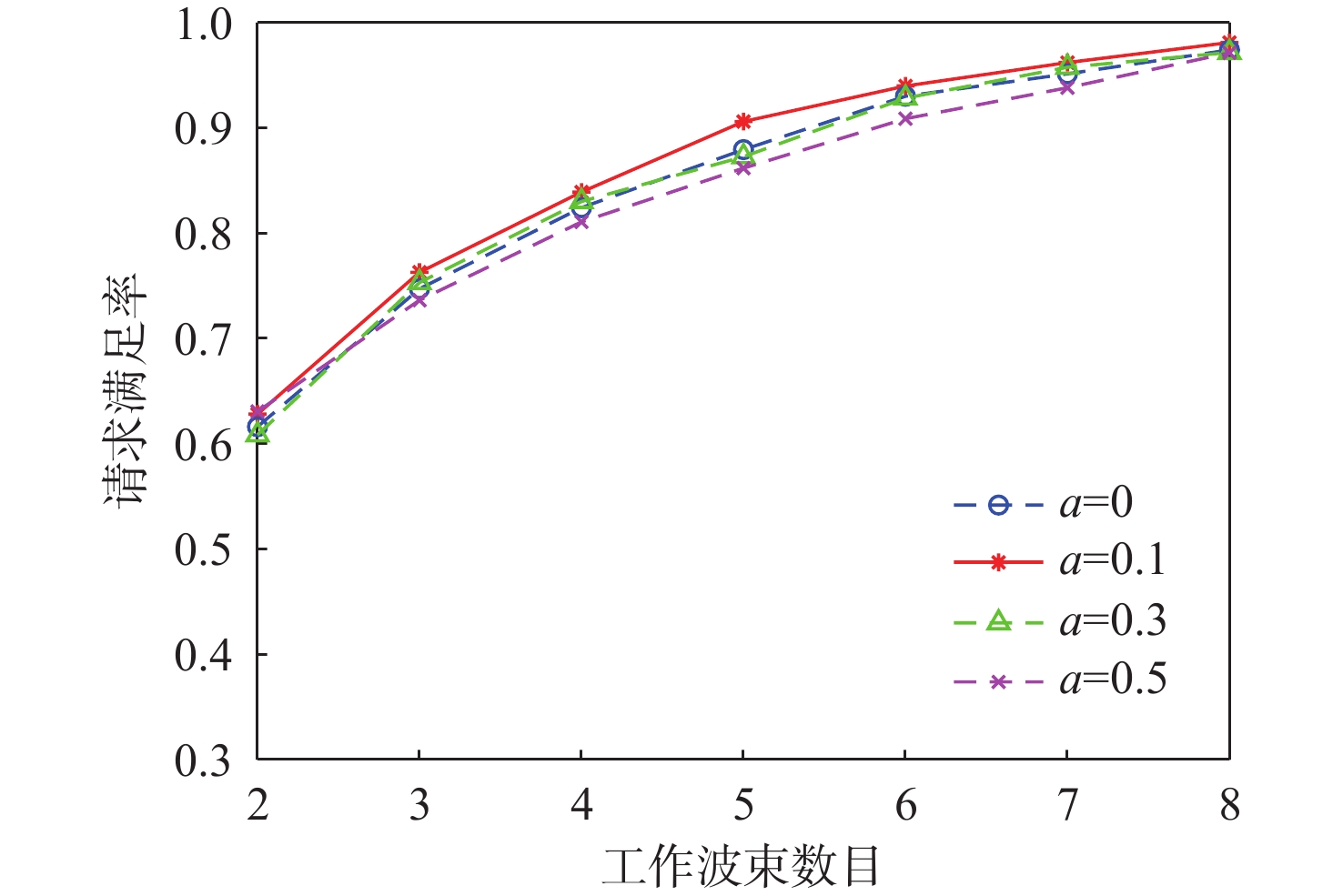
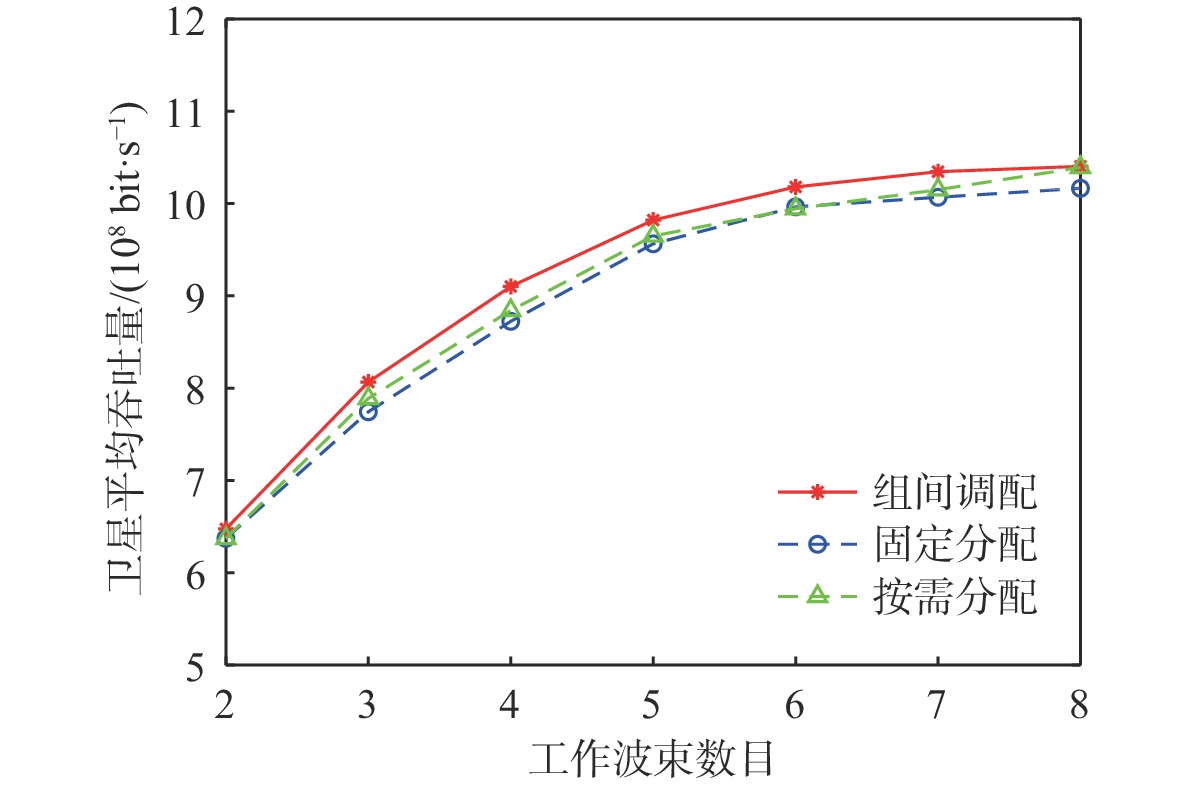
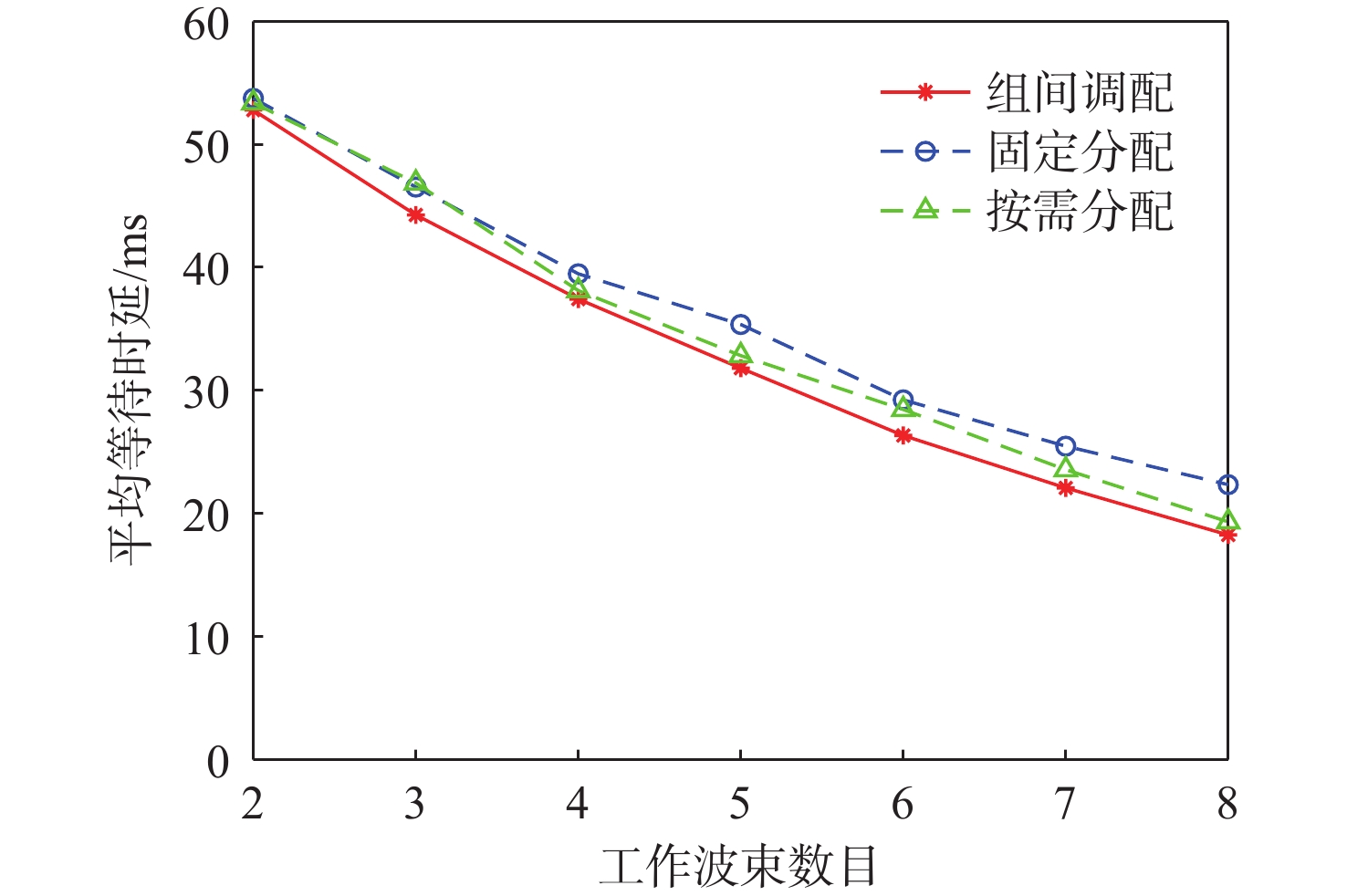
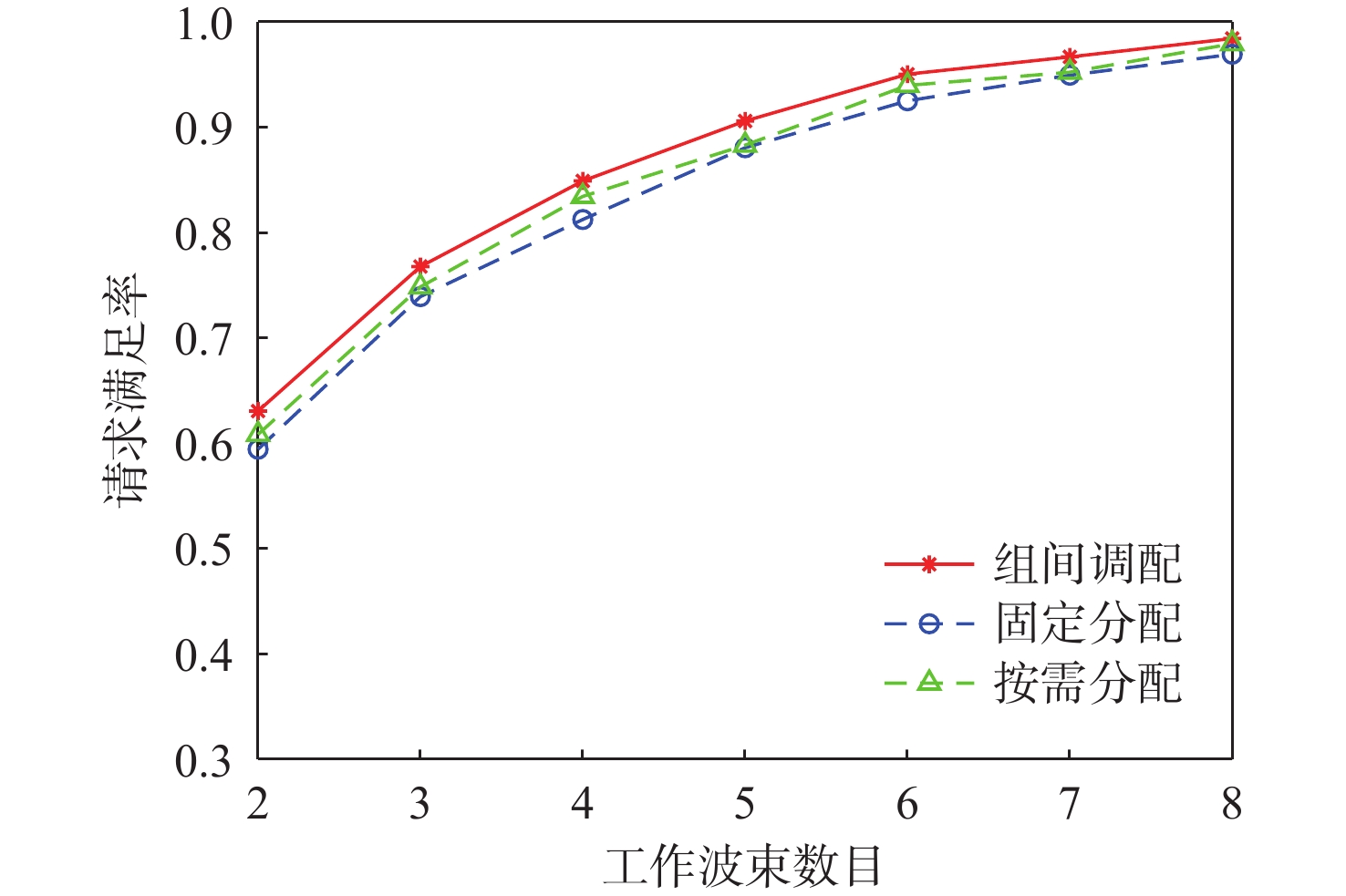
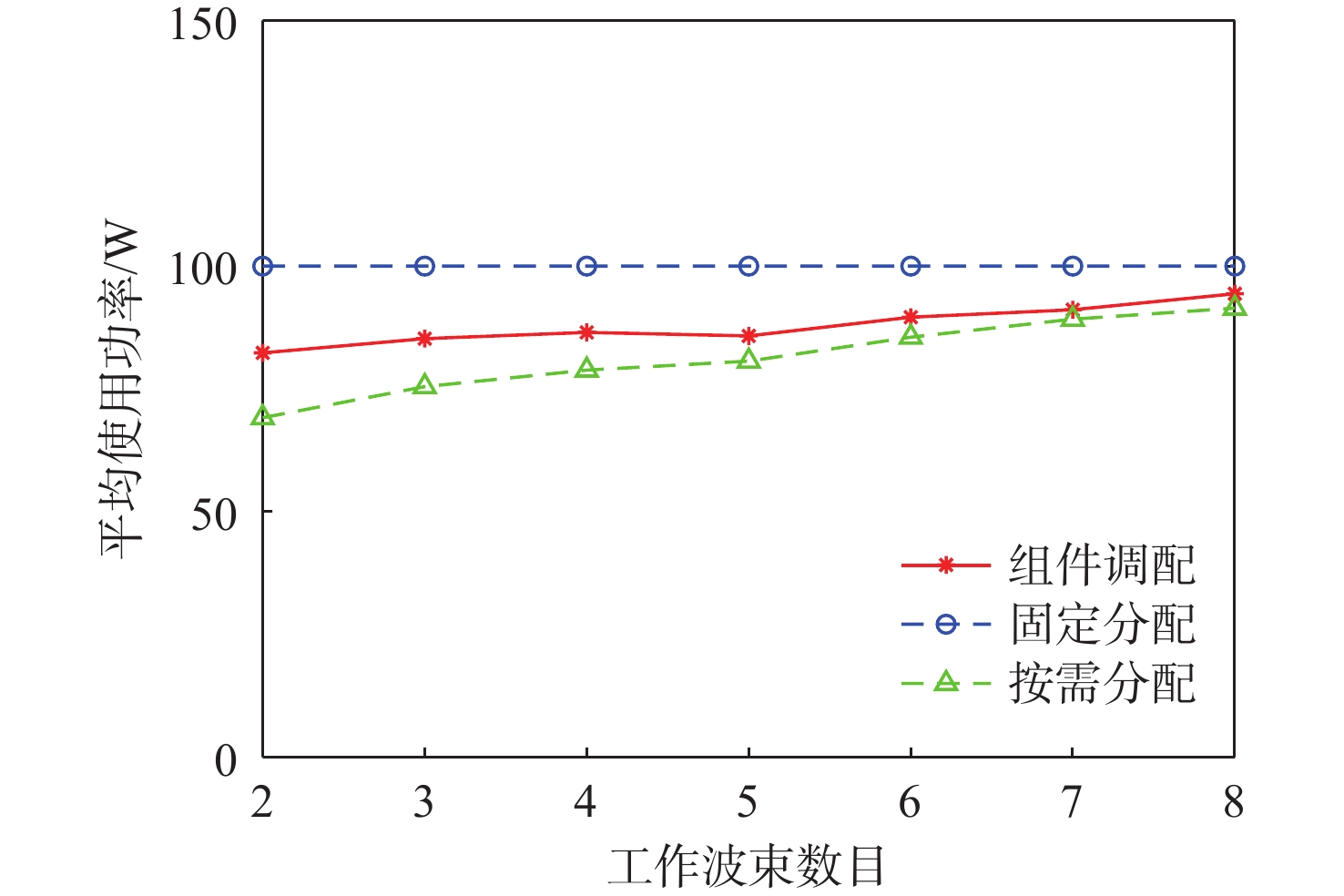
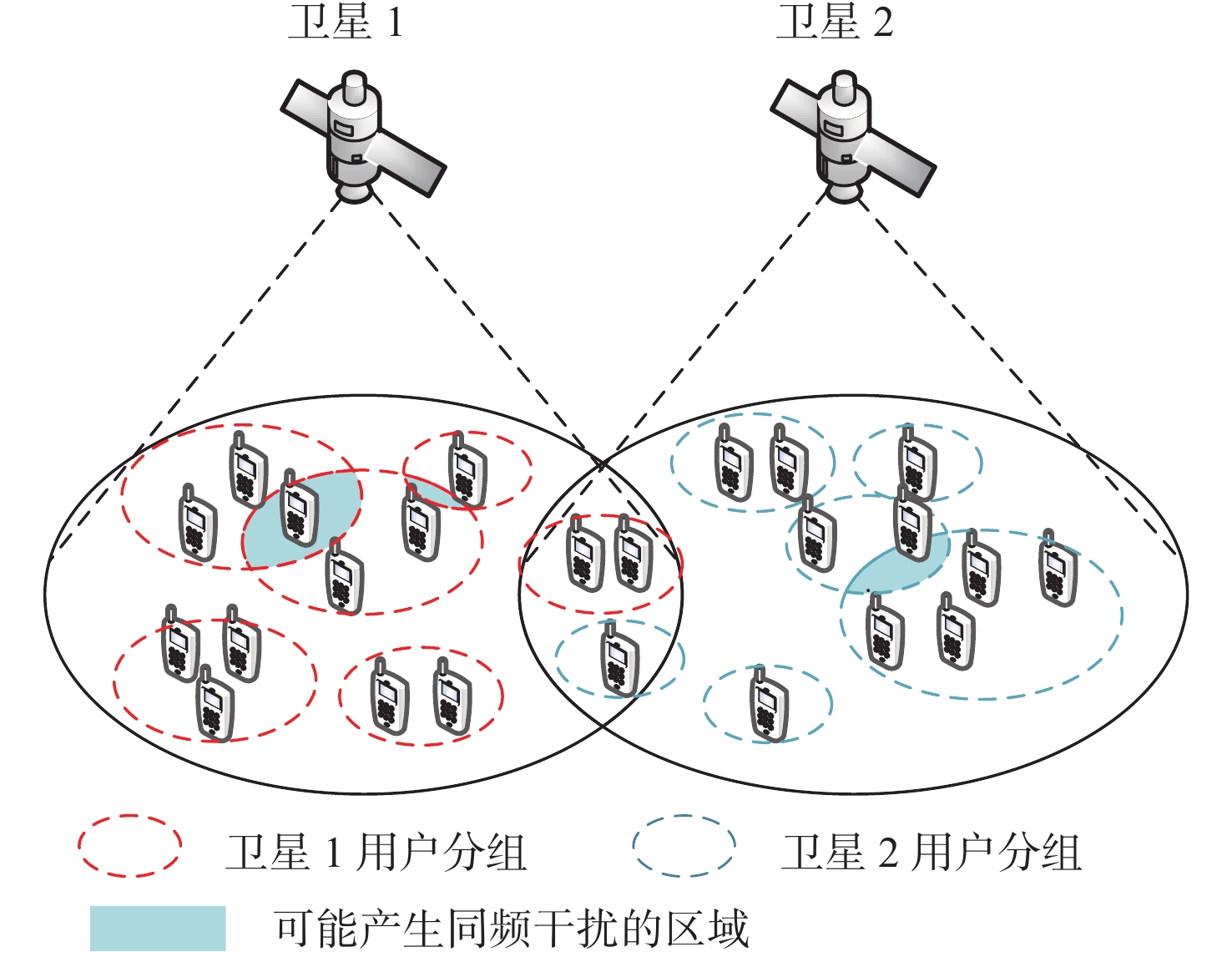
与地面网络设施相比,卫星的机载资源十分有限,面对用户地理位置及流量需求分布的不均匀,传统的固定分组和固定资源分配方式缺乏灵活性,限制了系统容量。基于地理位置的用户分组,利用相控阵天线产生的具有灵活方向和波束宽度的动态波束和跳波的时间分片技术,可以实现对卫星资源的合理分配和高效利用。在低轨多波束卫星场景下,利用P中心问题模拟用户分组问题算法对卫星用户进行分组,实现用户平均信息速率的最大化。基于分组结果提出一套适用于用户分组方案的灵活资源分配算法,并在最后加入一个组间资源调配的过程,以避免空闲资源的浪费。经过实验数据模拟和性能评估,所提算法比传统的用户分组和资源分配算法更能够有效提升系统吞吐量,降低用户平均排队时延。
Abstract:Compared with terrestrial network facilities, the resources of satellites are very limited, and the traditional fixed grouping and fixed resource allocation methods lack flexibility and limit the system capacity in the face of the uneven distribution of user geographic locations and traffic demands. User grouping based on user geographic location, using a dynamic beam with flexible direction and flexible beamwidth generated by phased array antennas and time-slicing technology of beam-hopping technique can achieve reasonable allocation and efficient utilization of satellite resources. Reasonable allocation and efficient usage of satellite resources can be achieved through user grouping based on user geographic location, phased array antenna-generated dynamic beam with flexible beamwidth and direction, and time-slicing technology of beam-hopping technique. Then a set of flexible resource allocation strategies for the user grouping scheme is proposed based on the grouping results, and an inter-group resource allocation process is added at the end to prevent the waste of free resources. In comparison to the conventional user grouping and resource allocation technique, the suggested approach can successfully increase system throughput and decrease users’ average queuing delays after experimental data simulation and performance evaluation.
-
Key words:
- multi-beam satellite /
- beam-hopping /
- user grouping /
- timeslot allocation /
- power allocation
-
表 1 主要仿真参数
Table 1. Main simulation parameters
参数 数值 地球半径/km
间隔半径rkeep/km
可用带宽B/MHz
噪声功率谱密度N0 /(dBm·Hz−1)
波长λ /m
卫星高度h /km
功率衰减α
接收机天线增益Gr /dB
天线效率η
用户数目
卫星数目
总功率Ptotal/W
波束最小功率Pmin/W
波束最小功率Pmax/W
时隙长度tslot /ms
请求的生存周期Tttl
流量请求取值范围/(Mb·s−1)
卫星覆盖范围/km
波束最大半径rmax /km
波束最小半径rmin /km
跳波束周期Ts /ms6371
150
200
−174
0.0151000
1
21.8
0.65
300
2
100
10
50
10
8
[2, 15]
500
75
402560 -
[1] STOREK K U, KNOPP A. Fair user grouping for multibeam satellites with MU-MIMO precoding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-7. [2] ARANITI G, BISIO I, DE SANCTIS M, et al. Joint coding and multicast subgrouping over satellite-eMBMS networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(5): 1004-1016. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2832818 [3] LYU J B, ZENG Y, ZHANG R, et al. Placement optimization of UAV-mounted mobile base stations[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(3): 604-607. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2633248 [4] PARK H, PARK S, SONG T, et al. An incremental multicast grouping scheme for mmWave networks with directional antennas[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2013, 17(3): 616-619. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2013.011513.122519 [5] LIU B K, JIANG C X, KUANG L L, et al. Joint user grouping and beamwidth optimization for satellite multicast with phased array antennas[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-6. [6] TANG J Y, BIAN D M, LI G X, et al. Optimization method of dynamic beam position for LEO beam-hopping satellite communication systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 57578-57588. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3072104 [7] DREZNER Z. The P-centre problem—Heuristic and optimal algorithms[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1984, 35(8): 741-748. [8] 张晨, 张更新, 王显煜. 基于跳波束的新一代高通量卫星通信系统设计[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(7): 59-72.ZHANG C, ZHANG G X, WANG X Y. Design of next generation high throughput satellite communication system based on beam-hopping[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(7): 59-72 (in Chinese). [9] 王琳, 张晨, 王显煜, 等. 基于多波束卫星系统的跳波束技术研究[J]. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(3): 25-30.WANG L, ZHANG C, WANG X Y, et al. Research of beam-hopping technology based on multi-beam satellite system[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 39(3): 25-30(in Chinese). [10] WANG L, ZHANG C, QU D X, et al. Resource allocation for beam-hopping user downlinks in multi-beam satellite system[C]//Proceedings of the 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 925-929. [11] LIU W Y, TIAN F, JIANG Z Y, et al. Beam-hopping based resource allocation algorithm in LEO satellite network[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Information Network. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 113-123. [12] TIAN F, HUANG L L, LIANG G, et al. An efficient resource allocation mechanism for beam-hopping based LEO satellite communication system[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-5. [13] HAN H, ZHENG X Q, HUANG Q F, et al. QoS-equilibrium slot allocation for beam hopping in broadband satellite communication systems[J]. Wireless Networks, 2015, 21(8): 2617-2630. doi: 10.1007/s11276-015-0934-z [14] HU X, ZHANG Y C, LIAO X L, et al. Dynamic beam hopping method based on multi-objective deep reinforcement learning for next generation satellite broadband systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(3): 630-646. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2960940 [15] WANG C, BIAN D M, SHI S C, et al. A novel cognitive satellite network with GEO and LEO broadband systems in the downlink case[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 25987-26000. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2831218 [16] ANZALCHI J, COUCHMAN A, GABELLINI P, et al. Beam hopping in multi-beam broadband satellite systems: System simulation and performance comparison with non-hopped systems[C]//Proceedings of the 5th Advanced Satellite Multimedia Systems Conference and the 11th Signal Processing for Space Communications Workshop. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 248-255. [17] ALEGRE R, ALAGHA N, VÁZQUEZ-CASTRO M Á. Heuristic algorithms for flexible resource allocation in beam hopping multi-beam satellite systems[C]//Proceedings of the 29th AIAA International Communications Satellite Systems Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [18] LEI J, VÁZQUEZ-CASTRO M Á. Multibeam satellite frequency/time duality study and capacity optimization[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2011, 13(5): 472-480. doi: 10.1109/JCN.2011.6112304 [19] SHI S C, LI G X, LI Z Q, et al. Joint power and bandwidth allocation for beam-hopping user downlinks in smart gateway multibeam satellite systems[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2017, 13(5): 155014771770946. [20] WELZL E. Smallest enclosing disks (balls and ellipsoids)[M]// New Results and New Trends in Computer Science. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 359-370. [21] European Telecommunications Standards Institute. Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB); Second generation framing structure, channel coding and modulation systems for broadcasting, interactive services, news gathering and other broadband satellite applications; part II: S2‐extensions (DVB‐S2X). ETSI EN 302 307‐2[S]. Grand Saconnex: European Telecommunications Standards Institute, 2014:100-126. -







 下载:
下载: